Cholecalciferol Supplementation Impacts Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroglial Reorganization in Vitamin D-Deficient Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs and Reagents
2.2.1. Drugs and Reagents
2.2.2. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS/MS)
2.3. Behavioral Tests
2.3.1. Open Field (OF) Test
2.3.2. Novel Object Recognition (NOR)
2.3.3. Morris Water Maze (MWM)
2.3.4. Radial Arm Maze (RAM)
2.4. Serum and Brain Sampling
2.4.1. Vitamin D Status and Biochemical Parameters
2.4.2. Preparation of Tissues
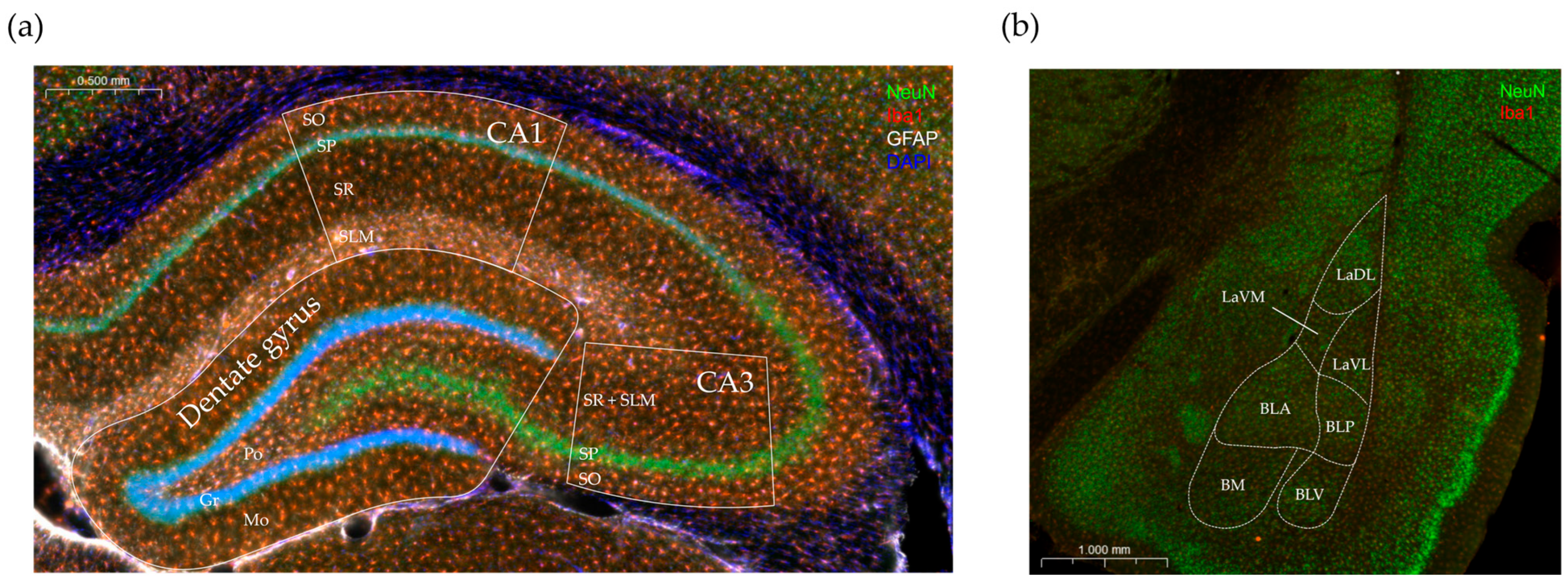
2.4.3. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.4.4. Evaluation of Immunostaining and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
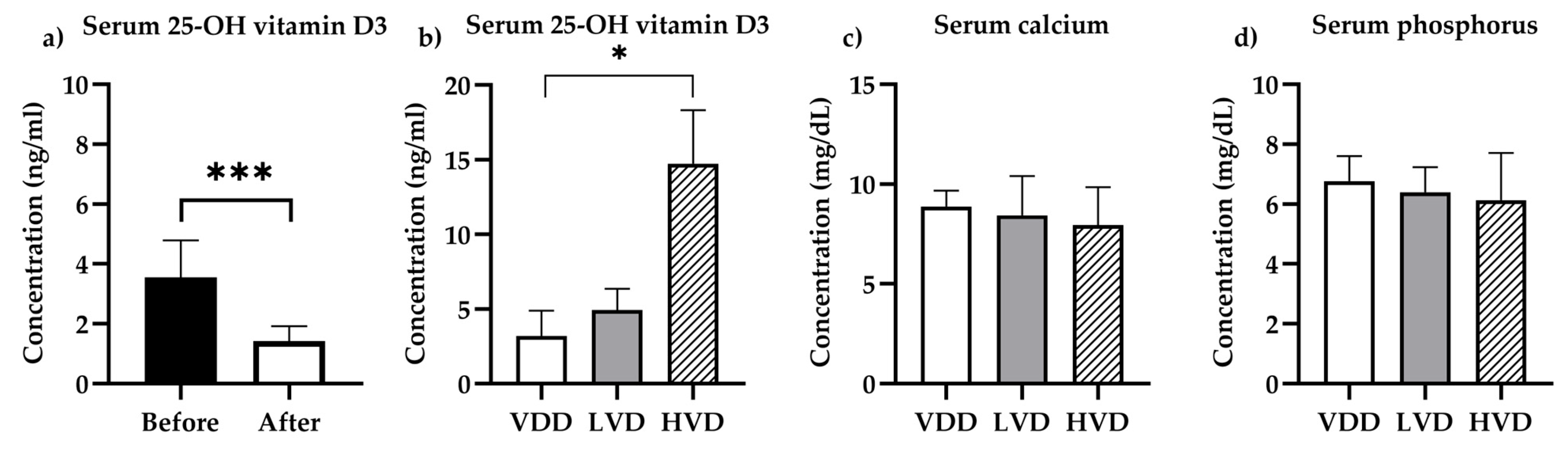
