Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Induced by High-Fat Diet Consumption Is Associated with Higher Otoacoustic Emissions Threshold in Mice C57BL/6
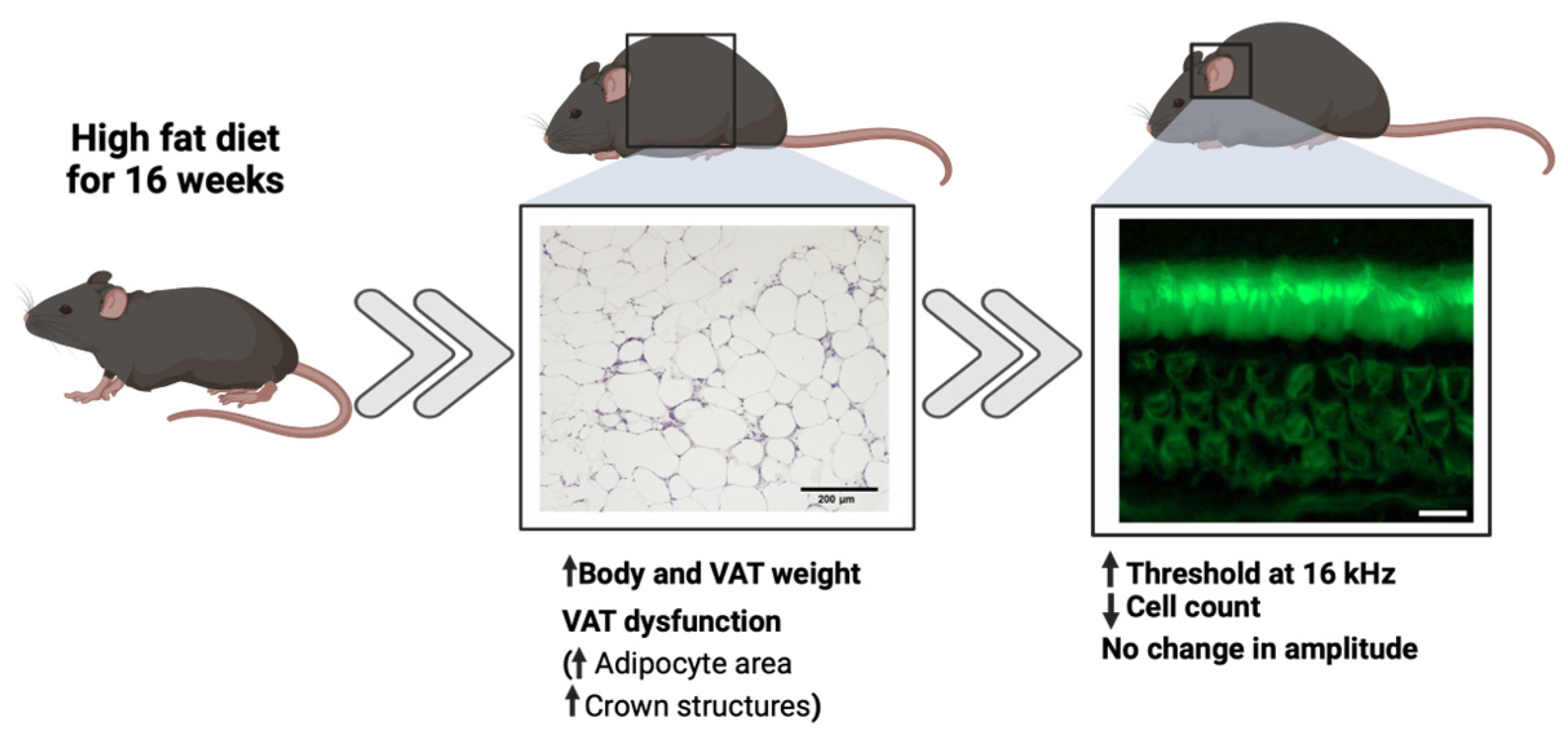
Highlights
- High-fat diet consumption for a period of 16 weeks induced adipose tissue dysfunction, which was found to be associated with auditory system impairments in young mice.
