Role of Vitamin D in Oral Lichen Planus: A Case Control Study
Abstract
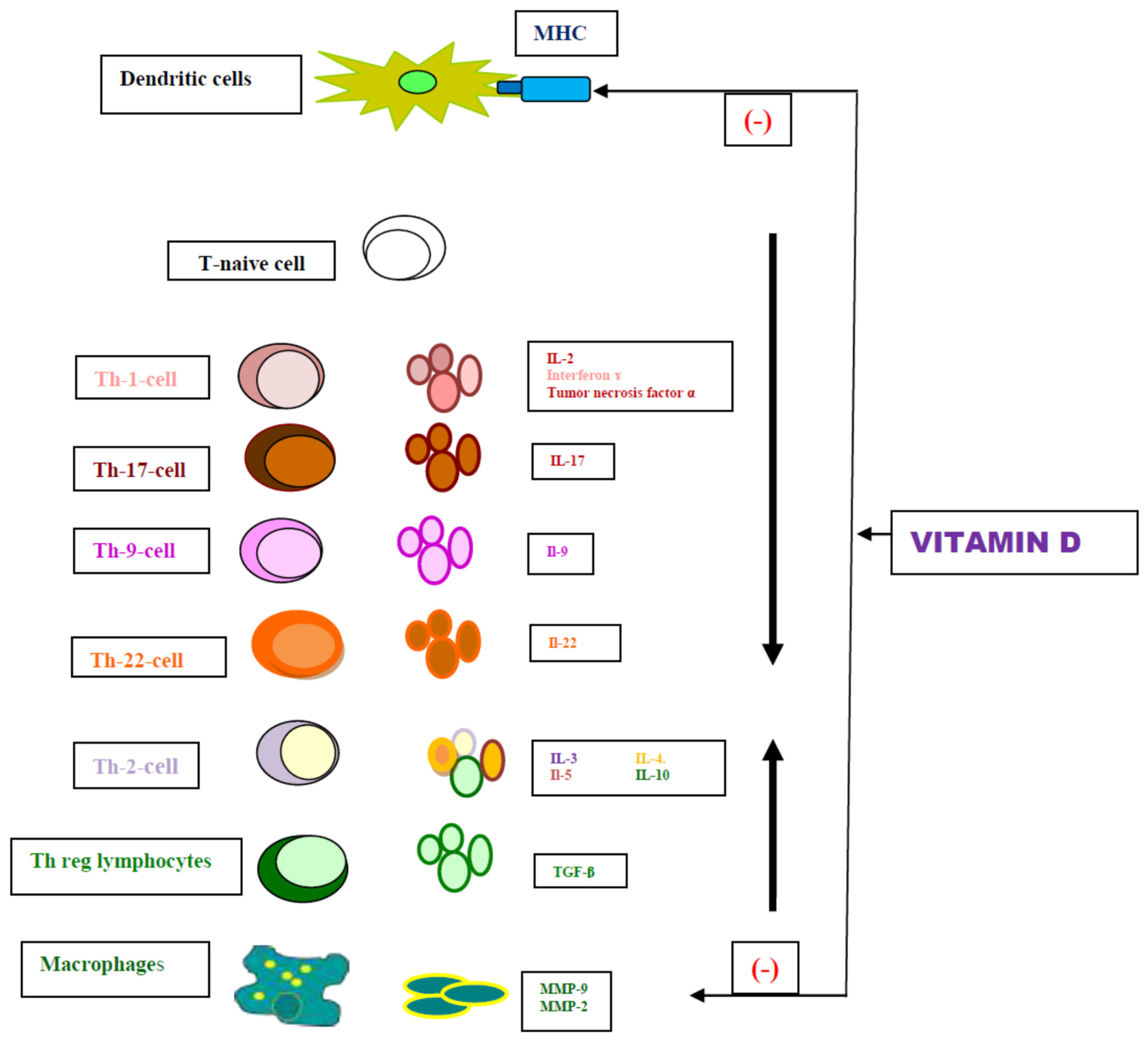
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Control Subjects
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. Characteristics of Patients with Vitamin D Deficiency
3.3. Characteristics of Patients with Vitamin D Treatment
3.4. Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González-Moles, M.Á.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; González-Ruiz, I.; González-Ruiz, L.; Ayén, Á.; Lenouvel, D.; Lenouvel, D.; Ruiz-Ávila, I.; Ramos-García, P. Worldwide prevalence of oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cleach, L.; Chosidow, O. Clinical practice. Lichen planus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Kujan, O.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Bagán, J.V.; González-Moles, M.A.; Kerr, A.R.; Lodi, G.; Mello, F.W.; Monteiro, L.; Ogden, G.R.; et al. Oral potentially malignant disorders: A consensus report from an international seminar on nomenclature and classification, convened by the WHO Collaborating Centre for Oral Cancer. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1862–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Moles, M.Á.; Ramos-García, P. An Evidence-Based Update on the Potential for Malignancy of Oral Lichen Planus and Related Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, L.M.; Cirillo, N.; McCullough, M.J. The immunopathogenesis of oral lichen planus-Is there a role for mucosal associated invariant T cells? J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2019, 48, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Porras-Carrique, T.; González-Moles, M.Á.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Ramos-García, P. Depression, anxiety, and stress in oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 1391–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Fonseca, L.; Llorente-Pendás, S.; García-Pola, M. Risk of Prediabetes and Diabetes in Oral Lichen Planus: A Case-Control Study according to Current Diagnostic Criteria. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Porras-Carrique, T.; Ramos-García, P.; González-Moles, M.Á. Hypertension in oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jornet, P.; Parra-Perez, F.; Pons-Fuster, A. Association of autoimmune diseases with oral lichen planus: A cross-sectional, clinical study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Porras-Carrique, T.; Ramos-García, P.; Aguilar-Diosdado, M.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; González-Moles, M.Á. Autoimmune disorders in oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 1382–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moles, M.Á.; de Porras-Carrique, T.; Ramos-García, P. Association of oral lichen planus with hepatic disorders and hepatocellular carcinoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2023, 28, e229–e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pola, M.; Rodríguez-Fonseca, L.; Suárez-Fernández, C.; Sanjuán-Pardavila, R.; Seoane-Romero, J.; Rodríguez-López, S. Bidirectional Association between Lichen Planus and Hepatitis C-An Update Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.R.; Gupta, P.; Khaitan, T.; Shukla, A.K. Reduced levels of serum vitamin B12 in symptomatic cases of oral lichen planus: A cross-sectional study. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 10, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.X.; Yang, X.W.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.F. The profile of hematinic deficiencies in patients with oral lichen planus: A case-control study. BMC Oral Health. 