The Impact of the Dietary Inflammatory Index, Fasting Blood Glucose, and Smoking Status on the Incidence and Survival of Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Case–Control Study and a Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Dietary Assessment and DII Score Calculation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
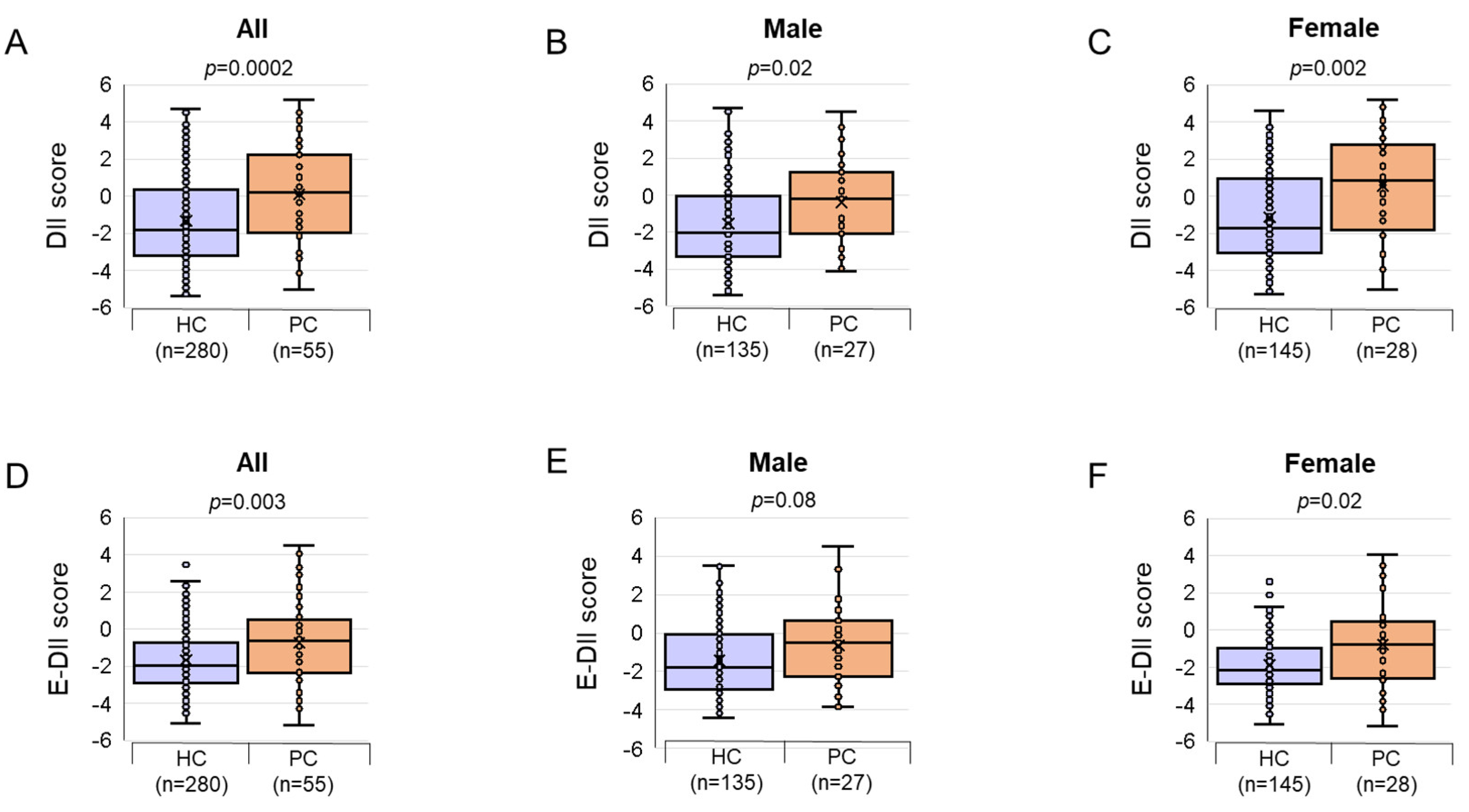
3.1. General and Clinical Characteristics of Patients in the PC and HC Groups
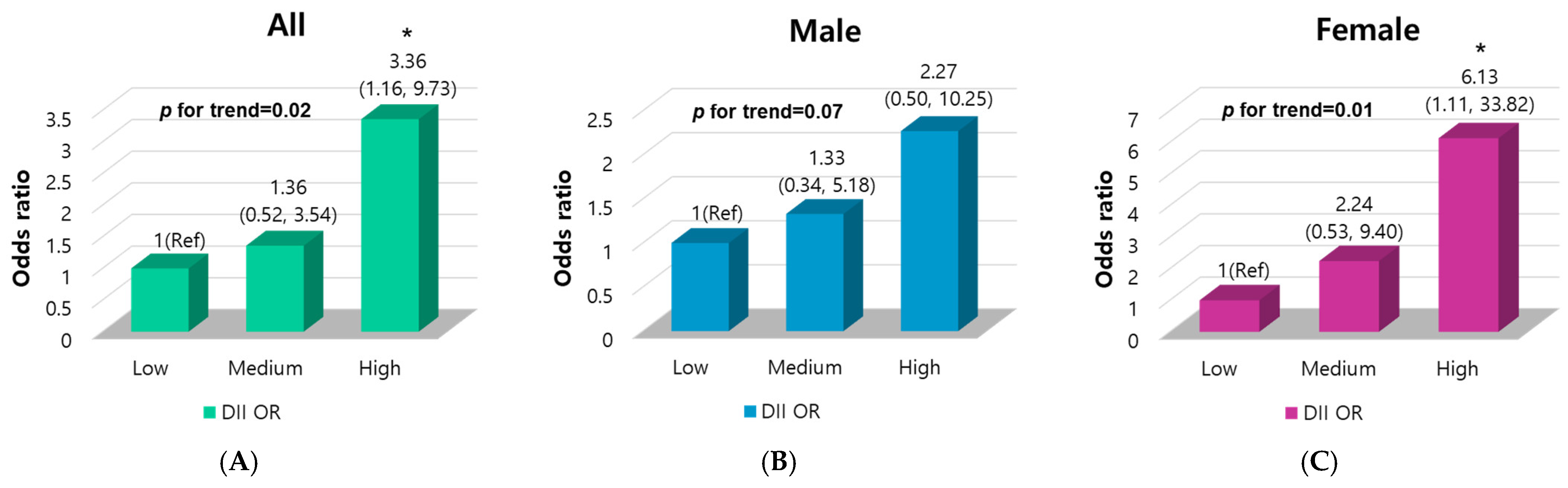
3.2. Association of DII Score with PC Risk
3.3. Associations Between DII Components and PC Risk
3.4. Association of FBG Levels with PC Risk
3.5. Effect of Combination of DII Score with FBG Level or Smoking Status on PC Risk
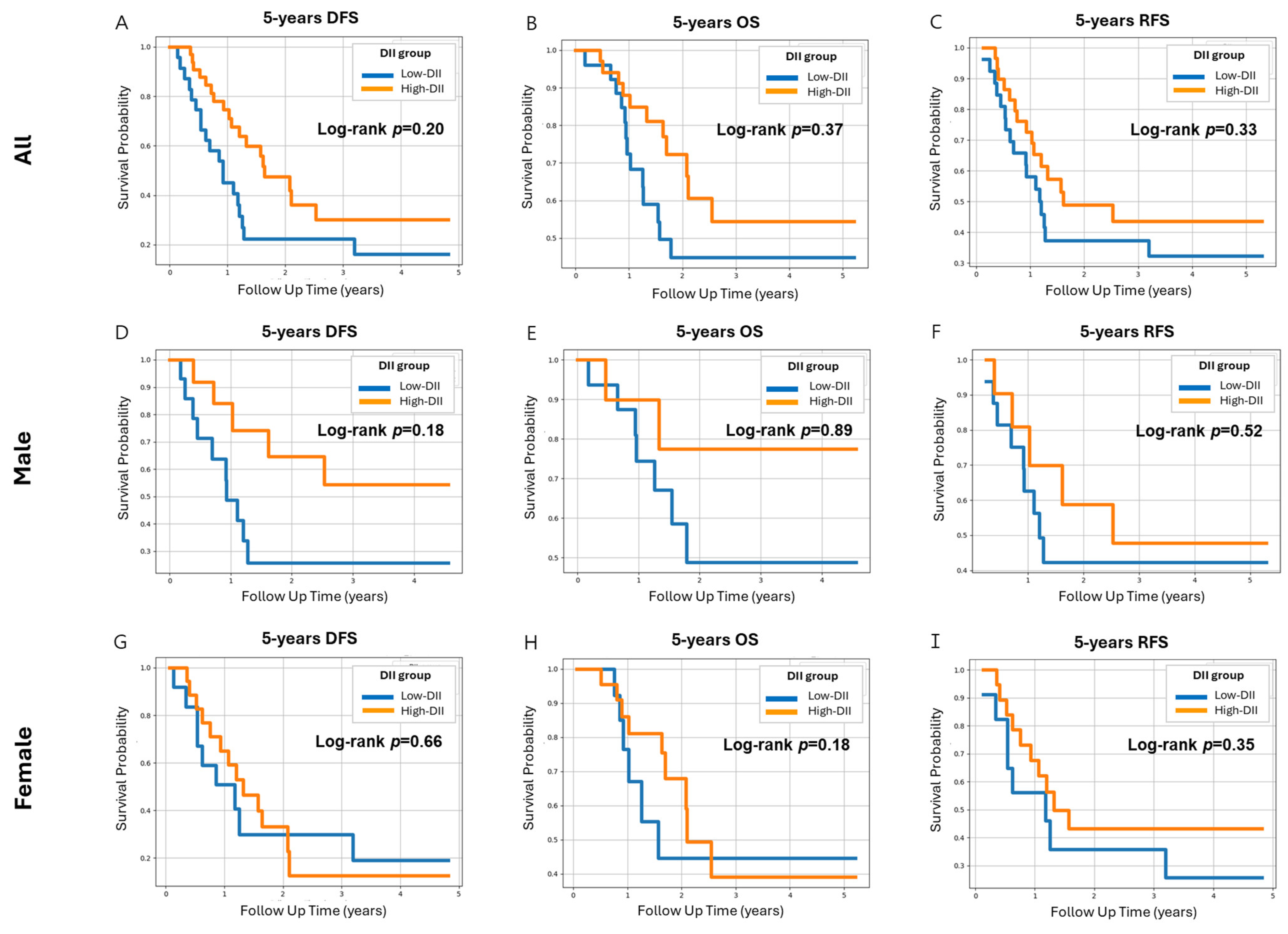
3.6. Effect of Variables on DFS and OS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ilic, I.; Ilic, M. International patterns in incidence and mortality trends of pancreatic cancer in the last three decades: A joinpoint regression analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4698–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.-W.; Kang, M.J.; Park, E.H.; Yun, E.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kong, H.-J.; Im, J.-S.; Seo, H.G. Prediction of cancer incidence and mortality in Korea, 2023. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.-W.; Kang, M.J.; Park, E.H.; Yun, E.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-E.; Kong, H.-J.; Im, J.-S.; Seo, H.G. Prediction of cancer incidence and mortality in Korea, 2024. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 56, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoffel, E.M.; Brand, R.E.; Goggins, M. Pancreatic cancer: Changing epidemiology and new approaches to risk assessment, early detection, and prevention. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 752–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.D.; Canto, M.I.; Jaffee, E.M.; Simeone, D.M. Pancreatic cancer: Pathogenesis, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 386–402.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, J.B.; Whitcomb, D.C. Inflammation and pancreatic cancer: An evidence-based review. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.P. Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: Understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannala, R.; Leirness, J.B.; Bamlet, W.R.; Basu, A.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer—Associated diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kandlakunta, H.; Nagpal, S.J.S.; Feng, Z.; Hoos, W.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Model to determine risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with new-onset diabetes. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 730–739.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; de la Fuente, J.; Murad, M.H.; Majumder, S. Chronic pancreatitis is a risk factor for pancreatic cancer and incidence increases with duration of disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e00463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, A.J.; Streicher, S.A.; Stram, D.O.; Wang, S.; Pandol, S.J.; Le Marchand, L.; Setiawan, V.W. Racial/ethnic disparities in weight or BMI change in adulthood and pancreatic cancer incidence: The multiethnic cohort. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 4097–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naudin, S.; Li, K.; Jaouen, T.; Assi, N.; Kyrø, C.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Boutron-Ruault, M.; Rebours, V.; Védié, A.; et al. Lifetime and baseline alcohol intakes and risk of pancreatic cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Sahoo, J.; Kamalanathan, S.; Naik, D.; Mohan, P.; Kalayarasan, R. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: Exploring the two-way traffic. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4939–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, L. Diet and Inflammation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2010, 25, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, M.S. Nutrition and cancer: A review of the evidence for an anti-cancer diet. Nutr. J. 2004, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner-McGrievy, G.; Wirth, M.D.; Hill, K.L.; Dear, E.R.; Hébert, J.R. Examining commonalities and differences in food groups, nutrients, and diet quality among popular diets. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 41, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.R. Chapter 16. What constitutes an anti-inflammatory diet? How does this contrast with a pro-inflammatory diet? In Diet, Inflammation, and Health; Hebert, J.R., Hofseth, L.J., Eds.; Academic Press/Elsevier: London, UK, 2022; pp. 787–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hébert, J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Hong, Y.; Cheng, Y. Dietary inflammatory index and pancreatic cancer risk: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 6427–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Bosetti, C.; Zucchetto, A.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Hébert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of pancreatic cancer in an Italian case–control study. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 113, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, S.O.; Oberg, A.L.; Shivappa, N.; Bamlet, W.R.; Chaffee, K.G.; Steck, S.E.; Hébert, J.R.; Petersen, G.M. Pancreatic cancer: Associations of inflammatory potential of diet, cigarette smoking and long-standing diabetes. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antwi, S.O.; Bamlet, W.R.; Pedersen, K.S.; Chaffee, K.G.; Risch, H.A.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Anderson, K.E.; Bracci, P.M.; Polesel, J.; et al. Pancreatic cancer risk is modulated by inflammatory potential of diet and ABO genotype: A consortia-based evaluation and replication study. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accardi, G.; Shivappa, N.; Di Maso, M.; Hébert, J.R.; Fratino, L.; Montella, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Caruso, C.; Serraino, D.; Libra, M.