Dehydration and Suboptimal Sleep Aggravate Early Renal Impairment in Children: Longitudinal Findings from the PROC Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Urine Assays and Outcomes
2.3. Exposure and Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sleep Duration and Renal Impairment in Children
3.2. Hydration Status and Renal Impairment in Children
3.3. Impact of Suboptimal Sleep and Dehydration on Pediatric Renal Impairment
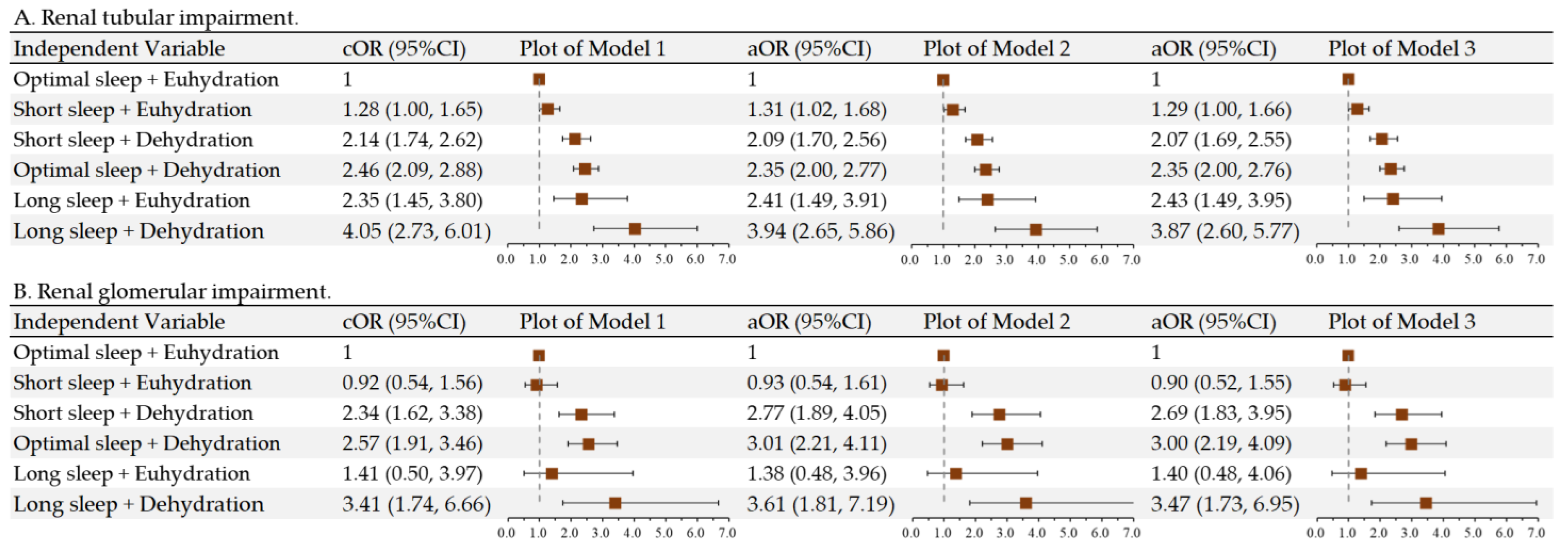
3.4. Interaction of Sleep and Hydration on Pediatric Renal Impairment
3.5. Supporting Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaivada, T.; Oh, C.; Carducci, B.; Bhutta, Z.A. Rationale and Approach to Evaluating Interventions to Promote Child Health in LMICs. Pediatrics 2022, 149, e2021053852B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Tao, L.; Li, C.; Zhong, X.; Wang, H.; Ding, J. The spectrum and changes of biopsy-proven kidney diseases in Chinese children. J. Nephrol. 2022, 36, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Bakker, E.; Bökenkamp, A.; Haffner, D. Assessment of Kidney Function in Children. Pediatr. Clin. 2022, 69, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, V.; Verduci, E.; Vandoni, M.; Rossi, V.; Fiore, G.; Massini, G.; Berardo, C.; Gatti, A.; Baldassarre, P.; Bianchi, A.; et al. The Effect of Healthy Lifestyle Strategies on the Management of Insulin Resistance in Children and Adolescents with Obesity: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Kadam, P.; Yachha, M.; Srivastava, G.; Pillai, A.; Pandita, A. Urinary beta-2 microglobulin as an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury in neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Huang, J.W.; Peng, Y.S.; Hung, K.Y.; Wu, K.D.; Lai, M.S.; Chien, K.L. Microalbuminuria screening for detecting chronic kidney disease in the general population: A systematic review. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Tabara, Y.; Ohler, A.; Gozal, D.; Minami, T.; Kanai, O.; Takeyama, H.; Takahashi, N.; Hamada, S.; et al. Association of Sleep-disordered Breathing and Blood Pressure with Albuminuria: The Nagahama Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022, 19, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Shimbo, T.; Nakata, H.; Kobayashi, D. Longitudinal relationship between long sleep duration and future kidney function decline. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.; Kang, M.W.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.C.; Han, S.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.P.; et al. Short or Long Sleep Duration and CKD: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2937–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Fan, J.; Yuan, F.; Feng, G.; Gong, W.; Song, C.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, A. Association between Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviors, Sleep, Diet, and Adiposity among Children and Adolescents in China. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaerjiang, N.; Xiao, H.; Zunong, J.; Shu, W.; Li, M.; Pérez-Escamilla, R.; Hu, Y. Sleep disturbances in children newly enrolled in elementary school are associated with parenting stress in China. Sleep Med. 2021, 88, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; zhang, N. Improve the drinking water literacy of children and adolescents and to strengthen the study of hydration state and health. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2020, 41, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaerjiang, N.; Li, M.; Xiao, H.; Zunong, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, D.; Vermund, S.H.; Pérez-Escamilla, R.; Jiang, X.; Hu, Y. Dehydration Status Aggravates Early Renal Impairment in Children: A Longitudinal Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shu, W.; Amaerjiang, N.; Xiao, H.; Zunong, J.; Vermund, S.H.; Huang, D.; Hu, Y. Interaction of Hydration Status and Physical Activity Level on Early Renal Damage in Children: A Longitudinal Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 910291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; García-Arroyo, F.E.; Gonzaga-Sánchez, G.; Vélez-Orozco, K.A.; Álvarez-Álvarez, Y.Q.; Aparicio-Trejo, O.E.; Tapia, E.; Osorio-Alonso, H.; Andrés-Hernando, A.