Isatidis Folium Represses Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis and Suppresses the Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting Inflammasome Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of EIF
2.2. Animal Studies
2.2.1. Animals
2.2.2. The Intestinal Barrier-Protective Effects of EIF on Ulcerative Colitis
2.3. In Vitro Study
2.3.1. Cell Culture
2.3.2. Cell Viability and Toxicity of EIF
2.3.3. Measurement of Nitic Oxide (NO) and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels
2.3.4. NF-κB Luciferase Reporter-Based Assay
2.3.5. Western Blotting
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
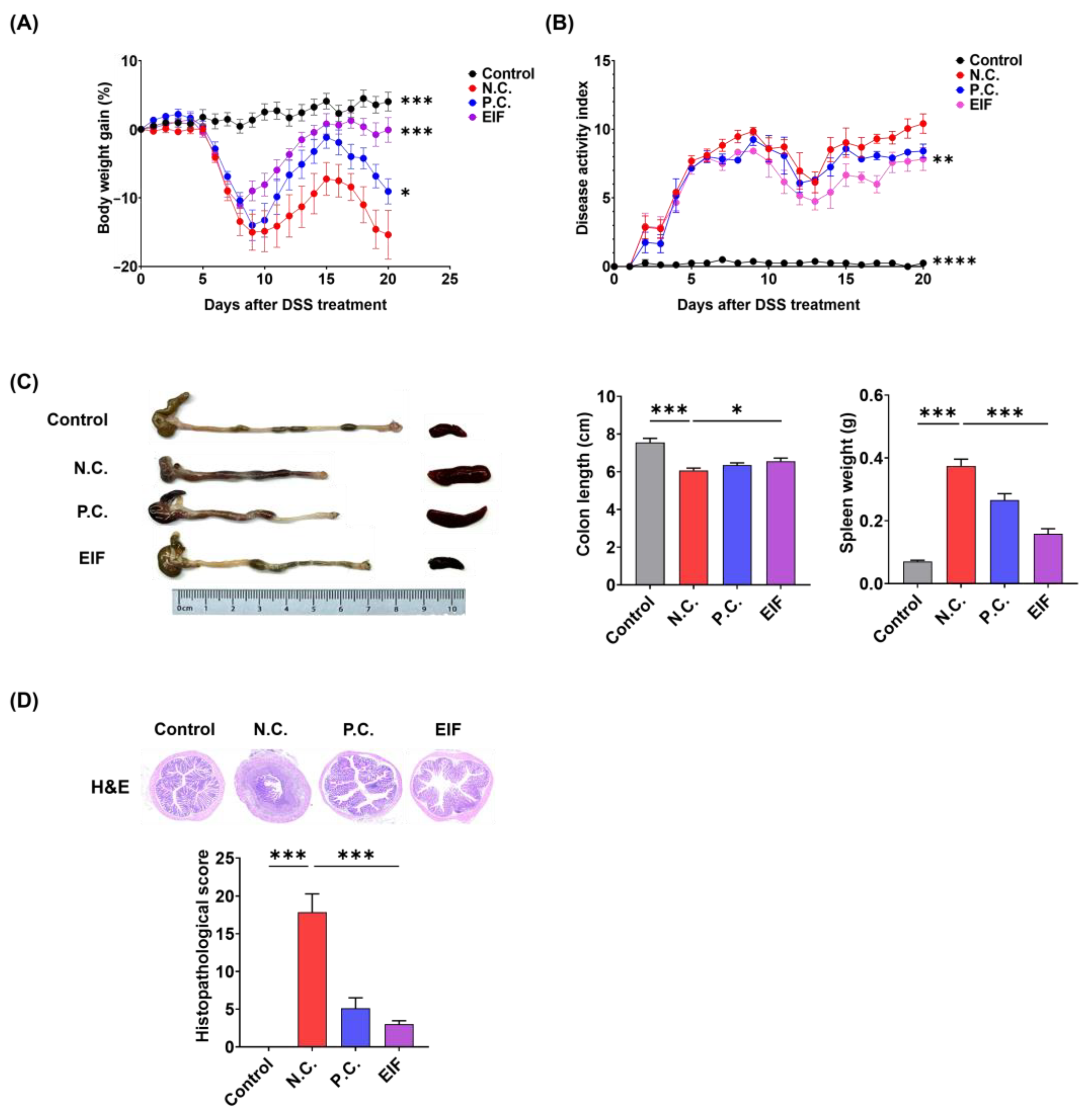
3.1. Effects of EIF in DSS-Induced Colitis
3.2. Modulatory Effects of EIF on Histopathological Changes in DSS-Induced Colitis
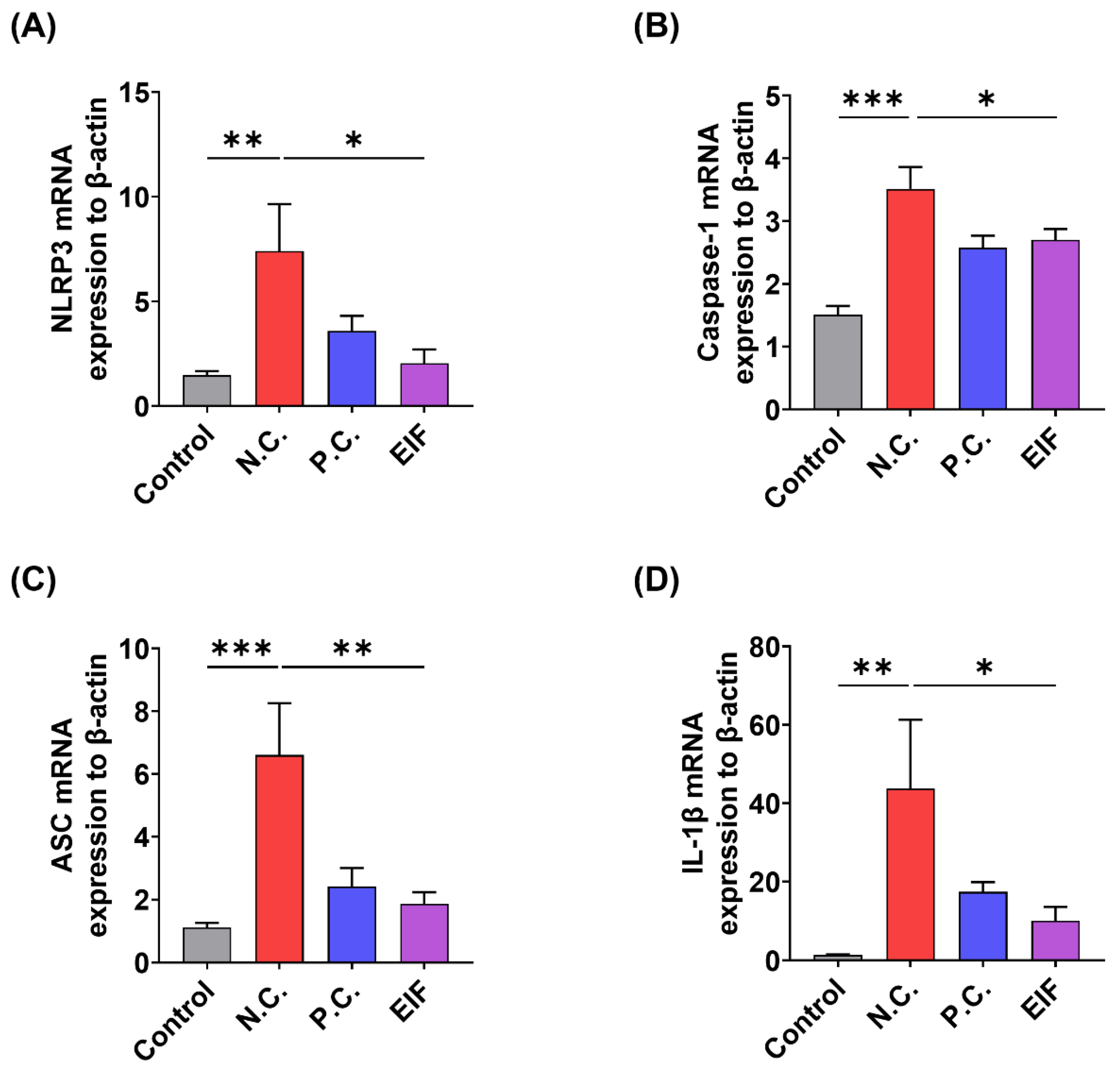
3.3. Modulatory Effects of EIF on Inflammasome Component Levels in DSS-Induced Colitis
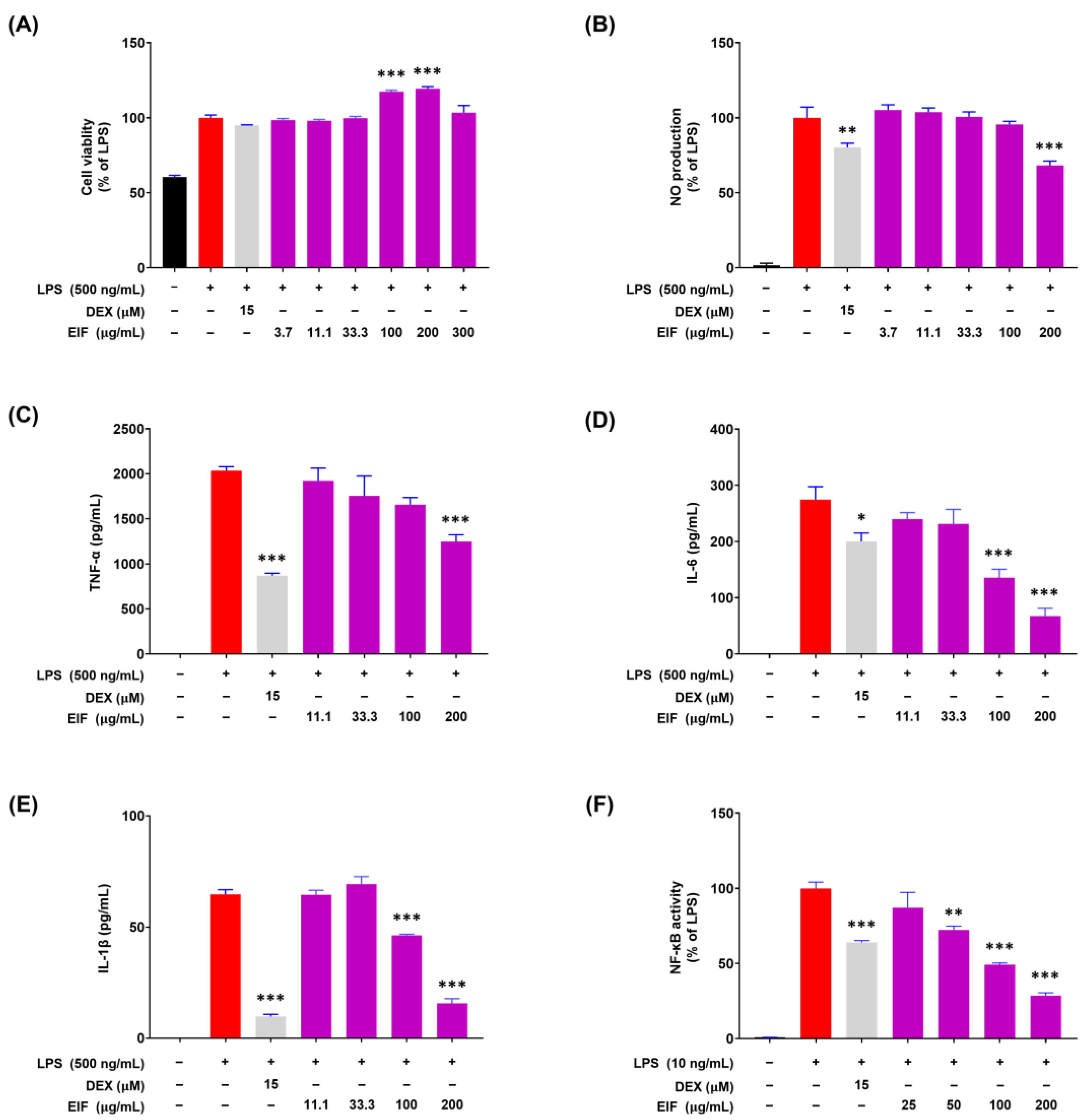
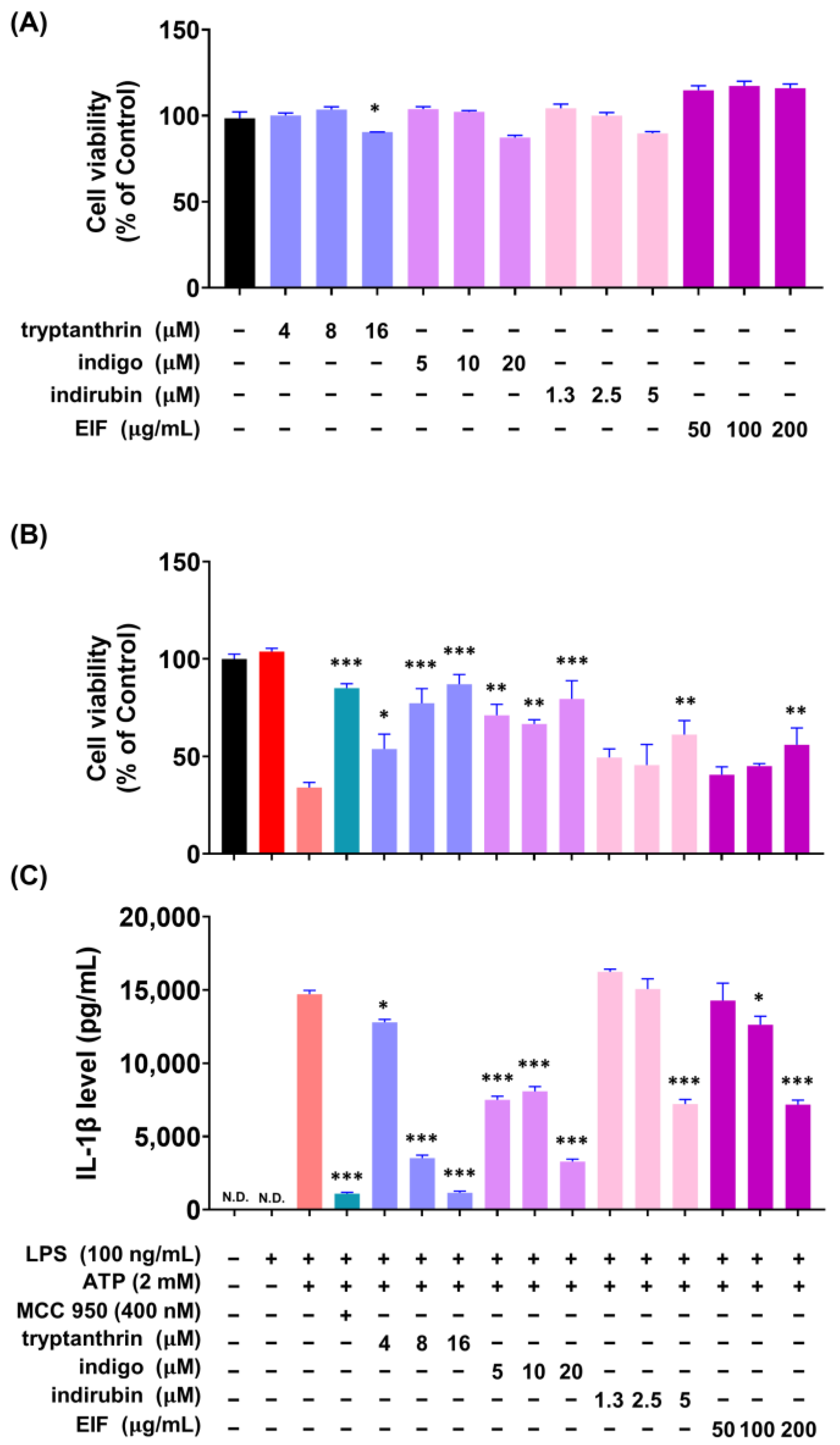
3.4. Modulatory Effects of EIF on LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Cells
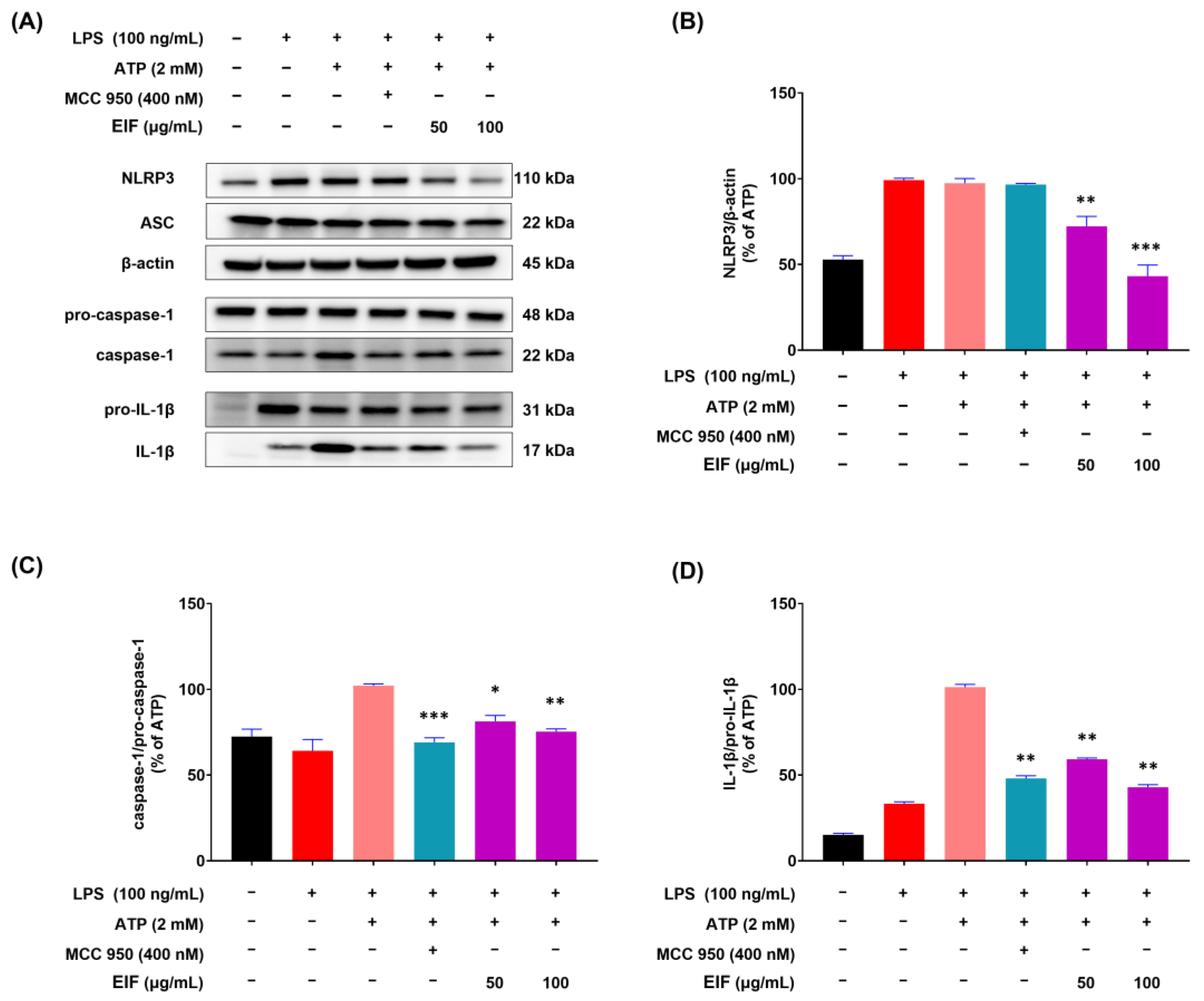
3.5. Effect of EIF on the Inhibition of Proteins Related to LPS/ATP-Induced Inflammasomes
3.6. Effect of EIF Contituents on J774a.1 and BMDM Cells Induced by LPS/ATP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2012, 380, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolsky, D.K. Inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, C.; Medzhitov, R. Interactions between the host innate immune system and microbes in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaser, A.; Zeissig, S.; Blumberg, R.S. Inflammatory bowel disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 573–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, R.B. Microbial influences in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Lee, M.; Chang, E.B. The gut