Study on the Dose–Response Relationship between Magnesium and Type 2 Diabetes of Childbearing Women in the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance 2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Basic Information and Sample Collection
2.3. Plasma Mg and Laboratory Index Detection
2.4. Evaluation Standards of Glucose Parameters
2.5. Calculation and Quality Control of Dietary Magnesium
2.6. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Magnesium Distribution of 2912 Childbearing Women
3.2. The Basic Characteristic of 2912 Subjects
3.3. The Associations of Plasma Magnesium Concentration with Glucose Parameters
3.4. The Dose–Response Relationship between Plasma Mg and the Risk of T2DM
3.5. Daily Dietary Nutrient Intake of the Subjects
3.6. The Associations of Dietary Magnesium Concentration with Glucose Parameters
3.7. The Dose–Response Relationship between Dietary Mg and the Risk of T2DM
3.8. Consistency Analysis of Dose–Response Effect of Dietary Magnesium and Plasma Magnesium on Glucose Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altura, B.M. Basic Biochemistry and Physiology of Magnesium: A Brief Review. Magnes. Trace Elem. 1991, 10, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M. Magnesium in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Veronese, N.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium in Aging, Health and Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckett, A.G.; Lewis, J.G. Serum Magnesium in Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Sci. 1959, 18, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pham, P.C.T.; Pham, P.M.T.; Pham, S.V.; Miller, J.M.; Pham, P.T.T. Hypomagnesemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Valk, H.W. Magnesium in Diabetes Mellitus. Neth. J. Med. 1999, 54, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Magnesium Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 262, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gommers, L.M.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M.; De Baaij, J.H.F. Hypomagnesemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Vicious Circle? Diabetes 2016, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, V.; Maia, I.; Neves, J.S.; Salazar, D.; Ferreira, M.J.; Mendonça, F.; Silva, M.M.; Viana, S.; Costa, C.; Pedro, J.; et al. Adequate Magnesium Level as an Associated Factor of Pre-Diabetes and Diabetes Mellitus Remission in Patients with Obesity Submitted to Bariatric Surgery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F.; Liou, H.H.; Kuo, C.