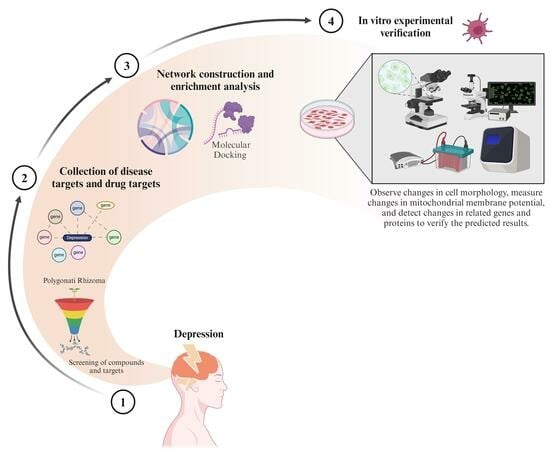
Interpreting the Mechanism of Active Ingredients in Polygonati Rhizoma in Treating Depression by Combining Systemic Pharmacology and In Vitro Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Retrieval and Screening of Active Compounds in Polygonati Rhizoma
2.2. Target Acquisition of Candidate Compounds in Polygonati Rhizoma
2.3. Acquisition of Depression-Related Targets
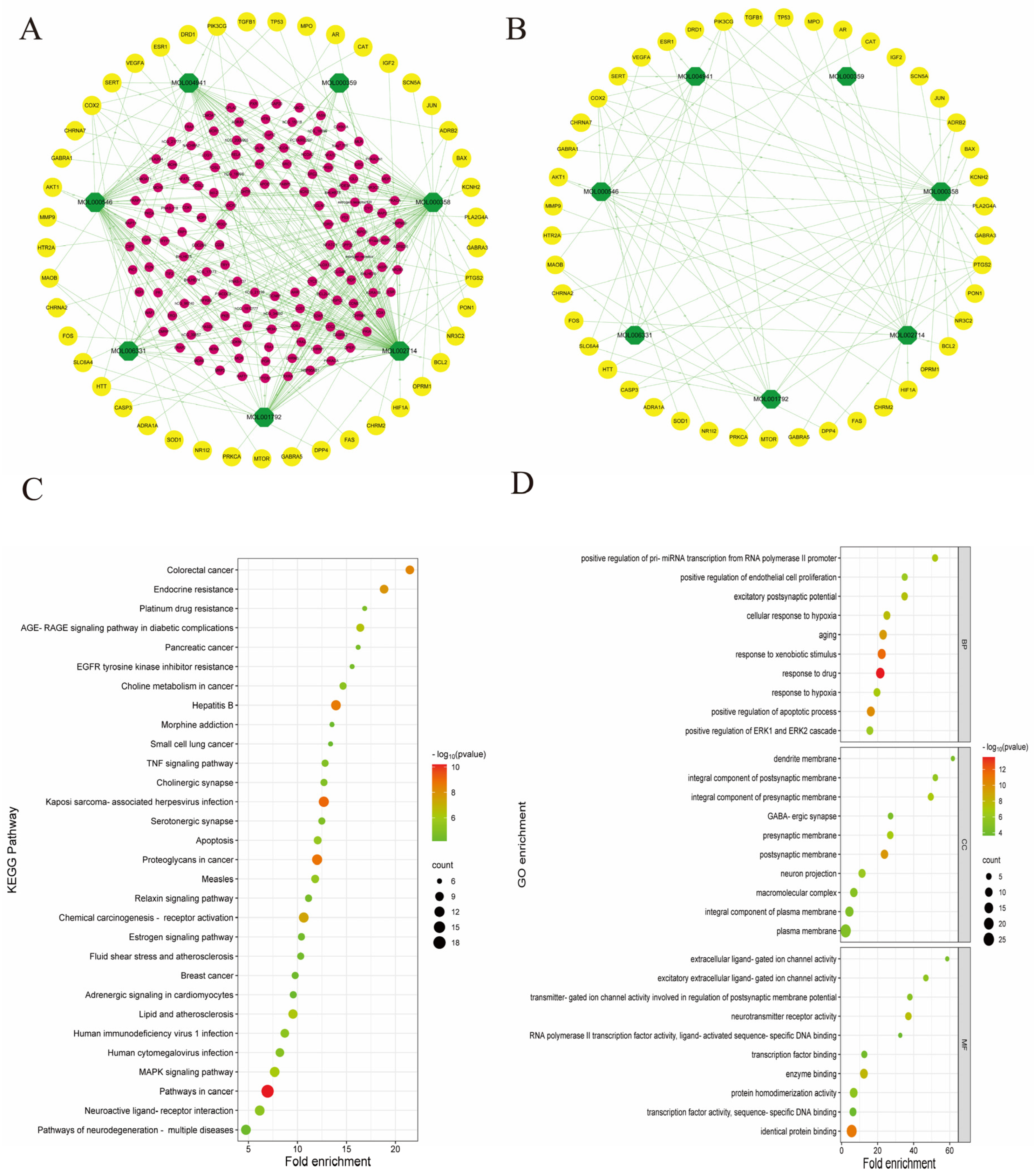
2.4. Networks Construction
2.5. Enrichment Analysis
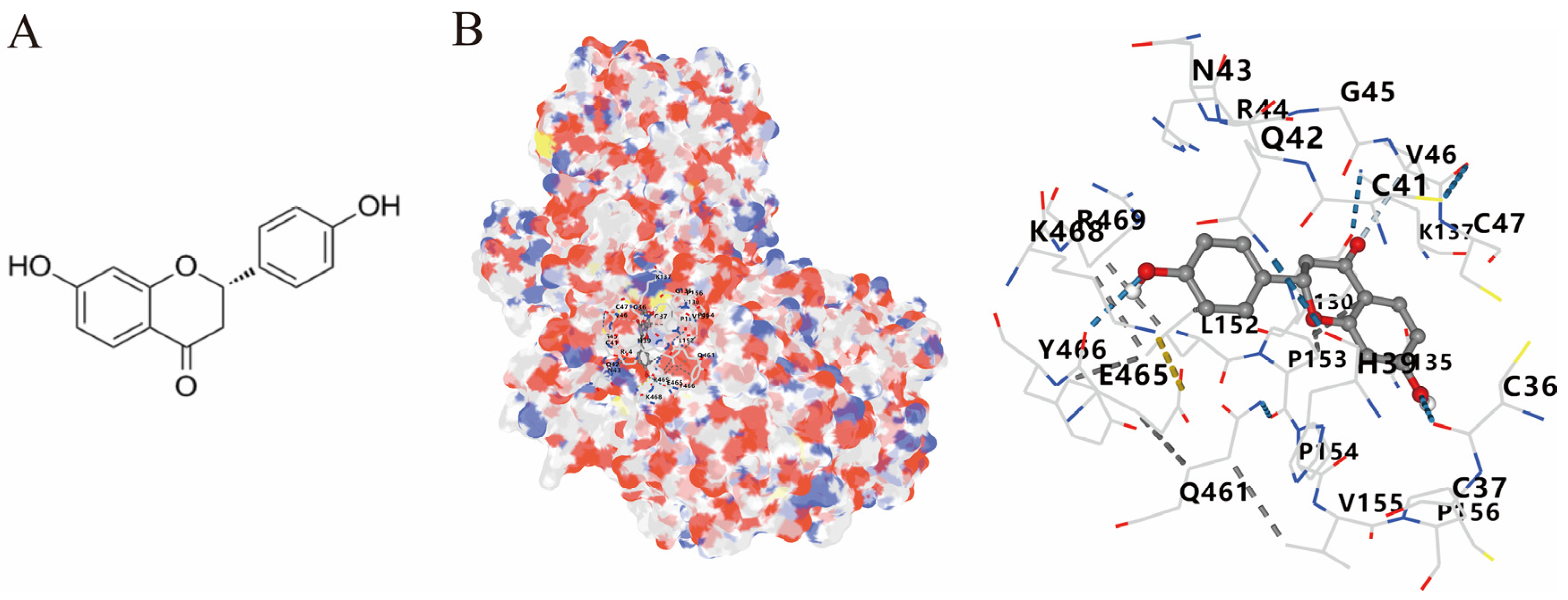
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. Reagents
2.8. CCK8 Assay
2.9. SOD and MDA Detection
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay
2.11. Morphologic Observation of BV-2 Cells and Rhodamine123 Staining
2.12. Western Blot Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
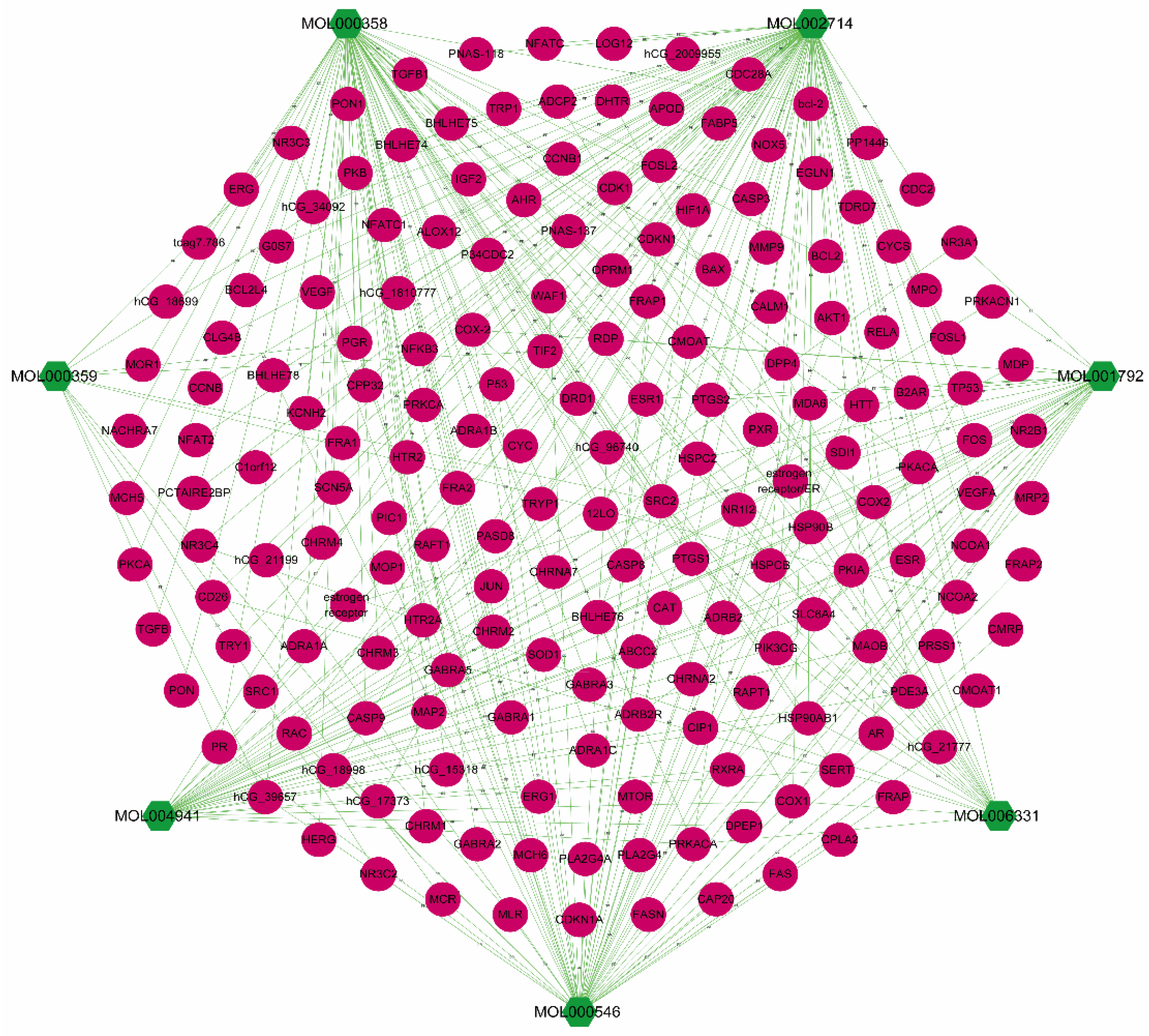
3.1. Acquisition of Candidate Compounds and Targets in Polygonati Rhizoma
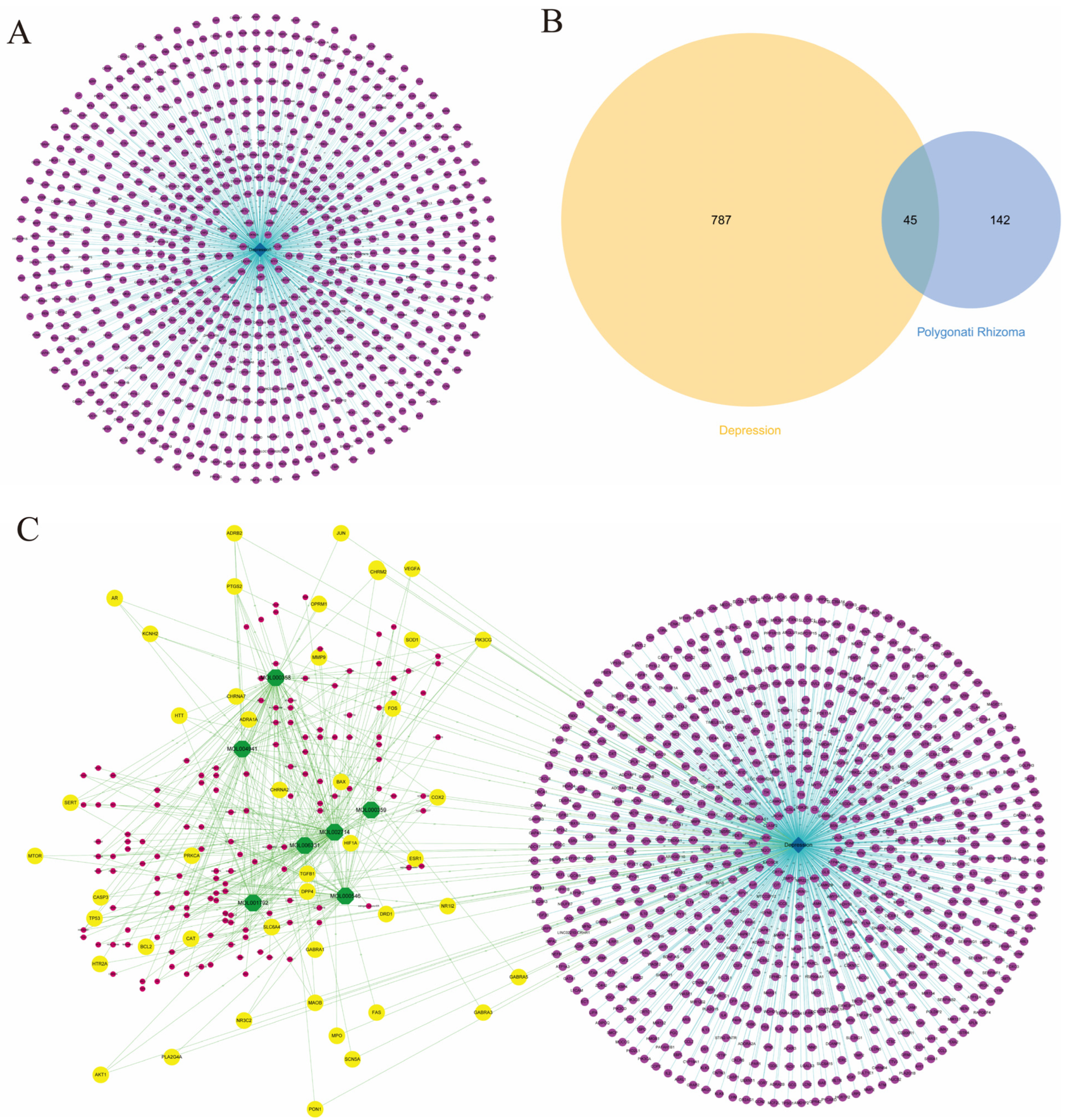
3.2. Targets Collection for Depression
3.3. PR–Depression Targets Network Construction and Enrichment Analysis
3.4. Molecular Docking of COX2 with Correlative Compounds
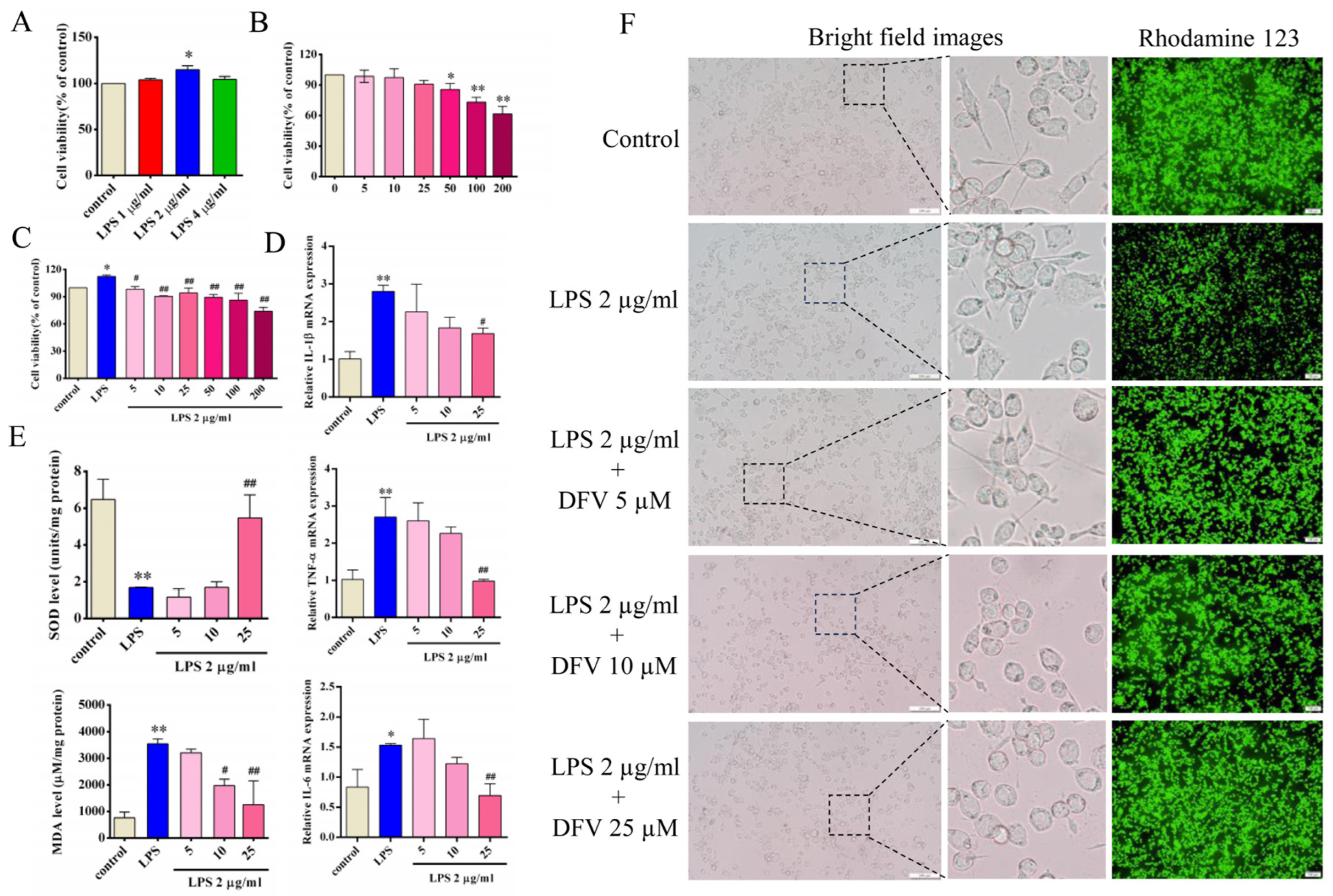
3.5. Effect of DFV on Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Induced BV-2 Cells
3.6. Effect of DFV on MDA and SOD Release in LPS-Induced BV-2 Cells
3.7. Effect of DFV on Mitochondrial Membrane Potential of LPS-Induced BV-2 Cells
3.8. Effects of DFV on the Expression of COX2, NLRP3, and Caspase1 in LPS-Induced BV-2 Cells
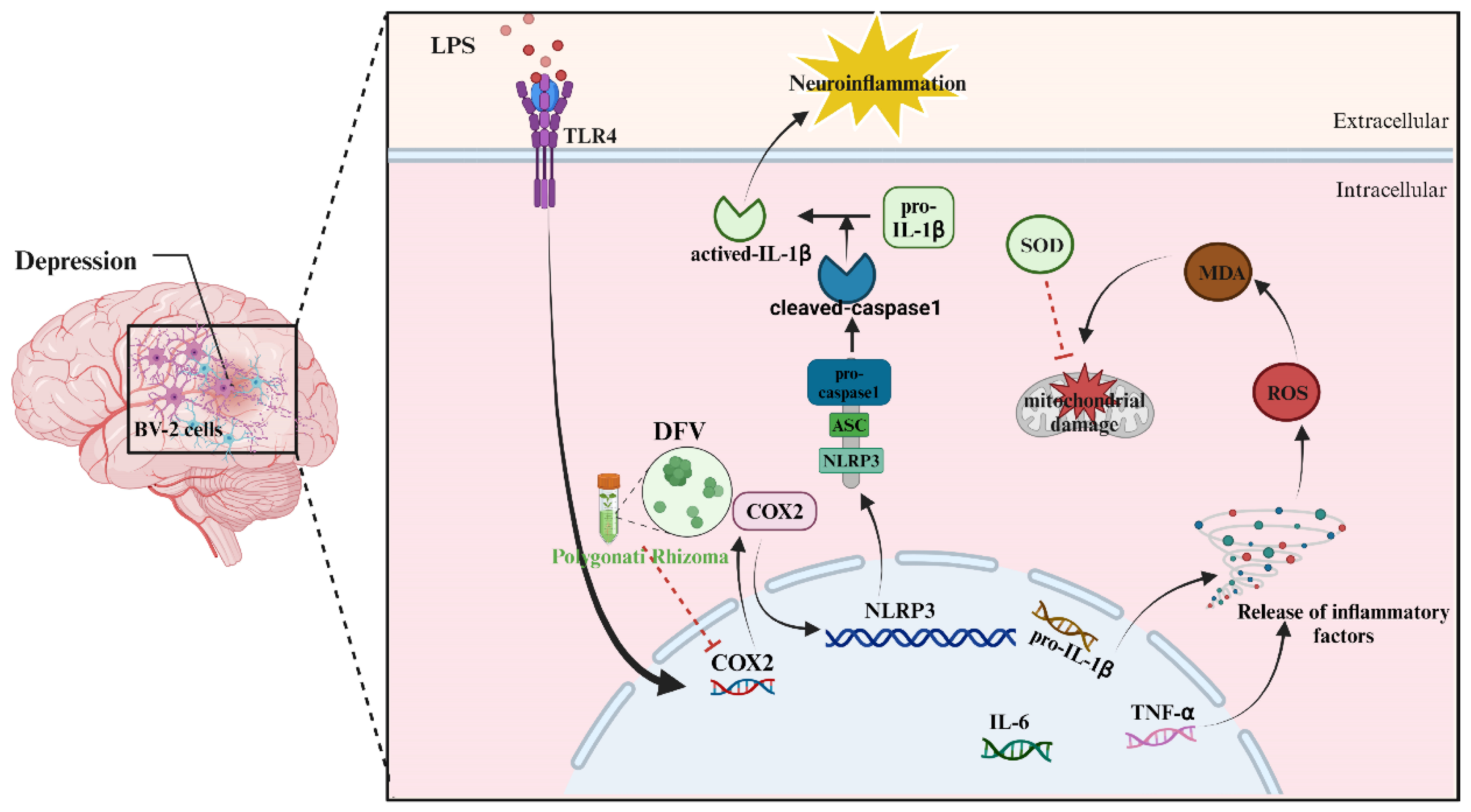
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bachmann, S. Epidemiology of Suicide and the Psychiatric Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, F.; Gao, J.; Guan, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Qin, Z.; Tang, K.; Liu, S. Proteomics-based screening of the target proteins associated with antidepressant-like effect and mechanism of Saikosaponin A. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, M.; Robinson, E. Depression and anxiety during COVID-19. Lancet 2022, 399, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.R.; Qin, X. Depression hurts, depression costs: The medical spending attributable to depression and depressive symptoms in China. Health Econ. 2018, 27, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Amin, A.; Li, X.; Xie, Y. Potential compound from herbal food of Rhizoma Polygonati for treatment of COVID-19 analyzed by network pharmacology: Viral and cancer signaling mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 77, 104149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, C.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, Z. Polygonati Rhizoma with the homology of medicine and food: A review of ethnopharmacology, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and applications. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, P.; Xu, G.; Sun, T. Immunological regulation of the active fraction from Polygonatum sibiricum F. Delaroche based on improvement of intestinal microflora and activation of RAW264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.J.; Wu, W.; Fang, S.F. Exploration of the Treatment of Vascular Depression with Peiyuan Kaiyu Method. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Inf. 2009, 16, 85–86. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.J.; Pan, J.H.; Wang, Y.Y. Application of Huangjing in depression and exploration of its antidepressant mechanism. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Inf. 2015, 22, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.Y.; Xu, W.P.; Wei, W.; Chen, C.; Xu, T.J. The effect of Huangjing saponins on behavior and monoamine neurotransmitters in the brain of depression model mice. Chin. J. New Drugs 2009, 18, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.L.; Xu, W.P.; Wei, W.; Xu, T.J. Behavioral effects of total saponins from Polygonatum sibiricum on chronic stress model rats and their effects on BDNF and TrkB expression in the hippocampus. Chin. J. New Drugs 2010, 19, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, W.P.; Wei, W.; Xu, T.J. Effects of Huangjing saponins on behavior and trace elements in serum of rats with chronic mild unpredictable stress depression model. J. Anhui Med. Univ. 2012, 47, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, T.T.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.M.; Xu, T.J.; Xu, W.P.; Wei, W. Effects of Huangjing saponins on 5-HT1A R-β-arrestin2-akt signaling pathway in cerebral cortex of chronic stress and depression rats. J. Anhui Med. Univ. 2013, 48, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.H.; Xu, W.P.; Wei, W.; Chen, C. The effect of Huangjing saponins on the 5-HT1AR/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway in the hippocampus of chronic stress-induced depression rats. J. Anhui Med. Univ. 2012, 47, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: Theory, methodology and application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, X.J.; Liu, L.Q. Mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of Qingfeiyin in treating acute lung injury based on GEO datasets, network pharmacology and molecular docking. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wei, S.; Niu, S.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Jing, M.; Zhao, Y. Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against sepsis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 144, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, F.; Liang, G.; Han, Y.; Xu, N.; Pan, J.; Luo, M.; Yang, W.; Zeng, L. Exploration of the Molecular Mechanism of Polygonati Rhizoma in the Treatment of Osteoporosis Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 815891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Mu, C.; Kazybay, B.; Sun, Q.; Kutzhanova, A.; Nazarbek, G.; Xu, N.; Nurtay, L.; Wang, Q.; Amin, A.; et al. Network pharmacology and experimental investigation of Rhizoma polygonati extract targeted kinase with herbzyme activity for potent drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 2187–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y. Integrated comparative metabolomics and network pharmacology approach to uncover the key active ingredients of Polygonati rhizoma and their therapeutic potential for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 934947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar-Colucci, S.; Landreth, G.E. Mandrekar-Colucci, S.; Landreth, G.E. Microglia and inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 9, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Min, J.S.; Kim, B.; Chae, U.B.; Yun, J.W.; Choi, M.S.; Kong, I.K.; Chang, K.T.; Lee, D.S. Mitochondrial ROS govern the LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response in microglia cells by regulating MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.E.; Hwang, C.J.; Lee, H.P.; Kim, C.S.; Son, D.J.; Ham, Y.W.; Hellstrom, M.; Han, S.B.; Kim, H.S.; Park, E.K.; et al. Inhibitory effect of punicalagin on lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and memory impairment via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB. Neuropharmacology 2017, 117, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.W.; Cheon, S.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Song, J.; Lee, J.H. Tryptanthrin Suppresses the Activation of the LPS-Treated BV2 Microglial Cell Line via Nrf2/HO-1 Antioxidant Signaling. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Ren, D.; Liu, P. Liquiritigenin Confers Liver Protection by Enhancing NRF2 Signaling through Both Canonical and Non-canonical Signaling Pathways. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 11324–11334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Qi, J.; He, Q.; Ma, D.; Li, J.; Chu, X.; Zuo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Chu, L. Liquiritigenin protects against myocardial ischemic by inhibiting oxidative stress, apoptosis, and L-type Ca(2+) channels. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 3619–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.; Zhang, H.; Gao, H.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, N.; Du, J.; Yue, J.; Du, P.; Zhao, B.; Yin, L. Liquiritigenin decreases tumorigenesis by inhibiting DNMT activity and increasing BRCA1 transcriptional activity in triple-negative breast cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 246, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.M.; Suh, K.S.; Lee, Y.S. Liquiritigenin Restores Osteoblast Damage through Regulating Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Phytother. Res. 2013, 28, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnovali, M.; Luzi, L.; Terruzzi, I.; Banfi, G.; Mariotti, M. Liquiritigenin Reduces Blood Glucose Level and Bone Adverse Effects in Hyperglycemic Adult Zebrafish. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Tao, W.; Huang, H.; Du, Y.; Chu, X.; Chen, G. Protective effect of liquiritigenin on depressive-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 240, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Dong, Y.; Su, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Xue, W.; Chen, C.; Xia, B.; Duan, J.; Chen, G. Liquiritigenin reverses depression-like behavior in unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced mice by regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR mediated BDNF/TrkB pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 308, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Cheung, F.; Chen, F.; Feng, Y. Integrating Network Pharmacology and Pharmacological Evaluation for Deciphering the Action Mechanism of Herbal Formula Zuojin Pill in Suppressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Lee, H.J.; Barden, C.J.; Weaver, D.F. The Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) Score. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 9824–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Cheng, F.; Ma, C.; Fan, S.; Xu, W.; Jin, N.; Liu, S.; Lv, K.; Wang, Q. Network Pharmacology-Based Approach to Revealing Biological Mechanisms of Qingkailing Injection against IschemicStroke: Focusing on Blood-Brain Barrier. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 2914579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Ling, Y. A novel chemometric method for the prediction of human oral bioavailability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6964–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbal Radix Curcumae formula for application to cardiovascular disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Y. A novel systems pharmacology model for herbal medicine injection: A case using Reduning injection. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, U. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarino, J.M.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB: A worldwide resource for pharmacogenomic information. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 2018, 10, e1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yu, X.; Shen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, F. TTD: Therapeutic Target Database describing target druggability information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1465–D1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; Schiettecatte, F.; Scott, A.F.; Hamosh, A. OMIM.org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D789–D798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.G.; Barnes, K.C.; Bright, T.J.; Wang, S.A. The genetic association database. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yang, X.; Guo, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Sun, M.; Xi, C.; et al. Network pharmacology-based prediction and verification of the active ingredients and potential targets of Huagan Decoction for reflux esophagitis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Fu, W.; Zhou, R.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.; Hu, W. Systemic pharmacological investigation of the Feng Shi Gu Tong capsule in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganathan, Y.; Jain, M.; Thiyagarajan, S.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Mariappan, S.K.; Kizhakedathil, M.P.J.; Saravanakumar, T. An Insilico evaluation of phytocompounds from Albizia amara and Phyla nodiflora as cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme inhibitors. Daru 2021, 29, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analyses of the potential target proteins and molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-arrhythmic effects of Sophora Flavescens. Medicine 2023, 102, e34504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, N.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J. Platycodin D Inhibits β-Amyloid-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in BV-2 Cells Via Suppressing TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Cho, M.S.; Thiagarajan, P.; Aung, F.M.; Sood, A.K.; Afshar-Kharghan, V. A small amount of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) is constitutively expressed in platelets. Platelets 2017, 28, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.S.; Leem, Y.H.; Park, J.E.; Kim, H.S. The Potent PDE10A Inhibitor MP-10 (PF-2545920) Suppresses Microglial Activation in LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation and MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Models. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qi, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, R. Dihydromyricetin improves LPS-induced sickness and depressive-like behaviors in mice by inhibiting the TLR4/Akt/HIF1a/NLRP3 pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 423, 113775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Sun, C.; Zhou, R.-P.; Ma, G.-G.; Yang, Y.; Lu, C.; Hu, W. Nerve growth factor promotes ASIC1a expression via the NF-κB pathway and enhances acid-induced chondrocyte apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 82, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Huang, L.; Xiao, P.; Gao, W. The genus Polygonatum: A review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; He, F.; Wu, H.; Xiang, F.; Zheng, H.; Wu, W.; Li, S. Health-Promoting Activities and Associated Mechanisms of Polygonati Rhizoma Polysaccharides. Molecules 2023, 28, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowlati, Y.