Hepatoprotection of a Standardized Extract of Cultured Lentinula edodes Mycelia against Liver Injury Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion and Partial Hepatectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Animals
2.2. Induction of HIRI+PH in Rats
2.3. Histopathological Analysis
2.4. Weight Change of the Remnant Liver
2.5. Serum Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
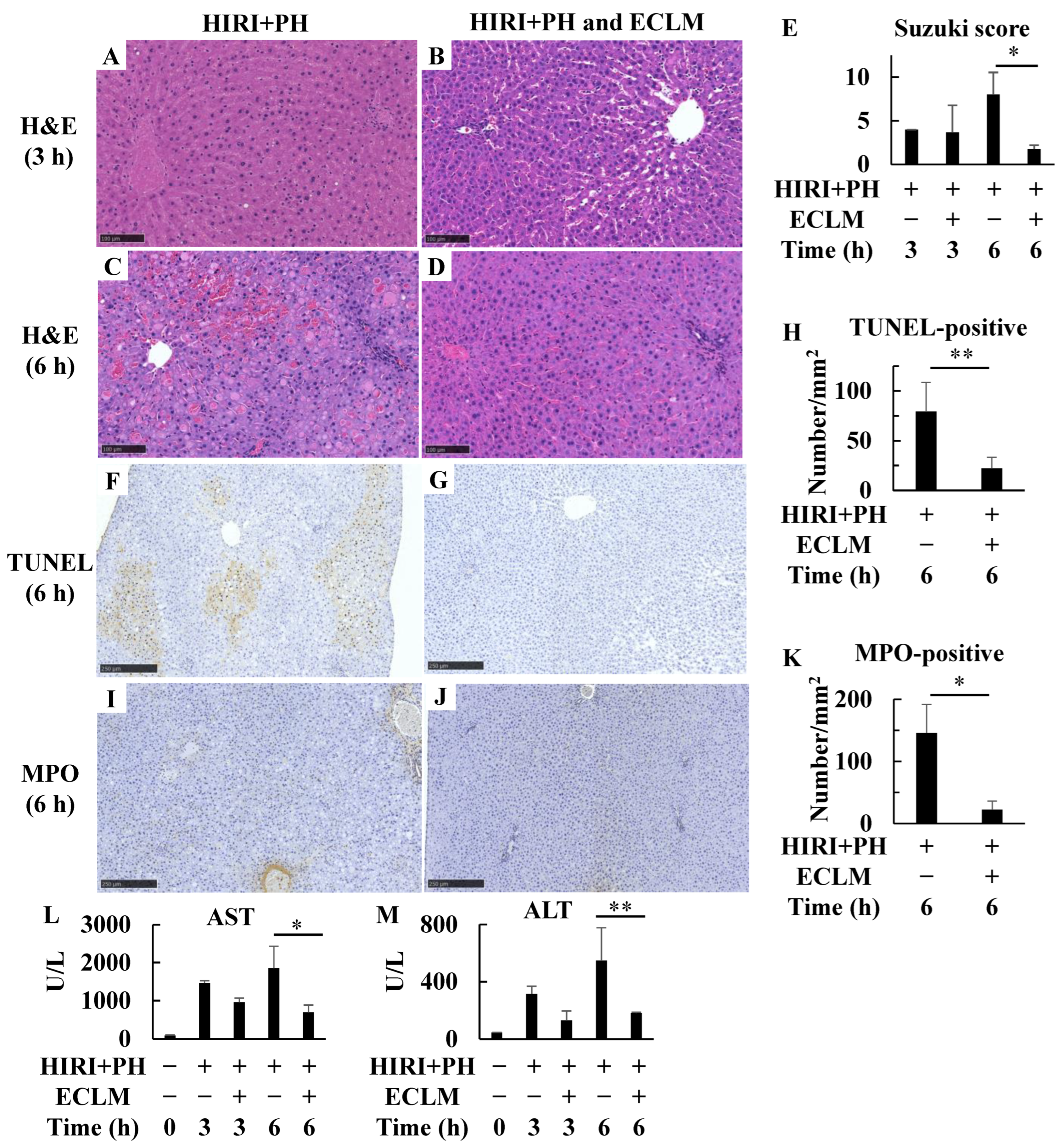
3.1. Pretreatment with ECLM Improved HIRI+PH-Triggered Liver Damage
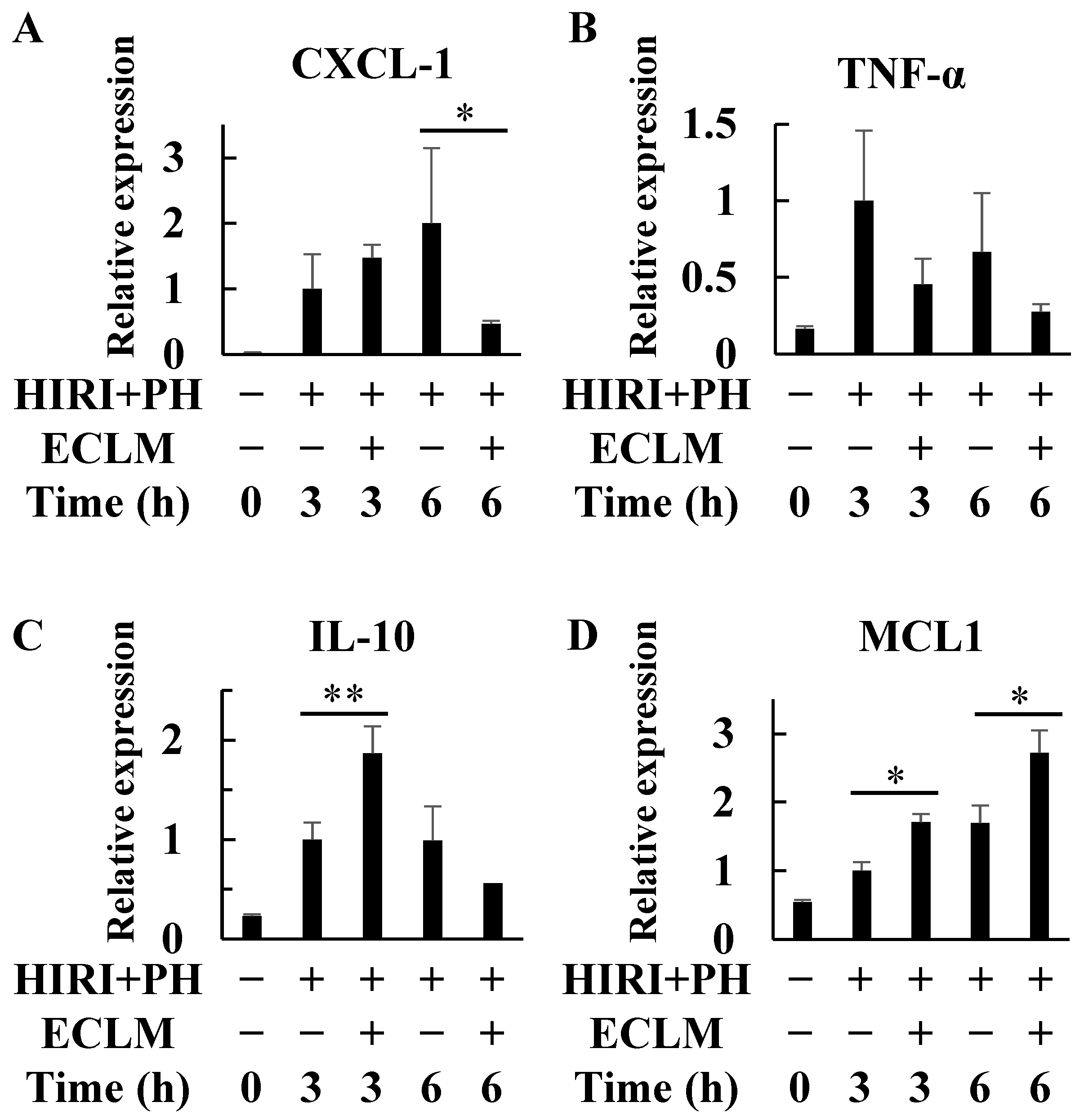
3.2. ECLM Affects Inflammation- and Apoptosis-Related Gene Expression in the HIRI+PH-Treated Rats
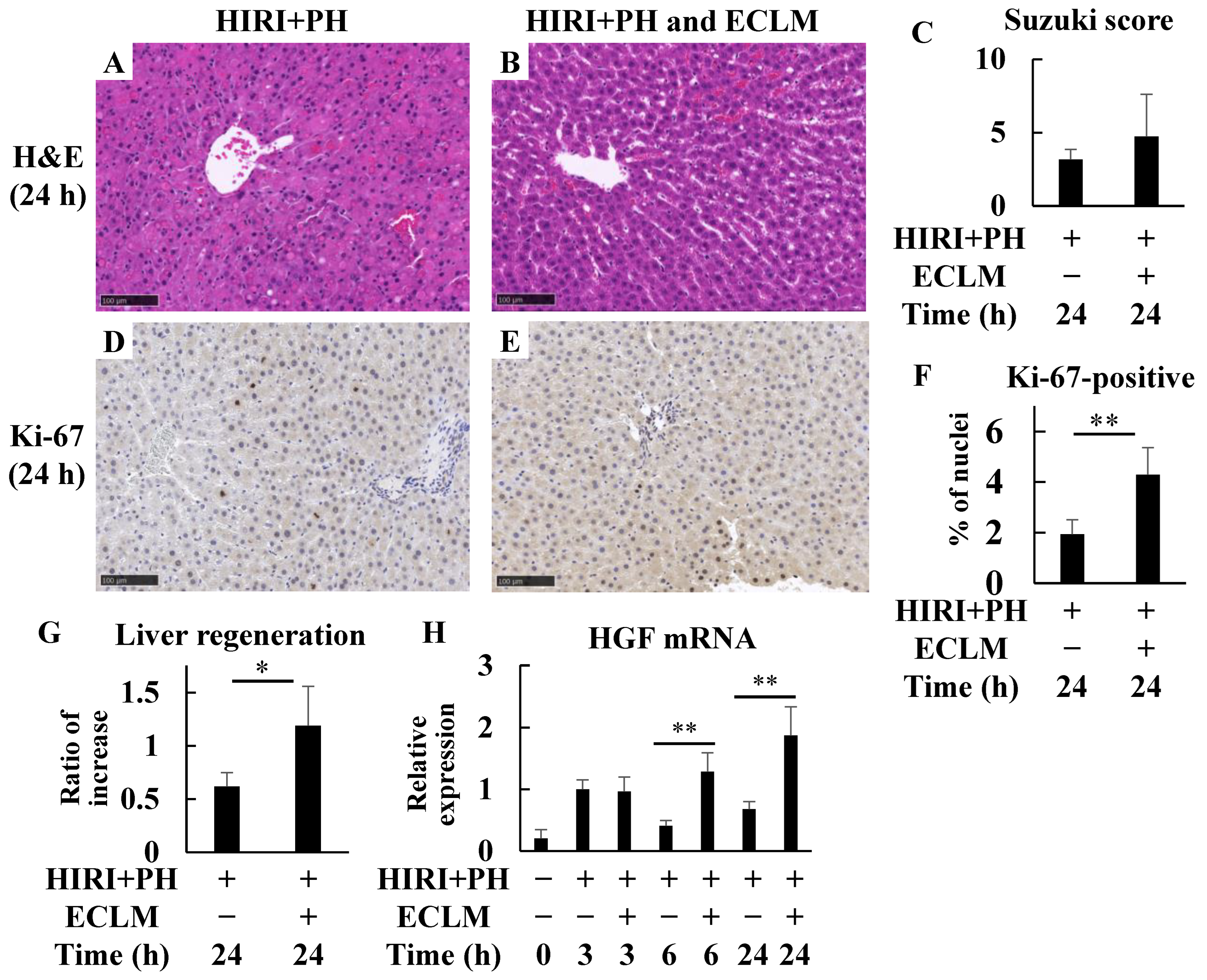
3.3. ECLM Improves Liver Regeneration in the HIRI+PH-Treated Rats
3.4. ECLM Reduces NO Production and iNOS Induction and Elevates Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Induction after HIRI+PH Treatment
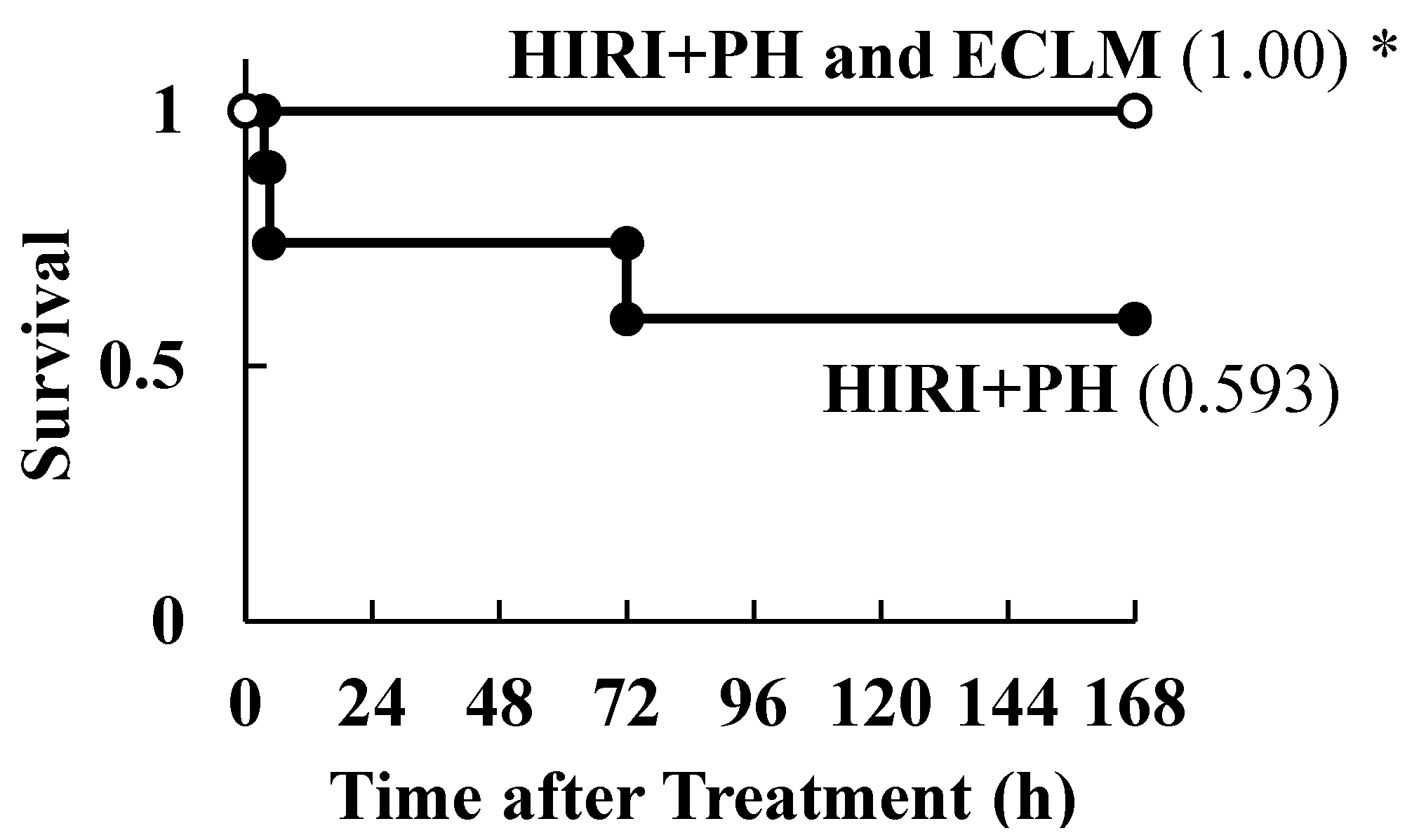
3.5. Effects of ECLM on HIRI-Induced Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pringle, J.H.V. Notes on the Arrest of Hepatic Hemorrhage Due to Trauma. Ann. Surg. 1908, 48, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belghiti, J.; Noun, R.; Malafosse, R.; Jagot, P.; Sauvanet, A.; Pierangeli, F.; Marty, J.; Farges, O. Continuous versus intermittent portal triad clamping for liver resection: A controlled study. Ann. Surg. 1999, 229, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, N.C. Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: Contemporary perspectives on pathogenic mechanisms and basis for hepatoprotection-the good, bad and deadly. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26 (Suppl. 1), 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wagensveld, B.A.; van Gulik, T.M.; Gelderblom, H.C.; Scheepers, J.J.; Bosma, A.; Endert, E.; Obertop, H.; Gouma, D.J. Continuous or intermittent vascular clamping during hemihepatectomy in pigs: Hyaluronic acid kinetics in the assessment of early microvascular liver damage. Eur. J. Surg. 2000, 166, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delva, E.; Camus, Y.; Nordlinger, B.; Hannoun, L.; Parc, R.; Deriaz, H.; Lienhart, A.; Huguet, C. Vascular occlusions for liver resections. Operative management and tolerance to hepatic ischemia: 142 cases. Ann. Surg. 1989, 209, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagimoto, H.; Satoi, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirooka, S.; Yamaki, S.; Kotsuka, M.; Ryota, H.; Michiura, T.; Inoue, K.; Matsui, Y.; et al. Alleviating Effect of Active Hexose Correlated Compound (AHCC) on Chemotherapy-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Unresectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Nutr. Cancer. 