Eriocitrin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
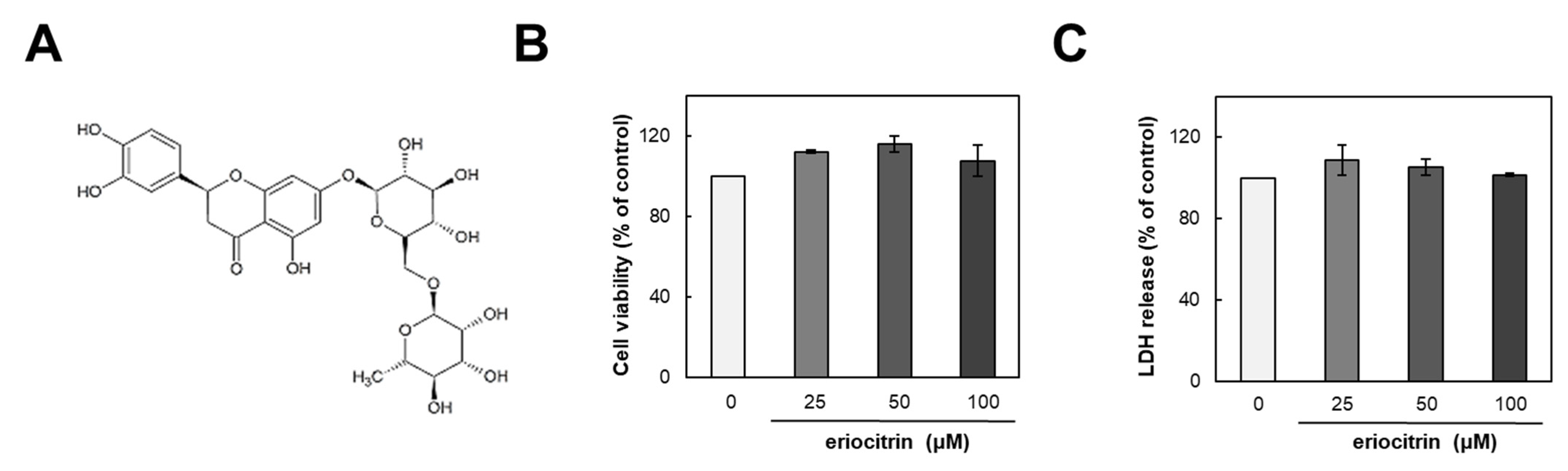
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release Assay
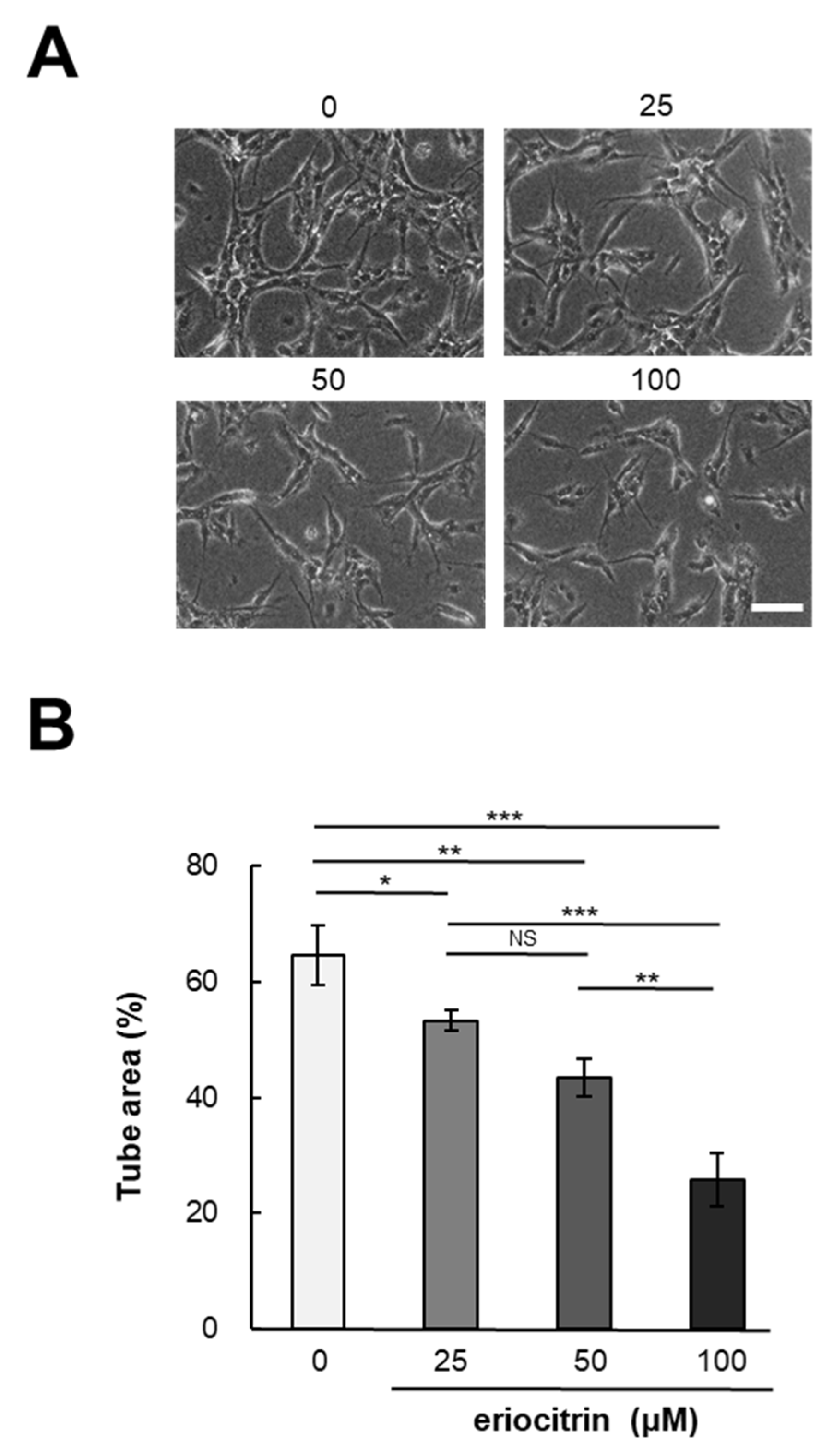
2.5. Tube Formation Assay
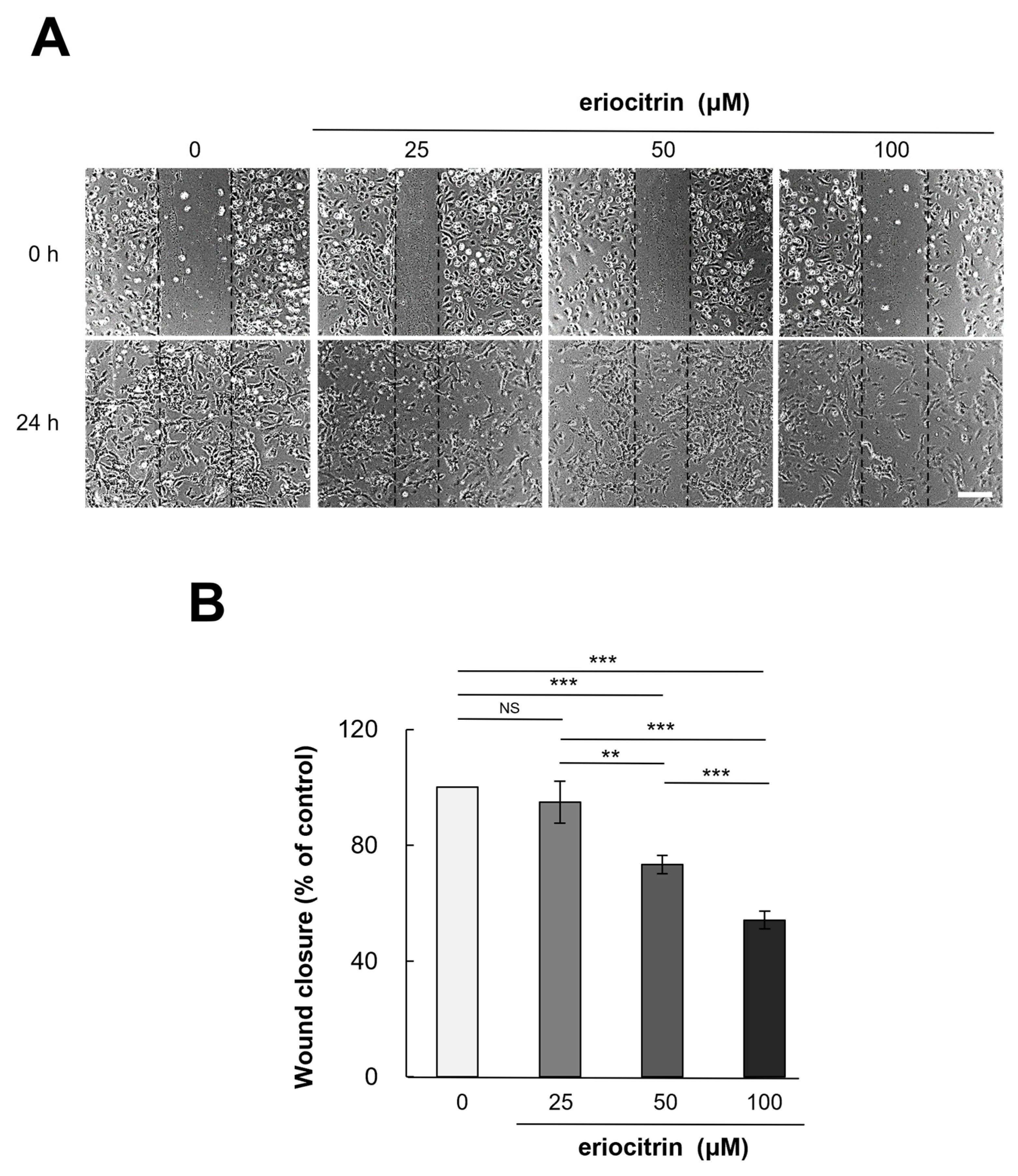
2.6. Migration Assay
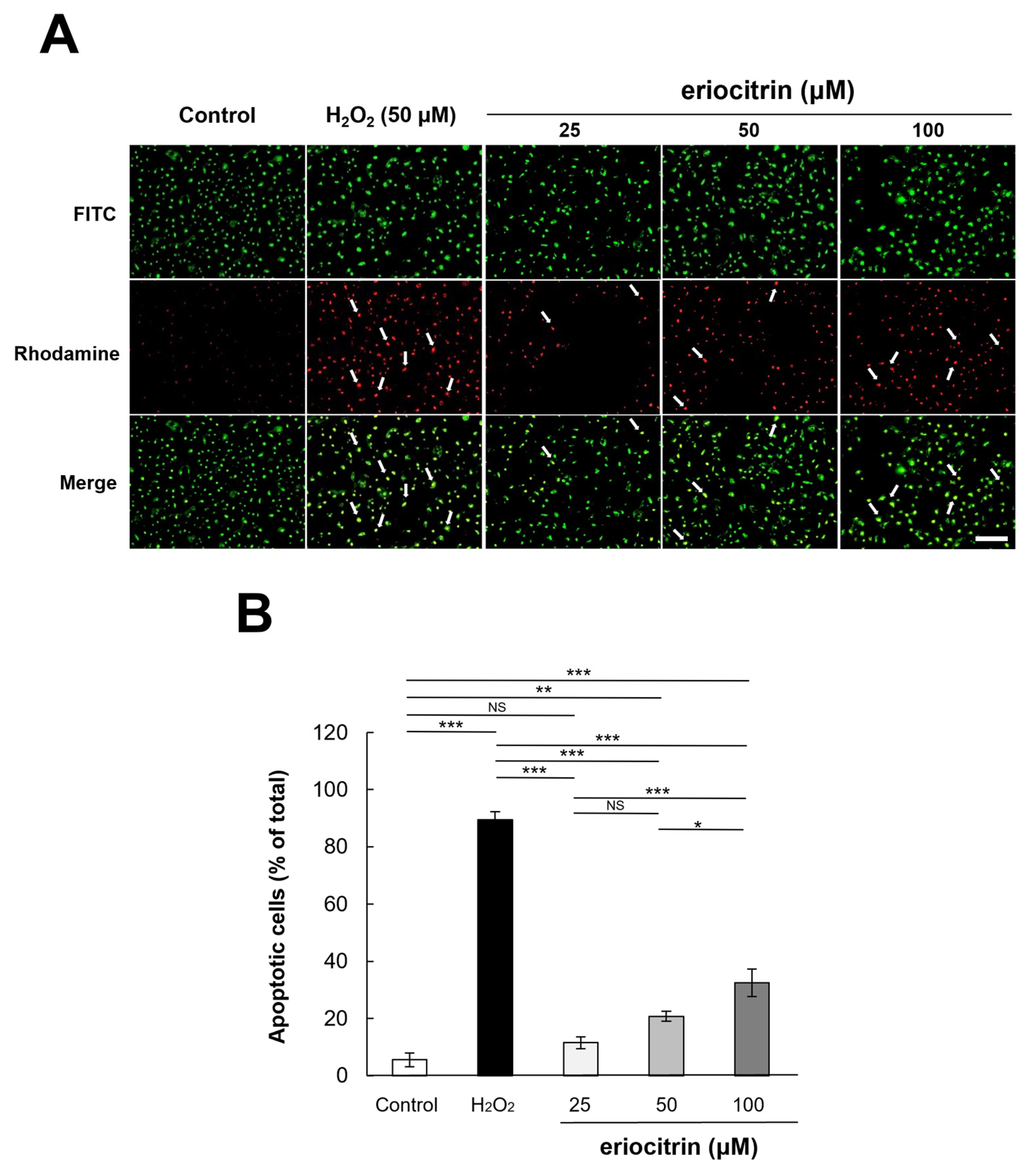
2.7. Apoptosis
2.8. AO/EB Staining
2.9. TUNEL Assay
2.10. Chick Embryo Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay
2.11. Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Eriocitrin on Proliferation
3.2. Effect of Eriocitrin on In Vitro Angiogenesis
3.3. Effect of Eriocitrin on Migration
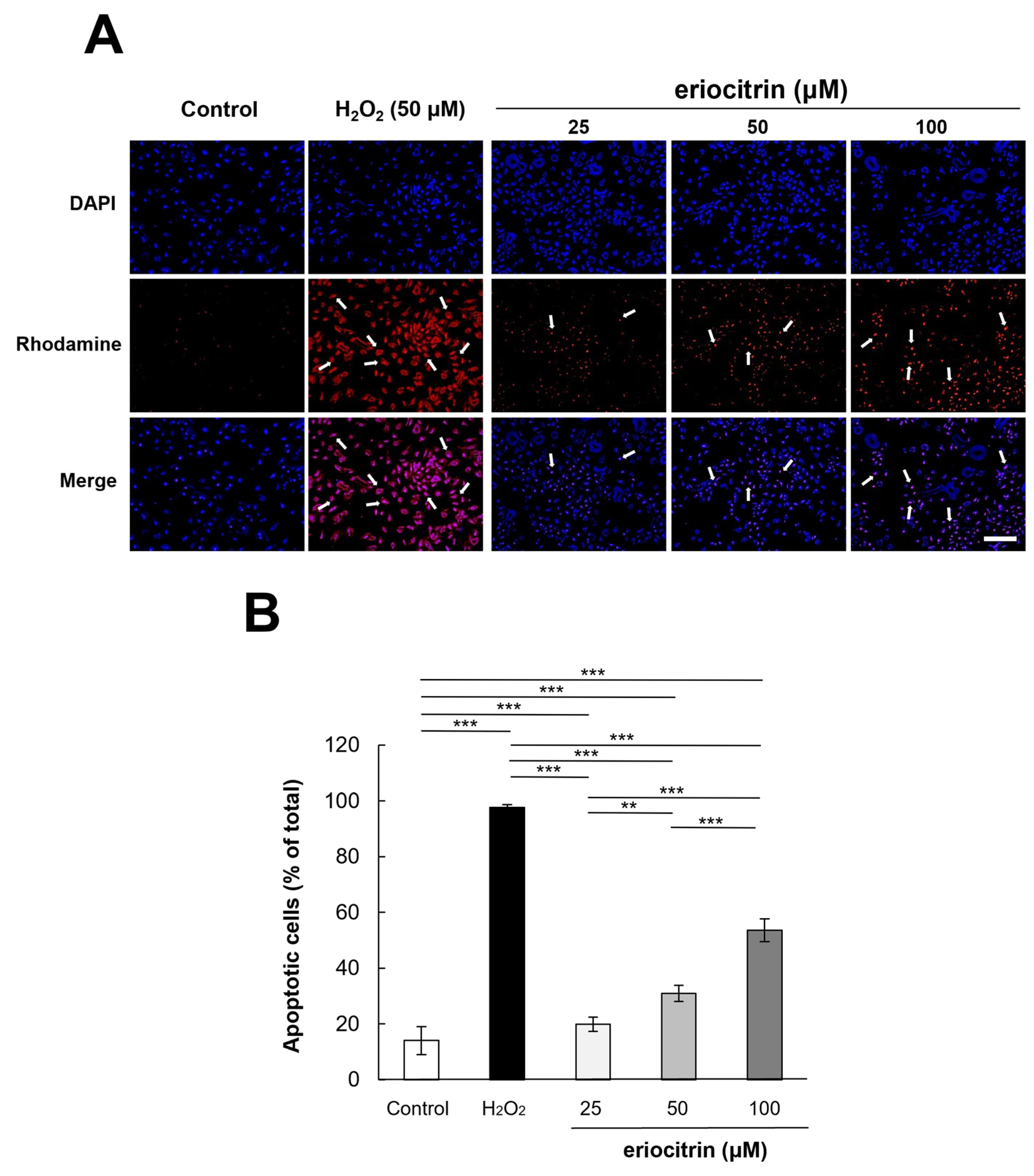
3.4. Analysis of Apoptosis by Annexin V/PI Staining
3.5. Analysis of Apoptosis by AO/EB Staining
3.6. Analysis of Apoptosis by TUNEL Staining
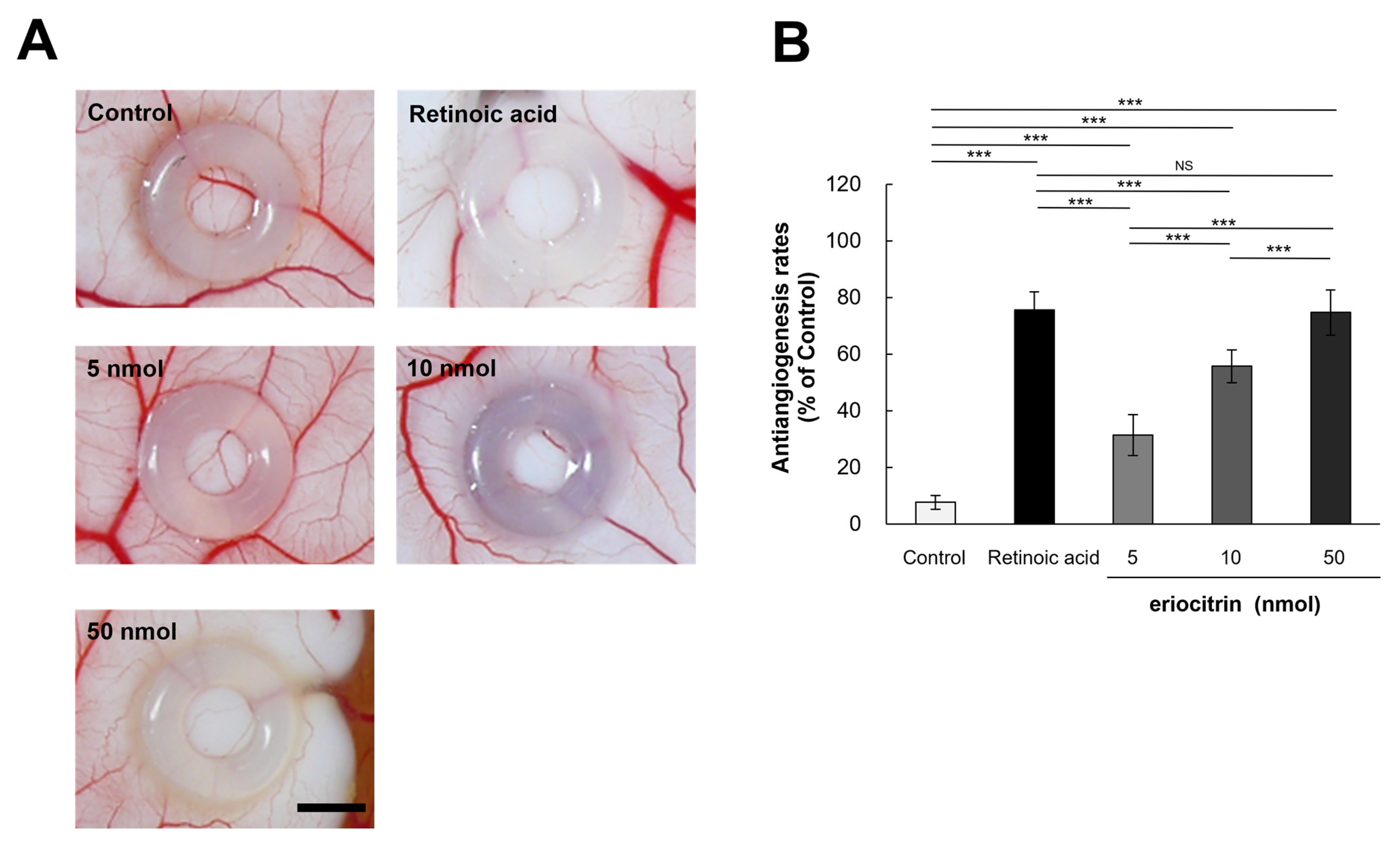
3.7. Inhibitory Effect of Eriocitrin on Angiogenesis in CAM
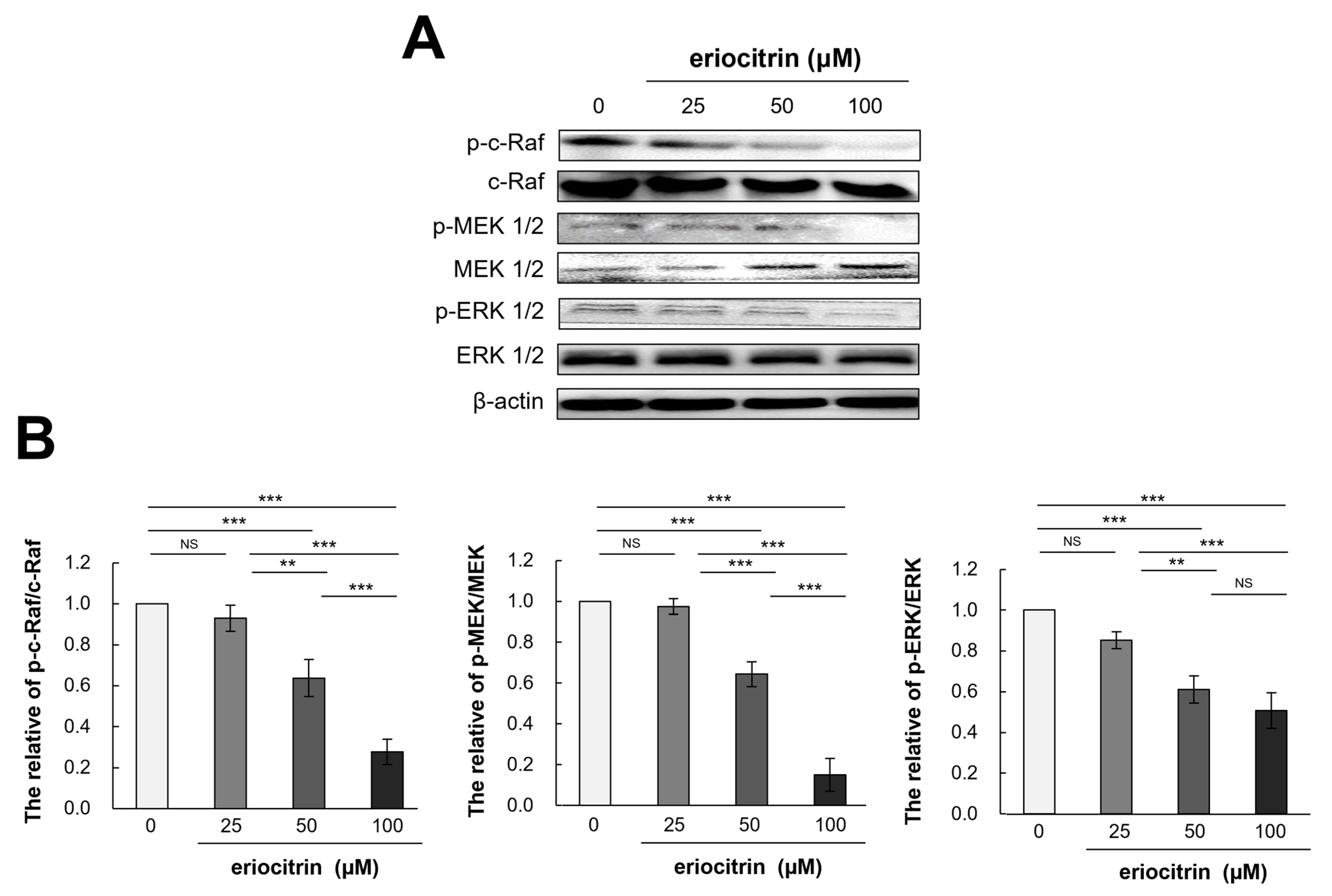
3.8. Effects of Eriocitrin on Raf/MEK/ERK Pathways
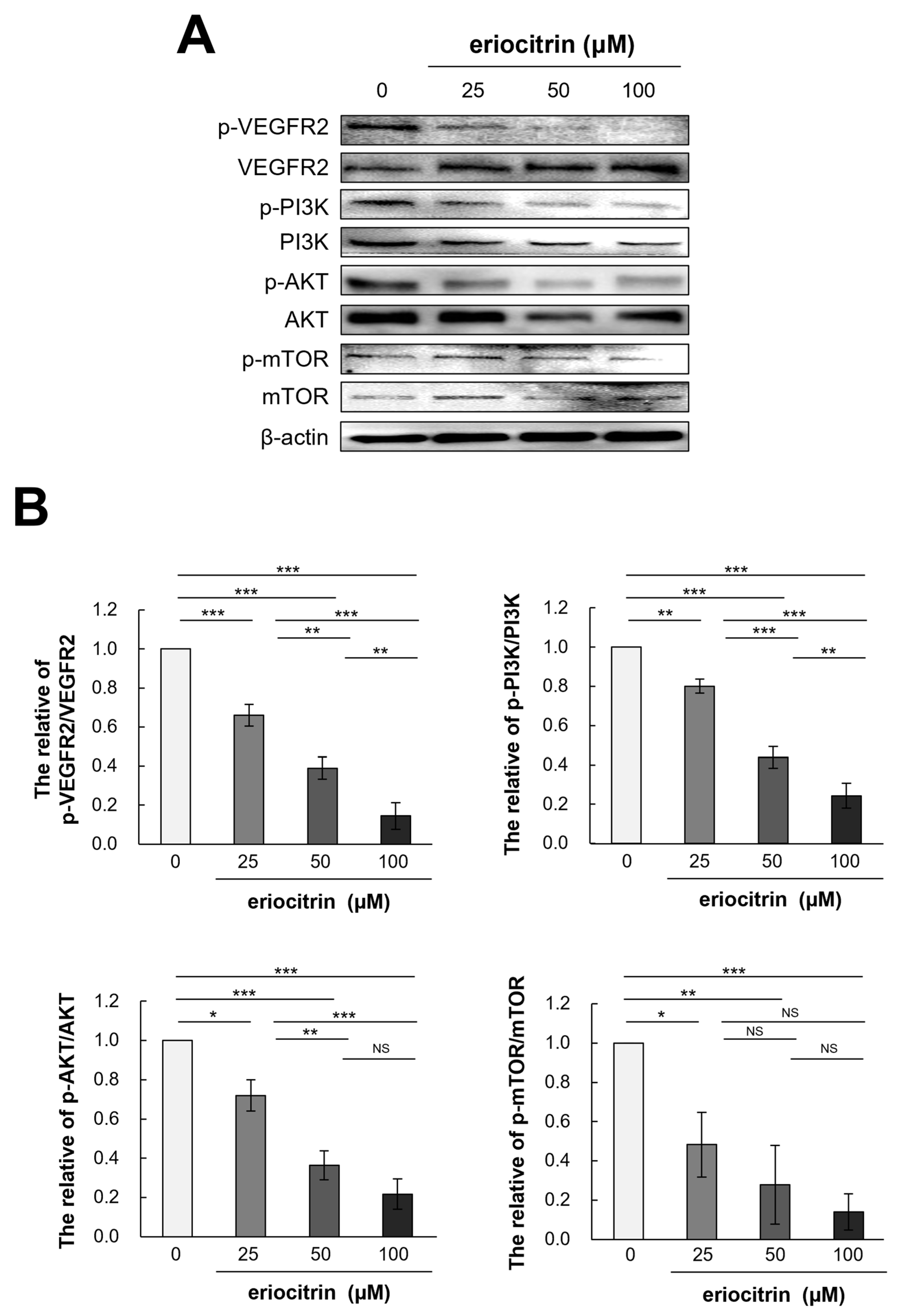
3.9. Effects of Eriocitrin on VEGFR2-Mediated Downstream Signaling Pathways
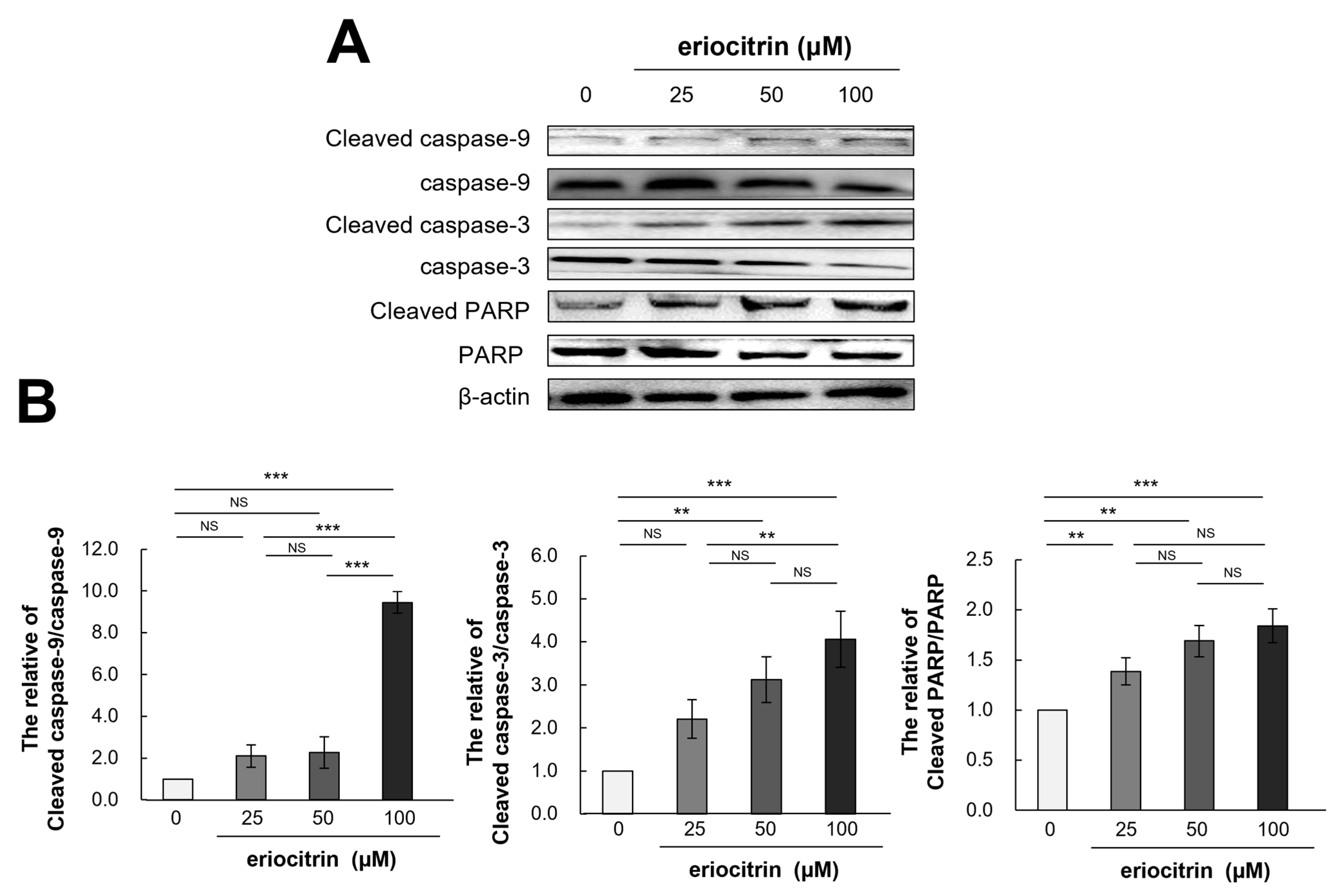
3.10. Effects of Eriocitrin on Caspase Pathways
