Conjugated Linoleic Acid Ameliorates High Fat-Induced Insulin Resistance via Regulating Gut Microbiota–Host Metabolic and Immunomodulatory Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment
2.2. Glucose and Insulin Tolerance Test
2.3. Biochemical Analyses
2.4. Analysis of Histology and Immunofluorescence Staining
2.5. Gut Microbiota and SCFAs Analysis
2.6. Analysis of the Hepatic Transcriptome Profiling
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CLA Attenuated Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia and IR in HF-Fed Mice
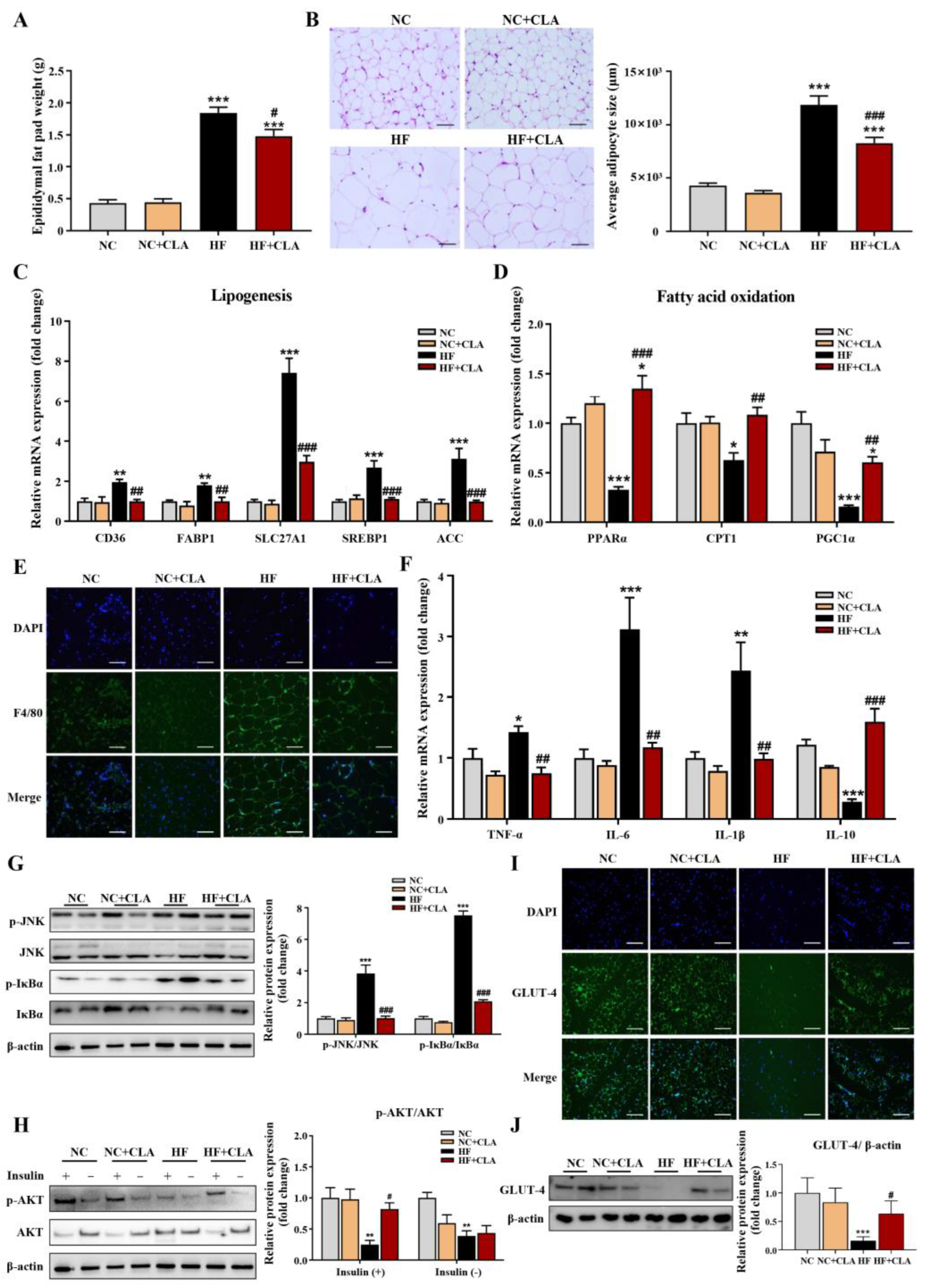
3.2. CLA Alleviated Adipocyte Hypertrophy, Metabolic Disorder, Inflammation and IR in HF-Fed Mice
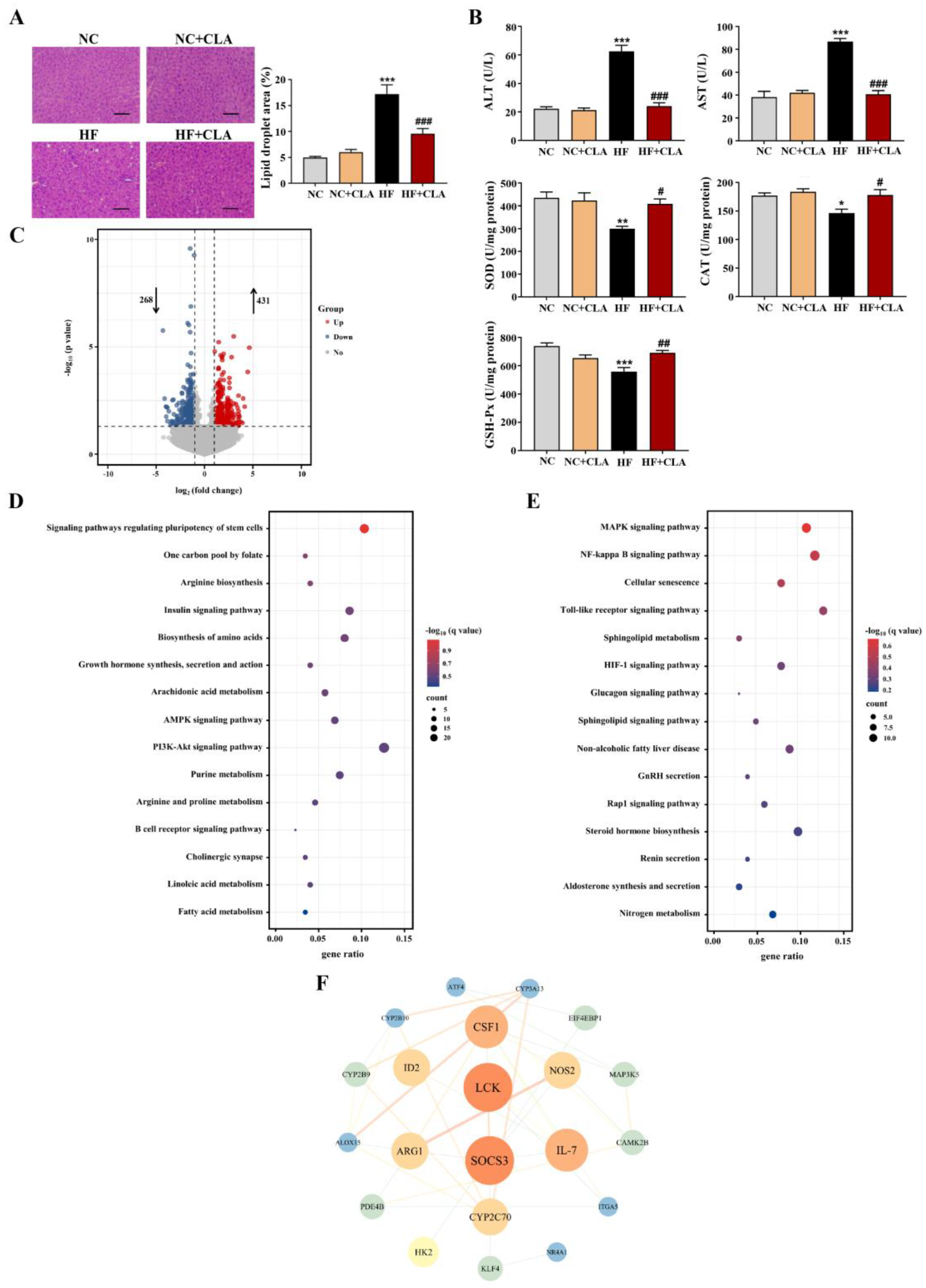
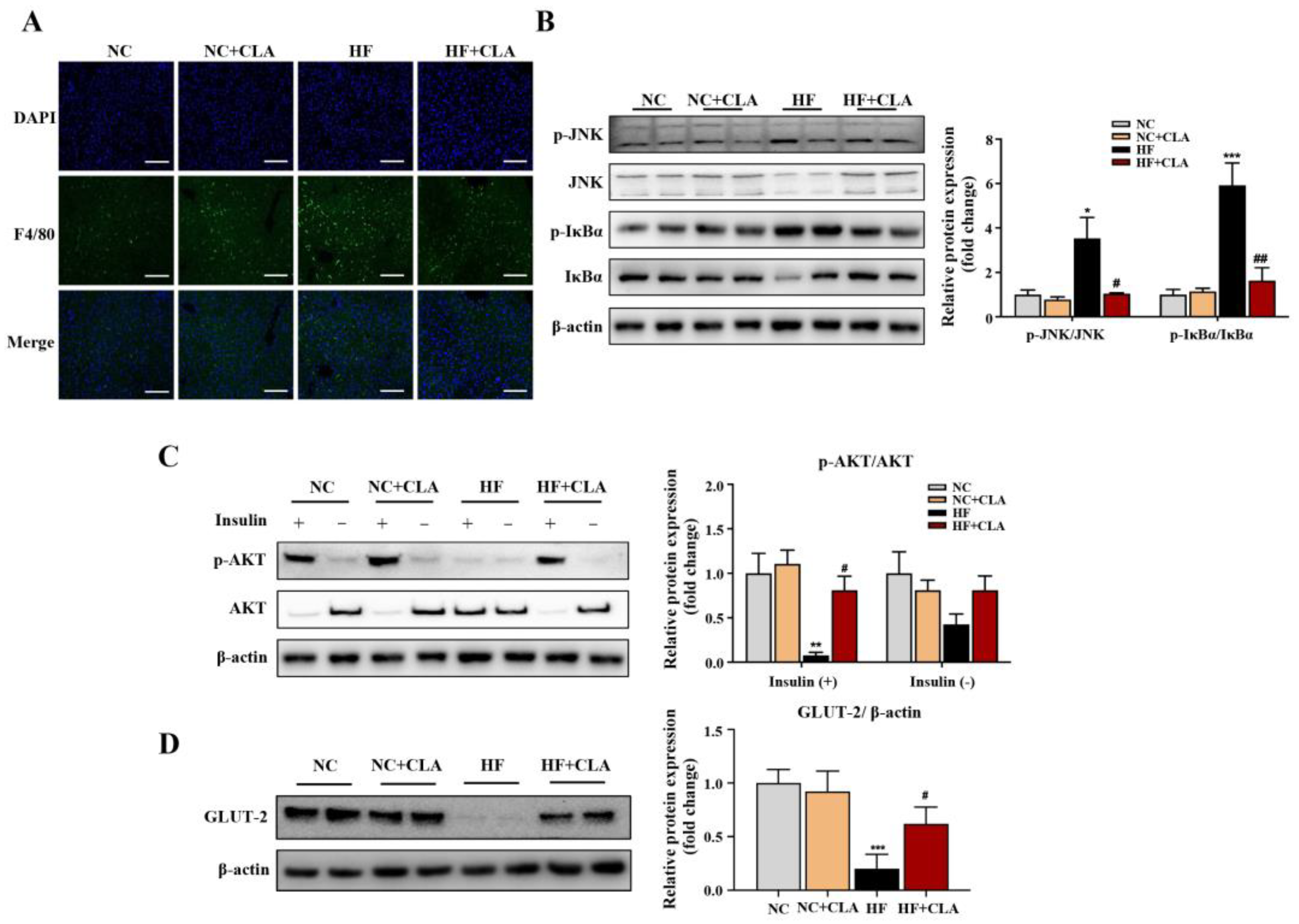
3.3. CLA Altered Hepatic Lipid Accumulation, Gene Expression Profile and IR-Related Signaling in HF-Fed Mice
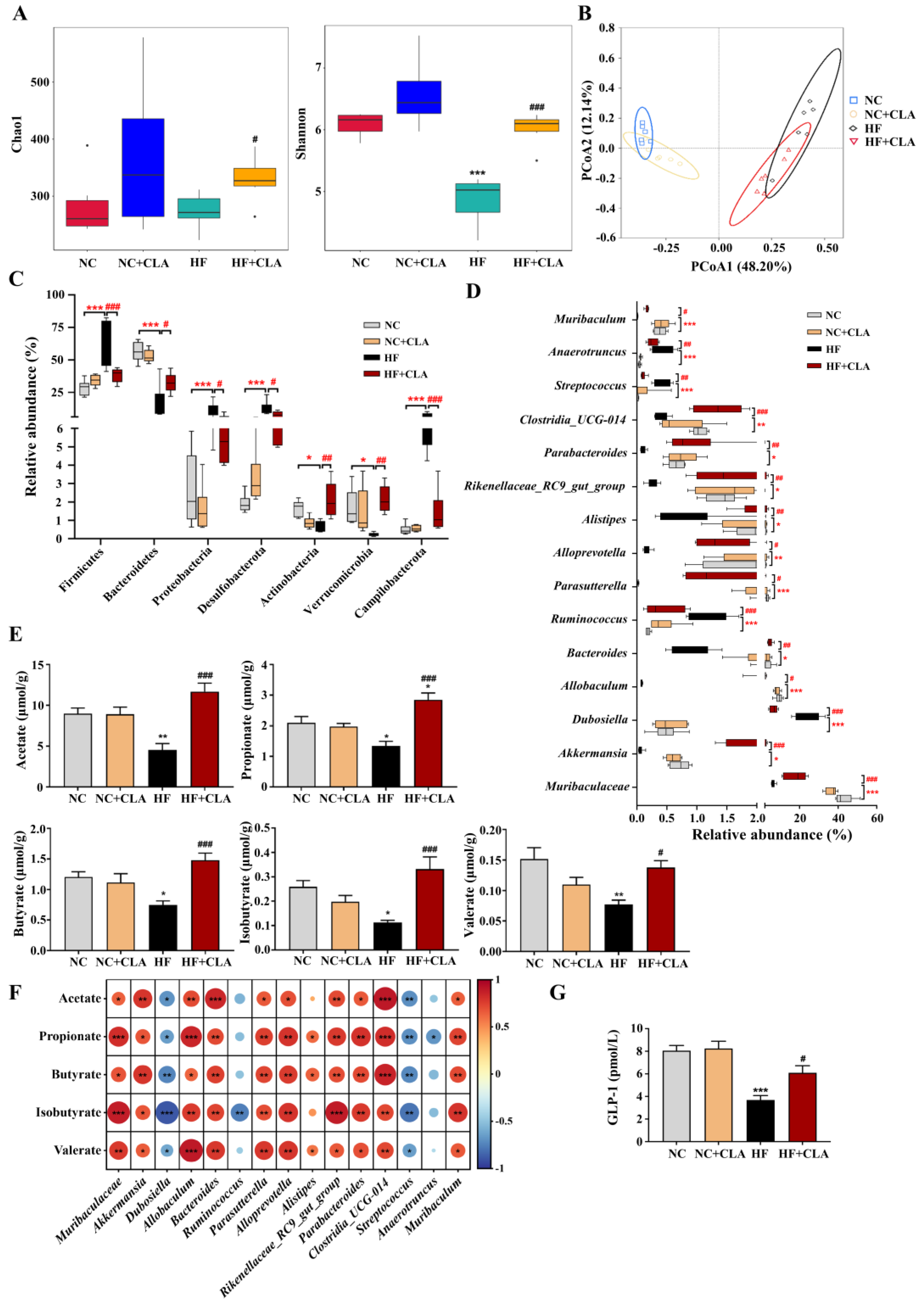
3.4. CLA Altered the Gut Microbiota in HF-Fed Mice
3.5. CLA Modulated the Microbiota-Derived SCFAs Production in HF-Fed Mice
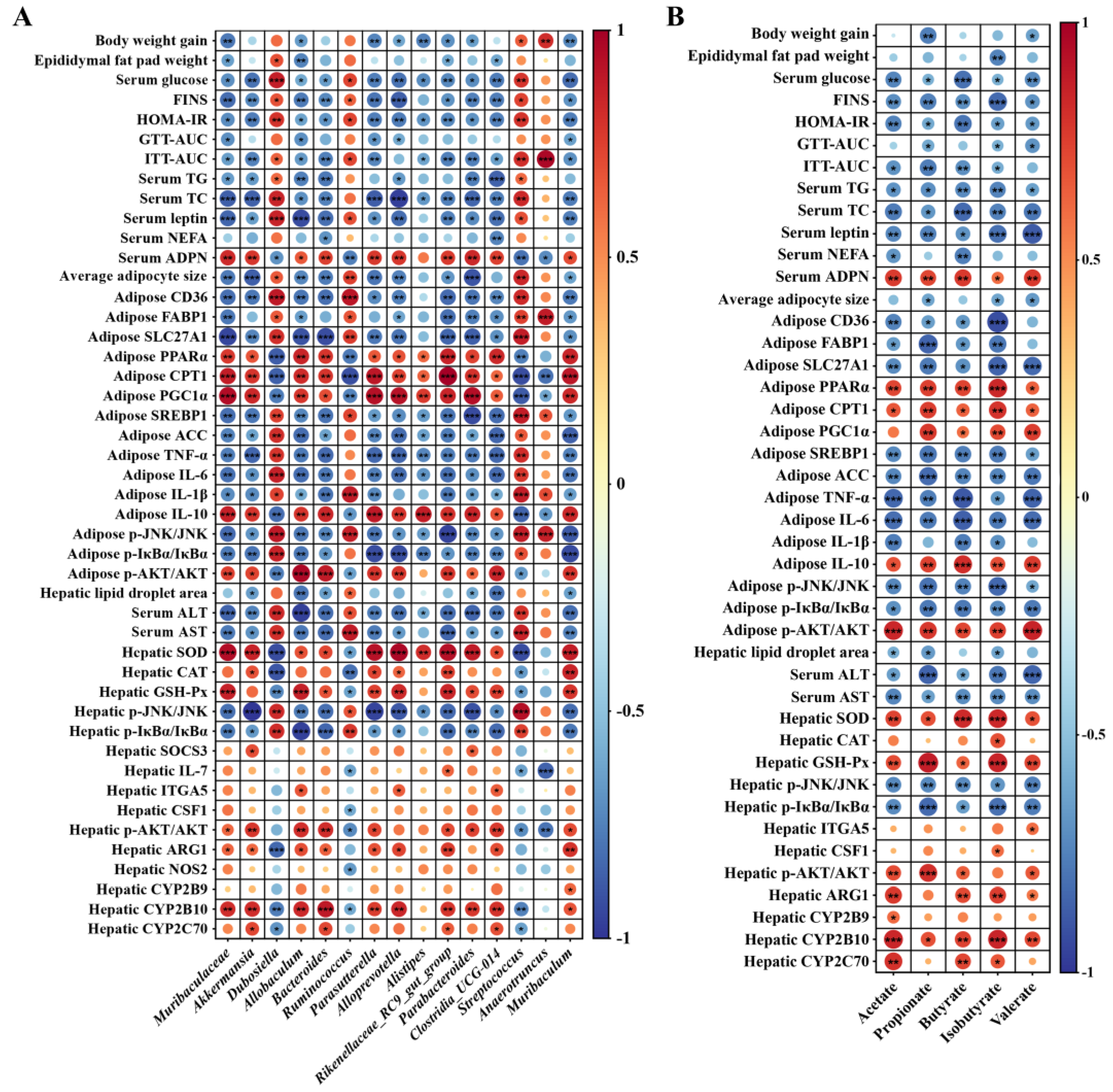
3.6. Gut Microbiome Orchestrates CLA-Induced IR Restoration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanriover, C.; Copur, S.; Gaipov, A.; Ozlusen, B.; Akcan, R.E.; Kuwabara, M.; Hornum, M.; Van Raalte, D.H.; Kanbay, M. Metabolically healthy obesity: Misleading phrase or healthy phenotype? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 111, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dludla, P.V.; Mabhida, S.E.; Ziqubu, K.; Nkambule, B.B.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Hanser, S.; Basson, A.K.; Pheiffer, C.; Kengne, A.P. Pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: Implications of inflammation and oxidative stress. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlien-Søborg, M.C.; Madsen, M.A.; Dal, J.; Krusenstjerna-Hafstrøm, T.; Ringgaard, S.; Skou, N.; Høgild, M.; Jørgensen, J.O.L. Ectopic lipid deposition and insulin resistance in patients with GH disorders before and after treatment. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 188, lvac014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankararaman, S.; Noriega, K.; Velayuthan, S.; Sferra, T.; Martindale, R. Gut microbiome and its impact on obesity and obesity-related disorders. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2023, 25, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, K.S.; Nunez, C.E.C.; Cazarin, C.B.B.; Maróstica Júnior, M.R.; Kristiansen, K.; Danneskiold-Samsøe, N.B. Pot-pollen supplementation reduces fasting glucose and modulates the gut microbiota in high-fat/high-sucrose fed C57BL/6 mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3982–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajinka, O.; Tan, Y.; Darboe, A.; Ighaede-Edwards, I.G.; Abdelhalim, K.A. The gut microbiota pathway mechanisms of diabetes. AMB Express 2023, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murru, E.; Carta, G.; Manca, C.; Sogos, V.; Pistis, M.; Melis, M.; Banni, S. Conjugated linoleic acid and brain metabolism: A possible anti-neuroinflammatory role mediated by PPARα activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 587140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruen, R.; Fitzsimons, S.; Belton, O. Atheroprotective effects of conjugated linoleic acid. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, L.E.; Collene, A.L.; Asp, M.L.; Hsu, J.C.; Liu, L.F.; Richardson, J.R.; Li, D.; Bell, D.; Osei, K.; Jackson, R.D.; et al. Comparison of dietary conjugated linoleic acid with safflower oil on body composition in obese postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaullier, J.M.; Halse, J.; Høye, K.; Kristiansen, K.; Fagertun, H.; Vik, H.; Gudmundsen, O. Supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid for 24 months is well tolerated by and reduces body fat mass in healthy, overweight humans. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.M.; McIntosh, M.K. Conjugated linoleic acid in humans: Regulation of adiposity and insulin sensitivity. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.M.; Toubro, S.; Gudmundsen, O.; Astrup, A. Conjugated linoleic acid supplementation for 1 y does not prevent weight or body fat regain. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedman, A.; Vessby, B. Conjugated linoleic acid supplementation in humans–metabolic effects. Lipids 2001, 36, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokryzadan, P.; Rajion, M.A.; Meng, G.Y.; Boo, L.J.; Ebrahimi, M.; Royan, M.; Sahebi, M.; Azizi, P.; Abiri, R.; Jahromi, M.F. Conjugated linoleic acid: A potent fatty acid linked to animal and human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighatdoost, F.; Hariri, M. Effect of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on serum leptin concentration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Qu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Miao, J. Conjugated linoleic acid ameliorates hepatic steatosis by modulating intestinal permeability and gut microbiota in ob/ob mice. Food Nutr. Res. 2022, 66, 8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zheng, A.; Ni, L.; Wu, L.; Hu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Z.; Ni, Y. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis lkm512 attenuates obesity-associated inflammation and insulin resistance through the modification of gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, e2100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabeta, K.; Hase-Tamaru, S.; Yuasa, M.; Suruga, K.; Sugano, M.; Koba, K. Dietary β-conglycinin modulates insulin sensitivity, body fat mass, and lipid metabolism in obese Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, A.L.; Carvalho, L.; Oliveira, A.C.; Santos, V.N.; Vieira, J.G.; Parise, E.R. Insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) in the differentiation of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and healthy individuals. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2010, 47, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, K.; Mareninov, S.; Diaz, M.F.P.; Yong, W.H. An introduction to performing immunofluorescence staining. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1897, 299–311. [Google Scholar]