microbiome and inflammatory bowel diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werts, C.; Rubino, S.; Ling, A.; Girardin, S.E.; Philpott, D.J. Nod-like receptors in intestinal homeostasis, inflammation, and cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanneganti, T.D.; Ozören, N.; Body-Malapel, M.; Amer, A.; Park, J.H.; Franchi, L.; Whitfield, J.; Barchet, W.; Colonna, M.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. Bacterial RNA and small antiviral compounds activate caspase-1 through cryopyrin/Nalp3. Nature 2006, 440, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villani, A.C.; Lemire, M.; Fortin, G.; Louis, E.; Silverberg, M.S.; Collette, C.; Baba, N.; Libioulle, C.; Belaiche, J.; Bitton, A.; et al. Common variants in the NLRP3 region contribute to Crohn’s disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.S.; Warrington, R.; Watson, W.; Kim, H.L. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzopalic, T.; Rajkovic, I.; Dragicevic, A.; Colic, M. The response of human dendritic cells to co-ligation of pattern-recognition receptors. Immunol. Res. 2012, 52, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Q.; Yao, Q.; Wang, P. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in macrophages possess prognosis and immunotherapy potential for melanoma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 765615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicherska-Pawłowska, K.; Wróbel, T.; Rybka, J. Toll-like receptors (TLRs), NOD-like receptors (NLRs), and RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) in innate Immunity. TLRs, NLRs, and RLRs ligands as immunotherapeutic agents for hematopoietic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blevins, H.M.; Xu, Y.; Biby, S.; Zhang, S. The NLRP3 inflammasome pathway: A review of mechanisms and inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 879021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Kouadir, M.; Song, H.; Shi, F. Recent advances in the mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and its inhibitors. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zito, G.; Buscetta, M.; Cimino, M.; Dino, P.; Bucchieri, F.; Cipollina, C. Cellular models and assays to study NLRP3 inflammasome biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Luo, H.; Tan, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhoung, Z.; Wang, S.; Vong, C.T.; Wang, Y. A recent update on the use of Chinese medicine in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravina, A.G.; Pellegrino, R.; Palladino, G.; Coppola, A.; Brandimarte, G.; Tuccillo, C.; Ciardiello, F.; Romano, M.; Federico, A. Hericium erinaceus, in combination with natural flavonoid/alkaloid and B3/B8 vitamins, can improve inflammatory burden in Inflammatory bowel diseases tissue: An ex vivo study. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1215329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, A.G.; Pellegrino, R.; Auletta, S.; Palladino, G.; Brandimarte, G.; D’Onofrio, R.; Arboretto, G.; Imperio, G.; Ventura, A.; Cipullo, M.; et al. Hericium erinaceus, a medicinal fungus with a centuries-old history: Evidence in gastrointestinal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 3048–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Fu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liao, W. Isatidis radix and isatidis folium: A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotts, T.; Kabrodt, K.; Hummel, J.; Binder, D.; Schellenberg, I.; Ständer, S.; Agelopoulos, K. Isatis tinctoria L.-derived petroleum ether extract mediates anti-inflammatory effects via inhibition of interleukin-6, interleukin-33 and mast cell degranulation. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Xiao, H. Antiviral activity of the effective monomers from folium isatidis against influenza virus in vivo. Virol. Sinica 2010, 25, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Jin, J.; Dong, L.; Xu, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Liang, G.; Shan, X. n-Butanol extract from Folium isatidis inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages and protects mice against lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 5601–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Cho, C.W.; Kim, C.T.; Jeong, W.S.; Kang, J.S. Evaluation of the antiwrinkle activity of enriched isatidis folium extract and an HPLC-UV method for the quality control of its cream products. Plants 2020, 9, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.Y.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, W.K.; Yang, J.H.; Ma, J.Y. Anti-atopic effect of isatidis folium water extract in TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced HaCaT cells and DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis mouse model. Molecules 2023, 28, 3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Yang, H.; Kim, T.; Ha, H.; Hwang, Y.H. Identification and pharmacokinetics of bioavailable anti-resorptive phytochemicals after oral administration of Psoralea corylifolia L. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, B.C.; Jong, T.T.; Lee, M.R.; Chen, S.S. LC-APCI-MS method for detection and analysis of tryptanthrin, indigo, and indirubin in daqingye and banlangen. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.K.; Chen, T.T.; Crampton, L. Chinese Medical Herbology and Pharmacology; Art of Medicine Press: City of Industry, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zheng, J.; Sun, G.; Yang, H.; Sun, X.; Yao, X.; Lin, A.; Liu, H. 5-Aminosalicylic acid ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by modulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseaux, C.; Lefebvre, B.; Dubuquoy, L.; Lefebvre, P.; Romano, O.; Auwerx, J.; Metzger, D.; Wahli, W.; Desvergne, B.; Naccari, G.C.; et