Effect of Selenium and Selenoproteins on Radiation Resistance
Abstract
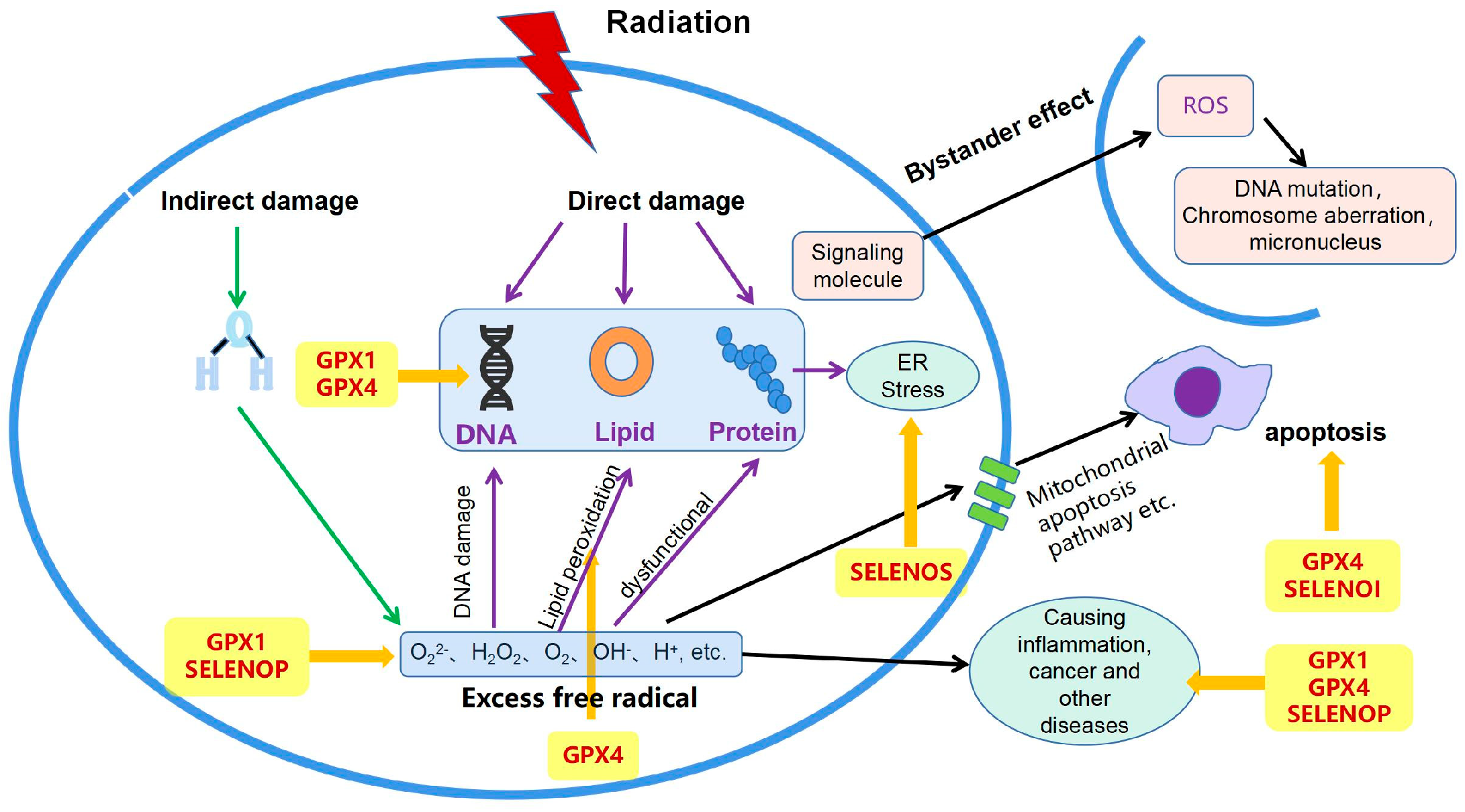
1. Introduction
2. Selenoproteins and Their Anti-Radiation Effects
2.1. Glutathione Peroxidases (GPXs)
2.1.1. Glutathione Peroxidase 1 (GPX1)
2.1.2. Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (GPX4)
2.2. Selenoprotein P (SELENOP)
2.3. Selenoprotein S (SELENOS)
2.4. Selenoprotein I (SELENOI)
3. Radiation Resistance Mechanism of Selenium and Selenoproteins
3.1. Improves Oxidative Damage
3.2. Protecting DNA
3.3. Regulating Cell Apoptosis
3.4. Regulating Immune System
3.4.1. MAPK Signaling Pathways and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
3.4.2. Inflammation Signaling Pathway
4. The Application of Selenium and Selenoproteins in the Treatment of Radiation-Related Diseases
4.1. Lung Injury and Treatment
4.2. Hematopoietic System
4.3. Gastrointestinal System
4.4. Kidney and Liver
4.5. Cardiovascular System
5. Effects of Selenium and Selenoproteins Doses on Radiation Resistance
6. Summary and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Soule, B.P.; Hyodo, F.; Matsumoto, K.; Simone, N.L.; Cook, J.A.; Krishna, M.C.; Mitchell, J.B. Therapeutic and clinical applications of nitroxide compounds. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havránková, R. Biological effects of ionizing radiation. Cas. Lek. Cesk. 2020, 159, 258–260. [Google Scholar]
- Meador, J.A.; Morris, R.J.; Balajee, A.S. Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Damage Response in Primary Melanocytes and Keratinocytes of Human Skin. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2022, 162, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carante, M.P.; Ramos, R.L.; Ballarini, F. Radiation Damage in Biomolecules and Cells 2.0. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.M.; Li, J.J. NF-kappa B-mediated adaptive resistance to ionizing radiation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liang, Z.; Ma, S.; Li, L.; Liu, X. Radioprotective countermeasures for radiation injury (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. Radioprotective effects and mechanisms of animal, plant and microbial polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, M.; Sun, H.; Yang, J.C.; Huang, Y.X.; Huang, J.Q.; Lei, X.; Sun, L.H. Selenium deficiency-induced multiple tissue damage with dysregulation of immune and redox homeostasis in broiler chicks under heat stress. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 2056–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Huang, J.Q. Selenoproteins Protect Against Avian Liver Necrosis by Metabolizing Peroxides and Regulating Receptor Interacting Serine Threonine Kinase 1/Receptor Interacting Serine Threonine Kinase 3/Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-Like and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 696256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Prabhu, K.S.; Das, A.; Mastro, A.M. Dietary selenium supplementation modifies breast tumor growth and metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Huang, Y.X.; Sun, H.; Liu, M.; Zhao, L.; Sun, L.H. Selenium Deficiency Dysregulates One-Carbon Metabolism in Nutritional Muscular Dystrophy of Chicks. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliga, M.S.; Diwadkar-Navsariwala, V.; Koh, T.; Fayad, R.; Fantuzzi, G.; Diamond, A.M. Selenoprotein deficiency enhances radiation-induced micronuclei formation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoytcheva, Z.R.; Berry, M.J. Transcriptional regulation of mammalian selenoprotein expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xie, L.; Song, A.; Zhang, C. Selenium Status and Its Antioxidant Role in Metabolic Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7009863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kursvietiene, L.; Mongirdiene, A.; Bernatoniene, J.; Sulinskiene, J.; Staneviciene, I. Selenium Anticancer Properties and Impact on Cellular Redox Status. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Yang, S.; Li, T.; Huang, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, J. Advances in the Study of the Mechanism by Which Selenium and Selenoproteins Boost Immunity to Prevent Food Allergies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, J.; Xiong, D.; Long, M. Detoxification of Selenium Yeast on Mycotoxins and Heavy Metals: A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 5441–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.; Davies, M.J.; Pattison, D.I. Reaction of low-molecular-mass organoselenium compounds (and their sulphur analogues) with inflammation-associated oxidants. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 750–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K.; Motevaseli, E.; Mirtavoos-Mahyari, H.; Shabeeb, D.; Eleojo Musa, A.; Sanikhani, N.S.; Najafi, M.; Ahmadi, A. Selenium as an adjuvant for modification of radiation response. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 18559–18571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Pan, X.; Wei, G.; Hua, Y. Research progress of glutathione peroxidase family (GPX) in redoxidation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1147414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, R. Biological Functions of Selenoprotein Glutathione Peroxidases (GPXs) and their Expression in Osteoarthritis. J. Inflammation Res. 2023, 16, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, T.; Nakashiro, C.; Fujiwara, K.; Shiga, R.; Sasatani, M.; Kamiya, K.; Ushiyama, A. Radiation affects glutathione redox reaction by reduced glutathione peroxidase activity in human fibroblasts. J. Radia. Res. 2022, 63, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Shao, Q. Glutathione Peroxidase GPX1 and Its Dichotomous Roles in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, D.E.; Loscalzo, J. The role of glutathione peroxidase-1 in health and disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 188, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Maiorino, M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3289–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerome-Morais, A.; Bera, S.; Rachidi, W.; Gann, P.H.; Diamond, A.M. The effects of selenium and the GPx-1 selenoprotein on the phosphorylation of H2AX. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3399–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Fu, G.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, R. Selenoprotein GPX1 is a prognostic and chemotherapy-related biomarker for brain lower grade glioma. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 74, 127082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidlin, C.J.; Shakya, A.; Dodson, M.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. The intricacies of NRF2 regulation in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 76, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, D.; Tew, K.D.; Marinelli, R.; Galli, F.; Wang, G.Y. Nrf2-modulation by seleno-hormetic agents and its potential for radiation protection. BioFactors 2020, 46, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.P.; Jemth, P.; Mannervik, B.; Williamson, G. Reduction of thymine hydroperoxide by phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase and glutathione transferases. Febs Lett. 1997, 410, 210–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, H.; Ou, Z.; Liu, J.; Duan, W.; Wang, H.; Ge, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, F.; et al. GPX4 and vitamin E cooperatively protect hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yant, L.J.; Ran, Q.T.; Rao, L.; Van Remmen, H.; Shibatani, T.; Belter, J.G.; Motta, L.; Richardson, A.; Prolla, T.A. The selenoprotein GPX4 is essential for mouse development and protects from radiation and oxidative damage insults. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Ran, Q.; Jang, Y.C.; Holstein, D.; Lechleiter, J.; McDonald-Marsh, T.; Musatov, A.; Song, W.; Van Remmen, H.; Richardson, A. Glutathione peroxidase 4 differentially regulates the release of apoptogenic proteins from mitochondria. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, T.; Zhu, K.; Dong, Y.; Lei, X.; Yu, Z.; Lv, C.; Huang, J. SELENOI Functions as a Key Modulator of Ferroptosis Pathway in Colitis and Colorectal Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2404073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomburg, L. Selenoprotein P—Selenium transport protein, enzyme and biomarker of selenium status. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 191, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckers, J.C.; Kalen, A.L.; Xiao, W.S.; Sarsour, E.H.; Goswami, P.C. Selenoprotein P Inhibits Radiation-Induced Late Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation and Normal Cell Injury. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, C.J.; Goswami, P.C. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant enzyme activity regulates radioresistance in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Thera. 2008, 7, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalen, A.L.; Sarsour, E.H.; Venkataraman, S.; Goswami, P.C. Mn-superoxide dismutase overexpression enhances G2 accumulation and radioresistance in human oral squamous carcinoma cells. Antiox. Redox Signaling 2006, 8, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, C.W.; Reddy, V.K.; Short, S.P.; Motley, A.K.; Lintel, M.K.; Bradley, A.M.; Freeman, T.; Vallance, J.; Ning, W.; Parang, B.; et al. Selenoprotein P influences colitis-induced tumorigenesis by mediating stemness and oxidative damage. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2646–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vunta, H.; Belda, B.J.; Arner, R.J.; Reddy, C.C.; Heuvel, J.P.V.; Prabhu, K.S. Selenium attenuates pro-inflammatory gene expression in macrophages. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.A.; Yoo, M.H.; Shrimali, R.K.; Irons, R.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Hatfield, D.L.; Park, J.M. Session 2: Micronutrients and the immune system Role of selenium-containing proteins in T-cell and macrophage function. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, L.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Tian, G.; Cai, J.; et al. Selenoproteins synergistically protect porcine skeletal muscle from oxidative damage via relieving mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghelichkhani, F.; Gonzalez, F.A.; Kapitonova, M.A.; Schaefer-Ramadan, S.; Liu, J.; Cheng, R.J.; Rozovsky, S. Selenoprotein S: A versatile disordered protein. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 731, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, T.; Yang, S.H.; Zhu, K.D.; Wang, L.S.; Dong, Y.L.; Huang, J.Q. Hepatocyte-specific Selenoi deficiency predisposes mice to hepatic steatosis and obesity. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e23717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Martinez-Rodriguez, V.; Hoffmann, P.R. Roles for Selenoprotein I and Ethanolamine Phospholipid Synthesis in T Cell Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Guy, C.S.; Chapman, N.M.; Palacios, G.; Wei, J.; Zhou, P.; Long, L.; Wang, Y.D.; Qian, C.; Dhungana, Y.; et al. Metabolic control of T(FH) cells and humoral immunity by phosphatidylethanolamine. Nature 2021, 595, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrini, C.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 931–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, T.P. Space flight and oxidative stress. Nutrition 2002, 18, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattman, C.L.; Schaefer, L.M.; Oury, T.D. Extracellular superoxide dismutase in biology and medicine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 236–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełczykowska, M.; Kocot, J.; Paździor, M.; Musik, I. Selenium—A fascinating antioxidant of protective properties. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.F.; Srinivasan, V.; Kumar, K.S.; Landauer, M.R. Radioprotection by metals: Selenium. Adv. Space Res. 1992, 12, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushakova, T.; Melkonyan, H.; Nikonova, L.; Afanasyev, V.; Gaziev, A.I.; Mudrik, N.; Bradbury, R.; Gogvadze, V. Modification of gene expression by dietary antioxidants in radiation-induced apoptosis of mice splenocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haan, J.B.; Crack, P.J.; Flentjar, N.; Iannello, R.C.; Hertzog, P.J.; Kola, I. An imbalance in antioxidant defense affects cellular function: The pathophysiological consequences of a reduction in antioxidant defense in the glutathione peroxidase-1 (Gpx1) knockout mouse. Redox Rep. 2003, 8, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, I.; Yoshida, Y.; Suda, M.; Minamino, T. DNA damage response and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; De Rosa, V.; Rachidi, W.; Diamond, A.M. Does a role for selenium in DNA damage repair explain apparent controversies in its use in chemoprevention? Mutagenesis 2013, 28, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Davis, C.D.; Finley, J.W. Effect of selenium-enriched broccoli diet on differential gene expression in min mouse liver(1,2). J. Nutr. Biochem. 2003, 14, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.L.; Lancia, J.K.; Mathur, A.; Smith, M.L. Selenium protection from DNA damage involves a Ref1/p53/Brca1 protein complex. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 899–904. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.Q.; Liu, M.; Xu, Z.J.; Xu, Z.J.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, X.M.; Chen, C.J.; Zuo, G.; Yang, J.C.; Lei, X.G.; et al. Optimum Doses and Forms of Selenium Maintaining Reproductive Health via Regulating Homeostasis of Gut Microbiota and Testicular Redox, Inflammation, Cell Proliferation, and Apoptosis in Roosters. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Huang, J.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Zhao, S. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) nuclear translocation mediated caspase-independent mechanism involves in X-ray-induced MCF-7 cell death. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, S.; Dharmaraj, S. Selenium and selenoproteins: It’s role in regulation of inflammation. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 667–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Cao, F.; Liu, H. Radiation-induced Cell Death and Its Mechanisms. Health Phys. 2022, 123, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Q.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Ren, F.Z.; Lei, X.G. Novel role and mechanism of glutathione peroxidase-4 in nutritional pancreatic atrophy of chicks induced by dietary selenium deficiency. Redox Biol. 2022, 57, 102482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Drake, A.C.; Hu, G.; Rudnick, S.; Chen, Q.; Phennicie, R.; Attar, R.; Nemeth, J.; Gaudet, F.; Chen, J. Induction and Therapeutic Targeting of Human NPM1c(+) Myeloid Leukemia in the Presence of Autologous Immune System in Mice. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zheng, L.; Li, M. Positive effects of selenium supplementation on selenoprotein S expression and cytokine status in a murine model of acute liver injury. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 71, 126927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, X. The MAPK Pathway-Based Drug Therapeutic Targets in Pituitary Adenomas. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shao, W.; Niu, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Immunomodulatory Effects of Colistin on Macrophages in Rats by Activating the p38/MAPK Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shi, X.; Cai, Y. Selenium Deficiency Induces Apoptosis and Necroptosis Through ROS/MAPK Signal in Human Uterine Smooth Muscle Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 3147–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M.; Rodemann, H.P. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling as a key mediator of tumor cell responsiveness to radiation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zeng, B.; Liu, C.; Gong, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Jin, M.; Guo, J.; et al. Triple Cross-linked Dynamic Responsive Hydrogel Loaded with Selenium Nanoparticles for Modulating the Inflammatory Microenvironment via PI3K/Akt/NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2303167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyapour, R.; Amini, P.; Rezapour, S.; Cheki, M.; Rezaeyan, A.; Farhood, B.; Shabeeb, D.; Musa, A.E.; Fallah, H.; Najafi, M. Radiation-induced inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Mil. Med. Res. 2018, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinar-Inglis, O.; DiCarlo, A.L.; Lapinskas, P.J.; Rios, C.I.; Satyamitra, M.M.; Silverman, T.A.; Winters, T.A.; Cassatt, D.R. Radiation-induced multi-organ injury. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2024, 100, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, J.; Jelveh, S.; Calveley, V.; Zaidi, A.; Doctrow, S.R.; Hill, R.P. Mitigation of lung injury after accidental exposure to radiation. Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, F.; Muir, S.A.; Cohen, E.P.; North, P.E.; Fish, B.L.; Irving, A.A.; Mader, M.; Moulder, J.E. High-Dose Selenium for the Mitigation of Radiation Injury: A Pilot Study in a Rat Model. Radiat. Res. 2009, 171, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunwar, A.; Jain, V.K.; Priyadarsini, K.I.; Haston, C.K. A selenocysteine derivative therapy affects radiation-induced pneumonitis in the mouse. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, L.Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles, characterization and X-ray induced radiotherapy for the treatment of lung cancer with interstitial lung disease. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2019, 191, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, Y.F.; Song, M.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.F. Selenium Improves Bone Microenvironment-Related Hematopoiesis and Immunity in T-2 Toxin-Exposed Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, K.; Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Huang, J. Stabilization by Chaperone GroEL in Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles Produced from Bifidobacterium animalis H15 for the Treatment of DSS-Induced Colitis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 13439–13452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, S.P.; Pilat, J.M.; Barrett, C.W.; Reddy, V.K.; Haberman, Y.; Hendren, J.R.; Marsh, B.J.; Keating, C.E.; Motley, A.K.; Hill, K.E.; et al. Colonic Epithelial-Derived Selenoprotein P Is the Source for Antioxidant-Mediated Protection in Colitis-Associated Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1694–1708.e1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, M.; Asri-Rezaei, S.; Dormanesh, B.; Nazarizadeh, A. Comparative study of radioprotective effects of selenium nanoparticles and sodium selenite in irradiation-induced nephropathy of mice model. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghazaly, M.A.; Fadel, N.; Rashed, E.; El-Batal, A.; Kenawy, S.A. Anti-inflammatory effect of selenium nanoparticles on the inflammation induced in irradiated rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.A.; Abd El Azim, A.S.; Gharib, O.A. Protective Effects of ω-3 fatty acids and/or Nano- selenium on Cisplatin and Ionizing radiation induced liver toxicity in rats. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2016, 50, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmoonfar, R.; Moslehi, M.; Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D. Radioprotective Effect of Selenium Nanoparticles: A Mini Review. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 2024, 5538107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, A.E.; Shabeeb, D. Radiation-Induced Heart Diseases: Protective Effects of Natural Products. Medicina 2019, 55, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, X.W.; Lee, C.P.; Chua, B.H.L.; Ho, Y.S. Attenuation of doxorubicin-induced contractile and mitochondrial dysfunction in mouse heart by cellular glutathione peroxidase. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.P.; Xiong, Y.; Ho, Y.S.; Liu, X.W.; Chua, C.C.; Xu, X.S.; Wang, H.; Hamdy, R.; Chua, B.H.L. Glutathione peroxidase 1-deficient mice are more susceptible to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippman, S.M.; Klein, E.A.; Goodman, P.J.; Lucia, M.S.; Thompson, I.M.; Ford, L.G.; Parnes, H.L.; Minasian, L.M.; Gaziano, J.M.; Hartline, J.A.; et al. Effect of selenium and vitamin E on risk of prostate cancer and other cancers: The Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT). JAMA 2009, 301, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamberger, R.J.; Frost, D.V. Possible protective effect of selenium against human cancer. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1969, 100, 682. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, D.J.; Shen, S.; Glickman, L.T.; Cooley, D.M.; Bostwick, D.G.; Qian, J.; Combs, G.F., Jr.; Morris, J.S. Prostate cancer risk and DNA damage: Translational significance of selenium supplementation in a canine model. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Huang, K. Selenium in the prevention of atherosclerosis and its underlying mechanisms. Metallomics 2017, 9, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Kang, M.M.; Schoene, N.W.; Cheng, W.H. Selenium compounds activate early barriers of tumorigenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12055–12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; He, J. Effect of Different Selenium Supplementation Levels on Oxidative Stress, Cytokines, and Immunotoxicity in Chicken Thymus. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 172, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Gutiérrez, M.; García-Montalvo, E.A.; Izquierdo-Vega, J.A.; Del Razo, L.M. Effect of dietary selenium deficiency on the in vitro fertilizing ability of mice spermatozoa. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2008, 24, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.C.; Zheng, S.; Mo, J.; Liang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gong, C.; Liu, X.L.; Lei, X.G. Dietary Selenium Deficiency or Excess Reduces Sperm Quality and Testicular mRNA Abundance of Nuclear Glutathione Peroxidase 4 in Rats. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, G.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, L.; Xue, J.; Zhao, M.; Yu, H.; et al. Dietary selenium excess affected spermatogenesis via DNA damage and telomere-related cell senescence and apoptosis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 171, 113556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Selenoprotein | Position | Action Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPX1 | Erythrocyte | Eliminate reactive oxygen species to reduce radiation damage; Promote DNA repair to prevent radiation injury; Exert anticancer effects to achieve the treat of radiation damage. | [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26] |
| GPX4 | Cytoplasm, mitochondria and nucleus | Inhibit lipid peroxidation to reduce radiation damage; Regulate apoptotic markers to alleviate radiation-induced cell apoptosis; Decrease the synthesis of 8-oxo-dG to minimize DNA damage. | [27,28,29,30] |
| SELENOP | Plasma | Inhibition of radiation-induced late reactive oxygen species accumulation; Reduction of tumor occurrence as a tumor suppressor in radiation-induced inflammatory carcinogenesis; Regulation of immune cell function as an antioxidant for immune cells. | [31,32,33,34,35,36,37] |
| SELENOS | Endoplasmic reticulum | Alleviate radiation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. | [38,39] |
| SELENOI | The Golgi apparatus | Plays a crucial role in T cell activation, enhancing the immune response of immune cells. | [40,41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Fang, B.; Huang, J. Effect of Selenium and Selenoproteins on Radiation Resistance. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172902
Zhang S, Zhang G, Wang P, Wang L, Fang B, Huang J. Effect of Selenium and Selenoproteins on Radiation Resistance. Nutrients. 2024; 16(17):2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172902
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shidi, Guowei Zhang, Pengjie Wang, Lianshun Wang, Bing Fang, and Jiaqiang Huang. 2024. "Effect of Selenium and Selenoproteins on Radiation Resistance" Nutrients 16, no. 17: 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172902
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhang, G., Wang, P., Wang, L., Fang, B., & Huang, J. (2024). Effect of Selenium and Selenoproteins on Radiation Resistance. Nutrients, 16(17), 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172902