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index and cancer risk in the elderly: A pooled-analysis of Italian case-control studies. Nutrition 2019, 63–64, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Merchant, A.T.; Wirth, M.D.; Zhang, J.; Antwi, S.O.; Shoaibi, A.; Shivappa, N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Hebert, J.R.; Steck, S.E. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk of pancreatic cancer in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wirth, M.D.; Merchant, A.T.; Zhang, J.; Shivappa, N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Hebert, J.R.; Steck, S.E. Inflammatory potential of diet, inflammation-related lifestyle factors, and risk of pancreatic cancer: Results from the NIH-AARP diet and health study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2019, 28, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qorbani, M.; Zahedi, H.; Djalalinia, S.; Asayesh, H.; Mansourian, M.; Abdar, Z.; Gorabi, A.; Ansari, H.; Noroozi, M. A higher dietary inflammatory index score is associated with a higher risk of incidence and mortality of cancer: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Chung, M.S.; Kang, S.S.; Park, Y. Association between the dietary inflammatory index and risk for cancer recurrence and mortality among patients with breast cancer. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Wei, N.; Du, K.; Jia, Q. Strong association between the dietary inflammatory index (DII) and breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging 2021, 13, 13039–13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Wu, Y.; Gong, J. Dietary inflammatory index and incidence of and death from primary liver cancer: A prospective study of 103,902 American adults. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, B.E.; Wirth, M.D.; Boushey, C.J.; Wilkens, L.R.; Draluck, E.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hofseth, L.; Haiman, C.A.; Le Marchand, L.; et al. The dietary inflammatory index is associated with colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galas, A.; Kulig, J. Low-grade dietary-related inflammation and survival after colorectal cancer surgery. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucchetto, A.; Gini, A.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Stocco, C.; Maso, L.D.; Birri, S.; Serraino, D.; Polesel, J. Dietary inflammatory index and prostate cancer survival. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2398–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Lorca, M.; Salcedo-Bellido, I.; Olmedo-Requena, R.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Amiano, P.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Gracia-Lavedan, E.; Gómez-Acebo, I.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index and prostate cancer risk: MCC-Spain study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.S.; Kang, S.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, K.A.; Moon, J.H.; Chon, S.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, M.K.; et al. 2023 clinical practice guidelines for diabetes management in Korea: Full version recommendation of the Korean diabetes association. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 546–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hussey, J.R.; Hurley, T.G. Perspective: The dietary inflammatory index (DII)—Lessons learned, improvements made, and future directions. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2019, 10, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeja, S.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Kwon, M.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Kim, M.K. dietary inflammatory index and its relationship with cervical carcinogenesis risk in Korean women: A case-control study. Cancers 2019, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schottenfeld, D. Epidemiology: An introduction. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 156, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, T.; Alfredsson, L.; Källberg, H.; Zdravkovic, S.; Ahlbom, A. Calculating measures of biological interaction. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 20, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, T.J.; Bradbury, K.E.; Perez-Cornago, A.; Sinha, R.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Tsugane, S. Diet, nutrition, and cancer risk: What do we know and what is the way forward? BMJ 2020, 368, m511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, B.; Evers, B. Inflammation and the development of pancreatic cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2002, 10, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, U.S.; Tan, B.W.Q.; Vellayappan, B.A.; Jeyasekharan, A.D. ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandy, D.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Growth Factor Mediated Signaling in Pancreatic Pathogenesis. Cancers 2011, 3, 841–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Oh, C.-M.; Park, S.K.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, M.-H.; Ha, E.; Nam, D.J.; Kim, Y.; Yang, E.H.; Lee, H.C.; et al. Fasting blood glucose and risk of incident pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Nappo, F.; Marfella, R.; Giugliano, G.; Giugliano, F.; Ciotola, M.; Quagliaro, L.; Ceriello, A.; Giugliano, D. Inflammatory cytokine concentrations are acutely increased by hyperglycemia in humans: Role of oxidative stress. Circulation 2002, 106, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Gupta, N. Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis. In Fundamentals of Bacterial Physiology and Metabolism; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, D.; Höhn, A. Role of advanced glycation end products in carcinogenesis and their therapeutic implications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 24, 5245–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khangholi, S.; Majid, F.A.A.; Berwary, N.J.A.; Ahmad, F.; Aziz, R.B.A. The mechanisms of inhibition of advanced glycation end products formation through polyphenols in hyperglycemic condition. Planta Medica 2015, 82, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Petroianu, G.; Adem, A. Advanced glycation end products and diabetes mellitus: Mechanisms and perspectives. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengstie, M.A.; Abebe, E.C.; Teklemariam, A.B.; Mulu, A.T.; Agidew, M.M.; Azezew, M.T.; Zewde, E.A.; Teshome, A.A. Endogenous advanced glycation end products in the pathogenesis of chronic diabetic complications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1002710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bagge, S.; Fotheringham, A.K.; Leung, S.S.; Forbes, J.M. Targeting the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in type 1 diabetes. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 1200–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truty, M.J.; Urrutia, R. Basics of TGF-ß and pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 2007, 7, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wu, W.; Huang, C.; Cen, G.; Jiang, T.; Cao, J.; Huang, K.; Qiu, Z. SMAD4 and its role in pancreatic cancer. Tumor Biol. 2014, 36, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, S.; Sun, Y.L. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer: A review. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2646148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandol, S.J.; Apte, M.V.; Wilson, J.S.; Gukovskaya, A.S.; Edderkaoui, M. The burning question: Why is smoking a risk factor for pancreatic cancer? Pancreatology 2012, 12, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, S.; Gandini, S.; Maisonneuve, P.; Lowenfels, A.B. Tobacco and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A review and meta-analysis. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2008, 393, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.S. Tobacco carcinogens, their biomarkers and tobacco-induced cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopczyk, B.; Hoffmann, D.; Bologna, M.; Cunningham, A.J.; Trushin, N.; Akerkar, S.; Boyiri, T.; Amin, S.; Desai, D.; Colosimo, S.; et al. Identification of tobacco-derived compounds in human pancreatic juice. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002, 15, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, K. Tobacco smoke: Involvement of reactive oxygen species and stable free radicals in mechanisms of oxidative damage, carcinogenesis and synergistic effects with other respirable particles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laan, M.; Bozinovski, S.; Anderson, G.P. Cigarette smoke inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced production of inflammatory cytokines by suppressing the activation of activator protein-1 in bronchial epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4164–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Togo, S.; Al-Mugotir, M.; Kim, H.; Fang, Q.; Kobayashi, T.; Wang, X.; Mao, L.; Bitterman, P.; Rennard, S. NF-kappaB mediates the survival of human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to cigarette smoke extract. Respir. Res. 2008, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- for the Australian Ovarian Cancer Study; Nagle, C.M.; Ibiebele, T.