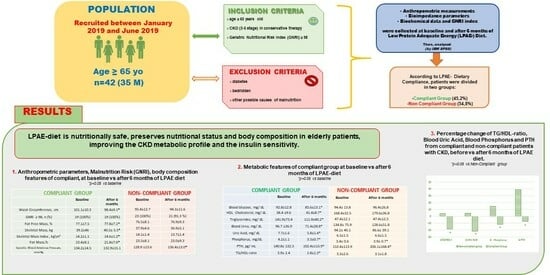
Effects of Dietary Intervention on Nutritional Status in Elderly Individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.1.1. Data Collection
2.1.2. Biochemical Parameters
2.1.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.1.4. Body Composition Analysis
2.1.5. Definition of the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index
2.1.6. Dietary Intake and Dietary Compliance
2.2. Endpoints
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, V.; Wang, A.Y.; Wang, H. The impact of CKD identification in large countries: The burden of illness. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27 (Suppl. S3), iii32–iii38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.; Duque, G.; McMahon, L.P. Sarcopenia and Frailty: Challenges in Mainstream Nephrology Practice. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2554–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsonello, A.; Freiberger, E.; Lattanzio, F. The screening for chronic kidney disease among older people across Europe (SCOPE) project: Findings from cross-sectional analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20 (Suppl. S1), 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponti, F.; Santoro, A.; Mercatelli, D.; Gasperini, C.; Conte, M.; Martucci, M.; Sangiorgi, L.; Franceschi, C.; Bazzocchi, A. Aging and Imaging Assessment of Body Composition: From Fat to Facts. Front Endocrinol. 2020, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127 (Suppl. S5), 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, G.L. Inflammation: Roles in aging and sarcopenia. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2008, 32, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamboni, M.; Mazzali, G.; Fantin, F.; Rossi, A.; Di Francesco, V. Sarcopenic obesity: A new category of obesity in the elderly. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, J.L.; Whincup, P.H.; Morris, R.W.; Lennon, L.T.; Papacosta, O.; Wannamethee, S.G. Sarcopenic obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: A population-based cohort study of older men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguso, C.A.; Kyle, U.; Kossovsky, M.P.; Roynette, C.; Paoloni-Giacobino, A.; Hans, D.; Genton, L.; Pichard, C. A 3-year longitudinal study on body composition changes in the elderly: Role of physical exercise. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavi, S.; Feiner, J.J.; Melendez, M.M.; Mynarcik, D.C.; Gelato, M.C.; McNurlan, M.A. Limb fat to trunk fat ratio in elderly persons is a strong determinant of insulin resistance and adiponectin levels. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2007, 62, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, E.; Shenoy, P.; Martinez Cantarin, M.P. Adipose tissue metabolic changes in chronic kidney disease. Immunometabolism 2023, 5, e00023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertow, J.; Ng, C.Z.; Mamede Branca, R.M.; Werngren, O.; Du, L.; Kjellqvist, S.; Hemmingsson, P.; Bruchfeld, A.; MacLaughlin, H.; Eriksson, P.; et al. Altered Protein Composition of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, B.; Pisano, A.; Zoccali, C. Insulin resistance in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2016, 311, F1087–F1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, G.; Barazzoni, R. Fighting protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease: A challenge of complexity. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrington, K.; Covic, A.; Nistor, I.; Aucella, F.; Clyne, N.; De Vos, L.; Findlay, A.; Fouque, D.; Grodzicki, T.; Iyasere, O.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline on management of older patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3b or higher (eGFR<45 mL/min/1.73 m2): A summary document from the European Renal Best Practice Group. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Cederholm, T.; Avesani, C.M.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Bellizzi, V.; Cuerda, C.; Cupisti, A.; Sabatino, A.; Schneider, S.; Torreggiani, M.; et al. Nutritional status and the risk of malnutrition in older adults with chronic kidney disease—Implications for low protein intake and nutritional care: A critical review endorsed by ERN-ERA and ESPEN. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massini, G.; Caldiroli, L.; Molinari, P.; Carminati, F.M.I.; Castellano, G.; Vettoretti, S. Nutritional Strategies to Prevent Muscle Loss and Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease: What Do We Currently Know? Nutrients 2023, 15, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Goisser, S.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.C.; et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 10–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Chronic Kidney Disease Guideline Development Work Group Members. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-Based Recommendations for Optimal Dietary Protein Intake in Older People: A Position Paper From the PROT-AGE Study Group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76 (Suppl. S1), S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupisti, A.; Brunori, G.; Di Iorio, B.R.; D’Alessandro, C.; Pasticci, F.; Cosola, C.; Bellizzi, V.; Bolasco, P.; Capitanini, A.; Fantuzzi, A.L.; et al. Nutritional treatment of advanced CKD: Twenty consensus statements. J. Nephrol. 2018, 31, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., III; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, T.; Abbasi, F.; Cheal, K.; Chu, J.; Lamendola, C.; Reaven, G. Use of metabolic markers to identify overweight individuals who are insulin resistant. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannel, W.B.; Vasan, R.S.; Keyes, M.J.; Sullivan, L.M.; Robins, S.J. Usefulness of the triglyceride-high-density lipoprotein versus the cholesterol-high-density lipoprotein ratio for predicting insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk (from the Framingham Offspring Cohort). Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanovski, S.; Hubbard, V.; Heymsfield, S.; Lukaski, H. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in body composition measurement: National Institutes of Health Technology Assessment Conference Statement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64 (Suppl. S3), 524S–532S. [Google Scholar]
