The Effects of Yeast Protein on Gut Microbiota in Mice When Compared with Soybean Protein and Whey Protein Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Histopathology
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.6. SCFAs Measurements in Feces
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
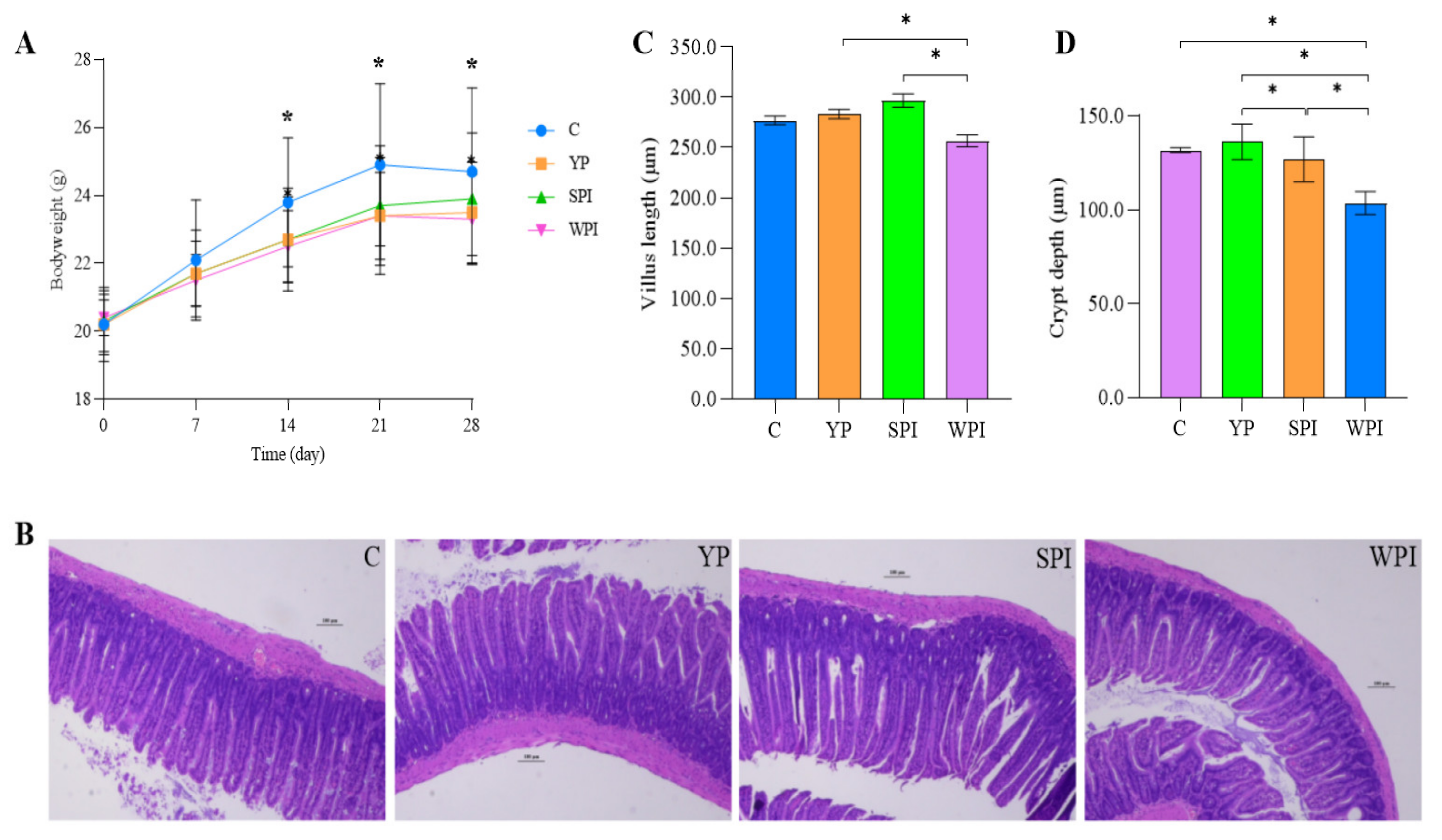
3.1. The Effects of Protein Supplementation on Mouse Body Weight
3.2. Histological Observations
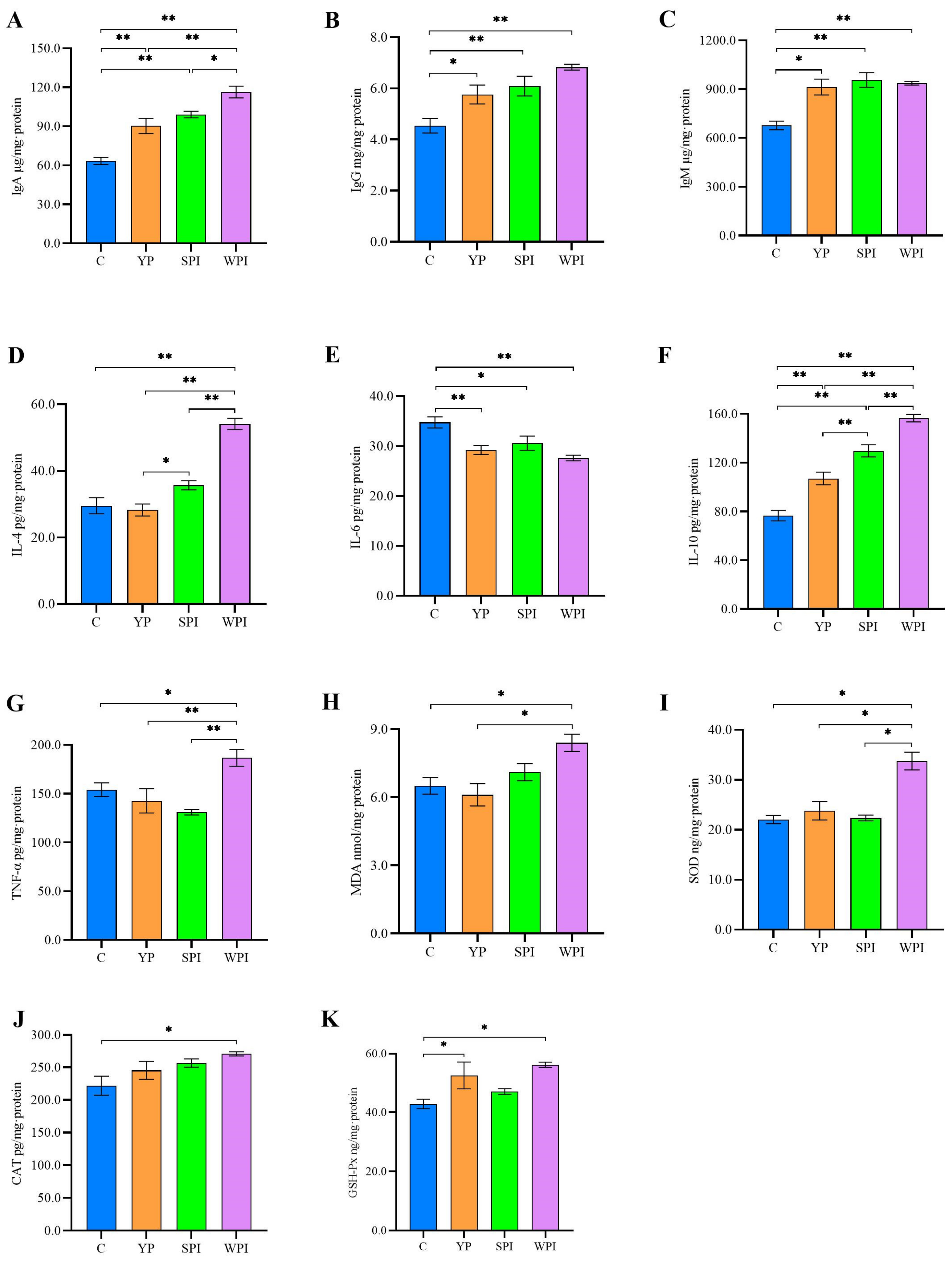
3.3. Immune, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress Levels in Ileum Tissues
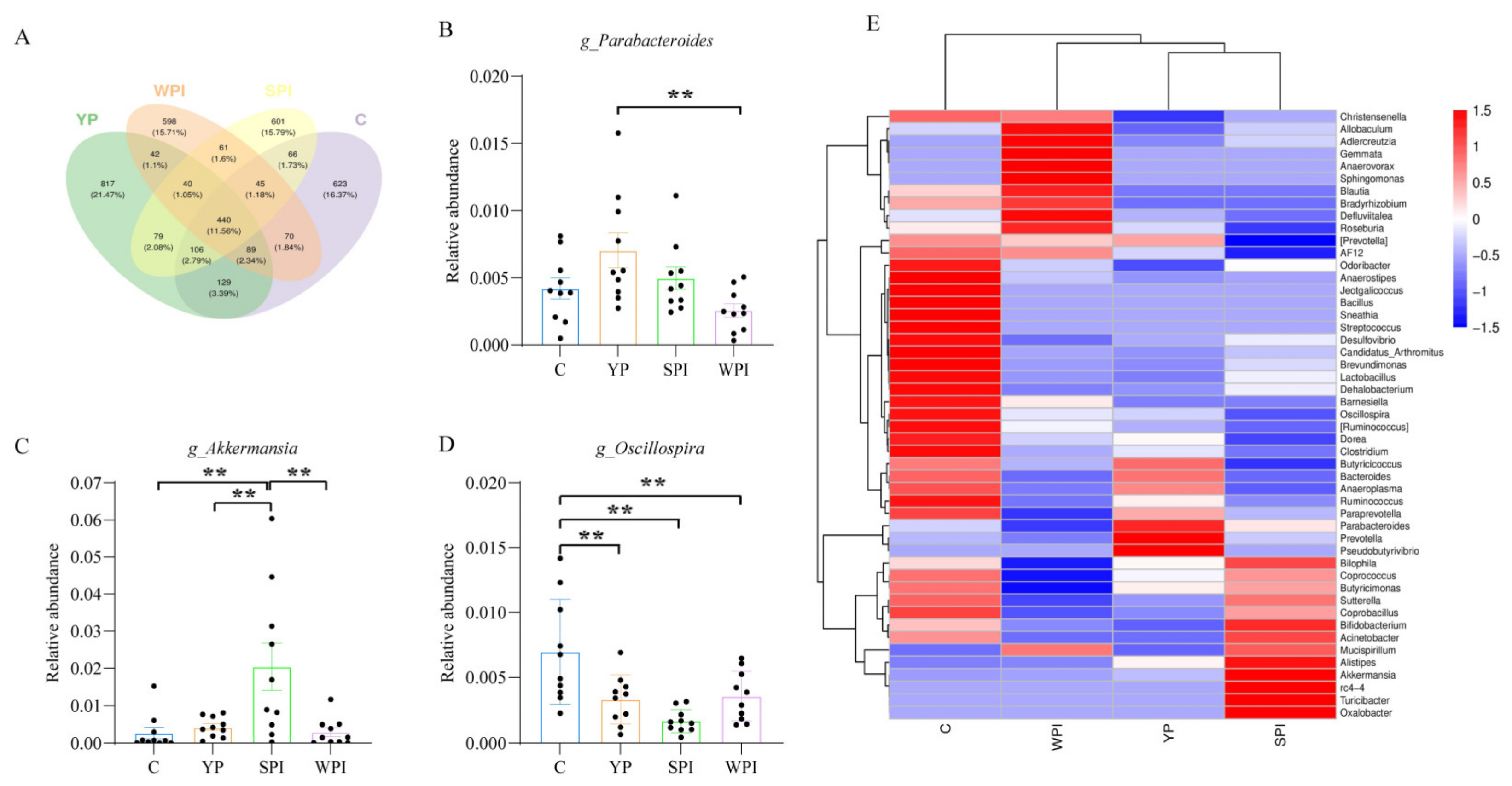
3.4. Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity
3.5. Gut Microbiota Structure and Abundance
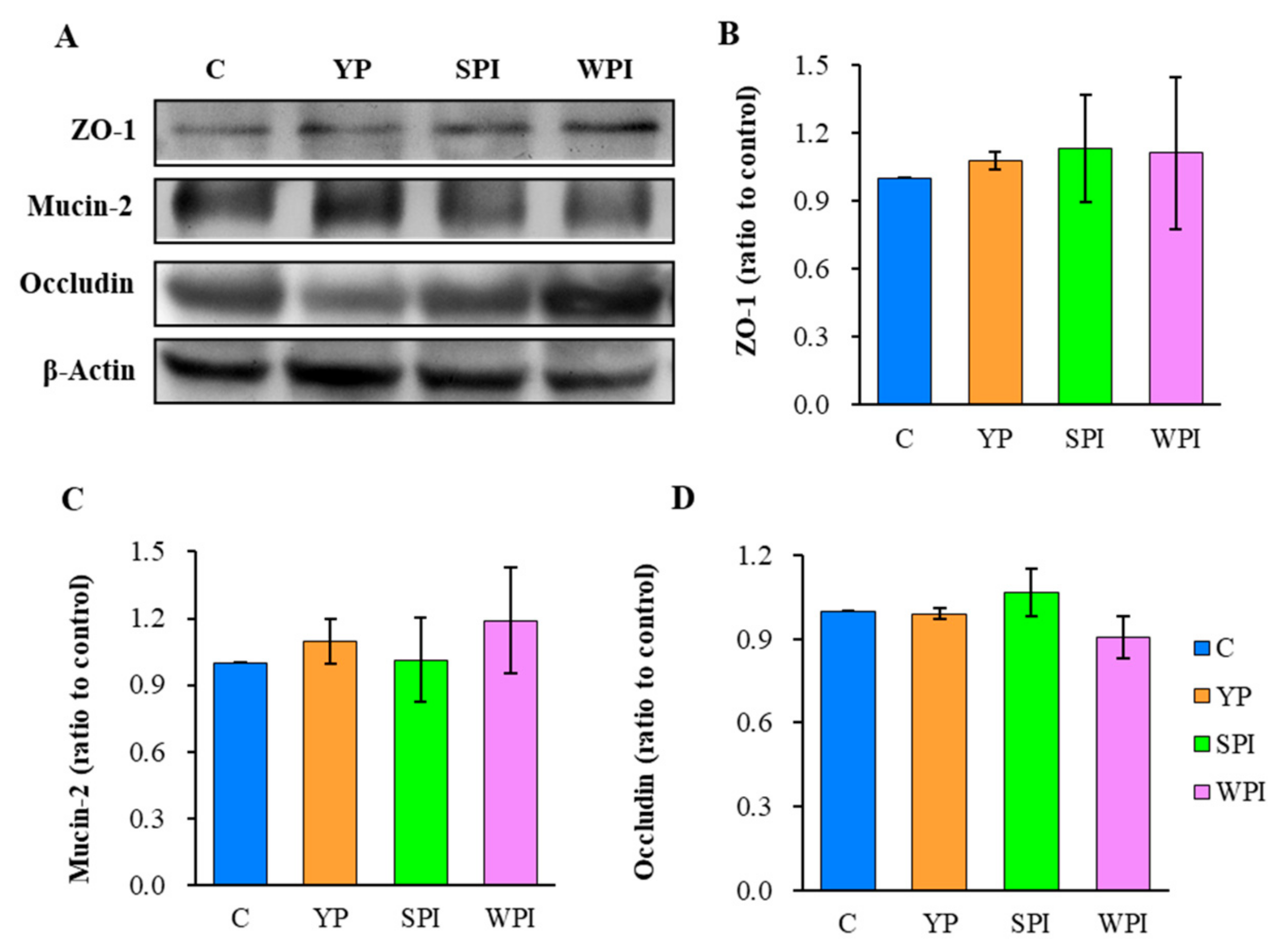
3.6. ZO-1, Occludin, and Mucin-2 Expression Levels in Ileum Tissues
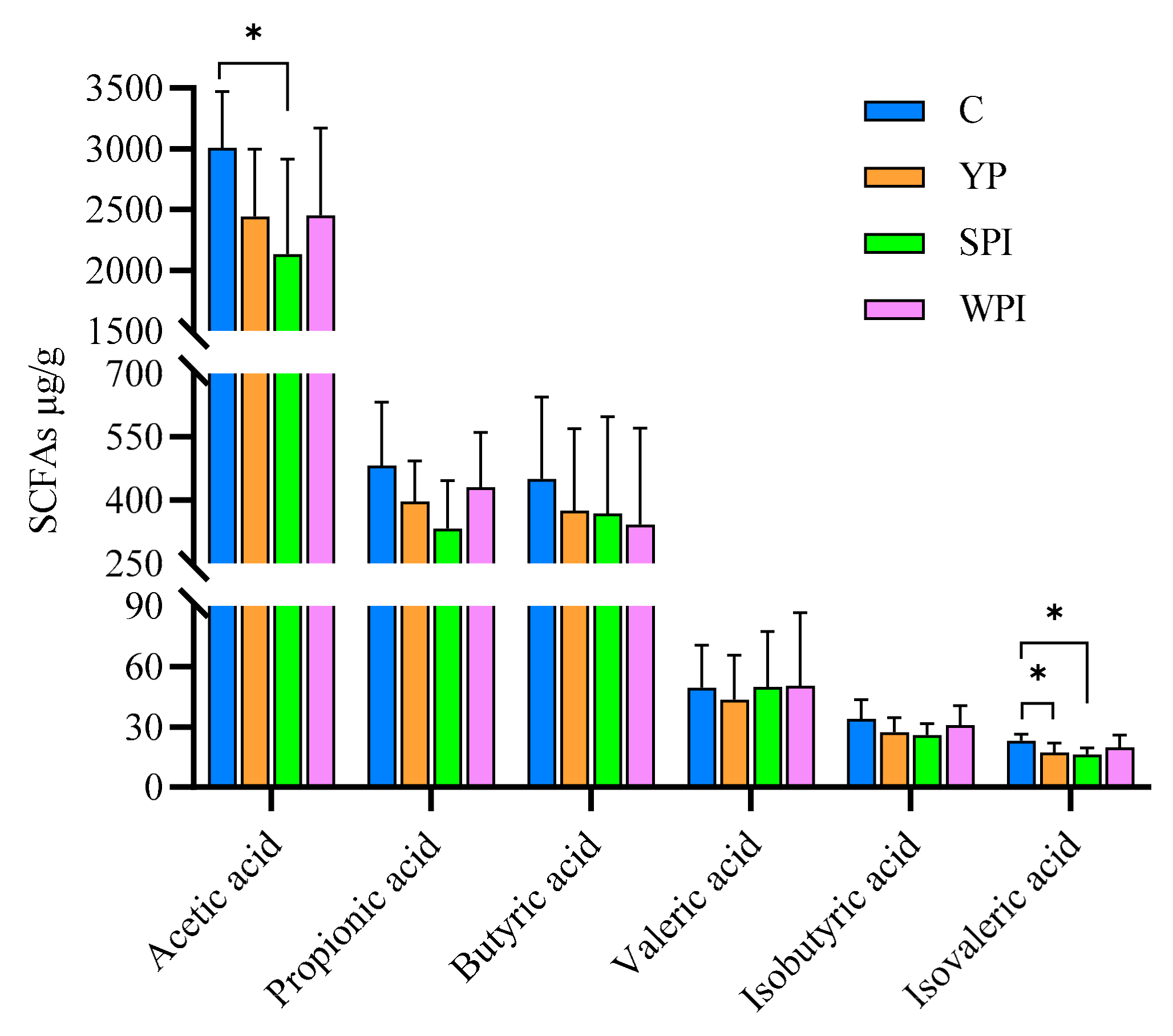
3.7. SCFA Levels in Feces
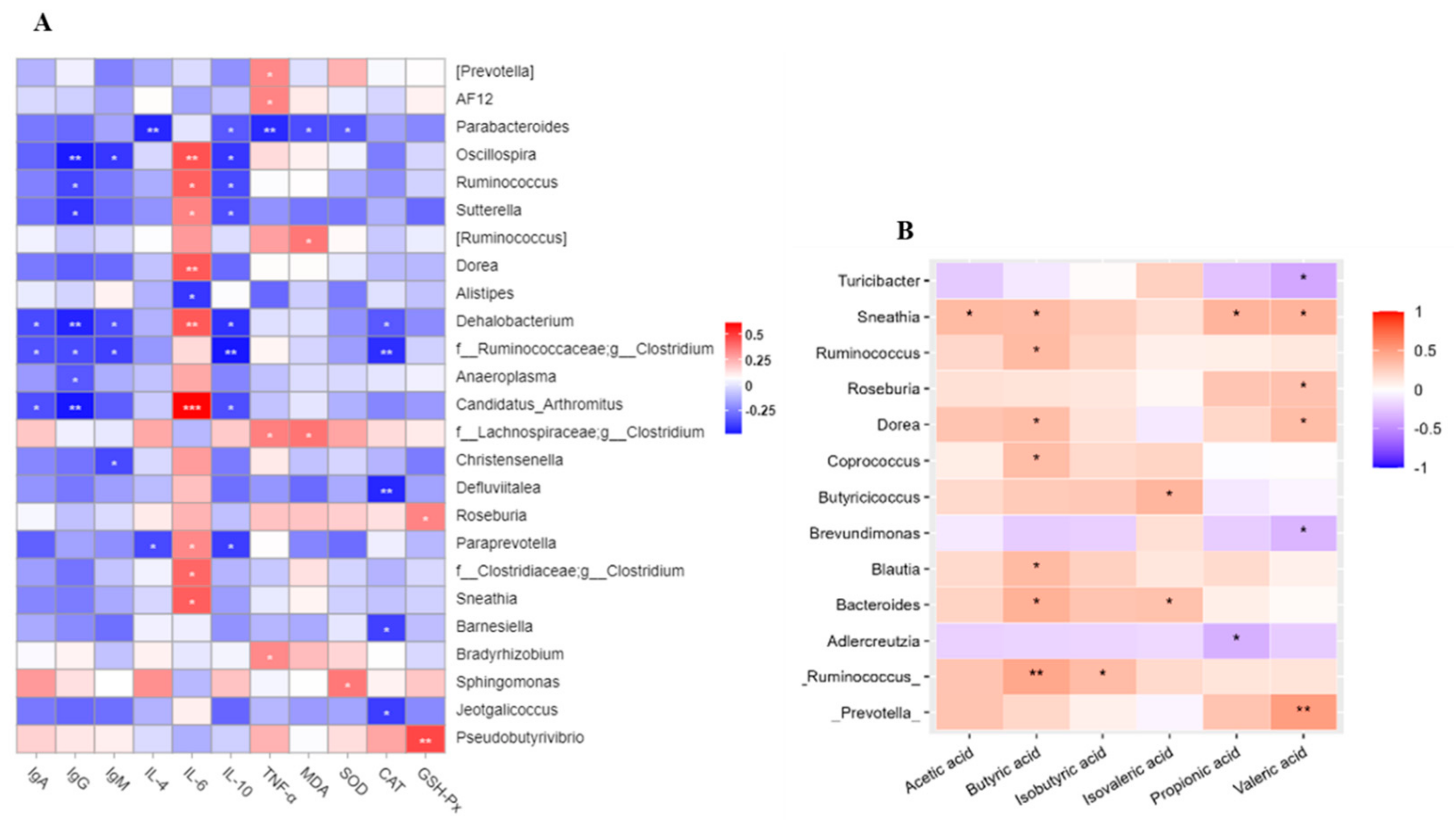
3.8. Correlations Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. YP, SPI, and WPI Supplementation Had Similar Effects with Respect to Body Weight Gain and Epithelial Barrier Function
4.2. Gut Microbiota Alterations and SCFAs’ Generation
4.3. YP Increases Immune and Antioxidant Status by Reducing Inflammation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartlett, A.; Kleiner, M. Dietary protein and the intestinal microbiota: An understudied relationship. iScience 