Mediterranean Diet, Obesity-Related Metabolic Cardiovascular Disorders, and Environmental Sustainability: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
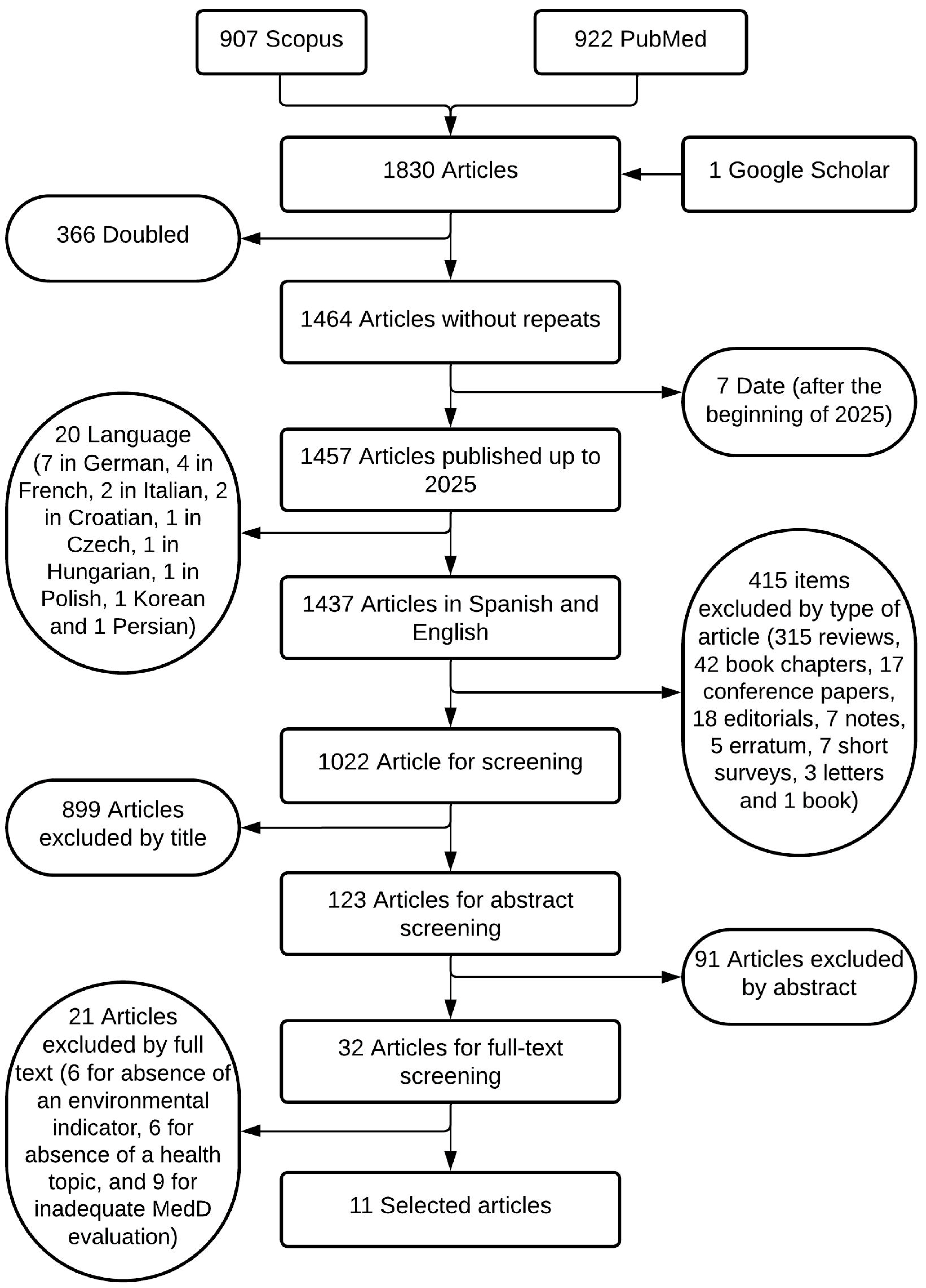
2.4. Selection of Studies
2.5. Extraction of Information
2.6. Bias Assessment
2.7. Synthesis Strategy
3. Results
3.1. Summary of the Search and Selection Process
3.2. Characteristics of the Studies
3.3. Assessment of MedD Adherence
| Article | Type of Study | Mediterranean Diet | Sustainability | Health Subject | Health Index | Article Results | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresán et al., 2019 [41] | Cohort study | MDS | GHG and resources consumption | Obesity | BMI | Negative relationship between BMI and MedD | 90.91% |
| Koelman et al. 2023 [48] | Cohort study | tMED | EAT-Lancet score | Chronic inflammation | Chemerin and PCR | Negative relationship between sustainability and the MedD with inflammation | 90.91% |
| Tan and Shin, 2023 [46] | Cohort study | aMED | GHG | Obesity and MS | BMI and MS | Positive relationship between BMI and GHG and between GHG and MS risk | 72.73% |
| Maritano et al., 2024 [50] | Cohort study | fMDS | GHG and land use | Obesity | BMI | Negative relationship between GHG and land use with MedD | 90.90% |
| Llanaj and Hanley-Cook, 2021 [44] | Cross-sectional study | KIDMED | EAT-Lancet score | Obesity and cardiovascular | BMI and DASH | Negative relationship between BMI and land use with MedD | 75.00% |
| García et al., 2023 [30] | Cross-sectional study | er-MEDAS | GHG | Obesity and MS | BMI and MS | Positive relationship between BMI and MS with GHG | 100.00% |
| Gualtieri et al., 2022 [38] | Cross-sectional study | MEDAS | GHG and water footprint | Obesity | BMI | Positive relationship between BMI and GHG and negative between environmental impact and MedD | 85.71% |
| Kocaadam-Bozkurt and Bozkurt, 2023 [34] | Cross-sectional study | MEDAS | SHE | Obesity | BMI | Positive relationship between BMI and GHG | 75.00% |
| Pınarlı Falakacılar and Yücecan, 2024 [35] | Cross-sectional study | MEDAS | GHG and water footprint | Obesity | BMI | Negative relationship between GHG and water footprint with MedD | 75.00% |
| Teixeira et al., 2024 [42] | Cross-sectional study | MDS | GHG and eutrophication | Obesity | BMI | No relationships where found between environmental impact, obesity and MedD | 75.00% |
| Monserrat-Mesquida et al., 2023 [39] | Randomized controlled trial | MEDAS | GHG | Chronic inflammation | DII | Negative relationship between inflammation with GHG and MedD | 69.23% |
| First Author | Year | Nº Patients | Mean Age (years) | % Women | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresán. Ujué [41] | 2019 | 18,429 | 36.50 | 61.79% | Spain |
| Koelman L. [48] | 2023 | 636 | 50.8 | 47.64% | Germany |
| Tan. Li-Juan [46] | 2023 | 41,659 | 54.4 | 69.16% | Republic of Korea |
| Maritano S. [50] | 2024 | 3358 | 4.5 | 49.60% | Italy |
| Llanaj. Erand [44] | 2021 | 289 | 18–24 | 0.87 | Albania |
| García. Silvia [30] | 2023 | 6646 | 32.5 | 48.42% | Spain |
| Gualtieri. Paola [38] | 2023 | 3353 | 36.00 | 76.10% | Italy |
| Kocaadam-Bozkurt. Betül [34] | 2023 | 1333 | 24.2 | 61.80% | Turkey |
