Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Beneficially Modulates Gut Microbiome in a Preclinical Model of Crohn’s-like Colitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Induction of Crohn’s-like Colitis and EEN Treatment
2.3. Colonic Tissue Preparations and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.4. Microbiome Analysis
2.4.1. Fecal DNA Extraction
2.4.2. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
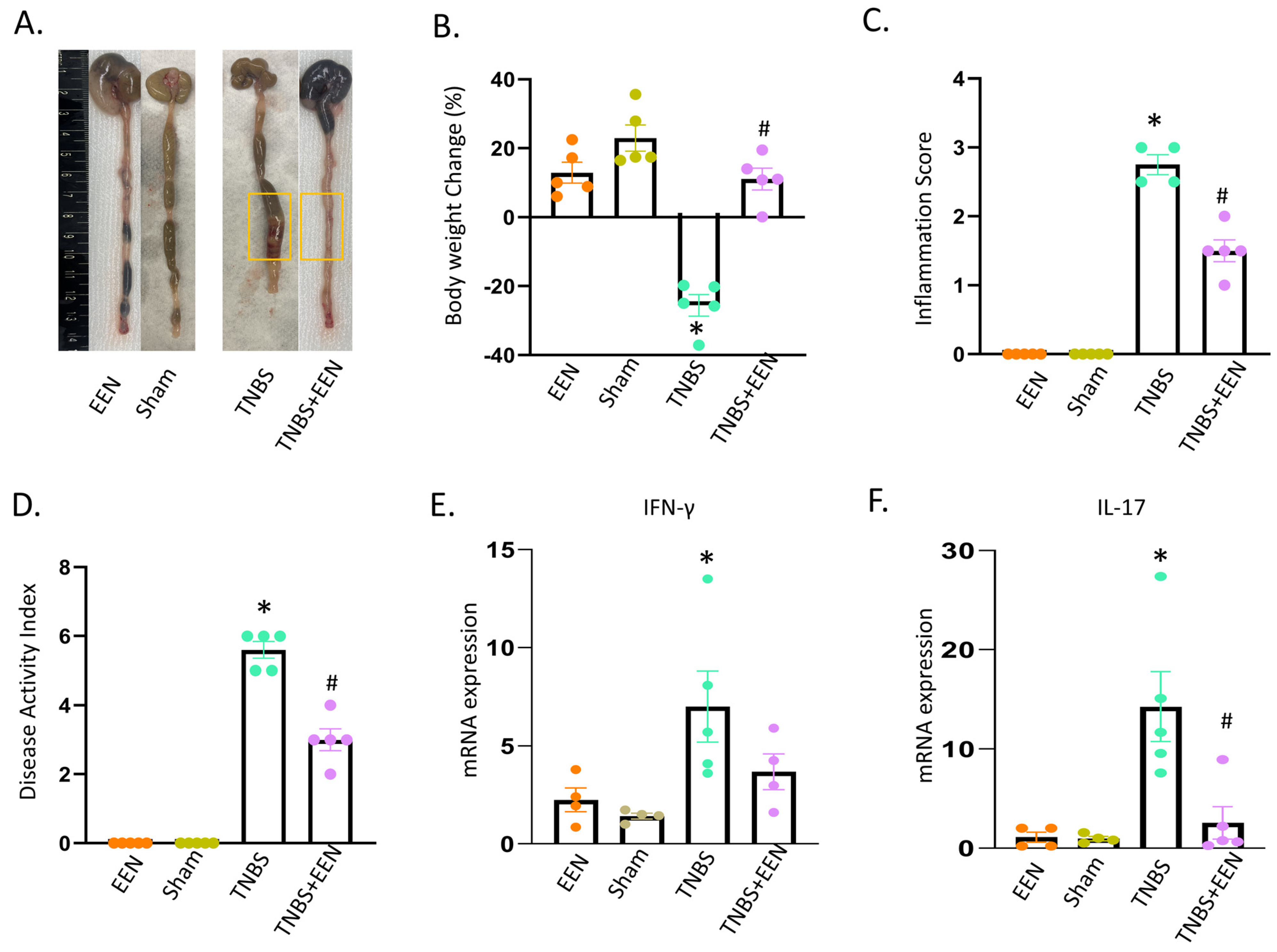
3.1. EEN Treatment Improves Intestinal Inflammation in the Rat Model of Crohn’s-like Colitis
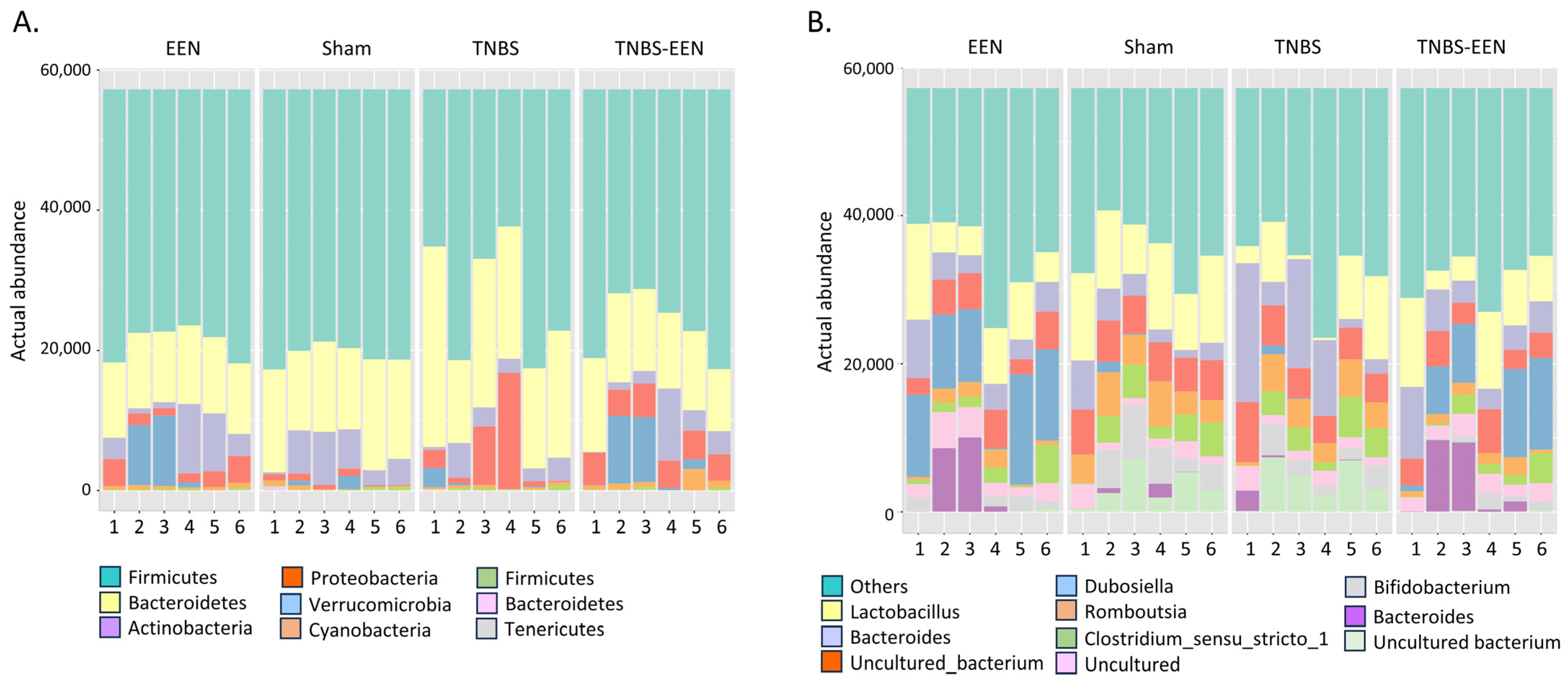
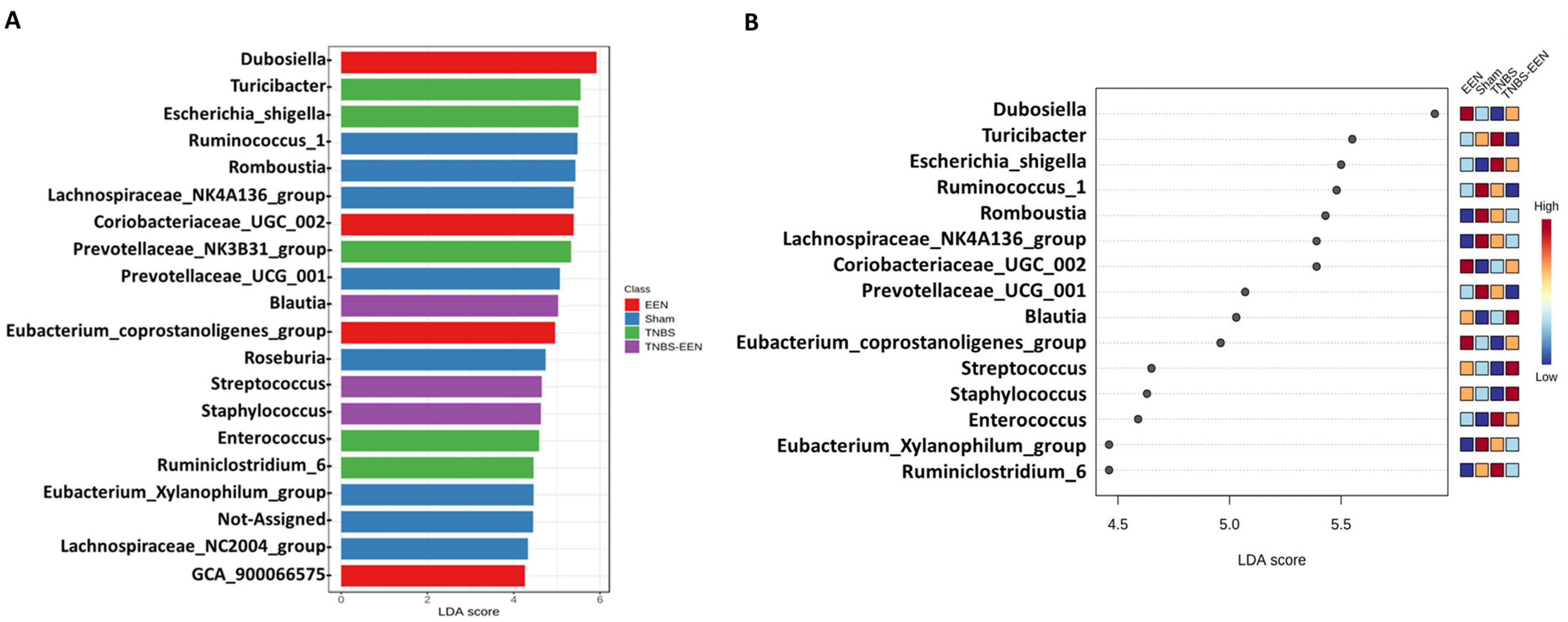
3.2. EEN Treatment Enriches the Diversity and Preserves Structure of the Gut Microbiota
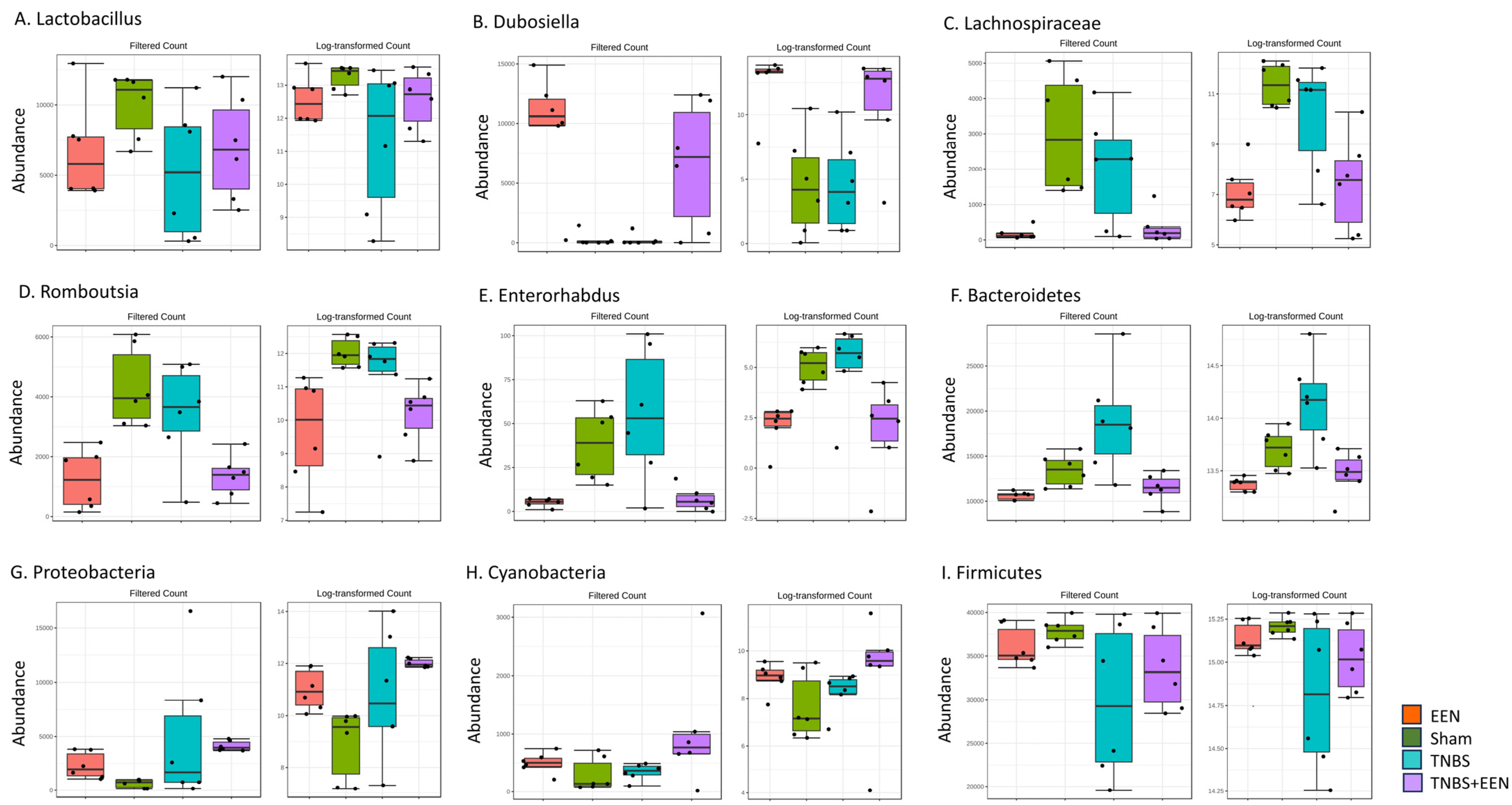
3.3. EEN Treatment Alters the Bacterial Composition at Phylum and Genus Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sartor, R.B. Mechanisms of disease: Pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 3, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, J.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Nguyen, H.T. Infectious etiopathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12102–12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joossens, M.; Huys, G.; Cnockaert, M.; De Preter, V.; Verbeke, K.; Rutgeerts, P.; Vandamme, P.; Vermeire, S. Dysbiosis of the faecal microbiota in patients with Crohn’s disease and their unaffected relatives. Gut 2011, 60, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caio, G.; Lungaro, L.; Caputo, F.; Zoli, E.; Giancola, F.; Chiarioni, G.; De Giorgio, R.; Zoli, G. Nutritional Treatment in Crohn’s Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rheenen, P.F.; Aloi, M.; Assa, A.; Bronsky, J.; Escher, J.C.; Fagerberg, U.L.; Gasparetto, M.; Gerasimidis, K.; Griffiths, A.; Henderson, P.; et al. The Medical Management of Paediatric Crohn’s Disease: An ECCO-ESPGHAN Guideline Update. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.; Macdonald, S.; Hill, S.M.; Thomas, A.; Murphy, M.S. Treatment of active Crohn’s disease in children using partial enteral nutrition with liquid formula: A randomised controlled trial. Gut 2006, 55, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedrychowicz, A.; Kowalska-Duplaga, K.; Jedynak-Wasowicz, U.; Pieczarkowski, S.; Sladek, M.; Tomasik, P.; Fyderek, K. Serum concentrations of VEGF and TGF-β1 during exclusive enteral nutrition in IBD. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, J.M.; Paintin, M.; Arnaud-Battandier, F.; Beattie, R.M.; Hollis, A.; Kitching, P.; Donnet-Hughes, A.; MacDonald, T.T.; Walker-Smith, J.A. Mucosal healing and a fall in mucosal pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA induced by a specific oral polymeric diet in paediatric Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Nakahigashi, M.; Umegae, S.; Kitagawa, T.; Matsumoto, K. Impact of elemental diet on mucosal inflammation in patients with active Crohn’s disease: Cytokine production and endoscopic and histological findings. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2005, 11, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhagamhmad, M.H.; Day, A.S.; Lemberg, D.A.; Leach, S.T. Exploring and Enhancing the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Polymeric Formula. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahidi, L.; Day, A.S.; Lemberg, D.A.; Leach, S.T. Differential effects of nutritional and non-nutritional therapies on intestinal barrier function in an in vitro model. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geesala, R.; Lin, Y.M.; Zhang, K.; Qiu, S.; Shi, X.Z. A TNBS-Induced Rodent Model to Study the Pathogenic Role of Mechanical Stress in Crohn’s Disease. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 2022, e63499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, N.S.; Leach, S.T.; Day, A.S. Polymeric formula has direct anti-inflammatory effects on enterocytes in an in vitro model of intestinal inflammation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, I.R.; Boulton, P.; Menzies, I.; Walker-Smith, J.A. Improvement of abnormal lactulose/rhamnose permeability in active Crohn’s disease of the small bowel by an elemental diet. Gut 1987, 28, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geesala, R.; Zhang, K.; Lin, Y.M.; Johnson, J.C.; Cong, Y.; Cohn, S.; Shi, X.Z. Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Alleviates Th17-Mediated Inflammation via Eliminating Mechanical Stress–Induced Th17-Polarizing Cytokines in Crohn’s-like Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, izad158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quince, C.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Loman, N.; Eren, A.M.; Saulnier, D.; Russell, J.; Haig, S.J.; Calus, S.T.; Quick, J.; Barclay, A.; et al. Extensive Modulation of the Fecal Metagenome in Children with Crohn’s Disease During Exclusive Enteral Nutrition. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Day, A.S.; Leach, S.T.; Lemberg, D.A.; Mitchell, H.M. Reduction in Gut Microbial Diversity as a Mechanism of Action of Exclusive Enteral Nutrition. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Day, A.S.; Leach, S.T.; Lemberg, D.A.; Nielsen, S.; Mitchell, H.M. Effect of exclusive enteral nutrition on the microbiota of children with newly diagnosed Crohn’s disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, E.; Margonis, G.A.; Angelou, A.; Pikouli, A.; Argiri, P.; Karavokyros, I.; Papalois, A.; Pikoulis, E. The TNBS-induced colitis animal model: An overview. Ann. Med. Surg. 2016, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Lin, Y.M.; Golovko, G.; Khanipov, K.; Cong, Y.; Savidge, T.; Fofanov, Y.; Shi, X.Z. Microbiota dysbiosis and its pathophysiological significance in bowel obstruction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.C.; Geesala, R.; Zhang, K.; Lin, Y.M.; M’Koma, A.E.; Shi, X.Z. Smooth muscle dysfunction in the pre-inflammation site in stenotic Crohn’s-like colitis: Implication of mechanical stress in bowel dysfunction in gut inflammation. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1215900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Khanipov, K.; Radnaa, E.; Ganguly, E.; Bento, G.F.C.; Urrabaz-Garza, R.; Kammala, A.K.; Yaklic, J.; Pyles, R.; Golovko, G.; et al. Amplification of microbial DNA from bacterial extracellular vesicles from human placenta. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1213234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtagh, F.; Legendre, P. Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: Which algorithms implement Ward’s criterion? J. Classif. 2014, 31, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, P.T.; Rosas, S.L.B.; Ribeiro, B.E.; Marinho, Y.; de Souza, H.S.P. Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenic Role and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.A.; Gubatan, J. Gut microbiome–based therapeutics in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Transl. Disc. 2023, 3, e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Feng, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Peng, Z.; Li, P.; Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Wu, P.; Fan, Z.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation through mid-gut for refractory Crohn’s disease: Safety, feasibility, and efficacy trial results. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wu, X.; Gao, X.; Lin, R.; Chen, L.; Sun, M.; Jia, J.; Liu, Z.; Fang, L.; Wu, W. Long-term exclusive enteral nutrition remodels the gut microbiota and alleviates TNBS-induced colitis in mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 1725–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, C.L.; Roulet, M.; Roy, C.C.; Weber, A. Continuous elemental enteral alimentation in children with Crohn’s disease and growth failure. Gastroenterology 1980, 79, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, S.; Mitchell, H.; Eng, W.; Zhang, L.; Day, A. Sustained