Importance of Energy, Dietary Protein Sources, and Amino Acid Composition in the Regulation of Metabolism: An Indissoluble Dynamic Combination for Life
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Energy Metabolism
3. Protein Synthesis and Regulatory Mechanisms
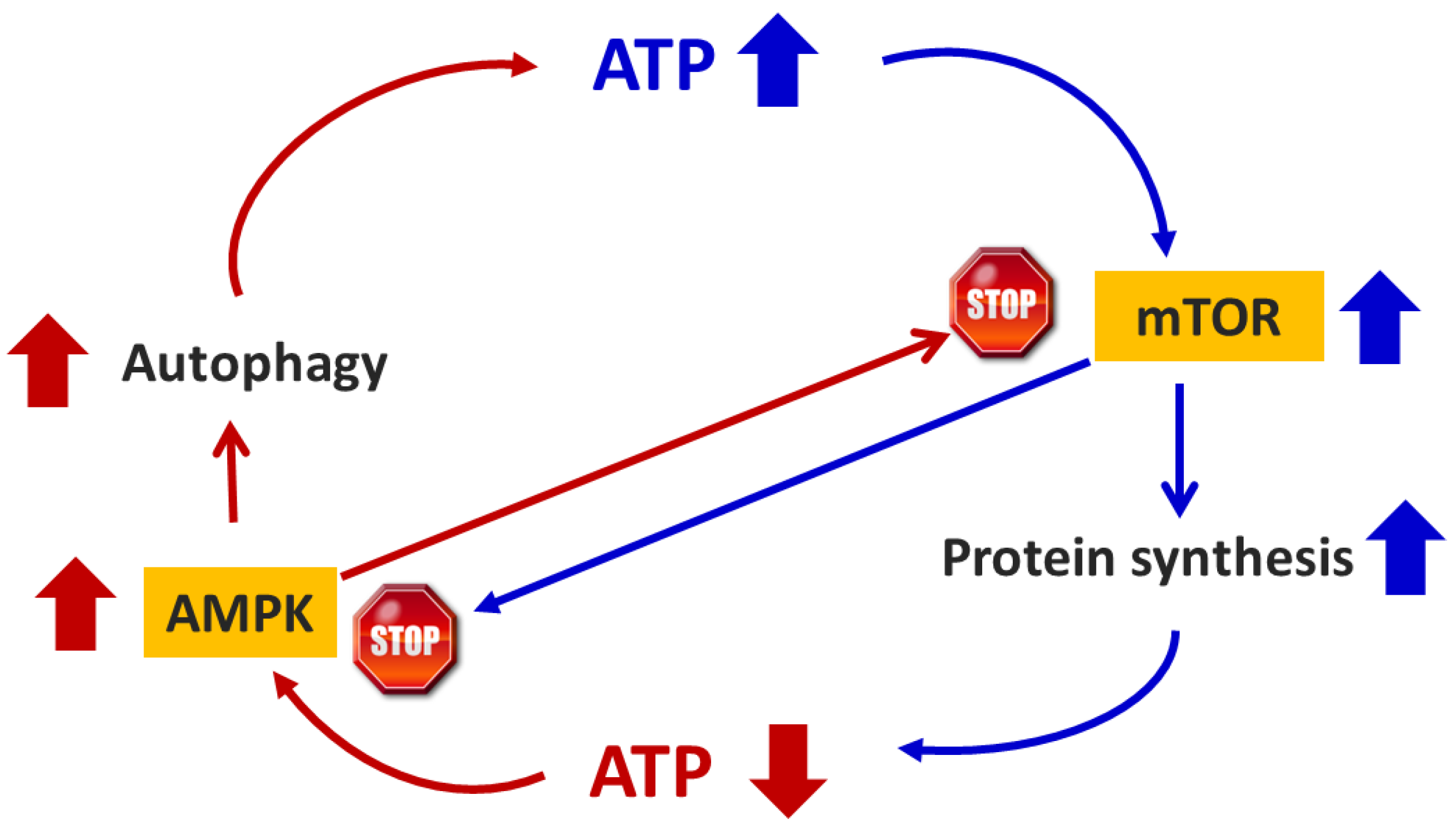
3.1. Energy Sensors
3.2. Amino Acid Availability
3.3. mTOR Signaling
3.4. Transcription Factors
4. Dietary Proteins: Quality and Sources
4.1. The Importance of Protein Quality
4.2. Plant or Animal Protein Sources and Intake
4.3. Insect Proteins
4.4. Protein Intake and Utilization
5. Protein Turnover and Requirements
5.1. Physical Activity and Hypercatabolic Syndrome
5.2. The Limits of Protein Intake
6. The Significance of EAA Supplementation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holman, R.L.; Mahoney, E.B.; Whipple, G.H. Blood plasma protein given by vein utilized in body metabolism: II. A dynamic equilibrium between plasma and tissue proteins. J. Exp. Med. 1934, 59, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenheimer, R. The Dynamic State of Body Constituents; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Taegtmeyer, H.; Harinstein, M.E.; Gheorghiade, M. More than bricks and mortar: Comments on protein and amino acid metabolism in the heart. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 3E–7E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Openstax Biology 2e, Section 6.3 The Laws of Thermodynamics. Available online: https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/6-3-the-laws-of-thermodynamics (accessed on 12 October 2023).
- Lehninger, A.L.; Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Principles of Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; Worth Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dioguardi, F.S.; Chen-Scarabelli, C.; Pasini, E.; Corsetti, G.; Scarabelli, T.M. Diet, muscle protein synthesis and autophagy relationships in cancer an attempt to understand where we are going, and why. Adv. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.D. Regulation analysis of energy metabolism. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Nielsen, J. Energy metabolism controls phenotypes by protein efficiency and allocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17592–17597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Locasale, J.W. Understanding metabolism with flux analysis: From theory to application. Metab. Eng. 2017, 43 Pt B, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.H.; Verway, M.J.; Johnson, R.M.; Roy, D.G.; Steadman, M.; Hayes, S. Metabolic profiling using stable isotope tracing reveals distinct patterns of glucose utilization by physiologically activated CD8(+) T cells. Immunity 2019, 51, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantrell, D.A.; Smith, K.A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: A new cell growth model. Science 1984, 224, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron-Harel, N.; Santos, D.; Ghergurovich, J.M.; Sage, P.T.; Reddy, A.; Lovitch, S.B. Mitochondrial biogenesis and proteome remodeling promote one-carbon metabolism for T cell activation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antona, G.; Ragni, M.; Cardile, A.; Tedesco, L.; Dossena, M.; Bruttini, F.; Caliaro, F.; Corsetti, G.; Bottinelli, R.; Carruba, M.O.; et al. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation promotes survival and supports cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in middle-aged mice. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsetti, G.; Pasini, E.; D’Antona, G.; Nisoli, E.; Flati, V.; Assanelli, D.; Dioguardi, F.D.; Bianchi, R. Morphometric changes induced by amino acid supplementation in skeletal and cardiac muscles of old mice. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 26E–34E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Princiotta, M.F.; Finzi, D.; Qian, S.B.; Gibbs, J.; Schuchmann, S.; Buttgereit, F.; Bennink, J.R.; Yewdell, J.W. Quantitating protein synthesis, degradation, and endogenous antigen processing. Immunity 2003, 18, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, S.C.; Carter, J.R.; Kattus, A.A.; Miller, L.L.; Whipple, G.H. Ten amino acids essential for plasma protein production effective orally or intravenously. J. Exp. Med. 1943, 77, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, W.K.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Phillips, B.E.; Lund, J.N.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J. Human skeletal muscle protein metabolism responses to amino acid nutrition. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 828S–838S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsetti, G.; Pasini, E.; Romano, C.; Calvani, R.; Picca, A.; Marzetti, E.; Flati, V.; Dioguardi, F.S. Body weight loss and tissue wasting in late middle-aged mice on slightly imbalanced essential/non-essential amino acids diet. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, C.; Corsetti, G.; Flati, V.; Pasini, E.; Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Marzetti, E.; Dioguardi, F.S. Influence of diets with varying essential/nonessential amino acid ratios on mouse lifespan. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Mukherjee, S.; Harikumar, K.G.; Strutzenberg, T.S.; Zhou, X.E.; Suino-Powell, K. Structure of an AMPK complex in an inactive, ATP-bound state. Science 2021, 373, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.M. Regulation and function of AMPK in physiology and diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuma, A.; Hatano, M.; Matsui, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Nakaya, H.; Yoshimori, T.; Ohsumi, Y.; Tokuhisa, T.; Mizushima, N. The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period. Nature 2004, 432, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Yuan, M.; Fan, H.; Cai, Z. Role of AMPK in autophagy. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1015500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy: Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 2011, 147, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, J.J.; Bauer, D.E.; Kong, M.; Harris, M.H.; Li, C.; Lindsten, T.; Thompson, C.B. Growth factor regulation of autophagy and cell survival in the absence of apoptosis. Cell 2005, 120, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen-Scarabelli, C.; Agrawal, P.R.; Saravolatz, L.; Abuniat, C.; Scarabelli, G.; Stephanou, A.; Loomba, L.; Narula, J.; Scarabelli, T.M.; Knight, R. The role and modulation of autophagy in experimental models of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Van Vleet, T.; Schnellmann, R.G. The role of calpain in oncotic cell death. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Lee, J.A. Role of the mammalian ATG8/LC3 family in autophagy: Differential and compensatory roles in the spatiotemporal regulation of autophagy. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsetti, G.; Chen-Scarabelli, C.; Romano, C.; Pasini, E.; Dioguardi, F.S.; Onorati, F.; Knight, R.; Patel, H.; Saravolatz, L.; Faggian, G.; et al. Autophagy and oncosis/necroptosis are enhanced in cardiomyocytes from heart failure patients. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic. Res. 2019, 25, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorissen, S.H.M.; Trommelen, J.; Kouw, I.W.K.; Holwerda, A.M.; Pennings, B.; Groen, B.B.L.; Wall, B.T.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Horstman, A.M.H.; Koopman, R.; et al. Protein type, protein dose, and age modulate dietary protein digestion and phenylalanine absorption kinetics and plasma phenylalanine availability in humans. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, R.L.; Chantranupong, L.; Saxton, R.A.; Shen, K.; Scaria, S.M.; Cantor, J.R.; Sabatini, D.M. Sestrin2 is a leucine sensor formTORC1 pathway. Science 2016, 351, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, S.R.; Jefferson, L.S. New functions for amino acids: Effects on gene transcription and translation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 500S–507S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Cuervo, A.M. Autophagy in the cellular energetic balance. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCannell, A.D.; Roberts, L.D. Metabokines in the regulation of systemic energy metabolism. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 67, 102286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, E.; Corsetti, G.; Dioguardi, F.S. Behind protein synthesis: Amino acids-metabokine regulators of both systemic and cellular metabolism. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buondonno, I.; Sassi, F.; Carignano, G.; Dutto, F.; Ferreri, C.; Pili, F.G.; Massaia, M.; Nisoli, E.; Ruocco, C.; Porrino, P.; et al. From mitochondria to healthy aging: The role of branched-chain amino acids treatment: MATeR a randomized study. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2080–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Maruki, Y.; Long, X.; Yoshino, K.; Oshiro, N.; Hidayat, S.; Tokunaga, C.; Avruch, J.; Yonezawa, K. Raptor, a binding partner of target of rapamycin (TOR), mediates TOR action. Cell 2002, 110, 177–189.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, K.G.; Fingar, D.C. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): Conducting the cellular signaling symphony. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14071–14077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewith, R.; Hall, M.N. Target of rapamycin (TOR) in nutrient signaling and growth control. Genetics 2011, 189, 1177–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Guan, K.L. mTOR: A pharmacologic target for autophagy regulation. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian, D.; Roux, P.P.; Mieulet, V.; Cohen, M.S.; Raught, B.; Taunton, J. The mTOR/PI3K and MAPK pathways converge on eIF4B to control its phosphorylation and activity. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaveroux, C.; Eichner, L.J.; Dufour, C.R.; Shatnawi, A.; Khoutorsky, A.; Bourque, G.; Sonenberg, N.; Giguere, V. Molecular and genetic crosstalks between mTOR and ERRalpha are key determinants of rapamycin-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Guo, H.; Hao, L.; Yao, P.; Liu, L.; et al. Leucine facilitates the insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and insulin signaling in skeletal muscle cells: Involving mTORC1 and mTORC2. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, M.A.; Patrini, C.; Pasini, E.; Brocca, L.; Flati, V.; Corsetti, G.; D’Antona, G. Amino acid supplementation counteracts metabolic and functional damage in the diabetic rat heart. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 49E–56E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flati, V.; Pasini, E.; D’Antona, G.; Speca, S.; Toniato, E.; Martinotti, S. Intracellular mechanisms of metabolism regulation: The role of signaling via the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway and other routes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 16E–21E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameri, K.; Harris, A.L. Activating transcription factor 4. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Sahra, I.; Hoxhaj, G.; Ricoult, S.J.H.; Asara, J.M.; Manning, B.D. 825 mTORC1 induces purine synthesis through control of the mitochondrial 826 tetrahydrofolate cycle. Science 2016, 351, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, P.; Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to 1032 homeostatic regulation. Science 2011, 334, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, L.R.G.; Singleton, D.C.; Buffa, F.; Abramczyk, O.; Phadwal, K.; Li, J.; Simon, A.K.; Murray, J.T.; Harris, A.L. Transcriptional up-regulation of ULK1 by ATF4 contributes to cancer cell survival. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghshi, S.; Sadeghi, O.; Willett, W.C.