2022, 25, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.T.; Wang, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, G.H.; Li, C.B. Processing method altered mouse intestinal morphology and microbial composition by affecting digestion of meat proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.S.Y.; Daniel, N.; Houde, V.P.; Ouellette, A.; Marcotte, B.; Varin, T.V.; Vors, C.; Feutry, P.; Ilkayeva, O.; Ståhlman, M.; et al. Feeding diversified protein sources exacerbates hepatic insulin resistance via increased gut microbial branched-chain fatty acids and mTORC1 signaling in obese mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, D.; Wang, C.; Li, C. Dietary proteins regulate serotonin biosynthesis and catabolism by specific gut microbes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5880–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.J.; Bhat, Z.F.; Gounder, R.S.; Mohamed Ahmed, I.A.; Al-Juhaimi, F.Y.; Ding, Y.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A. Effect of dietary protein and processing on gut microbiota—A systematic review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, S.; He, K.; Guo, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Zhong, L.; Wu, C.; Peng, X.; et al. Differential effects of dietary white meat and red meat on NAFLD progression by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites in rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6908934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekha, K.; Venkidasamy, B.; Samynathan, R.; Nagella, P.; Rebezov, M.; Khayrullin, M.; Ponomarev, E.; Bouyahya, A.; Sarkar, T.; Shariati, M.A.; et al. Short-chain fatty acid: An updated review on signaling, metabolism, and therapeutic effects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 26, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Piao, X. Different dietary protein sources influence growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immunity, fecal microbiota and metabolites in weaned piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Abrahamsson, T.R.; Jenmalm, M.C.; Harris, K.; Quince, C.; Jernberg, C.; Björkstén, B.; Engstrand, L.; Andersson, A.F. Decreased gut microbiota diversity, delayed Bacteroidetes colonisation and reduced Th1 responses in infants delivered by Caesarean section. Gut 2014, 63, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, D.M.; Pratiwi, Y.S.; Munarko, H.; Suzuki, T. Different dietary protein sources affect the intestinal tight junctions in the colon of mice. Nusant. Sci. Technol. Proc. 2020, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.G.; Shen, S.; Song, J.; Li, K.; Qin, X.W.; Jiang, X.M.; Xue, C.H.; Xue, Y. Physicochemical and structural properties of meat analogues from yeast and soy protein prepared via high-moisture extrusion. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jach, M.E.; Serefko, A.; Ziaja, M.; Kieliszek, M. Yeast protein as an easily accessible food source. Metabolites 2022, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukaegbu-Obi, K.M. Single cell protein—A resort to global protein challenge and waste management. J. Microbiol. Microb. Technol. 2016, 1, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ariëns, R.M.C.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; van de Berg-Somhorst, D.B.P.M.; El Bachrioui, K.; Boudewijn, A.; van den Dool, R.T.M.; de Jong, G.A.H.; Wichers, H.J.; Mes, J.J. Comparing nutritional and digestibility aspects of sustainable proteins using the INFOGEST digestion protocol. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Peng, Z.; Li, D.; Meng, Z.; Xu, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, W. Muscle aging amelioration by yeast protein supplementation was associated with gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 89, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Maqsood, I.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Rong, K. Correlation and Influence of Seasonal Variation of Diet with Gut Microbiota Diversity and Metabolism Profile of Chipmunk. Animals 2022, 12, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Guo, J.; You, Y.; Yin, M.; Ren, C.; Zhan, J.; Huang, W. A fast and accurate way to determine short chain fatty acids in mouse feces based on GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1099, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.-J. A sensitive GC/MS detection method for analyzing microbial metabolites short chain fatty acids in fecal and serum samples. Talanta 2019, 196, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Seo, J.; Yeun, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y.-I.; Chang, S.-Y. The role of mucosal barriers in human gut health. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2021, 44, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigle, D.S.; Breen, P.A.; Matthys, C.C.; Callahan, H.S.; Meeuws, K.E.; Burden, V.R.; Purnell, J.Q. A high-protein diet induces sustained reductions in appetite, ad libitum caloric intake, and body weight despite compensatory changes in diurnal plasma leptin and ghrelin concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Ahmed, M.I.; Zou, X.; Hussain, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, F.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Beef, casein, and soy proteins differentially affect lipid metabolism, triglycerides accumulation and gut microbiota of high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paone, P.; Cani, P.D. Mucus barrier, mucins and gut microbiota: The expected slimy partners? Gut 2020, 69, 2232–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basson, A.R.; Ahmed, S.; Almutairi, R.; Seo, B.; Cominelli, F. Regulation