Evaluation of a Novel Enteral Phosphorus Therapy with Enteral Nutrition during a National Intravenous Sodium Phosphate Shortage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, K.A.; Dickerson, R.N.; Morgan, L.M.; Alexander, K.H.; Minard, G.; Brown, R.O. A new graduated dosing regimen for phosphorus replacement in patients receiving nutrition support. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2006, 30, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, M.S.; Moshfegh, A.J.; Tucker, K.L. Assessing the health impact of phosphorus in the food supply: Issues and considerations. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.S.V.; Seres, D.S.; Sabino, K.; Adams, S.C.; Berdahl, G.J.; Citty, S.W.; Cober, M.P.; Evans, D.C.; Greaves, J.R.; Gura, K.M.; et al. ASPEN consensus recommendations for refeeding syndrome. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, R.P. Phosphorus nutrition and the treatment of osteoporosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2004, 79, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulbis, B.E.; Ruiz, M.C.; Denktas, A.E. The impact of drug shortages on the pharmacy, nursing, and medical staff’s ability to effectively care for critically ill patients. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2013, 36, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erstad, B.L. Dosing of medications in morbidly obese patients in the intensive care unit setting. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, R.N.; Pitts, S.L.; Maish, G.O., 3rd; Schroeppel, T.J.; Magnotti, L.J.; Croce, M.A.; Minard, G.; Brown, R.O. A reappraisal of nitrogen requirements for patients with critical illness and trauma. J. Trauma. Acute Care Surg. 2012, 73, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, D.Z.; Guenter, P.A.; Settle, R.G. Defining and reporting diarrhea in tube-fed patients—What a mess! Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 55, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubier, M.; Murciano, D.; Lecocguic, Y.; Viires, N.; Jacquens, Y.; Squara, P.; Pariente, R. Effect of hypophosphatemia on diaphragmatic contractility in patients with acute respiratory failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazzo, J.F.; Troche, G.; Ruel, P.; Maintenant, J. High incidence of hypophosphatemia in surgical intensive care patients: Efficacy of phosphorus therapy on myocardial function. Intensive Care Med. 1995, 21, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, G.F.; Grzyb, S. Phosphate depletion