2016, 68, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Kashimoto, M. Composition. In Clinician’s Guide to AHCC: Evidence-Based Nutritional Immunotherapy; Kulkarni, A.D., Calder, P., Ito, T., Eds.; International Congress on Nutrition and Integrative Medicine: Sapporo, Japan, 2016; pp. 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Urushima, H.; Sakaue, M.; Yukawa, S.; Honda, H.; Hirai, K.; Igura, T.; Hayashi, N.; Maeda, K.; Kitagawa, T.; et al. Reduction of adverse effects by a mushroom product, active hexose correlated compound (AHCC) in patients with advanced cancer during chemotherapy–The significance of the levels of HHV-6 DNA in saliva as a surrogate biomarker during chemotherapy. Nutr. Cancer. 2014, 66, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Yun, S.M.; Suh, D.H.; Kim, K.; No, J.H.; Jeong, E.H.; Kim, Y.B. Active Hexose Correlated Compound (AHCC) Inhibits the Proliferation of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Suppressing Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Activation. Nutr. Cancer. 2018, 70, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, B.E.; Beli, E.; Duriancik, D.M.; Gardner, E.M. Short-term supplementation with active hexose correlated compound improves the antibody response to influenza B vaccine. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviles, H.; Belay, T.; Fountain, K.; Vance, M.; Sun, B.; Sonnenfeld, G. Active hexose correlated compound enhances resistance to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in mice in the hindlimb-unloading model of spaceflight conditions. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 95, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviles, H.; O’Donnell, P.; Orshal, J.; Fujii, H.; Sun, B.; Sonnenfeld, G. Active hexose correlated compound activates immune function to decrease bacterial load in a murine model of intramuscular infection. Am. J. Surg. 2008, 195, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.F.; Ichimura, K.; Wakame, K.; Ohe, M. Suppressive effects of Active Hexose Correlated Compound on the increased activity of hepatic and renal ornithine decarboxylase induced by oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2003, 74, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Ozaki, T.; Tokuhara, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kaibori, M.; Matsui, Y.; Kamiyama, Y.; Wakame, K.; Miura, T.; et al. Effect of active hexose correlated compound on the production of nitric oxide in hepatocytes. J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2007, 31, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Ohashi, S.; Ohtsuki, A.; Kiyono, T.; Park, E.Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Sato, K.; Oishi, M.; Miki, H.; Tokuhara, K.; et al. Adenosine, a hepato-protective component in active hexose correlated compound: Its identification and iNOS suppression mechanism. Nitric Oxide 2014, 40, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatake, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Ueyama, Y.; Miki, H.; Ishizaki, M.; Matsui, K.; Kaibori, M.; Okumura, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Kon, M. Protective effects of active hexose correlated compound in a rat model of liver injury after hepatectomy. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2016, 6, 702–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, Y.; Tokuhara, K.; Miki, H.; Nakatake, R.; Sakaguchi, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Kaibori, M.; Okumura, T. Active Hexose Correlated Compound Has Protective Effects in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of the Rat Small Intestine. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 243, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 9001:2015; Quality Management Systems Requirements. 5th ed. International Standards Organisation (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO 22000:2018; Food Safety Management Requirements for Any Organization in the Food Chain. 2nd ed. International Standards Organisation (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Fujii, N.; Kudo, S. Manufacturing Process. In Clinician’s Guide to AHCC: Evidence-Based Nutritional Immunotherapy; Kulkarni, A.D., Calder, P., Ito, T., Eds.; International Congress on Nutrition and Integrative Medicine: Sapporo, Japan, 2016; pp. 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.; Clutton, R.E.; Lilley, E.; Hansen, K.E.A.; Brattelid, T. PREPARE: Guidelines for planning animal research and testing. Lab. Anim. 2018, 52, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kokuryo, T.; Watanabe, K.; Kitagawa, T.; Nagino, M. Inchinkoto, an herbal medicine, exerts beneficial effects in the rat liver under stress with hepatic ischemia-reperfusion and subsequent hepatectomy. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for Endpoints in Animal Study Proposals. Office of Animal Care and Use, NIH. Available online: https://oacu.oir.nih.gov/animal-research-advisory-committee-arac-guidelines (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Kanzler, S.; Rix, A.; Czigany, Z.; Tanaka, H.; Fukushima, K.; Kögel, B.; Pawlowsky, K.; Tolba, R.H. Recommendation for severity assessment following liver resection and liver transplantation in rats: Part I. Lab. Anim. 2016, 50, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Toledopereyra, L.H.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Cejalvo, D. Neutrophil Infiltration as an Important Factor in Liver Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury—Modulating Effects of Fk506 and Cyclosporine. Transplantation 1993, 55, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, M.; Nakajima, T.; Yasuda, K.; Kanzaki, H.; Sasaguri, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ito, S. Close kinship of human 20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene with three aldo-keto reductase genes. Genes Cells 2000, 5, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelerie, F.; Ben-Baruch, A.; Burkhardt, A.M.; Combadiere, C.; Farber, J.M.; Graham, G.J.; Horuk, R.; Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Locati, M.; Luster, A.D.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. [corrected]. LXXXIX. Update on the extended family of chemokine receptors and introducing a new nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santucci, L.; Fiorucci, S.; Chiorean, M.; Brunori, P.M.; Di Matteo, F.M.; Sidoni, A.; Migliorati, G.; Morelli, A. Interleukin 10 reduces lethality and hepatic injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in galactosamine-sensitized mice. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Kwon, A.H.; Tsuji, K.; Kamiyama, Y.; Okumura, T.; Hirao, Y. Fibronectin prevents D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced lethal hepatic failure in mice. Shock 2006, 25, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, R.W. The bcl-2 gene family. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1995, 6, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, S.; Teratani, T.; Fujimoto, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tsuruyama, T.; Masano, Y.; Kasahara, N.; Iida, T.; Yagi, S.; Uemura, T.; et al. Oral administration of polyamines ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes liver regeneration in rats. Liver Transpl. 