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Lin, T.M.; Hung, S.Y. The Association of Urinary Sclerostin and Renal Magnesium Handling in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2021, 46, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zou, F.; Gan, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W. Association of Magnesium Intake with Type 2 Diabetes and Total Stroke: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e032240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadler, J.L. A New Dietary Approach to Reduce the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Fang, H.; Guo, Q.; Xu, X.; Ju, L.; et al. China Nutrition and Health Surveys (1982–2017). China CDC Wkly. 2021, 3, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Classification of Diabetes Mellitus; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; He, L.; Zhao, W. Establishment and Application of Food Frequency Questionnaire Method among Chinese. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 2018, 47, 744–748+755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.X. China Food Composition Tables. ACTA Nutr. SINICA 2019, 41, 426. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, W.C.; Howe, G.R.; Kushi, L.H. Adjustment for Total Energy Intake in Epidemiologic Studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1220S–1228S, discussion 1229S–1231S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, H.E.; Wertman, M. Serum Potassium, Magnesium, and Calcium Levels in Diabetic Acidosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1947, 26, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Sharma, R.; Bansal, D.D. Implications of Magnesium Deficiency in Type 2 Diabetes: A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 134, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.H.; Song, I.K.; Ju, S.Y.; Ock, S.M. Serum Magnesium Level Is Negatively Associated with Fasting Serum Glucose Level in Korean Adults. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 143, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.; Joshi, S.; Shaw, J. Hypomagnesaemia Is Associated with Diabetes: Not Pre-Diabetes, Obesity or the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rascón-Pacheco, R.A.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; De La Peña, J.E.; Wacher, N.; Chavez-Negrete, A.; Madero, A.; Salcedo, A.; Medina-Escobedo, C.E.; Revilla-Monsalve, C.; et al. Hypomagnesaemia and Risk for Metabolic Glucose Disorders: A 10-Year Follow-up Study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 38, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zeng, C.; Li, X.X.; Gong, Q.Y.; Lei, G.H.; Yang, T.B. Association among Dietary Magnesium, Serum Magnesium, and Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2016, 35, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinato, J.; Wang, K.C.; Hayward, S. Serum Magnesium Concentrations in the Canadian Population and Associations with Diabetes, Glycemic Regulation, and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2017, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Doi, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Mukai, N.; Hirakawa, Y.; Hata, J.; Ozawa, M.; Uchida, K.; Shirota, T.; Kitazono, T.; et al. Magnesium Intake Decreases Type 2 Diabetes Risk through the Improvement of Insulin Resistance and Inflammation: The Hisayama Study. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jin, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, T.; Xie, M.; Bao, W.; Yu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Association of Plasma Magnesium with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Ehrlich, B.; Barbagallo, M.; Classen, H.G.; Guerrero-Romero, F.; Mooren, F.C.; Rodriguez-Moran, M.; Vierling, W.; Vormann, J.; Kisters, K. Significance of Magnesium in Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and Diabetes—Recommendations of the Association of Magnesium Research e.V. Trace Elem. Electrolytes 2017, 34, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elin, R.J. Assessment of Magnesium Status for Diagnosis and Therapy. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, C.J.; King, D.E. Serum Magnesium and the Development of Diabetes. Nutrition 2006, 22, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H. Guidance for the Determination of Status Indicators and Dietary Requirements for Magnesium. Magnes. Res. 2016, 29, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, R.B.; Elin, R.J.; Rosanoff, A.; Wallace, T.C.; Guerrero-Romero, F.; Hruby, A.; Lutsey, P.L.; Nielsen, F.H.; Rodriguez-Moran, M.; Song, Y.; et al. Perspective: The Case for an Evidence-Based Reference Interval for Serum Magnesium: The Time Has Come. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Y.; Xun, P.; He, K.; Qin, L.Q. Magnesium Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B.; Rosenberg, L.; Krishnan, S.; Palmer, J.R. Dietary Calcium and Magnesium, Major Food Sources, and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in U.S. Black Women. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirii, K.; Iso, H.; Date, C.; Fukui, M.; Tamakoshi, A. Magnesium Intake and Risk of Self-Reported Type 2 Diabetes among Japanese. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2010, 29, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.B.; Schulz, M.; Heidemann, C.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Hoffmann, K.; Boeing, H. Fiber and Magnesium Intake and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Study and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Manson, J.E.; Buring, J.E.; Liu, S. Dietary Magnesium Intake in Relation to Plasma Insulin Levels and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Women. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruby, A.; Meigs, J.B.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Jacques, P.F.; McKeown, N.M. Higher Magnesium Intake Reduces Risk of Impaired Glucose and Insulin Metabolism and Progression from Prediabetes to Diabetes in Middle-Aged Americans. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Shan, X.; Feng, J.; Lu, J.; Cai, S.; Zhao, L.; Yang, L. The Association of Dietary Magnesium and Prediabetes in Childbearing Chinese Women: Results from China Nutrition and Health Surveillance (2015–2017). Nutrients 2022, 14, 4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Chen, G.C.; Zhai, L.; Ke, K.F. Nonlinear Reduction in Risk for Type 2 Diabetes by Magnesium Intake: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Ding, G. Relationship between Dietary Magnesium Intake and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Lawson, A.B.; Liese, A.D.; Bell, R.A.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Dairy, Magnesium, and Calcium Intake in Relation to Insulin Sensitivity: Approaches to Modeling a Dose-Dependent Association. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.A.; Kushi, L.H.; Jacobs, D.R.; Slavin, J.; Sellers, T.A.; Folsom, A.R. Carbohydrates, Dietary Fiber, and Incident Type 2 Diabetes in Older Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
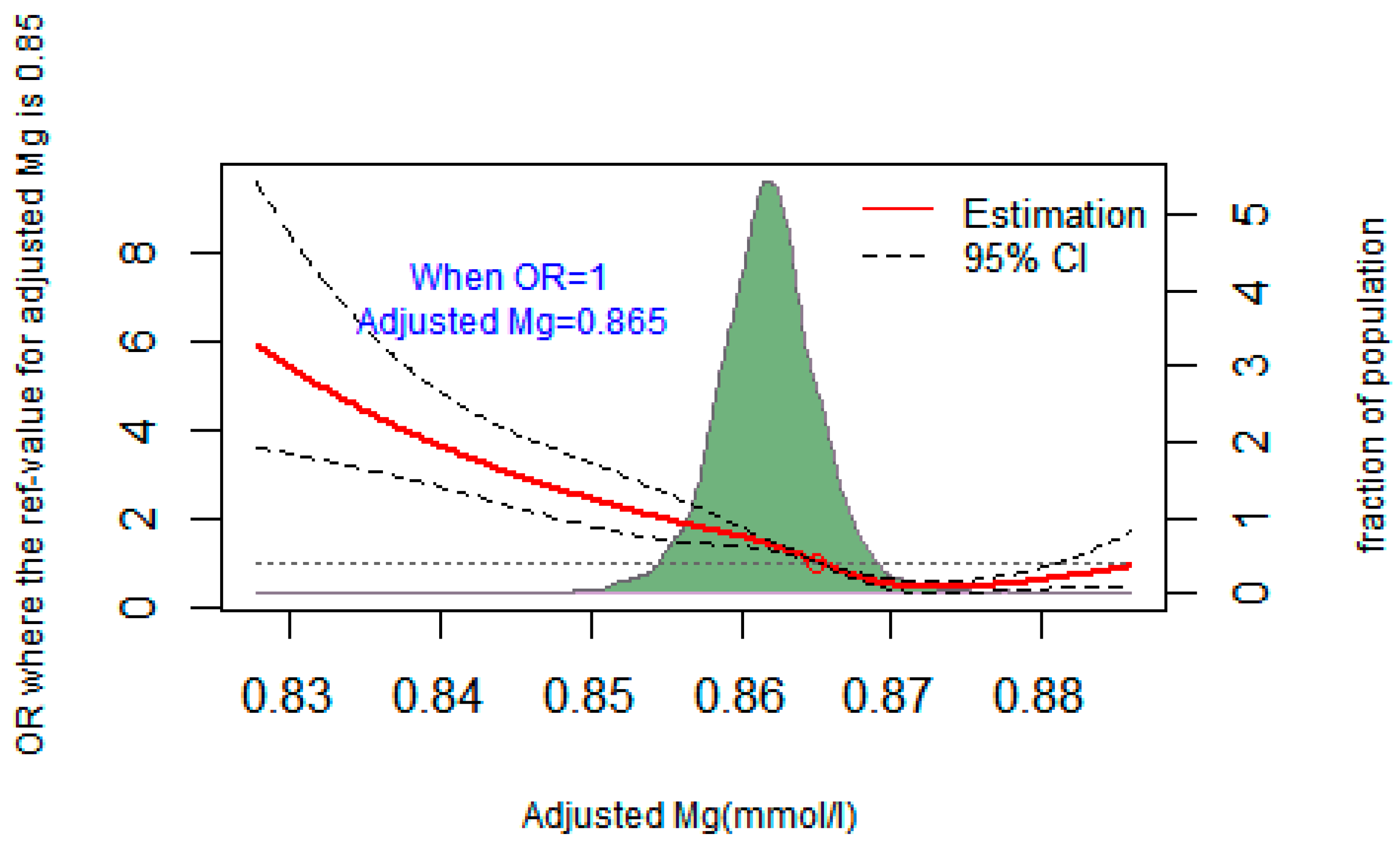
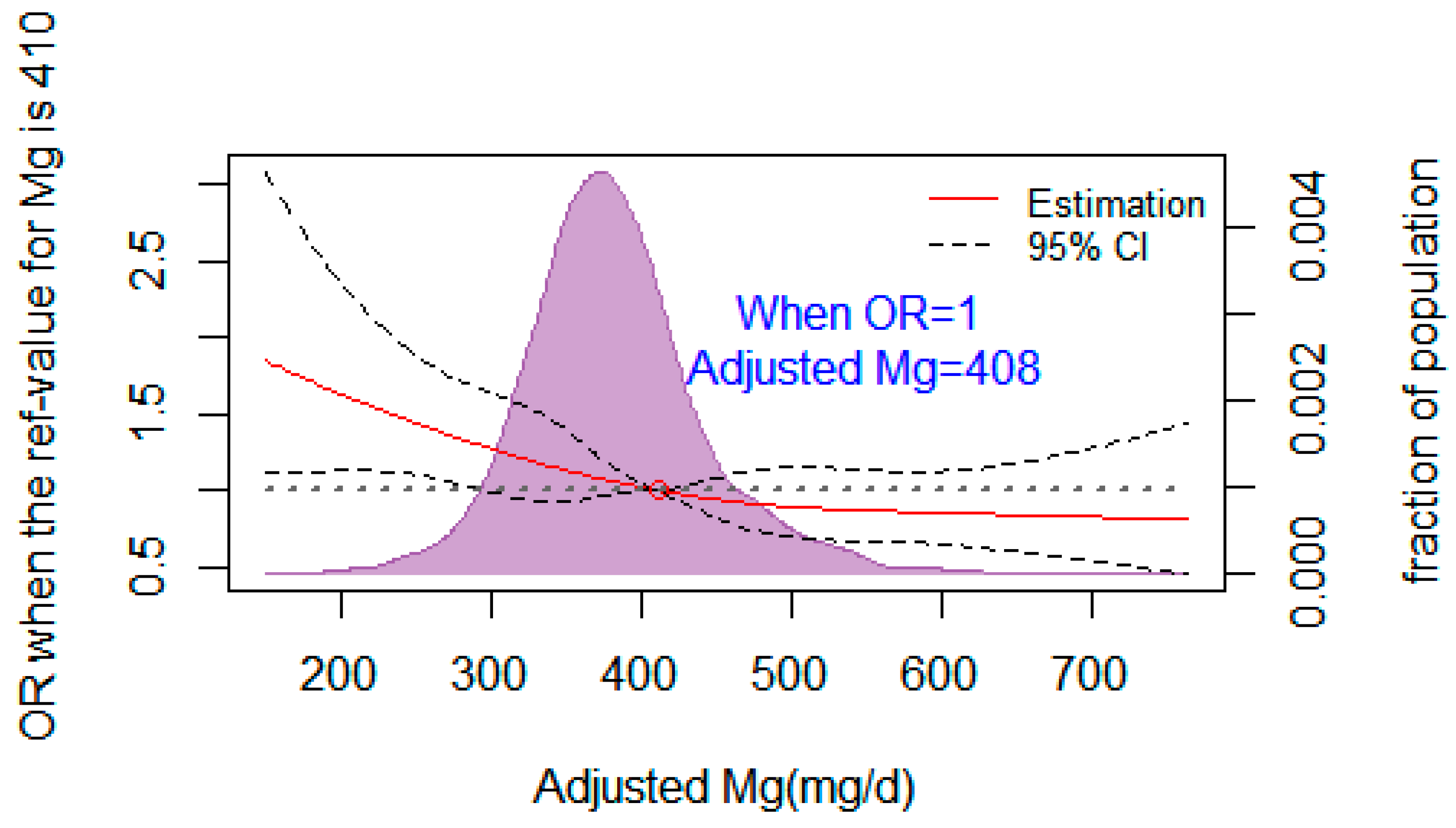
| Characteristics | Total | NFG | IFG | T2DM | p * | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | M # | P25–P75 | D * (%) | N | M # | P25–P75 | D * (%) | N | M # | P25–P75 | D * (%) | N | M # | P25–P75 | D * (%) | ||
| Total | 2912 | 0.86 | 7.73 | 7.73 | 1811 | 0.87 | 0.09 | 4.31 | 529 | 0.86 | 0.11 | 9.83 | 572 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 16.61 | 0.001 |
| Age group | |||||||||||||||||
| 18–25 y | 717 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 7.53 | 638 | 0.87 | 0.1 | 5.96 | 30 | 0.86 | 0.14 | 13.33 | 49 | 0.86 | 0.18 | 24.49 | 0.001 |
| 26–35 y | 932 | 0.86 | 0.09 | 7.19 | 619 | 0.88 | 0.09 | 3.55 | 160 | 0.85 | 0.10 | 10.00 | 153 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 18.95 | 0.001 |
| 36–45 y | 1263 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 8.23 | 554 | 0.88 | 0.1 | 3.25 | 339 | 0.86 | 0.11 | 9.44 | 370 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 14.59 | 0.001 |
| District | |||||||||||||||||
| Eastern | 972 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 8.02 | 590 | 0.88 | 0.11 | 3.22 | 180 | 0.86 | 0.09 | 8.89 | 202 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 21.29 | 0.001 |
| Central | 998 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 7.92 | 647 | 0.87 | 0.09 | 5.56 | 153 | 0.86 | 0.11 | 9.80 | 198 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 14.14 | 0.001 |
| Western | 942 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 7.22 | 574 | 0.88 | 0.09 | 4.01 | 196 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 10.71 | 172 | 0.85 | 0.12 | 13.95 | 0.001 |
| City type | |||||||||||||||||
| City | 1359 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 7.73 | 736 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 3.26 | 304 | 0.86 | 0.09 | 7.57 | 319 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 18.18 | 0.001 |
| Rural | 1553 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 7.73 | 1075 | 0.87 | 0.09 | 5.02 | 225 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 12.89 | 253 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 14.62 | 0.001 |
