Alleviation of Lipid Disorder and Liver Damage in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Selenium-Enriched Cardamine violifolia with Cadmium Accumulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diets and Animals
2.2. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) and Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT)
2.3. Sample Preparation and Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Elemental Analysis
2.5. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels and Total Antioxidant Capacity (T-AOC)
2.6. Histological Analysis
2.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.8. Western Blot Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
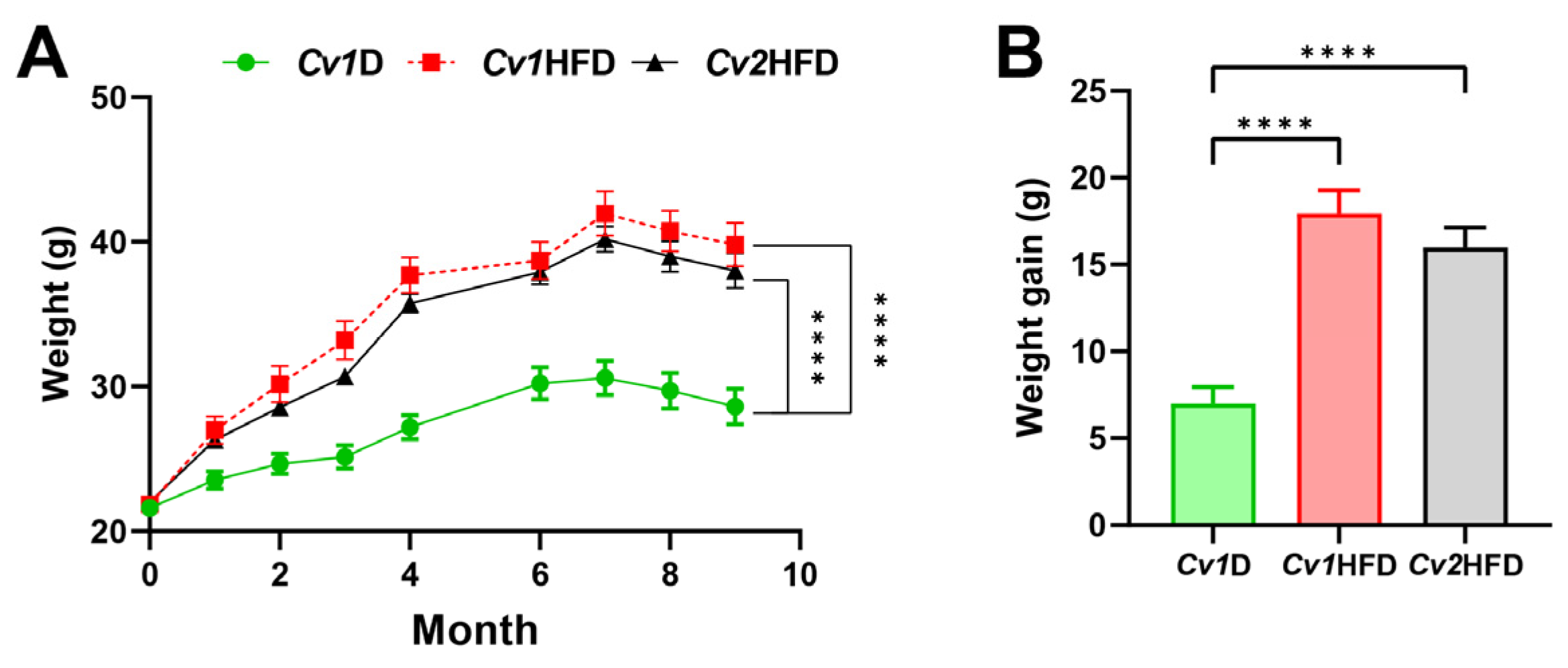
3.1. Growth Performance
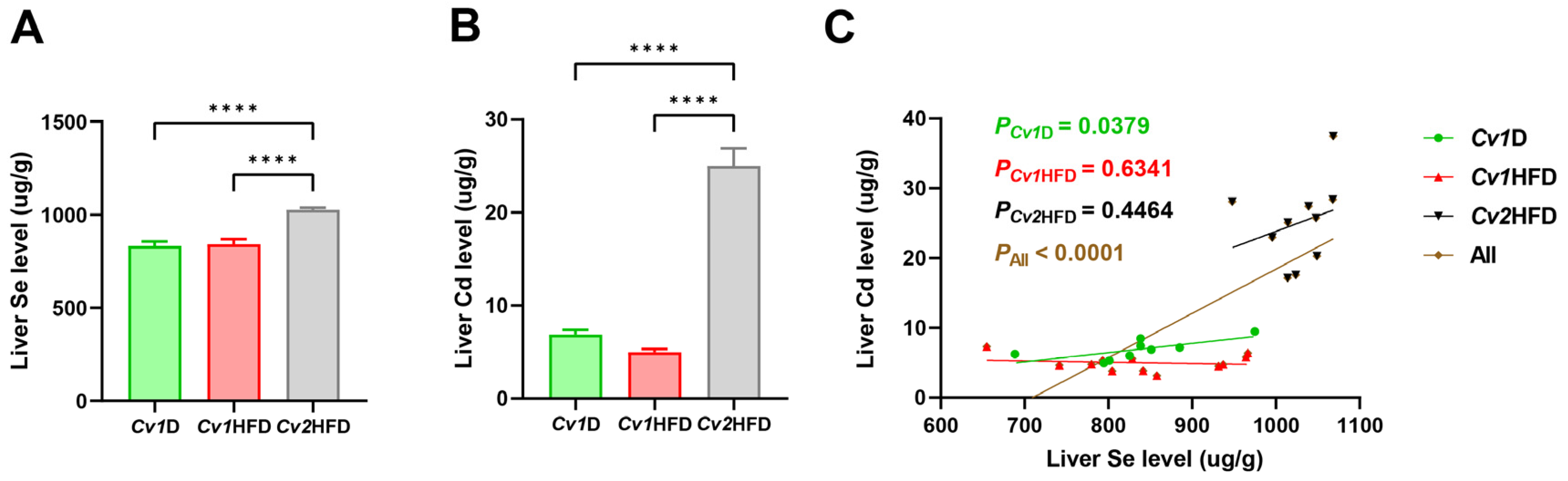
3.2. Concentrations of Trace Elements in the Liver
3.3. Glucose Metabolism
3.4. Lipid Disorder and Liver Injury
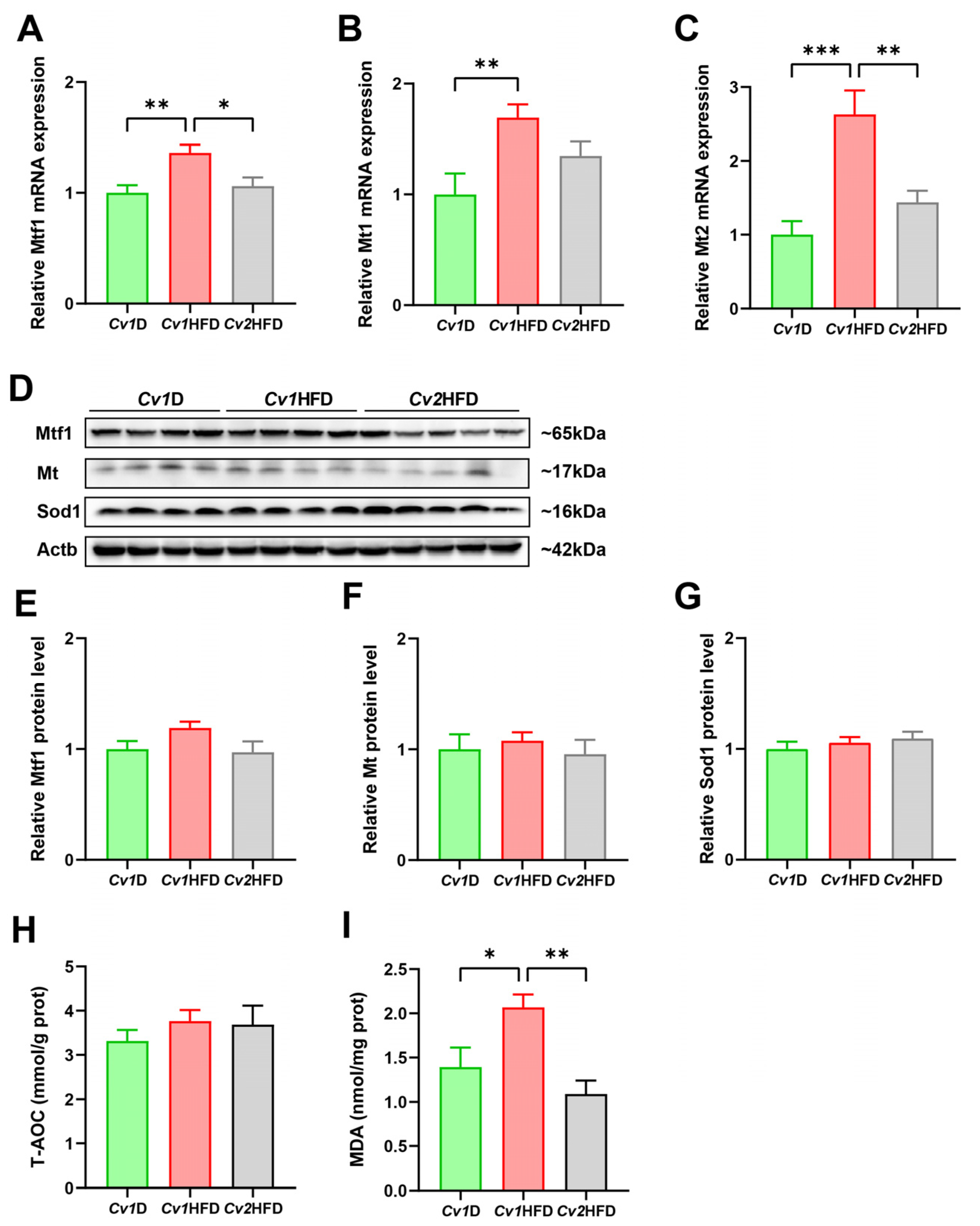
3.5. Regulating Gene and Protein Expression in Lipid Metabolism
3.6. Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense Capacity
3.7. Relative mRNA and Protein Expression of Selenoproteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramírez-Acosta, S.; Huertas-Abril, P.V.; Selma-Royo, M.; Prieto-Álamo, M.J.; Collado, M.C.; Abril, N.; García-Barrera, T. The role of selenium in shaping mice brain metabolome and selenoproteome through the gut-brain axis by combining metabolomics, metallomics, gene expression, and amplicon sequencing. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 117, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadrup, N.; Ravn-Haren, G. Toxicity of repeated oral intake of organic selenium, inorganic selenium, and selenium nanoparticles: A review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. (GMS) 2023, 79, 127235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somagattu, P.; Chinnannan, K.; Yammanuru, H.; Reddy, U.K.; Nimmakayala, P. Selenium dynamics in plants: Uptake, transport, toxicity, and sustainable management strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Yuan, Z.G.; Rao, S.; Zhang, W.W.; Ye, J.B.; Cheng, S.Y.; Xu, F. Identification, characterization, and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factors in Cardamine violifolia reveal the key genes involved in regulating selenium accumulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Y.-F. Translocation and transformation of selenium in hyperaccumulator plant Cardamine enshiensis from Enshi, Hubei, China. Plant Soil 2018, 425, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Ren, R.; Wang, L.; Zhi, Q.; Yu, T.; Hou, Q.; Yang, Z. Using machine learning to predict selenium and cadmium contents in rice grains from black shale-distributed farmland area. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wei, C.; Tu, S.; Ding, Y.; Song, Z. A dual role of Se on Cd toxicity: Evidences from the uptake of Cd and some essential elements and the growth responses in paddy rice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 151, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, W.Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.J.; Zheng, J.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Yuan, L.X.; Qin, L.Q. Protective effects and mechanism of chemical- and plant-based selenocystine against cadmium-induced liver damage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, W.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Sha, Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Shen, L.C.; Li, Y.H.; Yuan, L.X.; Qin, L.Q. Effects of selenium-cadmium co-enriched Cardamine hupingshanensis on bone damage in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 272, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tang, X.; Gu, C.; Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Chu, H.; Zhang, Z. Assessment of human exposure to cadmium and its nephrotoxicity in the Chinese population. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, H.; Tsuneyama, K.; Yazaki, M.; Nagata, K.; Minamisaka, T.; Tsuda, T.; Nomoto, K.; Hayashi, S.; Miwa, S.; Nakajima, T.; et al. The liver in itai-itai disease (chronic cadmium poisoning): Pathological features and metallothionein expression. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Wang, B.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, R.; Liu, F.; Chen, C. Cadmium exposure in infants and children: Toxicity, health effects, dietary risk assessment and mitigation strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismael, M.A.; Elyamine, A.M.; Moussa, M.G.; Cai, M.; Zhao, X.; Hu, C. Cadmium in plants: Uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers. Metallomics 2019, 11, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; He, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhu, M.; Zan, S.; Guo, F.; Wang, B.; Yang, B. The interaction between selenium and cadmium in the soil-rice-human continuum in an area with high geological background of selenium and cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; He, W.; Zhu, X.; Yang, S.; Yu, T.; Ma, W. Epidemiological study of kidney health in an area with high levels of soil cadmium and selenium: Does selenium protect against cadmium-induced kidney injury? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: As its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Friedman, S.L.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell 2021, 184, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątkiewicz, I.; Wróblewski, M.; Nuszkiewicz, J.; Sutkowy, P.; Wróblewska, J.; Woźniak, A. The role of oxidative stress enhanced by adiposity in cardiometabolic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, Z.; He, M.; Shi, B.; Lei, X.; Shan, A. The effects of endoplasmic-reticulum-resident selenoproteins in a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pig model induced by a high-fat diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Kim, J.; Lei, X.G. High Dietary Fat and Selenium Concentrations Exert Tissue- and Glutathione Peroxidase 1-Dependent Impacts on Lipid Metabolism of Young-Adult Mice. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Sun, G.; Gao, J.; Huang, T.