2016, 22, 1231–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentsch, A.B.; Kato, A.; Yoshidome, H.; McMasters, K.M.; Edwards, M.J. Inflammatory mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Hepatology 2000, 32, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, M.; Hayashi, T.; Yokota, R.; Shimamura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Matsushita, M.; Furukawa, H.; Todo, S. Lipid peroxidation during ischemia depends on ischemia time in warm ischemia and reperfusion of rat liver. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, G.; Fuller, B.J.; Davidson, B.R. Molecular mechanisms of liver ischemia reperfusion injury: Insights from transgenic knockout models. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1683–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H. Mechanisms of Liver Injury. II. Mechanisms of neutrophil-induced liver cell injury during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion and other acute inflammatory conditions. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G1083–G1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletti, L.M.; Kunkel, S.L.; Walz, A.; Burdick, M.D.; Kunkel, R.G.; Wilke, C.A.; Strieter, R.M. The role of cytokine networks in the local liver injury following hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in the rat. Hepatology 1996, 23, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomfret, E.A.; Pomposelli, J.J.; Jenkins, R.L. Live donor liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangnall, D.; Bird, N.C.; Majeed, A.W. The molecular physiology of liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy. Liver Int. 2003, 23, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendieta-Condado, E.; Pichardo-Olvera, M.; Sanchez-Sevilla, L.; Chagoya de Sanchez, V.; Hernandez-Munoz, R. Adenosine administration accelerates progression of the cell cycle during rat liver regeneration induced by one-third hepatectomy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 331, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, C.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Chang, C.; Xu, C. A preliminary in vivo study of the effects of OPN on rat liver regeneration induced by partial hepatectomy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 43, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, P.A.; Lin, A.J.; Golan, D.E.; Michel, T. Receptor-regulated dynamic