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; DeFazio, A.; Webb, P.M. Correction to: The association between the inflammatory potential of diet and risk of developing, and survival following, a diagnosis of ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Kang, Y.; Xu, W.; Yang, X. Association between fasting blood glucose levels at admission and overall survival of patients with pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, C.C.M.; Schneider, F.; Hilfenhaus, G.; Vecchione, L.; Benzing, C.; Ihlow, J.; Fehrenbach, U.; Malinka, T.; Keilholz, U.; Stintzing, S.; et al. Impact of smoking, body weight, diabetes, hypertension and kidney dysfunction on survival in pancreatic cancer patients—A single center analysis of 2323 patients within the last decade. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of the MDPI and/or editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
| Characteristics | PC | HC | p a | OR (95% CI) b | p c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size, n (%) | (n = 55) | (n = 280) | |||
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 27 (49.1%) | 134 (47.9%) | 1.00 | Ref | |
| Female | 28 (50.9%) | 146 (52.1%) | 1.04 (0.58, 1.85) | 0.91 | |
| Age, years | 63.0 (54.5–67.5) | 62.0 (56.0–66.0) | 0.74 | ||
| <60 | 23 (41.8%) | 125 (44.6%) | 1.00 | Ref | |
| ≥60 | 32 (58.2%) | 155 (55.4%) | 0.97 (0.54, 1.74) | 0.92 | |
| Education level | |||||
| <Middle school | 8 (15.1%) | 7 (2.50%) | <0.0001 | Ref | |
| Middle–high school | 31 (58.5%) | 131 (46.8%) | 0.21 (0.07, 0.61) | 0.005 | |
| ≥College | 14 (26.4%) | 142 (50.7%) | 0.09 (0.03, 0.27) | <0.0001 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.9 (21.1–24.6) | 24.2 (22.3–26.4) | 0.0002 | ||
| <23.0 | 28 (50.0%) | 90 (32.1%) | 0.005 | Ref | |
| 23.0–24.9 | 17 (30.9%) | 78 (27.9%) | 1.43 (0.73, 2.80) | 0.30 | |
| ≥25.0 | 10 (18.2%) | 112 (40.0%) | 0.41 (0.18, 0.94) | 0.04 | |
| Smoking | |||||
| Never | 26 (47.3%) | 158 (56.4%) | 0.39 | Ref | |
| Ex | 23 (41.8%) | 91 (32.5%) | 1.54 (0.83, 2.85) | 0.17 | |
| Current | 6 (10.9%) | 31 (11.1%) | 1.18 (0.45, 3.10) | 0.74 | |
| Alcohol drinking | |||||
| Never | 17 (30.9%) | 70 (25.0%) | <0.0001 | Ref | |
| Ex | 18 (32.7%) | 30 (10.7%) | 2.47 (1.12, 5.44) | 0.02 | |
| Current | 20 (36.4%) | 180 (64.3%) | 0.46 (0.23, 0.92) | 0.03 | |
| FBG, mg/dL | 127.5 (107.3–153.5) | 99.0 (92.0–111.0) | <0.0001 | ||
| <126 | 26 (48.1%) | 253 (90.7%) | <0.0001 | Ref | |
| ≥126 | 28 (51.9%) | 26 (9.32%) | 10.1 (5.21, 19.7) | <0.0001 | |
| AJCC staging | |||||
| Unknown | 8 (14.5%) | ||||
| 1 | 4 (7.30%) | ||||
| 2 | 7 (12.7%) | ||||
| 3 | 9 (16.4%) | ||||
| 4 | 27 (49.1%) | ||||
| Category | Logistic Regression | Group | Univariable | Multivariable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | HC | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p a | |||
| FBG | All | Continuous scale | 54 | 279 | 1.03 (1.02~1.04) | <0.0001 | 1.04 (1.03~1.05) | <0.0001 |
| FBG (≥126 mg/dL) | 28 | 26 | 10.5 (5.37~20.5) | <0.0001 | 13.4 (6.24~28.7) | <0.0001 | ||
| FBG (<126 mg/dL) | 26 | 253 | Ref | Ref | ||||
| Male | Continuous scale | 26 | 134 | 1.03 (1.01~1.04) | <0.0001 | 1.03 (1.02~1.05) | <0.0001 | |
| FBG (≥126 mg/dL) | 14 | 20 | 6.65 (2.69~16.4) | <0.0001 | 7.70 (2.65~22.5) | 0.0002 | ||
| FBG (<126 mg/dL) | 12 | 114 | Ref | Ref | ||||
| Female | Continuous scale | 28 | 145 | 1.05 (1.02~1.07) | <0.0001 | 1.05 (1.03~1.08) | <0.0001 | |
| FBG (≥126 mg/dL) | 14 | 6 | 23.2 (7.69~69.8) | <0.0001 | 32.3 (9.28~112.4) | <0.0001 | ||
| FBG (<126 mg/dL) | 14 | 139 | Ref | Ref | ||||
| Exposure | Group | Univariable | Multivariable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | HC | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p a | ||
| Low DII | with FBG <126 mg/dL | 10 | 134 | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| with FBG ≥126 mg/dL | 7 | 16 | 5.86 (1.96~17.6) | 0.001 | 7.50 (2.31~24.4) | 0.0008 | |
| High DII | with FBG <126 mg/dL | 16 | 119 | 1.80 (0.79~4.12) | 0.16 | 1.76 (0.64~4.80) | 0.27 |
| with FBG ≥126 mg/dL | 21 | 10 | 28.1 (10.5~75.7) | <0.0001 | 32.5 (9.85~106.9) | <0.0001 | |
| p for trend | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| RERI/S | 21.5/4.79 | 24.2/4.34 | |||||
| p for interaction | 0.01 | 0.04 | |||||
| Low DII | with non-smoker | 8 | 82 | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | 0.39 | |
| with ex/current smoker | 6 | 69 | 1.34 (0.49~3.65) | 0.57 | 1.67 (0.51~5.46) | 0.13 | |
| High DII | with non-smoker | 18 | 76 | 2.43 (1.00~2.77) | 0.05 | 2.20 (0.79~6.16) | 0.02 |
| with ex/current smoker | 20 | 53 | 3.87 (1.59~9.42) | 0.002 | 3.88 (1.25~12.0) | 0.01 | |
| p for trend | 0.0009 | 0.01 | |||||
| RERI/S | 1.10/1.63 | 1.01/1.54 | |||||
| p for interaction | 0.58 | 0.76 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, G.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Woo, S.M.; Lee, W.J.; Han, S.-S.; Park, S.-J.; Price, S.; Tembo, P.; Hébert, J.R.; Kim, M.K. The Impact of the Dietary Inflammatory Index, Fasting Blood Glucose, and Smoking Status on the Incidence and Survival of Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Case–Control Study and a Prospective Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16223941
Lee GH, Kim YH, Woo SM, Lee WJ, Han S-S, Park S-J, Price S, Tembo P, Hébert JR, Kim MK. The Impact of the Dietary Inflammatory Index, Fasting Blood Glucose, and Smoking Status on the Incidence and Survival of Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Case–Control Study and a Prospective Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(22):3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16223941
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ga Hyun, Yeon Hee Kim, Sang Myung Woo, Woo Jin Lee, Sung-Sik Han, Sang-Jae Park, Sherry Price, Penias Tembo, James R. Hébert, and Mi Kyung Kim. 2024. "The Impact of the Dietary Inflammatory Index, Fasting Blood Glucose, and Smoking Status on the Incidence and Survival of Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Case–Control Study and a Prospective Study" Nutrients 16, no. 22: 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16223941
APA StyleLee, G. H., Kim, Y. H., Woo, S. M., Lee, W. J., Han, S.-S., Park, S.-J., Price, S., Tembo, P., Hébert, J. R., & Kim, M. K. (2024). The Impact of the Dietary Inflammatory Index, Fasting Blood Glucose, and Smoking Status on the Incidence and Survival of Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Case–Control Study and a Prospective Study. Nutrients, 16(22), 3941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16223941







