Obesity as a Risk Factor for Complications and Mortality in Individuals with SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.5. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.6. Data Extraction
3. Results
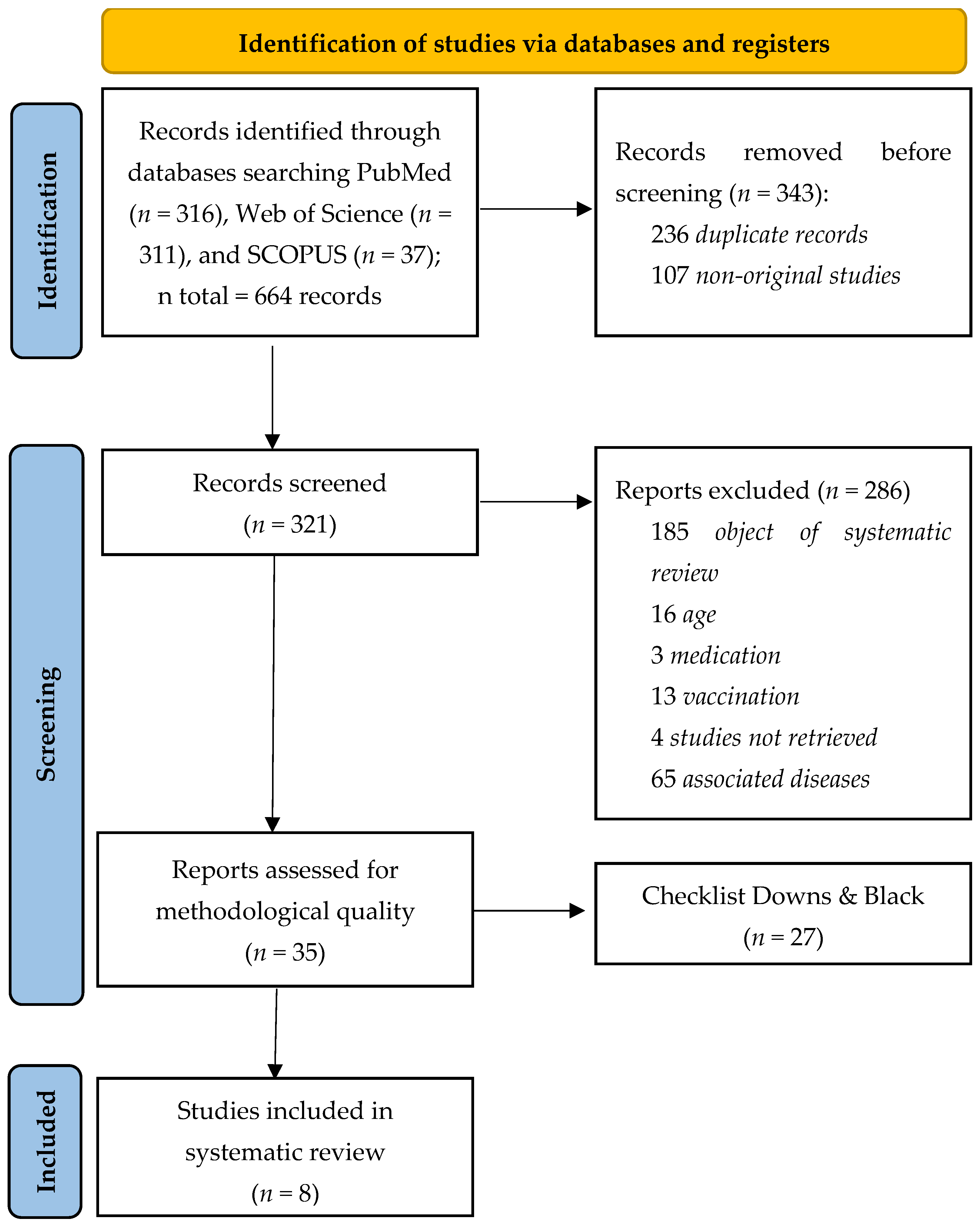
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Methodological Quality Assessment
3.3. Study Characteristics
3.4. Sample Characteristics
3.5. Categorization by Nutritional Status and Use of Respiratory Support
3.6. Biochemical and Hematological Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Practical Applications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Post-COVID Conditions: Information for Healthcare Professionals; CDC: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, A.H.A.; Passos, T.S.; de Lima Vale, S.; da Silva Maia, J.K.; Maciel, B.L. Obesity and the increased risk for COVID-19: Mechanisms and nutritional management. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2021, 34, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Hopkins (JHU); Coronavirus Resource Center. Global Map; Johns Hopkins University & Medicine: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2023; Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 6 January 2024).
