Assessing Sarcocornia as a Salt Substitute: Effects on Lipid Profile and Gelatinase Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Halophyte Plant
2.2. Study Sample
2.3. Instruments and Data Collection
2.3.1. Characterization of the Biochemical Profiles
2.3.2. Evaluation of the Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinases 2 and 9
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biochemical Evaluation
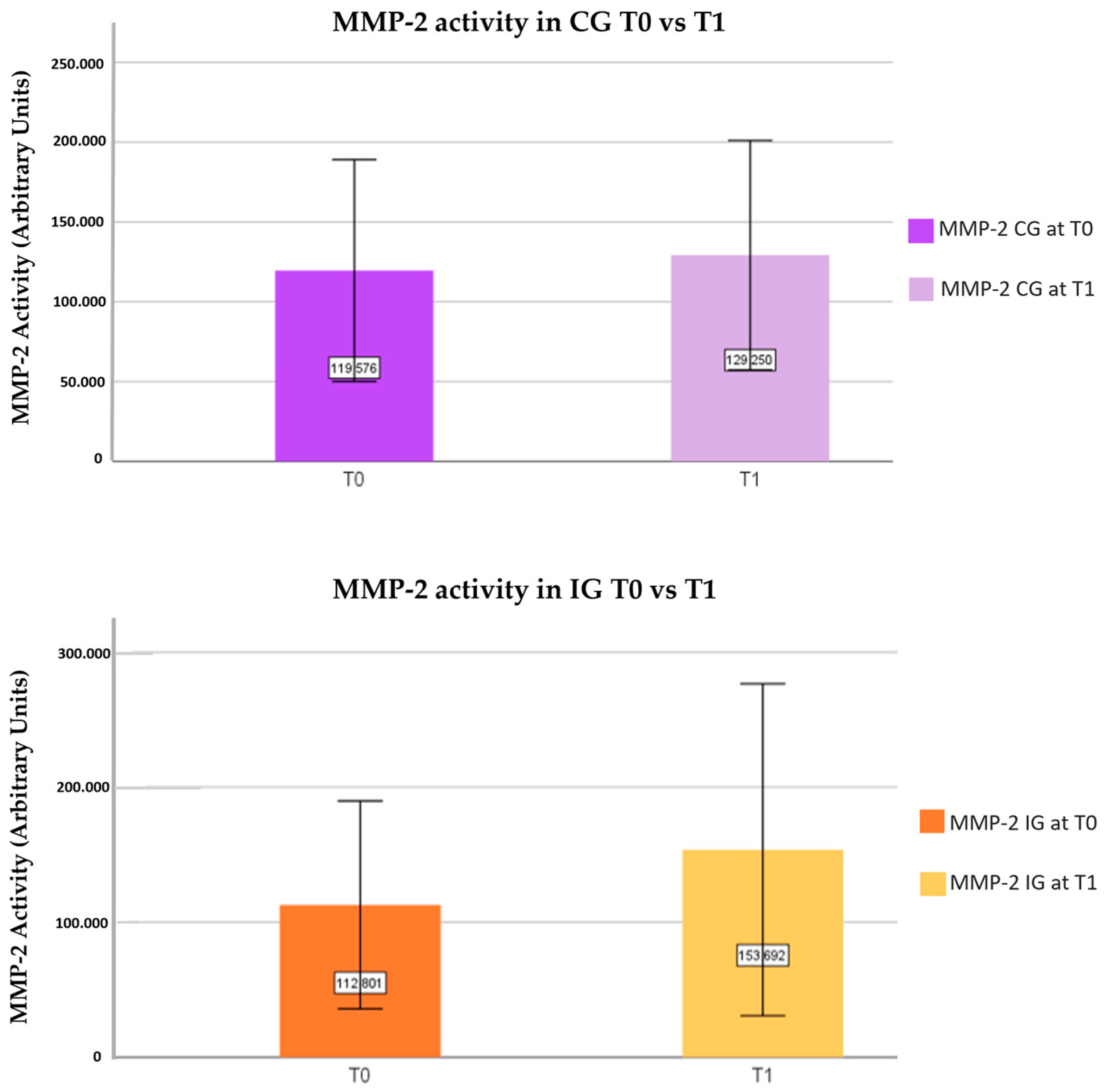
3.2. Evaluation of the MMPs’ Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernal, A.; Zafra, M.A.; Simón, M.J.; Mahía, J. Sodium Homeostasis, a Balance Necessary for Life. Nutrients 2023, 15, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumer-Harrison, C.; Breza, J.M.; Sumners, C.; Krause, E.G.; de Kloet, A.D. Sodium Intake and Disease: Another Relationship to Consider. Nutrients 2023, 15, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.; Caldeira, A.T.; Caseiro, A.; Osório, N.; da Silva, A.M.; Barroca, M.J. Randomized Pilot Study on the Effects of Sarcocornia as a Salt Substitute in Arterial Blood Pressure and Vascular Function in Healthy Young Adults. Foods 2022, 11, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosohata, K. Biomarkers of high salt intake. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 104, 71–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balafa, O.; Kalaitzidis, R.G. Salt sensitivity and hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 35, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, A.; Salvi, L.; Coruzzi, P.; Salvi, P.; Parati, G. Sodium Intake and Hypertension. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, M.P.; Brant, L.C.C.; Cunha, R.S.; Molina, M.d.C.B.; Griep, R.H.; Barreto, S.M.; Lotufo, P.A.; Bensenor, I.M.; Mill, J.G. The association between salt intake and arterial stiffness is influenced by a sex-specific mediating effect through blood pressure in normotensive adults: The ELSA-Brasil study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzemińska, J.; Wronka, M.; Młynarska, E.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz, J. Arterial Hypertension—Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custódio, L.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Pereira, C.G.; Castañeda-Loaiza, V.; Fernandes, E.; Standing, D.; Neori, A.; Shpigel, M.; Sagi, M. A Review on Sarcocornia Species: Ethnopharmacology, Nutritional Properties, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Propagation. Foods 2021, 10, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.-Q.; Li, Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, J.-F.; Guo, M.; Shi, H.-T.; Zhang, L.; Han, Q.-H. The Correlation Between Urinary Sodium Excretion and Blood Pressure in Hospitalized Adult Patients with Hypertension. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 2302–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Cavaleiro, C.; Ramos, F. Sodium Reduction in Bread: A Role for Glasswort (Salicornia ramosissima J. Woods). Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfheeaid, H.A.; Raheem, D.; Ahmed, F.; Alhodieb, F.S.; Alsharari, Z.D.; Alhaji, J.H.; BinMowyna, M.N.; Saraiva, A.; Raposo, A. Salicornia bigelovii, S. brachiata and S. herbacea: Their Nutritional Characteristics and an Evaluation of Their Potential as Salt Substitutes. Foods 2022, 11, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; He, T.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, T.; Jiang, E. The perspective of hypertension and salt intake in Chinese population. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1125608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Silva, A.S.; Séndon, R.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Cavaleiro, C.; Ramos, F. Towards the Sustainable Exploitation of Salt-Tolerant Plants: Nutritional Characterisation, Phenolics Composition, and Potential Contaminants Analysis of Salicornia ramosissima and Sarcocornia perennis alpini. Molecules 2023, 28, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, A.; Grygiel-Górniak, B.; Brożyna-Tkaczyk, K.; Myśliński, W.; Cholewka, A.; Zolghadri, S. The Influence of Dietary Interventions on Arterial Stiffness in Overweight and Obese Subjects. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J.F.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Han, Q.H. Study on the Correlation between Urinary Sodium and Potassium Excretion and Blood Pressure in Adult Hypertensive Inpatients of Different Sexes. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 1854475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; He, F.J.; Sun, Q.; Yuan, C.; Kieneker, L.M.; Curhan, G.C.; MacGregor, G.A.; Bakker, S.J.; Campbell, N.R.; Wang, M.; et al. 24-Hour Urinary Sodium and Potassium Excretion and Cardiovascular Risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalez, S.R.; Ferrão, F.M.; Souza, A.M.D.; Lowe, J.; Morcillo, L.d.S.L. Inappropriate activity of local renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system during high salt intake: Impact on the cardio-renal axis. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2018, 40, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Pérez, S.; Piernik, A.; Chanona-Pérez, J.J.; Grigore, M.N.; Perea-Flores, M.J. An overview of the emerging trends of the Salicornia L. genus as a sustainable crop. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 191, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loconsole, D.; Cristiano, G.; De Lucia, B. Glassworts: From Wild Salt Marsh Species to Sustainable Edible Crops. Agriculture 2019, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.D.; Gago, C.; Guerreiro, A.; Sousa, A.R.; Julião, M.; Miguel, M.G.; Faleiro, M.L.; Panagopoulos, T. Nutritional Characterization and Storage Ability of Salicornia ramosissima and Sarcocornia perennis for Fresh Vegetable Salads. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panth, N.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.-H.; Oak, M.-H. Protective Effect of Salicornia europaea Extracts on High Salt Intake-Induced Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accogli, R.; Tomaselli, V.; Direnzo, P.; Perrino, E.V.; Albanese, G.; Urbano, M.; Laghetti, G. Edible Halophytes and Halo-Tolerant Species in Apulia Region (Southeastern Italy): Biogeography, Traditional Food Use and Potential Sustainable Crops. Plants 2023, 12, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavel-Coibrié, E.; Sales, J.R.; da Silva, A.M.; Barroca, M.J.; Sousa, I.; Raymundo, A. Sarcocornia perennis: A Salt Substitute in Savory Snacks. Foods 2021, 10, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrigui, S.; Taieb, S.H.; Jemai, H.; Mbarek, S.; Benlarbi, M.; Feki, M.; Haouas, Z.; Zemmel, A.; Ben Chaouacha-Chekir, R.; Boudhrioua, N. Anti-Obesity and Anti-Dyslipidemic Effects of Salicornia arabica Decocted Extract in Tunisian Psammomys obesus Fed a High-Calorie Diet. Foods 2023, 12, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, N.N.; Verissimo, A.C.S.; Silva, H.; Pinto, D. Metabolomic Profile of Salicornia perennis Plant’s Organs under Diverse In Situ Stress: The Ria de Aveiro Salt Marshes Case. Metabolites 2023, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilló, A.; Alonso, M.Á.; Juan, A.; Crespo, M.B. Nomenclatural Notes on Sarcocornia perennis (Mill.) A. J. Scott (Amaranthaceae). Candollea 2011, 66, 331–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogni, V.; Cerasari, A.; Pucci, G.; Vaudo, G. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Hypertension-Mediated Organ Damage: Current Insights. Integr. Blood Press. Control 2020, 13, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases, Vascular Remodeling, and Vascular Disease. Adv. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 241–330. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, A.F.; Batista, R.I.M.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Gerlach, R.F. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Arterial Hypertension: Role of Oxidative Stress and Nitric Oxide in Vascular Functional and Structural Alterations. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; la Rosa, C.C.-D.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M. Matrix metalloproteinase profiling and their roles in disease. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 6304–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laronha, H.; Caldeira, J. Structure and Function of Human Matrix Metalloproteinases. Cells 2020, 9, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Patron, C.; Hardy, E. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Health and Disease in the Times of COVID-19. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, H.; Kurita, N.; Takahashi, S.; Sasaki, S.; Nishiwaki, H.; Omae, K.; Yajima, N.; Fukuma, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Fukuhara, S.; et al. Salt intake and body weight correlate with higher blood pressure in the very elderly population: The Sukagawa study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caseiro, A.; Ferreira, R.; Quintaneiro, C.; Pereira, A.; Marinheiro, R.; Vitorino, R.; Amado, F. Protease profiling of different biofluids in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caseiro, A.; Silva, A.M.; Ferreira, C.; Dias, B.; Silva, I.; Clemente, M.; de Figueiredo, J.P.; Pereira, T. Avaliação laboratorial do efeito antioxidante e anti-inflamatório do Resveratrol na função vascular. RevSALUS-Rev. Científica Int. Rede Académica Ciências Saúde Lusofonia 2019, 1, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caseiro, A.; Rocha, C.; Silva, A.M.; Ferreira, C.; Silva, I.; Clemente, M.; Cipriano, I.; Saraiva, M.; Barreira, R.; Azenha, J.; et al. Effects of A Personalized Intervention Program on the Biochemical and Hematological Profile in Community Dwelling Old Adults-The AGA@4life Intervention Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencsik, P.; Bartekova, M.; Görbe, A.; Kiss, K.; Pálóczi, J.; Radosinska, J.; Szűcs, G.; Ferdinandy, P. MMP Activity Detection in Zymograms. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1626, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, J.; Khalil, R.A. Zymography as a Research Tool in the Study of Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1626, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, R.; Barros, A.; Caseiro, A.; Domingues, P.; Duarte, J.; Amado, F. Towards defining the whole salivary peptidome. PROTEOMICS–Clin. Appl. 2009, 3, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoek-van Beurden, P.A.M.; Von Den Hoff, J.W. Zymographic techniques for the analysis of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. BioTechniques 2005, 38, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caseiro, A.; Vitorino, R.; Barros, A.S.; Ferreira, R.; Calheiros-Lobo, M.J.; Carvalho, D.; Duarte, J.A.; Amado, F. Salivary peptidome in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caseiro, A.; Barros, A.; Ferreira, R.; Padrão, A.; Aroso, M.; Quintaneiro, C.; Pereira, A.; Marinheiro, R.; Vitorino, R.; Amado, F. Pursuing type 1 diabetes mellitus and related complications through urinary proteomics. Transl. Res. 2014, 163, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caseiro, A.; Ferreira, R.; Padrão, A.; Quintaneiro, C.; Pereira, A.; Marinheiro, R.; Vitorino, R.; Amado, F. Salivary proteome and peptidome profiling in type 1 diabetes mellitus using a quantitative approach. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muth, B.J.; Brian, M.S.; Chirinos, J.A.; Lennon, S.L.; Farquhar, W.B.; Edwards, D.G. Central systolic blood pressure and aortic stiffness response to dietary sodium in young and middle-aged adults. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. JASH 2017, 11, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Gavilan, I.; Ramirez Chueca, E.; de la Fuente Garcia, V. Bioactive Compounds in Sarcocornia and Arthrocnemum, Two Wild Halophilic Genera from the Iberian Peninsula. Plants 2021, 10, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Yao, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Extraction, preliminary characterization and antioxidant properties of polysaccharides from the testa of Salicornia herbacea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Patel, M.K.; Jha, B. Non-targeted metabolomics and scavenging activity of reactive oxygen species reveal the potential of Salicornia brachiata as a functional food. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 13, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongelli, F.; Crupi, P.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Corbo, F.; Muraglia, M. Overview of the Polyphenols in Salicornia: From Recovery to Health-Promoting Effect. Molecules 2022, 27, 7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreira, L.; Resek, E.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Rocha, M.I.; Pereira, H.; Bandarra, N.; da Silva, M.M.; Varela, J.; Custódio, L. Halophytes: Gourmet food with nutritional health benefits? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 59, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, A.; Mariottini, G.; Gabriele, M.; Longo, V.; Souid, A.; Dauvergne, X.; Magné, C.; Foggi, G.; Conte, G.; Santin, M.; et al. Nutritional Composition and Bioactivity of Salicornia europaea L. Plants Grown in Monoculture or Intercropped with Tomato Plants in Salt-Affected Soils. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, M.R.; Chiang, M.; Hong, J. Evaluation and comparison of functional properties of freshwater-cultivated glasswort (Salicornia herbacea L.) with naturally-grown glasswort. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, M.; Cao, C.; Ju, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ye, T.; Xia, Z.; Chen, M. Effect and mechanism of Salicornia bigelovii Torr. plant salt on blood pressure in SD rats. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Di Cola, M.S.; Savino, I.; Galletti, F.; Strazzullo, P. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Dietary Sodium Restriction with or without Concomitant Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System-Inhibiting Treatment on Albuminuria. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2015, 10, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.Y.; Park, I.H.; Kang, K.S.; Shin, M.S. The Beneficial Effect of Salicornia herbacea Extract and Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside on Obesity. Processes 2023, 11, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Go, H.-K.; Kweon, M.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Desalted Salicornia europaea powder and its active constituent, trans-ferulic acid, exert anti-obesity effects by suppressing adipogenic-related factors. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaeKeun, K.; JunYong, K.; YoungJu, S. Effects of Salicornia herbacea L. supplementation on lipid peroxidation and antioxidative protein expression in rat skeletal muscle. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 8, 962–968. [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel, R.; Larson, M.G.; Dupuis, J.; Lunetta, K.L.; Lipinska, I.; Meigs, J.B.; Yin, X.; Rong, J.; Vita, J.A.; Newton-Cheh, C.; et al. Relations of inflammatory biomarkers and common genetic variants with arterial stiffness and wave reflection. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.-L.; Hsu, C.-N. Oxidative Stress-Induced Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Preventive Aspects of Antioxidant Therapy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Early Origins of Hypertension: Should Prevention Start Before Birth Using Natural Antioxidants? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Croft, K.D.; Kennedy, D.O.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozawa, A.; Jacobs, D.R.; Steffes, M.W.; Gross, M.D.; Steffen, L.M.; Lee, D.H. Relationships of circulating carotenoid concentrations with several markers of inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction: The Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA)/Young Adult Longitudinal Trends in Antioxidants (YALTA) study. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 447–455. [Google Scholar]
- May, J.M.; Harrison, F.E. Role of vitamin C in the function of the vascular endothelium. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 2068–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ascorbic Acid. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amponsah-Offeh, M.; Diaba-Nuhoho, P.; Speier, S.; Morawietz, H. Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants and Hypertension. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ülker, S.; McKeown, P.P.; Bayraktutan, U. Vitamins reverse endothelial dysfunction through regulation of eNOS and NAD(P)H oxidase activities. Hypertension 2003, 41, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohadwala, M.M.; Holbrook, M.; Hamburg, N.M.; Shenouda, S.M.; Chung, W.B.; Titas, M.; Kluge, M.A.; Na Wang, N.; Palmisano, J.; Milbury, P.E.; et al. Effects of cranberry juice consumption on vascular function in patients with coronary artery disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.S.; Seo, Y. Antiadipogenic activity of isohamnetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from Salicornia herbacea. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 34, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, Á.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Martínez-González, M.Á. Monounsaturated fatty acids, olive oil and blood pressure: Epidemiological, clinical and experimental evidence. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Babio, N.