and repletion: Relation to parenteral nutrition and oxygen transport. Ann. Surg. 1975, 182, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvis, S.E.; Paragas, P.D., Jr. Paresthesias, weakness, seizures, and hypophosphatemia in patients receiving hyperalimentation. Gastroenterology 1972, 62, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinsier, R.L.; Krumdieck, C.L. Death resulting from overzealous total parenteral nutrition: The refeeding syndrome revisited. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liamis, G.; Milionis, H.J.; Elisaf, M. Medication-induced hypophosphatemia: A review. QJM 2010, 103, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, V.; Schwartz, A.; Kalickman, I.; Nisman, B.; Gurman, G.; Shoenfeld, Y. Prevalence of hypophosphatemia in sepsis and infection: The role of cytokines. Am. J. Med. 1998, 104, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, R.; Khardori, R. Severe hypophosphatemia. Pathophysiologic implications, clinical presentations, and treatment. Medicine 2000, 79, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsey, K.A.; Brown, R.O.; Maish, G.O., 3rd; Croce, M.A.; Minard, G.; Dickerson, R.N. Influence of traumatic brain injury on potassium and phosphorus homeostasis in critically ill multiple trauma patients. Nutrition 2010, 26, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankenfield, D.C.; Coleman, A.; Alam, S.; Cooney, R.N. Analysis of estimation methods for resting metabolic rate in critically ill adults. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2009, 33, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, R.N.; Melnik, G. Osmolality of oral drug solutions and suspensions. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1988, 45, 832–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, R.N.; Crawford, C.N.; Tsiu, M.K.; Bujanowski, C.E.; Van Matre, E.T.; Swanson, J.M.; Filiberto, D.M.; Minard, G. Augmented renal clearance following traumatic injury in critically ill patients requiring nutrition therapy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, R.N.; Gervasio, J.M.; Sherman, J.J.; Kudsk, K.A.; Hickerson, W.L.; Brown, R.O. A comparison of renal phosphorus regulation in thermally injured and multiple trauma patients receiving specialized nutrition support. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2001, 25, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, G.S.; Perazella, M.A. Acute phosphate nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, K.R.; Govel, L.A.; Andritz, M.H. Gastrointestinal effects of sorbitol as an additive in liquid medications. Am. J. Med. 1994, 97, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velentzas, C.; Meindok, H.; Oreopoulos, D.G.; Meema, H.E.; Rabinovich, S.; Jones, M.; Sutton, D.; Rapoport, A.; deVeber, G. Visceral calcification and the CaXP product. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1978, 103, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, R.N.; Alexander, K.H.; Minard, G.; Croce, M.A.; Brown, R.O. Accuracy of methods to estimate ionized and “corrected” serum calcium concentrations in critically ill multiple trauma patients receiving specialized nutrition support. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2004, 28, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable * | Lower Dose | Higher Dose | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 22 | 11 | - |
| Age, y | 49 [29, 64] | 34 [27, 48] | 0.331 |
| Actual weight, kg | 83 [68, 102] | 82 [72, 90] | 0.789 |
| Ideal body weight, kg | 65 (59, 75) | 71 (66, 78) | 0.292 |
| Adjusted dosing weight, kg | 76 [68, 85] | 75 [72, 84] | 0.619 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 26.3 [23.0, 33.1] | 27.0 [24.5, 28.8] | 0.717 |
| Sex, male/female, n/n | 14/8 | 9/2 | 0.430 |
| Race | |||
| Black, n | 13 | 7 | 0.586 |
| White, n | 7 | 4 | |
| Hispanic, n | 2 | 0 | |
| Admission diagnosis | |||
| Motor vehicle collision, n | 16 | 7 | 0.329 |
| GSW/KSW, n | 2 | 3 | |
| Fall/assault, n | 1 | 1 | |
| Other, n | 3 | 0 | |
| Severe TBI with ICP monitoring, n (%) | 7 (32%) | 2 (18%) | 0.681 |
| Ventilator dependent, n | 21 (95%) | 11 (100%) | 1.000 |
| TICU length of stay, d | 14 [9, 19] | 14 [12, 18] | 0.515 |
| Hospital length of stay, d | 28 [18, 45] | 21 [19, 41] | 0.390 |
| Ventilator dependent, n (%) | 21 (95%) | 11 (100%) | 1.000 |
| Survived, n (%) | 17 (77%) | 10 (91%) | 0.637 |
| Serum potassium, mEq/L | 4.2 [4.0, 4.3] | 4.2 [4.0, 4.4] | 0.546 |
| mmol/L | 4.2 [4.0, 4.3] | 4.2 [4.0, 4.4] | |
| White blood cell count, cells/µm3 | 10.7 [9.3, 13.5] | 10.5 [7.8. 14.3] | 0.717 |
| Serum magnesium, mg/dL | 2.0 [2.0, 2.1] | 1.8 [1.7, 2.1] | 0.055 |
| mmol/L | 0.82 [0.82, 0.86] | 0.74 [0.70, 0.86] | |
| C-reactive protein, mg/dL | 25.0 [17.9, 34.3] | 18.1 [10.9, 31.8] | 0.172 |
| mg/L | 250 [179, 343] | 181 [109, 318] | |
| Prealbumin, mg/dL | 9.0 [4.5, 13.5] | 10.0 [7.0, 14.3] | 0.364 |
| mg/L | 90 [45, 135] | 100 [70, 143] | |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 [0.6, 1.0] | 0.8 [0.7, 0.9] | 0.907 |