- Grigorova, E.V.; Belkova, N.L.; Nemchenko, U.M.; Klimenko, E.S.; Pogodina, A.V.; Romanitsa, A.I.; Novikova, E.A.; Rychkova, L.V. Metasequencing of V3-V4 variable regions of 16S rRNA gene in opportunistic microbiota and gut biocenosis in obese adolescents. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 170, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Suen, G.; Shao, D.; Li, S.; Diao, Q. Multiomics analysis reveals the presence of a microbiome in the gut of fetal lambs. Gut 2021, 70, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome. Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.-Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Deng, X.; Lund, P.; Liu, H.; Ding, X.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Dong, L. Rumen microbiota-host transcriptome interaction mediates the protective effects of trans-10, cis-12 CLA on facilitating weaning transition of lambs. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 12, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzoni, R.; Gortan Cappellari, G.; Ragni, M.; Nisoli, E. Insulin resistance in obesity: An overview of fundamental alterations. Eat. Weight Disord. 2018, 23, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garabadu, D.; Krishnamurthy, S. Metformin attenuates hepatic insulin resistance in type-2 diabetic rats through PI3K/Akt/GLUT-4 signalling independent to bicuculline-sensitive GABA(A) receptor stimulation. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, A.; Girdhar, K.; Kar, A.K.; Kushwaha, S.; Yadav, M.K.; Ghosh, D.; Mondal, P. Low-dose naltrexone rescues inflammation and insulin resistance associated with hyperinsulinemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 16359–16369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazıcı, D.; Sezer, H. Insulin