Use of Muscle Ultrasonography in Morphofunctional Assessment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Study Subjects
2.3. Variables
- -
- Anthropometric variables: usual weight (kg), actual weight (kg), height (m), body mass index (actual weight/height x height (kg/m2)), arm circumference (cm), and calf circumference (cm).
- -
- Electrical bioimpedanciometry (BIA) was performed with a bioimpedanciometer (BIA 101 Anniversary; EFG Akern). The BIA was performed between 8:00 and 9:15, after an overnight fast and after a time of 15 min in the supine position. The BIA measured the following raw electrical data: resistance (ohm), reactance (ohm), and phase angle (º). The following body composition parameters were estimated using validated formulas in Bodygram® software, https://www.akern.com/en/products-and-solutions/data-analysis-software/bodygram-dashboard/ (Access data: 29 March 2024) (EFG, Akern, Pisa, Italy): fat mass index (FMI) (kg/m2), fat-free mass index (FFMI) (kg/m2), muscle mass index (MMI) (kg/m2), and body cell mass index (BCMI) (kg/m2). Appendicular skeletal muscle mass index (ASMI) (kg/m2) was measured by Sergi’s formula [10].
- -
- Muscle ultrasonography (quadriceps rectus femoris (QRF) and vastus intermedius (VI)) of the dominant lower extremity was carried out with a 10–12 MHz probe and a multifrequency linear matrix (Mindray Z60, Madrid, Spain). The measurements of ultrasonography were made with the patient in a supine position [8]. The following muscle quantity parameters were measured: muscle area (cm2), muscle area index (muscle area/height × height) (cm2/m2), anteroposterior diameter of the QRF (Y-axis) (cm), transverse diameter of the QRF (X-axis) (cm), and the sum of the anteroposterior diameters of QRF and the vastus intermedius (RF+VI) (cm) [11].
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Description
3.2. Malnutrition and Ultrasonography in ALS Patients
3.3. Ultrasonography and Other Body Composition Variables in ALS Patients
