Biomarkers of Brain Dysfunction in Perinatal Iron Deficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Perinatal Iron Metabolism
3. Interorgan Prioritization of Iron
4. Effects of Perinatal ID on Neurodevelopment
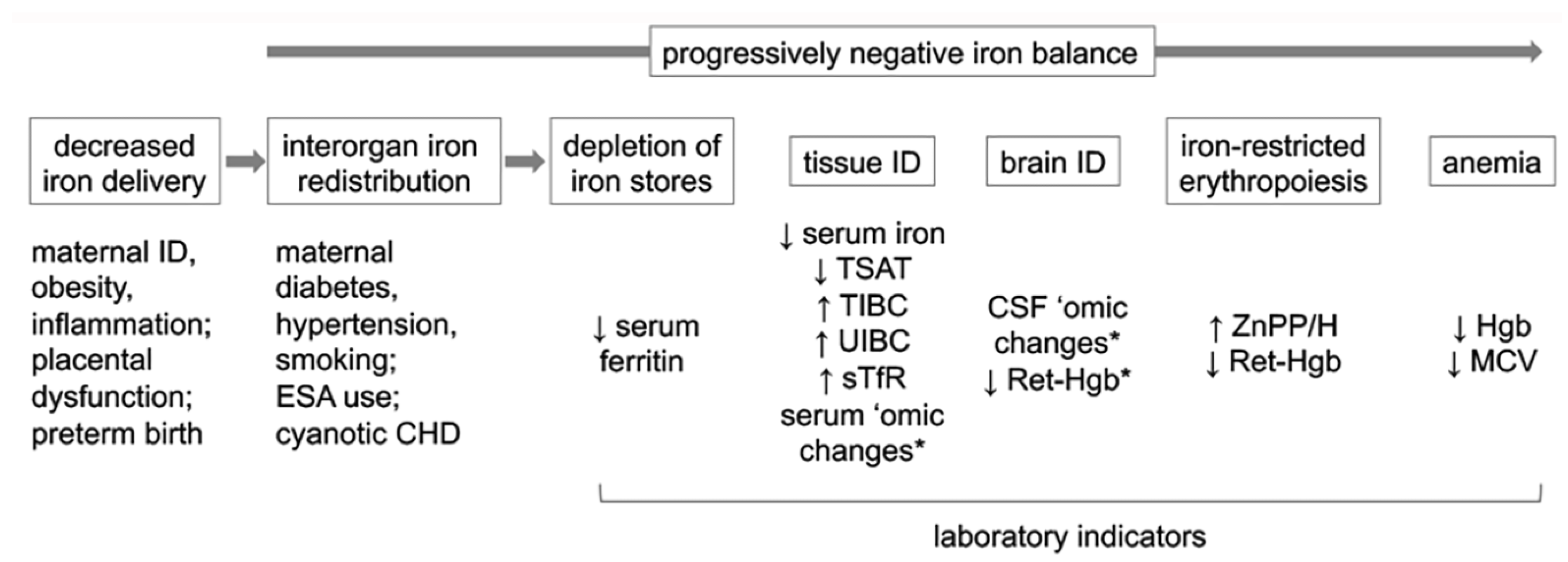
5. Biomarkers of Brain Dysfunction in Perinatal ID
5.1. Serum Iron Panel
5.1.1. Serum Ferritin
5.1.2. Serum Iron, Iron-Binding Capacity, and Transferrin Saturation
5.1.3. Hepcidin
5.1.4. Soluble Transferrin Receptor
5.2. RBC Parameters
5.2.1. Hemoglobin
5.2.2. Erythrocyte Zinc Protoporphyrin-to-Heme Ratio
5.2.3. Reticulocyte Hemoglobin Content
5.3. Maternal Peripartum Iron Biomarkers and Infant Neurodevelopment
5.4. Biomarkers of Iron-Dependent Brain Health
6. Biomarker-Based Iron Supplementation for Optimizing Neurodevelopment
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, G.A.; Paciorek, C.J.; Flores-Urrutia, M.C.; Borghi, E.; Namaste, S.; Wirth, J.P.; Suchdev, P.S.; Ezzati, M.; Rohner, F.; Flaxman, S.R.; et al. National, regional, and global estimates of anaemia by severity in women and children for 2000–2019: A pooled analysis of population-representative data. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e627–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, R.; Sable, C.; Wolfson, J.; Boro, K.; Rao, R. Prevalence of anemia in pregnant women and its effect on neonatal outcomes in Northeast India. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014, 27, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.E.; Shatzel, J.J.; Ryan, K.S.; Hedges, M.A.; Martens, K.; Aslan, J.E.; Lo, J.O. The incidence, complications, and treatment of iron deficiency in pregnancy. Eur. J. Haematol. 2022, 109, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, K.O.; Ru, Y. Iron status of North American pregnant women: An update on longitudinal data and gaps in knowledge from the United States and Canada. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106 (Suppl. S6), 1647S–1654S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R.; Wang, H.; Ahmed, R. Risk factors contributing to racial/ethnic disparities in iron deficiency in US women. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2021, 5, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.C.; Wiener, H.H.; Acton, R.T.; Adams, P.C.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Harris, E.L.; McLaren, C.E.; Harrison, H.; McLaren, G.D.; et al. Prevalence of iron deficiency in 62,685 women of seven race/ethnicity groups: The HEIRS Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, R.; Akhtar, S.S.; Venkatasubramaniam, A.; Wolfson, J.; Rao, R. Effect of 40-cm segment umbilical cord milking on hemoglobin and serum ferritin at 6 months of age in full-term infants of anemic and non-anemic mothers. J. Perinatol. 2015, 35, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, R.; Ramasamy, S.; Brown, B.; Wolfson, J.; Rao, R. Effect of iron supplementation from neonatal period on the iron status of6-month-old infants at-risk for early iron deficiency: A randomized interventional trial. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 34, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, C.D.; Eaton, M.A.; Wobken, J.D.; Mills, M.M.; Johnson, D.E.; Georgieff, M.K. Iron deficiency of liver, heart, and brain in newborn infants of diabetic mothers. J. Pediatr. 1992, 121, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieff, M.K.; MM, M.I.; Gordon, K.; Wobken, J.D. Reduced neonatal liver iron concentrations after uteroplacental insufficiency. J. Pediatr. 1995, 127, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddappa, A.M.; Rao, R.; Long, J.D.; Widness, J.A.; Georgieff, M.K. The assessment of newborn iron stores at birth: A review of the literature and standards for ferritin concentrations. Neonatology 2007, 92, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marell, P.S.; Blohowiak, S.E.; Evans, M.D.; Georgieff, M.K.; Kling, P.J.; Tran, P.V. Cord Blood-Derived Exosomal CNTN2 and BDNF: Potential Molecular Markers for Brain Health of Neonates at Risk for Iron Deficiency. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algarin, C.; Nelson, C.A.; Peirano, P.; Westerlund, A.; Reyes, S.; Lozoff, B. Iron-deficiency anemia in infancy and poorer cognitive inhibitory control at age 10 years. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2013, 55, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukowski, A.F.; Koss, M.; Burden, M.J.; Jonides, J.; Nelson, C.A.; Kaciroti, N.; Jimenez, E.; Lozoff, B. Iron deficiency in infancy and neurocognitive functioning at 19 years: Evidence of long-term deficits in executive function and recognition memory. Nutr. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozoff, B.; Brittenham, G.M.; Viteri, F.E.; Wolf, A.W.; Urrutia, J.J. The effects of short-term oral iron therapy on developmental deficits in iron-deficient anemic infants. J. Pediatr. 1982, 100, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozoff, B.; Jimenez, E.; Hagen, J.; Mollen, E.; Wolf, A.W. Poorer behavioral and developmental outcome more than 10 years after treatment for iron deficiency in infancy. Pediatrics 2000, 105, E51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arija, V.; Hernandez-Martinez, C.; Tous, M.; Canals, J.; Guxens, M.; Fernandez-Barres, S.; Ibarluzea, J.; Babarro, I.; Soler-Blasco, R.; Llop, S.; et al. Association of Iron Status and Intake during Pregnancy with Neuropsychological Outcomes in Children Aged 7 Years: The Prospective Birth Cohort Infancia y Medio Ambiente (INMA) Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegersma, A.M.; Dalman, C.; Lee, B.K.; Karlsson, H.; Gardner, R.M. Association of Prenatal Maternal Anemia with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Richards, B.; Kaciroti, N.; Zhu, B.; Clark, K.M.; Lozoff, B. Contribution of iron status at birth to infant iron status at 9 months: Data from a prospective maternal-infant birth cohort in China. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkermans, M.D.; Uijterschout, L.; Abbink, M.; Vos, P.; Rovekamp-Abels, L.; Boersma, B.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Brus, F. Predictive factors of iron depletion in late preterm infants at the postnatal age of 6 weeks. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srai, S.K.; Bomford, A.; McArdle, H.J. Iron transport across cell membranes: Molecular understanding of duodenal and placental iron uptake. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2002, 15, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangkhae, V.; Nemeth, E. Placental iron transport: The mechanism and regulatory circuits. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaugg, J.; Solenthaler, F.; Albrecht, C. Materno-fetal iron transfer and the emerging role of ferroptosis pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 202, 115141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdowson, E.M.; Spray, C.M. Chemical development in utero. Arch. Dis. Child. 1951, 26, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josephs, H.W. Iron metabolism and the hypochromic anemia of infancy. Medicine 1953, 32, 125–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, T.G.; Guiang, S.F., 3rd; Widness, J.A.; Georgieff, M.K. Iron is prioritized to red blood cells over the brain in phlebotomized anemic newborn lambs. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddappa, A.M.; Georgieff, M.K.; Wewerka, S.; Worwa, C.; Nelson, C.A.; Deregnier, R.A. Iron deficiency alters auditory recognition memory in newborn infants of diabetic mothers. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 55, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, E.S.; Fretham, S.J.B.; Unger, E.; O’Connor, M.; Petryk, A.; Schallert, T.; Rao, R.; Tkac, I.; Georgieff, M.K. Hippocampus specific iron deficiency alters competition and cooperation between developing memory systems. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2010, 2, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fretham, S.J.; Carlson, E.S.; Wobken, J.; Tran, P.V.; Petryk, A.; Georgieff, M.K. Temporal manipulation of transferrin-receptor-1-dependent iron uptake identifies a sensitive period in mouse hippocampal neurodevelopment. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geguchadze, R.N.; Coe, C.L.; Lubach, G.R.; Clardy, T.W.; Beard, J.L.; Connor, J.R. CSF proteomic analysis reveals persistent iron deficiency-induced alterations in non-human primate infants. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.L.; Unger, E.L.; Bianco, L.E.; Paul, T.; Rundle, S.E.; Jones, B.C. Early postnatal iron repletion overcomes lasting effects of gestational iron deficiency in rats. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddappa, A.J.; Rao, R.B.; Wobken, J.D.; Leibold, E.A.; Connor, J.R.; Georgieff, M.K. Developmental changes in the expression of iron regulatory proteins and iron transport proteins in the perinatal rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 68, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.R. Iron acquisition and expression of iron regulatory proteins in the developing brain: Manipulation by ethanol exposure, iron deprivation and cellular dysfunction. Dev. Neurosci. 1994, 16, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, D.; Anupurba, S.; Verma, A.; Kumar, A. Effect of maternal iron deficiency anemia on fetal neural development. J. Perinatol. 2018, 38, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- deUngria, M.; Rao, R.; Wobken, J.D.; Luciana, M.; Nelson, C.A.; Georgieff, M.K. Perinatal iron deficiency decreases cytochrome c oxidase (CytOx) activity in selected regions of neonatal rat brain. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 48, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Tkac, I.; Townsend, E.L.; Gruetter, R.; Georgieff, M.K. Perinatal iron deficiency alters the neurochemical profile of the developing rat hippocampus. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3215–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.L.; Tkac, I.; Jing, Y.; Felt, B.; Beard, J.; Connor, J.; Schallert, T.; Georgieff, M.K.; Rao, R. Gestational and lactational iron deficiency alters the developing striatal metabolome and associated behaviors in young rats. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, E.L.; Hurst, A.R.; Georgieff, M.K.; Schallert, T.; Rao, R.; Connor, J.R.; Kaciroti, N.; Lozoff, B.; Felt, B. Behavior and monoamine deficits in prenatal and perinatal iron deficiency are not corrected by early postnatal moderate-iron or high-iron diets in rats. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2040–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.T.; Alvarez, G.C.; Grove, W.M.; Rao, R.; Georgieff, M.K. Early Iron Deficiency Enhances Stimulus-response Learning of Adult Rats in the Context of Competing Spatial Information. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2012, 2, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Geng, F.; Mai, X.; Zhan, J.