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Ros, E.; Martín-Peláez, S.; Estruch, R.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Fiol, M.; et al. Dietary fat intake and risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in a population at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, R.N.; King, I.B.; Mozaffarian, D.; Kuller, L.H.; Tracy, R.P.; Siscovick, D.S. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids, fatal ischemic heart disease, and nonfatal myocardial infarction in older adults: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafeiadou, K.; Weech, M.; Altowaijri, H.; Todd, S.; Yaqoob, P.; Jackson, K.G.; Lovegrove, J.A. Replacement of saturated with unsaturated fats had no impact on vascular function but beneficial effects on lipid biomarkers, E-selectin, and blood pressure: Results from the randomized, controlled Dietary Intervention and VAScular function (DIVAS) study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, F.; Bhanger, M.I.; Nasir, M.K.A.; Ismail, S. Analytical characterization of Salicornia bigelovii seed oil cultivated in Pakistan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4210–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajhya, R.B.; Patel, R.S.; Beeton, C. Detection of Matrix Metalloproteinases by Zymography. In Matrix Metalloproteases. Methods in Molecular Biology; Galea, C., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Valente, F.M.; de Andrade, D.O.; Cosenso-Martin, L.N.; Cesarino, C.B.; Guimarães, S.M.; Guimarães, V.B.; Lacchini, R.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Yugar-Toledo, J.C.; Vilela-Martin, J.F. Plasma levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 are elevated in individuals with hypertensive crisis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, V.; Silva, P.S.; Belo, V.A.; Antonio, R.C.; Ceron, C.S.; Biagi, C.; Gerlach, R.F.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Consistent alterations of circulating matrix metalloproteinases levels in untreated hypertensives and in spontaneously hypertensive rats: A relevant pharmacological target. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvin, P.; Nilsson, L.; Carstensen, J.; Jonasson, L.; Kristenson, M. Circulating Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Is Associated with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in a Middle-Aged Normal Population. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumiza, S.; Chahed, K.; Tabka, Z.; Jacob, M.P.; Norel, X.; Ozen, G. MMPs and TIMPs levels are correlated with anthropometric parameters, blood pressure, and endothelial function in obesity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campino, C.; Baudrand, R.; Valdivia, C.A.; Carvajal, C.; Vecchiola, A.; Tapia-Castillo, A.; Martínez-Aguayo, A.; Garcia, H.; García, L.; Allende, F.; et al. Sodium Intake Is associated with Endothelial Damage Biomarkers and Metabolic Dysregulation. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancemi, P.; Aiello, A.; Accardi, G.; Caldarella, R.; Candore, G.; Caruso, C.; Ciaccio, M.; Cristaldi, L.; Di Gaudio, F.; Siino, V.; et al. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in Ageing and Longevity: Focus on Sicilian Long-Living Individuals (LLIs). Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8635158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malemud, C.J. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Synovial Joint Pathology. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 148, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’avila-Mesquita, C.; Couto, A.E.; Campos, L.C.; Vasconcelos, T.F.; Michelon-Barbosa, J.; Corsi, C.A.; Mestriner, F.; Petroski-Moraes, B.C.; Garbellini-Diab, M.J.; Couto, D.M.; et al. MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels in plasma are altered and associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112067. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, A.; Blázquez-Prieto, J.; Amado-Rodriguez, L.; López-Alonso, I.; Batalla-Solís, E.; González-López, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, M.; Mayoral-Garcia, C.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, A.; Albaiceta, G.M. Matrix metalloproteinase-14 triggers an anti-inflammatory proteolytic cascade in endotoxemia. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 —Student’s t-test was performed, which was statistically significant; p-value ≤ 0.05.