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. Current Hydration Habits: The Disregarded Factor for the Development of Renal and Cardiometabolic Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankir, L.; Bichet, D.G.; Morgenthaler, N.G. Vasopressin: Physiology, assessment and osmosensation. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 282, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosinger, A.Y.; Chang, A.M.; Buxton, O.M.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Gao, X. Short sleep duration is associated with inadequate hydration: Cross-cultural evidence from US and Chinese adults. Sleep 2019, 42, zsy1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shu, W.; Zunong, J.; Amaerjiang, N.; Xiao, H.; Li, D.; Vermund, S.H.; Hu, Y. Predictors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Amaerjiang, N.; Li, Z.; Xiao, H.; Zunong, J.; Gao, L.; Vermund, S.H.; Hu, Y. Insufficient Fruit and Vegetable Intake and Low Potassium Intake Aggravate Early Renal Damage in Children: A Longitudinal Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Carson, V.; Chaput, J.P.; Connor Gorber, S.; Dinh, T.; Duggan, M.; Faulkner, G.; Gray, C.E.; Gruber, R.; Janson, K.; et al. Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Children and Youth: An Integration of Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour, and Sleep. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, S311–S327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiao, H.; Shu, W.; Amaerjiang, N.; Zunong, J.; Huang, D.; Hu, Y. Good Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Lowered Risk of Renal Glomerular Impairment in Children: A Longitudinal Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazek, K.; van Zwieten, A.; Saglimbene, V.; Teixeira-Pinto, A. A practical guide to multiple imputation of missing data in nephrology. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzing, T.; Salant, D. Insights into Glomerular Filtration and Albuminuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Ding, C.; Gong, W.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, G.; Song, C.; Liu, A. Association of Sleep Duration and Overweight/Obesity among Children in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.J.; Xin, F.; Liang, G.; Chen, Y. Associations between sleep duration, sleep quality, and weight status in Chinese children and adolescents. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koa, T.B.; Seah, J.X.; Ong, J.Q.W.; Lo, J.C. Short Sleep Duration in School-Age Children: Differential Factors on Weekdays and Weekends. Behav. Sleep Med. 2023, 21, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.; Jacinto, G.; Infante, P.; Engana, T. Primary School Children’s Sleep Habits: Association with Socioeconomic Factors and Physical Activity Habits. Children 2022, 9, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Contreras, C.; Santamaría-Orleans, A.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Zerón-Rugerio, M.F. Sleep dimensions are associated with obesity, poor diet quality and eating behaviors in school-aged children. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 959503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Treviño, I.M.; Arrona-Palacios, A.; Núñez-Rocha, G.M.; Jansen, E.C. Association between self-reported sleep duration and dietary quality in Mexican school-aged children. Appetite 2022, 178, 106177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, F.; Luo, J.; Jing, J. Short sleep duration is associated with specific food intake increase among school-aged children in China: A national cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, N.; Knell, G.; Gabriel, K.P.; Plasqui, G.; Crutzen, R.; Hoor, G.T. Bidirectional Day-to-Day Associations of Reported Sleep Duration with Accelerometer Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Time Among Dutch Adolescents: An Observational Study. J. Meas. Phys. Behav. 