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Georgieff, M.; Shao, J.; Lozoff, B. Impact of Fetal-Neonatal Iron Deficiency on Recognition Memory at 2 Months of Age. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Goldenberg, R.L.; Hou, J.; Johnston, K.E.; Cliver, S.P.; Ramey, S.L.; Nelson, K.G. Cord serum ferritin concentrations and mental and psychomotor development of children at five years of age. J. Pediatr. 2002, 140, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, S.K.; Chmielewska, A.; Starnberg, J.; Westrup, B.; Hagglof, B.; Norman, M.; Domellof, M. Effects of iron supplementation of low-birth-weight infants on cognition and behavior at 7 years: A randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radlowski, E.C.; Johnson, R.W. Perinatal iron deficiency and neurocognitive development. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggins, T.; Miller, N.C.; Bauer, P.J.; Georgieff, M.K.; Nelson, C.A. Consequences of low neonatal iron status due to maternal diabetes mellitus on explicit memory performance in childhood. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2009, 34, 762–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, K.R.; Vu, P.T.; Comstock, B.A.; Ohls, R.K.; Heagerty, P.J.; Mayock, D.E.; Georgieff, M.; Rao, R.; Juul, S.E.; Consortium, P. Enteral Iron Supplementation in Infants Born Extremely Preterm and its Positive Correlation with Neurodevelopment; Post Hoc Analysis of the Preterm Erythropoietin Neuroprotection Trial Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pediatr. 2021, 238, 102–109.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, S.C.; Nawaz, S.; Chakrabarti, A.; Gressens, P.; Mani, S. Spatial memory deficits in maternal iron deficiency paradigms are associated with altered glucocorticoid levels. Horm. Behav. 2013, 64, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, S.C.; Rose, A.; Rao, M.; Gallego, J.; Gressens, P.; Mani, S. Different types of nutritional deficiencies affect different domains of spatial memory function checked in a radial arm maze. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyshon, B.J.; Radlowski, E.C.; Mudd, A.T.; Steelman, A.J.; Johnson, R.W. Postnatal Iron Deficiency Alters Brain Development in Piglets. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, A.T.; Fil, J.E.; Knight, L.C.; Lam, F.; Liang, Z.P.; Dilger, R.N. Early-Life Iron Deficiency Reduces Brain Iron Content and Alters Brain Tissue Composition Despite Iron Repletion: A Neuroimaging Assessment. Nutrients 2018, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, E.S.; Tkac, I.; Magid, R.; O’Connor, M.B.; Andrews, N.C.; Schallert, T.; Gunshin, H.; Georgieff, M.K.; Petryk, A. Iron is essential for neuron development and memory function in mouse hippocampus. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fretham, S.J.; Carlson, E.S.; Georgieff, M.K. Neuronal-specific iron deficiency dysregulates mammalian target of rapamycin signaling during hippocampal development in nonanemic genetic mouse models. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barks, A.; Fretham, S.J.; Georgieff, M.K.; Tran, P.V. Early-Life Neuronal-Specific Iron Deficiency Alters the Adult Mouse Hippocampal Transcriptome. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachs, T.D.; Pollitt, E.; Cueto, S.; Jacoby, E.; Creed-Kanashiro, H. Relation of neonatal iron status to individual variability in neonatal temperament. Dev. Psychobiol. 2005, 46, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.C.C.; Angulo-Barroso, R.M.; Li, M.; Bian, Y.; Sturza, J.; Richards, B.; Lozoff, B. Timing, duration, and severity of iron deficiency in early development and motor outcomes at 9 months. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Shi, D.; Xu, W.; Zhu, L.; Hao, X.; Zhu, B.; Shu, Q.; Lozoff, B.; Geng, F.; Shao, J. Differentiation between fetal and postnatal iron deficiency in altering brain substrates of cognitive control in pre-adolescence. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, E.K.; Murray, D.M.; Hourihane, J.O.B.; Kenny, L.C.; Irvine, A.D.; Kiely, M.E. Behavioral consequences at 5 y of neonatal iron deficiency in a low-risk maternal-infant cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armony-Sivan, R.; Eidelman, A.I.; Lanir, A.; Sredni, D.; Yehuda, S. Iron status and neurobehavioral development of premature infants. J. Perinatol. 2004, 24, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.B.; Orlando, M.; Eddins, A.; MacDonald, M.; Monczynski, C.; Wang, H. In utero iron status and auditory neural maturation in premature infants as evaluated by auditory brainstem response. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.B.; Orlando, M.; Wang, H. Latent iron deficiency in utero is associated with abnormal auditory neural myelination in >/= 35 weeks gestational age infants. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, S.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Georgieff, M.K.; Brittenham, G.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Hurrell, R.F.; McArdle, H.J.; Raiten, D.J. Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development (BOND)-Iron Review. J. Nutr. 2018, 148 (Suppl. S1), 1001S–1067S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group. BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and Other Tools) Resource; Food and Drug Administration: Silverspring, MD, USA; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- German, K.R.; Juul, S.E. Serum Measures of Brain Iron Status—A Major Barrier to Optimizing Iron Status in Neonates. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 797–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.G.; Kennedy, T.S.; Colaizzi, J.; Aubuchon-Endsley, N.; Grant, S.; Stoecker, B.; Duell, E. Multiple Biomarkers of Maternal Iron Predict Infant Cognitive Outcomes. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2017, 42, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, R.M.; Wang, Q.; Willette, A.; Styner, M.A.; Lubach, G.R.; Kling, P.J.; Georgieff, M.K.; Rao, R.B.; Coe, C.L. Infantile Iron Deficiency Affects Brain Development in Monkeys Even After Treatment of Anemia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 624107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.; deRegnier, R.A.; Shaw, M.D.; Rao, R.; Georgieff, M. Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency in Infants. Lab. Med. 2007, 38, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, L.; Peter, A.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. A review of cord blood concentrations of iron status parameters to define reference ranges for preterm infants. Neonatology 2013, 104, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, B.J.; Kim, J.; Lubach, G.R.; Lock, E.F.; Ennis-Czerniak, K.; Kling, P.J.; Georgieff, M.K.; Coe, C.L.; Rao, R.B. Prognostic Performance of Hematological and Serum Iron and Metabolite Indices for Detection of Early Iron Deficiency Induced Metabolic Brain Dysfunction in Infant Rhesus Monkeys. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennis, K.M.; Dahl, L.V.; Rao, R.B.; Georgieff, M.K. Reticulocyte hemoglobin content as an early predictive biomarker of brain iron deficiency. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczynski, J.; Slomka, A.; Lecka, M.; Albrecht, K.; Romiszewski, M.; Pogorzala, M.; Kubicka, M.; Kurylo-Rafinska, B.; Tejza, B.; Gadomska, G.; et al. Soluble Hemojuvelin and Ferritin: Potential Prognostic Markers in Pediatric Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Cancers 2023, 15, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.C.; Georgieff, M.K.; Ennis, K.M.; Dodge, N.C.; Wainwright, H.; Meintjes, E.M.; Duggan, C.P.; Molteno, C.D.; Jacobson, J.L.; Jacobson, S.W. Prenatal alcohol-related alterations in maternal, placental, neonatal, and infant iron homeostasis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, K.; Yadav, R.K.; Kishore, S.S.; Garewal, G.; Jain, V.; Narang, A. Iron status at birth and at 4 weeks in preterm-SGA infants in comparison with preterm and term-AGA infants. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddappa, A.M.; Olson, R.M.; Spector, M.; Northrop, E.; Zamora, T.; Brearley, A.M.; Georgieff, M.K.; Rao, R. High Prevalence of Iron Deficiency Despite Standardized High-Dose Iron Supplementation during Recombinant Erythropoietin Therapy in Extremely Low Gestational Age Newborns. J. Pediatr. 2020, 222, 98–105.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Lou, J.; Rao, R.; Georgieff, M.K.; Kaciroti, N.; Felt, B.T.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Lozoff, B. Maternal serum ferritin concentration is positively associated with newborn iron stores in women with low ferritin status in late pregnancy. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2004–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahr, T.M.; Baer, V.L.; Ohls, R.K.; Christensen, T.R.; Ward, D.M.; Bennett, S.T.; Christensen, R.D. Reconciling markedly discordant values of serum ferritin versus reticulocyte hemoglobin content. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, K.; Vu, P.T.; Grelli, K.N.; Denton, C.; Lee, G.; Juul, S.E. Zinc Protoporphyrin-to-Heme Ratio and Ferritin as Measures of Iron Sufficiency in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Pediatr. 2018, 194, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.B.; Myers, G.; Wang, H. Association between neonatal iron overload and early human brain development in premature infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, T.M.; Tan, S.; Smith, E.; Beauman, S.S.; Schibler, K.R.; Grisby, C.A.; Lowe, J.R.; Bell, E.F.; Laptook, A.R.; Shankaran, S.; et al. Serum ferritin values in neonates <29 weeks’ gestation are highly variable and do not correlate with reticulocyte hemoglobin content. J. Perinatol. 2023, 43, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, K.R.; Vu, P.T.; Neches, S.; Juul, S.E. Comparison of two markers of iron sufficiency and neurodevelopmental outcomes. Early Hum. Dev. 2021, 158, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, R.J.; Griffin, I. Iron Balance and Iron Nutritional Status in Preterm Infants During the First Four Months of Life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 73, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerday, E.; Brereton, J.B.; Bahr, T.M.; Elmont, J.O.; Fullmer, S.; Middleton, B.A.; Ward, D.M.; Ohls, R.K.; Christensen, R.D. Urinary ferritin; a potential noninvasive way to screen NICU patients for iron deficiency. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, T.M.; Christensen, R.D.; Ward, D.M.; Meng, F.; Jackson, L.K.; Doyle, K.; Christensen, D.R.; Harvey, A.G.; Yaish, H.M. Ferritin in serum and urine: A pilot study. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2019, 76, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarnath, U.M.; Ophoven, J.J.; Mills, M.M.; Murphy, E.L.; Georgieff, M.K. The relationship between decreased iron stores, serum iron and neonatal hypoglycemia in large-for-date newborn infants. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1989, 78, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, J.H.; Prentice, A.M.; Cerami, C. Hepcidin, Serum Iron, and Transferrin Saturation in Full-Term and Premature Infants during the First Month of Life: A State-of-the-Art Review of Existing Evidence in Humans. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, nzaa104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozovic, B.; Burland, W.L.; Simpson, K.; Lord, J. Iron status of preterm low birthweight infants and their response to oral iron. Arch. Dis. Child. 1974, 49, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yamada, R.T.; Leone, C.R. Hematological and iron content evolution in exclusively breastfed late-preterm newborns. Clinics 2014, 69, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, D.G.; Savage, G.A.; Tubman, R.; Lappin, T.R.; Halliday, H.L. Cord blood transferrin receptors to assess fetal iron status. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2001, 85, F46–F48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarinen, U.M.; Siimes, M.A. Developmental changes in serum iron, total iron-binding capacity, and transferrin saturation in infancy. J. Pediatr. 1977, 91, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balai, K.S.; Pendse, V.; Gupta, R.; Gupta, S. Effect of maternal anemia on iron status of the new born. Indian. J. Matern. Child Health 1992, 3, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lao, T.T.; Loong, E.P.; Chin, R.K.; Lam, C.W.; Lam, Y.M. Relationship between newborn and maternal iron status and haematological indices. Biol. Neonate 1991, 60, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva Ade, A.; Rondo, P.H.; Pagliusi, R.A.; Latorre Mdo, R.; Cardoso, M.A.; Gondim, S.S. Relationship between the iron status of pregnant women and their newborns. Rev. Saude Publica 2007, 41, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, N.; Srivastava, R.; Kumar, A. Maternal and Cord Blood Hepcidin Concentrations in Severe Iron Deficiency Anemia. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2016, 57, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stripeli, F.; Kapetanakis, J.; Gourgiotis, D.; Drakatos, A.; Tsolia, M.; Kossiva, L. Post-transfusion changes in serum hepcidin and iron parameters in preterm infants. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Lam, C.W.; Lee, C.H.; To, K.F.; Fok, T.F.; Chan, I.H.; Wong, E. Hepatic iron storage in very low birthweight infants after multiple blood transfusions. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2001, 84, F101–F105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruqi, A.; Mukkamalla, S.K.R. Iron Binding Capacity. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chelchowska, M.; Laskowska-Klita, T. Effect of maternal smoking on some markers of iron status in umbilical cord blood. Rocz. Akad. Med. Bialymst. 2002, 47, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc, C.P.; Rioux, F.M. Iron deficiency anemia following prenatal nutrition interventions. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2007, 68, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandyo, R.K.; Henjum, S.; Ulak, M.; Thorne-Lyman, A.L.; Ulvik, R.J.; Shrestha, P.S.; Locks, L.; Fawzi, W.; Strand, T.A. The prevalence of anemia and iron deficiency is more common in breastfed infants than their mothers in Bhaktapur, Nepal. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, C.; Wu, A.; Armsby, C.; Rieber, S.; Wingerter, S.; Brugnara, C.; Shapiro, D.; Bernstein, H. Screening healthy infants for iron deficiency using reticulocyte hemoglobin content. JAMA 2005, 294, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.B.; Lubach, G.R.; Ennis-Czerniak, K.M.; Lock, E.F.; Kling, P.J.; Georgieff, M.K.; Coe, C.L. Reticulocyte Hemoglobin Equivalent has Comparable Predictive Accuracy as Conventional Serum Iron Indices for Predicting Iron Deficiency and Anemia in a Nonhuman Primate model of Infantile Iron Deficiency. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, K.R.; Comstock, B.A.; Parikh, P.; Whittington, D.; Mayock, D.E.; Heagerty, P.J.; Bahr, T.M.; Juul, S.E. Do Extremely Low Gestational Age Neonates Regulate Iron Absorption via Hepcidin? J. Pediatr. 2022, 241, 62–67.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, S.; Lonnerdal, B.; Westrup, B.; Domellof, M. Effects of iron supplementation on serum hepcidin and serum erythropoietin in low-birth-weight infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, S.K.; Chmielewska, A.M.; Domellof, M.; Andersson, O. Hepcidin is a relevant iron status indicator in infancy: Results from a randomized trial of early vs. delayed cord clamping. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, T.M.; Ward, D.M.; Jia, X.; Ohls, R.K.; German, K.R.; Christensen, R.D. Is the erythropoietin-erythroferrone-hepcidin axis intact in human neonates? Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2021, 88, 102536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, L.; Herbst, J.; Engel, C.; Peter, A.; Abele, H.; Poets, C.F.; Westerman, M.; Franz, A.R. Gestational age-specific reference ranges of hepcidin in cord blood. Neonatology 2014, 106, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, K.F.; Lorenz, L.; Poets, C.F.; Westerman, M.; Franz, A.R. Hepcidin concentrations in serum and urine correlate with iron homeostasis in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2012, 160, 949–953.