—Student’s t-test was performed, which was statistically significant; p-value ≤ 0.05.
 —Student’s t-test was performed, which was statistically significant; p-value ≤ 0.05.
—Student’s t-test was performed, which was statistically significant; p-value ≤ 0.05.
 —Student’s t-test was performed, which was statistically significant; p-value ≤ 0.05.
—Student’s t-test was performed, which was statistically significant; p-value ≤ 0.05.
 —Student’s t-test was performed, which was statistically significant; p-value ≤ 0.05.
—Student’s t-test was performed, which was statistically significant; p-value ≤ 0.05.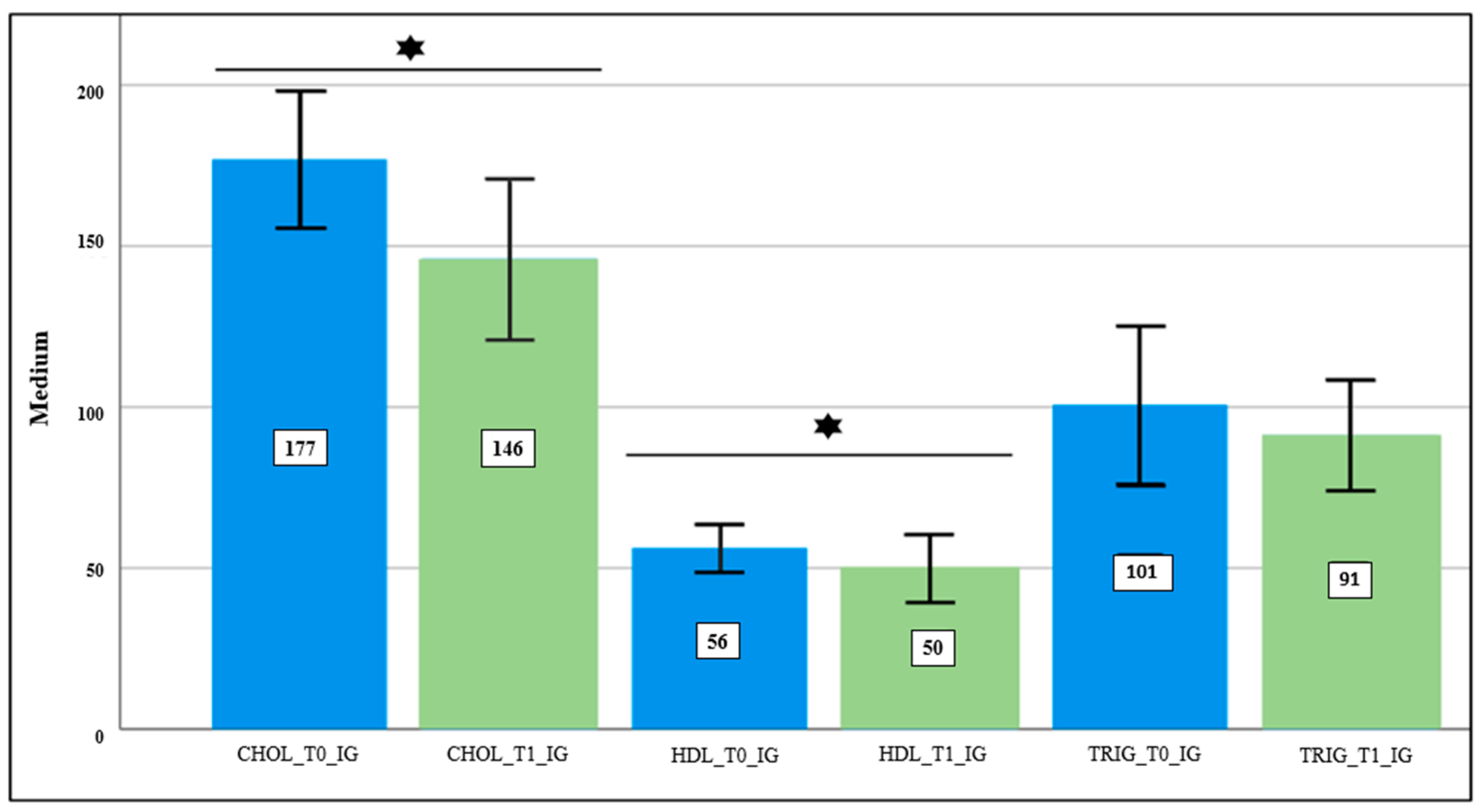

| CG (n = 15) | IG (n = 15) | Total (n = 30) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 20.6 ± 1.5 | 20.2 ± 0.9 | 20.4 ± 1.2 | 0.379 |
| BMI | 22.8 ± 1.9 | 21.3 ± 2.7 | 22.1 ± 2.4 | 0.085 |
| Waist | 74.6 ± 8.0 | 77.8 ± 8.4 | 76.2 ± 8.1 | 0.296 |
| Hip | 94.4 ± 8.4 | 94.8 ± 7.9 | 94.6 ± 7.9 | 0.894 |
| Ad. MD | 7.3 ± 1.4 | 6.6 ± 1.7 | 7.0 ± 1.5 | 0.205 |
| CG (n = 15) | IG (n = 15) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cholesterol * | 183.5 ± 32.6 | 176.9 ± 35.8 | 0.372 |
| HDL-c * | 59.8 ± 13.8 | 56.1 ± 12.5 | 0.206 |
| Glucose * | 84.0 ± 9.2 | 82.5 ± 5.2 | 0.419 |
| Creatinine * | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.372 |
| ALAT | 17.2 ± 10.0 | 18.3 ± 8.7 | 0.372 |
| ASAT | 21.7 ± 4.7 | 20.6 ± 5.4 | 0.218 |
| Triglycerides * | 74.3 ± 31.1 | 100.7 ± 42.4 | 0.368 |
| CG (n = 15) | IG (n = 15) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | P | T0 | T1 | P | |
| Total Cholesterol * | 183.5 ± 32.6 | 173.0 ± 29.4 | 0.008 | 176.9 ± 35.8 | 149.7 ± 43.8 | 0.031 |