- Mice with high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue dysfunction exhibited an elevated distortion product otoacoustic emission threshold at 16 kHz and a reduced outer hair cell count in the medial cochlear region.
- Impairment of outer hair cell function was positively correlated with body and AT weight, specifically when AT dysfunction became pronounced after 16 weeks of HFD treatment.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animal Preparation
2.3. Glucose Tolerance Test and Biochemical Determinations
2.4. Evocated Otoacoustic Emissions
2.5. Tissue Samples and Histological Analysis
2.6. Cochlear Immunofluorescence
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HFD Induces Weight Gain and Adipose Tissue Dysfunction
3.2. HFD Treatment Increased DPOAE Threshold at 16 KHz After 16 Weeks of Treatment
3.3. HFD Consumption for 16 Weeks Impairs Outer Hair Cells in the Medial Cochlea
3.4. DPOAE Threshold and DPOAE Amplitudes Differentially Correlate with Body Weight and Adipose Tissue (AT) Weight Dependent on Length of Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AT | Adipose tissue |
| CD | Control diet |
| DPOAE | Distortion product otoacoustic emission |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SNHL | Sensorineural hearing loss |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| VAT | Adipose tissue |
References
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. Obesity, Oxidative Stress, Adipose Tissue Dysfunction, and the Associated Health Risks: Causes and Therapeutic Strategies. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2015, 13, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilyeva, O.N.; Frisina, S.T.; Zhu, X.; Walton, J.P.; Frisina, R.D. Interactions of Hearing Loss and Diabetes Mellitus in the Middle Age CBA/CaJ Mouse Model of Presbycusis. Hear. Res. 2009, 249, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.H.; Wu, C.C.; Hsu, C.J.; Liu, T.C.; Yang, W.S. Association of Central Obesity with the Severity and Audiometric Configurations of Age-Related Hearing Impairment. Obesity 2009, 17, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Tomita, K.; Kuwahara, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Uehara, A.; Kochi, T.; Eguchi, M.; Okazaki, H.; Hori, A.; Sasaki, N.; et al. Obesity and Risk of Hearing Loss: A Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, N.; Taheri, S. A Narrative Review of Obesity and Hearing Loss. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, C.L.; Oh, E.S. Hearing Loss. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, ITC81–ITC96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, L.L.; Tucci, D.L. Hearing Loss in Adults BURDEN OF HEARING LOSS HHS Public Access. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 792–803. [Google Scholar]
- Haile, L.M.; Kamenov, K.; Briant, P.S.; Orji, A.U.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Abdoli, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Afshin, A.; Ahmed, H.; et al. Hearing Loss Prevalence and Years Lived with Disability, 1990–2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2021, 397, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Sommerlad, A.; Orgeta, V.; Costafreda, S.G.; Huntley, J.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care. Lancet 2017, 390, 2673–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwander, M.; Kachar, B.; Müller, U. The Cell Biology of Hearing. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Kong, W.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y. Programmed Cell Death Pathways in Hearing Loss: A Review of Apoptosis, Autophagy and Programmed Necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keithley, E.M. Pathology and Mechanisms of Cochlear Aging. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinec, G.M.; Lomberk, G.; Urrutia, R.A.; Kalinec, F. Resolution of Cochlear Inflammation: Novel Target for Preventing or Ameliorating Drug-, Noise- and Age-Related Hearing Losss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Gakidou, E.; Lo, J.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, N.; Abbasian, M.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Adult Overweight and Obesity, 1990–2021, with Forecasts to 2050: A Forecasting Study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillana, N.; Astudillo-Guerrero, C.; D’Espessailles, A.; Cruz, G. White Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Emergent Measurements. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.; Telang, R.; Kociszewska, D.; Thorne, P.R.; Vlajkovic, S.M. A High-Fat Diet Induces Low-Grade Cochlear Inflammation in CD-1 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-H.; Hsu, C.-J.; Yu, W.-H.; Liu, T.-C.; Yang, W.-S. Diet-Induced Obesity Exacerbates Auditory Degeneration via Hypoxia, Inflammation, and Apoptosis Signaling Pathways in CD/1 Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.C.; Cox, B.C. Whole Mount Dissection and Immunofluorescence of the Adult Mouse Cochlea. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 1, 53561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, H.; Karabulut, I.; Daǧli, M.; Bayazit, Y.A.; Bilen, Ş.; Aydin, Y.; Güler, S.; Bayramoǧlu, I. Evaluation of Outer Hair Cell Function and Medial Olivocochlear Efferent System in Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus. Turkish J. Med. Sci. 2014, 44, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, J.K. A Mouse Model of Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance. In Mtor: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 421–433. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.S.; Park, S.W.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, E.B.; Chung, J.W.; So, H.-S. Visceral Adipose Tissue Is Significantly Associated with Hearing Thresholds in Adult Women. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Metabolic Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction as Determinant of Obesity-Associated Metabolic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafontan, M. Adipose Tissue and Adipocyte Dysregulation. Diabetes Metab. 2014, 40, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavazos, A.E.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Iacobellis, G.; Basilico, S.; Dubini, C.; Morricone, L.; Menicanti, L.; Luca, T.; Giordano, A.; Castorina, S.; et al. The Density of Crown-like Structures in Epicardial Adipose Tissue Could Play a Role in Cardiovascular Diseases. Eat. Weight. Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2022, 27, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Tordjman, J.; Clément, K.; Scherer, P.E. Fibrosis and Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carobbio, S.; Pellegrinelli, V.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Determines Lipotoxicity and Triggers the Metabolic Syndrome: Current Challenges and Clinical Perspectives. Obes. Lipotoxicity 2024, 1460, 231–272. [Google Scholar]
- Duval, C.; Thissen, U.; Keshtkar, S.; Accart, B.; Stienstra, R.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Roskams, T.; Kersten, S.; Müller, M. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Signals Progression of Hepatic Steatosis Towards Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in C57Bl/6 Mice. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Gajbhiye, A.; Lyu, A.-R.; Kim, T.H.; Shin, S.-A.; Kwon, H.C.; Park, Y.-H.; Park, M.J. Sex Differences in Hearing Impairment Due to Diet-Induced Obesity in CBA/Ca Mice. Biol. Sex Differ. 2023, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Yamashita, D.; Uehara, N.; Inokuchi, G.; Hasegawa, S.; Otsuki, N.; Nibu, K. A High-Fat Diet Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss Progression in C57BL/6J Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, G.; Xue, N.; Wang, Y.; Du, T.; Liu, H.; Xiong, W.; Shang, W.; Wu, H.; Song, L. Differential Outcomes of High-fat Diet on Age-related Rescaling of Cochlear Frequency Place Coding. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Someya, S.; Xu, J.; Kondo, K.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R.J.; Yamasoba, T.; Rabinovitch, P.S.; Weindruch, R.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Tanokura, M.; et al. Age-Related Hearing Loss in C57BL/6J Mice Is Mediated by Bak-Dependent Mitochondrial Apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2009, 106, 19432–19437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Palma, F.; Pellegrino, R.; Noben-Trauth, K. Genomic Structure, Alternative Splice Forms and Normal and Mutant Alleles of Cadherin 23 (Cdh23). Gene 2001, 281, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, S.C.; Carvalho, C.; Cardoso, S.; Santos, R.X.; Santos, M.S.; Oliveira, C.R.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X.; Smith, M.A.; Moreira, P.I. Correia Mitochondrial Preconditioning: A Potential Neuroprotective Strategy. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2010, 2, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Hsu, C.J.; Liu, T.C.; Yang, W.S. Association of Plasma Adiponectin Levels with Hearing Thresholds in Adults. Clin. Endocrinol. 