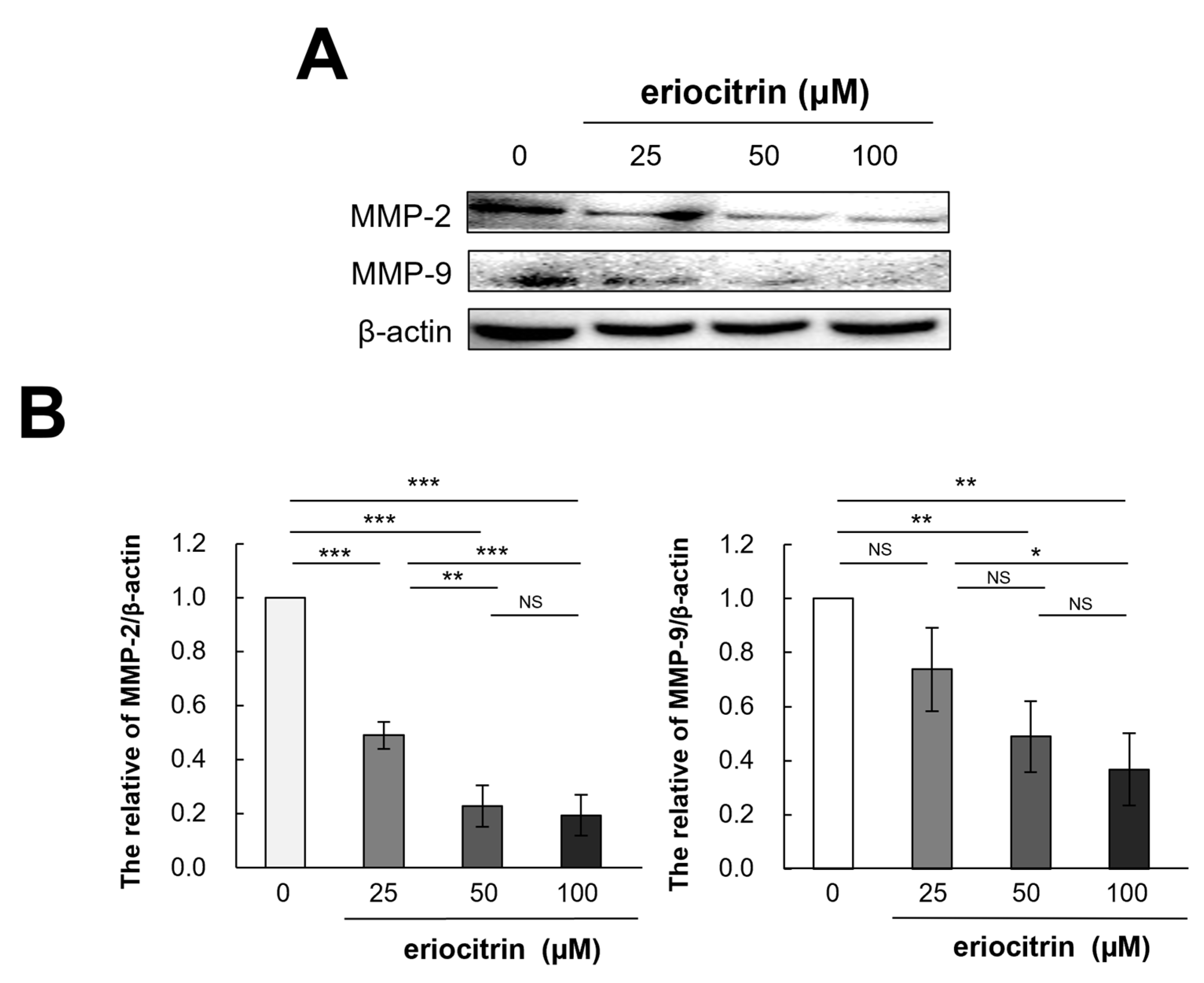
3.11. Effects of Eriocitrin on MMP-2 and MMP-9 Protein Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, K.; Liu, C.F.; Rao, G.W. Anti-angiogenic agents: A review on vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 2540–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risau, W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 1997, 386, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Bove, A.M.; Simone, G.; Ma, B. Molecular bases of VEGFR-2-mediated physiological function and pathological role. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 599281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Kempf, R.C.; Long, J.; Laidler, P.; Mijatovic, S.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D.; Stivala, F.; Mazzarino, M.C.; et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth and sensitivity to therapy-implications for cancer and aging. Aging 2011, 3, 192–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis and apoptosis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2003, 13, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sroka, Z.; Fecka, I.; Cisowski, W. Antiradical and anti-H2O2 properties of polyphenolic compounds from an aqueous peppermint extract. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2005, 60, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minato, K.; Miyake, Y.; Fukumoto, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kato, Y.; Shimomura, Y.; Osawa, T. Lemon flavonoid, eriocitrin, suppresses exercise-induced oxidative damage in rat liver. Life Sci. 2003, 72, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannan, H.; Ghazaleh, M.; Seyed, M.; Naficeh, M.; Mohammad, R.O.; Behrooz, J. Total antioxidant activity, and hesperidin, diosmin, eriocitrin and quercetin contents of various lemon juices. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 951–956. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Lai, K.; Deng, Y.; Lu, Z.; Song, C.; Wang, W.; Xu, C.; Li, N.; Geng, Q. Eriocitrin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) in lung adenocarcinoma cells via triggering ferroptosis. Aging 2023, 15, 10089–10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Martin, R.C. Herbal medicine and hepatocellular carcinoma: Applications and challenges. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 541209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Xia, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, J. Multispectroscopic exploration and molecular docking analysis on interaction of eriocitrin with bovine serum albumin. J. Mol. Recognit. 2019, 32, e2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Hao, Y.; Liang, X.; Qiu, G.; Xue, W. Eriocitrin alleviates the arterial occlusion-mediated cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury through the modulation of apoptotic proteins and immune markers in mice. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2021, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, P.S.; Spolidorio, L.C.; Manthey, J.A.; Cesar, T.B. Citrus flavanones prevent systemic inflammation and ameliorate oxidative stress in C57BL/6J mice fed high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2675–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Liu, W.; Bashir, M.; Nisar, M.F.; Wan, C.C. Eriocitrin: A review of pharmacological effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Chen, G.; Jing, C.; Liu, M.; Liang, B.; Gong, G.; Yu, M. Eriocitrin, a dietary flavonoid suppressed cell proliferation, induced apoptosis through modulation of JAK2/STAT3 and JNK/p38 MAPKs signaling pathway in MCF-7 cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e22943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.R.; Kunimasa, K.; Ohta, T.; Kumazawa, S.; Kamihira, M.; Kaji, K.