Hyperglycemia from Diabetes Potentiates Uncarboxylated Osteocalcin-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Rat INS-1 Pancreatic β-Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Measurement of Insulin Secretion
2.4. Real-Time Calcium Imaging Analysis
2.5. RT-qPCR
| List of primers (forward/reverse [5′–3′]): |
| CACCCAAGTCCCGTCGTGAAGT/GATCCACAATGCCACGCTTCTG (Ins) |
| GAAATTCAAGAAGCGAAAAG/CCTGCTGTCACTCTGGTAGTAG (Cav1.2) |
| TAAGGGGCACTGAGGACATC/TGCCAGCTGTCTGAAAAATG (GLUT2) |
| AAGGGAACAACATCGTAGGA/CATTGGCGGTCTTCATAGTA (GK) |
| TCCACCAGGTAGACATCCC/TAGGAGCCAGGTCGTAGAG (Kir6.2) |
| GCGTGACATCAAAGAGAAG/ACTGTGTTGGCATAGAGG (β-actin) |
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
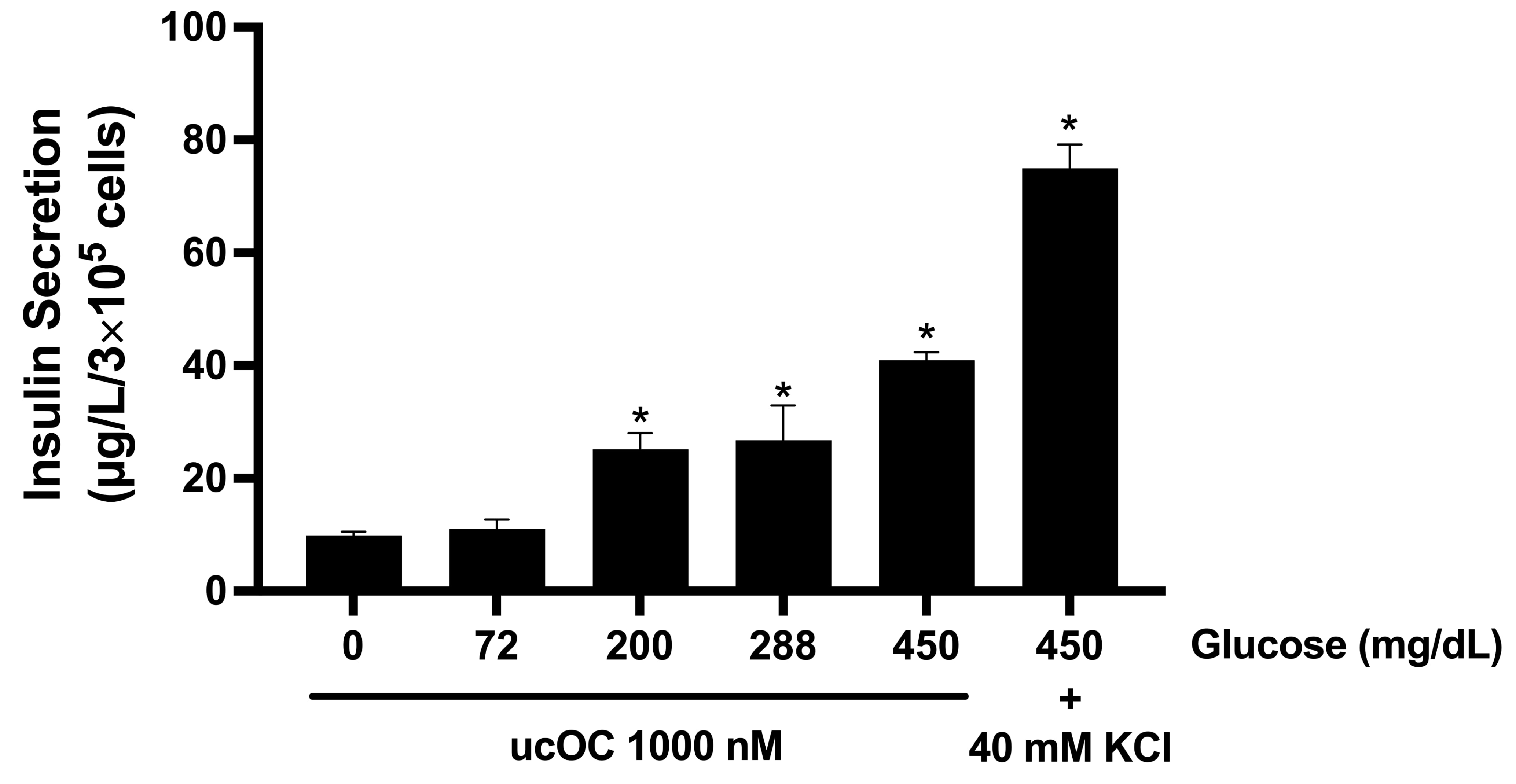
3.1. High Glucose Concentrations Potentiated Osteocalcin-Induced Insulin Secretion
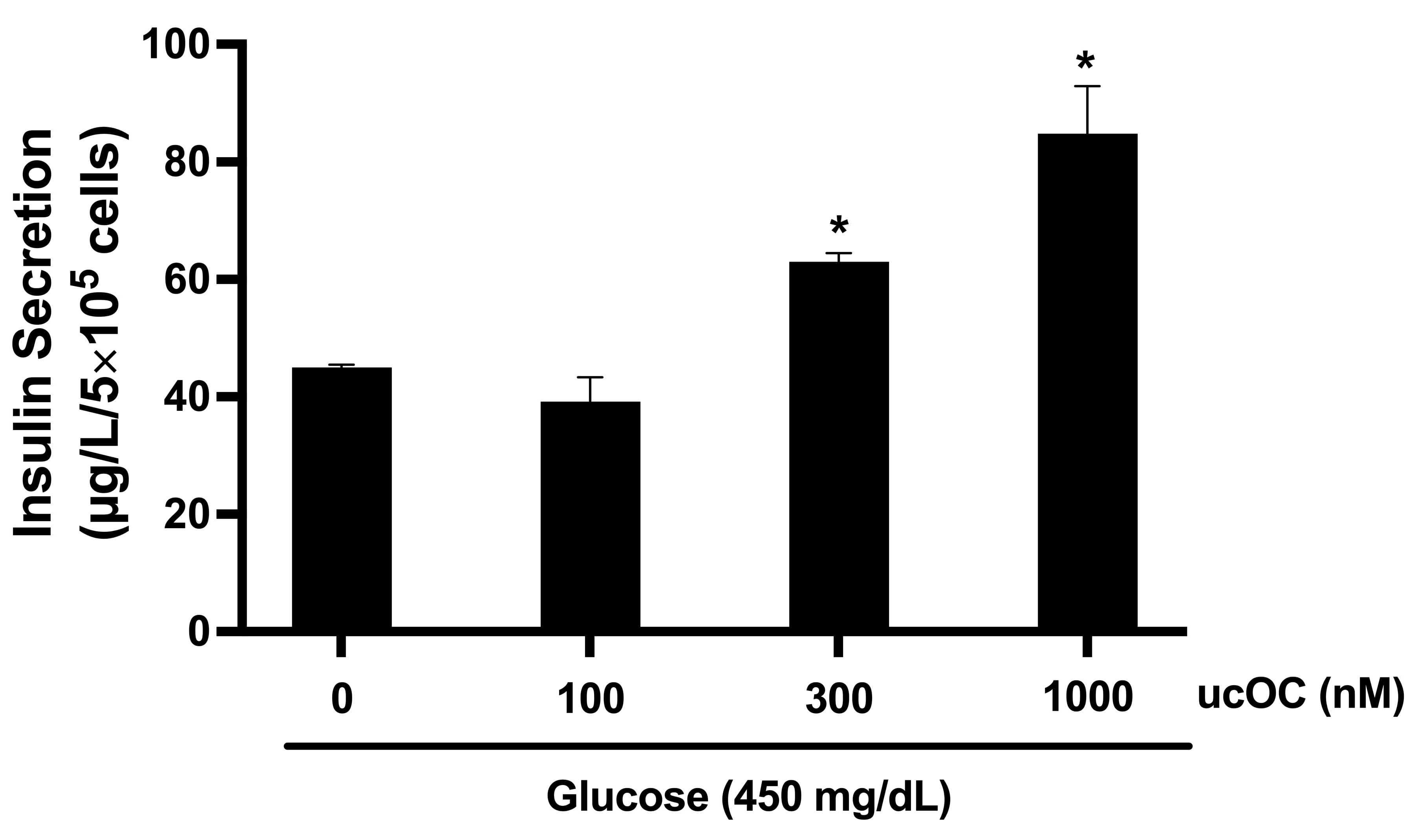
3.2. Osteocalcin Increased Insulin Secretion in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
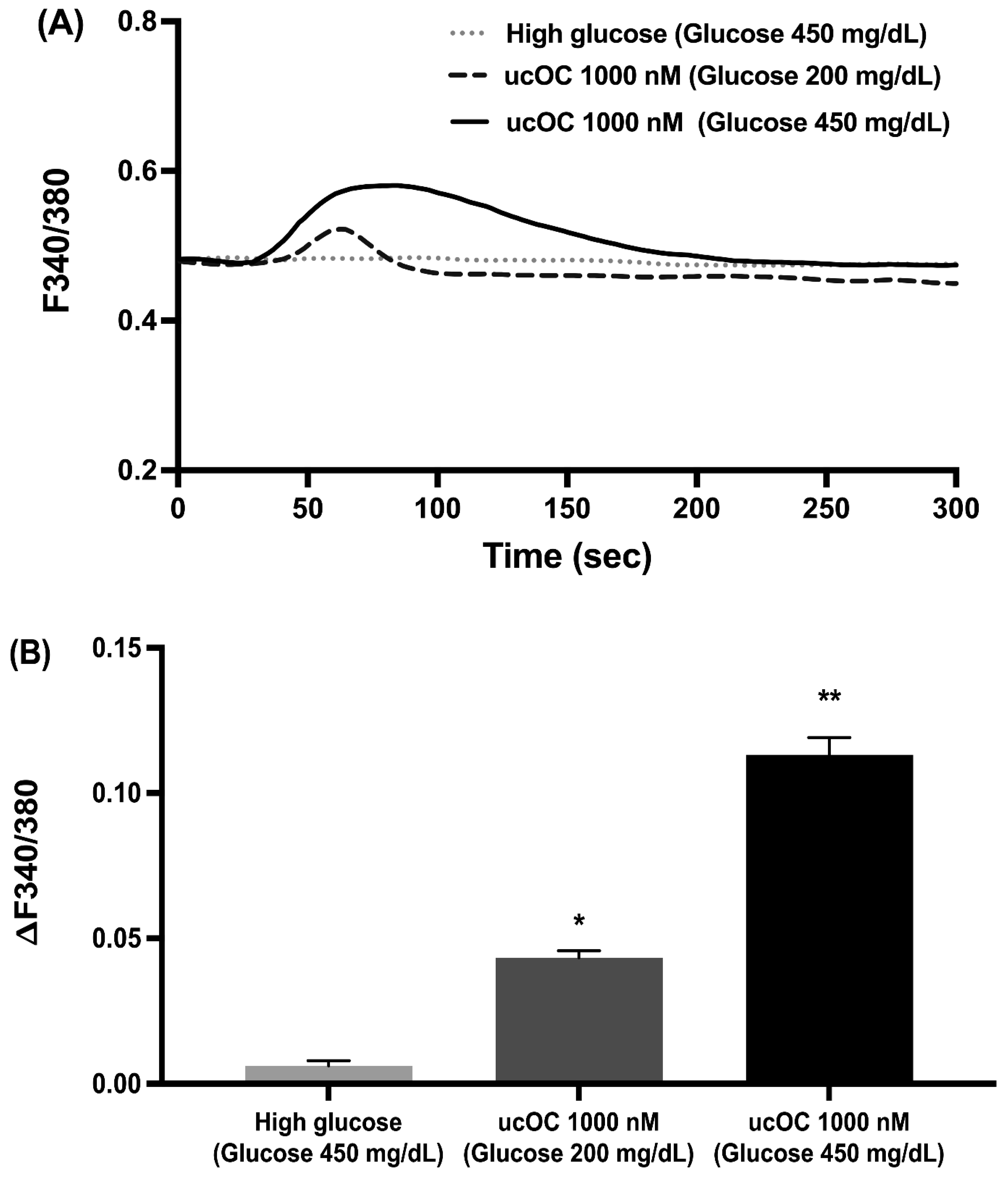
3.3. High Glucose Concentration Potentiated Osteocalcin-Induced Intracellular Calcium Signals
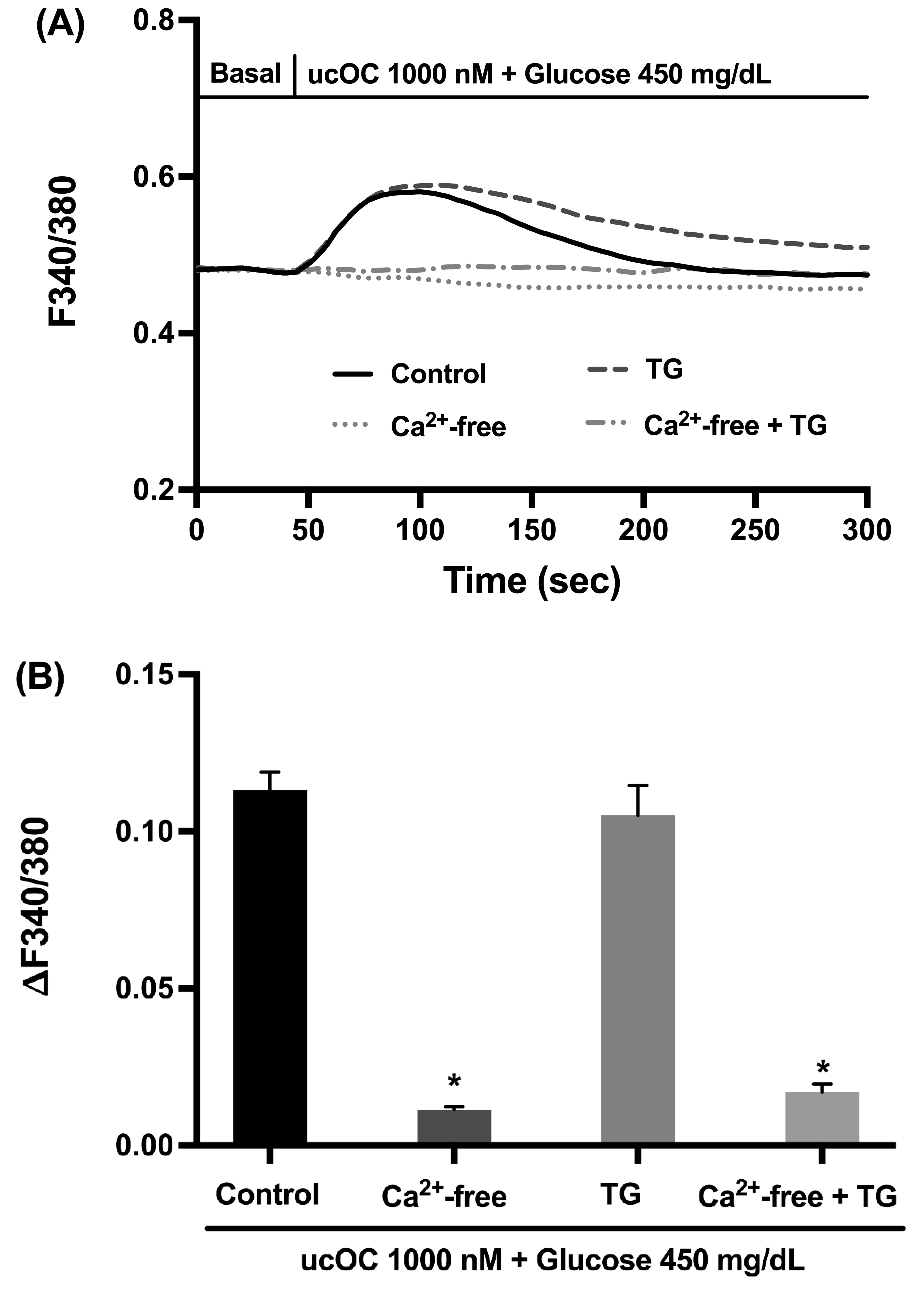
3.4. Extracellular Calcium Is Required for the Osteocalcin Response