2020, 20, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, N.; Sheykhbahaei, N. Micronutrients Profile in Oral Lichen Planus: A Review Literature. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurago, Z.B. Etiology and pathogenesis of oral lichen planus: An overview. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 122, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopashree, M.R.; Gondhalekar, R.V.; Shashikanth, M.C.; George, J.; Thippeswamy, S.H.; Shukla, A. Pathogenesis of oral lichen planus--a review. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2010, 39, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungell, P. Oral lichen planus. A review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1991, 20, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Howati, A.; Thornhill, M.H.; Colley, H.E.; Murdoch, C. Immune mechanisms in oral lichen planus. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 1400–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Q. Updates on immunological mechanistic insights and targeting of the oral lichen planus microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1023213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrashdan, M.S.; Cirillo, N.; McCullough, M. Oral lichen planus: A literature review and update. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2016, 308, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aribi, M.; Mennechet, F.J.D.; Touil-Boukoffa, C. The role of vitamin D as an immunomodulator. Front. Immunol. 2023, 28, 1186635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, L.; Kostoglou-Athanassiou, I.; Koutsilieris, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vitamin D and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Biomolecules. 2023, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaca, G.; Tonacci, A.; Negrini, S.; Greco, M.; Borro, M.; Puppo, F.; Gangemi, S. Emerging role of vitamin D in autoimmune diseases: An update on evidence and therapeutic implications. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brożyna, A.A.; Slominski, R.M.; Nedoszytko, B.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Slominski, A.T. Vitamin D Signaling in Psoriasis: Pathogenesis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenngam, N.; Holick, M.F. Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, F.; Tamone, C.; D’Amelio, P. Vitamin, D: Nutrient, Hormone, and Immunomodulator. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, R. Vitamin D and allergic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1420883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berretta, M.; Quagliariello, V.; Bignucolo, A.; Facchini, S.; Maurea, N.; Di Francia, R.; Fiorica, F.; Sharifi, S.; Bressan, S.; Richter, S.N.; et al. The Multiple Effects of Vitamin D against Chronic Diseases: From Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation to Updated Evidence from Clinical Studies. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Mazzei, L.; García Menéndez, S.; Martín Giménez, V.M.; Al Anouti, F.; Manucha, W. Genomic or Non-Genomic? A Question about the Pleiotropic Roles of Vitamin D in Inflammatory-Based Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.V.T.; Nguyen, Y.T.; Kim, N.; Lee, H.J. Vitamin A, D, E, and K as Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/9 Regulators That Affect Expression and Enzymatic Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patini, R.; Favetti Giaquinto, E.; Gioco, G.; Castagnola, R.; Perrotti, V.; Rupe, C.; Di Gennaro, L.; Nocca, G.; Lajolo, C. Malnutrition as a Risk Factor in the Development of Oral Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analyses. Nutrients 2024, 16, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Raman, P.; Gheena, S.; Abilasha, R.; Krishnan, R.P.; Selvaraj, J. Salivary