modulation of intestinal bacteria by exclusive enteral nutrition used to treat children with Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, P.; Callegari, M.L.; Ferrari, S.; Cavicchi, M.C.; Pozzi, E.; de Martino, M.; Morelli, L. Enteral nutrition, and microflora in pediatric Crohn’s disease. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2005, 29, S173–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerasimidis, K.; Bertz, M.; Hanske, L.; Junick, J.; Biskou, O.; Aguilera, M.; Garrick, V.; Russell, R.K.; Blaut, M.; McGrogan, P.; et al. Decline in Presumptively Protective Gut Bacterial Species and Metabolites Are Paradoxically Associated with Disease Improvement in Pediatric Crohn’s Disease During Enteral Nutrition. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 861–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Fang, L.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Lv, L.; Niu, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W. Exploring Different Effects of Exclusive Enteral Nutrition (EEN) and Corticosteroids on the Gut Microbiome in Crohn’s Disease Based on a Three-Stage Strategy. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 6147124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Precone, V.; Casaburi, G.; Miele, E.; Martinelli, M.; Staiano, A.; Salvatore, F.; Sacchetti, L. An altered gut microbiome profile in a child affected by Crohn’s disease normalized after nutritional therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, L.; Farbod, Y.; Szamosi, J.C.; Yamamoto, M.; Britz-McKibbin, P.; Halgren, C.; Zachos, M.; Pai, N. Effect of Exclusive Enteral Nutrition and Corticosteroid Induction Therapy on the Gut Microbiota of Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Peng, K.; Xiao, S.; Long, Y.; Yu, Q. The role of Lactobacillus in inflammatory bowel disease: From actualities to prospects. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-h.