S-nitrosylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 19888–19894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koti, R.S.; Seifalian, A.M.; Davidson, B.R. Protection of the liver by ischemic preconditioning: A review of mechanisms and clinical applications. Dig. Surg. 2003, 20, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cescon, M.; Grazi, G.L.; Grassi, A.; Ravaioli, M.; Vetrone, G.; Ercolani, G.; Varotti, G.; D’Errico, A.; Ballardini, G.; Pinna, A.D. Effect of ischemic preconditioning in whole liver transplantation from deceased donors. A pilot study. Liver Transpl. 2006, 12, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Ding, N.; Zeng, Y.F.; Xiang, Y.Y.; Yang, M.W.; Hong, F.F.; Yang, S.L. New progress in roles of nitric oxide during hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2505–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatake, R.; Schulz, M.; Kalvelage, C.; Benstoem, C.; Tolba, R.H. Effects of iNOS in Hepatic Warm Ischaemia and Reperfusion Models in Mice and Rats: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colasanti, M.; Suzuki, H. The dual personality of NO. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatake, R.; Hishikawa, H.; Kotsuka, M.; Ishizaki, M.; Matsui, K.; Nishizawa, M.; Yoshizawa, K.; Kaibori, M.; Okumura, T. The Proton Pump Inhibitor Lansoprazole Has Hepatoprotective Effects in In Vitro and In Vivo Rat Models of Acute Liver Injury. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 2854–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, K.; Ozaki, T.; Oishi, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kaibori, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Okumura, T.; Kwon, A.H. Active Hexose Correlated Compound Inhibits the Expression of Proinflammatory Biomarker iNOS in Hepatocytes. Eur. Surg. Res. 2011, 47, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, B.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Q. Longer duration of the Pringle maneuver is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence following curative resection. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 114, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, Y.; Mori, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Ito, T.; Iida, T.; Yagi, S.; Okajima, H.; Kaido, T.; Uemoto, S. Longer warm ischemia can accelerate tumor growth through the induction of HIF-1alpha and the IL-6-JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway in a rat hepatocellular carcinoma model. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2016, 23, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, Y.; Uhara, J.; Satoi, S.; Kaibori, M.; Yamada, H.; Kitade, H.; Imamura, A.; Takai, S.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kwon, A.H.; et al. Improved prognosis of postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma patients when treated with functional foods: A prospective cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2002, 37, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T.; Orimo, T.; Wakayama, K.; Kakisaka, T.; Shimada, S.; Nagatsu, A.; Asahi, Y.; Aiyama, T.; Kamachi, H.; Taketomi, A. Preventing Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Curative Hepatectomy With Active Hexose-correlated Compound Derived From Lentinula edodes Mycelia. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 15347354211073066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakatake, R.; Okuyama, T.; Ishizaki, M.; Yanagida, H.; Kitade, H.; Yoshizawa, K.; Nishizawa, M.; Sekimoto, M. Hepatoprotection of a Standardized Extract of Cultured Lentinula edodes Mycelia against Liver Injury Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion and Partial Hepatectomy. Nutrients 2024, 16, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16020256
Nakatake R, Okuyama T, Ishizaki M, Yanagida H, Kitade H, Yoshizawa K, Nishizawa M, Sekimoto M. Hepatoprotection of a Standardized Extract of Cultured Lentinula edodes Mycelia against Liver Injury Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion and Partial Hepatectomy. Nutrients. 2024; 16(2):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16020256
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakatake, Richi, Tetsuya Okuyama, Morihiko Ishizaki, Hidesuke Yanagida, Hiroaki Kitade, Katsuhiko Yoshizawa, Mikio Nishizawa, and Mitsugu Sekimoto. 2024. "Hepatoprotection of a Standardized Extract of Cultured Lentinula edodes Mycelia against Liver Injury Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion and Partial Hepatectomy" Nutrients 16, no. 2: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16020256
APA StyleNakatake, R., Okuyama, T., Ishizaki, M., Yanagida, H., Kitade, H., Yoshizawa, K., Nishizawa, M., & Sekimoto, M. (2024). Hepatoprotection of a Standardized Extract of Cultured Lentinula edodes Mycelia against Liver Injury Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion and Partial Hepatectomy. Nutrients, 16(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16020256