| µmol/L | 71 [53, 88] | 77 [62, 80] | |
| Serum urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 18 [13, 27] | 18 [10, 27] | 0.804 |
| mmol/L | 6.4 [4.6, 9.6] | 6.4 [3.6, 9.6] | |
| Serum glucose, mg/dL | 135 [113, 164] | 113 [104, 122] | 0.070 |
| mmol/L | 7.5 [6.3, 9.1] | 6.3 [5.8, 6.8] | |
| Total fluid intake, L/d | 2.9 [2.2, 3.5] | 3.1 [1.8, 3.4] | 0.954 |
| Total fluid output, L/d | 1.9 [1.4, 3.0] | 2.2 [1.1, 3.7] | 0.554 |
| Received vasopressors during EN, n (%) | 2 (9%) | 1 (9%) | 1.000 |
| Variable * | Lower Dose | Higher Dose | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 22 | 11 | - |
| Phosphorus dose, mmol | 34 | 68 | - |
| Phosphorus dose, mmol/kg dosing weight | 0.45 [0.40, 0.50] | 0.91 [0.81, 0.94] | 0.001 |
| EN phosphorus intake, mmol ¶ | 19.5 [8.8, 34] | 24 [12, 33] | 0.789 |
| Day of EN, d ¶ | 2 [1, 7] | 2 [1, 4] | 0.556 |
| TICU day, d ¶, | 5 [3, 10] | 4 [2, 6] | 0.317 |
| Caloric intake, kcals/d ¶ | 899 [423, 1405] | 1035 [443, 1513] | 0.717 |
| Carbohydrate intake, g/d ¶ | 64 [39, 136] | 107 [55, 161] | 0.480 |
| Insulin intake, units/d ¶ | 0 [0, 3] | 0 [0, 0] | 0.477 |
| Arterial pH pre-dose | 7.42 [7.36, 7.47] | 7.42 [7.37, 7.45] | 0.560 |
| Arterial pH post-dose | 7.45 [7.39, 7.49] | 7.44 [7.29, 7.50] | 0.830 |
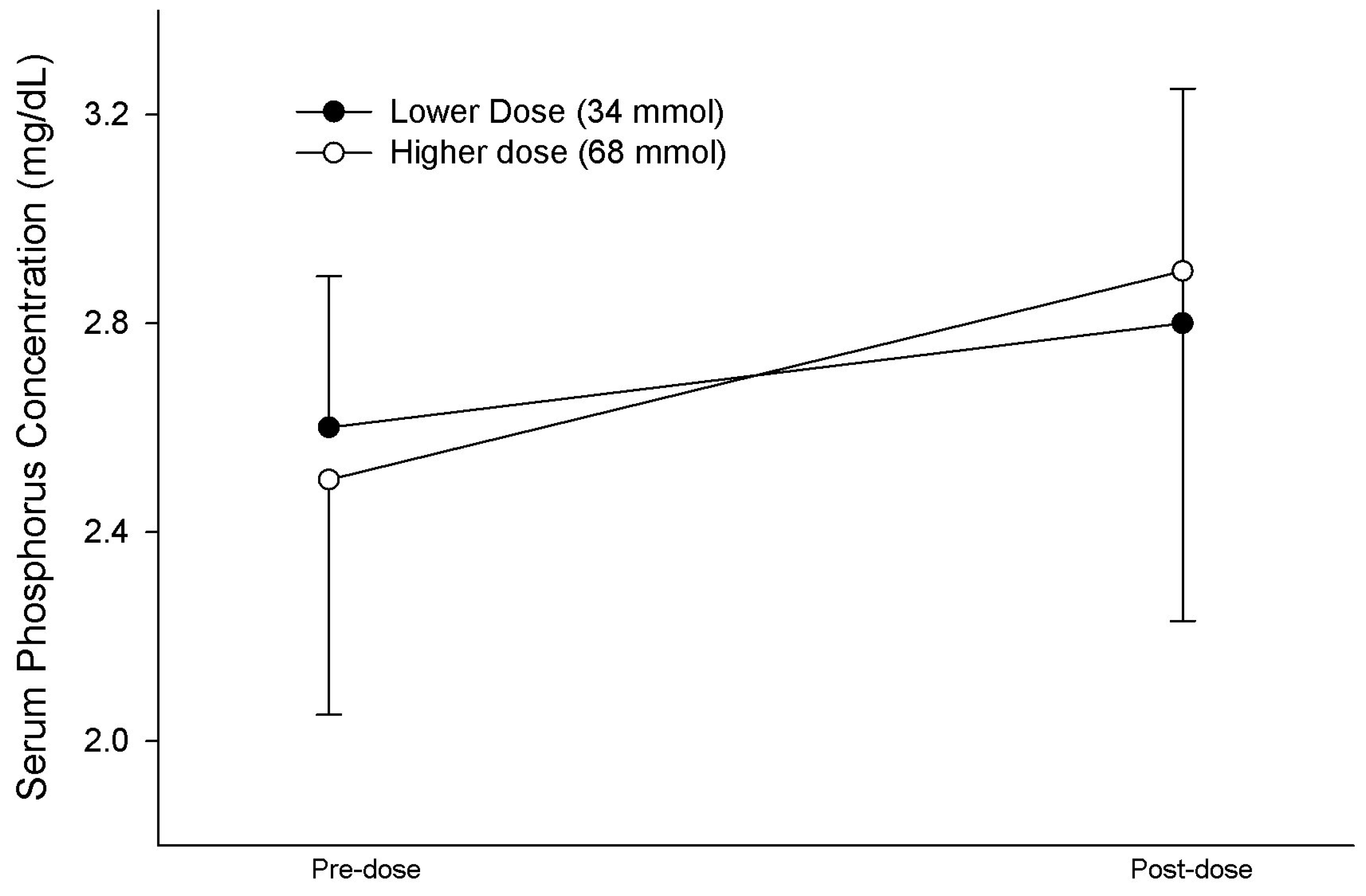
| Initial serum phosphorus, mg/dL | 2.6 [2.4, 2.8] | 2.5 [2.1, 2.8] | 0.465 |
| mmol/L | 0.84 [0.77, 0.90] | 0.81 [0.68, 0.90] | |
| Final serum phosphorus, mg/dL | 2.8 [1.9, 3.3] | 2.9 [2.2, 3.0] | 0.878 |
| mmol/L | 0.90 [0.61, 1.07] | 0.94 [0.71, 0.97] | |
| ∆ in serum phosphorus, mg/dL | 0.2 [−0.5, 0.7] | 0.6 [−0.3, 0.8] | 0.646 |
| mmol/L | 0.06 [−0.16, 0.23] | 0.19 [−0.10, 0.26] | |
| Improvement in serum phosphorus, n (%) | 12 (55%) | 8 (73%) | 0.436 |
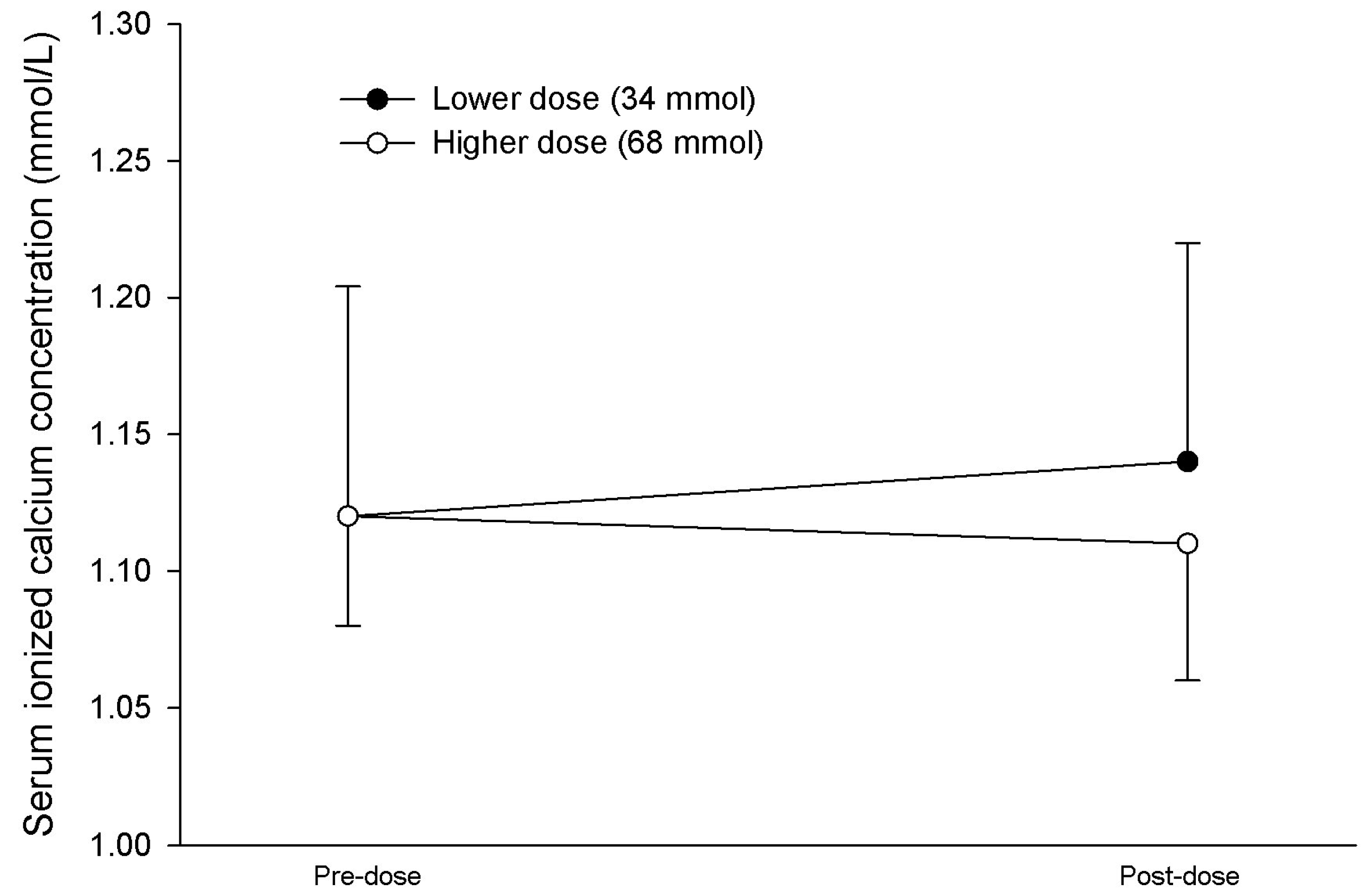
| Initial serum iCa, mmol/L | 1.11 [1.07, 1.17] | 1.14 [1.11, 1.15] | 0.984 |
| Final serum iCa, mmol/L | 1.15 [1.09, 1.20] | 1.12 [1.08, 1.16] | 0.251 |
| Diarrhea, n (%) | 3 (14%) | 0 (0%) | 0.534 |
| Variable * | Responded | Not Responded | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 20 | 13 | - |
| Initial serum phosphorus, mg/dL | 2.6 [2.3, 2.8] | 2.6 [2.3, 2.8] | 0.811 |
| mmol/L | 0.84 [0.74, 0.90] | 0.84 [0.74, 0.90] | |
| Final serum phosphorus, mg/dL | 3.1 [2.9, 3.6] | 1.9 [1.6, 2.3] | 0.001 |
| mmol/L | 1.0 [0.94, 1.16] | 0.61 [0.52, 0.74] | |
| Phosphorus dose, mmol | 35 [35, 70] | 35 [35, 53] | 0.332 |
| Phosphorus dose, mmol/kg dosing weight | 0.53 [0.44, 0.85] | 0.51 [0.42, 0.80] | 0.495 |
