Macronutrient Intake and Food Categories’ Contribution to Daily Energy Intake According to BMI in Primary School Children in Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Anthropometric Measurement and Dietary Intake Assessment
2.3. Data Analysis
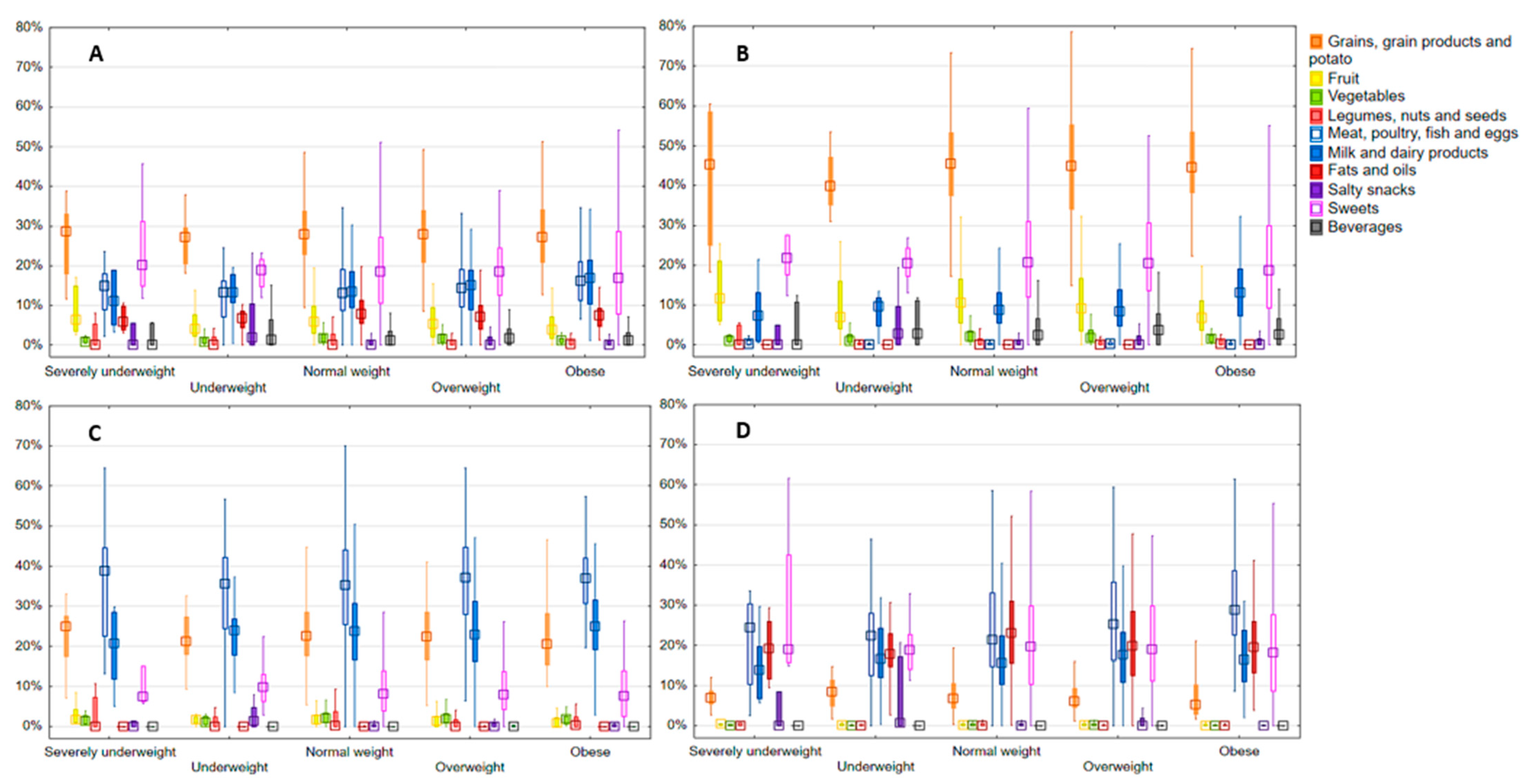
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic and Anthropometric Characteristics
3.2. Energy and Macronutrient Intake and Adherence to DRVs
3.3. Main Food Categories’ Contribution to Energy Intake and Energy from Macronutrients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNICEF. Feeding a child for life. In The State of the World’s Children 2019. Children, Food and Nutrition: Growing Well in a Changing World; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 64–94. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, V.J.B.; Florêncio, T.M.M.; Grillo, L.P.; Do Carmo, P.; Franco, M.; Martins, P.A.; Clemente, A.P.G.; Santos, C.D.L.; de Fatima, A.; Vieira, M.; et al. Long-lasting effects of undernutrition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 1817–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollis, J.L.; Collins, C.E.; DeClerck, F.; Chai, L.K.; McColl, K.; Demaio, A.R. Defining healthy and sustainable diets for infants, children and adolescents. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 27, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Suárez-Varela, M.; Rubio-López, N.; Ruso, C.; Llopis-Gonzalez, A.; Ruiz-Rojo, E.; Redondo, M.; Pico, Y. Anthropometric Status and Nutritional Intake in Children (6–9 Years) in Valencia (Spain): The ANIVA Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 16082–16095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, E.; Krijger, A.; Verkaik-Kloosterman, J.; Elstgeest, L.E.M.; ter Borg, S.; Joosten, K.F.M.; van Rossum, C.T.M. Evaluation of Nutrient Intake and Food Consumption among Dutch Toddlers. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, E.; Marinoni, M.; Fiori, F.; Concina, F.; Ronfani, L.; Dalmin, P.; Barbone, F.; Edefonti, V.; Parpinel, M. Adherence to Dietary Recommendations of 7-Year_Old Children from a Birth Cohort in Friuli Venezia Giulia, Italy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, D.; He, M.; Han, D.; Su, D.; Zhang, R. Food and Nutrient Intake in Children and Adolescents with or without Overweight/Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Report on the Fifth Round of Data Collection, 2018–2020: WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (COSI); WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Musić Milanović, S.; Križan, H.; Lang Morović, M.; Meštrić, S.; Šlaus, N.; Pezo, A. Europska Inicijativa Praćenja Debljine u Djece, Hrvatska 2021/2022. (CroCOSI); Croatian Institute of Public Health: Zagreb, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nittari, G.; Scuri, S.; Petrelli, F.; Pirillo, I.; di Luca, N.M.; Grappasonni, I. Fighting obesity in children from European World Health Organization member states. Epidemiological data, medical-social aspects, and prevention programs. Clin. Ter. 2019, 170, e223–e230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hyska, J.; Burazeri, G.; Menza, V.; Dupouy, E. Assessing nutritional status and nutrition-related knowledge, attitudes and practices of Albanian schoolchildren to support school food and nutrition policies and programmes. Food Policy 2020, 96, 101888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babio, N.; Becerra-Tomás, N.; Nishi, S.K.; López-González, L.; Paz-Graniel, I.; García-Gavilán, J.; Schröder, H.; Martín-Calvo, N.