Nutraceutical Strategies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Path to Liver Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Plant-Based Nutraceuticals and Polyphenols
3.1. Green Tea
3.1.1. Background
3.1.2. Mechanism of Action
3.1.3. Clinical Efficacy
3.1.4. Lifestyle Integration
3.2. Caffeine
3.2.1. Background
3.2.2. Mechanism of Action
3.2.3. Clinical Efficacy
3.2.4. Lifestyle Integration
3.3. Curcumin
3.3.1. Background
3.3.2. Mechanism of Action
3.3.3. Clinical Efficacy
3.3.4. Lifestyle Integration
3.4. MilkThistle (Silymarin)
3.4.1. Background
3.4.2. Mechanism of Action
3.4.3. Clinical Efficacy
3.4.4. Lifestyle Integration
3.5. Berberine
3.5.1. Background
3.5.2. Mechanism of Action
3.5.3. Clinical Efficacy
3.5.4. Lifestyle Integration
3.6. Artichoke
3.6.1. Background
3.6.2. Mechanism of Action
3.6.3. Clinical Efficacy
3.6.4. Lifestyle Integration
4. Antioxidants
4.1. Vitamin E
4.1.1. Background
4.1.2. Mechanism of Action
4.1.3. Clinical Efficacy
4.1.4. Lifestyle Integration
4.2. Coenzyme Q10
4.2.1. Background
4.2.2. Mechanism of Action
4.2.3. Clinical Efficacy
4.2.4. Lifestyle Integration
4.3. Vitamin D
4.3.1. Background
4.3.2. Mechanism of Action
4.3.3. Clinical Efficacy
4.3.4. Lifestyle Integration
5. Metabolic Modulators
5.1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
5.1.1. Background
5.1.2. Mechanism of Action
5.1.3. Clinical Efficacy
5.1.4. Lifestyle Integration
5.2. Probiotics and Prebiotics and Synbiotics
5.2.1. Background
5.2.2. Mechanism of Action
5.2.3. Clinical Efficacy
5.2.4. Lifestyle Integration
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MASH | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| RCTs | randomized controlled trials |
| EGCG | epigallocatechin gallate |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| ALT | alanine transaminase |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| AST | aspartate transaminase |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TC | Total Cholesterol |
| LDL | Low-density Lipoprotein |
| SMD | Standardized Mean Difference |
| TLR4 | toll-like receptor 4 |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NF-Κb | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| RR | risk ratio |
| OR | odds ratio |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| TNF-a | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| MD | Mean difference |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| HOMA-IR | homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance |
| ALE | artichoke leaf extract |
| DNL | de novo lipogenesis |
| SREBP-1 | Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein 1 |
| IU | International units |
| CoQ10 | Coenzyme Q10 |
| PPARα | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| VDR | vitamin D receptor |
| omega-3 PUFAs | Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| EPA | eicosapentaenoic acid |
| DHA | docosahexaenoic acid |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharides |
| PPS | probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics |
References
- Guo, X.; Yin, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Pathogenesis and Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Henry, L.; Gerber, L.H. Lifestyle interventions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, S.; Ji, X.; Shen, X.; You, J.; Liang, X.; Yin, H.; Zhao, L. Current innovations in nutraceuticals and functional foods for intervention of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 166, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Li, H.B.; Feng, Y.B. Green Tea and Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) for the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases (NAFLD): Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Mechanism. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y. Therapeutic Activity of Green Tea Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Metabolic Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases: The Current Updates. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour-Ghanaei, F.; Hadi, A.; Pourmasoumi, M.; Joukar, F.; Golpour, S.; Najafgholizadeh, A. Green tea as a safe alternative approach for nonalcoholic fatty liver treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1876–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Hosseini, R.; Kazemi, A.; Ofori-Asenso, R.; Mazidi, M.; Mazloomi, S.M. Effects of green tea or green tea catechin on liver enzymes in healthy individuals and people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranoff, J.A. Coffee as chemoprotectant in fatty liver disease: Caffeine-dependent and caffeine-independent effects. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2023, 324, G419–G421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kositamongkol, C.; Kanchanasurakit, S.; Auttamalang, C.; Inchai, N.; Kabkaew, T.; Kitpark, S.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Duangjai, A.; Saokaew, S.; Phisalprapa, P. Coffee Consumption and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Umbrella Review and a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 786596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Pozada, E.; Ramos-Tovar, E.; Rodriguez-Callejas, J.D.; Cardoso-Lezama, I.; Galindo-Gómez, S.; Talamás-Lara, D.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R.; Arellanes-Robledo, J.; Tsutsumi, V.; Villa-Treviño, S.; et al. Caffeine Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Downregulating TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in an Experimental NASH Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Pozada, E.; Ramos-Tovar, E.; Acero-Hernández, C.; Cardoso-Lezama, I.; Galindo-Gómez, S.; Tsutsumi, V.; Muriel, P. Caffeine mitigates experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and the progression of thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis by blocking the MAPK and TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathways. Ann. Hepatol. 2022, 27, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiyama, G.; Minowa, K.; Rodriguez-Agudo, D.; Martin, R.; Takei, H.; Mitamura, K.; Ikegawa, S.; Suzuki, M.; Nittono, H.; Fuchs, M.; et al. Coffee modulates insulin-hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α-Cyp7b1 pathway and reduces oxysterol-driven liver toxicity in a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mouse model. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2022, 323, G488–G500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, U.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Okut, H.; Afroz, S.; Tasleem, S.; Haris, A. The effect of coffee consumption on the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis: A meta-analysis of 11 epidemiological studies. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 20, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewter, R.; Heaney, S.; Patterson, A. Coffee Consumption and the Progression of NAFLD: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Mohseni, S.; Safargar, M.; Mohtashamian, A.; Niknam, S.; Bakhoda, M.; Afshari, S.; Jafari, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Fooladshekan, S.; et al. Curcumin effects on glycaemic indices, lipid profile, blood pressure, inflammatory markers and anthropometric measurements of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2024, 80, 103025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Różański, G.; Kujawski, S.; Newton, J.L.; Zalewski, P.; Słomko, J. Curcumin and Biochemical Parameters in Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)—A Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukkunaprasit, T.; Tansawet, A.; Boonmanunt, S.; Sobhonslidsuk, A.; McKay, G.J.; Attia, J.; Thakkinstian, A. An updated meta-analysis of effects of curcumin on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease based on available evidence from Iran and Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, Z.; Bagherniya, M.; Khoram, Z.; Ebrahimi Varzaneh, A.; Heidari, Z.; Sahebkar, A.; Askari, G. The effect of curcumin on anthropometric indices, blood pressure, lipid profiles, fasting blood glucose, liver enzymes, fibrosis, and steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty livers. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1163950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, M.H.; Norhayati, M.N.; Rosnani, Z.; Zulkifli, M.M. Curcumin as adjuvant treatment in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD) disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2022, 68, 102843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Malik, M. Effects of curcumin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. Liver J. 2024, 7, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, A.; Schmidt, H.H.J. Silymarin as Supportive Treatment in Liver Diseases: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1279–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Muñoz, A.M.; Victoria-Montesinos, D.; Ballester, P.; Cerdá, B.; Zafrilla, P. A Descriptive Review of the Antioxidant Effects and Mechanisms of Action of Berberine and Silymarin. Molecules 2024, 29, 4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Duan, F.; Li, S.; Lu, B. Administration of silymarin in NAFLD/NASH: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Malik, M.; Qureshi, S. Effects of silymarin use on liver enzymes and metabolic factors in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. Liver J. 2024, 7, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, H.M.; Bader Ul Ain, H.; Tufail, T.; Hanif, A.; Malik, T. Impact of silymarin-supplemented cookies on liver enzyme and inflammatory markers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 7273–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, C. The mechanism of berberine alleviating metabolic disorder based on gut microbiome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 854885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koperska, A.; Wesołek, A.; Moszak, M.; Szulińska, M. Berberine in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Li, M.; Huang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, Q.; Ma, X.; Qiu, T.; Li, J. The clinical efficacy and safety of berberine in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita-Radu, F.; Patoni, C.; Nancoff, A.S.; Marin, F.S.; Gaman, L.; Bucurica, A.; Socol, C.; Jinga, M.; Dutu, M.; Bucurica, S. Berberine Effects in Pre-Fibrotic Stages of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Clinical and Pre-Clinical Overview and Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Gunn, N.; Neff, G.W.; Kohli, A.; Liu, L.; Flyer, A.; Goldkind, L.; Di Bisceglie, A.M. A phase 2, proof of concept, randomised controlled trial of berberine ursodeoxycholate in patients with presumed non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Y.; Kianpour, P.; Mohtashami, R.; Atkin, S.L.; Butler, A.E.; Jafari, R.; Badeli, R.; Sahebkar, A. Efficacy of artichoke leaf extract in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot double-blind randomized controlled trial. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majnooni, M.B.; Ataee, M.; Bahrami, G.; Heydarpour, F.; Aneva, I.Y.; Farzaei, M.H.; Ahmadi-Juoibari, T. The effects of co-administration of artichoke leaf extract supplementation with metformin and vitamin E in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6324–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Shokri-Mashhadi, N.; Saraf-Bank, S.; Mohammadi, H.; Zobeiri, M.; Clark, C.C.T.; Rouhani, M.H. The effects of Cynara scolymus L. supplementation on liver enzymes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, A.M.; Farag, M.A. Therapeutic Potential of Artichoke in the Treatment of Fatty Liver: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podszun, M.C.; Frank, J. Impact of vitamin E on redox biomarkers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podszun, M.C.; Alawad, A.S.; Lingala, S.; Morris, N.; Huang, W.C.A.; Yang, S.; Schoenfeld, M.; Rolt, A.; Ouwerkerk, R.; Valdez, K.; et al. Vitamin E treatment in NAFLD patients demonstrates that oxidative stress drives steatosis through upregulation of de-novo lipogenesis. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Fang, C.; Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Jia, J. Vitamin E intake is inversely associated with NAFLD measured by liver ultrasound transient elastography. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogli, S.; Naska, A.; Marinos, G.; Kasdagli, M.I.; Orfanos, P. The Effect of Vitamin E Supplementation on Serum Aminotransferases in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Bakhtawar, N. Vitamin E as an Adjuvant Treatment for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cureus 2020, 12, e9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karedath, J.; Javed, H.; Talpur, F.A.; Lal, B.; Kumari, A.; Kivan, H.; Chunchu, V.A.; Hirani, S. Effect of Vitamin E on Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2022, 14, e32764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Maboud, M.; Menshawy, A.; Menshawy, E.; Emara, A.; Alshandidy, M.; Eid, M. The efficacy of vitamin E in reducing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820974917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Gawrieh, S.; Ghabril, M.; Saxena, R.; Cummings, O.W.; Chalasani, N. Vitamin E Improves Transplant-Free Survival and Hepatic Decompensation Among Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Advanced Fibrosis. Hepatology 2020, 71, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrentzos, E.; Ikonomidis, I.; Pavlidis, G.; Katogiannis, K.; Korakas, E.; Kountouri, A.; Pliouta, L.; Michalopoulou, E.; Pelekanou, E.; Boumpas, D.; et al. Six-month supplementation with high dose coenzyme Q10 improves liver steatosis, endothelial, vascular and myocardial function in patients with metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Xue, H.; Zhang, P.; Fang, W.; Chen, X.; Ling, W. Coenzyme Q10 attenuates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through activation of the AMPK pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dludla, P.V.; Orlando, P.; Silvestri, S.; Marcheggiani, F.; Cirilli, I.; Nyambuya, T.M.; Mxinwa, V.; Mokgalaboni, K.; Nkambule, B.B.; Johnson, R.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation Improves Adipokine Levels and Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Peroxidation in Conditions of Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardekani, A.; Tabrizi, R.; Maleki, E.; Bagheri Lankarani, K.; Heydari, S.T.; Moradinazar, M.; Akbari, M. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on lipid profiles and liver enzymes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, F.; Mohammadshahi, M.; Alavinejad, P.; Rezazadeh, A.; Zarei, M.; Ahmadi Engali, K. Functions of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Liver Enzymes, Markers of Systemic Inflammation, and Adipokines in Patients Affected by Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, A.; Romano, A.; Cuozzo, S.; Di Nicola, A.; Grassi, O.; Schiaroli, D.; Nocera, G.F.; Pironti, M. Silymarin in Combination with Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Coenzyme Q10 and Selenomethionine to Improve Liver Enzymes and Blood Lipid Profile in NAFLD Patients. Medicina 2020, 56, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Tabrizi, R.; Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, P.; Jalali, M.; Shabani-Borujeni, M.; Modaresi, S.; Gholamalizadeh, M.; Doaei, S. The Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Anthropometric and Biochemical Indices in Patients With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 732496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhughosa, D.A.; Wibawa, I.D.N.; Mariadi, I.K.; Somayana, G. Additional treatment of vitamin D for improvement of insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, L. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on some metabolic parameters in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 8 RCTs. Medicine 2023, 102, e35717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Chen, L. Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 18, e97205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, T.; Niraj, M.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R.; Parveen, H. Effectiveness of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e68002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Fu, Y.; Yang, S.J.; Chi, C.C. Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Fernández-Galilea, M.; Martínez-Fernández, L.; González-Muniesa, P.; Pérez-Chávez, A.; Martínez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. Oxidative Stress and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Venditti, C.; Lee, H.Y.; Darch, M.; Floyd, S.; West, S.; Simon, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled intervention studies on the effectiveness of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 581–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmíd, V.; Dvořák, K.; Šedivý, P.; Kosek, V.; Leníček, M.; Dezortová, M.; Hajšlová, J.; Hájek, M.; Vítek, L.; Bechyňská, K.; et al. Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Lipid Metabolism in Patients With Metabolic Syndrome and NAFLD. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Karampela, I.; Tsilingiris, D.; Magkos, F.; Stratigou, T.; Kounatidis, D.; Dalamaga, M. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome and Microbial Metabolites in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Perspectives. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, B.; Seyfried, N.; Hartmann, D.; Hartmann, P. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and alcohol-associated liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2023, 325, G42–G61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Duan, F.; Jia, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, S. The promising role of probiotics/prebiotics/synbiotics in energy metabolism biomarkers in patients with NAFLD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 862266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanasurakit, S.; Kositamongkol, C.; Lanoi, K.; Nunta, M.; Saetuan, T.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Saokaew, S.; Phisalprapa, P. Effects of Synbiotics, Probiotics, and Prebiotics on Liver Enzymes of Patients With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 880014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C. Efficacy of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on liver enzymes, lipid profiles, and inflammation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghipour, A.; Amini-Salehi, E.; Orang Gorabzarmakhi, M.; Shahdkar, M.; Fouladi, B.; Alipourfard, I.; Momayez Sanat, Z. Effects of gut microbial therapy on lipid profile in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An umbrella meta-analysis study. Syst. Rev. 2023, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wei, C.B.; Gu, W.; Hou, L.L. Relevance of vitamin D on NAFLD and liver fibrosis detected by vibration controlled transient elastography in US adults: A cross-sectional analysis of NHANES 2017–2018. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2209335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Heterogeneous pathomechanisms and effectiveness of metabolism-based treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hashmi, K.; Giglio, R.V.; Pantea Stoian, A.; Patti, A.M.; Al Waili, K.; Al Rasadi, K.; Ciaccio, M.; Rizzo, M. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Current therapeutic strategies. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1355732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrickson, G.; Barrow, F.; Dietsche, K.; Parthiban, P.; Khan, S.; Robert, S.; Demirchian, M.; Rhoades, H.; Wang, H.; Adeyi, O.; et al. Exercise of high intensity ameliorates hepatic inflammation and the progression of NASH. Mol. Metab. 