2011, 75, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Choo, O.; Kim, Y.J.; Gil, E.S.; Jang, J.H.; Kang, Y.; Choung, Y.-H. Atorvastatin Prevents Hearing Impairment in the Presence of Hyperlipidemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, M.; Schäfer, A.; Seelig, A.; Schultheiß, J.; Wu, M.; Aichler, M.; Leonhardt, J.; Rathkolb, B.; Rozman, J.; Sarioglu, H.; et al. High Fat Diet-Induced Modifications in Membrane Lipid and Mitochondrial-Membrane Protein Signatures Precede the Development of Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Mice. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani-Ghahnaviyeh, S.; Zhao, Z.; Tajkhorshid, E. Lipid-Mediated Prestin Organization in Outer Hair Cell Membranes and Its Implications in Sound Amplification. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.-P.; Surguchev, A.; Ogando, Y.; Song, L.; Bian, S.; Santos-Sacchi, J.; Navaratnam, D. Prestin Surface Expression and Activity Are Augmented by Interaction with MAP1S, a Microtubule-Associated Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 20834–20843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.W.; Park, M.-H.; Jeong, S.J.; Lee, K.L.; Kim, J.W.; Jeong, J.B. Sex Differences in Associated Factors for Age-Related Hearing Loss. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

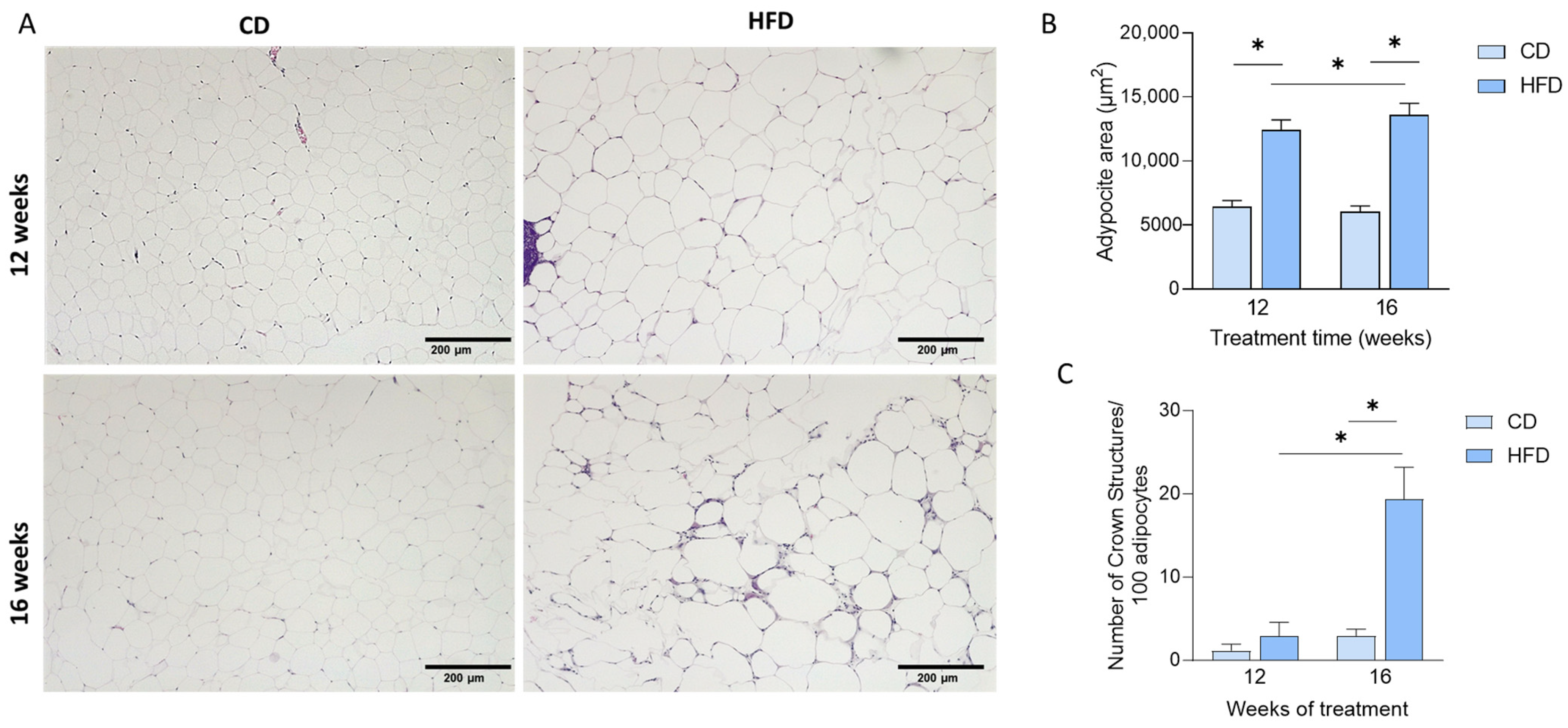
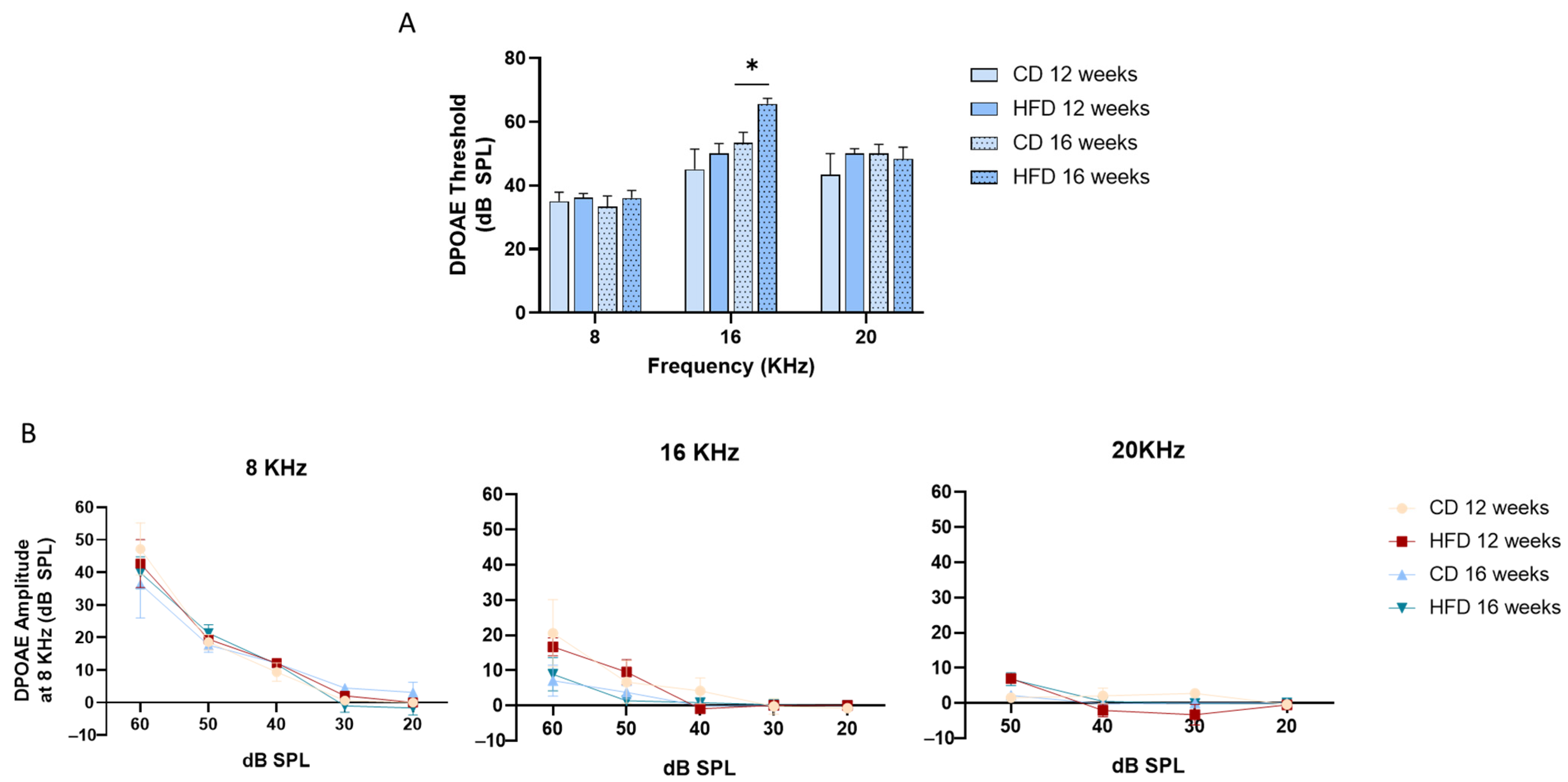
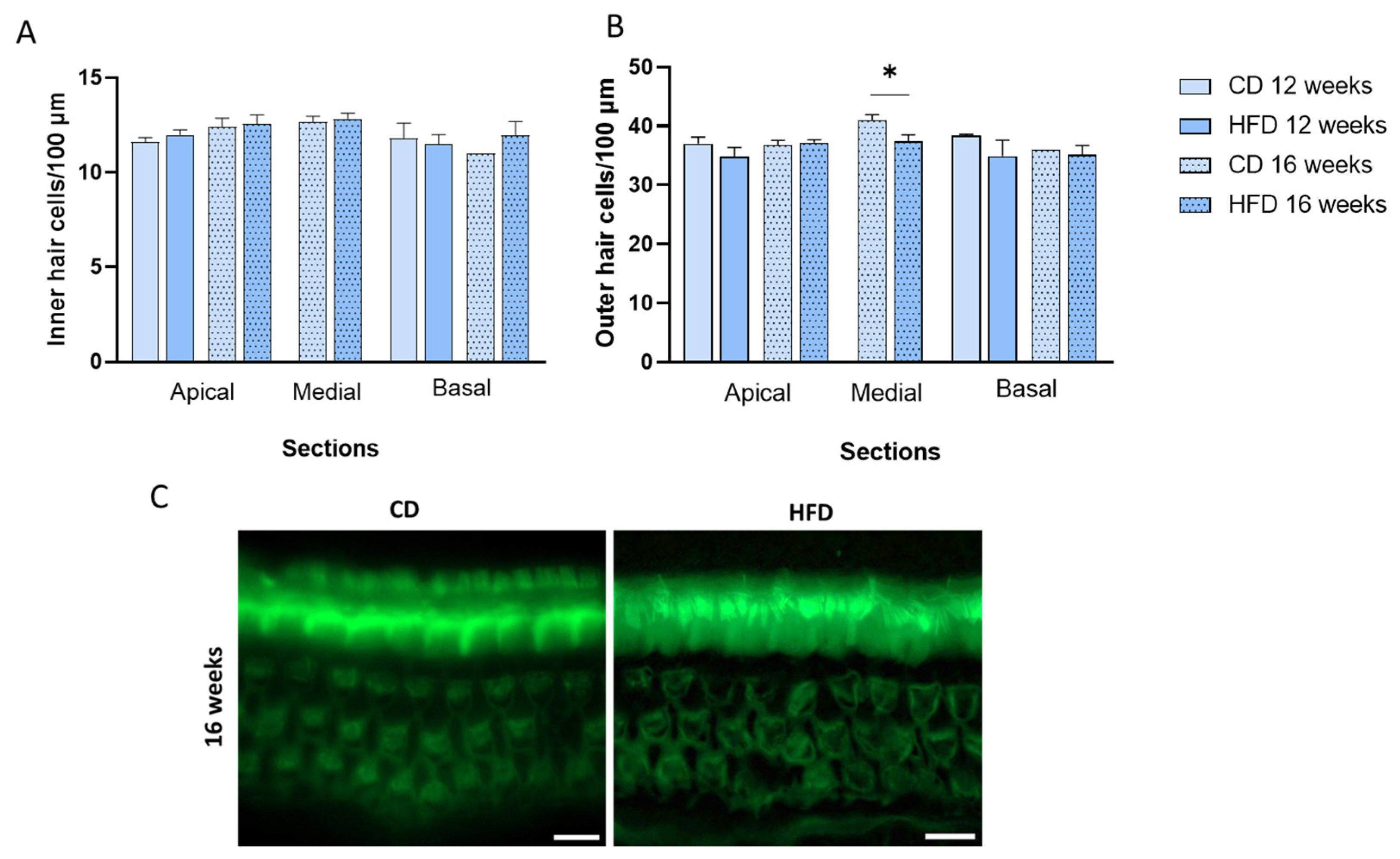
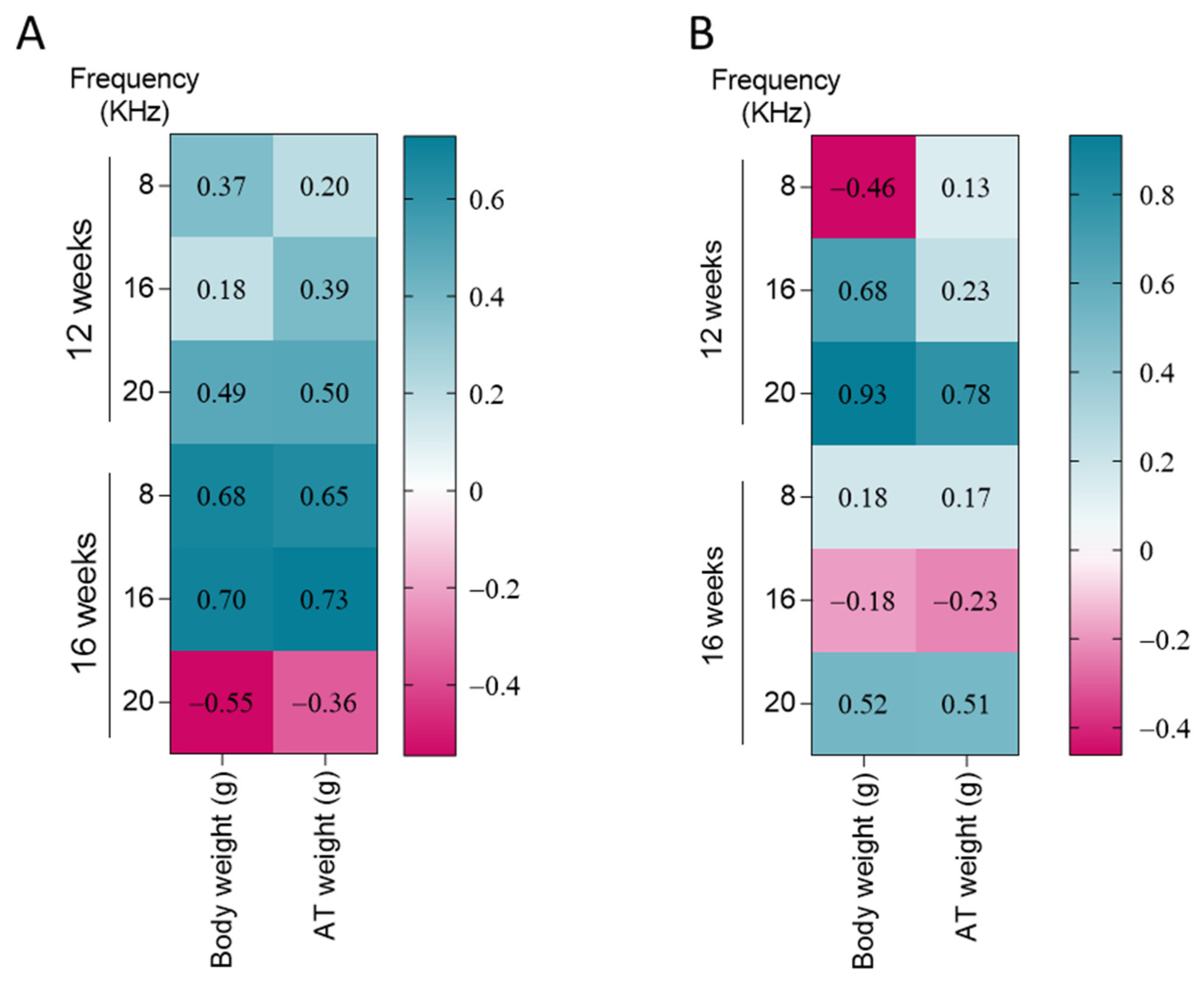
| 12 Weeks | 16 Weeks | p (2-Way ANOVA) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | HFD | CD | HFD | Diet | Weeks | Interaction | |
| Final weight (g) | 32.1 ± 2.48 a | 50.3 ± 5.23 b,d | 31.3 ± 1.5 a,c | 57.8 ± 6.4 d | <0.0001 | 0.0776 | 0.2036 |