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; He, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.Y.; et al. Dietary selenomethionine attenuates obesity by enhancing beiging process in white adipose tissue. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 113, 109230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Guo, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Cong, X. Protective effects of selenium-enriched peptides from Cardamine violifolia against high-fat diet induced obesity and its associated metabolic disorders in mice. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 31411–31424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Young, J.L.; Men, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Lin, Q.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Sex differences in the effects of whole-life, low-dose cadmium exposure on postweaning high-fat diet-induced cardiac pathogeneses. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 152176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.L.; Yan, X.; Xu, J.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X.; Arteel, G.E.; Barnes, G.N.; States, J.C.; Watson, W.H.; Kong, M.; et al. Cadmium and High-Fat Diet Disrupt Renal, Cardiac and Hepatic Essential Metals. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liang, X.; Lei, C.; Huang, Q.; Song, W.; Fang, R.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Mo, H.; Sun, N.; et al. High-Fat Diet Affects Heavy Metal Accumulation and Toxicity to Mice Liver and Kidney Probably via Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Elsherif, L.; Song, Z.; Zhou, G.; Prabhu, S.D.; Saari, J.T.; Cai, L. Cardiac metallothionein induction plays the major role in the prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy by zinc supplementation. Circulation 2006, 113, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, H.; Wang, J.; Leng, R.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Q.; He, K.; Liu, D.; Huang, B. Effect of selenium-enriched kiwifruit on body fat reduction and liver protection in hyperlipidaemic mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2044–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Li, F.; Zhu, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y. Selenium-enriched and ordinary black teas regulate the metabolism of glucose and lipid and intestinal flora of hyperglycemic mice. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2023, 78, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Kong, A.; Guo, C.; Liu, J.; Li, K.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, M.; Shi, H. Cadmium perturbed lipid profile and induced liver dysfunction in mice through phosphatidylcholine remodeling and promoting arachidonic acid synthesis and metabolism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 247, 114254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kang, W.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Gan, F.; Huang, K. Gut microbiota-bile acid-intestinal Farnesoid X receptor signaling axis orchestrates cadmium-induced liver injury. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, K.; Kuang, W.; Huang, L. Exploration of the optimal strategy for dietary calcium intervention against the toxicity of liver and kidney induced by cadmium in mice: An in vivo diet intervention study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.L.; Cave, M.C.; Xu, Q.; Kong, M.; Xu, J.; Lin, Q.; Tan, Y.; Cai, L. Whole life exposure to low dose cadmium alters diet-induced NAFLD. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 436, 115855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Chandler, J.D.; Fernandes, J.; Orr, M.L.; Hao, L.; Uppal, K.; Neujahr, D.C.; Jones, D.P.; Go, Y.M. Selenium supplementation prevents metabolic and transcriptomic responses to cadmium in mouse lung. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Sheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Tao, S.; Zhang, Z. Effects of combined exposure to cadmium and high-fat diet on bone quality in male mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Alarcon, M.; Cabrera-Vique, C. Selenium in food and the human body: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.R.; Talukder, M.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, C.; Ge, J.; Li, J.L. Nanoselenium alleviates cadmium-induced cerebral injury via regulating cerebral metal transporters and metal-regulatory transcription factor 1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 9896–9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, X.; Chen, P.; Chen, F.; Pan, Y.; Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Luo, T. Tyrosol regulates hepatic lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3752–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Yi, Y.; Wen, X.; Li, T.; Qin, S. Extract of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Glycolipid Metabolism Disorder in Rats by Targeting Gut Microbiota and TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB Pathway. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Qi, Z.; Hou, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.X. Effects of chronic cadmium exposure at food limitation-relevant levels on energy metabolism in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wan, Y. Potential Protective Effect of Selenium-Enriched Lactobacillus plantarum on Cadmium-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.M.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, X.L. Puerarin attenuates cadmium-induced hepatic lipid metabolism disorder by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation in mice. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 222, 111521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, T.; Yuan, M.; Sun, X. Kiwifruit Peel Extract Improves the Alterations in Lipid Metabolism in High-fat Diet-fed Model Rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2024, 79, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Yang, H.; Song, B.L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, F.; Farhat, D.; Gursu, G.; Samnani, S.; Lee, J.Y. Snapshots of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8: A Sterol’s Journey to Cross the Cellular Membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funes, A.K.; Avena, V.; Boarelli, P.V.; Monclus, M.A.; Zoppino, D.F.; Saez-Lancellotti, T.E.; Fornes, M.W. Cholesterol dynamics in rabbit liver: High-fat diet, olive oil, and synergistic dietary effects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 733, 150675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogushi, S.; Kimura, T. The difference in zinc concentrations required for induction among metallothionein isoforms can be explained by the different MTF1 affinities to MREs in its promoter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, M.; Nordberg, G.F. Metallothionein and Cadmium Toxicology-Historical Review and Commentary. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeque, J.Z.; Jansen van Rensburg, P.J.; Louw, R.; van der Westhuizen, F.H.; Florit, S.; Ramírez, L.; Giralt, M.; Hidalgo, J. Obesity and metabolomics: Metallothioneins protect against high-fat diet-induced consequences in metallothionein knockout mice. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2015, 19, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Kawakami, T.; Kondoh, M.; Takiguchi, M.; Kadota, Y.; Himeno, S.; Suzuki, S. Development of high-fat-diet-induced obesity in female metallothionein-null mice. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banni, M.; Messaoudi, I.; Said, L.; El Heni, J.; Kerkeni, A.; Said, K. Metallothionein gene expression in liver of rats exposed to cadmium and supplemented with zinc and selenium. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 59, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirovic, A.; Cirovic, A.; Yimthiang, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Satarug, S. Modulation of Adverse Health Effects of Environmental Cadmium Exposure by Zinc and Its Transporters. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasiewicz, T.A.; Smith, J.C. Properties of the cadmium and selenium complex formed in rat plasma in vivo and in vitro. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 1978, 23, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasiewicz, T.A.; Smith, J.C. Interaction between cadmium and selenium in rat plasma. Environ. Health Perspect. 1978, 25, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Wang, Z.; Ma, M.; Xu, P.; Liu, L.; Tinkov, A.A.; Lei, X.G.; Zhou, J.C. Associations between Circulating SELENOP Level and Disorders of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: A Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, B.; Wilkinson, D.; Hutchison, A.T.; Thompson, C.H.; Wittert, G.A.; Heilbronn, L.K. Selenoprotein P is elevated in individuals with obesity, but is not independently associated with insulin resistance. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 11, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ren, B.; Li, X.; Yan, H.; Xie, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Tian, J.; Huang, K. Selenoprotein F knockout leads to glucose and lipid metabolism disorders in mice. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 25, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z. The protective effect of selenoprotein M on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of the AMPKα1–MFN2 pathway and Parkin mitophagy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2022, 79, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Men, L.; Yu, S.; Yao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Wang, N.; Ran, L.; Wu, Y.; et al. Hepatic deficiency of selenoprotein S exacerbates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Feng, T.; Liu, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, K.; Zhou, J. Hepatic proteomic analysis of selenoprotein T knockout mice by TMT: Implications for the role of selenoprotein T in glucose and lipid metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L.; Huang, J.-Q.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Chen, L.-B.; Li, S.-P.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Ren, F.-Z.; Lei, X.-G. Loss of Selenov predisposes mice to extra fat accumulation and attenuated energy expenditure. Redox Biol. 2021, 45, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Acosta, S.; Uhlírová, R.; Navarro, F.; Gómez-Ariza, J.L.; García-Barrera, T. Antagonistic interaction of selenium and cadmium in human hepatic cells through selenoproteins. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 891933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Cao, H.; Huang, A.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, G.; Mao, Y.; Luo, J.; et al. The protection of selenium against cadmium-induced mitophagy via modulating nuclear xenobiotic receptors response and oxidative stress in the liver of rabbits. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Lv, Q.; Li, F.; Xu, P.; Han, Z.; Yang, A.; Shi, Z.; Wang, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Alleviation of Lipid Disorder and Liver Damage in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Selenium-Enriched Cardamine violifolia with Cadmium Accumulation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183208
Zhu J, Lv Q, Li F, Xu P, Han Z, Yang A, Shi Z, Wang C, Jiang J, Zhu Y, et al. Alleviation of Lipid Disorder and Liver Damage in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Selenium-Enriched Cardamine violifolia with Cadmium Accumulation. Nutrients. 2024; 16(18):3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183208
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Junying, Qingqing Lv, Fengna Li, Ping Xu, Ziyu Han, Aolin Yang, Zhan Shi, Chao Wang, Jie Jiang, Yunfen Zhu, and et al. 2024. "Alleviation of Lipid Disorder and Liver Damage in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Selenium-Enriched Cardamine violifolia with Cadmium Accumulation" Nutrients 16, no. 18: 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183208
APA StyleZhu, J., Lv, Q., Li, F., Xu, P., Han, Z., Yang, A., Shi, Z., Wang, C., Jiang, J., Zhu, Y., Chen, X., Sun, L., Lei, X. G., & Zhou, J.-C. (2024). Alleviation of Lipid Disorder and Liver Damage in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Selenium-Enriched Cardamine violifolia with Cadmium Accumulation. Nutrients, 16(18), 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183208







