Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: A Window into Breastfeeding Outcomes in Varied Healthcare Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting
2.3. Participants
2.4. Variable Definitions and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diagnosis by Hospital Location
3.2. Infant Maturity by Hospital Location
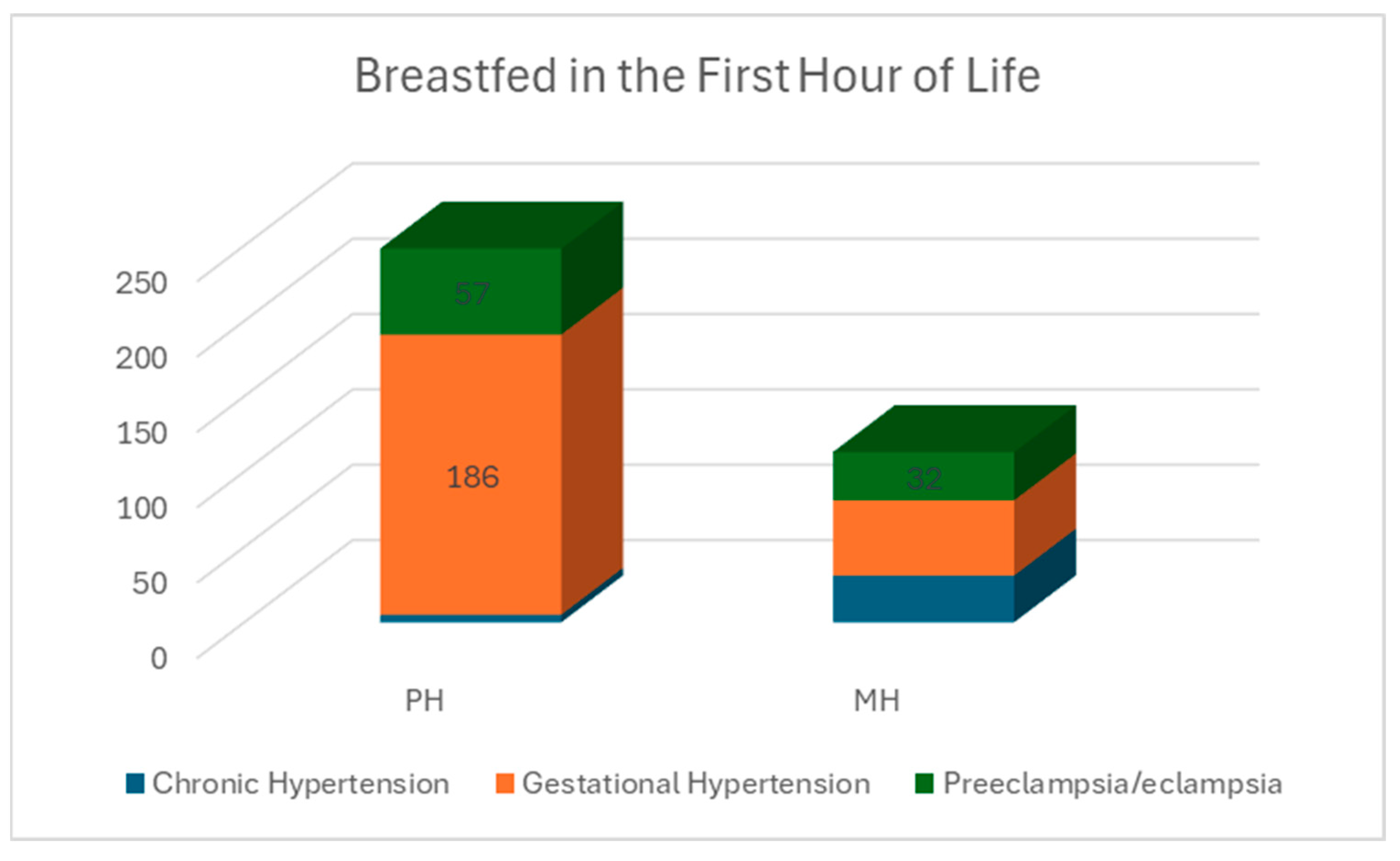
3.3. Breastfeeding Intention
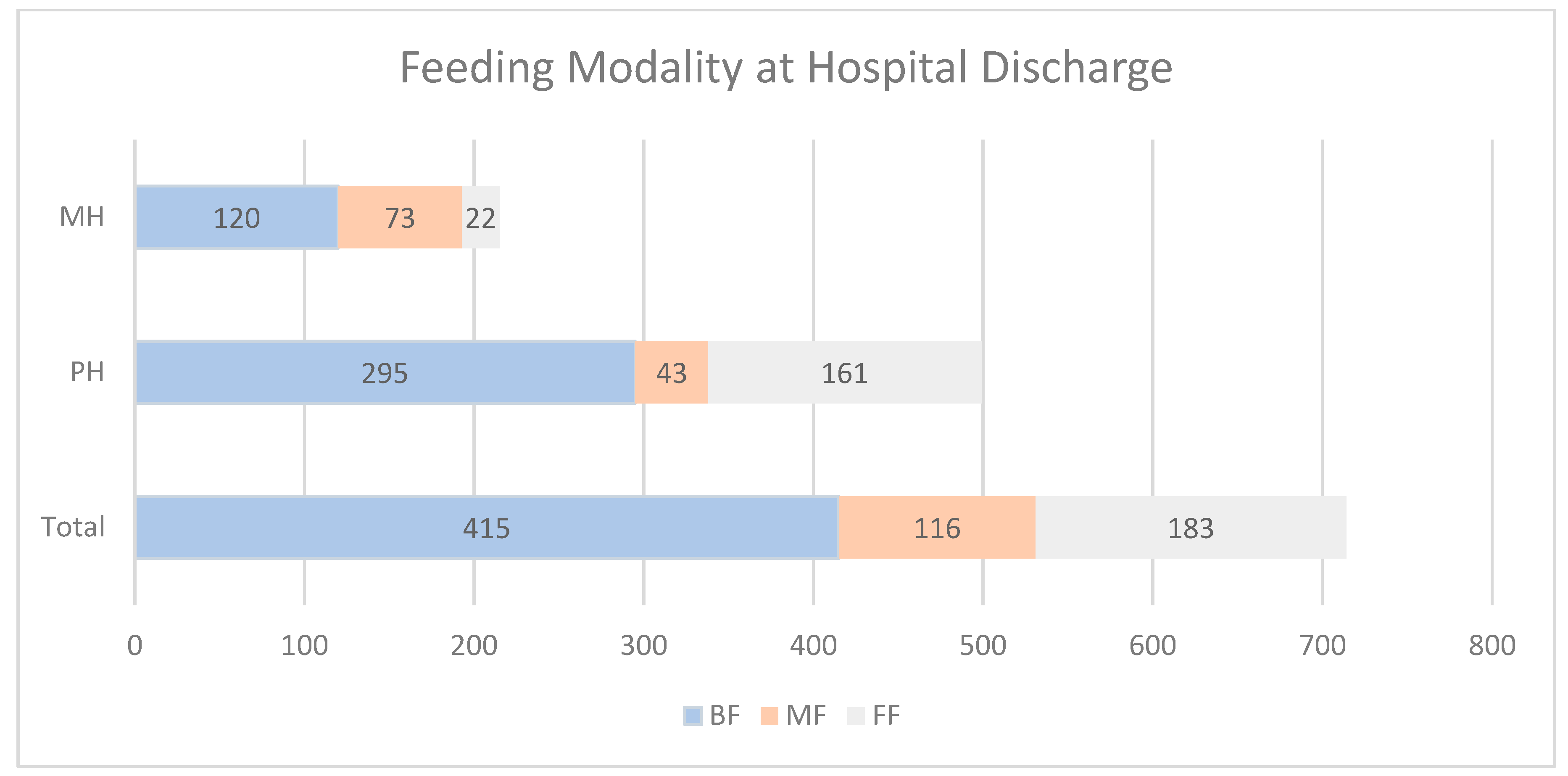
3.4. Feeding Modality at Hospital Discharge
Infant Maturity by Hospital Location by Diagnosis and Feeding Modality at Hospital Discharge
3.5. Strengths and Limitations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khorrami, N.; Stone, J.; Small, M.J.; Stringer, E.M.; Ahmadzia, H.K. An overview of advances in global maternal health: From broad to specific improvements. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2019, 146, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halcrow, S.; Warren, R.; Kushnick, G.; Nowell, A. Care of Infants in the Past: Bridging evolutionary anthropological and bioarchaeological approaches. Evol. Hum. Sci. 2020, 2, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Aviles, P.; Gei, A.F.; Martinez-Dominguez, P. Caring for Patients with Gestational Hypertensive Disorders: Essential Takeaways. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2024, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Kumar, V. Hypertension in Pregnancy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 956, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Bundy, J.D.; Kelly, T.N.; Reed, J.; Kearney, P.M.; Reynolds, K.; Chen, J.; He, J. Global Disparities of Hypertension Prevalence and Control: A systematic Analysis of Population-Based Studies from 90 Countries. Circulation 2016, 134, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohamadike, O.; Lim, S.L.; Siegel, A.; Zemtsov, G.; Kuller, J.A.; Dotters-Katz, S. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: Common Clinical Conundrums. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2022, 77, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Green, M.; Myers, J.E. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. BMJ 2023, 381, e071653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.; McHugh, S.; Browne, J.; Kenny, L.C.; Fitzgerald, A.; Khashan, A.S.; Dempsey, E.; Fahy, C.; O’nEill, C.; Kearney, P.M. Estimating the Cost of Preeclampsia in the Healthcare System. Hypertension 2017, 70, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, N.D.; Cox, S.; Ko, J.Y.; Ouyang, L.; Romero, L.; Colarusso, T.; Ferre, C.D.; Kroelinger, C.D.; Hayes, D.K.; Barfield, W.D. Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy and Mortality at Delivery Hospitalization—United States, 2017–2019. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, S.M.; Filion, K.B.; Yoon, S.; Ayele, H.T.; Doyle, C.M.; Hutcheon, J.A.; Smith, G.N.; Gore, G.C.; Ray, J.G.; Nerenberg, K.; et al. Cardiovascular Disease-Related Morbidity and Mortality in Women with a History of Pregnancy Complications: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circulation 2019, 139, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cífková, R. Hypertension in Pregnancy: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Overview. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2023, 30, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brohan, M.P.; Daly, F.P.; Kelly, L.; McCarthy, F.P.; Khashan, A.S.; Kublickiene, K.; Barrett, P.M. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and long-term risk of maternal stroke—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 229, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, M.D.R.; Margotto, P.R.; Costa, K.N.; Garbi Novaes, M.R.C. Hypertension induced by pregnancy and neonatal outcome: Results from a retrospective cohort study in preterm under 34 weeks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, N.K. Breastfeeding and Maternal Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmelmair, H.; Fleddermann, M.; Koletzko, B. Infant Feeding Choices during the First Post-Natal Months and Anthropometry at Age Seven Years: Follow-Up of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattari, M.; Serwint, J.R.; Levine, D.M. Maternal Implications of Breastfeeding: A Review for the Internist. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, P.A.R.; Vaz, J.S.; Maia, F.S.; Baker, P.; Gatica-Domínguez, G.; Piwoz, E.; Rollins, N.; Victora, C.G. Rates and time trends in the consumption of breastmilk, formula, and animal milk by children younger than 2 years from 2000 to 2019: Analysis of 113 countries. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headeya, D.; Heidkampb, R.; Osendarpc, S.; Ruela, M.; Scottd, N.; Blackb, R.; Shekare, M.; Bouisa, H.; Floryf, A.; Haddadg, L.; et al. Impacts of COVID-19 on childhood malnutrition and nutrition-related mortality. Lancet 2020, 396, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Mercado, E.; Vásquez-Garibay, E.M.; Sánchez Ramírez, C.A.; Muñoz-Esparza, N.C.; Larrosa-Haro, A.; Meza Arreola, P.L. Full Breastfeeding Modifies Anthropometric and Body Composition Indicators in Nursing Mothers. Breastfeed. Med. 2021, 16, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhasselt, V. Breastfeeding, a Personalized Medicine with Influence on Short- and Long-Term Immune Health. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2020, 94, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Countouris, M.E.; Schwarz, E.B.; Rossiter, B.C.; Althouse, A.D.; Berlacher, K.L.; Jeyabalan, A.; Catov, J.M. Effects of Lactaion on Postpartum Blood Pressure among Women with Gestational Hypertension and Preclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 241.e1–241.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miliku, K.; Moraes, T.J.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Sears, M.R.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; Azad, M.B. Breastfeeding in the first days of life is associated with lower blood pressure at 3 years of age. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, 19067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathirana, M.M.; Andraweera, P.H.; Aldridge, E.; Harrison, M.; Harrison, J.; Leemaqz, S.; Arstall, M.A.; Dekker, G.A.; Roberts, C.T. The association of breastfeeding for at least six months with hemodynamic and metabolic health of women and their children aged three years: An observational cohort study. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2023, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H. Breastfeeding is associated with reduced risks of central obesity and hypertension in young school-aged children: A large, population-based study. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2023, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, S.; Ho, F.K.; Celis-Morales, C.; Pell, J.P. Association between being breastfed and cardiovascular disease: A population cohort study of 320,249 participants. J. Public Health 2023, 45, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, J.; Dancisak, B.; Brewer, M.; Trichilo-Lucas, R.; Stefanescu, A. Breastfeeding-supportive hospital practices and breastfeeding maintenance: Results from the Louisiana pregnancy risk assessment monitoring system. J. Perinatol. 2022, 42, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, E.; Gruber, S.; Medina, A.; Zhou, H.; Darmstadt, G.L. Associations of in-hospital postpartum feeding experiences with exclusive breastfeeding practices among infants in rural Sichuan, China. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2023, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Xian, X.; Feng, J.; Mao, Y.; Balakrishnan, S.; Weber, A.M.; Darmstadt, G.L.; Chen, Y.; Sylvia, S.; et al. In-Hospital Formula Feeding Hindered Exclusive Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding Self-Efficacy as a Mediating Factor. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.; Dickton, D. Emergent Acute Hypertension during Pregnancy-Anomaly or Future Trend? J. Gynecol. Women’s Health 2018, 13, 555866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.; Waller, K.; Wilson, A.; Dickton, D. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy in a Military Hospital Birth Cohort. Women’s Health Rep. 2022, 3, 740–748. Available online: http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/whr.2022.0034 (accessed on 20 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Feldman-Winter, L.; Douglass-Bright, A.; Bartick, M.C.; Matranga, J. The new mandate from the joint commission on the perinatal care core measure of exclusive breast milk feeding: Implications for practice and implementation in the United States. J. Hum. Lact. 2013, 29, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Breastfeeding. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/breastfeeding#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Lambermon, F.; Vandenbussche, F.; Dedding, C.; van Duijnhoven, N. Maternal self-care in the early postpartum period: An integrative review. Midwifery 2020, 90, 102799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Rosanoff, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y. Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trials. Hypertension 2016, 68, 324–333. Available online: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07664 (accessed on 28 June 2024). [CrossRef]
- Braunthal, S.; Brateanu, A. Hypertension in pregnancy: Pathophysiology and treatment. SAGE Open Med. 2019, 7, 2050312119843700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Dadelszen, P.; Magee, L.A. Preventing deaths due to the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2016, 36, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulet, S.L.; Platner, M.; Joseph, N.T.; Campbell, A.; Williams, R.; Stanhope, K.K.; Jamieson, D.J. Original Contribution Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy, Cesarean Delivery, and Severe Maternal Morbidity in an Urban Safety-Net Population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 189, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, K.; Norouzkhani, N.; Kargar, M.; Ghasemirad, H.; Ashtiani, A.J.; Kiani, S.; Far, M.S.; Dianati, M.; Salimi, Y.; Khalaji, A.; et al. Impact of Educational Interventions on Knowledge about Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy among Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 886679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macphail, M.G.; Juul, S.; Wollny, K.; Negre, J.Y.; Metcalfe, A.; Chaput, K.H.; Butalia, S.; Nerenberg, K.A. Nutrition Interventions for Lowering Cardiovascular Risk after Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. CJC Open 2024, 6, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metoki, H.; Iwama, N.; Hamada, H.; Satoh, M.; Murakami, T.; Ishikuro, M.; Obara, T. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: Definition, management, and out-of-office blood pressure measurement. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chronic Hypertension % (n) | Gestational Hypertension % (n) | Preeclampsia/ Eclampsia % (n) | Total (n) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital | PH | 2.1% (11) * | 78.6% (416) * | 19.3% (102) * | 529 |
| MH | 21.1% (39) * | 44.3% (82) * | 34.6% 64 * | 185 | |
| Total | 7% (50) | 69.7% (498) | 23.3% (166) | 714 | |
| Preterm % (n) | Chronic Hypertension % (n) | Term % (n) | Late Term % (n) | Total (n) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital | PH | 178 (33.7%) | 195 (37%) | 147 (27.8%) | 9 (1.7%) b | 529 |
| MH | 7 (3.8%) | 114 (61%) | 60 (32.4%) | 4 (2.2%) b | 185 | |
| Total | 185 (25.9%) | 309 (43.3%) | 207 (28.9%) | 13 (1.8%) | ||
| Feeding Modality at Discharge | Diagnosis of | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Hypertension | Gestational Hypertension | Preeclampsia/Eclampsia | ||||
| MF | Hospital Location | Private | 1 | 64 | 8 | 73 |
| Military | 6 | 21 | 16 | 43 | ||
| Total | 7 | 85 | 24 | 116 | ||
| FF | Hospital Location | Private | 5 | 135 | 21 | 161 |
| Military | 2 | 11 | 9 | 22 | ||
| Total | 7 | 146 | 30 | 183 | ||
| BF | Hospital Location | Private | 5 | 217 | 73 | 295 |
| Military | 31 | 50 | 39 | 120 | ||
| Total | 36 | 267 | 112 | 415 | ||
| Total | Hospital Location | Private | 11 | 416 | 102 | 529 |
| Military | 39 | 82 | 64 | 185 | ||
| Total | 50 | 498 | 166 | 714 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francis, J.; Gelner, E.; Dickton, D. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: A Window into Breastfeeding Outcomes in Varied Healthcare Systems. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193239
Francis J, Gelner E, Dickton D. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: A Window into Breastfeeding Outcomes in Varied Healthcare Systems. Nutrients. 2024; 16(19):3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193239
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancis, Jimi, Elizabeth Gelner, and Darby Dickton. 2024. "Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: A Window into Breastfeeding Outcomes in Varied Healthcare Systems" Nutrients 16, no. 19: 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193239
APA StyleFrancis, J., Gelner, E., & Dickton, D. (2024). Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: A Window into Breastfeeding Outcomes in Varied Healthcare Systems. Nutrients, 16(19), 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193239