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H.; Nagasawa, H.; Nakayama, T. Suppression of tumor-induced angiogenesis by Brazilian propolis: Major component artepillin C inhibits in vitro tube formation and endothelial cell proliferation. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Wang, G.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Gong, Z. Antiangiogenic effects of AA-PMe on HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish in vivo. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Ohta, T.; Kumazawa, S.; Jun, M.; Ahn, M.R. Korean propolis suppresses angiogenesis through inhibition of tube formation and endothelial cell proliferation. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, T.; Eguchi, R.; Suzuki, A.; Miyakaze, S.; Ayuzawa, R.; Kaji, K. Hypoxia-inducedapoptosis and tube breakdown are regulated by p38 MAPK but not by caspase cascade in an in vitro capillary model composed of human endothelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 211, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.R.; Kunimasa, K.; Kumazawa, S.; Nakayama, T.; Kaji, K.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H.; Nagasawa, H.; Ohta, T. Correlation between antiangiogenic activity and antioxidant activity of various components from propolis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.L.; Chen, H.H.; Zheng, L.L.; Sun, L.P.; Shi, L. Angiogenic signaling pathways and anti-angiogenic therapy for cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liskova, A.; Koklesova, L.; Samec, M.; Varghese, E.; Abotaleb, M.; Samuel, S.M.; Smejkal, K.; Biringer, K.; Petras, M.; Blahutova, D.; et al. Implications of flavonoids as potential modulators of cancer neovascularity. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 3079–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motallebi, M.; Bhia, M.; Rajani, H.F.; Bhia, I.; Tabarraei, H.; Mohammadkhani, N.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Kasaii, M.S.; Nouri-Majd, S.; Mueller, A.L.; et al. Naringenin: A potential flavonoid phytochemical for cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2022, 305, 120752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.; Tuli, H.S.; Thakral, F.; Singhal, P.; Aggarwal, D.; Srivastava, S.; Pandey, A.; Sak, K.; Varol, M.; Khan, A.