3.4. Relationship between Morphofunctional Variables and Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grad, L.I.; Rouleau, G.A.; Ravits, J.; Cashman, N.R. Clinical Spectrum of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a024117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, D.I. Nutrition management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 28, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, J.J.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Torres-Torres, B.; De la Maza, B.P.; Penacho-Lázaro, M.Á.; Palacio-Mures, J.M.; Abreu-Padín, C.; López-Guzmán, A.; De Luis-Román, D.A. Malnutrition at diagnosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (als) and its influence on survival: Using glim criteria. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2020, 40, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellogg, J.; Bottman, L.; Arra, E.J.; Selkirk, S.M.; Kozlowski, F. Nutrition management methods effective in increasing weight, survival time and functional status in ALS patients: A systematic review. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2018, 19, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, R.; Bretón, I.; Cereda, E.; Desport, J.C.; Dziewas, R.; Genton, L.; Gomes, F.; Jésus, P.; Leischker, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; et al. ESPEN guideline clinical nutrition in neurology. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2018, 37, 354–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, O.C.; de Oliveira, C.E.P.; Candia-Luján, R.; Romero-Pérez, E.M.; de Paz Fernandez, J.A. Methods of evaluation of muscle mass: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Almeida, J.M.; García García, C.; Vegas Aguilar, I.M.; Bellido Castañeda, V.; Bellido Guerrero, D. Morphofunctional assessment of patient’s nutritional status: A global approach. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Almeida, J.M.; García-García, C.; Vegas-Aguilar, I.M.; Pomar, M.D.B.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.M.; Medina, B.F.; Román, D.A.d.L.; Guerrero, D.B.; Lesmes, I.B.; Madueño, F.J.T. Nutritional ultrasound®: Conceptualisation, technical considerations and standardisation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2022, 70, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Almeida, J.M.; García-García, C.