- Kushner, R.F. Bioelectrical impedance analysis: A review of principles and applications. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1992, 11, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Ross, R. Estimation of skeletal muscle mass by bioelectrical impedance analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillanne, O.; Morineau, G.; Dupont, C.; Coulombel, I.; Vincent, J.P.; Nicolis, I.; Benazeth, S.; Cynober, L.; Aussel, C. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index: A new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, J.; Thompson, R.; Burley, V.; Warm, D. Development, validation and utilisation of food-frequency questionnaires—A review. Public. Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Oh, K.; Kim, H.C. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiologic studies. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, R.J.; Midthune, D.; Subar, A.F.; Shumakovich, M.; Freedman, L.S.; Thompson, F.; Kipnis, V. Taking Advantage of the Strengths of Two Different Dietary Assessment Instruments to Improve Intake Estimates for Nutritional Epidemiology. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 175, 340–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.E.; Hwang, S.J.; Chen, H.C.; Hung, C.C.; Hung, H.C.; Liu, S.C.; Wu, T.J.; Huang, M.C. Correlations of dietary energy and protein intakes with renal function impairment in chronic kidney disease patients with or without diabetes. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupisti, A.; Brunori, G.; Di Iorio, B.R.; D’Alessandro, C.; Pasticci, F.; Cosola, C.; Bellizzi, V.; Bolasco, P.; Capitanini, A.; Fantuzzi, A.L.; et al. Nutritional diet therapy in the management of the patient with Chronic Kidney Disease in advanced phase to delay the beginning and reduce the frequency of dialysis. An option also in the pre-emptive transplant program. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2018, 35, 2018-vol5. [Google Scholar]
- Beto, J.A.; Schury, K.A.; Bansal, V.K. Strategies to promote adherence to nutritional advice in patients with chronic kidney disease: A narrative review and commentary. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc Dis. 2016, 9, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickson, M. Malnutrition and ageing. Postgrad. Med. J. 2006, 82, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldiroli, L.; Vettoretti, S.; Armelloni, S.; Mattinzoli, D.; Ikehata, M.; Molinari, P.; Alfieri, C.; Messa, P.; Castellano, G. Possible Benefits of a Low Protein Diet in Older Patients With CKD at Risk of Malnutrition: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 782499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunori, G.; Viola, B.F.; Parrinello, G.; De Biase, V.; Como, G.; Franco, V.; Garibotto, G.; Zubani, R.; Cancarini, G.C. Efficacy and safety of a very-low-protein diet when postponing dialysis in the elderly: A prospective randomized multicenter controlled study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopple, J.D.; Levey, A.S.; Greene, T.; Chumlea, W.C.; Gassman, J.J.; Hollinger, D.L.; Maroni, B.J.; Merrill, D.; Scherch, L.K.; Schulman, G.; et al. Effect of dietary protein restriction on nutritional status in the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Kidney Int. 1997, 52, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.J.; Yen, C.H.; Wu, I.W.; Liu, M.H.; Cheng, H.Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Lee, C.C.; Hsu, K.H.; Sun, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. The association between low protein diet and body composition, muscle function, inflammation, and amino acid-based metabolic profile in chronic kidney disease stage 3-5 patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barril, G.; Nogueira, A.; Ruperto López, M.; Castro, Y.; Sánchez-Tomero, J.A. Influence of dietary protein intake on body composition in chronic kidney disease patients in stages 3-5: A cross-sectional study. Nefrologia 2018, 38, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.M.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Low-protein diet for conservative management of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouque, D.; Pelletier, S.; Mafra, D.; Chauveau, P. Nutrition and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouque, D.; Aparicio, M. Eleven reasons to control the protein intake of patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2007, 3, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopple, J.D.; Coburn, J.W. Metabolic studies of low protein diets in uremia. II. Calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. Medicine 1973, 52, 597–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsotti, G.; Morelli, E.; Giannoni, A.; Guiducci, A.; Lupetti, S.; Giovannetti, S. Restricted phosphorus and nitrogen intake to slow the progression of chronic renal failure: A controlled trial. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1983, 16, S278–S284. [Google Scholar]
- Newsome, B.; Ix, J.H.; Tighiouart, H.; Sarnak, M.J.; Levey, A.S.; Beck, G.J.; Block, G. Effect of protein restriction on serum and urine phosphate in the modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 1045–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatopolsky, E.; Caglar, S.; Gradowska, L.; Canterbury, J.; Reiss, E.; Bricker, N.S. On the prevention of secondary hyperparathyroidism in experimental chronic renal disease using “proportional reduction” of dietary phosphorus intake. Kidney Int. 1972, 2, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.L.; Vaziri, N.D. Urea, a true uremic toxin: The empire strikes back. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R.; Van Laecke, S.; Glorieux, G.; Verbeke, F.; Castillo-Rodriguez, E.; Ortiz, A. Deleting Death and Dialysis: Conservative Care of Cardio-Vascular Risk and Kidney Function Loss in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Toxins 2018, 10, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Koppe, L.; Nyam, E.; Vivot, K.; Manning Fox, J.E.; Dai, X.Q.; Nguyen, B.N.; Trudel, D.; Attané, C.; Moullé, V.S.; MacDonald, P.E.; et al. Urea impairs β cell glycolysis and insulin secretion in chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Invest 2016, 126, 3598–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Montagnana, M.; Franchini, M.; Favaloro, E.J.; Targher, G. The paradoxical relationship between serum uric acid and cardiovascular disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 392, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Jha, V.; Neal, B.; Patrice, H.M.; Okpechi, I.; Zhao, M.H.; Lv, J.; Garg, A.X.; Knight, J.; et al. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: A systematic review. Lancet 2015, 385, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, W.; McRae, S.; Marek, G.; Wymer, D.; Pannu, V.; Baylis, C.; Johnson, R.J.; Sautin, Y.Y. Hyperuricemia as a mediator of the proinflammatory endocrine imbalance in the adipose tissue in a murine model of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1258–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yuan, H.; Li, X. Triglycerides to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio Is the Best Surrogate Marker for Insulin Resistance in Nonobese Middle-Aged and Elderly Population: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 6676569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigalleau, V.; Blanchetier, V.; Combe, C.; Guillot, C.; Deleris, G.; Aubertin, J.; Aparicio, M.; Gin, H. A low-protein diet improves insulin sensitivity of endogenous glucose production in predialytic uremic patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bellizzi, V.; Di Iorio, B.R.; De Nicola, L.; Minutolo, R.; Zamboli, P.; Trucillo, P.; Catapano, F.; Cristofano, C.; Scalfi, L.; Conte, G. ERIKA Study-group. Very low protein diet supplemented with ketoanalogs improves blood pressure control in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline Anthropometric Features, Body Composition Characteristics, and Metabolic Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Male sex, n (%) | 35 (83.3%) |
| Age, years | 71.5 ± 5.5 |
| Weight, Kg | 74.7 ± 13.4 |
| BMI, Kg/m2 | 27.3 ± 4.1 |
| Waist circumference (WC), cm | 97.7 ± 11.9 |
| Fat-free mass, % | 75.9 ± 7.9 |
| Skeletal muscle mass, Kg | 38.6 ± 4.6 |
| Skeletal mass index, Kg/m² | 14.1 ± 1.3 |
| Fat mass,% | 24.2 ± 8.1 |
| Phase angle, Φ | 5.4 ± 1.1 |
| Systolic blood arterial pressure, mmHg | 131.2 ± 14.1 |
| Diastolic blood arterial pressure, mmHg | 77.4 ± 9.7 |
| Hypertension (n, %) | n. 37 (88.1%) |
| Dyslipidemia (n, %) | n. 21 (50.0%) |
| Glomerular filtration rate (mL/min/1.73 m²) | 25.8 ± 11.5 |
| CKD stage | Stage 3 (N.15; 35.7%) Stage 4 (N 19; 45.2%) Stage 5 (N 8; 19.0%) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 2.9 ± 1.2 |
| Blood urea, mg/dL | 95.3 ± 38.3 |
| Potassium, mg/dL | 4.9 ± 0.6 |
| Phosphorus, mg/dL | 3.8 ± 1.0 |
| Total calcium, mg/dL | 9.4 ± 0.5 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.2 ± 0.4 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 165.9 ± 37.3 |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 43.3 ± 11.8 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 138.0 ± 73.9 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 12.9 ± 1.7 |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 93.4 ± 13.2 |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 7.0 ± 1.6 |
| PTH, pg/mL | 147.9 ± 120.9 |
| TG/HDL ratio | 3.6 ± 2.5 |
| Compliant n. 19, 45.2% | Non-Compliant n. 23, 54.8% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prescribed | After 6 Months | Prescribed | After 6 Months | |
| Protein Intake (g/IBW/day) | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 * |
| Energy Intake (kcal/IBW/day) | 29.0 ± 3.2 | 28.8 ± 3.1 | 30.7 ± 3.1 | 25.6 ± 3.4 * |
| Compliant Group n. 19 | Non-Compliant Group n. 23 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 6 Months | Baseline | After 6 Months | |
| Weight, Kg | 77.4 ± 15.7 | 75.7 ± 14.5 | 72.5 ± 11.0 | 71.3 ± 8.8 |
| BMI, Kg/m2 | 27.8 ± 4.1 | 27.2 ± 3.7 | 26.9 ± 4.1 | 26.5 ± 3.3 |
| Waist circumference, cm | 101.1 ± 10.3 | 98.4 ± 9.1 * | 95.4 ± 12.7 | 94.3 ± 11.6 |