resistance, obesity and lipotoxicity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aoi, W.; Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Role of oxidative stress in impaired insulin signaling associated with exercise-induced muscle damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Vatner, D.F.; Goedeke, L.; Hirabara, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Perry, R.J.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms by which adiponectin reverses high fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32584–32593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R.; Roden, M. NAFLD and diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, R. Arctigenin improves lipid metabolism by regulating AMP-activated protein kinase and downstream signaling pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 13275–13288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Cai, H.; Sun, H.; Hu, Y.; Huang, X.; Kong, W.; Kong, W. The role of sodium hydrosulfide in attenuating the aging process via PI3K/AKT and CaMKKβ/AMPK pathways. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Thring, R.W.; Wu, M.; Gao, Y.; et al. Sulforaphane alleviates high fat diet-induced insulin resistance via AMPK/Nrf2/GPx4 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariniello, K.; Min, Y.; Ghebremeskel, K. Phosphorylation of protein kinase B, the key enzyme in insulin-signaling cascade, is enhanced in linoleic and arachidonic acid-treated HT29 and HepG2 cells. Nutrition 2019, 57, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Niu, C.; Liao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, F. Serum untargeted metabolomics analysis of the mechanisms of evodiamine on type 2 diabetes mellitus model rats. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6623–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Sailani, M.R.; Contrepois, K.; Zhou, Y.; Ahadi, S.; Leopold, S.R.; Zhang, M.J.; Rao, V.; Avina, M.; Mishra, T.; et al. Longitudinal multi-omics of host-microbe dynamics in prediabetes. Nature 2019, 569, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Sears, C.L.; Maruthur, N. Gut microbiome and its role in obesity and insulin resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1461, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Coker, O.O.; Chu, E.S.; Fu, K.; Lau, H.C.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Chan, A.W.H.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Dietary cholesterol drives fatty liver-associated liver cancer by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gut 2021, 70, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, R.A.; Aronoff, D.M.; Gaddy, J.A.; Petroff, M.G.; Manning, S.D. Distinct group B Streptococcus sequence and capsule types differentially impact macrophage stress and inflammatory signaling responses. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00647-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, S.; van Zuydam, N.R.; Mahajan, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Võsa, U.; Mujagic, Z.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.; Oosting, M.; et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Shen, X.; Chu, Q.; Zheng, X. Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. fruit extract reduces high-fat diet-induced obesity with modulation of the gut microbiota in obese mice. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Q.; Liu, H.; Nie, C.; Zhang, Z.; An, W.; Li, J. Lycium ruthenicum anthocyanins attenuate high-fat diet-induced colonic barrier dysfunction and inflammation in mice by modulating the gut microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2000745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, X.; Hou, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Effects of pomegranate peel polyphenols combined with inulin on gut microbiota and serum metabolites of high-fat-induced obesity rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 