A Novel Interaction between a 23-SNP Genetic Risk Score and Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Intake on HbA1c Levels in Southeast Asian Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Anthropometry Measurements
2.3. Biochemical and Clinical Measures
2.4. Assessment of Dietary Intake
2.5. Assessment of Physical Activity
2.6. SNP Selection and Genotyping
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants Stratified Based on GRS
3.2. Interactions between GRS and Lifestyle Factors on Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- diseases W-RFoN-c: Risk Factors of Non-Cummunicable Diseases. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/noncommunicable-diseases-risk-factors#:~:text=Most%20noncommunicable%20diseases%20are%20the,blood%20glucose%20and%20raised%20cholesterol (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- World Health Organisation. Obesity and Overweight in South East Asia. Available online: https://www.who.int/southeastasia/health-topics/obesity (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Sulistiadi, W.; Kusuma, D.; Amir, V.; Tjandrarini, D.H.; Nurjana, M.A. Growing Up Unequal: Disparities of Childhood Overweight and Obesity in Indonesia’s 514 Districts. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusnedi, G.; Fahmida, U.; Witjaksono, F.; Nurwidya, F.; Mansyur, M.; Djuwita, R.; Dwiriani, C.M.; Abdullah, M. Effectiveness of optimized food-based recommendation promotion to improve nutritional status and lipid profiles among Minangkabau women with dyslipidemia: A cluster-randomized trial. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herningtyas, E.H.; Ng, T.S. Prevalence and distribution of metabolic syndrome and its components among provinces and ethnic groups in Indonesia. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, P.; Ventura, E.F.; Dhanapal, A.; Cheah, E.S.G.; Loganathan, A.; Quen, P.L.; Appukutty, M.; Taslim, N.A.; Hardinsyah, H.; Md Noh, M.F.; et al. Gene-Diet Interactions on Metabolic Disease-Related Outcomes in Southeast Asian Populations: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alathari, B.E.; Aji, A.S.; Ariyasra, U.; Sari, S.R.; Tasrif, N.; Yani, F.F.; Sudji, I.R.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Lipoeto, N.I.; Vimaleswaran, K.S. Interaction between Vitamin D-Related Genetic Risk Score and Carbohydrate Intake on Body Fat Composition: A Study in Southeast Asian Minangkabau Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsulami, S.; Aji, A.S.; Ariyasra, U.; Sari, S.R.; Tasrif, N.; Yani, F.F.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Sudji, I.R.; Lipoeto, N.I.; Vimaleswaran, K.S. Interaction between the genetic risk score and dietary protein intake on cardiometabolic traits in Southeast Asian. Genes. Nutr. 2020, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H.F.L.; Sulistyoningrum, D.C.; Huriyati, E.; Lee, Y.Y.; Manan Wan Muda, W.A. The Interaction between Coffee: Caffeine Consumption, UCP2 Gene Variation, and Adiposity in Adults-A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 2019, 9606054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, S.; Aji, A.S.; Ariyasra, U.; Sari, S.R.; Malik, S.G.; Tasrif, N.; Yani, F.F.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Sudji, I.R.; Lipoeto, N.I.; et al. A nutrigenetic approach for investigating the relationship between vitamin B12 status and metabolic traits in Indonesian women. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2019, 18, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H.F.L.; Sulistyoningrum, D.C.; Huriyati, E.; Lee, Y.Y.; Muda, W. The interaction between energy intake, physical activity and UCP2 -866G/A gene variation on weight gain and changes in adiposity: An Indonesian Nutrigenetic Cohort (INDOGENIC). Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huriyati, E.; Luglio, H.F.; Ratrikaningtyas, P.D.; Tsani, A.F.; Sadewa, A.H.; Juffrie, M. Dyslipidemia, insulin resistance and dietary fat intake in obese and normal weight adolescents: The role of uncoupling protein 2 -866G/A gene polymorphism. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2016, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.I. Single nucleotide polymorphisms and disease gene mapping. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4 (Suppl. 3), S273–S278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudbridge, F. Polygenic Epidemiology. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüls, A.; Krämer, U.; Carlsten, C.; Schikowski, T.; Ickstadt, K.; Schwender, H. Comparison of weighting approaches for genetic risk scores in gene-environment interaction studies. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimaleswaran, K.S. GeNuIne (gene-nutrient interactions) Collaboration: Towards implementing multi-ethnic population-based nutrigenetic studies of vitamin B(12) and D deficiencies and metabolic diseases. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiruvenkataswamy, C.S.; Appukutty, M.; Vimaleswaran, K.S. Role of precision nutrition in improving military performance. Per. Med. 2022, 19, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimaleswaran, K.S. A nutrigenetics approach to study the impact of genetic and lifestyle factors on cardiometabolic traits in various ethnic groups: Findings from the GeNuIne Collaboration. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanapal, A.; Wuni, R.; Ventura, E.F.; Chiet, T.K.; Cheah, E.S.G.; Loganathan, A.; Quen, P.L.; Appukutty, M.; Noh, M.F.M.; Givens, I.; et al. Implementation of Nutrigenetics and Nutrigenomics Research and Training Activities for Developing Precision Nutrition Strategies in Malaysia. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimaleswaran, K. Gene–nutrient interactions on metabolic diseases: Findings from the GeNuIne Collaboration. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.H.; Yeh, W.T. How to define obesity? Evidence-based multiple action points for public awareness, screening, and treatment: An extension of Asian-Pacific recommendations. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 370–374. [Google Scholar]
- Lipoeto, N.I.; Agus, Z.; Oenzil, F.; Wahlqvist, M.; Wattanapenpaiboon, N. Dietary intake and the risk of coronary heart disease among the coconut-consuming Minangkabau in West Sumatra, Indonesia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 13, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C.; Howe, G.R.; Kushi, L.H. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1220S–1228S; discussion 1229S–1231S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, T.; Bull, F. Development of the World Health Organization Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). J. Public Health 2006, 14, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapik, I.A.; Ranjit, R.; Galchenko, A.V. Impact of KCNJ11 rs5219, UCP2 rs659366, and MTHFR rs1801133 Polymorphisms on Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2021, 17, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropano, C.; Santoro, N.; Groop, L.; Dalla Man, C.; Cobelli, C.; Galderisi, A.; Kursawe, R.; Pierpont, B.; Goffredo, M.; Caprio, S. The rs7903146 Variant in the TCF7L2 Gene Increases the Risk of Prediabetes/Type 2 Diabetes in Obese Adolescents by Impairing β-Cell Function and Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bego, T.; Čaušević, A.; Dujić, T.; Malenica, M.; Velija-Asimi, Z.; Prnjavorac, B.; Marc, J.; Nekvindová, J.; Palička, V.; Semiz, S. Association of FTO Gene Variant (rs8050136) with Type 2 Diabetes and Markers of Obesity, Glycaemic Control and Inflammation. J. Med. Biochem. 2019, 38, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sull, J.W.; Kim, G.; Jee, S.H. Association of MC4R (rs17782313) with diabetes and cardiovascular disease in Korean men and women. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klünder-Klünder, M.; Mejía-Benitez, M.A.; Flores-Huerta, S.; Burguete-García, A.I.; García-Mena, J.; Cruz, M. rs12255372 variant of TCF7L2 gene is protective for obesity in Mexican children. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.M.; Furtado, J.M.; Mascarenhas, P.; Ferraz, M.E.; Ferreira, J.C.; Monteiro, M.P.; Vilanova, M.; Ferraz, F.P. Association between LEPR, FTO, MC4R, and PPARG-2 polymorphisms with obesity traits and metabolic phenotypes in school-aged children. Endocrine 2018, 60, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Song, K.; Shen, X.; Cai, Y. The association between KCNQ1 gene polymorphism and type 2 diabetes risk: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, E.; Lima, S.; Galdino, O.A.; Arrais, R.F.; de Souza, K.S.C.; de Rezende, A.A. Association of CYP2R1 and VDR Polymorphisms with Metabolic Syndrome Components in Non-Diabetic Brazilian Adolescents. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucan, L.; Vélayoudom-Céphise, F.L.; Larifla, L.; Armand, C.; Deloumeaux, J.; Fagour, C.; Plumasseau, J.; Portlis, M.L.; Liu, L.; Bonnet, F.; et al. Polymorphisms in GC and NADSYN1 Genes are associated with vitamin D status and metabolic profile in Non-diabetic adults. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2013, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, R.; Huang, G.; et al. The influence of CYP2R1 polymorphisms and gene-obesity interaction with hypertension risk in a Chinese rural population. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, C.D.; Meyers, K.J.; Ziegler, J.T.; Taylor, K.D.; Palmer, N.D.; Haffner, S.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Rotter, J.I.; Bowden, D.W.; et al. Genome-wide association study of vitamin D concentrations in Hispanic Americans: The IRAS family study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 122, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimi, M.; Goodarzi, M.T.; Nekoei, M. Association of ADIPOQ rs266729 and rs1501299 gene polymorphisms and circulating adiponectin level with the risk of type 2 diabetes in a population of Iran: A case-control study. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2021, 20, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, T.Q.; Thu, N.T.; Phuong, P.T.; Nhung, B.T.; Nhung, T.T. CDKN2A-rs10811661 polymorphism, waist-hip ratio, systolic blood pressure, and dyslipidemia are the independent risk factors for prediabetes in a Vietnamese population. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fronczek, M.; Osadnik, T.; Banach, M. Impact of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in selected metabolic disorders. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2023, 26, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlajamäki, J.; Salmenniemi, U.; Vänttinen, M.; Ruotsalainen, E.; Kuusisto, J.; Vauhkonen, I.; Kainulainen, S.; Ng, M.C.; Cox, N.J.; Bell, G.I.; et al. Common polymorphisms of calpain-10 are associated with abdominal obesity in subjects at high risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Allin, K.H.; Friedrich, N.; Pietzner, M.; Grarup, N.; Thuesen, B.H.; Linneberg, A.; Pisinger, C.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Sandholt, C.H. Genetic determinants of serum vitamin B12 and their relation to body mass index. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongmaithem, S.S.; Joglekar, C.V.; Krishnaveni, G.V.; Sahariah, S.A.; Ahmad, M.; Ramachandran, S.; Gandhi, M.; Chopra, H.; Pandit, A.; Potdar, R.D.; et al. GWAS identifies population-specific new regulatory variants in FUT6 associated with plasma B12 concentrations in Indians. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2551–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendran, S.; Adaikalakoteswari, A.; Saravanan, P.; Shatwaan, I.A.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Vimaleswaran, K.S. An update on vitamin B12-related gene polymorphisms and B12 status. Genes. Nutr. 2018, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Chatterjee, D.; Bandyopadhyay, A.R. Effect of MTHFR (rs1801133) and FTO (rs9939609) genetic polymorphisms and obesity in T2DM: A study among Bengalee Hindu caste population of West Bengal, India. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2021, 48, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimaleswaran, K.S.; Bodhini, D.; Lakshmipriya, N.; Ramya, K.; Anjana, R.M.; Sudha, V.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Kinra, S.; Mohan, V.; Radha, V. Interaction between FTO gene variants and lifestyle factors on metabolic traits in an Asian Indian population. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unoki, H.; Takahashi, A.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hara, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Andersen, G.; Ng, D.P.; Holmkvist, J.