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Total dairy consumption in relation to overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto da Costa, M.; Durão, C.; Lopes, C.; Vilela, S. Adherence to a healthy eating index from pre-school age to its association with sociodemographic and early life factors. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, S.; Oliveira, A.; Pinto, E.; Moreira, P.; Barros, H.; Lopes, C. The influence of socioeconomic factors and family context on energy-dense food consumption among 2-year-old children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyttälä, P.; Erkkola, M.; Lehtinen-Jacks, S.; Ovaskainen, M.-L.; Uusitalo, L.; Veijola, R.; Simell, O.; Knip, M.; Virtanen, S.M. Finnish Children Healthy Eating Index (FCHEI) and its associations with family and child characteristics in pre-school children. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2519–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demory-Luce, D.; Morales, M.; Nicklas, T.; Baranowski, T.; Zakeri, I.; Brenson, G. Changes in food Group Consumption Patterns from Childhood to Young Adulthood: The Bogalusa Heart Study. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardon, G.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Iotova, V.; Latomme, J.; Socha, P.; Koletzko, B.; Moreno, L.; Manios, Y.; Androutsos, O.; De Craemer, M. Health related behaviors in normal weight and overweight preschoolers of a large Pan-European sample: The ToyBox-Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, A.; Androutsos, O.; Chouliaras, G.; Charmandri, E. Do Children and Adolescents with Overweight or Obesity Adhere to the National Food-Based Dietary Guidelines in Greece? Children 2022, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Guidance on the EU Menu methodology. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3944. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolić, D.; Kenjerić, D.; Colić-Barić, I.; Rumbak, I.; Pucarin-Cvetković, J.; Šarlija, N.; Pavlić, M.; Šoher, L. Croatian national food consumption survey on children from 3 months to 9 years of age. EFSA Support. Publ. 2022, 19, 7724E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocké, M.; de Boer, E.; Brants, H.; van der Laan, J.; Niekerk, M.; van Rossum, C.; Temme, L.; Freisling, H.; Nicolas, G.; Casagrande, C.; et al. PANCAKE –Pilot study for the Assessment of Nutrient intake and food Consumption among Kids in Europe. 2012. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.2903/sp.efsa.2012.EN-339 (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO AnthroPlus for Personal Computers Manual: Software for Assessing Growth of the World’s Children and Adolescents; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/growth-reference-data-for-5to19-years (accessed on 23 November 2023).