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, H.; Sham, L.; Reim, E.K.; Lanctot, K.L. A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.H.; Son, H.; Hwang, S.; Kim, S.H. Neuropathological abnormalities of astrocytes, GABAergic neurons, and pyramidal neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortices of patients with major depressive disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 22, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Han, Y.; Liao, X.; Zou, M.; Wang, Y. Biology of cyclooxygenase-2: An application in depression therapeutics. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1037588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Fan, C.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yu, S.Y. Hippocampal CA1 betaCaMKII mediates neuroinflammatory responses via COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathways in depression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udompong, S.; Mankhong, S.; Jaratjaroonphong, J.; Srisook, K. Involvement of p38 MAPK and ATF-2 signaling pathway in anti-inflammatory effect of a novel compound bis[(5-methyl)2-furyl](4-nitrophenyl)methane on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 50, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, C. The Flavonoid Quercetin Induces AP-1 Activation in FRTL-5 Thyroid Cells. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaris, A.; Sohl, E.; Whitham, E.A. Treatment-Resistant Depression Revisited: A Glimmer of Hope. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cremoux, P.; Hamy, A.S.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Scott, V.; Sigal, B.; Mathieu, M.C.; Bertheau, P.; Guinebretiere, J.M.; Pierga, J.Y.; Giacchetti, S.; et al. COX2/PTGS2 Expression Is Predictive of Response to Neoadjuvant Celecoxib in HER2-negative Breast Cancer Patients. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kim, J.S.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Im, H.J. Osteoarthritic tissues modulate functional properties of sensory neurons associated with symptomatic OA pain. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 5335–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares Pereira, M.; Gram, A.; Nowaczyk, R.; Boos, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Janowski, T.; Kowalewski, M.P. Prostaglandin-mediated effects in early canine corpus luteum: In vivo effects on vascular and immune factors. Reprod. Biol. 2019, 19, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, M.G.; Perrini, C.; Esposti, P.; Corradetti, B.; Bizzaro, D.; Riccaboni, P.; Fantinato, E.; Urbani, G.; Gelati, G.; Cremonesi, F.; et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma in a model of bovine endometrial inflammation in vitro. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2016, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Y.; Cui, F.Y.; Zheng, S.J.; Jiang, J.X.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Yu, C.M.; Yang, B. Response surface optimization of total saponins and flavonoids extraction methods from Polygonatum sibiricum roots and stems and their application in comparing the content of Polygonatum sibiricum components from different regions. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Huang, J.X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Chen, W.S. Determination of Five Active Chemical Constituents in Huangjing by High Performance Liquid Chromatography Dual Wavelength Method. Phys. Chem. Test. (Chem. Vol.) 2018, 54, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Z.; He, L.J.; Tian, D.F.; Gao, Q.; Ling, J.F.; Wang, Y.C.; Han, Z.Y.; Guo, R.J. Therapeutic Targets and Mechanism of Xingpi Jieyu Decoction in Depression: A Network Pharmacology Study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5516525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; He, J.; Huang, D.; Xi, Y.; Xiao, T.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wan, S.; Chen, X. Potential mechanisms underlying the therapeutic roles of sinisan formula in depression: Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking study. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1063489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.H.; Park, K.I.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, E.J.; Ku, S.K.; Kim, S.C.; Suk, H.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Baek, S.Y.; et al. Liquiritigenin inhibits hepatic fibrogenesis and TGF-beta1/Smad with Hippo/YAP signal. Phytomedicine 2019, 62, 152780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, B.; Li, L.; Chu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Wu, Z.; et al. Liquiritigenin protects against arsenic trioxide-induced liver injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and enhancing mTOR-mediated autophagy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fang, H.; Yu, Y.H.; Liu, S.X.; Yang, Z.Q. Liquiritigenin attenuates isoprenaline-induced myocardial fibrosis in mice through the TGF-beta1/Smad2 and AKT/ERK signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.J.; Park, G.H.; Song, K.S. Neuroprotective effects of liquiritigenin isolated from licorice roots on glutamate-induced apoptosis in hippocampal neuronal cells. Neurotoxicology 2013, 39, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.T.; Zou, L.B.; Lu, Q.J. Liquiritigenin inhibits Abeta(25-35)-induced neurotoxicity and secretion of Abeta(1-40) in rat hippocampal neurons. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N, N.; C, G.P.; Chakraborty, C.; V, K.; D, T.K.; V, B.; R, S.; Lu, A.; Ge, Z.; Zhu, H. Mechanism of artemisinin resistance for malaria PfATP6 L263 mutations and discovering potential antimalarials: An integrated computational approach. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Shao, Q.; Gong, Y.Z.; Hu, J.W.; Liu, W.H.; Wu, Z.J.; Wang, J.; Ma, S.B.; et al. Screening of rosmarinic acid from Salvia miltiorrhizae acting on the novel target TRPC1 based on the ‘homology modelling-virtual screening-molecular docking-affinity assay-activity evaluation’ method. Pharm. Biol. 2023, 61, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Sequences |
|---|---|
| COX2 | (F) 5′-TGAGCATCTACGGTTTGCTG-3′ (R) 5′-TGCTTGTCTGGAACAACTGC-3′ |
| TNF-α | (F) 5′-AAAATTCGAGTGACAAGCCTGTAG-3′ (R) 5′-CCCTTGAAGAGA-ACCTGGGAGTAG-3′ |
| IL-6 | (F) 5′-AGATACAAAGAAATGATGGATGCTA-3′ (R) 5′-TCTTGGTTGAAGATATGAATTAGAG-3′ |
| IL-1β | (F) 5′-GTGTCTTTCCCGTGGACCTT-3′ (R) 5′-CGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCTTG-3′ |
| GAPDH | (F) 5′-TAGATTATTCTCTGATTTGGTCGTATTGG-3′ (R) 5′-GCTCCTGGAAGATGGTGATGG-3′ |
| Mol ID | Molecular Name | OB (%) | DL | BBB | HL | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOL001792 | DFV | 32.76 | 0.18 | −0.29 | 17.89 | 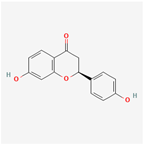 |
| MOL002714 | baicalein | 33.52 | 0.21 | −0.05 | 16.25 |  |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 5.36 |  |
| MOL000359 | sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 5.37 | 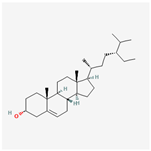 |
| MOL004941 | (2R)-7-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) chroman-4-one | 71.12 | 0.18 | −0.25 | 18.09 |  |
| MOL000546 | diosgenin | 80.88 | 0.81 | 0.27 | 4.14 | 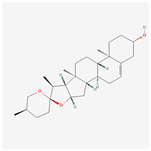 |
| MOL006331 | 4′,5-Dihydroxyflavone | 48.55 | 0.19 | −0.03 | 18.01 | 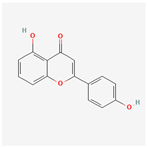 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Niu, J.; Xu, W. Interpreting the Mechanism of Active Ingredients in Polygonati Rhizoma in Treating Depression by Combining Systemic Pharmacology and In Vitro Experiments. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081167
Wei X, Wang D, Liu J, Zhu Q, Xu Z, Niu J, Xu W. Interpreting the Mechanism of Active Ingredients in Polygonati Rhizoma in Treating Depression by Combining Systemic Pharmacology and In Vitro Experiments. Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081167
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xin, Dan Wang, Jiajia Liu, Qizhi Zhu, Ziming Xu, Jinzhe Niu, and Weiping Xu. 2024. "Interpreting the Mechanism of Active Ingredients in Polygonati Rhizoma in Treating Depression by Combining Systemic Pharmacology and In Vitro Experiments" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081167
APA StyleWei, X., Wang, D., Liu, J., Zhu, Q., Xu, Z., Niu, J., & Xu, W. (2024). Interpreting the Mechanism of Active Ingredients in Polygonati Rhizoma in Treating Depression by Combining Systemic Pharmacology and In Vitro Experiments. Nutrients, 16(8), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081167