vitamin D levels among OSCC and normal Indian patients. Bioinformation 2022, 18, 884–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturana-Ramírez, A.; Aitken-Saavedra, J.; Guevara-Benítez, A.L.; Espinoza-Santander, I. Hypovitaminosis D, oral potentially malignant disorders, and oral squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2022, 27, e135–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Družijanić, A.; Cigić, L.; Glavina, A.; Draganja, M.; Martinović, D.; Ković, M. Serum Concentration of Vitamin D in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2023, 57, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, R.; Yu, F.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, F. Experimental study on 1,25(OH)(2) D(3) amelioration of oral lichen planus through regulating NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Mohan, R.P.; Malik, S.; Goel, S.; Gupta, S. Serum Vitamin D Level in Oral Lichen Planus Patients of North India- A Case-Control Study Kamarthi, N Serum Vitamin D Level in Oral Lichen Planus Patients of North India—A Case-Control Study. J. Dermatol. Res. Ther. 2017, 1, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.B.; Anwar, M.K.; Shaker, O.G.; El Sharkawy, D.A. Possible Relation between Vitamin D and Interleukin-17 in the Pathogenesis of Lichen Planus. Dermatology 2021, 237, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar Vinaya, R.; Krishna, S.; Deepak, T.A.; Prarthana, G.A.; Vyavahare, S.; Jujare Rashmi, D. Association of Vitamin D Serum Concentration and Oral Lichen Planus: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Indian Acad. Oral Med. Radiol. 2022, 34, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Zarabadipour, M.; Azmodeh, F.; Mirzadeh, M.; Golezari, A.S. Association of serum level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D with Oral Lichen Planus. A case-control study. J. Oral Res. 2020, 9, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, M.M.; Chalkoo, A.H. Vitamin D deficiency- A possible contributing factor in the aetiopathogenesis of oral lichen planus. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2017, 6, 4769–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangarpoor, M.; Khademi, B.; Mardani, M.; Malekzadeh, M.; Jaafari-Ashkavandi, Z. Vitamin D serum levels in oral lichen planus and oral cancer patients. Middle East J. Cancer 2023, 14, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thum-Tyzo, K.J.; Tyzo, B.J.; Chałas, R. Oral lichen planus among patients from Lublin Region in relation to 25-hydroxy-vitamin D3 serum level. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2024, 31, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahramian, A.; Bahramian, M.; Mehdipour, M.; Falsafi, P.; Khodadadi, S.; Dabaghi Tabriz, F.; Deljavanghodrati, M. Comparing Vitamin D Serum Levels in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus and Healthy Subjects. J. Dent. 2018, 19, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, N.; Pirzadeh, F.; Mirzaii-Dizgah, I.; Sheykhbahaei, N. Relationship between salivary vitamin D deficiency and oral lichen planus. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2020, 36, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosratzehi, T. Serum vitamin D and antinuclear antibody level in oral lichen planus patients: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezazadeh, F.; Haghighat, S. Serum Vitamin Profile in Oral Lichen Planus Patients in Southwest of Iran. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 24, 8627435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egido-Moreno, S.; Valls-Roca-Umbert, J.; Parra-Moreno, F.J.; Jané-Salas, E.; Blanco-Carrión, A.; López-López, J. Association of vitamin D levels and oral lichen planus. Systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2024, 22, 26603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M.; STROBE Initiative. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 805–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, I.R.; Pindborg, J.J.; Bezroukov, V.; Infirri, J.S. Guide to epidemiology and diagnosis of oral mucosal diseases and conditions. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1980, 8, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- van der Meij, E.H.; van der Waal, I. Lack of clinicopathologic correlation in the diagnosis of oral lichen planus based on the presently available diagnostic criteria and suggestions for modifications. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2003, 32, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Alberdi-Navarro, J.; Lafuente-Ibáñez de Mendoza, I.; Marichalar-Mendia, X.; Martínez-Revilla, B.; Parra-Pérez, C.; Juan-Galíndez, A.D.; Echebarria-Goicouria, M.Á. Clinicopathological and prognostic characterization of oral lichenoid disease and its main subtypes: A series of 384 cases. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2020, 25, e554–e562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirito, F.; Dioguardi, M.; Caponio, V.C.; Ambrosino, M.; Lo Muzio, E.; Lo Muzio, L. Oral lichen planus in children: A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2024, 29, e152–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, C.; Gonzalez, L. Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem? Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144 Pt A, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durá-Travé, T.; Gallinas-Victoriano, F. Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, and Vitamin D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Arduino, P.G.; Carrozzo, M.; Gandolfo, S.; Argiolas, M.R.; Bertolusso, G.; Conrotto, D.; Pentenero, M.; Broccoletti, R. Course of oral lichen planus: A retrospective study of 808 northern Italian patients. Oral Dis. 2009, 15, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorici, S.; Corrao, S.; Natoli, G.; Difalco, P. Prevalence and distribution of oral mucosal non-malignant lesions in the western Sicilian population. Minerva Stomatol. 2016, 65, 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, D.; Calabria, E.; Canfora, F.; Coppola, N.; Lo Muzio, L.; Spirito, F.; Giuliani, M.; Azzi, L.; Maurino, V.; SIPMO (Italian Society of Oral Pathology and Medicine). Where do you live? North versus Central-South differences in relation to Italian patients with oral lichen planus: A cross-sectional study from the SIPMO (Italian Society of Oral Pathology and Medicine). BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, A.; Shariff, J.; Philipone, E. Association between oral lichen planus and systemic conditions and medications: Case-control study. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, D. The clinical features, malignant potential, and systemic associations of oral lichen planus: A study of 723 patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 46, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovaru, S.; Parlatescu, I.; Gheorghe, C.; Tovaru, M.; Costache, M.; Sardella, A. Oral lichen planus: A retrospective study of 633 patients from Bucharest, Romania. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2013, 18, e201–e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, S., Jr.; Gorsky, M.; Lozada-Nur, F. A prospective follow-up study of 570 patients with oral lichen planus: Persistence, remission, and malignant association. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1985, 60, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduino, P.G.; Karimi, D.; Tirone, F.; Sciannameo, V.; Ricceri, F.; Cabras, M.; Gambino, A.; Conrotto, D.; Salzano, S.; Carbone, M.; et al. Evidence of earlier thyroid dysfunction in newly diagnosed oral lichen planus patients: A hint for endocrinologists. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitak-Arnnop, P.; Subbalekha, K.; Sirintawat, N.; Tangmanee, C.; Auychai, P.; Muangchan, C.; Sukphopetch, P.; Meningaud, J.P.; Neff, A. Are oral lichen planus patients at high risk of hepatitis C? A case-control study. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 123, e37–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, D.; Arrica, M.; Lucchese, A.; Valente, M.; Pannone, G.; Lajolo, C.; Ninivaggi, R.; Petruzzi, M. Oral lichen planus clinical characteristics in Italian patients: A retrospective analysis. Head Face Med. 2016, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümrü, B. A retrospective study of 370 patients with oral lichen planus in Turkey. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2013, 18, e427–e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingafou, M.; Leao, J.C.; Porter, S.R.; Scully, C. Oral lichen planus: A retrospective study of 690 British patients. Oral Dis. 2006, 12, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprasom, K.; Mravak-Stipetić, M.; Luckprom, P.; Canjuga, I.; Biocina-Lukenda, D.; Vidović-Juras, D.; Sikora, M.; Brailo, V.; Jirawechwongsakul, S. Oral lichen planus: A retrospective comparative study between Thai and Croatian patients. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2009, 17, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.L.; Fan, M.W.; Wang, S.Z.; Chen, X.M.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. A clinical study of 674 patients with oral lichen planus in China. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2005, 34, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Suresh, C.S. Oral lichen planus in relation to transaminase levels and hepatitis C virus. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2007, 36, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo-Sierra, J.; Mattsson, U.; Jontell, M. Use of systemic medication in patients with oral lichen planus—A possible association with hypothyroidism. Oral Dis. 2013, 19, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorsky, M.; Epstein, J.B.; Hasson-Kanfi, H.; Kaufman, E. Smoking habits among patients diagnosed with oral lichen planus. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2004, 2, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pippi, R.; Romeo, U.; Santoro, M.; Del Vecchio, A.; Scully, C.; Petti, S. Psychological disorders and oral lichen planus: Matched case-control study and literature review. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Jornet, P.; Camacho-Alonso, F.; Rodríguez-Martínes, M.A. Alterations in serum lipid profile patterns in oral lichen planus: A cross-sectional study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 13, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksu Arica, D.; Baykal Selcuk, L.; Orem, A.; Ural, Z.; Yayli, S. Evaluation of serum vitamin D levels in patients with lichen. Turkderm-Turk. Arch. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 54, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, S.C.; Cantwell, H.M.; Imhof, R.L.; Torgerson, R.R.; Tolkachjov, S.N. Lichen Planopilaris in Women: A Retrospective Review of 232 Women Seen at Mayo Clinic From 1992 to 2016. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 1684–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Kang, H.; Heo, Y.W.; Lee, W.S.; Lee, S. Prevalence and incidence of comorbid diseases and mortality risk associated with lichen planopilaris: A Korean nationwide population-based study. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 48, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimalawansa, S.J. Physiology of Vitamin D-Focusing on Disease Prevention. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Wang, H.W.; Jiang, M.Y. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and associated risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality among middle-aged and older adults in the United States. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1163737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, P.; Fan, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, Y. Global and regional prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in population-based studies from 2000 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 7.9 million participants. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1070808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, J.; Friedel, A.; Herr, R.; Rausch, T.; Roos, F.; Wahl, D.A.; Pierroz, D.D.; Weber, P.; Hoffmann, K. A systematic review of vitamin D status in populations worldwide. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Marssafy, L.M.; Sadek, H.S.; Hussein, F.F.; Wahdan, M.A.; Elkwateh, W. Serum vitamin D level in healthy individuals versus patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic oral lichen planus. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsbak, M.; Levring, T.B.; Geisler, C.; von Essen, M.R. The vitamin d receptor and T cell function. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, F.; Xu, J.; Zhao, B.; Du, J. MicroRNA-122 promotes apoptosis of keratinocytes in oral lichen planus through suppressing VDR expression. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 3400–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Xu, N.; Yu, F.; Yang, F.; Li, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, B.; Du, J. Vitamin D/VDR signaling inhibits LPS-induced IFN gamma and IL-1beta in Oral epithelia by regulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha signaling pathway. Cell. Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, H.; Li, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, B.; Du, J. 1,25(OH)(2) D(3) blocks IFNbeta production through regulating STING in epithelial layer of oral lichen planus. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3751–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.P.; Nayfeh, T.; Alsawaf, Y.; Saadi, S.; Farah, M.; Zhu, Y.; Firwana, M.; Seisa, M.; Wang, Z.; Scragg, R.; et al. A Systematic Review Supporting the Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guidelines on Vitamin D. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demay, M.B.; Pittas, A.G.; Bikle, D.D.; Diab, D.L.; Kiely, M.E.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Lips, P.; Mitchell, D.M.; Murad, M.H.; Powers, S.; et al. Vitamin D for the Prevention of Disease: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 3, dgae290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazeer, J.; Singh, S.; Jayam, C.; Singh, R.; Iqubal, M.A.; Singh, R. Assessment of the Role of Vitamin D in the Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2020, 21, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S.; Choudhury, P.; Ahmad, S.A.; Alam, T.; Panigrahi, R.; Aziz, S.; Kaleem, S.M.; Priyadarshini, S.R.; Sahoo, P.K.; Hasan, S. Vitamin D in the Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | OLP (%, n = 120) | Control(%, n = 120) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average years (SD) | 61.06 ± 11.60 | 61.06 ± 11.60 | 1 |
| ≤60 years | 51 (42.5) | 51 (42.5) | |
| >60 years | 69 (57.5) | 69 (57.5) | |