- de Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaić-Rak, A.; Antonić, K. Tablice Sastava Hrane i Pića [Food and Drink Composition Database]; Zavod za zaštitu zdravlja SR Hrvatske: Zagreb, Croatia, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rumbak, I.; Sokolić, D.; Blažok, T.; Šakić, D.; Vukman, D.; Niseteo, T.; Colić-Barić, I. Validation of photograph series as a portion size measurement aid in dietary assessment in children. Paediatr. Croat. 2019, 63, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolle, E.; Vandevijvere, S.; Ruprich, J.; Ege, M.; Dofková, M.; de Boer, E.; Ocké, M. Validation of a food quantification picture book targeting children of 0–10 years of age for pan- European and national dietary surveys. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Dietary Reference Values for the EU. Available online: https://multimedia.efsa.europa.eu/drvs/index.htm?lang=en (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Zeković, M.; Milešević, J.; Takić, M.; Knez, M.; Šarac, I.; Kadvan, A.; Gurinović, M.; Glibetić, M. Evaluation of Dietary Intake and Anthropometric Status in 1-9-Year-old Children Living in Serbia: National Food Consumption survey According to the EU Menu Methodology. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozza Santos, L.; Formoso Assunção, M.C.; Matijasevich, A.; Santos, I.S.; Barros, A.J.D. Dietary intake patterns of children aged 6 years and their association with socioeconomic and demographic characteristics, early feeding practices and body mass index. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1055. [Google Scholar]
- Zaragoza-Jordana, M.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Luque, V.; Ferré, N.; Grote, V.; Koletzko, B.; Pawellek, I.; Verduci, E.; ReDionigi, A.; Socha, J.; et al. Micronutrient intake adequacy in children from birth to 8 years. Data from the Childhood Obesity Project. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosi, A.; Mena, P.; Castello, F.; Del Rio, D.; Scazzina, F. Comprehensive dietary evaluation of Italian primary school children: Food consumption and intake of energy, nutrients and phenolic compounds. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnard, C.; Fleith, M. Total Fat and Fatty Acid Intake among 1-7-Year-Old children from 33 Countries: Comparison with International Recommendations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, L.; Hwalla, N.; Al Zahraa Chokor, F.; Naja, F.; O’Neill, L.; Jomma, L. Food and nutrient intake of school-aged children in Lebanon and their adherence to dietary guidelines and recommendations. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M.; Steer, C.D.; Hays, N.P.; Emmett, P.M. Growth and body composition in children who are picky eaters: A longitudinal view. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCharty, R.; Kehoe, L.; Flynn, A.; Walton, J. The role of fruit and vegetables in diets of children in Europe: Current state of knowledge on dietary recommendations, intakes and contribution to energy and nutrient intakes. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, D.D.; Brader, L.; Meldgaard Bruun, J. Association between Food, Beverages and Overweight/Obesity in Children and Adolescents-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health. National Dietary Guidelines for Children in Primary Schools; Ministry of Health: Zagreb, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Arnesen, E.K.; Thorisdottir, B.