| EN phosphorus intake, mmol/d | 16 [7, 31] | 24 [16, 35] | 0.172 |
| Age, y | 36 [26, 60] | 48 [40, 66] | 0.167 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27.5 [24.5, 31.5] | 25.8 [22.6, 30.0] | 0.585 |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 [0.6, 0.9] | 0.8 [0.8, 1.0] | 0.202 |
| µmol/L | 71 [53, 80] | 71 [71, 88] | |
| C-reactive protein, mg/dL ¶ | 25.0 [16.5, 34.3] | 19.6 [10.0, 29.5] | 0.144 |
| mg/L ¶ | 250 [165, 343] | 196 [100, 295] | |
| Prealbumin, mg/dL ¶ | 8.5 [5.8, 13.0] | 10.0 [6.0, 16.0] | 0.518 |
| mg/L ¶ | 85 [58, 130] | 100 [60, 160] | |
| WBC, cells/µm3 | 10.6 [9.0, 12.0] | 11.9 [9.5, 15.8] | 0.308 |
| Arterial pH pre-dose | 7.42 [7.36, 7.48] | 7.40 [7.36, 7.44] | 0.639 |
| Arterial pH post-dose | 7.44 [7.34, 7.47] | 7.45 [7.41, 7.51] | 0.208 |
| Admit diagnosis of MVC, n (%) | 15 (75%) | 8 (62%) | 0.745 |
| Traumatic brain injury, n (%) | 5 (25%) | 4 (31%) | 1.000 |
| Survived, n (%) | 16 (80%) | 11 (85%) | 1.000 |
| Day of EN, d ¶ | 2 [1, 4] | 2 [1, 8] | 0.955 |
| TICU day, d ¶, | 4 [3, 6] | 4 [2, 11] | 0.741 |
| Caloric intake, kcals/d ¶ | 703 [340, 1469] | 985 [777, 1467] | 0.261 |
| Carbohydrate intake, g/d ¶ | 60 [28, 123] | 108 [63, 162] | 0.203 |
| Serum glucose, mg/dL ¶ | 118 [109, 139] | 136 [115, 161] | 0.196 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harris, T.D.; Farrar, J.E.; Byerly, S.; Filiberto, D.M.; Dickerson, R.N. Evaluation of a Novel Enteral Phosphorus Therapy with Enteral Nutrition during a National Intravenous Sodium Phosphate Shortage. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091394
Harris TD, Farrar JE, Byerly S, Filiberto DM, Dickerson RN. Evaluation of a Novel Enteral Phosphorus Therapy with Enteral Nutrition during a National Intravenous Sodium Phosphate Shortage. Nutrients. 2024; 16(9):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091394
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarris, Tinia D., Julie E. Farrar, Saskya Byerly, Dina M. Filiberto, and Roland N. Dickerson. 2024. "Evaluation of a Novel Enteral Phosphorus Therapy with Enteral Nutrition during a National Intravenous Sodium Phosphate Shortage" Nutrients 16, no. 9: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091394
APA StyleHarris, T. D., Farrar, J. E., Byerly, S., Filiberto, D. M., & Dickerson, R. N. (2024). Evaluation of a Novel Enteral Phosphorus Therapy with Enteral Nutrition during a National Intravenous Sodium Phosphate Shortage. Nutrients, 16(9), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091394