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of action of hesperidin in cancer: Recent trends and advancements. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, K.; Huang, Z. Eriocitrin from lemon suppresses the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inducing apoptosis and arresting cell cycle. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavria, G.; Vercoulen, Y.; Yeo, M.; Paterson, H.; Karasarides, M.; Marais, R.; Bird, D.; Marshall, C.J. ERK-MAPK signaling opposes Rho-kinase to promote endothelial cell survival and sprouting during angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006, 9, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ji, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, J.; Cai, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, Q. Norcantharidin inhibits tumor angiogenesis via blocking VEGFR2/MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.D.; Cheong, O.J.; Bae, S.Y.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.K. 6″-Debromohamacanthin A, a bis (indole) alkaloid, inhibits angiogenesis by targeting the VEGFR2-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, O.; Wells, J.A. Caspases and their substrates. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niland, S.; Riscanevo, A.X.; Eble, J.A. Matrix metalloproteinases shape the tumor microenvironment in cancer progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, A.H.; Gao, B.T.; Goldsmith, Z.K.; Irvine, A.S.; Saleh, N.; Lee, R.P.; Lendermon, J.B.; Bheemreddy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Brennan, R.C.; et al. Inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 decreases cellular migration, and angiogenesis in in vitro models of retinoblastoma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, J.-Y.; Kwak, J.-E.; Ahn, M.-R. Eriocitrin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071091
Baek J-Y, Kwak J-E, Ahn M-R. Eriocitrin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071091
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Ji-Yoon, Jeong-Eun Kwak, and Mok-Ryeon Ahn. 2024. "Eriocitrin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071091
APA StyleBaek, J.-Y., Kwak, J.-E., & Ahn, M.-R. (2024). Eriocitrin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Targeting VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Nutrients, 16(7), 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071091