| GNRI ≥ 98, n (%) | 19 (100%) | 19 (100%) | 23 (100%) | 21 (91.3%) |
| Fat-free mass, % | 77.1 ± 7.5 | 77.8 ± 7.1 * | 76.5 ± 8.1 | 76.9 ± 9.3 |
| Skeletal mass, Kg | 39.2 ± 46 | 40.5 ± 5.5 * | 37.9 ± 4.6 | 36.9 ± 5.1 |
| Skeletal mass index, Kg/m² | 14.2 ± 1.1 | 14.6 ± 1.2 * | 14.1 ± 1.4 | 13.7 ± 1.4 |
| Fat mass, % | 23.4 ± 8.1 | 21.8 ± 7.6 * | 23.5 ± 8.1 | 23.0 ± 9.3 |
| Phase angle, Φ | 5,3 ± 0.9 | 5.4 ± 0.8 | 5.6 ± 1.1 | 5.7 ± 1.4 |
| Systolic blood arterial pressure, mmHg | 134.2 ± 14.5 | 132.9 ± 15.1 | 128.9 ± 13.6 | 136.4 ± 13.0 * |
| Diastolic blood arterial pressure, mmHg | 79.1 ± 11.1 | 76.1 ± 11.7 | 76.0 ± 8.5 | 79.5 ± 9.8 |
| Compliant n. 19 | Non-Compliant n. 23 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 6 Months | Baseline | After 6 Months | |
| Blood glucose, mg/dL | 92.8 ± 12.8 | 85.6 ± 13.1 * | 94.4 ± 13.8 | 96.4 ± 26.8 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 162.8 ± 43.2 | 160.0 ± 35.1 | 168.4 ± 32.5 | 179.6 ± 36.8 |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 38.4 ± 9.6 | 41.4 ± 8.7 * | 47.4 ± 12.1 | 47.4 ± 12.5 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 141.9 ± 73.4 | 111.9 ± 40.2 * | 134.8 ± 75.9 | 128.6 ± 51.8 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 2.8 ± 1.2 | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 2.9 ± 1.2 | 3.2 ± 1.6 |
| Blood urea, mg/dL | 96.7 ± 36.9 | 71.4 ± 28.8 * | 94.2 ± 40.1 | 86.6 ± 39.1 |
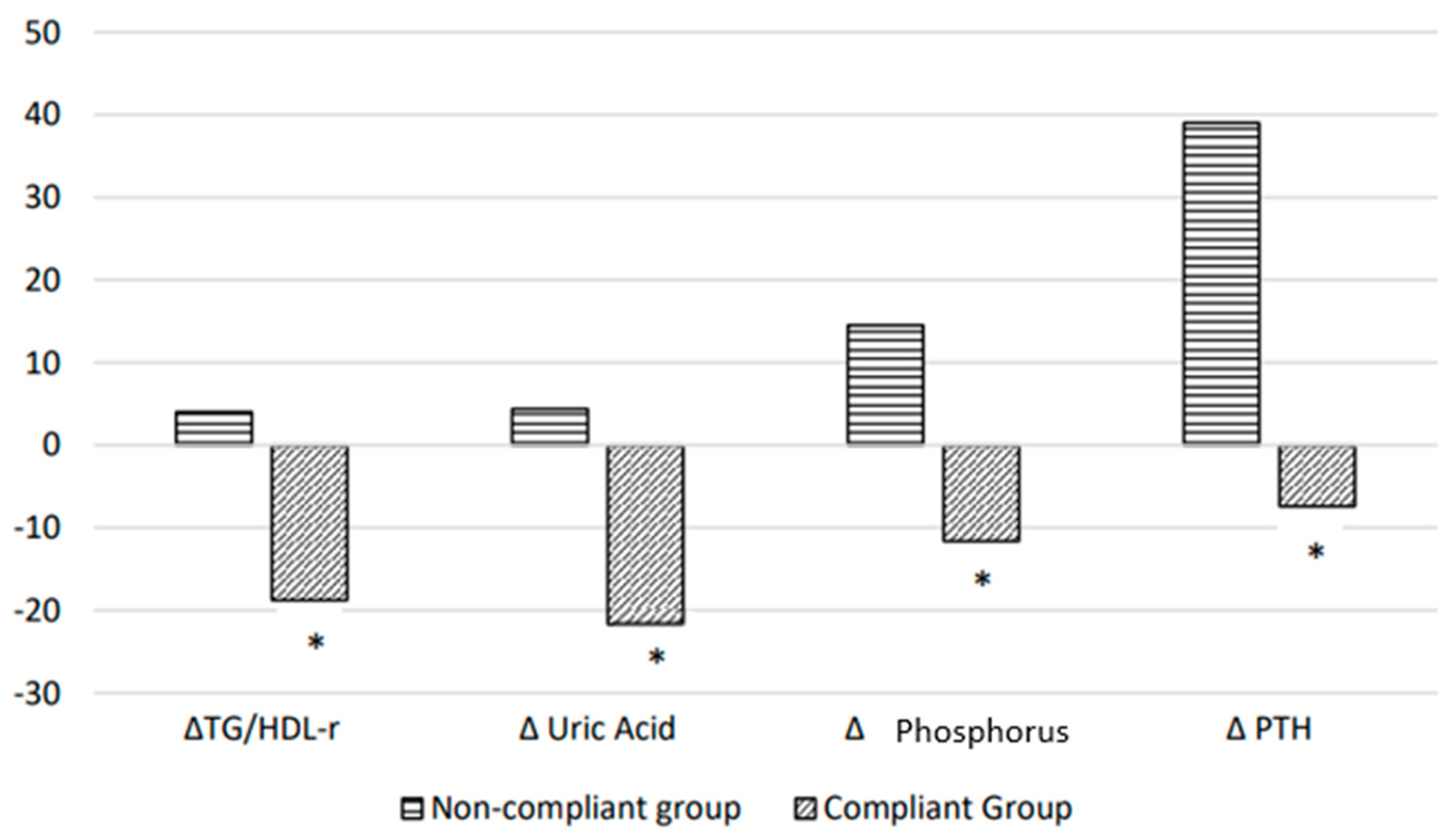
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 7.7 ± 1.6 | 5.8 ± 1.4 * | 6.5 ± 1.5 | 6.6 ± 1.5 |
| Phosphorus, mg/dL | 4.2 ± 1.1 | 3.5 ± 0.7 * | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 0.7 * |
| Potassium, mg/dL | 4.8 ± 0.6 | 4.8 ± 0.4 | 5.0 ± 0.6 | 5.1 ± 0.6 |
| Calcium, mg/dL | 9.5 ± 0.7 | 9.4 ± 0.6 | 9.2 ± 0.3 | 9.4 ± 0.6 |
| PTH, pg/mL | 140.8 ± 132.5 | 102.4 ± 115.9 * | 153.4 ± 113.9 | 206.1 ± 168.4 * |
| eGFR (CKD-EPI), mL/min/1.73 m2 | 26.7 ± 10.1 | 28.5 ± 14.1 | 25.4 ± 12.7 | 24.4 ± 12.4 |
| TG/HDL ratio | 3.9 ± 2.4 | 2.8 ± 1.3 * | 3.3 ± 2.6 | 3.1 ± 1.8 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.2 ± 1.9 | 13.0 ± 1.7 | 12.7 ± 1.5 | 12.4 ± 1.6 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 4.1 ± 0.3 | 4.1 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cacciapuoti, N.; Lonardo, M.S.; Di Lauro, M.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Aurino, L.; Pacella, D.; Guida, B. Effects of Dietary Intervention on Nutritional Status in Elderly Individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050632
Cacciapuoti N, Lonardo MS, Di Lauro M, Di Lorenzo M, Aurino L, Pacella D, Guida B. Effects of Dietary Intervention on Nutritional Status in Elderly Individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050632
Chicago/Turabian StyleCacciapuoti, Nunzia, Maria Serena Lonardo, Mariastella Di Lauro, Mariana Di Lorenzo, Laura Aurino, Daniela Pacella, and Bruna Guida. 2024. "Effects of Dietary Intervention on Nutritional Status in Elderly Individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050632
APA StyleCacciapuoti, N., Lonardo, M. S., Di Lauro, M., Di Lorenzo, M., Aurino, L., Pacella, D., & Guida, B. (2024). Effects of Dietary Intervention on Nutritional Status in Elderly Individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients, 16(5), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050632