2021, 53, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Colletti, A.; Penson, P.E.; Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Toth, P.P.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Mancini, J.; Marais, D.; Moriarty, P.; et al. Nutraceutical approaches to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP). Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 189, 106679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Morze, J.; Hoffmann, G. Mediterranean diet and health status: Active ingredients and pharmacological mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, N.; Merota, V.; Joshi, R.; Kaur, G.; Tuli, H.S.; Buttar, H.S. The Impact of Antioxidant Diets, Nutraceuticals and Physical Activity Interventions in the Prevention of Cardiometabolic Diseases: An Overview. Scr. Medica 2023, 54, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciumărnean, L.; Sârb, O.F.; Drăghici, N.C.; Sălăgean, O.; Milaciu, M.V.; Orășan, O.H.; Vlad, C.V.; Vlad, I.M.; Alexescu, T.; Para, I.; et al. Obesity Control and Supplementary Nutraceuticals as Cofactors of Brain Plasticity in Multiple Sclerosis Populations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAli, M.; Alqubaisy, M.; Aljaafari, M.N.; AlAli, A.O.; Baqais, L.; Molouki, A.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lai, K.S.; Lim, S.H.E. Nutraceuticals: Transformation of Conventional Foods into Health Promoters/Disease Preventers and Safety Considerations. Molecules 2021, 26, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, V.J.; Khan, I.; Björnsson, E.; Seeff, L.B.; Serrano, J.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Liver injury from herbal and dietary supplements. Hepatology 2017, 65, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fravel, M.A.; Ernst, M.E.; Gilmartin-Thomas, J.; Woods, R.L.; Orchard, S.G.; Owen, A.J. Dietary supplement and complementary and alternative medicine use among older adults in Australia and the United States. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2023, 71, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.T.; Coates, P.M.; Smith, M.J. Dietary Supplements: Regulatory Challenges and Research Resources. Nutrients 2018, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.L. Current regulatory guidelines and resources to support research of dietary supplements in the United States. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Yasuda, S.; Kimoto, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Nakade, Y.; Ito, K.; Osonoi, T.; Yoneda, M. Comparison of Efficacy between Pemafibrate and Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Ester in the Liver: The PORTRAIT Study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2024, 31, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Iida, S.; Katsuyama, H. Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-Its Pathophysiology, Association with Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease, and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 2019, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.S.; Rinella, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, P.; Prejbisz, A.; Kuryłowicz, A.; Baska, A.; Burchardt, P.; Chlebus, K.; Dzida, G.; Jankowski, P.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Jaworski, P.; et al. Metabolic syndrome—A new definition and management guidelines: A joint position paper by the Polish Society of Hypertension, Polish Society for the Treatment of Obesity, Polish Lipid Association, Polish Association for Study of Liver, Polish Society of Family Medicine, Polish Society of Lifestyle Medicine, Division of Prevention and Epidemiology Polish Cardiac Society, “Club 30” Polish Cardiac Society, and Division of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Society of Polish Surgeons. Arch. Med. Sci. 2022, 18, 1133–1156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Valenti, L. A Nutrigenomic Approach to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