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Olveira, G.; Lopez-Gomez, J.J.; Bellido, V.; Lesmes, I.B.; Burgos, R.; Sanz-Paris, A.; Matia-Martin, P.; et al. Expert Consensus on Morphofunctional Assessment in Disease-Related Malnutrition. Grade Review and Delphi Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, G.; De Rui, M.; Veronese, N.; Bolzetta, F.; Berton, L.; Carraro, S.; Bano, G.; Coin, A.; Manzato, E.; Perissinotto, E. Assessing appendicular skeletal muscle mass with bioelectrical impedance analysis in free-living Caucasian older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, J.J.; García-Beneitez, D.; Jiménez-Sahagún, R.; Izaola-Jauregui, O.; Primo-Martín, D.; Ramos-Bachiller, B.; Gómez-Hoyos, E.; Delgado-García, E.; Pérez-López, P.; De Luis-Román, D.A. Nutritional Ultrasonography, a Method to Evaluate Muscle Mass and Quality in Morphofunctional Assessment of Disease Related Malnutrition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.J.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasarskis, E.J.; Mendiondo, M.S.; Matthews, D.E.; Mitsumoto, H.; Tandan, R.; Simmons, Z.; Bromberg, M.B.; Kryscio, R.J. Estimating daily energy expenditure in individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-Y.; Sun, X.-H.; Cai, Z.-Y.; Shen, D.-C.; Yang, X.-Z.; Liu, M.-S.; Cui, L.-Y. Correlation of weight and body composition with disease progression rate in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gómez, J.J.; Torres-Torres, B.; Gómez-Hoyos, E.; Fernández-Buey, N.; Ortolá-Buigues, A.; Castro-Lozano, Á.; Arenillas-Lara, J.F.; De Luis-Román, D.A. Influence of a multidisciplinary protocol on nutritional status at diagnosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nutrition 2018, 48, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heritier, A.-C.; Janssens, J.-P.; Adler, D.; Ferfoglia, R.I.; Genton, L. Should patients with ALS gain weight during their follow-up? Nutrition 2015, 31, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiello, R.; Amaral, M.A.; Mundstock, E.; Ziegelmann, P.K. Reference values for the phase angle of the electrical bioimpedance: Systematic review and meta-analysis involving more than 250,000 subjects. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubeau, V.; Blasco, H.; Maillot, F.; Corcia, P.; Praline, J. Nutritional assessment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in routine practice: Value of weighing and bioelectrical impedance analysis. Muscle Nerve 2015, 51, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, R.M.; Syddall, H.E.; Cooper, R.; Benzeval, M.; Deary, I.J.; Dennison, E.M.; Der, G.; Gale, C.R.; Inskip, H.M.; Jagger, C.; et