al. Intestinal antiinflammatory effect of 5-aminosalicylic acid is dependent on peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Lu, Q.; Li, J.; Shi, R.; Shi, L.; Mao, T.; Ge, D.; Niu, H.; et al. Investigation of the active ingredients and mechanism of Hudi enteric-coated capsules in DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mice based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 4259–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, D.; Niu, J.; Miao, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, K.; Miao, Y. Expression of guanylate cyclase-C, guanylin and uroguanylin is downregulated proportionally to the ulcerative colitis disease activity index. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.; Ou, S.; Luo, J.; Peng, X. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide improves rat DSS-induced colitis by altering cecal microbiota and gene expression of colonic epithelial cells. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 63, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Lee, A.; Ryuk, J.A.; Hwang, Y.H. Isodorsmanin A prevents inflammatory response in LPS-stimulated macrophages by inhibiting the JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassaing, B.; Aitken, J.D.; Malleshappa, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2014, 104, 15.25.11–15.25.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okayasu, I.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yamada, M.; Ohkusa, T.; Inagaki, Y.; Nakaya, R. A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRoche, T.C.; Xiao, S.Y.; Liu, X. Histological evaluation in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2014, 2, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.E.; Sjövall, H.; Hansson, G.C. The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoo, L.; Noti, M.; Krebs, P. Keep calm: The intestinal barrier at the interface of peace and war. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.-K.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Soni, T.; Aring, L.; Muraleedharan, K.M.; Garcia-Hernandez, V.; Kamada, N.; Samuelson, L.C.; Nusrat, A.; Iwase, S.; et al. The manganese transporter SLC39A8 links alkaline ceramidase 1 to inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Commun. 2024, 15, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhao, F.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Lu, S.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X. Differential effects of EPA and DHA on DSS-induced colitis in mice and possible mechanisms involved. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Qian, P.; Huang, H. Inflammation and aging: Signaling pathways and intervention therapies. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P.Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Qin, S.; Zhan, X.; Li, H.; Wei, Z.; Fang, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, T.; et al. Tryptanthrin suppresses multiple inflammasome activation to regulate NASH progression by targeting ASC protein. Phytomedicine 2024, 131, 155758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, G.X.; Niu, Y.T.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Yang, J.M.; Sun, T.; Niu, J.G.; Yu, J.Q. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of indigo through regulating the IKKβ/IκB/NF-κB pathway in mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8537–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Li, H.; Li, S. Indirubin improves antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions in lipopolysaccharide-challenged mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36658–36663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K.S.; Gu, D.R.; Hwang, Y.H.; Yang, H.; Ryuk, J.A.; Ha, H. Water extract of Fritillariae