| Pınarlı Falakacılar Ç [35] | 2024 | 160 | 21.13 | 85.60% | Turkey |
| Teixeira B. [42] | 2024 | 521; 632 | 5.7; 13.3 | 49.3%; 48.7% | Portugal |
| Monserrat-Mesquida. Margalida [39] | 2023 | 100 | 55–75 | Not specified | Spain |
3.4. Assessment of Environmental Sustainability
3.5. Health Themes
3.6. Article Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ceccarelli, G.; Branda, F.; Giovanetti, M.; Ciccozzi, M.; Scarpa, F. The Urgent Need for Arbovirus Surveillance and Control Following a Catastrophic Event: The Case of the DANA Flood Event in Valencia. New Microbes New Infect. 2024, 62, 101547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owino, V.; Kumwenda, C.; Ekesa, B.; Parker, M.E.; Ewoldt, L.; Roos, N.; Lee, W.T.; Tome, D. The Impact of Climate Change on Food Systems, Diet Quality, Nutrition, and Health Outcomes: A Narrative Review. Front. Clim. 2022, 4, 941842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Informe de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible. 2023. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2023/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2023_Spanish.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Crippa, M.; Solazzo, E.; Guizzardi, D.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Tubiello, F.N.; Leip, A. Food Systems Are Responsible for a Third of Global Anthropogenic GHG Emissions. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, J.; Garces, L.; Quintero, M.A.; Pignac-Kobinger, J.; Santander, A.M.; Fernández, I.; Ban, Y.J.; Kwon, D.; Phillips, M.C.; Knight, K.; et al. Low-Fat, High-Fiber Diet Reduces Markers of Inflammation and Dysbiosis and Improves Quality of Life in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 1189–1199.e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.M.G.; Falkenberg, T.; Nöthlings, U.; Heinzel, C.; Borgemeister, C.; Escobar, N. Changing Dietary Patterns Is Necessary to Improve the Sustainability of Western Diets from a One Health Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Yeh, T.L.; Shih, M.C.; Tu, Y.K.; Chien, K.L. Dietary Sodium Intake and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Global Diets Link Environmental Sustainability and Human Health. Nature 2014, 515, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, L. Diet and Inflammation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2010, 25, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, V.S.; Hu, F.B. Fructose and Cardiometabolic Health: What the Evidence from Sugar-Sweetened Beverages Tells Us. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán Agüero, S.; Carrasco Piña, E.; Araya Pérez, M. Food and Diabetes. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poti, J.M.; Braga, B.; Qin, B. Ultra-Processed Food Intake and Obesity: What Really Matters for Health-Processing or Nutrient Content? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT–Lancet Commission on Healthy Diets from Sustainable Food Systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, J.; Ramirez-Bajo, M.J.; Bañon-Maneus, E.; Ventura-Aguiar, P.; Arias-Guillén, M.; Romano-Andrioni, B.; Ojeda, R.; Revuelta, I.; García-Calderó, H.; Barberà, J.A.