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.-y.; Zhao, L.; Sheng, Y.-y.; Tao, G.-s.; Xue, Y.-z. Gut microbial characteristical comparison reveals potential anti-aging function of Dubosiella newyorkensis in mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1133167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, F.; Han, H.; Zhong, R.; Wang, M.; Tang, S.; Zhang, S.; Hou, F.; Yi, B.; Zhang, H. Dihydroquercetin supplement alleviates colonic inflammation potentially through improved gut microbiota community in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11420–11434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geesala, R.; Recharla, N.; Zhang, K.; Johnson, J.C.; Golovko, G.; Khanipov, K.; Brining, D.L.; Shi, X.-Z. Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Beneficially Modulates Gut Microbiome in a Preclinical Model of Crohn’s-like Colitis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030363
Geesala R, Recharla N, Zhang K, Johnson JC, Golovko G, Khanipov K, Brining DL, Shi X-Z. Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Beneficially Modulates Gut Microbiome in a Preclinical Model of Crohn’s-like Colitis. Nutrients. 2024; 16(3):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030363
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeesala, Ramasatyaveni, Neeraja Recharla, Ke Zhang, John C. Johnson, George Golovko, Kamil Khanipov, Douglas L. Brining, and Xuan-Zheng Shi. 2024. "Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Beneficially Modulates Gut Microbiome in a Preclinical Model of Crohn’s-like Colitis" Nutrients 16, no. 3: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030363
APA StyleGeesala, R., Recharla, N., Zhang, K., Johnson, J. C., Golovko, G., Khanipov, K., Brining, D. L., & Shi, X.-Z. (2024). Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Beneficially Modulates Gut Microbiome in a Preclinical Model of Crohn’s-like Colitis. Nutrients, 16(3), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030363





