Effects of Enteric-Coated Formulation of Sodium Bicarbonate on Bicarbonate Absorption and Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Participants in the Experimental Human Trial
2.3. Preparation of Uncoated and Enteric-Coated Sodium Carbonate Tablets for the Experimental Human Trial
2.4. Experimental Human Trial
2.5. Data Analysis
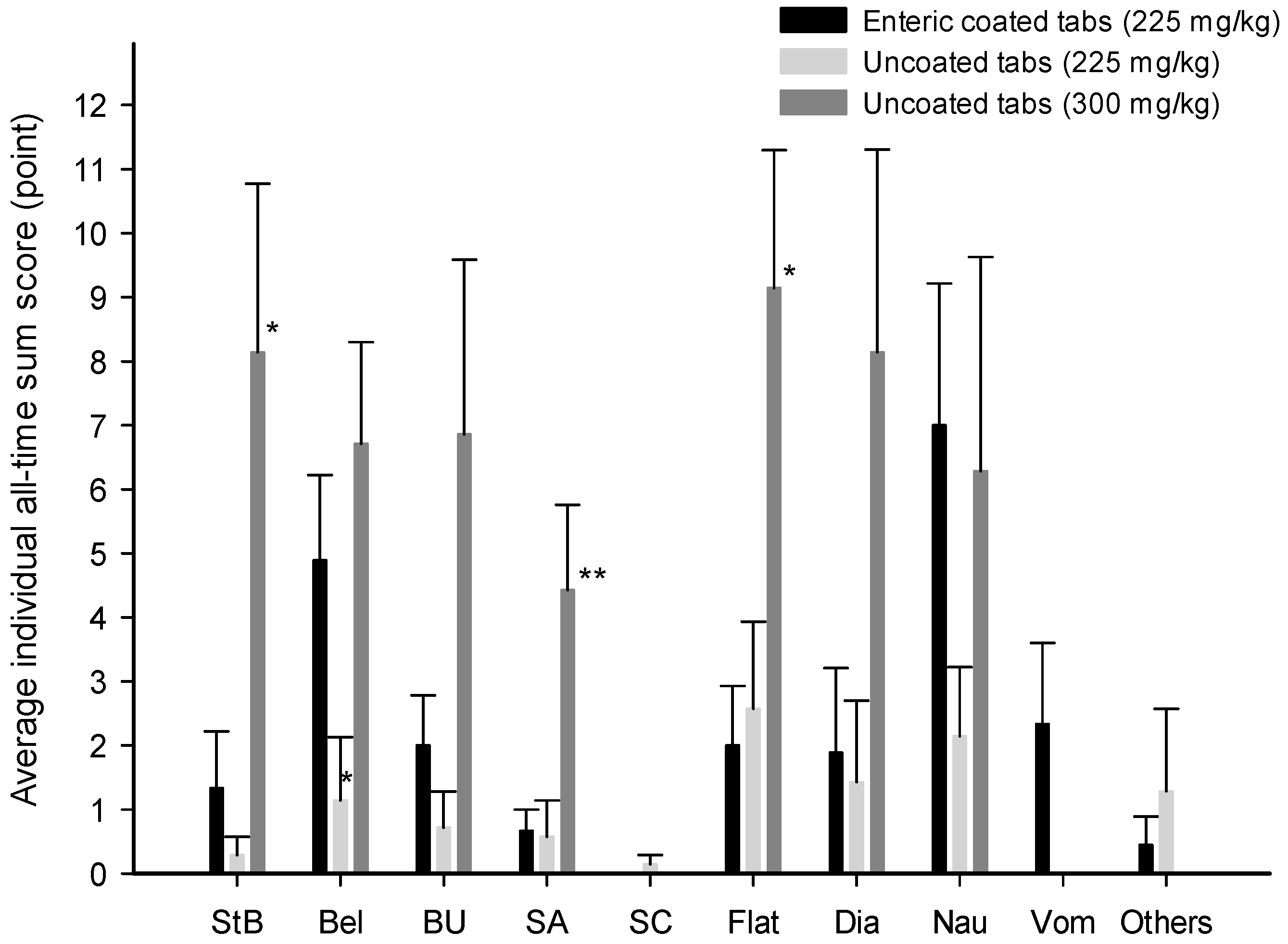
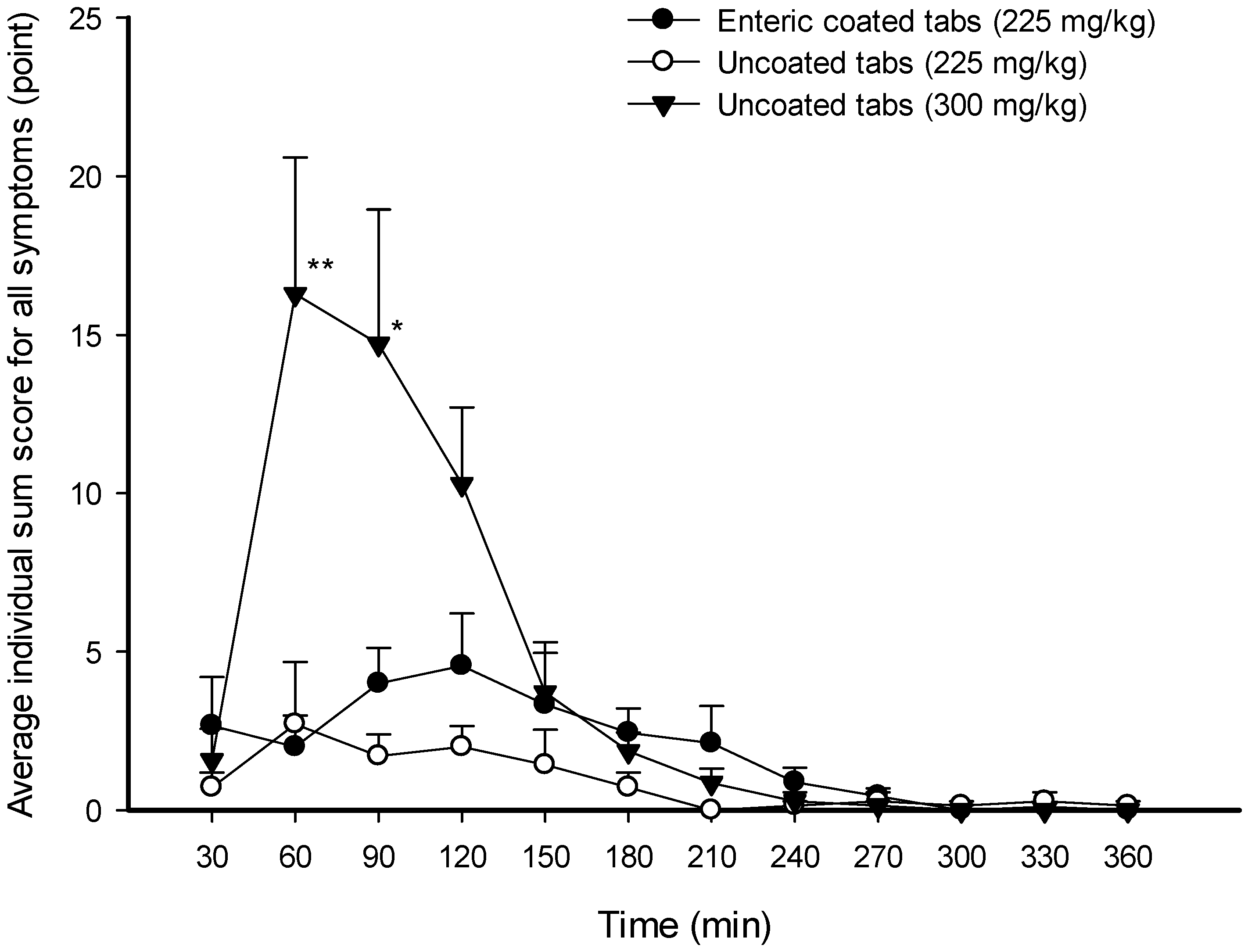
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Uncoated and Enteric-Coated Sodium Bicarbonate Tablets
3.2. Administration of Uncoated and Enteric-Coated Tablets in the Experimental Human Trial
3.3. Gastrointestinal Symptoms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghauri, S.K.; Javaeed, A.; Mustafa, K.J.; Podlasek, A.; Khan, A.S. Bicarbonate Therapy for Critically Ill Patients with Metabolic Acidosis: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2019, 11, e4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraut, J.A.; Kurtz, I. Use of base in the treatment of acute severe organic acidosis by nephrologists and critical care physicians: Results of an online survey. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2006, 10, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senewiratne, N.L.; Woodall, A.; Can, A.S. Sodium Bicarbonate. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, N.P.; Leach, N.K.; Sparks, S.A.; Gough, L.A.; Craig, M.M.; Deb, S.K.; McNaughton, L.R. A Novel Ingestion Strategy for Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation in a Delayed-Release Form: A Randomised Crossover Study in Trained Males. Sports Med. -Open 2019, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, N.P.; Leach, N.K.; Hilton, M.M.; Sparks, S.A.; McNaughton, L.R. Enteric-coated sodium bicarbonate supplementation improves high-intensity cycling performance in trained cyclists. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent-Braun, J.A.; Fitts, R.H.; Christie, A. Skeletal muscle fatigue. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 997–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.G.; Westerblad, H.; Lännergren, J. The role of intracellular acidosis in muscle fatigue. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1995, 384, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitts, R.H. Cellular mechanisms of muscle fatigue. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 49–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkalec-Michalski, K.; Nowaczyk, P.M.; Adrian, J.; Kamińska, J.; Podgórski, T. The influence of progressive-chronic and acute sodium bicarbonate supplementation on anaerobic power and specific performance in team sports: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkalec-Michalski, K.; Zawieja, E.E.; Podgórski, T.; Łoniewski, I.; Zawieja, B.E.; Warzybok, M.; Jeszka, J. The effect of chronic progressive-dose sodium bicarbonate ingestion on CrossFit-like performance: A double-blind, randomized cross-over trial. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkalec–Michalski, K.; Zawieja, E.E.; Zawieja, B.E.; Michałowska, P.; Podgórski, T. The gender dependent influence of sodium bicarbonate supplementation on anaerobic power and specific performance in female and male wrestlers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegler, J.C.; McNaughton, L.R.; Midgley, A.W.; Keatley, S.; Hillman, A. Metabolic Alkalosis, Recovery and Sprint Performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, T.A.; Lindstrøm, L.; Lønbro, S.; Madsen, K. Increased Performance in Elite Runners Following Individualized Timing of Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2021, 31, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Silva, J.P.; Da Silva Santos, J.F.; Artioli, G.G.; LoTurco, I.; Abbiss, C.; Franchini, E. Sodium bicarbonate ingestion increases glycolytic contribution and improves performance during simulated taekwondo combat. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delextrat, A.; Mackessy, S.; Arceo-Rendon, L.; Scanlan, A.; Ramsbottom, R.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J. Effects of Three-Day Serial Sodium Bicarbonate Loading on Performance and Physiological Parameters During a Simulated Basketball Test in Female University Players. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krustrup, P.; Ermidis, G.; Mohr, M. Sodium bicarbonate intake improves high-intensity intermittent exercise performance in trained young men. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegler, J.C.; Gleadall-Siddall, D.O. Sodium Bicarbonate Ingestion and Repeated Swim Sprint Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 3105–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindh, A.M.; Peyrebrune, M.C.; Ingham, S.A.; Bailey, D.M.; Folland, J.P. Sodium Bicarbonate Improves Swimming Performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 2007, 29, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.; Claudius, B. Effects of Induced Metabolic Alkalosis on Prolonged Intermittent-Sprint Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.; Moss, P.; Rance, S. Effects of Sodium Bicarbonate Ingestion on Prolonged Intermittent Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J.; Grgic, I.; Del Coso, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Pedisic, Z. Effects of sodium bicarbonate supplementation on exercise performance: An umbrella review. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maughan, R.J.; Burke, L.M.; Dvorak, J.; Larson-Meyer, D.E.; Peeling, P.; Phillips, S.M.; Rawson, E.S.; Walsh, N.P.; Garthe, I.; Geyer, H.; et al. IOC Consensus Statement: Dietary Supplements and the High-Performance Athlete. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, J.L.; Xu, H.; Mon-López, D.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Jiménez, S.L. Effect of sodium bicarbonate contribution on energy metabolism during exercise: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegler, J.C.; Marshall, P.W.; Bray, J.; Towlson, C. Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation and Ingestion Timing: Does it matter? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.J.; Slater, G.J.; Gore, C.J.; Dawson, B.; Burke, L.M. Effect of Sodium Bicarbonate on [HCO3−], pH, and Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.J.; Hopkins, W.G.; Gore, C.J. Effects of Acute Alkalosis and Acidosis on Performance: A meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.M.; Pyne, D.B. Bicarbonate Loading to Enhance Training and Competitive Performance. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2007, 2, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNaughton, L.R. Bicarbonate ingestion: Effects of dosage on 60 s cycle ergometry. J. Sports Sci. 1992, 10, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heibel, A.B.; Perim, P.H.L.; Oliveira, L.F.; McNaughton, L.R.; Saunders, B. Time to Optimize Supplementation: Modifying Factors Influencing the Individual Responses to Extracellular Buffering Agents. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, B.; Sale, C.; Harris, R.C.; Sunderland, C. Sodium Bicarbonate and High-Intensity-Cycling Capacity: Variability in Responses. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.L.; Stellingwerff, T.; Artioli, G.G.; Saunders, B.; Cooper, S.; Sale, C. Dose-Response of Sodium Bicarbonate Ingestion Highlights Individuality in Time Course of Blood Analyte Responses. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2016, 26, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, L.E.; Kelly, P.V.; Eliot, K.A.; Weiss, E.P. Acute sodium bicarbonate loading has negligible effects on resting and exercise blood pressure but causes gastrointestinal distress. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L.; McLay-Cooke, R.T.; Brown, R.C.; Gray, A.R.; Fairbairn, K.A. Increased Blood pH but Not Performance with Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation in Elite Rugby Union Players. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2010, 20, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fordtran, J.S.; Morawski, S.G.; Ana, C.A.S.; Rector, F.C. Gas Production After Reaction of Sodium Bicarbonate and Hydrochloric Acid. Gastroenterology 1984, 87, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, L.F.; Saunders, B.; Artioli, G.G. Is Bypassing the Stomach a Means to Optimize Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation? A Case Study with a Postbariatric Surgery Individual. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, N.P.; Leach, N.K.; Craig, M.M.; Sparks, S.A.; McNaughton, L.R. Enteric-Coated Sodium Bicarbonate Attenuates Gastrointestinal Side-Effects. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2020, 30, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maderuelo, C.; Lanao, J.M.; Zarzuelo, A. Enteric coating of oral solid dosage forms as a tool to improve drug bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 138, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, S.; Ju, X.; Barone, S.; Seidler, U.; Alper, S.L.; Lohi, H.; Kere, J.; Soleimani, M. Identification of a basolateral Cl−/HCO 3 − exchanger specific to gastric parietal cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 284, G1093–G1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J.; Pedisic, Z.; Saunders, B.; Artioli, G.G.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; McKenna, M.J.; Bishop, D.J.; Kreider, R.B.; Stout, J.R.; Kalman, D.S.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Sodium bicarbonate and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnberg, L.A.; Fordtran, J.S.; Carter, N.W.; Rector, F.C. Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J. Clin. Investig. 1970, 49, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
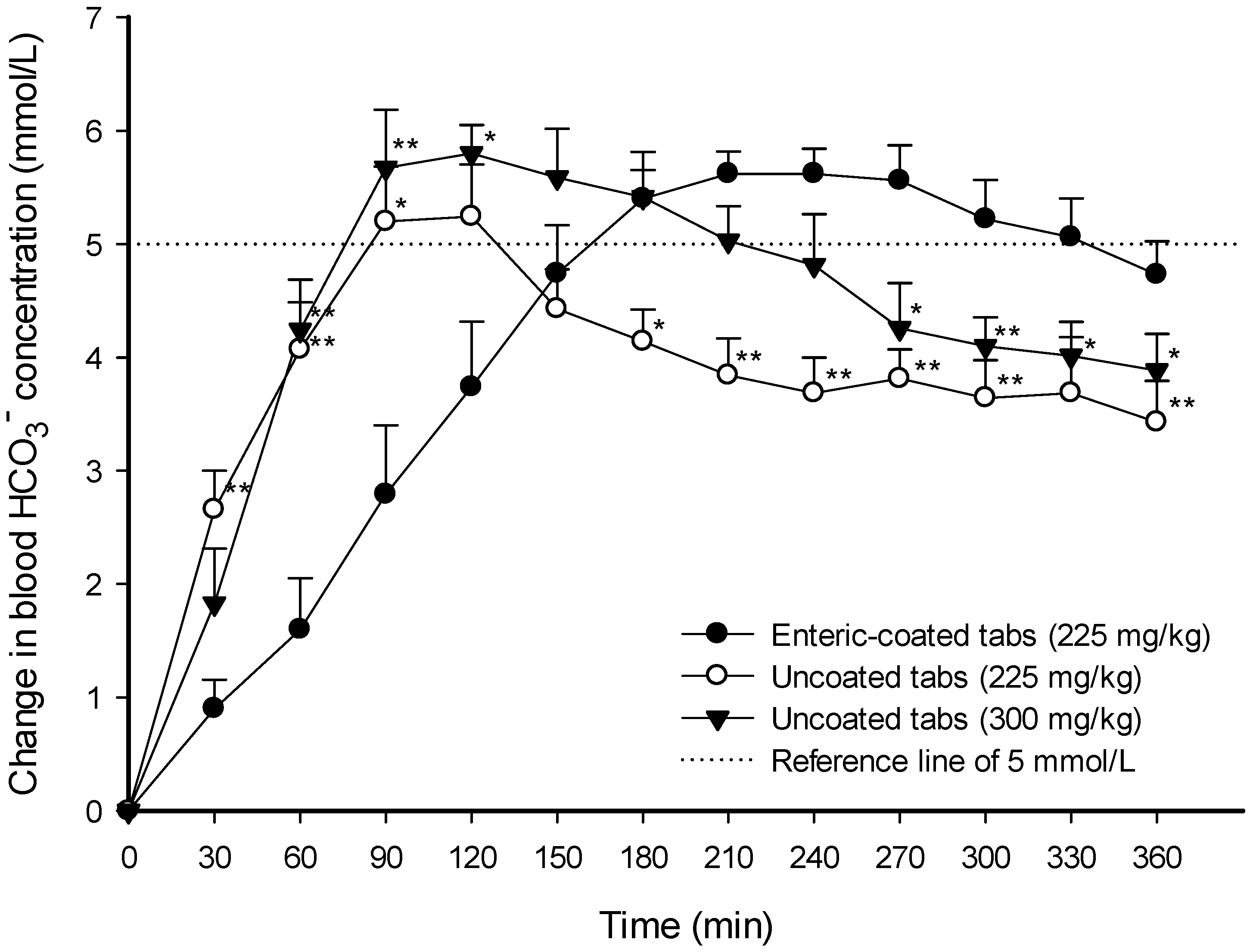
| AUC0–360 min (min∙μmol∙mL−1) | Cmax (μmol∙mL−1) | Tmax (min) | ΔAUC over Δ5 mmol∙L−1 (min∙μmol∙mL−1) | ΔCmax (μmol∙mL−1) | Duration Time over Δ5 mmol∙L−1 (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enteric-coated tabs (225 mg∙kg−1) | 10,345 ± 110 | 31.0 ± 0.49 | 198.0 ± 16.9 | 118.5 ± 36.2 | 6.28 ± 0.26 | 143.3 ± 18.8 |
| Uncoated tabs (225 mg∙kg−1) | 10,420 ± 136 (g = 0.21) | 30.6 ± 0.63 (g = 0.20) | 107.1 ± 6.1 ** (g = 2.14) | 44.6 ± 30.2 * (g = 0.72) | 5.54 ± 0.46 (g = 0.74) | 57.8 ± 34.8 * (g = 1.15) |
| Uncoated tabs (300 mg∙kg−1) | 10,972 ± 161 ** (g = 1.64) | 32.6 ± 0.53 (g = 1.10) | 132.9 ± 22.5 * (g = 1.16) | 123.2 ± 46.2 (g = 0.04) | 6.53 ± 0.35 (g = 0.29) | 147.2 ± 26.7 (g = 0.06) |