2020, 3, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyanga, T.; Barnes, J.D.; Chaput, J.P.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Prista, A.; Tremblay, M.S. Prevalence and correlates of adherence to movement guidelines among urban and rural children in Mozambique: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Wang, H.E.; Liu, Y.C.; Zheng, C.M.; Chu, P.; Lu, K.C.; Chu, C.M.; Chang, Y.T. Sleeping, Smoking, and Kidney Diseases: Evidence from the NHANES 2017–2018. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 745006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Xie, M.; Zhu, L.; Dou, Y.; Dai, M.; Wu, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, Q. Association of sleep duration with chronic kidney disease and proteinuria in adults: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Xiao, H.; Asihaer, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y. Suboptimal hydration status increases the risk of incident MASLD: A pediatric cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, e145–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Boustany, R.; Tasevska, I.; Meijer, E.; Kieneker, L.M.; Enhörning, S.; Lefèvre, G.; Mohammedi, K.; Marre, M.; Fumeron, F.; Balkau, B.; et al. Plasma copeptin and chronic kidney disease risk in 3 European cohorts from the general population. JCI Insight 2018, 3, 121479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, R.M.; Hurtado-Alvarado, G.; Soto-Tinoco, E. Vasopressin: An output signal from the suprachiasmatic nucleus to prepare physiology and behaviour for the resting phase. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 33, e12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colwell, C.S. Preventing dehydration during sleep. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, E.; Bourque, C.W. Central clock excites vasopressin neurons by waking osmosensory afferents during late sleep. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, P.; Silvestre, R.A.; Fernández-Reyes, M.J.; Díez, J.J. The role of copeptin in kidney disease. Endocrine 2022, 79, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, N.S.; Theilade, S.; Winther, S.A.; Tofte, N.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Jeppesen, J.L.; Persson, F.; Hansen, T.W.; Goetze, J.P.; Rossing, P. Copeptin and renal function decline, cardiovascular events and mortality in type 1 diabetes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 37, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Short Sleep (n = 472) | Optimal Sleep (n = 1378) | Long Sleep (n = 64) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys [n (%)] a | 232 (49.2) | 697 (50.6) | 27 (42.2) | 0.39 |
| Age (year) b | 6.6 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.3 | 0.69 |
| Height z-score b | 0.65 ± 0.98 | 0.66 ± 0.96 | 0.80 ± 0.83 | 0.48 |
| Weight z-score b | 0.76 ± 1.40 | 0.68 ± 1.42 | 0.73 ± 1.14 | 0.56 |
| Body mass index z-score b | 0.50 ± 1.53 | 0.36 ± 1.55 | 0.33 ± 1.33 | 0.25 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) b | 101 ± 9 | 101 ± 8 | 102 ± 9 | 0.61 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) b | 56 ± 6 | 56 ± 6 | 57 ± 6 | 0.40 |
| Long screen time (≥2 h/d) a | 28 (5.9) | 67 (4.9) | 0 (0) | 0.12 |
| Insufficient physical activity (<1 h/d) a | 373 (79.0) | 1036 (75.2) | 42 (65.6) | 0.037 |
| Poor Mediterranean diet adherence a | 72 (15.3) | 97 (7.0) | 4 (6.3) | <0.001 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cOR (95% CI) | p | aOR (95% CI) | p | aOR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Renal tubular impairment | Short sleep | 1.04 (0.87, 1.16) | 0.95 | 1.02 (0.88, 1.12) | 0.79 | 1.01 (0.87, 1.17) | 0.91 |