3.1. Pharmacokinetic and Biochemical Determinations
3.1.1. Vitamin D Status
3.1.2. Biochemistry
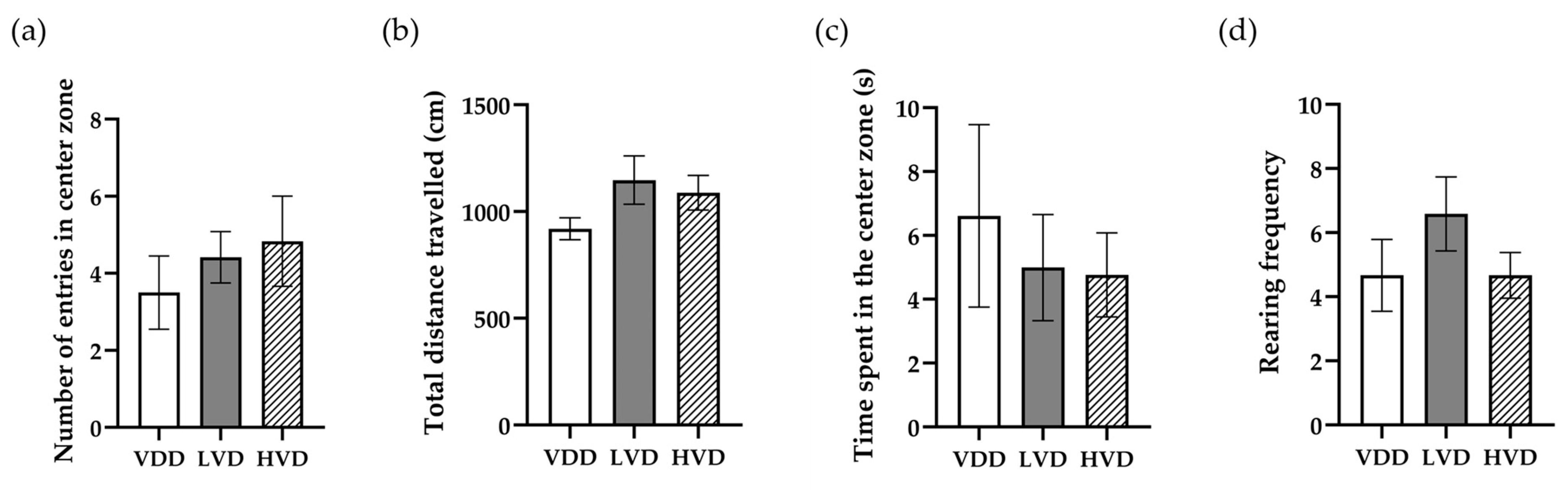
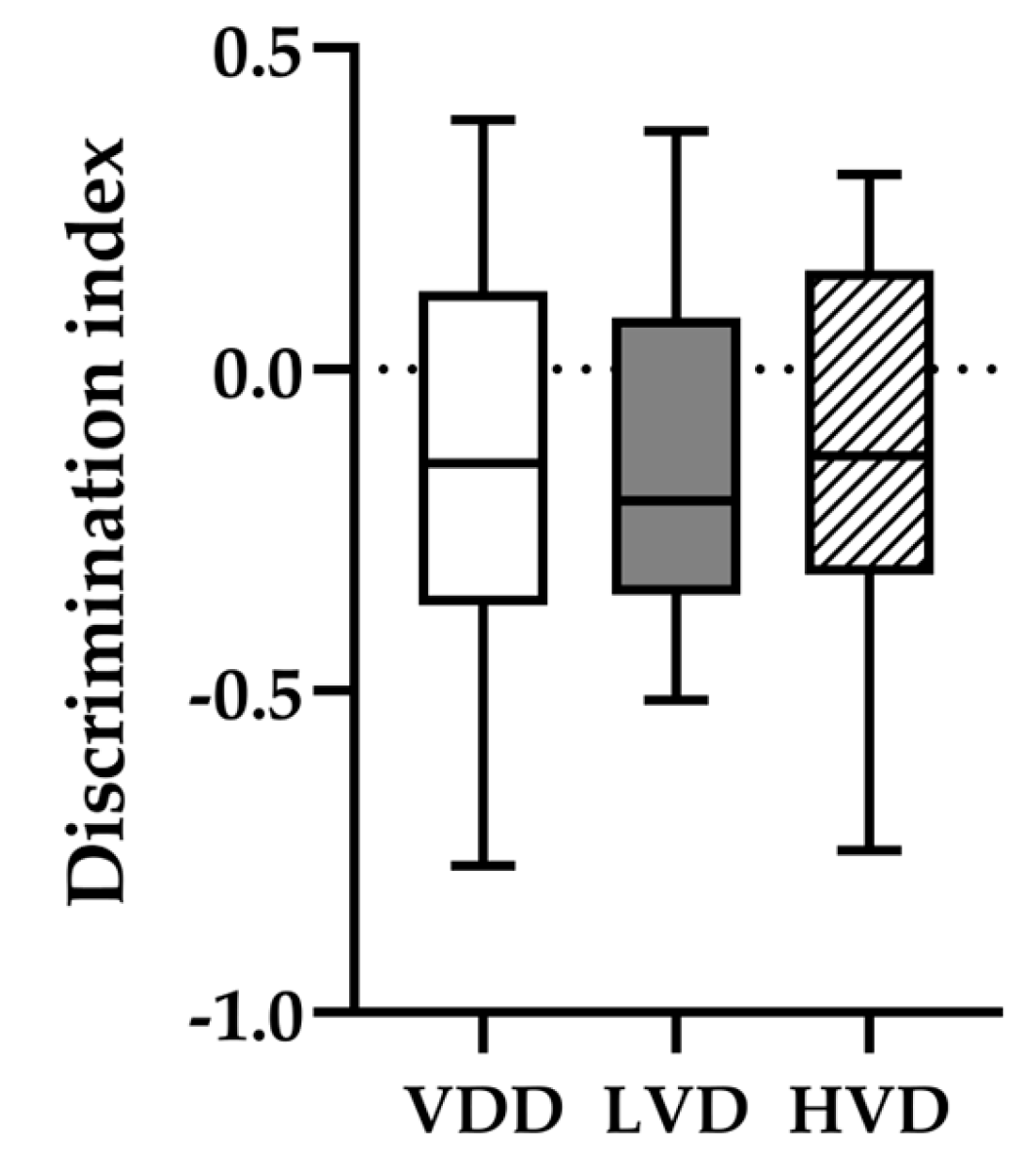
3.2. Behavioral Assays
3.2.1. Open Field (OF) Test
3.2.2. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
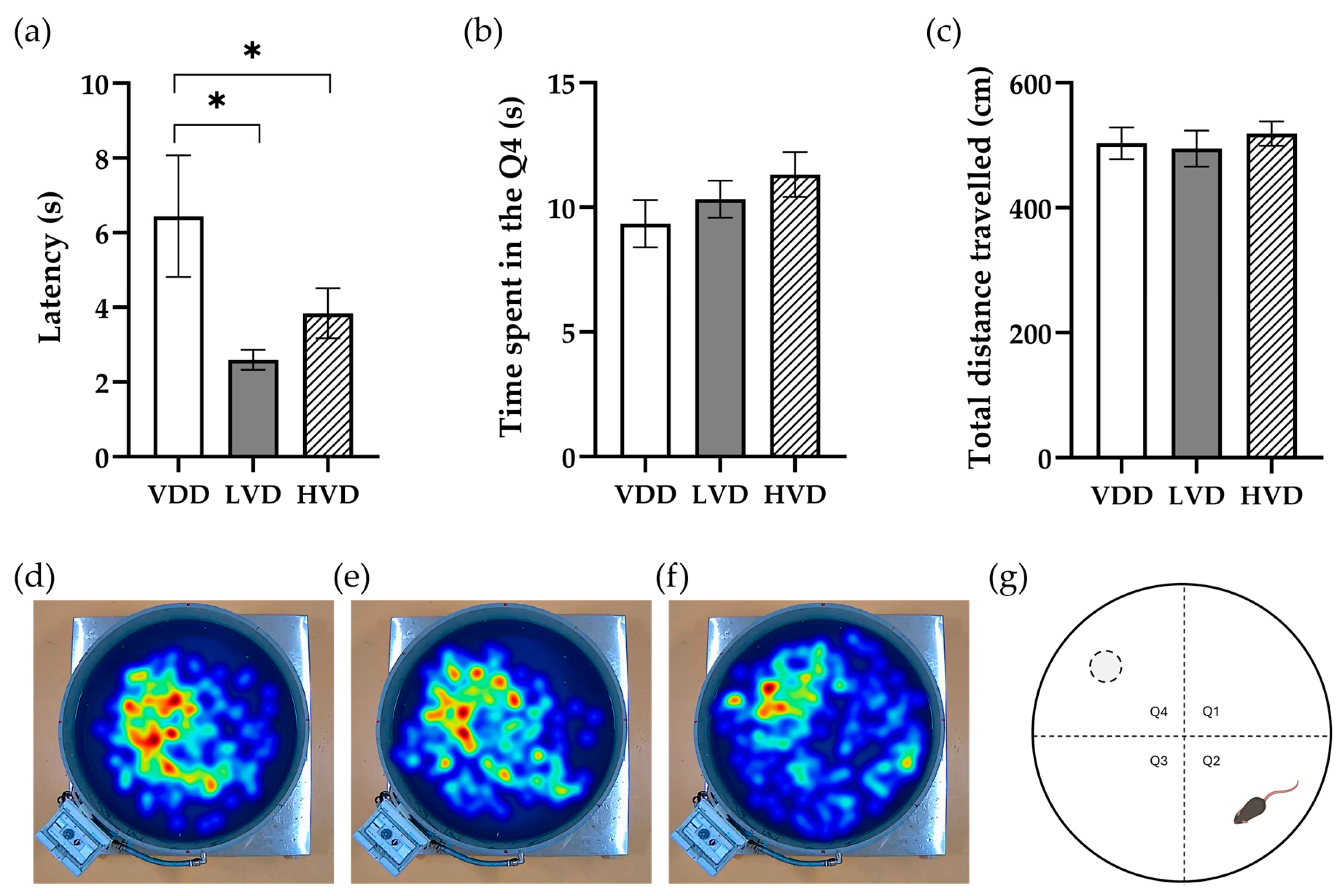
3.2.3. Morris Water Maze (MWM) Test
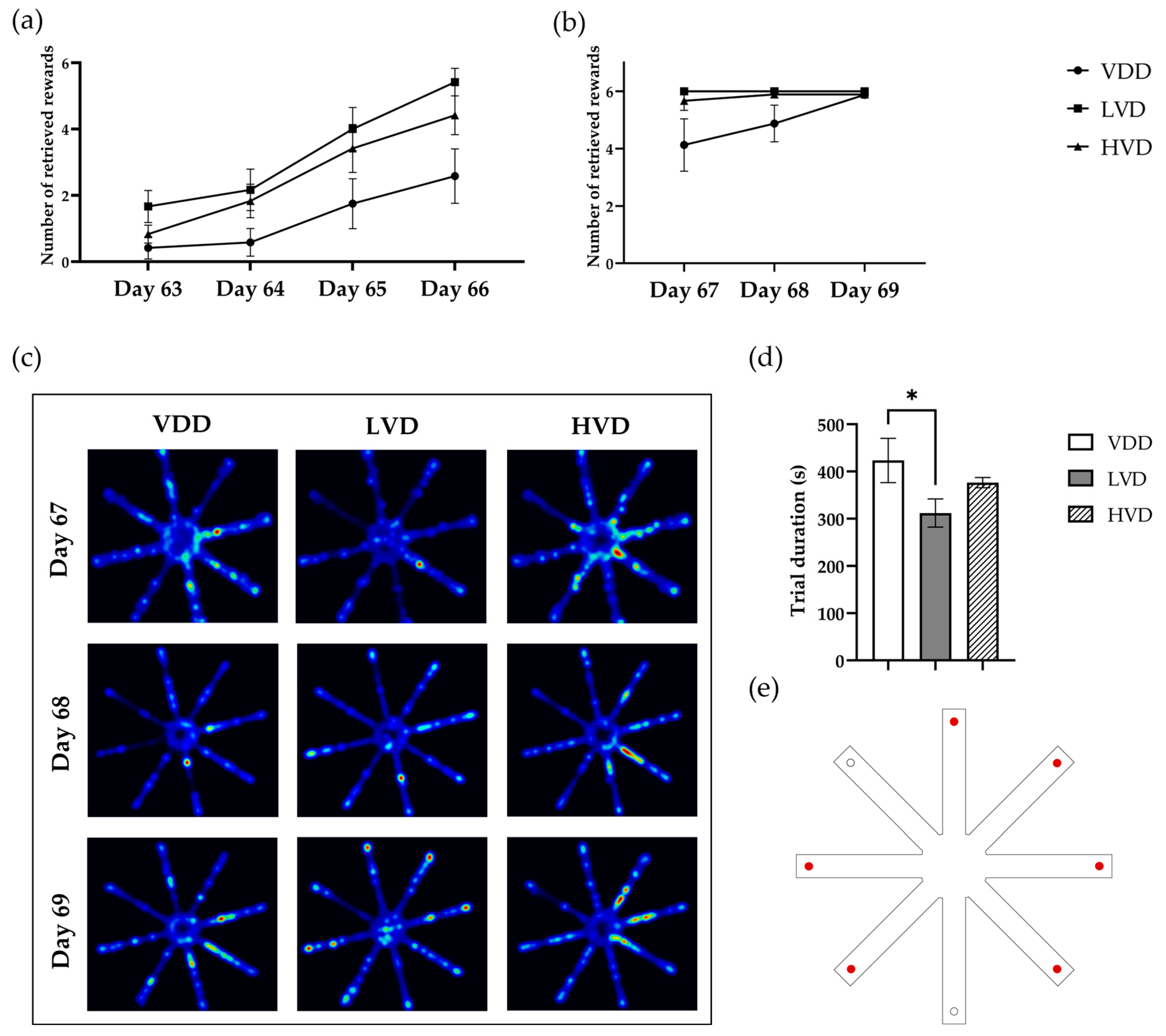