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Pattern: Potential Impact on the Different Altered Pathways Related to Cardiovascular Risk in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, J.; Di Giuseppe, R.; Boeing, H.; Weikert, C. A Mediterranean-Style Diet, Its Components and the Risk of Heart Failure: A Prospective Population-Based Study in a Non-Mediterranean Country. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhn, S.; Masouleh, S.K.; Villringer, A.; Witte, A.V. Components of a Mediterranean Diet and Their Impact on Cognitive Functions in Aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambeses-Franco, C.; González-García, S.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T. Driving Commitment to Sustainable Food Policies within the Framework of American and European Dietary Guidelines. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bôto, J.M.; Rocha, A.; Miguéis, V.; Meireles, M.; Neto, B. Sustainability Dimensions of the Mediterranean Diet: A Systematic Review of the Indicators Used and Its Results. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 2015–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, J. Environmental Sustainability: A Definition for Environmental Professionals. J. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Barquero, S.; Ruiz-León, A.M.; Sierra-Pérez, M.; Estruch, R.; Casas, R. Dietary Strategies for Metabolic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Lista, J.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Fuentes, F.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Ortiz-Morales, A.M.; Gonzalez-Requero, A.I.; Perez-Caballero, A.I.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; et al. Long-Term Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet and a Low-Fat Diet (CORDIOPREV): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, P.; Liu, R.H. Whole Food Approach for Type 2 Diabetes Prevention. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1819–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Veronese, N.; Baiamonte, E.; Guarrera, M.; Parisi, A.; Ruffolo, C.; Tagliaferri, F.; Barbagallo, M. Healthy Aging and Dietary Patterns. Nutrients 2022, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Willett, W.C. The Mediterranean Diet and Health: A Comprehensive Overview. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Sulu, C.; Katsiki, N.; Hassapidou, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cucalón, G.; Pazderska, A.; Yumuk, V.D.; Colao, A.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Obesity-Related Disorders: What Is the Evidence? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Hill, J.; Tilman, D. The Diet, Health, and Environment Trilemma. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2018, 43, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes-Nuñez, J.J.; Urrútia, G.; Romero-García, M.; Alonso-Fernández, S. Declaración PRISMA 2020: Una Guía Actualizada Para La Publicación de Revisiones Sistemáticas. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2021, 74, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JBI Critical Appraisal Tools | JBI. Available online: https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools (accessed on 19 February 2024).
- García, S.; Bouzas, C.; Mateos, D.; Pastor, R.; Álvarez, L.; Rubín, M.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Goday, A.; et al. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions and Adherence to Mediterranean Diet in an Adult Population: The Mediterranean Diet Index as a Pollution Level Index. Environ. Health 2023, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, S.; Pastor, R.; Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Álvarez-Álvarez, L.; Rubín-García, M.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Goday, A.; Martínez, J.A.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome Criteria and Severity and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions in an Adult Population. Global Health 2023, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.; Ros, E.; Salaverría, I.; Fiol, M.; et al. A Short Screener Is Valid for Assessing Mediterranean Diet Adherence among Older Spanish Men and Women. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Kouris-Blazos, A.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Gnardellis, C.; Lagiou, P.; Polychronopoulos, E.; Vassilakou, T.; Lipworth, L.; Trichopoulos, D. Diet and Overall Survival in Elderly People. BMJ 1995, 311, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Zomeño, M.D.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Vioque, J.; Romaguera, D.; Martínez, J.A.; Tinahones, F.J.; Miranda, J.L.; et al. Validity of the Energy-Restricted Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4971–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocaadam-Bozkurt, B.; Bozkurt, O. Relationship between Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, Sustainable and Healthy Eating Behaviors, and Awareness of Reducing the Ecological Footprint. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2023, 33, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pınarlı Falakacılar, Ç.; Yücecan, S. The Impact of Sustainability Courses: Are They Effective in Improving Diet Quality and Anthropometric Indices? Nutrients 2024, 16, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivanoğlu, E.F.Ö.; Balcıoğlu, H.; Ünlüoğlu, İ. Akdeniz Diyeti Bağlılık Ölçeği’nin Türkçe’ye Uyarlanması Geçerlilik ve Güvenilirliği. Osman. Tıp Derg. 2020, 42, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekar, C.; Goktas, Z. Validation of the 14-Item Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 53, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, P.; Marchetti, M.; Frank, G.; Cianci, R.; Bigioni, G.; Colica, C.; Soldati, L.; Moia, A.; De Lorenzo, A.; Di Renzo, L. Exploring the Sustainable Benefits of Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Italy. Nutrients 2022, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Bouzas, C.; García, S.; Quetglas-Llabrés, M.M.; Mateos, D.; Ugarriza, L.; Gómez, C.; Sureda, A.; Tur, J.A. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Dietary Emissions Are Related to Oxidative and Inflammatory Status in Adult Population. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Survival in a Greek Population. New Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresán, U.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Sabaté, J.; Bes-Rastrollo, M. Global Sustainability (Health, Environment and Monetary Costs) of Three Dietary Patterns: Results from a Spanish Cohort (the SUN Project). BMJ Open 2019, 9, 21541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, B.; Afonso, C.; Severo, M.; Carvalho, C.; Torres, D.; Lopes, C.; Oliveira, A. Exploring Dietary Patterns and Their Association with Environmental Sustainability and Body Mass Index in Children and Adolescents: Insights from the National Food, Nutrition and Physical Activity Survey 2015–2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; García, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, Youth and the Mediterranean Diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean Diet Quality Index in Children and Adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llanaj, E.; Hanley-Cook, G.T. Adherence to Healthy and Sustainable Diets Is Not Differentiated by Cost, but Rather Source of Foods among Young Adults in Albania. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 126, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.T.; McCullough, M.L.; Newby, P.; Manson, J.E.; Meigs, J.B.; Rifai, N.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Diet-Quality Scores and Plasma Concentrations of Markers of Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.J.; Shin, S. Low Greenhouse Gas Emission Self-Selective Diets and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults 40 and Older: A Prospective Cohort Study in South Korea. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 117010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.; Gerber, M. Evaluating and Adapting the Mediterranean Diet for Non-Mediterranean Populations: A Critical Appraisal. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelman, L.; Herpich, C.; Norman, K.; Jannasch, F.; Börnhorst, C.; Schulze, M.B.; Aleksandrova, K. Adherence to Healthy and Sustainable Dietary Patterns and Long-Term Chronic Inflammation: Data from the EPIC-Potsdam Cohort. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2023, 27, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognon, G.; Hebestreit, A.; Lanfer, A.; Moreno, L.A.; Pala, V.; Siani, A.; Tornaritis, M.; De Henauw, S.; Veidebaum, T.; Molnár, D.; et al. Mediterranean Diet, Overweight and Body Composition in Children from Eight European Countries: Cross-Sectional and Prospective Results from the IDEFICS Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maritano, S.; Moirano, G.; Isaevska, E.; Pizzi, C.; Ponzo, V.; Moccia, C.; Maule, M.; Lastrucci, V.; Alderotti, G.; Ronfani, L.; et al. Examining the Relationship between the Environmental Impact of Diet and Child Growth from a Co-Benefit Perspective. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuppel, A.; Papier, K.; Key, T.J.; Travis, R.C. EAT-Lancet Score and Major Health Outcomes: The EPIC-Oxford Study. Lancet 2019, 394, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köksal, E.; Bilici, S.; Dazlroǧlu, M.E.Ç.; Gövez, N.E. Validity and Reliability of the Turkish Version of the Sustainable and Healthy Eating Behaviors Scale. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 129, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellen, P.B.; Gao, S.K.; Vitolins, M.Z.; Goff, D.C. Deteriorating Dietary Habits Among Adults with Hypertension: DASH Dietary Accordance, NHANES 1988–1994 and 1999–2004. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, J.F.; Carrington, M.J. A Metabolic Syndrome Severity Score: A Tool to Quantify Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors. Prev. Med. 2016, 88, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leydon, C.L.; Leonard, U.M.; McCarthy, S.N.; Harrington, J.M. Aligning Environmental Sustainability, Health Outcomes, and Affordability in Diet Quality: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 1270–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo-Requena, R.; González-Donquiles, C.; Dávila-Batista, V.; Romaguera, D.; Castelló, A.; de la Torre, A.J.M.; Amiano, P.; Dierssen-Sotos, T.; Guevara, M.; Fernández-Tardón, G.; et al. Agreement among Mediterranean Diet Pattern Adherence Indexes: MCC-Spain Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’innocenzo, S.; Biagi, C.; Lanari, M. Obesity and the Mediterranean Diet: A Review of Evidence of the Role and Sustainability of the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, R.J.; Flammer, A.J.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. The Mediterranean Diet, Its Components, and Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiortsis, D.N.; Simos, Y.V. Mediterranean Diet for the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. Angiology 2013, 65, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigalou, C.; Konstantinidis, T.; Paraschaki, A.; Stavropoulou, E.; Voidarou, C.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Mediterranean Diet as a Tool to Combat Inflammation and Chronic Diseases. An Overview. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernini, S.; Berry, E.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; La Vecchia, C.; Capone, R.; Medina, F.X.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Belahsen, R.; Burlingame, B.; Calabrese, G.; et al. Med Diet 4.0: The Mediterranean Diet with Four Sustainable Benefits. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnolo, D.F.; Selmin, O.I. Mediterranean Diet and Prevention of Chronic Diseases. Nutr. Today 2017, 52, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Salomone, F.; Mlynarsky, L. The Mediterranean Dietary Pattern as the Diet of Choice for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Evidence and Plausible Mechanisms. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critselis, E.; Panagiotakos, D. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Healthy Ageing: Current Evidence, Biological Pathways, and Future Directions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.A.; Sharda, P.; Patel, J.; Gubbi, S.; Bansal, R.; Bartel, M.J. Climate Change and Obesity. Horm. Metab. Res. 2021, 53, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gil, J.F.; García-Hermoso, A.; Sotos-Prieto, M.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Kales, S.N. Mediterranean Diet-Based Interventions to Improve Anthropometric and Obesity Indicators in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Peláez, S.; Fito, M.; Castaner, O. Mediterranean Diet Effects on Type 2 Diabetes Prevention, Disease Progression, and Related Mechanisms. A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, M.Á.; Hershey, M.S.; Zazpe, I.; Trichopoulou, A. Transferability of the Mediterranean Diet to Non-Mediterranean Countries. What Is and What Is Not the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Aveyard, P.; Garnett, T.; Hall, J.W.; Key, T.J.; Lorimer, J.; Pierrehumbert, R.T.; Scarborough, P.; Springmann, M.; Jebb, S.A. Meat Consumption, Health, and the Environment. Science 2018, 361, eaam5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, K.A.; Michelsen, M.K.; Carpenter, C.L. Modern Diets and the Health of Our Planet: An Investigation into the Environmental Impacts of Food Choices. Nutrients 2023, 15, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarnau, C.; Stracker, D.M.; Funtikov, A.; da Silva, R.; Estruch, R.; Bach-Faig, A. Worldwide Adherence to Mediterranean Diet between 1960 and 2011. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulle, R.; Semyonov, L.; La Torre, G. Cost and Cost-Effectiveness of the Mediterranean Diet: Results of a Systematic Review. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4566–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY ((“diet, mediterranean” OR (“diet” AND “mediterranean”) OR “mediterranean diet” OR “diet mediterranean”) AND (“sustain” OR “sustainability” OR “sustainable” OR “sustainably” OR “sustained” OR “sustaining” OR “sustainment” OR “sustains” OR (“environ” OR “environment” OR “environment” OR “environments” OR “environment s” OR “environs”) OR (“climate change” OR (“climate” AND “change”) OR “climate change”) OR (“greenhouse effect” OR (“greenhouse” AND “effect”) OR “greenhouse effect”) OR (“sustainable development” OR (“sustainable” AND “development”) OR “sustainable development”) OR “co2” OR (“carbon footprint” OR (“carbon” AND “footprint”) OR “carbon footprint”) OR (“land basel”[Journal] OR “land”) OR (“fresh water” OR (“fresh” AND “water”) OR “fresh water”) OR (“acidification” OR “acidifications”) OR (“eutrophic” OR “eutrophicated” OR “eutrophication” OR “eutrophication” OR “eutrophications” OR “eutrophics” OR “eutrophized”) OR (“water pollution” OR (“water” AND “pollution”) OR “water pollution”) OR (“air pollution” OR (“air” AND “pollution”) OR “air pollution”) OR (“biodiverse” OR “biodiversities” OR “biodiversity” OR “biodiversity”) OR (“conservation of natural resources” OR (“conservation” AND “natural” AND “resources”) OR “conservation of natural resources” OR “deforestation” OR “deforestations” OR “deforested” OR “deforesting”) OR (“overexploitation” OR “overexploited” OR “overexploiting”) OR “WISH”) AND (“overweight” OR “overweight” OR “overweighted” OR “overweightness” OR “overweights” OR (“obeses” OR “obesity” OR “obesity” OR “obese” OR “obesities” OR “obesity s”) OR (“body mass index” OR (“body” AND “mass” AND “index”) OR “body mass index” OR “BMI”) OR (“weight loss” OR (“weight” AND “loss”) OR “weight loss”) OR (“anti obesity agents” OR “anti obesity agents” OR (“anti obesity” AND “agents”) OR “anti obesity agents” OR (“anti” AND “obesity” AND “agents”) OR “anti obesity agents”) OR (“weight reduction programs” OR (“weight” AND “reduction” AND “programs”) OR “weight reduction programs”) OR (“diet, reducing” OR (“diet” AND “reducing”) OR “reducing diet” OR “diet reducing”) OR (“body weight” OR (“body” AND “weight”) OR “body weight”) OR (“heart disease risk factors” OR (“heart” AND “disease” AND “risk” AND “factors”) OR “heart disease risk factors”) OR (“cardiovascular diseases” OR (“cardiovascular” AND “diseases”) OR “cardiovascular diseases”) OR (“blood pressure” OR (“blood” AND “pressure”) OR “blood pressure” OR “blood pressure determination” OR (“blood” AND “pressure” AND “determination”) OR “blood pressure determination” OR “arterial pressure” OR (“arterial” AND “pressure”) OR “arterial pressure”) OR (“metabolic syndrome” OR (“metabolic” AND “syndrome”) OR “metabolic syndrome”) OR ((“chronic” OR “chronical” OR “chronically” OR “chronicities” OR “chronicity” OR “chronicization” OR “chronics”) AND (“inflammation” OR “inflammation” OR “inflammations” OR “inflammation s”)) OR (“diabetes mellitus” OR (“diabetes” AND “mellitus”) OR “diabetes mellitus”) OR (“glycaemic index” OR “glycemic index” OR (“glycemic” AND “index”) OR “glycemic index” OR (“glucose” OR “glucose” OR “glucoses” OR “glucose s”)) OR “WISH” OR (“glycosylated haemoglobin” OR “glycated hemoglobin” OR (“glycated” AND “hemoglobin”) OR “glycated hemoglobin” OR (“glycosylated” AND “hemoglobin”) OR “glycosylated hemoglobin”))) |
| PubMed | (“diet, mediterranean”[MeSH Terms] OR (“diet”[All Fields] AND “mediterranean”[All Fields]) OR “mediterranean diet”[All Fields] OR “diet mediterranean”[All Fields]) AND (“sustain”[All Fields] OR “sustainability”[All Fields] OR “sustainable”[All Fields] OR “sustainably”[All Fields] OR “sustained”[All Fields] OR “sustaining”[All Fields] OR “sustainment”[All Fields] OR “sustains”[All Fields] OR (“environ”[All Fields] OR “environment”[MeSH Terms] OR “environment”[All Fields] OR “environments”[All Fields] OR “environment s”[All Fields] OR “environs”[All Fields]) OR (“climate change”[MeSH Terms] OR (“climate”[All Fields] AND “change”[All Fields]) OR “climate change”[All Fields]) OR (“greenhouse effect”[MeSH Terms] OR (“greenhouse”[All Fields] AND “effect”[All Fields]) OR “greenhouse effect”[All Fields]) OR (“sustainable development”[MeSH Terms] OR (“sustainable”[All Fields] AND “development”[All Fields]) OR “sustainable development”[All Fields]) OR “co2”[All Fields] OR (“carbon footprint”[MeSH Terms] OR (“carbon”[All Fields] AND “footprint”[All Fields]) OR “carbon footprint”[All Fields]) OR (“land basel”[Journal] OR “land”[All Fields]) OR (“fresh water”[MeSH Terms] OR (“fresh”[All Fields] AND “water”[All Fields]) OR “fresh water”[All Fields]) OR (“acidification”[All Fields] OR “acidifications”[All Fields]) OR (“eutrophic”[All Fields] OR “eutrophicated”[All Fields] OR “eutrophication”[MeSH Terms] OR “eutrophication”[All Fields] OR “eutrophications”[All Fields] OR “eutrophics”[All Fields] OR “eutrophized”[All Fields]) OR (“water pollution”[MeSH Terms] OR (“water”[All Fields] AND “pollution”[All Fields]) OR “water pollution”[All Fields]) OR (“air pollution”[MeSH Terms] OR (“air”[All Fields] AND “pollution”[All Fields]) OR “air pollution”[All Fields]) OR (“biodiverse”[All Fields] OR “biodiversities”[All Fields] OR “biodiversity”[MeSH Terms] OR “biodiversity”[All Fields]) OR (“conservation of natural resources”[MeSH Terms] OR (“conservation”[All Fields] AND “natural”[All Fields] AND “resources”[All Fields]) OR “conservation of natural resources”[All Fields] OR “deforestation”[All Fields] OR “deforestations”[All Fields] OR “deforested”[All Fields] OR “deforesting”[All Fields]) OR (“overexploitation”[All Fields] OR “overexploited”[All Fields] OR “overexploiting”[All Fields]) OR “WISH”[All Fields]) AND (“overweight”[MeSH Terms] OR “overweight”[All Fields] OR “overweighted”[All Fields] OR “overweightness”[All Fields] OR “overweights”[All Fields] OR (“obeses”[All Fields] OR “obesity”[MeSH Terms] OR “obesity”[All Fields] OR “obese”[All Fields] OR “obesities”[All