- Gandhi, R.T.; Lynch, J.B.; Del Rio, C. Mild or Moderate COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, B.; Bluemke, D.A.; Lüscher, T.F.; Neubauer, S. Long COVID: Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 with a cardiovascular focus. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryal, J.J.; Perli, V.A.S.; Marques, D.C.S.; Sordi, A.F.; Marques, M.G.S.; Camilo, M.L.; Milani, R.G.; Mota, J.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Magnani Branco, B.H. Effects of a Multi-Professional Intervention on Mental Health of Middle-Aged Overweight Survivors of COVID-19: A Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghazadeh, A.; Rezaei, N. Immune-epidemiological parameters of the novel coronavirus—A perspective. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skevaki, C.; Fragkou, P.C.; Cheng, C.; Xie, M.; Renz, H. Laboratory characteristics of patients infected with the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.R. COVID-19 and the nervous system. J. Neurovirol. 2020, 26, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia de Sá, T.; Soares, C.; Rocha, M. Acute pancreatitis and COVID-19: A literature review. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 13, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Wen, J.; Yuan, X.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, X.; Liu, C.; Min, X. Potential biochemical markers to identify severe cases among COVID-19 patients. medrxiv 2020. medrXiv:20034447. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Hou, D. Obesity and COVID-19 Pandemics: Epidemiology, Mechanisms, and Management. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 4147–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.; Bhatia, S.; Albarrati, A.; Albratty, M.; Meraya, A.M.; Najmi, A.; Bungau, S. Reviving the mutual impact of SARS-CoV-2 and obesity on patients: From morbidity to mortality. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Rathore, S.S.; Khan, H.; Karale, S.; Chawla, Y.; Iqbal, K.; Bhurwal, A.; Tekin, A.; Jain, N.; Mehra, I.; et al. Association of Obesity With COVID-19 Severity and Mortality: An Updated Systemic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 780872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalligeros, M.; Shehadeh, F.; Mylona, E.K. Association of Obesity with Disease Severity Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Obesity 2020, 28, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Schulze, M.B. Global pandemics interconnected—Obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, P.; Falcone, C.; Romano, L.; Macheda, S.; Correale, P.; Arciello, P.; Polimeni, N.; Lorenzo, A. Body Composition Findings by Computed Tomography in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: Increased Risk of Muscle Wasting in Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbinden-Foncea, H.; Francaux, M.; Deldicque, L.; Hawley, J.A. Does High Cardiorespiratory Fitness Confer Some Protection Against Pro-inflammatory Responses After Infection by SARS-CoV-2? Obesity 2020, 28, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, M.M.; Cavalini, G.R.; Pugliese Henrique, C.R.; Perli, V.A.S.; de Moraes Marchiori, G.; Marchiori, L.L.M.; Sordi, A.F.; Franzói de Moraes, S.M.; de Paula Ramos, S.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; et al. Body composition and cardiorespiratory fitness in overweight or obese people post COVID-19: A comparative study. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 949351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perli, V.A.S.; Sordi, A.F.; Lemos, M.M.; Fernandes, J.S.A.; Capucho, V.B.N.; Silva, B.F.; de Paula Ramos, S.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Mota, J.; Branco, B.H.M. Body composition and cardiorespiratory fitness of overweight COVID-19 survivors in different severity degrees: A cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freke, M.; Kemp, J.; Svege, I.; Risberg, M.; Semciw, A.; Crossley, K. Physical impairments in symptomatic femoroacetabular impingement: A systematic review of the evidence. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Badilla, P.A.; Obreque Villagrán, D.; Levín Catrilao, A.; Carimán San Martín, A.; Segura Contanzo, D.; Núñez-Espinosa, C.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Magnani Branco, B.H. Diferencias morfológicas Y De condición física En Futbolistas Adolescentes Según posición De Juego: Una revisión sistemática. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Hum. Diet. 2021, 25, e1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, S.H.; Black, N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1998, 52, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, D.A.; Schulz, K.F. An overview of clinical research: The lay of the land. Lancet 2002, 359, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Leung, V.; Nayudu, S.K.; Galiveeti, S.; Mantri, N.; Sun, H.; Gongati, S.; Perugu, V.; Chilimuri, S. Role of body mass index in outcomes of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 illness. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2022, 8, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvy, S.J.; Datta, G.D.; Yu, Q.; Lauzon, M.; Hussain, S.K.; Cheng, S.; Ebinger, J.E.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Figueiredo, J.C. How useful are body mass index and history of diabetes in COVID-19 risk stratification? PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevanovic, D.; Zdravkovic, V.; Poskurica, M.; Petrovic, M.; Cekerevac, I.; Zdravkovic, N.; Mijailovic, S.; Todorovic, D.; Divjak, A.; Bozic, D.; et al. The Role of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Predicting COVID-19 Outcome. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 906659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, M.; Tuncay, E.; Yıldırım, E.; Yıldız, R.; Sevim, T.; Ernam, D.; Yılmaz, N.O.; Teke, N.H.; Yavuz, S.; Karakurt, Z.; et al. Is Obesity a Potential Risk factor for Poor Prognosis of COVID-19? Infect. Chemother. 2021, 53, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, S.; Jacob Filho, W.; Shinjo, S.K.; Ferriolli, E.; Busse, A.L.; Avelino-Silva, T.J.; Longobardi, I.; de Oliveira Júnior, G.N.; Swinton, P.; Gualano, B.; et al. Muscle strength and muscle mass as predictors of hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A prospective observational study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaraayan, A.; Nimkar, A.; Pant, S.; Hasan, A.; Durdevic, M.; Elenius, H.; Nava Suarez, C.; Jesmajian, S. Sex Disparity in the Effect of Obesity in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study from the New York City Metropolitan Area. Cureus 2021, 13, e15235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Jia, W.; Han, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; He, Y. The association between BMI and metabolically unhealthy status with COVID-19 mortality: Based on 3019 inpatients from Wuhan, China. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 3219–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakeshbandi, M.; Maini, R.; Daniel, P.; Rosengarten, S.; Parmar, P.; Wilson, C.; Kim, J.M.; Oommen, A.; Mecklenburg, M.; Salvani, J.; et al. The impact of obesity on COVID-19 complications: A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Piernas, C.; Astbury, N.M.; Hippisley-Cox, J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Aveyard, P.; Jebb, S.A. Associations between body-mass index and COVID-19 severity in 6·9 million people in England: A prospective, community-based, cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlBahrani, S.; Al-Maqati, T.N.; Al Naam, Y.A.; Alqahtani, J.S.; Alqahtani, A.S.; AlRabeeah, S.; Aldhahir, A.M.; Alkhalaf, F.; Alzuraiq, H.R.; Alenezi, M.H.; et al. The Association of Body Mass Index with COVID-19 Complications and Survival Rate at a Tertiary Hospital. Life 2023, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrego-Ellacuría, M.; Rubio-Herrera, M.A.; González López-Valcárcel, B.; Fuentes-Ferrer, M.E.; Martín, V.; Poyato, F.; Barber-Pérez, P.; Santucci, C.; Nuñez, A.; González-Pérez, C.; et al. Clinical and economic impact of COVID-19 on people with obesity in a Spanish cohort during the first pandemic peak. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1146517. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.; Khani, M.; Lu, Q.; Taylor, B.; Osinski, K.; Luo, J. Association between body-mass index, patient characteristics, and obesity-related comorbidities among COVID-19 patients: A prospective cohort study. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 17, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Ichikawa, S.; Suzuki, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Dohi, K.; Yamamoto, N. Impact of body composition on patient prognosis after SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caccialanza, R.; Formisano, E.; Klersy, C.; Ferretti, V.; Ferrari, A.; Demontis, S.; Mascheroni, A.; Masi, S.; Crotti, S.; Lobascio, F.; et al. Nutritional parameters associated with prognosis in non-critically ill hospitalized COVID-19 patients: The NUTRI-COVID-19 study. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2980–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarkar, Z.; Salehiniya, H.; Kazemi, T.; Abbaszadeh, H. Epidemiological, imaging, laboratory, and clinical characteristics and factors related to mortality in patients with COVID-19: A single-center study. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2021, 12, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.S.; Kong, K.A. Body mass index and severity/fatality from coronavirus disease 2019: A nationwide epidemiological study in Korea. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Urbistondo, M.; Mora Vargas, A.; Expósito Palomo, E.; Aparicio de Miguel, M.; Castejón Díaz, R.; Daimiel, L.; Ramos López, O.; San Cristóbal, R.; Martínez, J.A.; Vargas Núñez, J.A. Evolution of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 according to previous metabolic status. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinuzzi, A.L.N.; Manzanares, W.; Quesada, E.; Reberendo, M.J.; Baccaro, F.; Aversa, I.; Kecskes, C.E.; Magnífico, L.; González, V.; Bolzico, D.; et al. Nutritional risk and clinical outcomes in critically ill adult patients with COVID-19. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeill, J.N.; Lau, E.S.; Paniagua, S.M.; Liu, E.E.; Wang, J.K.; Bassett, I.V.; Selvaggi, C.A.; Lubitz, S.A.; Foulkes, A.S.; Ho, J.E. The role of obesity in inflammatory markers in COVID-19 patients. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 15, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Cruz, E.; Castañón-González, J.A.; Ortiz-Gutiérrez, S.; Garduño-López, J.; Luna-Camacho, Y. Impact of obesity and diabetes mellitus in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 15, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabah, S.; Al-Haddad, M.; Al-Youha, S.; Jamal, M.; Almazeedi, S. COVID-19: Impact of obesity and diabetes on disease severity. Clin. Obes. 2020, 10, e12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.R.; Geleris, J.; Anderson, D.R.; Zucker, J.; Nobel, Y.R.; Freedberg, D.; Small-Saunders, J.; Rajagopalan, K.N.; Greendyk, R.; Chae, S.R.; et al. Body Mass Index and Risk for Intubation or Death in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Tong, S.; Wang, G.; Wu, G.; Zhou, R. The importance of overweight in COVID-19: A retrospective analysis in a single center of Wuhan, China. Medicine 2020, 99, e22766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonietto, R.G.; Bortolini, G.C.; Figueiró, G.L.; Raupp, I.S.; Côcco, M.L.C.; Coser, T.B.S.; Lima, L.K.M.; Fighera, T.M. Clinical profile and severity predictors of coronavirus disease 19 infection in a reference center from southern Brazil: A cross-sectional study. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2023, 69, e20221271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiodimos, L.; Ali, R.; Teo, H.O.; Parthasarathy, S.; Karamanis, D.; Chamorro-Pareja, N.; Kokkinidis, D.G.; Kaur, S.; Kladas, M.; Sperling, J.; et al. Obesity, Inflammation, and Mortality in COVID-19: An Observational Study from the Public Health Care System of New York City. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salameh, A.; Lanoix, J.P.; Bennis, Y.; Andrejak, C.; Brochot, E.; Deschasse, G.; Dupont, H.; Goeb, V.; Jaureguy, M.; Lion, S.; et al. The association between body mass index class and coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ye, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, G.; Gu, J.; Lian, J.; Hao, S.; et al. High body mass index is a significant risk factor for the progression and prognosis of imported COVID-19: A multicenter, retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanama, K.; Srichatrapimuk, S.; Thammavaranucupt, K.; Kirdlarp, S.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Wongsinin, T.; Nanthatanti, N.; Phusanti, S.; Pitidhammabhorn, D.; Sungkanuparph, S. The association between body mass index and severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guen, C.L.; King, N.A.; Zhao, H.; Renza-Stingone, E.P.; Gerhard, G.S.; Soans, R.S. COVID-19 patients with obesity at risk for worse outcomes despite younger age and fewer inflammatory derangements. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2021, 17, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucar, J.; Wingler, M.J.B.; Cretella, D.A.; Ward, L.M.; Sims Gomillia, C.E.; Chamberlain, N.; Shimose, L.A.; Brock, J.B.; Harvey, J.; Wilhelm, A.; et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: Early Experience from an Academic Medical Center in Mississippi. South Med. J. 2021, 114, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, T.; Otsubo, K.; Hoshino, T.; Shimokawa, M.; Nakazawa, M.; Sato, Y.; Mikumo, H.; Kawakami, S.; Mizusaki, S.; Mori, Y.; et al. Risk factors for disease progression in Japanese patients with COVID-19 with no or mild symptoms on admission. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okauchi, Y.; Matsuno, K.; Nishida, T.; Sawada, K.; Kawasaki, A.; Ito, N.; Morimura, O.; Otani, Y.; Yokoe, M.; Abe, K.; et al. Obesity, glucose intolerance, advanced age, and lymphocytopenia are independent risk factors for oxygen requirement in Japanese patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, P.; Pang, R.; Li, L.; Li, H.R.; Liu, S.L.; Zhao, L. Both Underweight and Obesity Are Associated with an Increased Risk of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Severity. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 649422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeuffer, C.; Le Hyaric, C.; Fabacher, T.; Mootien, J.; Dervieux, B.; Ruch, Y.; Hugerot, A.; Zhu, Y.J.; Pointurier, V.; Clere-Jehl, R.; et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with severe COVID-19: Prospective analysis of 1.045 hospitalised cases in North-Eastern France, March 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaghim, A.; Sinha, P.; Bielick, C.; Knudsen, S.; Beeram, I.; White, L.F.; Apovian, C.; Sagar, M.; Hochberg, N.S. Clinical outcomes and inflammatory marker levels in patients with COVID-19 and obesity at an inner-city safety net hospital. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; Report of a WHO Consultation, Geneva, 3–5 June 1997; (WHO/NUT/98.1); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Drafting Committee of Chinese Consensus on Overweight/Obesity Medical Nutrition Therapy. Chinese consensus on overweight/obesity medical nutrition theray. Chin. J. Diabetes Mellit. 2016, 8, 525–540. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapater, P.; Novalbos, J.; Gallego-Sandín, S.; Hernández, F.T.; Abad-Santos, F. Gender differences in angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity and inhibition by enalaprilat in healthy volunteers. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004, 43, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Dong, X.; Cao, Y.Y.; Yuan, Y.D.; Yang, Y.B.; Yan, Y.Q.; Akdis, C.A.; Gao, Y.D. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy 2020, 75, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Ortega, O.; Moreno-Corona, N.C.; Cruz-Holguin, V.J.; Garcia-Gonzalez, L.D.; Helguera-Repetto, A.C.; Romero-Valdovinos, M.; Arevalo-Romero, H.; Cedillo-Barron, L.; León-Juárez, M. The Immune Response in Adipocytes and Their Susceptibility to Infection: A Possible Relationship with Infectobesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, S.C.S.; Godoi, E.T.A.M.; Cordeiro, L.H.O.; Bezerra, C.S.; Ramos, J.O.X.; Arruda, G.F.A.; Lins, E.M. COVID-19 and obesity: The meeting of two pandemics. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Obesity Federation (WOF). World Obesity Atlas; World Obesity Federation: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://pt.worldobesityday.org/assets/downloads/World_Obesity_Atlas_2023_Report.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2024).
- Coelho, M.; Oliveira, T.; Fernandes, R. Biochemistry of adipose tissue: An endocrine organ. Arch. Med. Sci. 2013, 9, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolsoni-Lopes, A.; Furieri, L.B.; Alonso-Vale, M.I.C. Obesity and COVID-19: A reflection on the relationship between pandemics. Rev. Gaúcha Enferm. 2021, 42, e20200216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottoli, M.; Bernante, P.; Belvedere, A.; Balsamo, F.; Garelli, S.; Giannella, M.; Cascavilla, A.; Tedeschi, S.; Ianniruberto, S.; Rosselli Del Turco, E.; et al. How important is obesity as a risk factor for respiratory failure, intensive care admission and death in hospitalised COVID-19 patients? Results from a single Italian centre. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrilli, C.M.; Jones, S.A.; Yang, J.; Rajagopalan, H.; O’Donnell, L.; Chernyak, Y.; Tobin, K.A.; Cerfolio, R.J.; Francois, F.; Horwitz, L.I. Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zheng, K.I.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, Q.F.; Pan, K.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; George, J.; et al. Obesity Is a Risk Factor for Greater COVID-19 Severity. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, e72–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paravidino, V.B.; Leite, T.H.; Mediano, M.F.F.; Sichieri, R.; Azevedo e Silva, G.; Cravo, V.; Balduino, A.; Salgueiro, E.; Besen, B.A.; Moreira, R.D.; et al. Association between obesity and COVID-19 mortality and length of stay in intensive care unit patients in Brazil: A retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompaniyets, L.; Pennington, A.F.; Goodman, A.B.; Rosenblum, H.G.; Belay, B.; Ko, J.Y.; Chevinsky, J.R.; Schieber, L.Z.; Summers, A.D.; Lavery, A.M.; et al. Underlying Medical Conditions and Severe Illness Among 540,667 Adults Hospitalized With COVID-19, March 2020-March 2021. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2021, 18, E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariq, O.A.; McKenzie, T.J. Obesity-related hypertension: A review of pathophysiology, management, and the role of metabolic surgery. Gland Surg. 2020, 9, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Tozzi, R.; Risi, R.; Tuccinardi, D.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Lubrano, C.; Gnessi, L. Beneficial effects of the ketogenic diet on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; He, J.; Xue, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, S.; Gong, Z. Role of Hypertension on the Severity of COVID-19: A Review. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 78, e648–e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, L.; Fabre, R.; Courjon, J.; Carles, M.; Dellamonica, J.; Pradier, C. Obesity, diabetes, hypertension and severe outcomes among inpatients with coronavirus disease 2019: A nationwide study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Li, M.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, C.; Qin, R.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Du, K.; et al. Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.C.W.; Holt, R.I.G. COVID-19 and diabetes. Diabetes Med. 2020, 37, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.D.C.; Cibien, S.T.; Carnielli-Queiroz, L.; de Araújo, D.C.S.A.; Ayres, L.R.; Borges, B.J.P.; do Bem, D.A.M.G. Impacts of diabetes mellitus on COVID-19: A literature review. Rev. Bras. Pesq. Saúde 2022, 24, 144–155. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Gupta, R.; Ghosh, A.; Misra, A. Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Khunti, K. COVID-19 and Diabetes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssentongo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Witmer, L.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Ba, D.M. Association of COVID-19 with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Arora, A.; Sharma, P.; Anikhindi, S.A.; Bansal, N.; Singla, V.; Khare, S.; Srivastava, A. Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida-Pititto, B.; Dualib, P.M.; Zajdenverg, L.; Dantas, J.R.; de Souza, F.D.; Rodacki, M.; Bertoluci, M.C. Severity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severin, R.; Arena, R.; Lavie, C.J.; Bond, S.; Phillips, S.A. Respiratory Muscle Performance Screening for Infectious Disease Management Following COVID-19: A Highly Pressurized Situation. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sant’Anna, M., Jr.; Carvalhal, R.F.; de Oliveira, F.d.F.B.; Zin, W.A.; Lopes, A.J.; Lugon, J.R.; Guimarães, F.S. Respiratory mechanics of patients with morbid obesity. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2019, 45, e20180311. [Google Scholar]
- Michalakis, K.; Ilias, I. SARS-CoV-2 infection and obesity: Common inflammatory and metabolic aspects. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, W.; Santos-Burgoa, C. Obesity and its implications for COVID-19 mortality. Obesity 2020, 28, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.P.; Zhang, H.P.; Wang, L.; Kang, Y.; Wood, L.G.; Wang, G. Systemic inflammation mediates the detrimental effects of obesity on asthma control. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018, 39, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiodimos, L.; Kokkinidis, D.G.; Li, W.; Karamanis, D.; Ognibene, J.; Arora, S.; Southern, W.N.; Mantzoros, C.S. Severe obesity, increasing age and male sex are independently associated with worse in-hospital outcomes, and higher in-hospital mortality, in a cohort of patients with COVID-19 in the Bronx, New York. Metabolism 2020, 108, 154262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonnet, A.; Chetboun, M.; Poissy, J.; Raverdy, V.; Noulette, J.; Duhamel, A.; Labreuche, J.; Mathieu, D.; Pattou, F.; Jourdain, M.; et al. High Prevalence of Obesity in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Requiring Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Obesity 2020, 28, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.E.; Peters, U. The effect of obesity on lung function. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Murugesan, P.; Huang, K.; Cai, H. NADPH Oxidases and Oxidase Crosstalk in Cardiovascular Diseases: Novel Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 170–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavazos, A.E.; Corsi Romanelli, M.M.; Bandera, F.; Iacobellis, G. Targeting the adipose tissue in COVID-19. Obesity 2020, 28, 1178–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, H.; Karadag, A.S.; Wollina, U. Angiotensin II Receptors: Impact for COVID-19 Severity. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.Q. Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19: Interleukin-6 Receptor Antagonist Tocilizumab may be the Key to Reduce mortality. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhin, I.O.; Lentz, S.R. Mechanisms of Thrombosis in Obesity. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2013, 20, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, F.; Ruf, W. Inflammation, obesity, and thrombosis. Blood 2013, 122, 3415–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, A.; Singh, D. Increased ACE2 expression in bronchial epithelium of COPD patients who are overweight. Obesity 2020, 28, 1586–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruglikov, I.L.; Scherer, P.E. The Role of Adipocytes and Adipocyte-Like Cells in the Severity of COVID-19 Infections. Obesity 2020, 28, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulanandam, B.; Beladi, H.; Chakrabarti, A. Obesity and COVID-19 mortality are correlated. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, E.; Kassim, G.; Soffer, S.; Freeman, R.; Levin, M.A.; Reich, D.L. Severe Obesity as an Independent Risk Factor for COVID-19 Mortality in Hospitalized Patients Younger than 50. Obesity 2020, 28, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, M.D.; Ofori, K.; Rai, A.J. Laboratory Biomarkers in the Management of Patients With COVID-19. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 155, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, A.; Baral, N.; Lamsal, M.; Bataju, M.; Thapa, S. Potential role of biochemical markers in the prognosis of COVID-19 patients. SAGE Open Med. 2022, 10, 20503121221108613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, M.T.; Mohanty, P.K.; Suganthy, K.; Manavalan, J.K.; Alexander, H. Utility of Biochemical Markers in Predicting Severe COVID-19: Experience from a Tertiary Hospital in South India. EJIFCC 2022, 33, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spruit, M.A.; Holland, A.E.; Singh, S.J.; Tonia, T.; Wilson, K.C.; Troosters, T. COVID-19: Interim Guidance on Rehabilitation in the Hospital and Post-Hospital Phase from a European Respiratory Society and American Thoracic Society-coordinated International Task Force. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frota, A.X.; Vieira, M.C.; Soares, C.C.S.; da Silva, P.S.; da Silva, G.M.S.; de Mendes, F.S.N.S.; Mazzoli-Rocha, F.; Veloso, H.H.; da Costa, A.D.; da Lamas, C.C.; et al. Functional capacity and rehabilitation strategies in COVID-19 patients: Current knowledge and challenges. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2021, 54, e07892020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordi, A.F.; Lemos, M.M.; de Souza Marques, D.C.; Ryal, J.J.; da Silva Lalucci, P.P.M.; Marques, M.G.; Amaro Camilo, M.L.; De Paula Ramos, S.; Franzói De Moraes, S.M.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; et al. Effects of a multi-professional intervention on body composition, physical fitness and biochemical markers in overweight COVID-19 survivors: A clinical trial. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1219252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Country | Study Design | Study Period | Age Group or Mean (Years) | Sex (%) | Adults | Mortality (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zahid et al. [27] | United States | Retrospective study | 03/2020–06/2020 | 64 | F 39.0 M 61.0 | 1.274 | NR |
| Salvy et al. [28] | United States | Retrospective study | 03/2020–01/2021 | <65 and ≥ 65 | F 48.5 M 51.5 | 3.861 | 8.6 |
| Stevanovic et al. [29] | Serbia | Prospective observational study | 10/2021–12/2021 | 67 | F 37.0 M 63.0 | 216 | 16.7 |