| Sex | 1 | ||
| Female | 97 (80.03) | 97 (80.03) | |
| Male | 23 (19.17) | 23 (19.17) | |
| Tobacco | 0.676 | ||
| Yes | 36 (30) | 39 (32.5) | |
| No | 84 (70) | 81 (67.5) | |
| Alcohol | 0.289 | ||
| Yes | 25 (20.8) | 32 (26.7) | |
| No | 95 (79.1) | 88 (73.3) | |
| Location | |||
| 2 | 50 (41.70) | ||
| ≥3 | 70 (58.3) | ||
| Clinical form | |||
| Reticular-papular | 41 (34.2) | ||
| Atrophic-erosive | 79 (65.8) | ||
| Vitamin D | |||
| Mean (SD) | 25.1019 ± 13.60 | 28.1951 ± 14.70 | 0.013 * |
| Vitamin D deficiency 1 | 0.003 * | ||
| Yes | 54 (45) | 32 (26.7) | |
| No | 66 (55) | 88 (73.3) | |
| Vitamin D intake | 0.007 * | ||
| Yes | 32 (26.7) | 15 (12.5) | |
| No | 88 (73.3) | 105 (87.5) |
| Variable | Vitamin D < 20 | Vitamin D Intake | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLP (%, n = 54) | Control (%, n = 32) | p Value | OLP (%, n = 32) | Control (%, n = 15) | p Value | |
| Average age (SD) | 60.84 ± 10.52 | 62.47 ± 9.31 | 64.09 ± 11.97 | 61.85 ± 9.59 | ||
| (39–85) | (44–81) | (43–83) | (39–81) | |||
| ≤60 years> | 0.003 * | 0.055 | ||||
| ≤60 | 15 (27.77) | 11 (34.37) | 9 (28.12) | 5 (33.33) | ||
| >60 | 39 (72.33) | 21 (65.63) | 23 (71.88) | 10 (66.66) | ||
| Sex | 0.217 | 0.263 | ||||
| Female | 41(75.92) | 28 (87.5) | 28 (87.5) | 13 (86.66) | ||
| Male | 13 (24.08) | 4 (12.5) | 4 (12.5) | 2 (13.34) | ||
| Tobacco | 0.378 | 0.242 | ||||
| Yes | 14 (25.92) | 12 (37.5) | 7 (21.8) | 1 (6.6) | ||
| No | 40 (74.08) | 20 (62.5) | 25 (79.2) | 14 (93.4) | ||
| Alcohol | 0.429 | 0.865 | ||||
| Yes | 13 (24.07) | 12 (37.5) | 7 (21.8) | 4 (26.6) | ||
| No | 41 (65.93) | 20 (62.5) | 25 (78.2) | 11 (73.4) | ||
| Location | 0.352 | 0.780 | ||||
| 2 | 20 (37.0) | 14 (43.8) | ||||
| ≥3 | 34 (63.0) | 18 (56.2) | ||||
| Clinical form | 0.182 | 0.685 | ||||
| Reticular–papular | 15 (27.8) | |||||
| Atrophic–erosive | 39 (72.2) |
| Variable | OLP n (%) | Control Group n (%) | OR Univariate (CI, p Value) | OR Multivariate (CI, p Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Female (%) | 97 (50.0) | 97 (50.0) | - | - |
| Male (%) | 23 (50.0) | 23 (50.0) | 1.00 (0.52–1.91, p = 1.000) | 0.90 (0.45–1.77, p = 0.754) |
| Age | ||||
| ≤60 (%) | 51 (50.0) | 51 (50.0) | - | - |
| >60 (%) | 69 (50.0) | 69 (50.0) | 1.00 (0.60–1.67, p =1.000) | 0.77 (0.44–1.33, p = 0.344) |
| Tobacco | ||||
| No (%) | 84 (50.9) | 81 (49.1) | - | - |
| Yes (%) | 36 (48.0) | 39 (52.0) | 0.89 (0.51–1.54, p = 0.676) | 1.19 (0.64–2.22, p = 0.578 |
| Alcohol use | ||||
| No (%) | 95 (51.7) | 88 (48.1) | - | - |
| Yes (%) | 25 (43.9) | 32 (56.1) | 0.72 (0.40–1.31, p = 0.289) | 0.62 (0.32–1.22, p = 0.170) |
| Vitamin D <20 ng/mL | ||||
| No (%) | 88 (57.1) | 66 (42.9) | - | - |
| Yes (%) | 54 (62.8) | 32 (37.2) | 2,25 (1.32–3.89, p = 0.003) * | 2.24 (1.28–3.98, p = 0.005) * |
| Vitamin D Treatment | ||||
| No (%) | 105 (54.4) | 88 (45.6) | - | |
| Yes (%) | 32 (68.1) | 15 (31.9) | 2.55 (1.32–5.12, p = 0.007) * | 2.51 (1.25–5.22, p = 0.011) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Pola, M.; Rodríguez-Fonseca, L. Role of Vitamin D in Oral Lichen Planus: A Case Control Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162761
García-Pola M, Rodríguez-Fonseca L. Role of Vitamin D in Oral Lichen Planus: A Case Control Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162761
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Pola, María, and Lucía Rodríguez-Fonseca. 2024. "Role of Vitamin D in Oral Lichen Planus: A Case Control Study" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162761
APA StyleGarcía-Pola, M., & Rodríguez-Fonseca, L. (2024). Role of Vitamin D in Oral Lichen Planus: A Case Control Study. Nutrients, 16(16), 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162761