| Glucose * | 84.0 ± 9.2 | 83.7 ± 7.3 | 0.314 | 82.5 ± 5.2 | 80.1 ± 14.8 | 0.128 |
| Creatinine * | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.275 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.014 |
| ALAT | 17.2 ± 10.0 | 15.3 ± 4.5 | 0.324 | 18.3 ± 8.7 | 16.2 ± 8.4 | 0.426 |
| ASAT | 21.7 ± 4.7 | 20.7 ± 2.8 | 0.239 | 20.6 ± 5.4 | 18.6 ± 5.8 | 0.091 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Louçano, B.; Maletti, S.; Timóteo, H.; Figueiredo, J.P.; Osório, N.; Barroca, M.J.; da Silva, A.M.; Pereira, T.; Caseiro, A. Assessing Sarcocornia as a Salt Substitute: Effects on Lipid Profile and Gelatinase Activity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070929
Louçano B, Maletti S, Timóteo H, Figueiredo JP, Osório N, Barroca MJ, da Silva AM, Pereira T, Caseiro A. Assessing Sarcocornia as a Salt Substitute: Effects on Lipid Profile and Gelatinase Activity. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070929
Chicago/Turabian StyleLouçano, Beatriz, Sara Maletti, Helena Timóteo, João Paulo Figueiredo, Nádia Osório, Maria João Barroca, Aida Moreira da Silva, Telmo Pereira, and Armando Caseiro. 2024. "Assessing Sarcocornia as a Salt Substitute: Effects on Lipid Profile and Gelatinase Activity" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070929
APA StyleLouçano, B., Maletti, S., Timóteo, H., Figueiredo, J. P., Osório, N., Barroca, M. J., da Silva, A. M., Pereira, T., & Caseiro, A. (2024). Assessing Sarcocornia as a Salt Substitute: Effects on Lipid Profile and Gelatinase Activity. Nutrients, 16(7), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070929