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Jørgensen, T.; et al. SNPs in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in East Asian and European populations. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.T.; Rodrigues, D.; Guimarães, J.; Lemos, M.C. Vitamin D Pathway Genetic Variation and Type 1 Diabetes: A Case-Control Association Study. Genes 2020, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Monounsaturated fatty acids and risk of cardiovascular disease: Synopsis of the evidence available from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1989–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Khurana, L.; Isharwal, S.; Bhardwaj, S. South Asian diets and insulin resistance. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Strasser, B.; Hoffmann, G. Effects of monounsaturated fatty acids on glycaemic control in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 58, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Martinez, P.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Ferguson, J.F.; Gulseth, H.L.; Williams, C.M.; Karlström, B.; Kieć-Wilk, B.; Blaak, E.E.; Helal, O.; et al. Calpain-10 interacts with plasma saturated fatty acid concentrations to influence insulin resistance in individuals with the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.F.; Thorleifsson, G.; Reynisdottir, I.; Benediktsson, R.; Manolescu, A.; Sainz, J.; Helgason, A.; Stefansson, H.; Emilsson, V.; Helgadottir, A.; et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayling, T.M.; Timpson, N.J.; Weedon, M.N.; Zeggini, E.; Freathy, R.M.; Lindgren, C.M.; Perry, J.R.; Elliott, K.S.; Lango, H.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science 2007, 316, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steemburgo, T.; Azevedo, M.J.; Gross, J.L.; Milagro, F.I.; Campión, J.; Martínez, J.A. The rs9939609 polymorphism in the FTO gene is associated with fat and fiber intakes in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Nutr. Nutr. 2013, 6, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.P.; Urhammer, S.A.; Eiberg, H.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Jørgensen, T.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O. Variation in CAPN10 in relation to type 2 diabetes, obesity and quantitative metabolic traits: Studies in 6018 whites. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2006, 89, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppitt, S.D.; Keogh, G.F.; Mulvey, T.B.; Phillips, A.; McArdle, B.H.; MacGibbon, A.K.; Cooper, G.J. Effect of moderate changes in dietary fatty acid profile on postprandial lipaemia, haemostatic and related CVD risk factors in healthy men. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 58, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatma, R.D. Lipid profiles among diverse ethnic groups in Indonesia. Acta Medica Indones. 2011, 43, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gusnedi Fahmida, U.; Djuwita, R.; Witjaksono, F.; Abdullah, M. Food-based recommendations for Minangkabau women of reproductive age with dyslipidemia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 28, 310–320. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, S.B.; Park, J.S.; Lee, B.W.; Kang, E.S.; Ahn, C.W.; Lee, H.C.; Cha, B.S. Dietary monounsaturated fatty acids but not saturated fatty acids preserve the insulin signaling pathway via IRS-1/PI3K in rat skeletal muscle. Lipids 2010, 45, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardisson Korat, A.V.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Diet, lifestyle, and genetic risk factors for type 2 diabetes: A review from the Nurses’ Health Study, Nurses’ Health Study 2, and Health Professionals’ Follow-up Study. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2014, 3, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Merino, J.; Larsson, S.C. Causal factors underlying diabetes risk informed by Mendelian randomisation analysis: Evidence, opportunities and challenges. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Maiorino, M.I.; Ciotola, M.; Di Palo, C.; Scognamiglio, P.; Gicchino, M.; Petrizzo, M.; Saccomanno, F.; Beneduce, F.; Ceriello, A.; et al. Effects of a Mediterranean-style diet on the need for antihyperglycemic drug therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spranger, J.; Kroke, A.; Möhlig, M.; Bergmann, M.M.; Ristow, M.; Boeing, H.; Pfeiffer, A.F. Adiponectin and protection against type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 2003, 361, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashek, D.G.; Wu, C. MUFAs. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | GRS Groups | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Risk (n = 53) | High Risk (n = 53) | ||