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Bärebring, L.; Nwaru, B.; Dierkes, J.; Ramel, A.; Åkesson, A. Protein intake in children and growth and risk of overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Nutr. Res. 2022, 66, 8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čačić Kenjerić, D.; Sokolić, D. Food, nutrition and health in Croatia. In Nutritional and Health Aspects of Food in the Balkans; Gostin, A.-I., Bogueva, D., Kakurinov, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Farajian, P.; Risvas, G.; Karasouli, K.; Pounis, G.D.; Kastorini, C.M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Zampelas, A. Very high childhood obesity prevalence and low adherence rates to the Mediterranean diet in Greek children: The GRECO study. Atherosclerosis 2011, 217, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, J.L.; Landry, A.S.; Tussing-Humphrey, L.M.; Goodman, M.H. Diet quality of children in the United States by body mass index and sociodemographic characteristics. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2020, 6, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (N = 476) | Severely Underweight (n = 7; 1.5%) | Underweight (n = 12; 2.5%) | Normal Weight (n = 325; 68.3%) | Overweight (n = 84; 17.6%) | Obese (n = 48; 10.1%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | ||||||
| Boys | 260 (54.6) | 4 (57.1) | 8 (66.7) | 165 (50.8) | 53 (63.1) | 30 (62.5) |
| Girls | 216 (45.4) | 3 (42.9) | 4 (33.3) | 160 (49.2) | 31 (36.9) | 18 (37.5) |
| Age, mean (sd) | 7.7 (1.1) | 7.6 (0.7) | 7.2 (1.1) | 7.7 (1.1) | 7.8 (1.1) | 7.9 (1.0) |
| n (%) | ||||||
| 6 y | 146 (30.7) | 1 (14.2) | 6 (50.0) | 103 (31.7) | 24 (28.6) | 12 (25.0) |
| 7 y | 131 (27.5) | 3 (42.9) | 3 (25.0) | 81 (24.9) | 27 (32.1) | 17 (35.3) |
| 8 y | 130 (27.3) | 3 (42.9) | 2 (16.7) | 93 (28.6) | 19 (22.6) | 13 (27.1) |
| 9 y | 69 (14.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (8.3) | 48 (14.8) | 14 (16.7) | 6 (12.5) |
| Antropometric characteristics, mean (sd) | ||||||
| Height (cm) | 131.6 (8.8) | 137.6 (9.1) | 125.8 (5.9) | 130.7 (8.4) | 133.5 (8.8) | 135.0 (10.6) |
| Weight (kg) | 29.2 (7.4) | 21.9 (2.7) | 20.0 (2.0) | 26.7 (4.5) | 33.6 (5.9) | 41.8 (8.9) |
| BMI z-score | 0.32 (1.4) | −3.6 (0.7) | −2.5 (0.3) | −0.17 (0.8) | 1.5 (0.3) | 2.9 (0.8) |
| Season, n (%) | ||||||
| Spring | 109 (22.9) | 3 (42.8) | 3 (25.0) | 74 (22.8) | 16 (19.0) | 13 (27.1) |
| Summer | 110 (23.1) | 1 (14.3) | 3 (25.0) | 81 (24.9) | 17 (20.2) | 8 (16.7) |
| Fall | 149 (31.3) | 2 (28.6) | 2 (16.7) | 94 (28.9) | 35 (41.8) | 16 (33.3) |
| Winter | 108 (22.7) | 1 (14.3) | 4 (33.3) | 76 (23.4) | 16 (19.0) | 11 (22.9) |
| Region, n (%) | ||||||
| Dalmatia region | 88 (18.4) | 1 (14.3) | 3 (25.0) | 59 (18.2) | 19 (22.6) | 6 (12.5) |
| Istria, Primorje and Gorski kotar regions | 42 (8.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 35 (10.8) | 4 (4.8) | 3 (6.3) |
| Lika and Banovina regions | 40 (8.4) | 1 (14.3) | 1 (8.3) | 21 (6.4) | 6 (7.2) | 11 (22.8) |
| Northern Croatia region | 75 (15.8) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (8.3) | 55 (16.9) | 9 (10.7) | 10 (20.8) |
| Slavonia region | 96 (20.2) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (25.0) | 68 (20.9) | 16 (19.0) | 9 (18.8) |
| Zagreb region | 135 (28.4) | 5 (71.4) | 4 (33.4) | 87 (26.8) | 30 (35.7) | 9 (18.8) |
| Physical activity level, n (%) | ||||||
| High | 212 (44.5) | 1 (14.3) | 3 (25.0) | 152 (46.8) | 40 (47.6) | 16 (33.3) |
| Medium | 252 (52.9) | 6 (85.7) | 8 (66.7) | 167 (51.4) | 42 (50.0) | 29 (60.4) |