al. Grip strength across the life course: Normative data from twelve British studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musarò, A.; Dobrowolny, G.; Cambieri, C.; Onesti, E.; Ceccanti, M.; Frasca, V.; Pisano, A.; Cerbelli, B.; Lepore, E.; Ruffolo, G.; et al. Neuromuscular magnetic stimulation counteracts muscle decline in ALS patients: Results of a randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Paris, A.; González-Fernandez, M.; Río, L.E.H.-D.; Ferrer-Lahuerta, E.; Monge-Vazquez, A.; Losfablos-Callau, F.; Sanclemente-Hernández, T.; Sanz-Arque, A.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M. Muscle Thickness and Echogenicity Measured by Ultrasound Could Detect Local Sarcopenia and Malnutrition in Older Patients Hospitalized for Hip Fracture. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokura, Y.; Nishioka, S. Nutritional Risk Indicators for Predicting a Change in Quadriceps Muscle Thickness in Acute Patients with Stroke. JMA J. 2022, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Leo, A.D.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E. Malnutrition assessment by Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nutrition 2023, 109, 111997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandan, R.; Levy, E.A.; Howard, D.B.; Hiser, J.; Kokinda, N.; Dey, S.; Kasarskis, E.J. Body composition in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis subjects and its effect on disease progression and survival. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Yoon, S.H.; Sung, J.-J.; Lee, J.H. Association between Fat Depletion and Prognosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: CT-Based Body Composition Analysis. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 94, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Kazamel, M.; McPherson, T.; McAdam, J.; Bamman, M.; Amara, A.; Smith, D.L.; King, P.H. Fat mass loss correlates with faster disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients: Exploring the utility of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in a prospective study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e025108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvioni, C.; Oda, A.L.; Orsini, M.; Pauli, M.; Frabasile, L.M.; Alves, P.C.L.; Borges, R.M.; Sierra, H.N.M.; Menegatti, G.; Pinho, M.O.; et