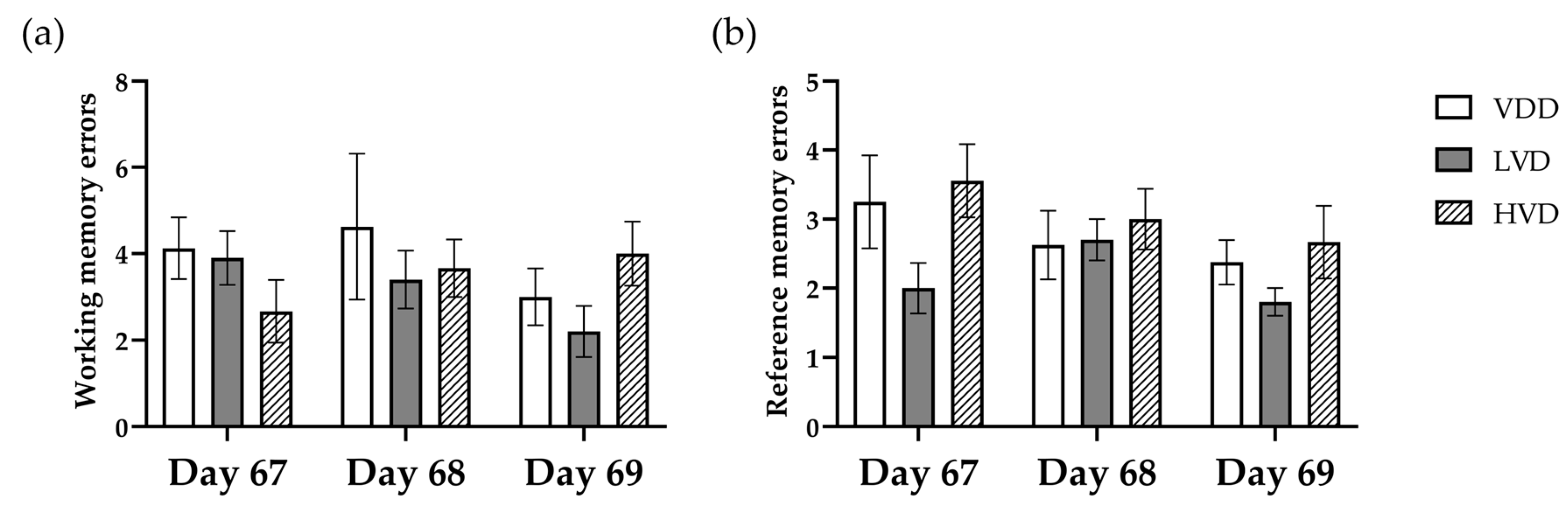
3.2.4. Radial Arm Maze Test (RAM)
3.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis
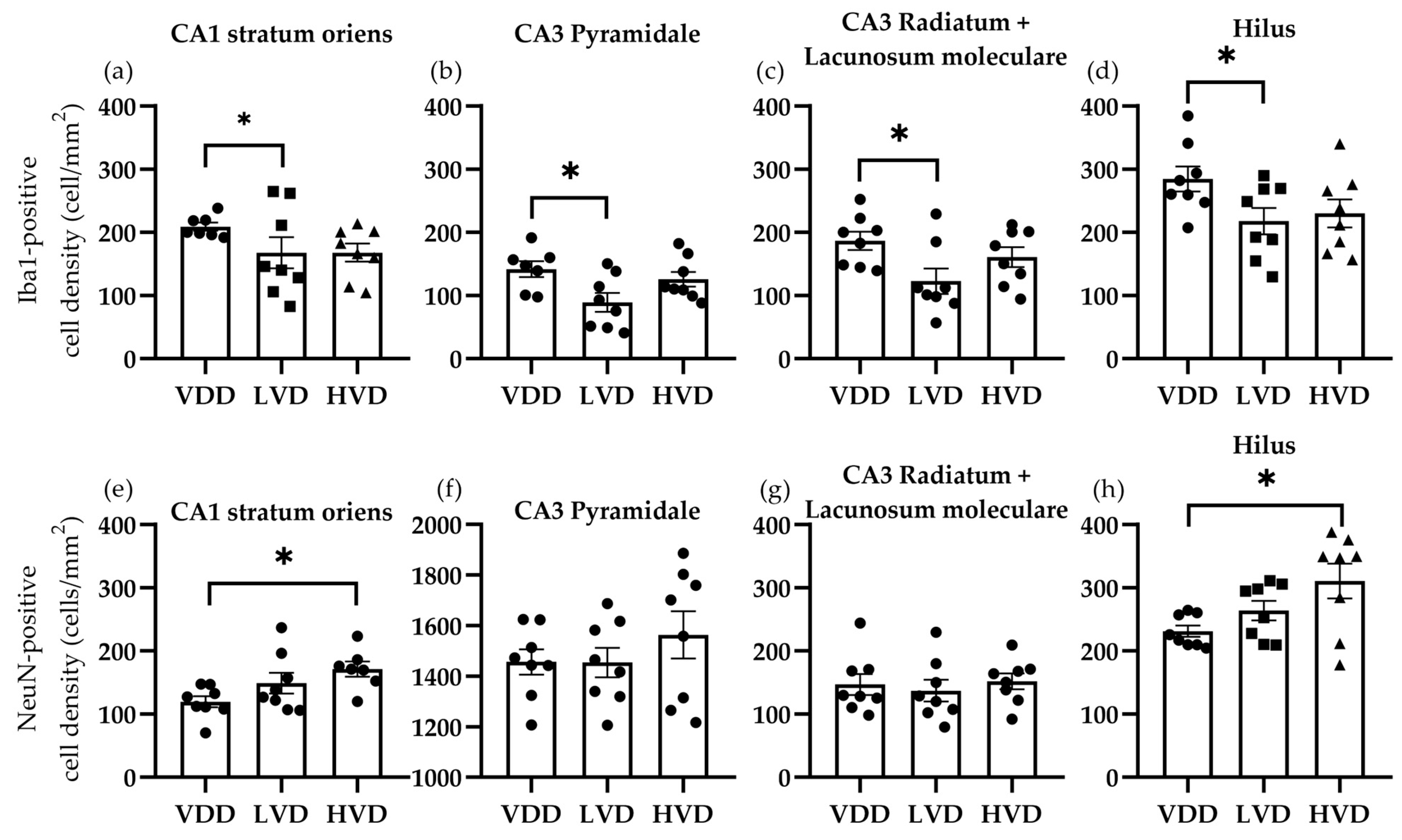
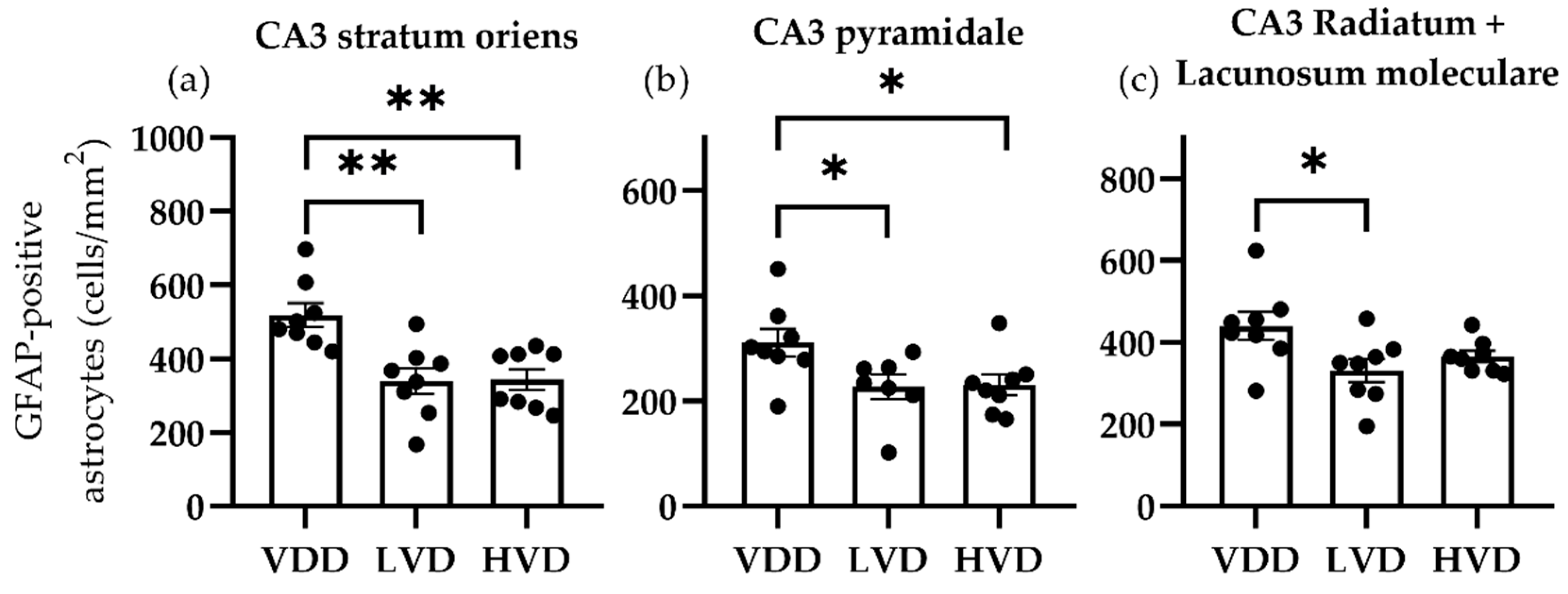
3.3.1. Effects of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on the Cellular Reorganization of the Hippocampus
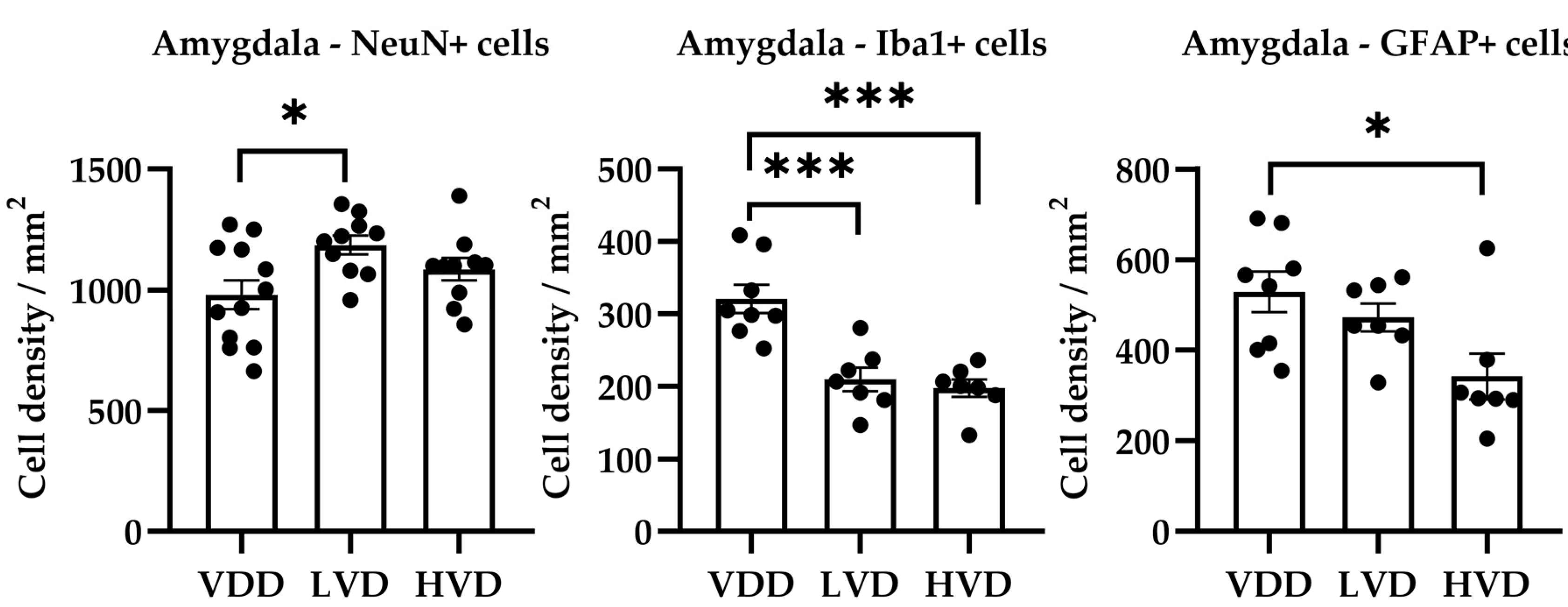