| Nationality | |||||||||||||||||
| Han | 2548 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 7.54 | 1594 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 4.39 | 459 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 9.80 | 495 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 15.56 | 0.001 |
| Ethnic minorities | 364 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 9.07 | 217 | 0.87 | 0.08 | 3.69 | 70 | 0.86 | 0.12 | 10.00 | 77 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 23.38 | 0.001 |
| BMI | |||||||||||||||||
| Underweight | 174 | 0.88 | 0.09 | 7.47 | 144 | 0.88 | 0.09 | 4.86 | 10 | 0.81 | 0.17 | 30.00 | 20 | 0.84 | 0.15 | 15.00 | 0.001 |
| Normal | 1415 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 6.78 | 1027 | 0.88 | 0.10 | 3.99 | 195 | 0.86 | 0.11 | 8.72 | 193 | 0.84 | 0.12 | 19.69 | 0.001 |
| Overweight | 856 | 0.86 | 0.09 | 7.83 | 445 | 0.87 | 0.09 | 4.94 | 200 | 0.86 | 0.09 | 8.00 | 211 | 0.84 | 0.10 | 13.74 | 0.001 |
| Obesity | 467 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 10.49 | 195 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 4.10 | 124 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 12.90 | 148 | 0.83 | 0.12 | 16.89 | 0.001 |
| Education | |||||||||||||||||
| Primary | 923 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 8.78 | 451 | 0.88 | 0.09 | 4.43 | 234 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 9.83 | 238 | 0.83 | 0.12 | 15.97 | 0.001 |
| Medium | 1564 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 7.74 | 1047 | 0.87 | 0.09 | 4.39 | 250 | 0.85 | 0.10 | 10.80 | 267 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 17.98 | 0.001 |
| Advanced | 425 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 5.41 | 313 | 0.88 | 0.09 | 3.83 | 45 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 4.44 | 67 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 13.43 | 0.019 |
| Drink | |||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 596 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 6.71 | 385 | 0.87 | 0.09 | 4.16 | 103 | 0.86 | 0.09 | 6.80 | 108 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 15.74 | 0.001 |
| No | 2316 | 0.86 | 0.10 | 7.99 | 1426 | 0.88 | 0.10 | 4.35 | 426 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 10.56 | 464 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 16.81 | 0.001 |
| Index | Total (n = 2469) | NFG (n = 1533) | IFG (n = 462) | T2DM (n = 451) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (cm) | 156.90 ± 6.24 | 157.24 ± 6.07 | 156.07 ± 6.42 | 156.54 ± 6.55 | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 59.08 ± 10.93 | 57.14 ± 10.07 | 61.86 ± 10.28 | 62.86 ± 12.61 | <0.001 |