al. Association between Body Composition and Dysphagia in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurol. Int. 2021, 13, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vito, E.L.; Monteiro, S.G.; Arce, S.C. Compartmental nutritional status and respiratory muscle function assessment in subjects with neuromuscular diseases. Medicina 2022, 82, 200–209. [Google Scholar]
| Total | Men | Women | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometry | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.52 (4.51) | 27.46 (4.54) | 25.45 (4.37) | 0.20 |
| %weight loss | 5.29 (6.07) | 4.74 (4.70) | 6.06 (7.76) | 0.59 |
| Arm circumference (cm) | 27.09 (2.27) | 27.58 (2.11) | 26.56 (2.37) | 0.20 |
| Calf circumference (cm) | 34.08 (3.91) | 34.53 (4.08) | 33.59 (3.78) | 0.49 |
| Bioelectrical Impedanciometry | ||||
| Resistance (ohm) | 575.24 (112.07) | 508.33 (64.33) | 655.53 (104.98) | <0.01 |
| Reactance (ohm) | 50.64 (15.41) | 44.06 (10.57) | 58.53 (16.88) | <0.01 |
| Phase angle (°) | 5.13 (1.50) | 5.02 (1.25) | 5.26 (1.79) | 0.66 |
| ASMM (kg) | 17.57 (4.00) | 20.48 (2.42) | 14.07 (2.36) | <0.01 |
| ASMI (kg/m2) | 6.53 (1.03) | 7.12 (0.74) | 5.82 (0.89) | <0.01 |
| FFM (kg) | 46.99 (10.07) | 54.48 (6.75) | 38.01 (4.23) | <0.01 |
| FFMI (kg/m2) | 17.45 (2.15) | 18.89 (1.57) | 15.72 (1.33) | <0.01 |
| BCM (kg) | 22.82 (6.99) | 26.31 (6.41) | 18.62 (5.24) | <0.01 |
| BCMI (kg/m2) | 7.97 (2.08) | 8.56 (1.91) | 7.27 (2.12) | 0.08 |
| FM (kg) | 22.09 (8.26) | 21.63 (7.61) | 22.65 (9.21) | 0.73 |
| FMI (kg/m2) | 8.38 (3.25) | 7.61 (3.00) | 9.31 (3.40) | 0.14 |
| Muscle Ultrasonography | ||||
| MARFI (cm2/m2) | 1.29 (0.51) | 1.44 (0.57) | 1.14 (0.41) | 0.09 |
| Y-axis (cm) | 1.17 (0.35) | 1.29 (0.38) | 1.03 (0.25) | 0.03 |
| X-axis (cm) | 3.27 (0.63) | 3.47 (0.59) | 3.05 (0.61) | 0.06 |
| RF+VI (cm) | 2.18 (0.68) | 2.49 (0.66) | 1.84 (0.54) | <0.01 |
| SCAT (cm) | 1.07 (0.72) | 0.59 (0.31) | 1.37 (0.41) | <0.01 |
| Y–X index | 0.36 (0.09) | 0.37 (0.10) | 0.34 (0.09) | 0.41 |
| Echogenicity (%) | 61.77 (4.63) | 61.67 (4.49) | 61.86 (4.29) | 0.91 |
| MUSCLE STRENGTH | ||||
| Handgrip strength (kg) | 14.54 (9.67) | 16.81 | 11.50 | 0.15 |
| Malnutrition | No Malnutrition | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 52.9%/47.1% | 56.3%43.8% | 0.72 |