5733–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, S. Coffee leaf tea extracts improve hyperuricemia nephropathy and its associated negative effect in gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17775–17787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Meng, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Z.; Hao, D.; Li, R.; Han, K.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; et al. Protection effect of gut microbiota composition and acetate absorption against hypertension-induced damages on the longevity population in Guangxi, China. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1070223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Xie, X.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Yang, L.; Jiang, T.; Du, M.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Metabolism of resistant starch RS3 administered in combination with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strain 84-3 by human gut microbiota in simulated fermentation experiments in vitro and in a rat model. Food Chem. 2023, 411, 135412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Lin, T.L.; Tsai, Y.L.; Wu, T.R.; Lai, W.F.; Lu, C.C.; Lai, H.C. Next generation probiotics in disease amelioration. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, E.C.; da Silva, J.F.; Navia-Pelaez, J.M.; Leonel, A.J.; Lopes, L.G.; Menezes-Garcia, Z.; Ferreira, A.V.M.; Capettini, L.; Teixeira, L.G.; Lemos, V.S.; et al. Sodium butyrate modulates adipocyte expansion, adipogenesis, and insulin receptor signaling by upregulation of PPAR-γ in obese Apo E knockout mice. Nutrition 2018, 47, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Lahham, S.; Roelofsen, H.; Rezaee, F.; Weening, D.; Hoek, A.; Vonk, R.; Venema, K. Propionic acid affects immune status and metabolism in adipose tissue from overweight subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dilidaxi, D.; Wu, Y.; Sailike, J.; Sun, X.; Nabi, X.H. Composite probiotics alleviate type 2 diabetes by regulating intestinal