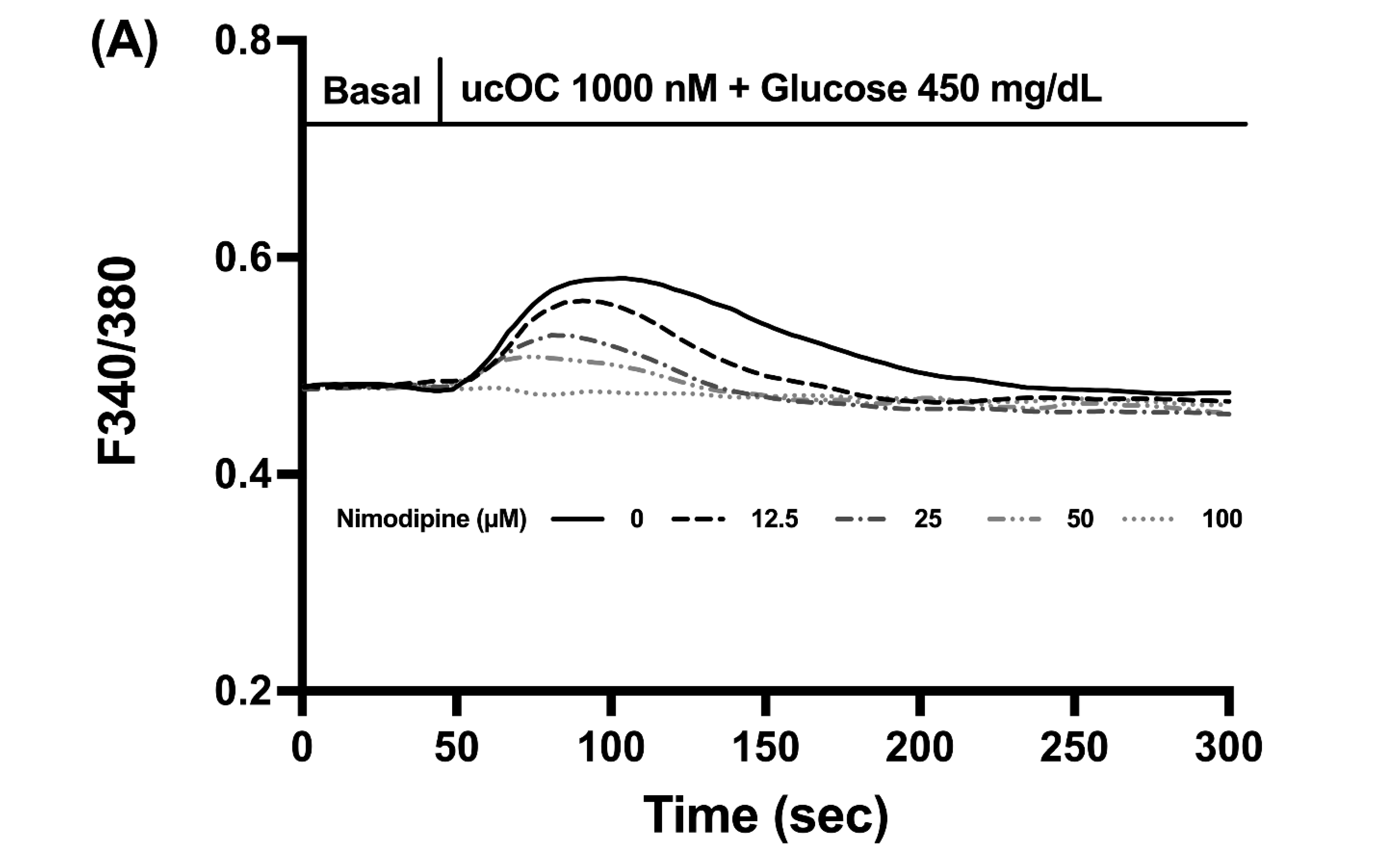
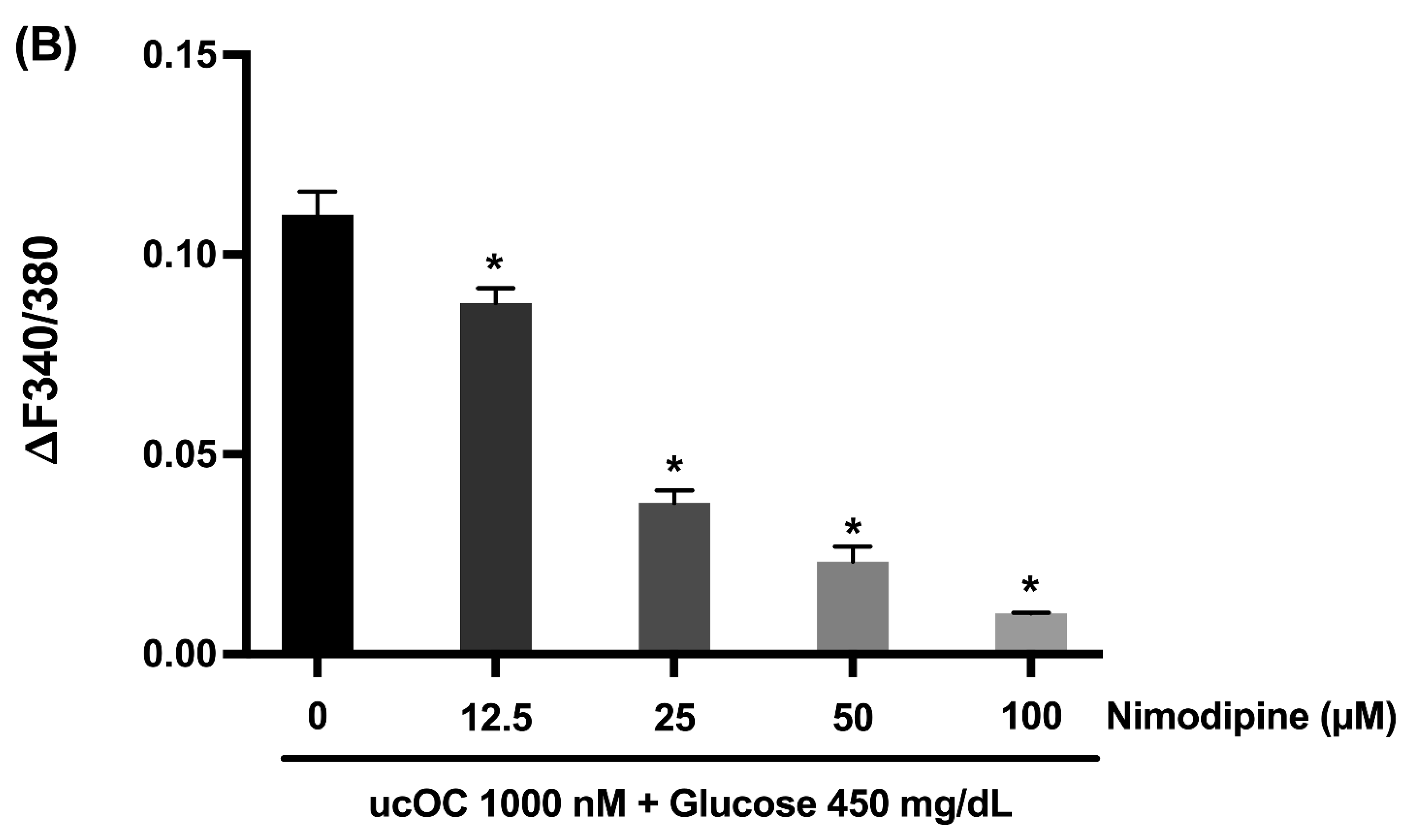
3.5. Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channels Are Activated in Response to Osteocalcin
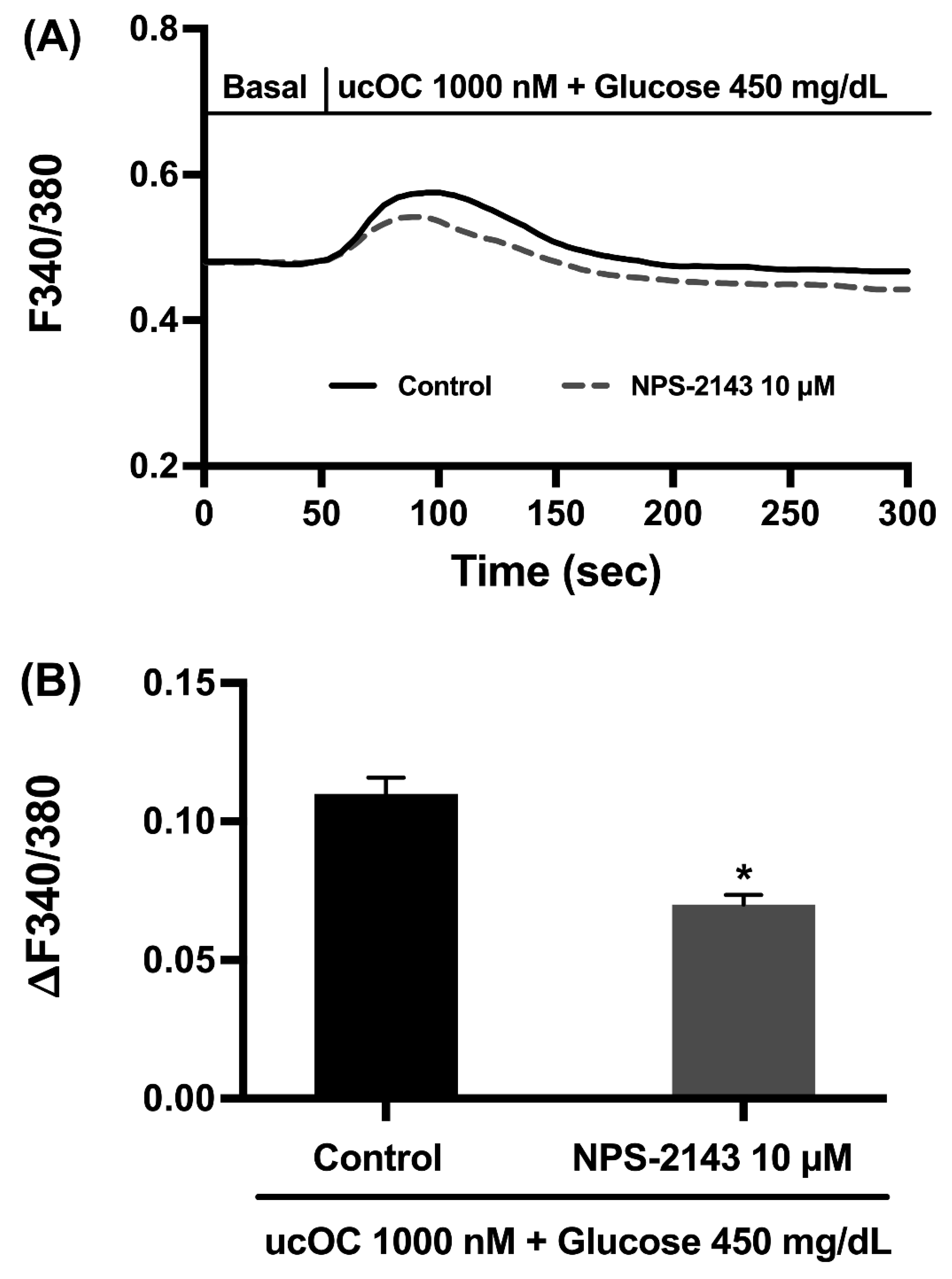
3.6. Osteocalcin Receptor in Pancreatic β-Cells
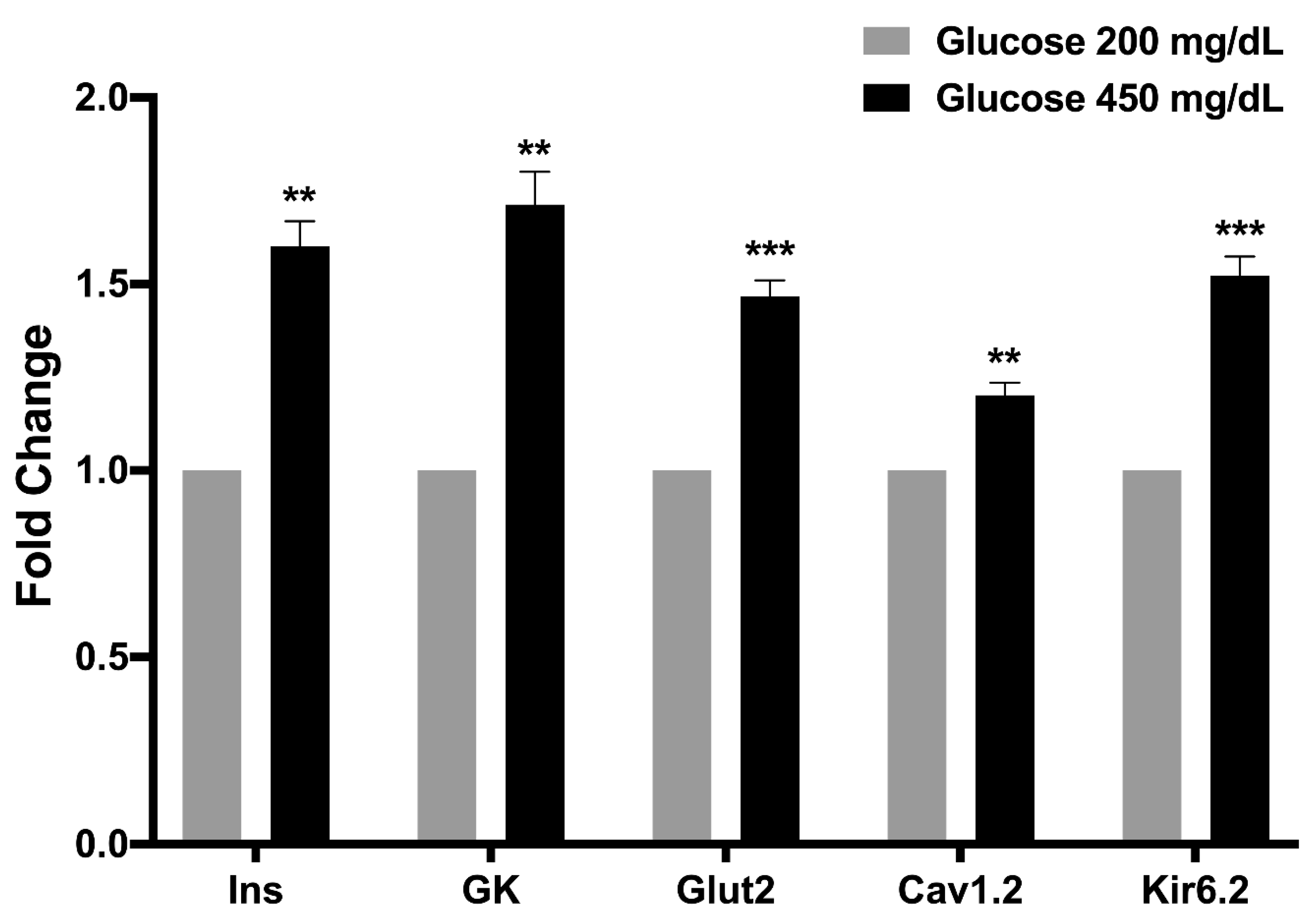
3.7. Osteocalcin Upregulated Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ucOC | Uncarboxylated osteocalcin |
| GSIS | Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion |
| VDCC | Voltage-dependent calcium channel |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| KRB | Krebs–Ringer bicarbonate buffer |
| GK | Glucokinase |
| Cav1.2 | L-type Ca2+ channel |
| Ins | Insulin |
| GLUT2 | Glucose transporter 2 |
| KATP | ATP-sensitive K+ channel |
| IP3 | Inositol triphosphate |
| GPRC6A | G protein-coupled receptor family C group 6 member A |
References
- Frodin, M.; Sekine, N.; Roche, E.; Filloux, C.; Prentki, M.; Wollheim, C.B.; Van, O.E. Glucose, other secretagogues, and nerve growth factor stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinase in the insulin-secreting beta-cell