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Dietary intake of total, animal, and plant proteins and risk of all cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: Systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2020, 370, m2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houchins, J.A.; Cifelli, C.J.; Demmer, E.; Fulgoni, V.L. Diet modeling in older Americans: The impact of increasing plant-based foods or dairy products on protein intake. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnen, R.T.; Jonnalagadda, S.S.; Slavin, J.L. Role of plant protein in nutrition, wellness, and health. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murefu, T.R.; Macheka, L.; Musundire, R.; Manditsera, F.A. Safety of wild harvested and reared edible insects: A review. Food Control 2019, 101, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukkens, S.G. The nutritional value of edible insects. Ecol. Food Nutr. 1997, 36, 287–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, E.; Karas, M.; Baraniak, B. Comparison of functional properties of edible insects and protein preparations thereof. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Suleria, H.A.R.; Rauf, A. Edible insects as innovative foods: Nutritional and functional assessments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Unlocking the biological potential of proteins from edible insects through enzymatic hydrolysis: A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 43, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Yong, H.I.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, Y.S. Edible insects as a protein source: A review of public perception, processing technology, and research trends. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2019, 39, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Huis, A.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B. The environmental sustainability of insects as food and feed A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Yong, H.I.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, Y.B.; Choi, Y.S. Functional properties of extracted protein from edible insect larvae and their interaction with transglutaminase. Foods 2020, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schluter, O.K. Nutritional composition and safety aspects of edible insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, V.; Garcia, M.; Sandoval, H.; Jimenez, H.D.; Calvo, C. Quality proteins from edible indigenous insect food of Latin America and Asia. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2011, 23, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Schluter, O.; Rumpold, B.; Holzhauser, T.; Roth, A.; Vogel, R.F.; Quasigroch, W.; Vogel, S.; Heinz, V.; Jäger, H.; Bandick, N.; et al. Safety aspects of the production of foods and food ingredients from insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlcek, J.; Rop, O.; Borkovcova, M.; Bednarova, M. A comprehensive look at the possibilities of edible insects as food in Europe–a review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 64, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Huis, A. Edible insects are the future? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoliart, G.R. Insects as human food: Gene DeFoliart discusses some nutritional and economic aspects. Crop Prot. 1992, 11, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszek, A.; Townsend, J.R.; Bender, D.; Vantrease, W.C.; Marshall, A.C.; Johnson, K.D. The Effects of whey vs. pea protein on physical adaptations following 8-weeks of high-intensity functional training (HIFT): A pilot study. Sports 2019, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Food and Nutrition Board; Committee to Review the Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium. Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium; Oria, M., Harrison, M., Stallings, V.A., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, N.; Posthauer, M.E.; Cereda, E.; Schols, J.M.G.A.; Haesler, E. The role of nutrition for pressure injury prevention and healing: The 2019 international clinical practice guideline recommendations. Adv. Skin. Wound Care 2020, 33, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.E. Proteins and amino acids. In Modern Nutrition and Health and Disease, 9th ed.; Shils, M., Olson, J., Shike, M., Ross, A., Eds.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1999; pp. 11–48. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, D.E.; Battezzati, A. Regulation of protein metabolism during stress. Curr. Opin. Gen. Surg. 1993, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Symons, T.B.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Wolfe, R.R.; Paddon-Jones, D. A moderate serving of high-quality protein maximally stimulates skeletal muscle protein synthesis in young and elderly subjects. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Guo, C.; Ge, X.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Q.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X. Immunosenescence: Molecular mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, E.; Corsetti, G.; Aquilani, R.; Romano, C.; Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Dioguardi, F.S. Protein-amino acid metabolism disarrangements: The hidden enemy of chronic age-related conditions. Nutrients 2018, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarabelli, T.M.; Townsend, P.A.; Chen Scarabelli, C.; Yuan, Z.; McCauley, R.B.; Di Rezze, J.; Patel, D.; Putt, J.; Allebban, Z.; Abboud, J.; et al. Amino acid supplementation differentially modulates STAT1 and STAT3 activation in the myocardium exposed to ischemia/reperfusion injury. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 63E–68E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilsborough, S.; Mann, N. A review of issues of dietary protein intake in humans. Int. J. Sport. Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2006, 16, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, H.E.K.; Voutilainen, S.; Koskinen, T.T.; Mursu, J.; Tuomainen, T.P.; Virtanen, J.K. In-take of different dietary proteins and risk of heart failure in men: The kuopioischaemic heart disease risk factor study. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kapoor, D.; Jeong, S.J.; Fappi, A.; Stitham, J.; Shabrish, V.; Sergin, I.; Yousif, E.; Rodriguez-Velez, A.; Yeh, Y.-S.; et al. Identification of a leucine-mediated threshold effect governing macrophage mTOR signalling and cardiovascular risk. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, M.; Castellino, P. Correlation between amino acid induced changes in energy expenditure and protein metabolism in humans. Nutrition 1997, 13, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berryman, C.E.; Cheung, S.N.; Collette, E.M.; Pasiakos, S.M.; Lieberman, H.R.; Fulgoni, V.L. Amino acid intake and conformance with the dietary reference intakes in the United States: Analysis of the national health and nutrition examination survey, 2001–2018. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, R.R. Branched-chain amino acids and muscle protein synthesis in humans: Myth or reality? J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsetti, G.; Stacchiotti, A.; D’Antona, G.; Nisoli, E.; Dioguardi, F.S.; Rezzani, R. Supplementation with essential amino acids in middle age maintains the health of rat kidney. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsetti, G.; Stacchiotti, A.; Tedesco, L.; D’Antona, G.; Pasini, E.; Dioguardi, F.S.; Nisoli, E.; Rezzani, R. Essential amino acid supplementation decreases liver damage induced by chronic ethanol consumption in rats. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsetti, G.; D’Antona, G.; Ruocco, C.; Stacchiotti, A.; Romano, C.; Tedesco, L.; Dioguardi, F.; Rezzani, R.; Nisoli, E. Dietary supplementation with essential amino acids boosts the beneficial effects of rosuvastatin on mouse kidney. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 2189–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tedesco, L.; Rossi, F.; Ragni, M.; Ruocco, C.; Brunetti, D.; Carruba, M.O.; Torrente, Y.; Valerio, A.; Nisoli, E. A special amino-acid formula tailored to boosting cell respiration prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress caused by Doxorubicin in mouse cardiomyocytes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsetti, G.; Romano, C.; Pasini, E.; Scarabelli, T.; Chen-Scarabelli, C.; Dioguardi, F.S. Essential amino acids-rich diet increases cardiomyocytes protection in Doxorubicin-treated mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flati, V.; Caliaro, F.; Speca, S.; Corsetti, G.; Cardile, A.; Nisoli, E.; Bottinelli, R.; D’ Antona, G. Essential amino acids improve insulin activation of akt/mTor signaling in soleus muscle of aged rats. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondanelli, M.; Aquilani, R.; Verri, M.; Boschi, F.; Pasini, E.; Perna, S.; Faliva, A.; Condino, A.M. Plasma kinetics of essential amino acids following their ingestion as free formula or as dietary protein components. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Alonso, J.J.; Guillén-Mancina, E.; Calderón-Montaño, J.M.; Jiménez-González, V.; Díaz-Ortega, P.; Burgos-Morón, E.; López-Lázaro, M. Artificial diets based on selective amino acid restriction versus capecitabine in mice with metastatic colon cancer. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llop-Hernández, À.; Verdura, S.; Cuyàs, E.; Menendez, J.A. Nutritional niches of cancer therapy-induced senescent cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudry, A.G.; Law, M.L. Leucine supplementation in cancer cachexia: Mechanisms and a review of the pre-clinical literature. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ying, B.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.Z.; et al. Crosstalk between metabolism and cell death in tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Chandel, N.S. Fundamentals of cancer metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilonze, O.J.; Parsly Read-Button, L.; Cogswell, R.; Hackman, A.; Breathett, K.; Saltzman, E.; Vest, A.R. Controversies and conundrums in cardiac cachexia: Key questions about wasting in patients with HFrEF. JACC Heart Fail. 2024, 30, S2213-1779(24)00254-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilani, R.; La Rovere, M.T.; Corbellini, D.; Pasini, E.; Verri, M.; Barbieri, A.; Condino, A.M.; Boschi, F. Plasma amino acid abnormalities in chronic heart failure. Mechanisms, potential risks and targets in human myocardium metabolism. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corsetti, G.; Pasini, E.; Scarabelli, T.M.; Romano, C.; Singh, A.; Scarabelli, C.C.; Dioguardi, F.S. Importance of Energy, Dietary Protein Sources, and Amino Acid Composition in the Regulation of Metabolism: An Indissoluble Dynamic Combination for Life. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152417
Corsetti G, Pasini E, Scarabelli TM, Romano C, Singh A, Scarabelli CC, Dioguardi FS. Importance of Energy, Dietary Protein Sources, and Amino Acid Composition in the Regulation of Metabolism: An Indissoluble Dynamic Combination for Life. Nutrients. 2024; 16(15):2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152417
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorsetti, Giovanni, Evasio Pasini, Tiziano M. Scarabelli, Claudia Romano, Arashpreet Singh, Carol C. Scarabelli, and Francesco S. Dioguardi. 2024. "Importance of Energy, Dietary Protein Sources, and Amino Acid Composition in the Regulation of Metabolism: An Indissoluble Dynamic Combination for Life" Nutrients 16, no. 15: 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152417
APA StyleCorsetti, G., Pasini, E., Scarabelli, T. M., Romano, C., Singh, A., Scarabelli, C. C., & Dioguardi, F. S. (2024). Importance of Energy, Dietary Protein Sources, and Amino Acid Composition in the Regulation of Metabolism: An Indissoluble Dynamic Combination for Life. Nutrients, 16(15), 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152417