microbiota and inducing GLP-1 secretion in db/db mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolhurst, G.; Heffron, H.; Lam, Y.S.; Parker, H.E.; Habib, A.M.; Diakogiannaki, E.; Cameron, J.; Grosse, J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 2012, 61, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.K.; Nikooienejad, A.; Bray, R.; Cui, X.; Wilson, J.; Duffin, K.; Milicevic, Z.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.A. Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide improves beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Metabolism and metabolic disorders and the microbiome: The intestinal microbiota associated with obesity, lipid metabolism, and metabolic health-pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 573–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Ye, S.; Deng, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, C. Conjugated Linoleic Acid Ameliorates High Fat-Induced Insulin Resistance via Regulating Gut Microbiota–Host Metabolic and Immunomodulatory Interactions. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081133
Wu L, Ye S, Deng X, Fu Z, Li J, Yang C. Conjugated Linoleic Acid Ameliorates High Fat-Induced Insulin Resistance via Regulating Gut Microbiota–Host Metabolic and Immunomodulatory Interactions. Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081133
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Linjun, Shijie Ye, Xiangfei Deng, Zhengwei Fu, Jinjun Li, and Chunlei Yang. 2024. "Conjugated Linoleic Acid Ameliorates High Fat-Induced Insulin Resistance via Regulating Gut Microbiota–Host Metabolic and Immunomodulatory Interactions" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081133
APA StyleWu, L., Ye, S., Deng, X., Fu, Z., Li, J., & Yang, C. (2024). Conjugated Linoleic Acid Ameliorates High Fat-Induced Insulin Resistance via Regulating Gut Microbiota–Host Metabolic and Immunomodulatory Interactions. Nutrients, 16(8), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081133