| Mean ± SD | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 0.084 |
| WC (cm) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 0.373 |
| Fat Mass (kg) | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 0.074 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 1.9 ± 0.0 | 1.9 ± 0.0 | 0.642 |
| HbA1c (ng/mL) | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 2.7 ± 0.3 | 0.385 |
| Fasting insulin (ml/UL) | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 0.380 |
| Total Energy (Kcal) | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 1.3 | 0.040 |
| Protein (g/day) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 0.791 |
| Fat (g/day) | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 0.206 |
| Fiber (g/day) | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.375 |
| SFA (g/day) | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.586 |
| MUFA (g/day) | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.770 |
| PUFA (g/day) | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.936 |
| Physical Activity (min/week) | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 0.897 |
| Protein (g/Day) | Fat (g/Day) | Fiber (g/Day) | SFA (g/Day) | MUFA (g/Day) | PUFA (g/Day) | Physical Activity (min/Week) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.907 | 0.590 | 0.290 | 0.948 | 0.858 | 0.961 | 0.819 |
| WC (cm) | 0.337 | 0.143 | 0.737 | 0.208 | 0.177 | 0.921 | 0.926 |
| Fat Mass (kg) | 0.769 | 0.863 | 0.270 | 0.713 | 0.917 | 0.652 | 0.626 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 0.302 | 0.259 | 0.762 | 0.379 | 0.165 | 0.414 | 0.366 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 0.277 | 0.327 | 0.158 | 0.627 | 0.386 | 0.339 | 0.753 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 0.953 | 0.831 | 0.722 | 0.250 | 0.661 | 0.978 | 0.087 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 0.791 | 0.841 | 0.387 | 0.957 | 0.581 | 0.821 | 0.215 |
| TGL (mg/dL) | 0.269 | 0.217 | 0.515 | 0.144 | 0.469 | 0.630 | 0.562 |
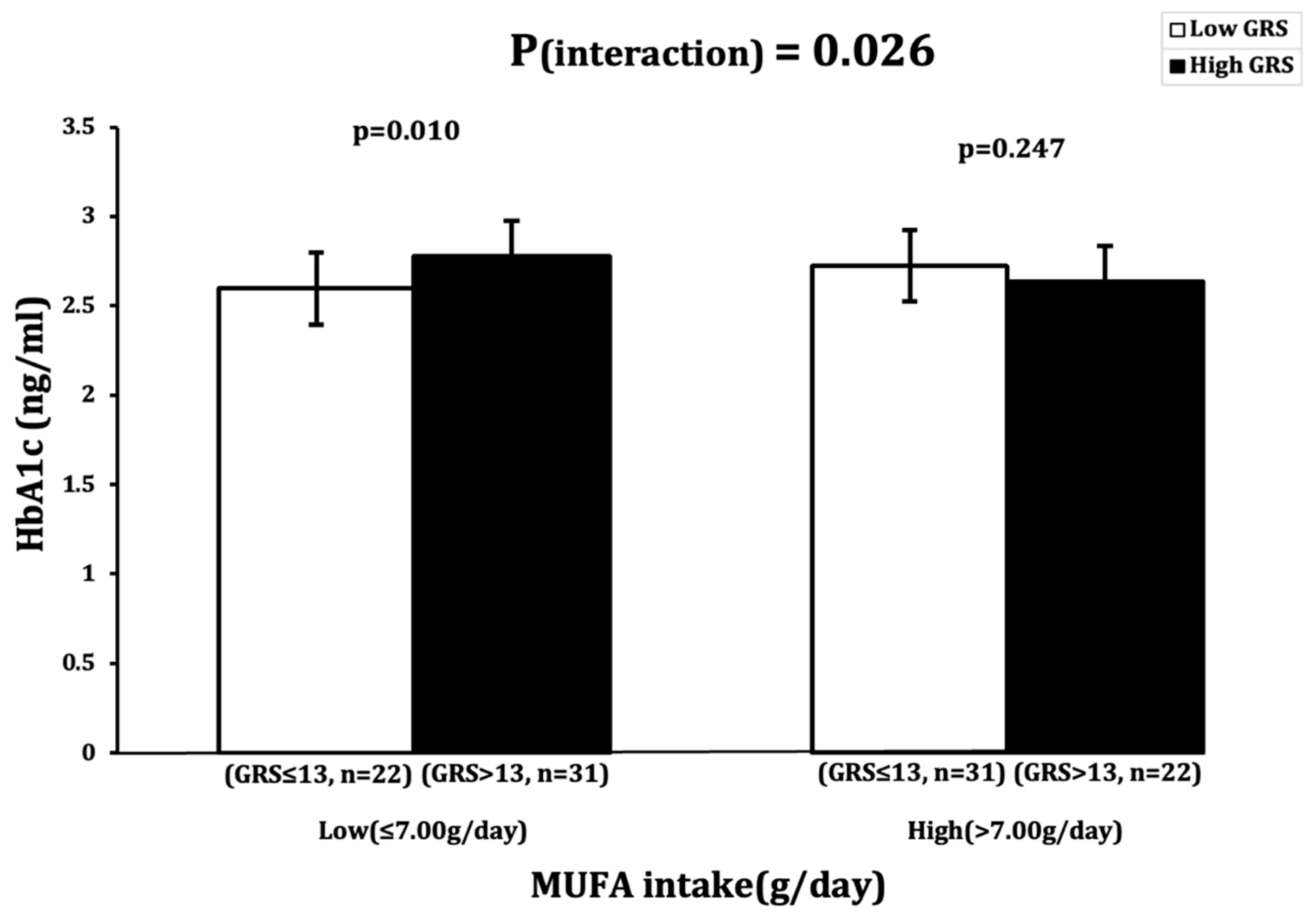
| HbA1c (ng/mL) | 0.526 | 0.376 | 0.132 | 0.225 | 0.026 | 0.127 | 0.936 |
| Fasting Insulin (mL/UL) | 0.844 | 0.809 | 0.985 | 0.576 | 0.172 | 0.211 | 0.623 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sekar, P.; Aji, A.S.; Ariyasra, U.; Sari, S.R.; Tasrif, N.; Yani, F.F.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Sudji, I.R.; Lipoeto, N.I.; Vimaleswaran, K.S. A Novel Interaction between a 23-SNP Genetic Risk Score and Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Intake on HbA1c Levels in Southeast Asian Women. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173022
Sekar P, Aji AS, Ariyasra U, Sari SR, Tasrif N, Yani FF, Lovegrove JA, Sudji IR, Lipoeto NI, Vimaleswaran KS. A Novel Interaction between a 23-SNP Genetic Risk Score and Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Intake on HbA1c Levels in Southeast Asian Women. Nutrients. 2024; 16(17):3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSekar, Padmini, Arif S. Aji, Utami Ariyasra, Sri R. Sari, Nabila Tasrif, Finny F. Yani, Julie A. Lovegrove, Ikhwan R. Sudji, Nur I. Lipoeto, and Karani S. Vimaleswaran. 2024. "A Novel Interaction between a 23-SNP Genetic Risk Score and Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Intake on HbA1c Levels in Southeast Asian Women" Nutrients 16, no. 17: 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173022
APA StyleSekar, P., Aji, A. S., Ariyasra, U., Sari, S. R., Tasrif, N., Yani, F. F., Lovegrove, J. A., Sudji, I. R., Lipoeto, N. I., & Vimaleswaran, K. S. (2024). A Novel Interaction between a 23-SNP Genetic Risk Score and Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Intake on HbA1c Levels in Southeast Asian Women. Nutrients, 16(17), 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173022