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, L.; Muller, K.F.; Poets, C.F.; Peter, A.; Olbina, G.; Westerman, M.; Franz, A.R. Short-Term Effects of Blood Transfusions on Hepcidin in Preterm Infants. Neonatology 2015, 108, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Huang, H.C.; Tang, K.S.; Su, L.T.; Huang, Y.H.; Huang, H.C.; Chen, I.L. Elevated Urinary Hepcidin Level and Hypoferremia in Infants with Febrile Urinary Tract Infection: A Prospective Cohort Study. Children 2023, 10, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kling, P.J.; Roberts, R.A.; Widness, J.A. Plasma transferrin receptor levels and indices of erythropoiesis and iron status in healthy term infants. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1998, 20, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.D.; Flowers, C.H.; Skikne, B.S. The quantitative assessment of body iron. Blood 2003, 101, 3359–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, S.; Mason, L.; Milosavljevic, B.; Mbye, E.; Touray, E.; Colley, A.; Johnson, W.; Lloyd-Fox, S.; Elwell, C.E.; Moore, S.E.; et al. Iron status in early infancy is associated with trajectories of cognitive development up to pre-school age in rural Gambia. PLoS Glob. Public. Health 2023, 3, e0002531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gire, C.; Fournier, N.; Pirrello, J.; Marret, S.; Patural, H.; Flamant, C.; Pierrat, V.; Kaminski, M.; Ancel, P.Y.; Tosello, B.; et al. Impact of Early Hemoglobin Levels on Neurodevelopment Outcomes of Two-Year-Olds in Very Preterm Children. Children 2023, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widness, J.A.; Seward, V.J.; Kromer, I.J.; Burmeister, L.F.; Bell, E.F.; Strauss, R.G. Changing patterns of red blood cell transfusion in very low birth weight infants. J. Pediatr. 1996, 129, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, S.E.; Zerzan, J.C.; Strandjord, T.P.; Woodrum, D.E. Zinc protoporphyrin/heme as an indicator of iron status in NICU patients. J. Pediatr. 2003, 142, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Waal, C.G.; Uijterschout, L.; Abbink, M.; Boersma, B.; Vos, P.; Rovekamp, W.W.; Hudig, F.; Akkermans, M.D.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Brus, F. Zinc protoporphyrin/heme ratio as parameter of iron status in moderately preterm infants: Natural course and associations in the first 4 months. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abd Almonaem, E.R.; Mostafa, M.A.; El-Shimi, O.S.; Saeed, Y.A.; Abdulsamea, S. Effectiveness of zinc protoporphyrin/heme ratio and ferritin for assessing iron status in preterm infants. J. Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2023, 16, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blohowiak, S.E.; Chen, M.E.; Repyak, K.S.; Baumann-Blackmore, N.L.; Carlton, D.P.; Georgieff, M.K.; Crenshaw, T.D.; Kling, P.J. Reticulocyte enrichment of zinc protoporphyrin/heme discriminates impaired iron supply during early development. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.F.; Zerzan, J.C.; Johnson, D.B.; Juul, S.E. Zinc protoporphyrin-to-heme ratios in high-risk and preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2012, 161, 81–87.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lott, D.G.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Labbe, R.F.; Kling, P.J.; Widness, J.A. Erythrocyte zinc protoporphyrin is elevated with prematurity and fetal hypoxemia. Pediatrics 2005, 116, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Blackmore, N.L.; Goetz, E.; Blohowiak, S.E.; Zaka, O.; Kling, P.J. Cord blood zinc protoporphyrin/heme ratio in minority neonates at risk for iron deficiency. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, A.K.; Roy, S.C.; Lundberg, R.; Guilbert, T.W.; Auger, A.P.; Blohowiak, S.E.; Coe, C.L.; Kling, P.J. Neonatal iron status is impaired by maternal obesity and excessive weight gain during pregnancy. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, I.J.; Reid, M.M.; McCormick, K.P.; Cooke, R.J. Zinc protoporphyrin/haem ratio and plasma ferritin in preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2002, 87, F49–F51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.M.; McPherson, R.J.; Juul, S.E. Iron sulfate supplementation decreases zinc protoporphyrin to heme ratio in premature infants. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, E.; Brugnara, C.; Spolaore, F.; Plebani, M. Clinical utility of reticulocyte parameters. Clin. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toki, Y.; Ikuta, K.; Kawahara, Y.; Niizeki, N.; Kon, M.; Enomoto, M.; Tada, Y.; Hatayama, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Ito, S.; et al. Reticulocyte hemoglobin equivalent as a potential marker for diagnosis of iron deficiency. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 106, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pinto, D.; Paz, M.; Adragna, M.; Lopez, L. Clinical usefulness of the reticulocyte hemoglobin equivalent in children on hemodialysis. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2020, 118, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinudomwong, P.; Binyasing, A.; Trongsakul, R.; Paisooksantivatana, K. Diagnostic performance of reticulocyte hemoglobin equivalent in assessing the iron status. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neef, V.; Schmitt, E.; Bader, P.; Zierfuss, F.; Hintereder, G.; Steinbicker, A.U.; Zacharowski, K.; Piekarski, F. The Reticulocyte Hemoglobin Equivalent as a Screening Marker for Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia in Children. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, M.; Jenkins, P.; Ullrich, C.; Brugnara, C.; Nghiem, B.T.; Bernstein, H. An economic analysis of anemia prevention during infancy. J. Pediatr. 2009, 154, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honemann, C.; Hagemann, O.; Doll, D.; Luedi, M.M.; Ruebsam, M.-L.; Meybohm, P. Reticulocyte Haemoglobin as a Routine Parameter in Preoperative Iron Deficiency Assessment. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 5, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyck, D.B.; Alcorn, H., Jr.; Gupta, R. Analytical and biological variation in measures of anemia and iron status in patients treated with maintenance hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.D.; Henry, E.; Bennett, S.T.; Yaish, H.M. Reference intervals for reticulocyte parameters of infants during their first 90 days after birth. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, L.; Peter, A.; Arand, J.; Springer, F.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Reference Ranges of Reticulocyte Haemoglobin Content in Preterm and Term Infants: A Retrospective Analysis. Neonatology 2017, 111, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, L.; Peter, A.; Arand, J.; Springer, F.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Reticulocyte Haemoglobin Content Declines More Markedly in Preterm than in Term Infants in the First Days after Birth. Neonatology 2017, 112, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, K.; Vu, P.T.; Irvine, J.D.; Juul, S.E. Trends in reticulocyte hemoglobin equivalent values in critically ill neonates, stratified by gestational age. J. Perinatol. 2019, 39, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, L.; Arand, J.; Buchner, K.; Wacker-Gussmann, A.; Peter, A.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Reticulocyte haemoglobin content as a marker of iron deficiency. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2015, 100, F198–F202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, E.M.; Hendricks, M.K.; Beard, J.L.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; Berg, A.; Tomlinson, M.; Irlam, J.; Isaacs, W.; Njengele, T.; Sive, A.; et al. Mother-infant interactions and infant development are altered by maternal iron deficiency anemia. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.L.; Hendricks, M.K.; Perez, E.M.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; Berg, A.; Vernon-Feagans, L.; Irlam, J.; Isaacs, W.; Sive, A.; Tomlinson, M. Maternal iron deficiency anemia affects postpartum emotions and cognition. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.V.; Fretham, S.J.; Carlson, E.S.; Georgieff, M.K. Long-term reduction of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor activity after fetal-neonatal iron deficiency in adult rats. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubach, G.R.; Coe, C.L. Preconception maternal iron status is a risk factor for iron deficiency in infant rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2345–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Patton, S.M.; Coe, C.L.; Lubach, G.R.; Connor, J.R. Quantitative proteomic analyses of cerebrospinal fluid using iTRAQ in a primate model of iron deficiency anemia. Dev. Neurosci. 2012, 34, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Ennis, K.; Oz, G.; Lubach, G.R.; Georgieff, M.K.; Coe, C.L. Metabolomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid indicates iron deficiency compromises cerebral energy metabolism in the infant monkey. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknese, E.J.; George, J.W.; Hird, D.W.; Paul-Murphy, J.; Anderson, J.A.; Roberts, J.R. Prevalence and risk factors for iron deficiency anemia in weanling rhesus macaques. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1993, 43, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Coe, C.L.; Lubach, G.R.; Busbridge, M.; Chapman, R.S. Optimal iron fortification of maternal diet during pregnancy and nursing for investigating and preventing iron deficiency in young rhesus monkeys. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 94, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coe, C.L.; Lubach, G.R.; Bianco, L.; Beard, J.L. A history of iron deficiency anemia during infancy alters brain monoamine activity later in juvenile monkeys. Dev. Psychobiol. 2009, 51, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Ennis, K.; Lubach, G.R.; Lock, E.F.; Georgieff, M.K.; Coe, C.L. Metabolomic analysis of CSF indicates brain metabolic impairment precedes hematological indices of anemia in the iron-deficient infant monkey. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, B.J.; Kim, J.; Lubach, G.R.; Lock, E.F.; Guerrero, C.; Higgins, L.; Markowski, T.W.; Kling, P.J.; Georgieff, M.K.; Coe, C.L.; et al. Multiomic Profiling of Iron Deficient Infant Monkeys Reveals Alterations in Neurologically Important Biochemicals in Serum and CSF Prior to the Onset of Anemia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2022, 322, R486–R500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, B.J.; Lubach, G.R.; Lock, E.F.; Georgieff, M.K.; Kling, P.J.; Coe, C.L.; Rao, R.B. Early-Life Iron Deficiency and Its Natural Resolution Are Associated with Altered Serum Metabolomic Profiles in Infant Rhesus Monkeys. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, B.J.; Lubach, G.R.; Lock, E.F.; Kling, P.J.; Georgieff, M.K.; Coe, C.L.; Rao, R.B. Correcting iron deficiency anemia with iron dextran alters the serum metabolomic profile of the infant Rhesus Monkey. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, C.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Peng, C. A review of pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties of stachydrine. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erecinska, M.; Cherian, S.; Silver, I.A. Energy metabolism in mammalian brain during development. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 73, 397–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, A.; He, X.; McNiven, E.M.; Hinde, K.; Haggarty, N.W.; Lonnerdal, B.; Slupsky, C.M. Metabolomic phenotyping validates the infant rhesus monkey as a model of human infant metabolism. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.D.; Greer, F.R.; Committee on Nutrition American Academy of Pediatrics. Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children (0–3 years of age). Pediatrics 2010, 126, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.P.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellof, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: Commentary from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domellof, M.; Braegger, C.; Campoy, C.; Colomb, V.; Decsi, T.; Fewtrell, M.; Hojsak, I.; Mihatsch, W.; Molgaard, C.; Shamir, R.; et al. Iron requirements of infants and toddlers. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, S.L.; Fenton, T.R.; Jetty, R.; Critch, J.N.; O’Connor, D.L. Iron requirements in the first 2 years of life. Paediatr. Child. Health 2019, 24, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, L.; Schanler, R.; Weinberger, B. Optimizing iron supplementation by monitoring serum ferritin levels in premature infants. J. Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2022, 15, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.R.; Comstock, B.A.; Patel, R.M.; Tolia, V.N.; Josephson, C.D.; Georgieff, M.K.; Rao, R.; Monsell, S.E.; Juul, S.E.; Ahmad, K.A.; et al. Iron supplementation and the risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely low gestational age newborns. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul, S.E.; Comstock, B.A.; Wadhawan, R.; Mayock, D.E.; Courtney, S.E.; Robinson, T.; Ahmad, K.A.; Bendel-Stenzel, E.; Baserga, M.; LaGamma, E.F.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Erythropoietin for Neuroprotection in Preterm Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, E.R.; Goldberg, S.N.; Lawrence, C.; Wenz, B. Clinical utility of serum tests for iron deficiency in hospitalized patients. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1990, 93, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchdev, P.S.; Williams, A.M.; Mei, Z.; Flores-Ayala, R.; Pasricha, S.R.; Rogers, L.M.; Namaste, S.M. Assessment of iron status in settings of inflammation: Challenges and potential approaches. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106 (Suppl. S6), 1626S–1633S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Laboratory Test | Indicator of | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean cellular volume | Anemia | Ease of determination. Immediate availability of results. | Lack sensitivity and specificity for ID, brain ID, and brain dysfunction. |
| Serum ferritin (SF) | Iron stores | Low SF is specific for ID. Known association between cord SF and short- and long-term neurodevelopment. | Falsely elevated in inflammation. Poor relationship between SF after birth and neurodevelopment. |
| Serum iron panel (iron, transferrin saturation, total iron-binding capacity, unsaturated iron-binding capacity) | Iron deficiency | Detects preanemic ID. Predicts ID-induced brain dysfunction in the preanemic period *. | Affected by diet and inflammation. Requires additional blood volume. Lack of reference values in preterm infants. |
| Soluble serum transferrin (sTfR) | Intracellular iron status | sTfR:SF ratio indicates body iron status and useful for monitoring response to iron treatment. Association between postnatal sTfR and neurodevelopment. | No data on relationship between cord/neonatal sTfR and neurodevelopment. |
| Hepcidin | Regulation of iron absorption | Availability of reference values across the gestational age spectrum. | Altered by multiple factors. No data on sensitivity for detection of brain ID or dysfunction. |
| Zinc protoporphyrin-to- heme ratio | Iron-deficient erythropoiesis | Predicts impending anemia. Association with neurodevelopment. | Not universally available. |
| Reticulocyte hemoglobin | Bone marrow iron deficiency | Predicts impending anemia, brain ID, and brain dysfunction *. Component of CBC in some analyzers. Does not require additional blood volume. | Not available in all analyzers. Falsely low in hemoglobinopathies. Sensitivity for predicting long-term neurodevelopment unknown. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, R.B. Biomarkers of Brain Dysfunction in Perinatal Iron Deficiency. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071092
Rao RB. Biomarkers of Brain Dysfunction in Perinatal Iron Deficiency. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071092
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Raghavendra B. 2024. "Biomarkers of Brain Dysfunction in Perinatal Iron Deficiency" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071092
APA StyleRao, R. B. (2024). Biomarkers of Brain Dysfunction in Perinatal Iron Deficiency. Nutrients, 16(7), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071092