| Agca et al. [30] | Turkey | Observational, cross-sectional, and retrospective study | 03/2020–05/2020 | 54 | F 42.6 M 57.4 | 284 | 8.0 |
| Gil et al. [31] | Brazil | Prospective observational study | 03/2020–10/2020 | 59.0 ± 15.0 | F 50.0 M 50.0 | 186 | 6.5 |
| Naaraayan et al. [32] | United States | Retrospective study | 03/2020–05/2020 | 71 | F 43.4 M 56.6 | 348 | 40.5 |
| Zeng et al. [33] | China | Retrospective cohort study | 02/2020–04/2020 | 58.5 ± 14.3 | F 49.3 M 50.7 | 3.019 | 2.2 |
| Nakeshbandi et al. [34] | United States | Retrospective cohort study | 03/2020–04/2020 | 68.0 ± 15.0 | F 48.0 M 52.0 | 504 | 43.0 |
| Studies | BMI kg/m² (Mean) | Categorization by BMI kg/m² | Respiratory Support (%) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zahid et al. [27] | 28.7 | Overweight, 4.9% Obesity, 42.2% | 34.0 |
| Salvy et al. [28] | <65 years: 25.8≥65 years: 26.0 | Overweight, 30.7% Obesity, 35.6% | 3.6 |
| Stevanovic et al. [29] | NR | Overweight, 38.4% Obesity, 39.3% | 91.9 |
| Agca et al. [30] | 25.9 | Overweight, 41.0% Obesity, 24.0% | 11.0 |
| Gil et al. [31] | 29.5 ± 6.9 | Obesity, 40.9% | Oxygen therapy, 55.9 NIMV, 7.5 IMV, 3.8 |
| Naaraayan et al. [32] | NR | Overweight, 35.3% Obesity, 34.8% | NR |
| Zeng et al. [33] | NR | Overweight, 38.6% Obesity, 13.2% | NR |
| Nakeshbandi et al. [34] | NR | Overweight, 30.0% Obesity, 43.0% | 22.0 |
| Studies | Laboratory Tests |
|---|---|
| Zahid et al. [27] | Biochemical markers: - CRP: 112 mg/L - creatinine: 1.2 mg/dL - LDH: 484 µ/L - D-dimer: 524 ng/mL - ferritin: 756.05 ng/mL - hemoglobin A1c: 6.6% Hematological markers: - leukocytes: 7.7 K/µL - lymphocytes: 0.9 K/µL - neutrophils: 6.1 K/µl |
| Salvy et al. [28] | NR |
| Stevanovic et al. [29] | Biochemical markers = CRP: 100.0 mg/dL - IL-6: 67.0 pg/mL - ferritin: 877.0 ng/mL - LDH: 780.0 U/L - fibrinogen: 6.59 - PCT: 0.142 µg/L |
| Agca et al. [30] | Biochemical markers = glycemia: 127.0 mg/dL - albumin: 39.0 g/dL - calcium: 8.86 mmol/L - LDH: 267.0 U/L - D-dimer: 0.61 µd/L - CRP: 47.7 mg/mL - PCT: 0.089 µg/L - ferritin: 219.8 ng/mL Hematological markers = leukocytes: 5.9 10⁹/L - Hb: 13.2 g/dL - platelets: 214 10⁹/L - lymphocytes: 1.2 10⁹/L - neutrophils: 3.78 10⁹/L |
| Gil et al. [31] | Biochemical markers = CRP: 92.3 mg/dL - urea: 51.8 mg/dL - D-dimer: 2383.8 ng/mL - creatinine: 1.4 mg/dL Hematological markers = Hb: 12.6 g/L - neutrophils: 6.6 10³/mm³ - lymphocytes: 1.3 10³/mm³ - platelets: 255.8 10³/mm³ |
| Naaraayan et al. [32] | Biochemical markers = CRP: 176.4 mg/L - D-dimer: 1.5 mg/dL |
| Zeng et al. [33] | Biochemical markers = CRP: 2.33 mg/L - uric acid: 287.43 µmol/L - creatinine: 64.5 µmol/L - glycemia: 4.89 mmol/L - urea: 4.41 mmol/L - albumin: 37.26 g/L - ALT: 23.30 U/L - AST: 19.80 U/L - GGT: 30.20 U/L - LDH: 179.10 U/L - TBIL: 9.50 U/L - DBIL: 3.30 U/L - TP: 12.83 seg. - TTPa: 28.03 seg. - D-dimer: 0.42 mg/L Hematological markers = leukocytes: 5.70 10⁹/L - Hb: 123.93 g/L - platelets: 234.01 10⁹/L - lymphocytes: 26.28% - neutrophils: 63.3% |
| Nakeshbandi et al. [34] | NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Paula Silva-Lalucci, M.P.; Marques, D.C.d.S.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Andreato, L.V.; Magnani Branco, B.H. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Complications and Mortality in Individuals with SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040543
de Paula Silva-Lalucci MP, Marques DCdS, Valdés-Badilla P, Andreato LV, Magnani Branco BH. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Complications and Mortality in Individuals with SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2024; 16(4):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040543
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Paula Silva-Lalucci, Marielle Priscila, Déborah Cristina de Souza Marques, Pablo Valdés-Badilla, Leonardo Vidal Andreato, and Braulio Henrique Magnani Branco. 2024. "Obesity as a Risk Factor for Complications and Mortality in Individuals with SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review" Nutrients 16, no. 4: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040543
APA Stylede Paula Silva-Lalucci, M. P., Marques, D. C. d. S., Valdés-Badilla, P., Andreato, L. V., & Magnani Branco, B. H. (2024). Obesity as a Risk Factor for Complications and Mortality in Individuals with SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 16(4), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040543