3.3.2. Effects of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on the Cellular Reorganization of the Amygdala
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caccamo, D.; Ricca, S.; Currò, M.; Ientile, R. Health risks of hypovitaminosis D: A review of new molecular insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D.; Schwartz, J. Vitamin D binding protein, total and free Vitamin D levels in different physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landel, V.; Annweiler, C.; Millet, P.; Morello, M.; Féron, F.; Wion, D. Vitamin D, Cognition and Alzheimer’s Disease: The Therapeutic Benefit is in the D-Tails. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 53, 419–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlejohns, T.J.; Henley, W.E.; Lang, I.A.; Annweiler, C.; Beauchet, O.; Chaves, P.H.M.; Fried, L.; Kestenbaum, B.R.; Kuller, L.H.; Langa, K.M.; et al. Vitamin D and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2014, 83, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukaszyk, E.; Bień-Barkowska, K.; Bień, B. Cognitive functioning of geriatric patients: Is hypovitaminosis D the next marker of cognitive dysfunction and dementia? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchaine, C.S.; Talbot, D.; Nafti, M.; Giguère, Y.; Dodin, S.; Tourigny, A.; Carmichael, P.H.; Laurin, D. Vitamin D status, cognitive decline and incident dementia: The Canadian Study of Health and Aging. Can. J. Public Health 2020, 111, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayedi, A.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Shab-Bidar, S. