Sustained Effects of a Scaled-Up mHealth and School-Based Intervention for Salt Reduction (EduSaltS) in Schoolchildren and Their Families: 1-Year Follow-Up of a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
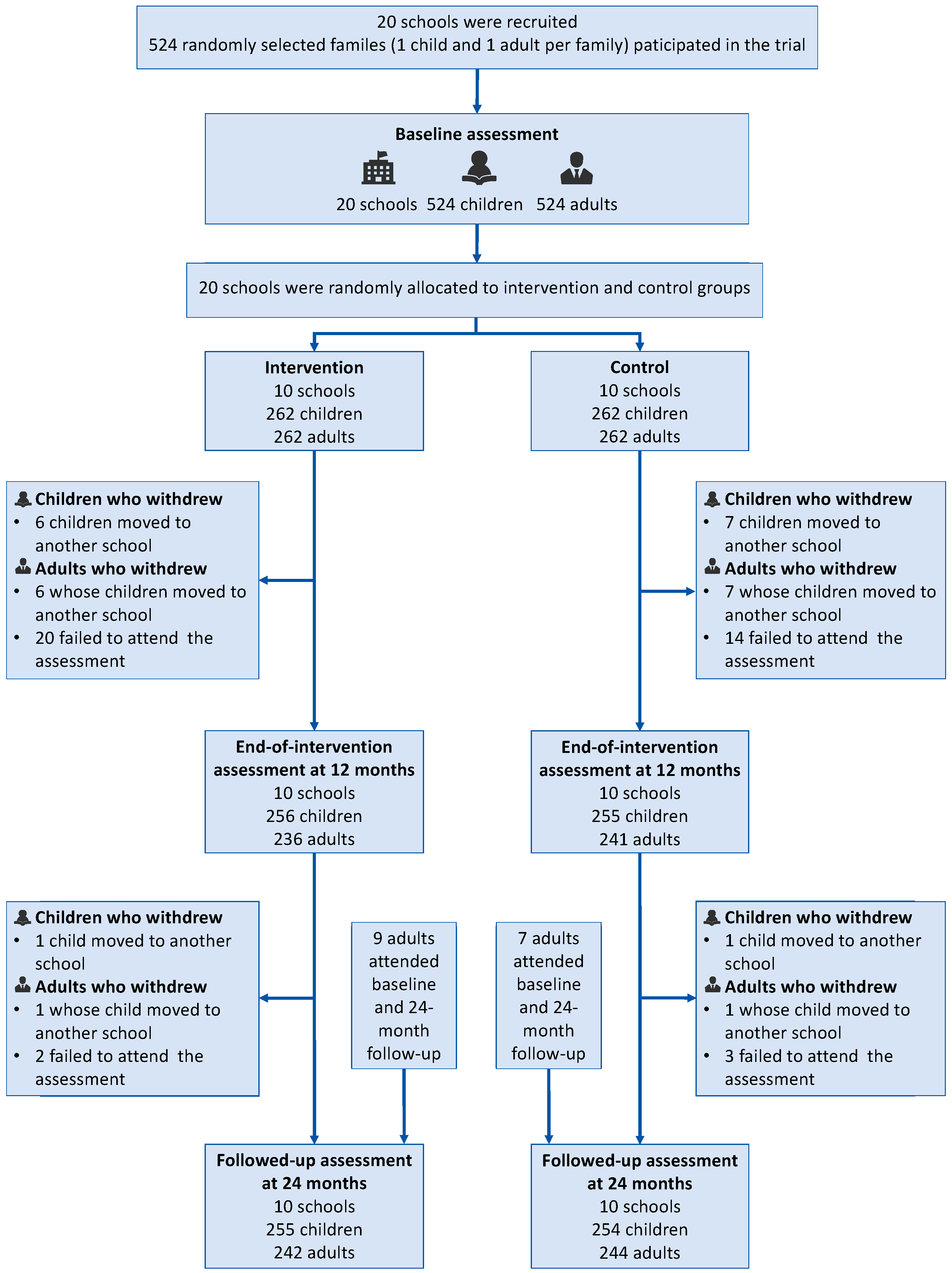
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Outcomes
2.4.1. Assessment of Salt Intake and Urinary Excretions
2.4.2. Assessment of Blood Pressure and Salt-Related KAP
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Yin, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 394, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Global Report on Hypertension: The Race Against a Silent Killer. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240081062 (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Goorani, S.; Zangene, S.; Imig, J.D. Hypertension: A Continuing Public Healthcare Issue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, S.E. Hypertension and cardiovascular risk: General aspects. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Zheng, P.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahpour, I.; et al. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Sodium Reduction. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sodium-reduction (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Borrelli, S.; Provenzano, M.; Gagliardi, I.; Michael, A.; Liberti, M.E.; De Nicola, L.; Conte, G.; Garofalo, C.; Andreucci, M. Sodium Intake and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieu, K.; Neal, B.; Hawkes, C.; Dunford, E.; Campbell, N.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, R.; Legetic, B.; McLaren, L.; Barberio, A.; Webster, J. Salt Reduction Initiatives around the World—A Systematic Review of Progress towards the Global Target. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Popkin, B.M. Dietary Potassium Intake Remains Low and Sodium Intake Remains High, and Most Sodium is Derived from Home Food Preparation for Chinese Adults, 1991–2015 Trends. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020–2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240020924 (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Agarwal, A.; Patel, M. Prescribing Behavior Change: Opportunities and Challenges for Clinicians to Embrace Digital and Mobile Health. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2020, 8, e17281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Holliday, J.; Daniel, R.; Campbell, R.; Moore, L. Diffusion of effects of the ASSIST school-based smoking prevention intervention to non-participating family members: A secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Addiction 2020, 115, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelling, A.; Hawkins, M.; McClave, R.; Irvine Belson, S. The Role of Teachers in Addressing Childhood Obesity: A School-Based Approach. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resaland, G.K.; Bartholomew, J.B.; Andersen, L.B.; Anderssen, S.A.; Aadland, E. Effects of a school-based physical activity intervention on cardiometabolic health 5 years after cessation. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2023, 33, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; Wu, Y.; Feng, X.X.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, J.; Lin, C.P.; Nowson, C.; et al. School based education programme to reduce salt intake in children and their families (School-EduSalt): Cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2015, 350, h770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; Zhang, P.; Luo, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; et al. App based education programme to reduce salt intake (AppSalt) in schoolchildren and their families in China: Parallel, cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2022, 376, e066982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Luo, R.; Wang, L.; Yi, G.; Zhang, G.; He, F.J.; Wang, C.; Wang, N.; et al. Process evaluation of an mHealth-based school education program to reduce salt intake scaling up in China (EduSaltS): A mixed methods study using the RE-AIM framework. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; He, F.J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, R.; Wan, D.; Xu, L.; et al. Effectiveness of an mHealth- and School-Based Health Education Program for Salt Reduction (EduSaltS) in China: Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial Within Scale-Up. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e60092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, P.S.; Wing, R.R.; Davidson, T.; Epstein, L.; Goodpaster, B.; Hall, K.D.; Levin, B.E.; Perri, M.G.; Rolls, B.J.; Rosenbaum, M.; et al. NIH working group report: Innovative research to improve maintenance of weight loss. Obesity 2014, 23, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humalda, J.K.; Klaassen, G.; de Vries, H.; Meuleman, Y.; Verschuur, L.C.; Straathof, E.J.M.; Laverman, G.D.; Bos, W.J.W.; van der Boog, P.J.M.; Vermeulen, K.M.; et al. A Self-management Approach for Dietary Sodium Restriction in Patients With CKD: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.; Judge, C.; Kerins, C.; McDermott, S.; Niland, A.; Corcoran, C.; Dineen, R.; Alvarez-Iglesias, A.; Nolan, A.; Mente, A.; et al. Dietary counselling to reduce moderate sodium intake: Effects on cardiovascular and renal biomarkers: Primary findings of the COSIP and STICK phase II feasibility randomised controlled trials. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 57, 101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, R.; Nie, X.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; He, F.J. An mHealth-based school health education system designed to scale up salt reduction in China (EduSaltS): A development and preliminary implementation study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1161282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Shen, D.; Li, Y.; He, F.J.; Ma, J.; Yan, W.; Gao, Y.; Jin, D.; Deng, Y.; et al. Effect of home cook interventions for salt reduction in China: Cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2023, 382, e074258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderbwih, E.; Mahanani, M.R.; Deckert, A.; Antia, K.; Agbaria, N.; Dambach, P.; Kohler, S.; Horstick, O.; Winkler, V.; Wendt, A.S. The Impact of School-Based Nutrition Interventions on Parents and Other Family Members: A Systematic Literature Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, J.; Cotter, M.J.; Oliveira, P.; Cunha, P.; Torres, E.; Polonia, J. Comparison of Salt Intake in Children to that of their Parents. Nephron 2019, 142, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malczyk, E.; Muc-Wierzgoń, M.; Fatyga, E.; Dzięgielewska-Gęsiak, S. Salt Intake of Children and Adolescents: Influence of Socio-Environmental Factors and School Education. Nutrients 2024, 16, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, B.; Santos, J.A.; Trieu, K.; Thout, S.R.; Johnson, C.; Arcand, J.; Webster, J.; McLean, R. The Science of Salt: A focused review on salt-related knowledge, attitudes and behaviors, and gender differences. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.A.; McKenzie, B.; Rosewarne, E.; Hogendorf, M.; Trieu, K.; Woodward, M.; Cobb, L.K.; Dodd, R.; Webster, J. Strengthening Knowledge to Practice on Effective Salt Reduction Interventions in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2021, 10, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondi, C.F.; Reynolds, A.J. Psychological well-being in midlife following early childhood intervention. Dev. Psychopathol. 2023, 35, 357–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trieu, K.; McMahon, E.; Santos, J.A.; Bauman, A.; Jolly, K.-A.; Bolam, B.; Webster, J. Review of behaviour change interventions to reduce population salt intake. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Global Report on Sodium Intake Reduction. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240069985 (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Hunter, R.W.; Dhaun, N.; Bailey, M.A. The impact of excessive salt intake on human health. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Kelly, M.J.; Must, A. Early Nutrition and Physical Activity Interventions in Childhood Cancer Survivors. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassavou, A.; Wang, M.; Mirzaei, V.; Shpendi, S.; Hasan, R. The Association Between Smartphone App-Based Self-monitoring of Hypertension-Related Behaviors and Reductions in High Blood Pressure: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2022, 10, e34767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Character | Control | Intervention | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster level | |||
| N of schools, by location, n (%) | |||
| Zhanggong District | 4 (40.00) | 4 (40.00) | 8 (40.00) |
| Nankang District | 3 (30.00) | 3 (30.00) | 6 (30.00) |
| Xinfeng County | 2 (20.00) | 2 (20.00) | 4 (20.00) |
| Yudu County | 1 (10.00) | 1 (10.00) | 2 (10.00) |
| Meal provision | |||
| Yes | 6 (60.00) | 6 (60.00) | 12 (60.00) |
| No | 4 (40.00) | 4 (40.00) | 8 (40.00) |
| N of families | 262 | 262 | 524 |
| Outdoor temperature (°C), mean (SD) | 24.81 (2.21) | 23.02 (1.68) | 23.93 (2.16) |
| Children level | |||
| Gender, n(%) | |||
| Boys | 146 (55.73) | 142 (54.20) | 288 (54.96) |
| Girls | 116 (44.27) | 120 (45.80) | 236 (45.04) |
| Age mean (SD) | 9.22 (0.34) | 9.10 (0.35) | 9.16 (0.35) |
| Weight mean (SD) | 29.30 (6.70) | 28.46 (5.95) | 28.88 (6.34) |
| BMI mean (SD) | 15.81 (2.79) | 15.93 (2.34) | 15.87 (2.57) |
| Physical activity, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 96 (36.64) | 91 (34.73) | 187 (35.69) |
| No | 166 (63.36) | 171 (65.27) | 337 (64.31) |
| Adult level | |||
| Gender, n (%) | |||
| Male | 97 (37.02) | 97 (37.02) | 194 (37.02) |
| Female | 165 (62.98) | 165 (62.98) | 330 (62.98) |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 41.01 (11.03) | 40.96 (11.07) | 40.99 (11.04) |
| Weight (kg), mean (SD) | 59.49 (10.02) | 59.98 (10.48) | 59.74 (10.24) |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 23.23 (3.20) | 23.76 (3.26) | 23.50 (3.24) |
| Relationship with children, n (%) | |||
| Parents | 217 (82.82) | 207 (79.01) | 424 (80.92) |
| Grandparents | 43 (16.41) | 50 (19.08) | 93 (17.75) |
| Other | 2 (0.76) | 5 (1.91) | 7 (1.34) |
| Physical activity, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 88 (33.59) | 98 (37.40) | 186 (35.50) |
| No | 174 (66.41) | 164 (62.60) | 338 (64.50) |
| Education | |||
| ≤Primary school | 39 (14.89) | 50 (19.08) | 89 (16.98) |
| Secondary education | 106 (40.46) | 117 (44.66) | 223 (42.56) |
| High school education | 57 (21.76) | 51 (19.47) | 108 (20.61) |
| College or above | 60 (22.90) | 44 (16.79) | 104 (19.85) |
| Smoking | |||
| Yes | 49 (18.70) | 52 (19.85) | 101 (19.27) |
| No | 213 (81.30) | 210 (80.15) | 423 (80.73) |
| Alcohol drinking, n (%) | |||
| Never | 151 (57.63) | 158 (60.31) | 309(58.97) |
| Occasional | 97 (37.02) | 96 (36.64) | 193 (36.83) |
| Regular | 14 (5.34) | 8 (3.05) | 22 (4.20) |
| Self-reported hypertension, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 20 (7.63) | 20 (7.63) | 40 (6.62) |
| No | 242 (92.37) | 242 (92.37) | 484 (92.37) |
| Intervention Group | Control Group | Adjusted Difference in Change (Intervention vs. Control) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted Difference (95%CI) † | p | Adjusted Difference (95%CI) † | p | Difference (95%CI) ‡ | p | |
| Salt intake (g/24 h) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 0.21 (−0.23 to 0.64) | 0.353 | 0.46 (0.02 to 0.89) | 0.039 | −0.25 (−0.86 to 0.35) | 0.412 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 0.56 (0.10 to 1.01) | 0.017 | 0.90 (0.44 to 1.36) | <0.001 | −0.34 (−0.94 to 0.26) | 0.265 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.35 (0.78 to −0.08) | 0.109 | 0.44 (0.88 to 0.00) | 0.049 | −0.09 (−0.69 to 0.51) | 0.775 |
| SBP (mmHg) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 0.43 (−1.00 to 1.86) | 0.554 | 1.10 (−0.33 to 2.53) | 0.132 | −0.67 (−2.27 to 0.94) | 0.414 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 5.10 (3.06 to 7.14) | <0.001 | 5.67 (3.91 to 7.44) | <0.001 | −0.57 (−2.22 to 1.08) | 0.497 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 4.67 (6.07 to 3.27) | <0.001 | 4.57 (5.82 to 3.33) | <0.001 | 0.10 (−1.56 to 1.75) | 0.907 |
| DBP (mmHg) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | −0.97 (−2.19 to 0.24) | 0.115 | 0.41 (−0.81 to 1.62) | 0.512 | −1.38 (−2.75 to −0.02) | 0.048 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | −1.05 (−2.77 to 0.68) | 0.233 | 0.29 (−1.20 to 1.78) | 0.702 | −1.34 (−2.74 to 0.06) | 0.061 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | −0.07 (1.12 to −1.26) | 0.903 | −0.12 (0.94 to −1.17) | 0.831 | 0.04 (−1.37 to 1.45) | 0.954 |
| Urinary sodium (mmol/24 h) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 3.52 (−3.91 to 10.94) | 0.353 | 7.84 (0.39 to 15.28) | 0.039 | −4.32 (−14.64 to 6.00) | 0.412 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 9.55 (1.74 to 17.35) | 0.017 | 15.37 (7.51 to 23.23) | <0.001 | −5.82 (−16.06 to 4.41) | 0.265 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 6.03 (13.40 to −1.35) | 0.109 | 7.53 (15.04 to 0.03) | 0.049 | −1.50 (−11.80 to 8.80) | 0.775 |
| Urinary potassium (mmol/24 h) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 1.95 (−0.10 to 4.00) | 0.062 | 1.02 (−1.04 to 3.08) | 0.330 | 0.93 (−1.93 to 3.79) | 0.524 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 3.19 (1.05 to 5.33) | 0.004 | 2.24 (0.08 to 4.39) | 0.042 | 0.95 (−1.89 to 3.78) | 0.511 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 1.24 (3.28 to −0.80) | 0.234 | 1.22 (3.29 to −0.86) | 0.250 | 0.02 (−2.83 to 2.87) | 0.988 |
| Sodium-to-potassium ratio | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | −0.01 (−0.39 to 0.36) | 0.941 | 0.26 (−0.12 to 0.64) | 0.176 | −0.27 (−0.80 to 0.25) | 0.301 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 0.09 (−0.31 to 0.49) | 0.650 | 0.38 (−0.02 to 0.78) | 0.063 | −0.29 (−0.81 to 0.23) | 0.273 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.11 (0.48 to −0.27) | 0.576 | 0.12 (0.50 to −0.26) | 0.535 | −0.01 (−0.53 to 0.51) | 0.958 |
| Score of knowledge | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 1.82 (1.49 to 2.14) | <0.001 | 0.16 (−0.16 to 0.49) | 0.320 | 1.65 (1.20 to 2.10) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 1.71 (1.36 to 2.06) | <0.001 | 0.02 (−0.33 to 0.36) | 0.932 | 1.69 (1.24 to 2.14) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | −0.11 (0.22 to −0.43) | 0.525 | −0.15 (0.18 to −0.48) | 0.373 | 0.04 (−0.41 to 0.50) | 0.850 |
| Score of attitudes | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 0.47 (0.24 to 0.69) | <0.001 | 0.01 (−0.21 to 0.24) | 0.897 | 0.45 (0.14 to 0.76) | 0.004 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 0.54 (0.31 to 0.78) | <0.001 | −0.03 (−0.26 to 0.21) | 0.815 | 0.57 (0.26 to 0.88) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.08 (0.30 to −0.15) | 0.504 | −0.04 (0.18 to −0.27) | 0.709 | 0.12 (−0.19 to 0.43) | 0.452 |
| Score of behaviors | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 1.19 (0.90 to 1.49) | <0.001 | 0.09 (−0.20 to 0.39) | 0.542 | 1.10 (0.70 to 1.51) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 1.27 (0.95 to 1.59) | <0.001 | 0.18 (−0.14 to 0.50) | 0.263 | 1.09 (0.68 to 1.50) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.07 (0.37 to −0.22) | 0.622 | 0.09 (0.39 to −0.21) | 0.555 | −0.02 (−0.42 to 0.39) | 0.942 |
| KAP scores | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 3.48 (2.92 to 4.03) | <0.001 | 0.27 (−0.28 to 0.83) | 0.334 | 3.20 (2.43 to 3.97) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 3.52 (2.93 to 4.12) | <0.001 | 0.17 (−0.43 to 0.77) | 0.571 | 3.35 (2.58 to 4.12) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.05 (0.60 to −0.51) | 0.872 | −0.10 (0.46 to −0.66) | 0.725 | 0.15 (−0.63 to 0.92) | 0.710 |
| Intervention Group | Control Group | Adjusted Difference in Change (Intervention vs. Control) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjusted Difference (95%CI) † | p | Adjusted Difference (95%CI) † | p | Difference (95%CI) ‡ | p | |
| Salt intake (g/24 h) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | −0.78 (−1.33 to −0.23) | 0.006 | 0.23 (−0.31 to 0.77) | 0.405 | −1.01 (−1.78 to −0.23) | 0.011 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | −0.42 (−0.96 to 0.12) | 0.128 | 0.30 (−0.24 to 0.83) | 0.278 | −0.72 (−1.48 to 0.05) | 0.065 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.36 (0.92 to −0.20) | 0.212 | 0.07 (0.62 to −0.48) | 0.814 | 0.29 (−0.50 to 1.08) | 0.468 |
| SBP (mmHg) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 0.62 (−1.06 to 2.31) | 0.467 | 2.95 (1.26 to 4.64) | 0.001 | −2.33 (−4.26 to −0.40) | 0.018 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 0.46 (−1.88 to 2.80) | 0.699 | 2.34 (0.29 to 4.38) | 0.025 | −1.88 (−3.83 to 0.08) | 0.060 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | −0.16 (1.50 to −1.83) | 0.847 | −0.61 (0.86 to −2.08) | 0.415 | 0.45 (−1.54 to 2.43) | 0.658 |
| DBP (mmHg) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | −0.45 (−1.75 to 0.85) | 0.497 | 1.93 (0.63 to 3.24) | 0.004 | −2.38 (−3.87 to −0.90) | 0.002 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | −0.40 (−2.22 to 1.42) | 0.667 | 1.29 (−0.30 to 2.88) | 0.112 | −1.69 (−3.19 to −0.18) | 0.028 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.05 (1.34 to −1.24) | 0.937 | −0.65 (0.49 to −1.78) | 0.266 | 0.70 (−0.84 to 2.23) | 0.372 |
| Urinary sodium (mmol/24 h) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | −13.27 (−22.70 to −3.85) | 0.006 | 3.93 (−5.34 to 13.20) | 0.405 | −17.2 (−30.42 to −3.99) | 0.011 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | −7.16 (−16.40 to 2.07) | 0.128 | 5.06 (−4.09 to 14.21) | 0.278 | −12.23 (−25.23 to 0.78) | 0.065 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 6.11 (15.71 to −3.50) | 0.212 | 1.13 (10.55 to −8.29) | 0.814 | 4.98 (−8.48 to 18.43) | 0.468 |
| Urinary potassium (mmol/24 h) | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 1.23 (−1.05 to 3.50) | 0.289 | −0.94 (−3.17 to 1.30) | 0.412 | 2.16 (−1.03 to 5.35) | 0.183 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 1.75 (−0.48 to 3.98) | 0.123 | 0.36 (−1.85 to 2.57) | 0.752 | 1.40 (−1.74 to 4.54) | 0.383 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.52 (2.84 to −1.79) | 0.657 | 1.29 (3.57 to −0.98) | 0.265 | −0.77 (−4.02 to 2.48) | 0.643 |
| Sodium-to-potassium ratio | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | −0.41 (−0.80 to −0.02) | 0.038 | 0.21 (−0.17 to 0.59) | 0.285 | −0.62 (−1.17 to −0.07) | 0.026 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | −0.16 (−0.54 to 0.22) | 0.408 | 0.15 (−0.23 to 0.52) | 0.448 | −0.31 (−0.84 to 0.23) | 0.262 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | 0.25 (0.65 to −0.15) | 0.215 | −0.06 (0.33 to −0.45) | 0.753 | 0.31 (−0.24 to 0.87) | 0.269 |
| Score of knowledge | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 1.38 (1.04 to 1.73) | <0.001 | 0.33 (−0.01 to 0.67) | 0.059 | 1.05 (0.57 to 1.54) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 1.29 (0.95 to 1.63) | <0.001 | 0.23 (−0.11 to 0.57) | 0.182 | 1.06 (0.58 to 1.54) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | −0.09 (0.26 to −0.44) | 0.607 | −0.10 (0.25 to −0.45) | 0.580 | 0.01 (−0.49 to 0.50) | 0.981 |
| Score of attitudes | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 0.99 (0.60 to 1.38) | <0.001 | −0.04 (−0.43 to 0.35) | 0.825 | 1.03 (0.48 to 1.58) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 0.82 (0.43 to 1.21) | <0.001 | −0.07 (−0.46 to 0.32) | 0.716 | 0.89 (0.34 to 1.44) | 0.002 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | −0.17 (0.23 to −0.57) | 0.403 | −0.03 (0.37 to −0.42) | 0.889 | −0.14 (−0.7 to 0.42) | 0.620 |
| Score of behaviors | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 0.60 (0.37 to 0.83) | <0.001 | −0.19 (−0.42 to 0.04) | 0.107 | 0.79 (0.46 to 1.12) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 0.33 (0.10 to 0.57) | 0.005 | −0.23 (−0.46 to 0.00) | 0.053 | 0.56 (0.24 to 0.89) | 0.001 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | −0.27 (−0.03 to −0.50) | 0.028 | −0.04 (0.20 to −0.27) | 0.754 | −0.23 (−0.56 to 0.10) | 0.179 |
| KAP scores | ||||||
| 12 months vs. baseline | 2.98 (2.29 to 3.66) | <0.001 | 0.11 (−0.57 to 0.78) | 0.756 | 2.87 (1.91 to 3.83) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. baseline | 2.44 (1.77 to 3.12) | <0.001 | −0.06 (−0.73 to 0.62) | 0.866 | 2.50 (1.55 to 3.45) | <0.001 |
| 24 months vs. 12 months | −0.53 (0.16 to −1.23) | 0.130 | −0.17 (0.52 to −0.85) | 0.636 | −0.37 (−1.34 to 0.61) | 0.458 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; He, F.J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, R.; Lu, Y.; Wan, D.; et al. Sustained Effects of a Scaled-Up mHealth and School-Based Intervention for Salt Reduction (EduSaltS) in Schoolchildren and Their Families: 1-Year Follow-Up of a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111845
Wang N, Zhang P, Li Y, Wang C, He FJ, Li L, Li Y, Luo R, Lu Y, Wan D, et al. Sustained Effects of a Scaled-Up mHealth and School-Based Intervention for Salt Reduction (EduSaltS) in Schoolchildren and Their Families: 1-Year Follow-Up of a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111845
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Naibo, Puhong Zhang, Yinghua Li, Chen Wang, Feng J. He, Li Li, Yuan Li, Rong Luo, Yuanan Lu, Dezhi Wan, and et al. 2025. "Sustained Effects of a Scaled-Up mHealth and School-Based Intervention for Salt Reduction (EduSaltS) in Schoolchildren and Their Families: 1-Year Follow-Up of a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111845
APA StyleWang, N., Zhang, P., Li, Y., Wang, C., He, F. J., Li, L., Li, Y., Luo, R., Lu, Y., Wan, D., Lu, T., Xu, L., Zhu, C., & Wu, L. (2025). Sustained Effects of a Scaled-Up mHealth and School-Based Intervention for Salt Reduction (EduSaltS) in Schoolchildren and Their Families: 1-Year Follow-Up of a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 17(11), 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111845