| Optimal sleep | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Long sleep | 1.84 (1.37, 2.48) | <0.001 | 1.89 (1.40, 2.55) | <0.001 | 1.88 (1.39, 2.54) | <0.001 | |
| Renal glomerular impairment | Short sleep | 0.93 (0.72, 1.21) | 0.61 | 0.94 (0.73, 1.23) | 0.67 | 0.91 (0.70, 1.19) | 0.50 |
| Optimal sleep | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Long sleep | 1.35 (0.79, 2.31) | 0.28 | 1.27 (0.74, 2.19) | 0.38 | 1.26 (0.73, 2.18) | 0.40 | |
| Renal tubular impairment | Euhydration | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Dehydration | 2.19 (1.91, 2.50) | <0.001 | 2.10 (1.83, 2.40) | <0.001 | 2.10 (1.83, 2.40) | <0.001 | |
| Renal glomerular impairment | Euhydration | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Dehydration | 2.55 (1.98, 3.29) | <0.001 | 2.98 (2.29, 3.89) | <0.001 | 2.97 (2.27, 3.88) | <0.001 | |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cOR (95% CI) | p | aOR (95% CI) | p | aOR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Renal tubular impairment | Short sleep | 0.99 (0.85, 1.14) | 0.84 | 1.01 (0.87, 1.16) | 0.94 | 1.00 (0.86, 1.16) | 0.98 |
| Optimal sleep | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Long sleep | 1.87 (1.39, 2.53) | <0.001 | 1.91 (1.41, 2.58) | <0.001 | 1.90 (1.40, 2.57) | <0.001 | |
| Euhydration | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Dehydration | 2.19 (1.92, 2.50) | <0.001 | 2.10 (1.84, 2.40) | <0.001 | 2.10 (1.83, 2.40) | <0.001 | |
| Renal glomerular impairment | Short sleep | 0.91 (0.70, 1.19) | 0.50 | 0.92 (0.71, 1.21) | 0.56 | 0.90 (0.68, 1.18) | 0.45 |
| Optimal sleep | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Long sleep | 1.35 (0.79, 2.32) | 0.28 | 1.24 (0.71, 2.17) | 0.44 | 1.22 (0.69, 2.14) | 0.49 | |
| Euhydration | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Dehydration | 2.55 (1.98, 3.29) | <0.001 | 2.98 (2.29, 3.89) | <0.001 | 2.97 (2.27, 3.88) | <0.001 | |
| Group | Exposure | Renal Tubular Impairment | Renal Glomerular Impairment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Optimal sleep | Dehydration | 1 | 1 | ||
| Euhydration | 0.43 (0.36, 0.50) | <0.001 | 0.33 (0.24, 0.46) | <0.001 | |
| Short sleep | Dehydration | 1 | 1 | ||
| Euhydration | 0.62 (0.47, 0.81) | <0.001 | 0.31 (0.17, 0.55) | <0.001 | |
| Long sleep | Dehydration | 1 | 1 | ||
| Euhydration | 0.61 (0.33, 1.13) | 0.11 | 0.44 (0.09, 2.17) | 0.32 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Xiao, H.; Amaerjiang, N.; Thapa, B.; Shu, W.; Asihaer, Y.; Guan, M.; Vermund, S.H.; Zou, Z.; Huang, D.; et al. Dehydration and Suboptimal Sleep Aggravate Early Renal Impairment in Children: Longitudinal Findings from the PROC Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203472
Li M, Xiao H, Amaerjiang N, Thapa B, Shu W, Asihaer Y, Guan M, Vermund SH, Zou Z, Huang D, et al. Dehydration and Suboptimal Sleep Aggravate Early Renal Impairment in Children: Longitudinal Findings from the PROC Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(20):3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203472
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Menglong, Huidi Xiao, Nubiya Amaerjiang, Bipin Thapa, Wen Shu, Yeerlin Asihaer, Mengying Guan, Sten H. Vermund, Zhiyong Zou, Dayong Huang, and et al. 2024. "Dehydration and Suboptimal Sleep Aggravate Early Renal Impairment in Children: Longitudinal Findings from the PROC Study" Nutrients 16, no. 20: 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203472
APA StyleLi, M., Xiao, H., Amaerjiang, N., Thapa, B., Shu, W., Asihaer, Y., Guan, M., Vermund, S. H., Zou, Z., Huang, D., & Hu, Y. (2024). Dehydration and Suboptimal Sleep Aggravate Early Renal Impairment in Children: Longitudinal Findings from the PROC Study. Nutrients, 16(20), 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203472