| MARFI (cm2/m2) | 1.13 (0.49) | 1.46 (0.52) | 0.08 |
| Y-axis (cm) | 0.99 (0.32) | 1.37 (0.27) | <0.01 |
| X-axis (cm) | 3.24 (0.68) | 3.33 (0.60) | 0.69 |
| RF+VI (cm) | 1.81 (0.64) | 2.61 (0.46) | <0.01 |
| SCAT (cm) | 0.95 (0.45) | 0.94 (0.63) | 0.96 |
| Y–X index | 0.30 (0.06) | 0.42 (0.09) | <0.01 |
| Echogenicity (%) | 62.94 (4.87) | 60.43 (4.29) | 0.17 |
| RF+VI | MARFI | Echogenicity | Y–X Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| %WL | r = −0.42; p = 0.04 * | r = −0.15; p = 0.47 | r = 0.04; p = 0.85 | r = −0.37; p = 0.07 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | r = 0.33; p = 0.06 | r = 0.05; p = 0.78 | r = −0.04; p = 0.83 | r = 0.40; p = 0.02 * |
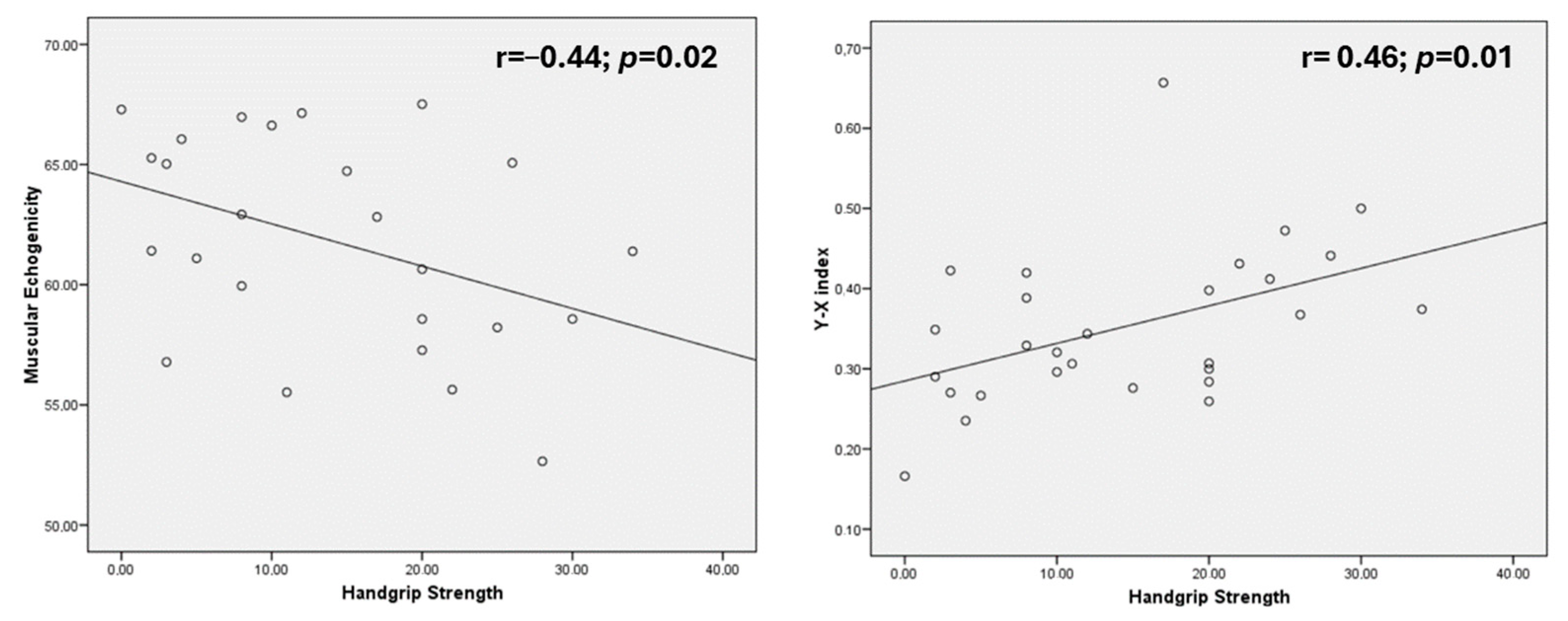
| Braquial circumference (cm) | r = 0.34; p = 0.06 | r = 0.17; p = 0.36 | r = −0.43; p = 0.02 * | r = 0.37; p = 0.04 * |
| Calf circumference (cm) | r = 0.34; p = 0.06 | r = 0.26; p = 0.14 | r = −0.27; p = 0.16 | r = 0.18; p = 0.33 |
| RF+VI | SCAT | MARFI | Echogenicity | Y–X Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance (ohm) | r = −0.59; p < 0.01 * | r = 0.59; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.5; p < 0.01 * | r = 0.44; p = 0.02 * | r = −0.19; p = 0.28 |
| Reactance (ohm) | r = −0.06; p = 0.72 | r = 0.42; p = 0.02 * | r = 0.24; p = 0.19 | r = −0.07; p = 0.72 | r = −0.05; p = 0.76 |
| Phase angle (°) | r = 0.28; p = 0.11 | r = 0.04; p = 0.83 | r = 0.54; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.30; p = 0.10 | r = 0.07; p = 0.71 |
| BCMI (kg/m2) | r = 0.62; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.26; p = 0.16 | r = 0.64; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.46; p < 0.01 * | r = 0.27; p = 0.14 |
| FFMI (kg/m2) | r = 0.75; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.53; p < 0.01 * | r = 0.52; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.38; p = 0.04 * | r = 0.36; p < 0.01 * |
| FMI (kg/m2) | r = −0.04; p = 0.83 | r = 0.59; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.17; p = 0.34 | r = 0.25; p = 0.19 | r = 0.26; p = 0.15 |
| ASMI (kg/m2) | r = 0.69; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.42; p = 0.02 * | r = 0.58; p < 0.01 * | r = −0.40; p = 0.03 * | R = 0.34; p = 0.06 |
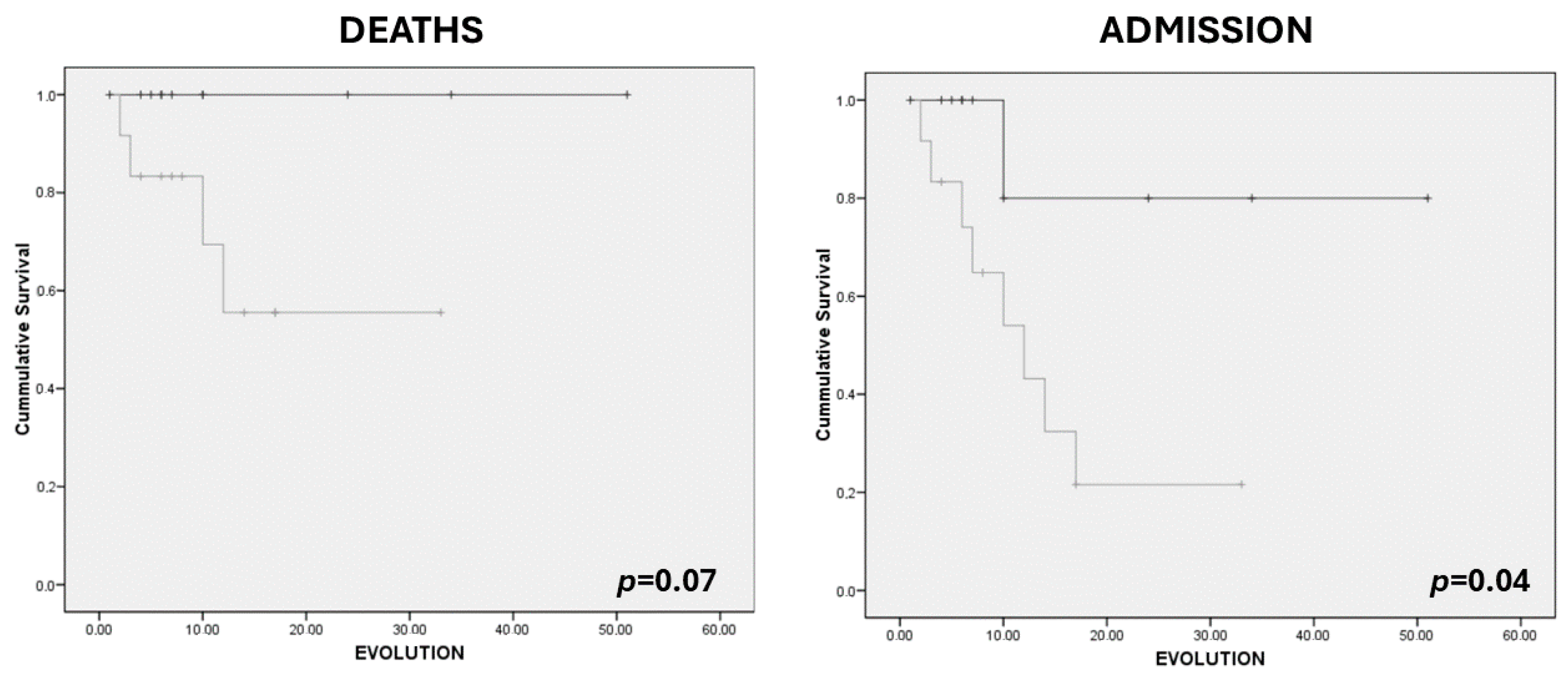