| ΔpH | Na+ (mmol∙L−1) | K+ (mmol∙L−1) | Cl− (mmol∙L−1) | Lactate (mmol∙L−1) | pCO2 (mmHg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enteric-coated tabs (225 mg∙kg−1) | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 5.20 ± 0.85 | 0.63 ± 0.11 | 3.80 ± 0.29 | 0.72 ± 0.14 | 35.09 ± 5.25 |
| Uncoated tabs (225 mg∙kg−1) | 0.09 ± 0.01 (p = 0.47, g = 0.17) | 4.86 ± 0.77 (p = 0.81, g = 0.14) | 0.74 ± 0.13 (p = 0.42, g = 0.33) | 4.14 ± 0.63 (p = 0.36, g = 0.27) | 0.43 ± 0.13 (p = 0.38, g = 0.74) | 25.37 ± 2.69 (p = 0.13, g = 0.71) |
| Uncoated tabs (300 mg∙kg−1) | 0.09 ± 0.01 (p = 0.81, g = 0.01) | 4.43 ± 0.48 (p = 0.54, g = 0.34) | 0.87 ± 0.18 (p = 0.31, g = 0.61) | 4.29 ± 0.47 (p = 0.60, g = 0.46) | 0.79 ± 0.13 (p = 0.45, g = 0.17) | 36.00 ± 4.24 (p = 0.47, g = 0.06) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, F.-L.; Jeong, D.-H.; Eom, S.-H.; Lee, H.-M.; Cha, B.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Kwon, R.; Nam, J.-Y.; Yu, H.-S.; Heo, S.-H.; et al. Effects of Enteric-Coated Formulation of Sodium Bicarbonate on Bicarbonate Absorption and Gastrointestinal Discomfort. Nutrients 2024, 16, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050744
Jiang F-L, Jeong D-H, Eom S-H, Lee H-M, Cha B-J, Park J-S, Kwon R, Nam J-Y, Yu H-S, Heo S-H, et al. Effects of Enteric-Coated Formulation of Sodium Bicarbonate on Bicarbonate Absorption and Gastrointestinal Discomfort. Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050744
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Fang-Lin, Dong-Ho Jeong, Seon-Ho Eom, Hae-Moon Lee, Bong-Jin Cha, Ju-Seong Park, RyoonKyoung Kwon, Jeong-Yeon Nam, Hyun-Seon Yu, Su-Hak Heo, and et al. 2024. "Effects of Enteric-Coated Formulation of Sodium Bicarbonate on Bicarbonate Absorption and Gastrointestinal Discomfort" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050744
APA StyleJiang, F.-L., Jeong, D.-H., Eom, S.-H., Lee, H.-M., Cha, B.-J., Park, J.-S., Kwon, R., Nam, J.-Y., Yu, H.-S., Heo, S.-H., Kim, C.-H., & Song, K.-H. (2024). Effects of Enteric-Coated Formulation of Sodium Bicarbonate on Bicarbonate Absorption and Gastrointestinal Discomfort. Nutrients, 16(5), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050744