thunbergii Bulbus inhibits RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis and ovariectomy-induced trabecular bone loss. Molecules 2021, 27, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Name | Assay ID | NCBI Reference Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) | Mm00840904_m1 | NG_007509.2 |
| Caspase-1 Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein (ASC) | Mm00438023_m1 Mm00445747_g1 | NM_001043585.1 NG_029446.1 |
| β-actin | Mm00607939_s1 | NM_007393.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, Y.C.; Lee, A.; Jang, C.H.; Ryuk, J.A.; Ha, H.; Hwang, Y.-H. Isatidis Folium Represses Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis and Suppresses the Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting Inflammasome Activation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193323
Chung YC, Lee A, Jang CH, Ryuk JA, Ha H, Hwang Y-H. Isatidis Folium Represses Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis and Suppresses the Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting Inflammasome Activation. Nutrients. 2024; 16(19):3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193323
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, You Chul, Ami Lee, Chan Ho Jang, Jin Ah Ryuk, Hyunil Ha, and Youn-Hwan Hwang. 2024. "Isatidis Folium Represses Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis and Suppresses the Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting Inflammasome Activation" Nutrients 16, no. 19: 3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193323
APA StyleChung, Y. C., Lee, A., Jang, C. H., Ryuk, J. A., Ha, H., & Hwang, Y.-H. (2024). Isatidis Folium Represses Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis and Suppresses the Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting Inflammasome Activation. Nutrients, 16(19), 3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193323