| Liver weight (g) | 1.42 ± 0.19 a | 2.03 ± 0.61 b | 1.4 ± 0.056 a,b | 2.1 ± 0.17 a,b | 0.003 | 0.98 | 0.80 |
| Liver/body weight ratio | 0.044 ± 0.0043 | 0.041 ± 0.011 | 0.044 ± 0.0014 | 0.036 ± 0.0044 | 0.1964 | 0.4809 | 0.4992 |
| VAT weight (g) | 0.96 ± 0.30 a | 2.07 ± 0.53 b | 0.8 ± 0.2 a,c | 3.2 ± 0.45 d | <0.0001 | 0.0214 | 0.0036 |
| VAT % ECM area | 0.65 ± 0.10 a | 0.84 ± 0.19 a | 8.02 ± 1.7 b | 11.77 ± 3.7 c | 0.0068 | <0.001 | 0.0024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terreros, G.; Munoz, F.; Magdalena, M.; Soto-Donoso, M.; Torres, N.; D’Espessailles, A. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Induced by High-Fat Diet Consumption Is Associated with Higher Otoacoustic Emissions Threshold in Mice C57BL/6. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111786
Terreros G, Munoz F, Magdalena M, Soto-Donoso M, Torres N, D’Espessailles A. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Induced by High-Fat Diet Consumption Is Associated with Higher Otoacoustic Emissions Threshold in Mice C57BL/6. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111786
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerreros, Gonzalo, Felipe Munoz, Matías Magdalena, Manuel Soto-Donoso, Nairo Torres, and Amanda D’Espessailles. 2025. "Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Induced by High-Fat Diet Consumption Is Associated with Higher Otoacoustic Emissions Threshold in Mice C57BL/6" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111786
APA StyleTerreros, G., Munoz, F., Magdalena, M., Soto-Donoso, M., Torres, N., & D’Espessailles, A. (2025). Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Induced by High-Fat Diet Consumption Is Associated with Higher Otoacoustic Emissions Threshold in Mice C57BL/6. Nutrients, 17(11), 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111786