Fields] OR “obesity s”[All Fields]) OR (“body mass index”[MeSH Terms] OR (“body”[All Fields] AND “mass”[All Fields] AND “index”[All Fields]) OR “body mass index”[All Fields] OR “BMI”[All Fields]) OR (“weight loss”[MeSH Terms] OR (“weight”[All Fields] AND “loss”[All Fields]) OR “weight loss”[All Fields]) OR (“anti obesity agents”[Pharmacological Action] OR “anti obesity agents”[MeSH Terms] OR (“anti obesity”[All Fields] AND “agents”[All Fields]) OR “anti obesity agents”[All Fields] OR (“anti”[All Fields] AND “obesity”[All Fields] AND “agents”[All Fields]) OR “anti obesity agents”[All Fields]) OR (“weight reduction programs”[MeSH Terms] OR (“weight”[All Fields] AND “reduction”[All Fields] AND “programs”[All Fields]) OR “weight reduction programs”[All Fields]) OR (“diet, reducing”[MeSH Terms] OR (“diet”[All Fields] AND “reducing”[All Fields]) OR “reducing diet”[All Fields] OR “diet reducing”[All Fields]) OR (“body weight”[MeSH Terms] OR (“body”[All Fields] AND “weight”[All Fields]) OR “body weight”[All Fields]) OR (“heart disease risk factors”[MeSH Terms] OR (“heart”[All Fields] AND “disease”[All Fields] AND “risk”[All Fields] AND “factors”[All Fields]) OR “heart disease risk factors”[All Fields]) OR (“cardiovascular diseases”[MeSH Terms] OR (“cardiovascular”[All Fields] AND “diseases”[All Fields]) OR “cardiovascular diseases”[All Fields]) OR (“blood pressure”[MeSH Terms] OR (“blood”[All Fields] AND “pressure”[All Fields]) OR “blood pressure”[All Fields] OR “blood pressure determination”[MeSH Terms] OR (“blood”[All Fields] AND “pressure”[All Fields] AND “determination”[All Fields]) OR “blood pressure determination”[All Fields] OR “arterial pressure”[MeSH Terms] OR (“arterial”[All Fields] AND “pressure”[All Fields]) OR “arterial pressure”[All Fields]) OR (“metabolic syndrome”[MeSH Terms] OR (“metabolic”[All Fields] AND “syndrome”[All Fields]) OR “metabolic syndrome”[All Fields]) OR ((“chronic”[All Fields] OR “chronical”[All Fields] OR “chronically”[All Fields] OR “chronicities”[All Fields] OR “chronicity”[All Fields] OR “chronicization”[All Fields] OR “chronics”[All Fields]) AND (“inflammation”[MeSH Terms] OR “inflammation”[All Fields] OR “inflammations”[All Fields] OR “inflammation s”[All Fields])) OR (“diabetes mellitus”[MeSH Terms] OR (“diabetes”[All Fields] AND “mellitus”[All Fields]) OR “diabetes mellitus”[All Fields]) OR (“glycaemic index”[All Fields] OR “glycemic index”[MeSH Terms] OR (“glycemic”[All Fields] AND “index”[All Fields]) OR “glycemic index”[All Fields] OR (“glucose”[MeSH Terms] OR “glucose”[All Fields] OR “glucoses”[All Fields] OR “glucose s”[All Fields])) OR “WISH”[All Fields] OR (“glycosylated haemoglobin”[All Fields] OR “glycated hemoglobin”[MeSH Terms] OR (“glycated”[All Fields] AND “hemoglobin”[All Fields]) OR “glycated hemoglobin”[All Fields] OR (“glycosylated”[All Fields] hemoglobin”[All Fields])) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez Núñez, S.; Rubín-García, M.; Martín-Sánchez, V.; Álvarez-Álvarez, L.; Molina, A.J. Mediterranean Diet, Obesity-Related Metabolic Cardiovascular Disorders, and Environmental Sustainability: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17122005
Rodríguez Núñez S, Rubín-García M, Martín-Sánchez V, Álvarez-Álvarez L, Molina AJ. Mediterranean Diet, Obesity-Related Metabolic Cardiovascular Disorders, and Environmental Sustainability: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(12):2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17122005
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez Núñez, Sergio, María Rubín-García, Vicente Martín-Sánchez, Laura Álvarez-Álvarez, and Antonio José Molina. 2025. "Mediterranean Diet, Obesity-Related Metabolic Cardiovascular Disorders, and Environmental Sustainability: A Systematic Review" Nutrients 17, no. 12: 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17122005
APA StyleRodríguez Núñez, S., Rubín-García, M., Martín-Sánchez, V., Álvarez-Álvarez, L., & Molina, A. J. (2025). Mediterranean Diet, Obesity-Related Metabolic Cardiovascular Disorders, and Environmental Sustainability: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 17(12), 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17122005