| Waist (cm) | 78.94 ± 10.56 | 76.45 ± 9.68 | 82.4 ± 10.32 | 83.96 ± 10.93 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 120.95 ± 16.52 | 116.64 ± 13.60 | 126.8 ± 17.06 | 129.75 ± 19.46 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 74.04 ± 10.74 | 71.6 ± 9.24 | 77.22 ± 10.95 | 79.12 ± 12.51 | <0.001 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.32 ± 1.06 | 1.09 ± 0.76 | 1.56 ± 1.24 | 1.88 ± 1.43 | <0.001 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.41 ± 1.04 | 4.27 ± 0.83 | 4.58 ± 1.30 | 4.73 ± 1.26 | <0.001 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.68 ± 0.86 | 2.53 ± 0.73 | 2.87 ± 1.01 | 3.01 ± 1.01 | <0.001 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.27 ± 0.33 | 1.31 ± 0.30 | 1.21 ± 0.39 | 1.17 ± 0.35 | <0.001 |
| UA (µmol/L) | 268.49 ± 73.87 | 261.21 ± 66.58 | 277.23 ± 77.84 | 284.40 ± 88.39 | <0.001 |
| FG (mmol/L) | 5.98 ± 2.36 | 4.86 ± 0.51 | 6.43 ± 0.24 | 9.24 ± 3.65 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.16 ± 1.29 | 4.72 ± 0.48 | 5.00 ± 0.69 | 6.78 ± 2.08 | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Plasma Mg (mmol/L) | p-Trend | Per 0.041 mmol/L of Mg | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.75 | 0.75– <0.85 | 0.85– <0.95 | 0.95– <1.05 | ≥1.05 | ||||
| NFG/T2DM | OR (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | |||||
| Model 1 | 3.99 (2.93–5.42) | 1.55 (1.25–1.92) | Reference | 0.88 (0.63–1.25) | 1.03 (0.48–2.22) | <0.001 | 0.81 (0.77–0.84) | <0.001 |
| Model 2 # | 3.77 (2.71–5.25) | 1.53 (1.22–1.93) | Reference | 0.85 (0.59–1.22) | 1.09 (0.48–2.48) | <0.001 | 0.82 (0.78–0.86) | <0.001 |
| NFG/IFG | OR (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | |||||
| Model 1 | 4.05 (3.01–5.45) | 1.49 (1.26–1.78) | Reference | 0.94 (0.72–1.22) | 0.69 (0.36–1.34) | <0.001 | 0.81 (0.78–0.85) | <0.001 |
| Model 2 * | 4.08 (2.92–5.71) | 1.47 (1.21–1.79) | Reference | 0.83 (0.62–1.12) | 0.69 (0.32–1.45) | <0.001 | 0.81 (0.77–0.84) | <0.001 |
| NFG/HbA1c-hyperglucose | OR (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | OR (95%CI) | |||||
| Model 1 | 3.90 (2.70–5.63) | 1.68 (1.27–2.22) | Reference | 0.87 (0.55–1.39) | 1.28 (0.49–3.30) | <0.001 | 0.80 (0.76–0.85) | <0.001 |
| Model 2 & | 3.53 (2.39–5.19) | 1.62 (1.21–2.16) | Reference | 0.85 (0.52–1.38) | 1.35 (0.50–3.62) | <0.001 | 0.82 (0.78–0.87) | <0.001 |
| Nutrients | Total (n = 2469) | NFG (n = 1533) | IFG (n = 462) | T2DM (n = 451) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal) | 1964.71 ± 749.90 | 1944.88 ± 757.26 | 1989.52 ± 727.68 | 2006.67 ± 746.36 | 0.224 |
| Protein (g) | 58.77 ± 24.00 | 58.49 ± 24.33 | 59.37 ± 22.61 | 59.12 ± 24.29 | 0.742 |
| Fat (g) | 25.78 ± 21.12 | 25.92 ± 21.54 | 26.22 ± 21.23 | 24.85 ± 19.51 | 0.567 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 408.78 ± 175.82 | 406.15 ± 177.04 | 408.81 ± 170.66 | 417.71 ± 176.94 | 0.471 |
| Calcium (mg) | 366.04 ± 290.27 | 372.95 ± 293.96 | 359.96 ± 290.34 | 348.76 ± 277.02 | 0.263 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 409.12 ± 176.50 | 410.97 ± 179.93 | 401.09 ± 167.19 | 411.03 ± 174.14 | 0.555 |
| Sextile of Dietary Magnesium Intake (mg/d) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | p |