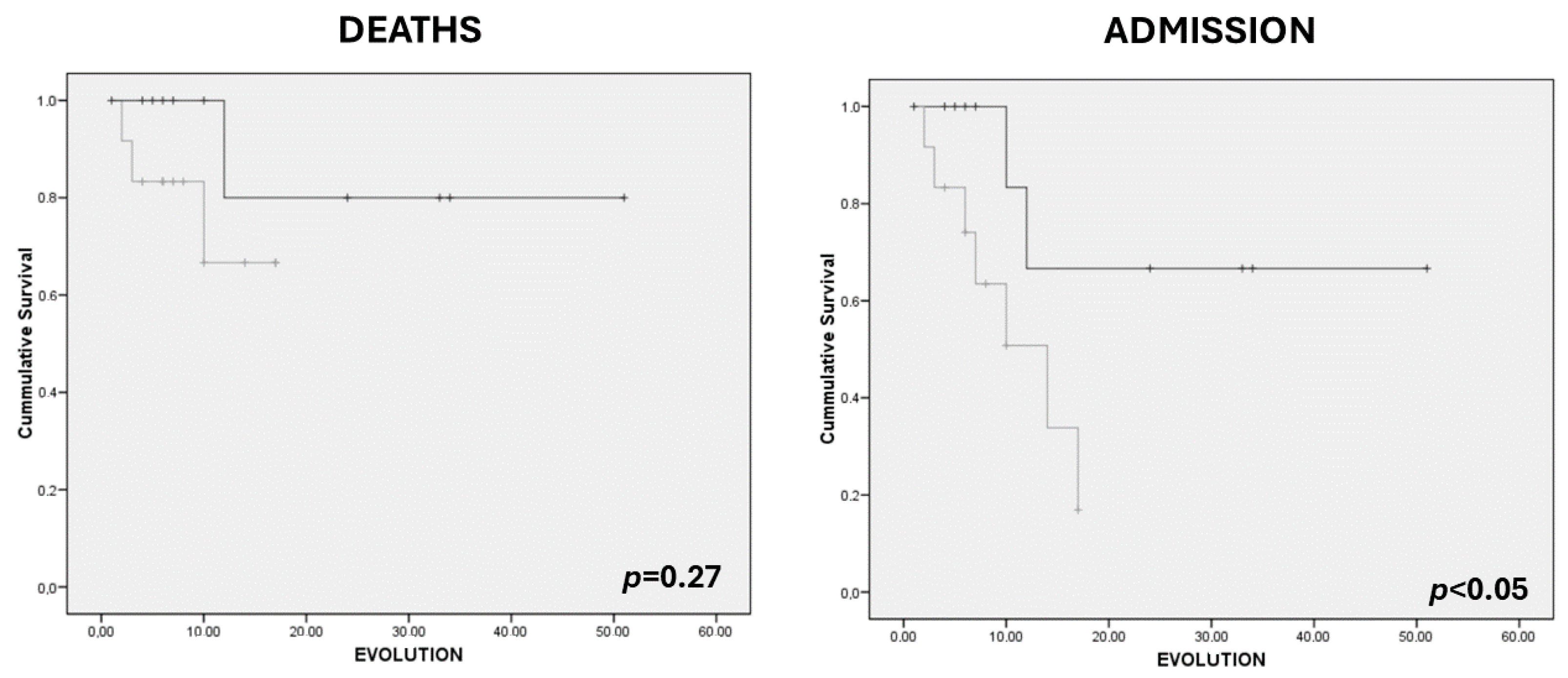
| Death | No Death | p-Value | Admission | No Admission | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (M/F) | 5.3/16.7 | 94.7/83.3 | 0.34 | 21.1/38.9 | 78.9/61.1 | 0.29 |
| Nutritional Ultrasonography | ||||||
| MARFI (cm2/m2) | 1.28 (0.27) | 1.29 (0.54) | 0.97 | 1.07 (0.46) | 1.40 (0.52) | 0.08 |
| Y-axis (cm) | 1.03 (0.22) | 1.19 (0.36) | 0.39 | 0.95 (0.28) | 1.27 (0.33) | 0.01 |
| X-axis (cm) | 3.44 (0.36) | 3.25 (0.66) | 0.57 | 3.31 (0.61) | 3.26 (0.65) | 0.83 |
| RF+VI (cm) | 1.66 (0.30) | 2.26 (0.69) | 0.09 | 1.65 (0.44) | 2.42 (0.64) | <0.01 |
| SCAT (cm) | 0.97 (0.54) | 0.96 (0.54) | 0.97 | 1.01 (0.43) | 0.94 (0.57) | 0.71 |
| Y–X index | 0.29 (0.06) | 0.37 (0.10) | 0.19 | 0.28 (0.06) | 0.39 (0.09) | <0.01 |
| Echogenicity (%) | 66.92 (3.03) | 61.28 (5.26) | <0.05 | 64.90 (4.05) | 60.59 (5.43) | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Gómez, J.J.; Izaola-Jauregui, O.; Almansa-Ruiz, L.; Jiménez-Sahagún, R.; Primo-Martín, D.; Pedraza-Hueso, M.I.; Ramos-Bachiller, B.; González-Gutiérrez, J.; De Luis-Román, D. Use of Muscle Ultrasonography in Morphofunctional Assessment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Nutrients 2024, 16, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071021
López-Gómez JJ, Izaola-Jauregui O, Almansa-Ruiz L, Jiménez-Sahagún R, Primo-Martín D, Pedraza-Hueso MI, Ramos-Bachiller B, González-Gutiérrez J, De Luis-Román D. Use of Muscle Ultrasonography in Morphofunctional Assessment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071021
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Gómez, Juan J., Olatz Izaola-Jauregui, Laura Almansa-Ruiz, Rebeca Jiménez-Sahagún, David Primo-Martín, María I. Pedraza-Hueso, Beatriz Ramos-Bachiller, Jaime González-Gutiérrez, and Daniel De Luis-Román. 2024. "Use of Muscle Ultrasonography in Morphofunctional Assessment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071021
APA StyleLópez-Gómez, J. J., Izaola-Jauregui, O., Almansa-Ruiz, L., Jiménez-Sahagún, R., Primo-Martín, D., Pedraza-Hueso, M. I., Ramos-Bachiller, B., González-Gutiérrez, J., & De Luis-Román, D. (2024). Use of Muscle Ultrasonography in Morphofunctional Assessment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Nutrients, 16(7), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071021