of Intestinal Inflammation by Soybean and Soy-Derived Compounds. Foods 2021, 10, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.R.; Ramsamooj, S.; Liang, R.J.; Katti, A.; Pozovskiy, R.; Vasan, N.; Hwang, S.-K.; Nahiyaan, N.; Francoeur, N.J.; Schatoff, E.M.; et al. Dietary fructose improves intestinal cell survival and nutrient absorption. Nature 2021, 597, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe Rosa, L.; Petersen, P.P.; Görtz, L.F.; Stolzer, I.; Kaden-Volynets, V.; Günther, C.; Bischoff, S.C. Vitamin A- and D-Deficient Diets Disrupt Intestinal Antimicrobial Peptide Defense Involving Wnt and STAT5 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, I. Protein digestibility of cereal products. Foods 2019, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippis, F.D.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; Storia, A.L.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Cagno, R.D.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut 2016, 65, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, N.; Duncan, S.H.; Young, P.; Belenguer, A.; McWilliam Leitch, C.; Scott, K.P.; Flint, H.J.; Louis, P. Phylogenetic distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the human gut microbiota. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ni, D.; Taitz, J.; Pinget, G.V.; Read, M.; Senior, A.; Wali, J.A.; Elnour, R.; Shanahan, E.; Wu, H.; et al. Dietary protein increases T-cell-independent sIgA production through changes in gut microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsopoulou, S.; Pollock, L.; Walker, C.; Tench, W.; Samad, S.S.; Bergey, F.; Lenzi, L.; Sheibani-Tezerji, R.; Rosenstiel, P.; Alam, M.T.; et al. Impact of interleukin 10 deficiency on intestinal epithelium responses to inflammatory signals. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 690817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; van der Veeken, J.; deRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Luo, J.; Xi, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Dietary soy protein isolate attenuates intestinal immunoglobulin and mucin expression in young mice compared with casein. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampen, C.V.; Gauldie, J.; Collins, S.M. Proinflammatory properties of IL-4 in the intestinal microenvironment. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver 2005, 288, G111–G117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Yang, Z.J.; Wang, F.F.; Shang, H.W.; Hua, R.; Xu, J.D. Biological characteristics of IL-6 and related intestinal diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polakowski, C.B.; Kato, M.; Preti, V.B.; Schieferdecker, M.E.M.; Ligocki Campos, A.C. Impact of the preoperative use of synbiotics in colorectal cancer patients: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutrition 2019, 58, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wu, Q.; Le, G.; Shi, Y. Effects of heat treatment on structural modification and in vivo antioxidant capacity of soy protein. Nutrition 2012, 28, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Liang, L.; Sun, B.; Li, K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y. The Effects of Yeast Protein on Gut Microbiota in Mice When Compared with Soybean Protein and Whey Protein Isolates. Nutrients 2024, 16, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030458
Zhou X, Liang L, Sun B, Li K, Guo H, Zhang Y. The Effects of Yeast Protein on Gut Microbiota in Mice When Compared with Soybean Protein and Whey Protein Isolates. Nutrients. 2024; 16(3):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030458
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xuewei, Li Liang, Baoguo Sun, Ku Li, Hui Guo, and Yuyu Zhang. 2024. "The Effects of Yeast Protein on Gut Microbiota in Mice When Compared with Soybean Protein and Whey Protein Isolates" Nutrients 16, no. 3: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030458
APA StyleZhou, X., Liang, L., Sun, B., Li, K., Guo, H., & Zhang, Y. (2024). The Effects of Yeast Protein on Gut Microbiota in Mice When Compared with Soybean Protein and Whey Protein Isolates. Nutrients, 16(3), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030458