| <321.35 | 321.35–<365.62 | 365.62–<401.16 | 401.16–<439.47 | 439.47–<492.89 | >492.89 | ||
| NFG/IFG | OR (95%CI) | ||||||
| Model 1 | 1 | 0.788 (0.595, 1.043) | 0.810 (0.612, 1.071) | 0.761 (0.575, 1.009) | 0.594 (0.446, 0.791) | 0.657 (0.495, 0.873) | 0.009 |
| Model 2 | 1 | 0.754 (0.552, 1.029) | 0.742 (0.541, 1.018) | 0.801 (0.582, 1.102) | 0.541 (0.392, 0.748) | 0.653 (0.472, 0.902) | 0.009 |
| Model 3 | 1 | 0.736 (0.527, 1.028) | 0.730 (0.520, 1.024) | 0.797 (0.566, 1.121) | 0.535 (0.378, 0.755) | 0.611 (0.431, 0.866) | 0.011 |
| NFG/T2DM | OR (95%CI) | ||||||
| Model 1 | 1 | 0.883 (0.619, 1.261) | 0.879 (0.615, 1.257) | 0.877 (0.614, 1.251) | 0.721 (0.502, 1.035) | 0.745 (0.519, 1.070) | 0.501 |
| Model 2 | 1 | 0.862 (0.586, 1.269) | 0.830 (0.560, 1.229) | 0.964 (0.650, 1.432) | 0.680 (0.457, 1.013) | 0.781 (0.523, 1.166) | 0.428 |
| Model 3 | 1 | 0.787 (0.514, 1.205) | 0.718 (0.465, 1.108) | 0.873 (0.564, 1.350) | 0.625 (0.404, 0.967) | 0.707 (0.456, 1.098) | 0.342 |
| Tertiles of Dietary Magnesium Intake (mg/Day) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | T1 | T2 | T3 | p |
| <330 mg/day | 330–<408 mg/day | ≥408 mg/d | ||
| Plasma Mg(mmol/L) | 0.86 ± 0.09 | 0.86 ± 0.08 | 0.87 ± 0.09 | 0.139 |
| NFG/FG | OR (95%CI) | |||
| Model 1 | 1 | 0.682 (0.652, 1.031) | 0.671 (0.539, 0.836) | 0.001 |
| Model 2 | 1 | 0.795 (0.614, 1.030) | 0.683 (0.530, 0.881) | 0.013 |
| Model 3 | 1 | 0.766 (0.578, 1.014) | 0.632 (0.478, 0.837) | 0.006 |
| NFG/T2DM | OR (95%CI) | |||
| Model 1 | 1 | 0.808 (0.605, 1.081) | 0.735 (0.558, 0.967) | 0.090 |
| Model 2 | 1 | 0.785 (0.571, 1.081) | 0.764 (0.560, 1.043) | 0.212 |
| Model 3 | 1 | 0.720 (0.504, 1.028) | 0.697 (0.489, 0.993) | 0.111 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Shan, X.; Yang, L. Study on the Dose–Response Relationship between Magnesium and Type 2 Diabetes of Childbearing Women in the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance 2015. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071018
Zhang H, Yang J, Cao Y, Shan X, Yang L. Study on the Dose–Response Relationship between Magnesium and Type 2 Diabetes of Childbearing Women in the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance 2015. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071018
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huidi, Jingxin Yang, Yang Cao, Xiaoyun Shan, and Lichen Yang. 2024. "Study on the Dose–Response Relationship between Magnesium and Type 2 Diabetes of Childbearing Women in the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance 2015" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071018
APA StyleZhang, H., Yang, J., Cao, Y., Shan, X., & Yang, L. (2024). Study on the Dose–Response Relationship between Magnesium and Type 2 Diabetes of Childbearing Women in the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance 2015. Nutrients, 16(7), 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071018