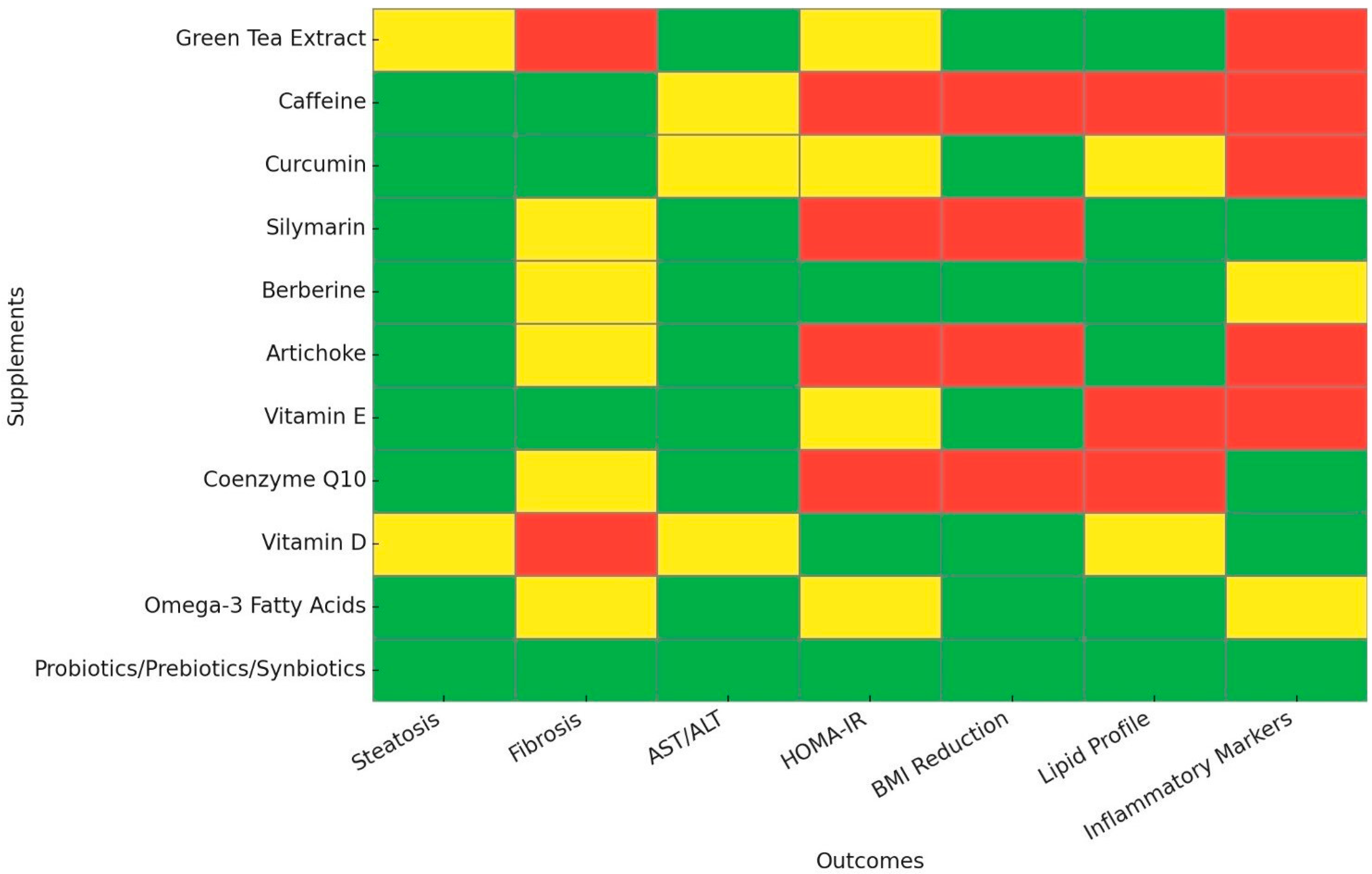
| Name | Mechanism of Action | Main Outcomes | Dose Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green Tea Extract | Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant via EGCG actions | ⬇ AST/ALT, ⬇ BMI, ⬇ TC/LDL-C/TG | 200–400 mg EGCG daily or 3–5 cups of tea |
| Caffeine | Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant via TLR4/MAPK/NF-Κb inhibition | ⬇ Liver fat, ⬇ Liver fibrosis | 2–4 cups of coffee per day |
| Curcumin | Activates AMPK, reduces inflammation via IL-6/TNF-a inhibition | ⬇ Liver fat, ⬇ Liver fibrosis, ⬇ ALT, ⬇ TG, ⬇ BMI | 250–3000 mg/day |
| Silymarin | Antioxidant via Nrf2 activation, anti-inflammatory via IL-6/TNF-a inhibition | ⬇ AST/ALT, ⬇ Liver fat, ⬇ TG, ⬆ HDL-C, ⬇ CRP | 420–600 mg/day |
| Berberine | Activates AMPK, modulates gut microbiota, improves insulin sensitivity | ⬇ Liver fat, ⬇ AST/ALT, ⬇ TC/TG, ⬇ HOMA-IR, ⬇ BMI | 500–1500 mg/day |
| Artichoke | HMG-CoA & NPC1L1 inhibition, ROS reduction | ⬇ Liver fat, ⬇ AST/ALT, ⬇ TC/LDL-C/TG, ⬆ Hepatic vein flow | 100–2700 mg/day |
| Vitamin E | Antioxidant, ROS reduction, SREBP-1 suppression | ⬇ AST/ALT, ⬇ Liver fat, ⬇ Liver fibrosis, ⬇ BMI | 400–800 IU/day |
| Coenzyme Q10 | AMPK activation, SREBP-1c/ROS downregulation | ⬇ Liver fat, ⬇ AST/ALT, ⬇ CRP | 100–240 mg/day |
| Vitamin D | Anti-inflammatory via IL-6/TNF-a inhibition, GLUT-4 upregulation | ⬇ ALT, ⬆ HDL-C, ⬇ HOMA-IR, ⬇ CRP, ⬇BMI | 2000–5000 IU/day |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | SREBP-1 suppression, PPAR-α activation | ⬇ Liver fat, ⬇ AST/ALT, ⬇ TC/LDL-C/TG, ⬆ HDL-C, ⬇ BMI | 2–4 g EPA/DHA per day |
| Probiotics/Prebiotics/Synbiotics | Modulates gut microbiota, reduces systemic inflammation | ⬇ AST/ALT, ⬇ TC/LDL-C/TG, ⬇ HOMA-IR, ⬇ Liver fibrosis, ⬇ TNF-a, ⬇ BMI | At least 12 weeks of PPS supplementation |
| Time | Meal | Drink | Supplements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7:00 AM | Scrambled eggs with avocado & whole-grain toast OR Greek yogurt with walnuts | Cup of Coffee (or decaf if sensitive) | Berberine (1000 mg) and Probiotic capsule (before meal) |
| 10:00 AM | A handful of almonds/sunflower seeds | Green Tea | None |
| 1:00 PM | Grilled salmon or lean chicken with roasted vegetables & quinoa | Water or Herbal Tea | Curcumin (800 mg), Silymarin (140 mg), Vitamin D (2000 IU) |
| 7:30 PM | Baked fish or grilled tofu with steamed greens & whole grains | Water or Chamomile Tea | Artichoke Leaf Extract (300 mg), Omega-3 (2 g EPA/DHA), Vitamin E (400 IU), Coenzyme Q10 (240 mg) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrentzos, E.; Pavlidis, G.; Korakas, E.; Kountouri, A.; Pliouta, L.; Dimitriadis, G.D.; Lambadiari, V. Nutraceutical Strategies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Path to Liver Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101657
Vrentzos E, Pavlidis G, Korakas E, Kountouri A, Pliouta L, Dimitriadis GD, Lambadiari V. Nutraceutical Strategies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Path to Liver Health. Nutrients. 2025; 17(10):1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101657
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrentzos, Emmanouil, George Pavlidis, Emmanouil Korakas, Aikaterini Kountouri, Loukia Pliouta, George D. Dimitriadis, and Vaia Lambadiari. 2025. "Nutraceutical Strategies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Path to Liver Health" Nutrients 17, no. 10: 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101657
APA StyleVrentzos, E., Pavlidis, G., Korakas, E., Kountouri, A., Pliouta, L., Dimitriadis, G. D., & Lambadiari, V. (2025). Nutraceutical Strategies for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Path to Liver Health. Nutrients, 17(10), 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101657