line, INS-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7882–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizokami, A.; Kawakubo-Yasukochi, T.; Hirata, M. Osteocalcin and its endocrine functions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 132, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paracha, N.; Mastrokostas, P.; Kello, E.; Gedailovich, Y.; Segall, D.; Rizzo, A.; Mitelberg, L.; Hassan, N.; Dowd, T.L. Osteocalcin improves glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and secretion in older male mice. Bone 2024, 182, 117048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Sowa, H.; Hinoi, E.; Ferron, M.; Ahn, J.D.; Confavreux, C.; Dacquin, R.; Mee, P.J.; McKee, M.D.; Jung, D.Y.; et al. Endocrine regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell 2007, 130, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Ferron, M.; Hinoi, E.; Karsenty, G.; Ducy, P. Osteocalcin differentially regulates beta cell and adipocyte gene expression and affects the development of metabolic diseases in wild-type mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Hinoi, E.; Gao, N.; Jung, D.Y.; Yadav, V.; Yoshizawa, T.; Myers, M.G.; Chua, S.C., Jr.; Kim, J.K., Jr.; Kaestner, K.H.; Karsenty, G. The sympathetic tone mediates leptin’s inhibition of insulin secretion by modulating osteocalcin bioactivity. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Alamri, T.M.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Wasti, A.Z. Assessment of Uncarboxylated Osteocalcin Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cureus 2023, 15, e35297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Darwish, L.; Nguyen, M.M.; Saleem, M.; Eakin, K.A.; Herrmann, N.; Sugamori, K.S.; Oh, P.I.; Yang, P.; Mitchell, J.; Lanctot, K.L.; et al. Lower serum osteocalcin concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes and relationships with vascular risk factors among patients with coronary artery disease. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 33, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme-Gallego, B.; Garcia-Molina, L.; Cano-Ibanez, N.; Andujar-Vera, F.; Gonzalez-Salvatierra, S.; Garcia-Fontana, C.; Bueno-Cavanillas, A.; Munoz-Torres, M.; Garcia-Fontana, B. Undercarboxylated Osteocalcin: A Promising Target for Early Diagnosis of Cardiovascular and Glycemic Disorders in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pi, M.; Kapoor, K.; Ye, R.; Nishimoto, S.K.; Smith, J.C.; Baudry, J.; Quarles, L.D. Evidence for Osteocalcin Binding and Activation of GPRC6A in beta-Cells. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1866–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rueda, P.; Harley, E.; Lu, Y.; Stewart, G.D.; Fabb, S.; Diepenhorst, N.; Cremers, B.; Rouillon, M.H.; Wehrle, I.; Geant, A.; et al. Murine GPRC6A Mediates Cellular Responses to L-Amino Acids, but Not Osteocalcin Variants. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khrimian, L.; Obri, A.; Ramos-Brossier, M.; Rousseaud, A.; Moriceau, S.; Nicot, A.S.; Mera, P.; Kosmidis, S.; Karnavas, T.; Saudou, F.; et al. Gpr158 mediates osteocalcin’s regulation of cognition. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2859–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qian, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Yang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Osteocalcin attenuates oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination via GPR37 signaling in the mouse brain. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, J.; Bai, T.; Ren, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhong, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. The PLC/PKC/Ras/MEK/Kv channel pathway is involved in uncarboxylated osteocalcin-regulated insulin secretion in rats. Peptides 2016, 86, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhong, X.; Ding, Y.; Bai, T.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Inhibition of voltage-gated potassium channels mediates uncarboxylated osteocalcin-regulated insulin secretion in rat pancreatic beta cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 777, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F.M.; Ashcroft, S.J.; Harrison, D.E. Properties of single potassium channels modulated by glucose in rat pancreatic beta-cells. J. Physiol. 1988, 400, 501–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henquin, J.C. Triggering and amplifying pathways of regulation of insulin secretion by glucose. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mera, P.; Laue, K.; Wei, J.; Berger, J.M.; Karsenty, G. Osteocalcin is necessary and sufficient to maintain muscle mass in older mice. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Otani, T.; Mizokami, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Inai, T.; Hirata, M. The role of adhesion molecules in osteocalcin-induced effects on glucose and lipid metabolism in adipocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Hanna, T.; Suda, N.; Karsenty, G.; Ducy, P. Osteocalcin promotes beta-cell proliferation during development and adulthood through Gprc6a. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Faure, H.; Gorojankina, T.; Rice, N.; Dauban, P.; Dodd, R.H.; Brauner-Osborne, H.; Rognan, D.; Ruat, M. Molecular determinants of non-competitive antagonist binding to the mouse GPRC6A receptor. Cell Calcium 2009, 46, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Ding, B.; Sui, X.; Guo, Z.; et al. Undercarboxylated osteocalcin inhibits the early differentiation of osteoclast mediated by Gprc6a. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mizokami, A.; Yasutake, Y.; Gao, J.; Matsuda, M.; Takahashi, I.; Takeuchi, H.; Hirata, M. Osteocalcin induces release of glucagon-like peptide-1 and thereby stimulates insulin secretion in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Channuwong, P.; Speight, V.; Yuan, Y.; Yao, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Bauermann, F.V.; Ranjan, A.; Adisakwattana, S.; Cheng, H. Hyperglycemia from Diabetes Potentiates Uncarboxylated Osteocalcin-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Rat INS-1 Pancreatic β-Cells. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152384
Channuwong P, Speight V, Yuan Y, Yao S, Yoshimura M, Bauermann FV, Ranjan A, Adisakwattana S, Cheng H. Hyperglycemia from Diabetes Potentiates Uncarboxylated Osteocalcin-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Rat INS-1 Pancreatic β-Cells. Nutrients. 2024; 16(15):2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152384
Chicago/Turabian StyleChannuwong, Pilailak, Victoria Speight, Yuanying Yuan, Shaomian Yao, Masami Yoshimura, Fernando V. Bauermann, Ashish Ranjan, Sirichai Adisakwattana, and Henrique Cheng. 2024. "Hyperglycemia from Diabetes Potentiates Uncarboxylated Osteocalcin-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Rat INS-1 Pancreatic β-Cells" Nutrients 16, no. 15: 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152384
APA StyleChannuwong, P., Speight, V., Yuan, Y., Yao, S., Yoshimura, M., Bauermann, F. V., Ranjan, A., Adisakwattana, S., & Cheng, H. (2024). Hyperglycemia from Diabetes Potentiates Uncarboxylated Osteocalcin-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Rat INS-1 Pancreatic β-Cells. Nutrients, 16(15), 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152384