| Low | 12 (2.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (8.3) | 6 (1.8) | 2 (2.4) | 3 (6.3) |
| Parents education level *, n (%) | ||||||
| High | 343 (72.1) | 6 (85.7) | 11 (91.7) | 238 (73.2) | 62 (73.8) | 26 (54.2) |
| Medium | 122 (25.6) | 1 (14.3) | 1 (8.3) | 80 (24.6) | 21 (25.0) | 19 (39.5) |
| Low | 11 (2.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (2.2) | 1 (1.2) | 3 (6.3) |
| Household income/month, n (%) | ||||||
| Not reported | 46 (9.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (8.3) | 34 (10.5) | 7 (8.3) | 4 (8.3) |
| <378 € | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) |
| 378–757 € | 18 (3.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (2.8) | 4 (4.8) | 5 (10.4) |
| 757–1141 € | 51 (10.7) | 1 (14.3) | 3 (25.0) | 31 (9.5) | 8 (9.5) | 8 (16.7) |
| 1141–1513 € | 98 (20.6) | 1 (14.3) | 2 (16.7) | 66 (20.3) | 14 (16.7) | 15 (31.3) |
| >1513 € | 262 (55.0) | 5 (71.4) | 6 (50.0) | 185 (56.9) | 50 (59.5) | 16 (33.3) |
| DRV Value | Total (N = 476) | Severely Underweight (n = 7; 1.5%) | Underweight (n = 12; 2.5%) | Normal Weight (n = 325; 68.3%) | Overweight (n = 84; 17.6%) | Obese (n = 48; 10.1%) | p Value ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy * (kcal/day) | 1312–2165 | 1598.4 ± 380.3 | 1565.8 ± 269.8 | 1606.6 ± 399.7 | 1607.8 ± 386.7 | 1564.4 ± 389.5 | 1595.9 ± 336.8 | 0.858 |
| % above DRV | 30.7 | 28.6 | 33.3 | 32.0 | 22.0 | 29.2 | ||
| Total fat (g/day) | 63.7 ± 21.5 | 59.9 ± 18.3 | 63.9 ± 21.1 | 63.9 ± 21.5 | 62.4 ± 23.4 | 65.0 ± 19.2 | 0.870 | |
| %E | 20–35%E | 35.4 ± 6.2 | 33.9 ± 6.7 | 35.5 ± 6.1 | 35.3 ± 6.2 | 35.5 ± 6.8 | 36.3 ± 5.4 | |
| % above DRV | 52.1 | 42.9 | 41.7 | 51.4 | 53.6 | 58.3 | ||
| Carbohydrates (g/day) | 194.2 ± 48.9 | 192.8 ± 35.3 | 199.1 ± 55.3 | 195.9 ± 49.6 | 189.3 ± 50.1 | 190.7 ± 42.3 | 0.893 | |
| %E | 45–60%E | 48.9 ± 6.5 | 49.6 ± 6.9 | 49.8 ± 7.0 | 49.0 ± 6.5 | 48.6 ± 7.3 | 48.0 ± 5.4 | |
| % above DRV | 3.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.3 | 4.8 | 0.0 | ||
| Proteins * (g/day) | 0.89–0.92 g/kg bw per day | 55.8 ± 14.1 | 56.7 ± 11.9 | 52.6 ± 14.5 | 56.1 ± 14.6 | 55.2 ± 13.8 | 55.6 ± 11.3 | 0.957 |
| % above DRV | 98.1 | 100 | 100 | 99.4 | 98.8 | 91.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šoher, L.; Čačić Kenjerić, D.; Pavlić, M.; Rumbak, I.; Šarlija, N.; Ilić, A.; Sokolić, D. Macronutrient Intake and Food Categories’ Contribution to Daily Energy Intake According to BMI in Primary School Children in Croatia. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16244400
Šoher L, Čačić Kenjerić D, Pavlić M, Rumbak I, Šarlija N, Ilić A, Sokolić D. Macronutrient Intake and Food Categories’ Contribution to Daily Energy Intake According to BMI in Primary School Children in Croatia. Nutrients. 2024; 16(24):4400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16244400
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠoher, Lidija, Daniela Čačić Kenjerić, Martina Pavlić, Ivana Rumbak, Nataša Šarlija, Ana Ilić, and Darja Sokolić. 2024. "Macronutrient Intake and Food Categories’ Contribution to Daily Energy Intake According to BMI in Primary School Children in Croatia" Nutrients 16, no. 24: 4400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16244400
APA StyleŠoher, L., Čačić Kenjerić, D., Pavlić, M., Rumbak, I., Šarlija, N., Ilić, A., & Sokolić, D. (2024). Macronutrient Intake and Food Categories’ Contribution to Daily Energy Intake According to BMI in Primary School Children in Croatia. Nutrients, 16(24), 4400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16244400









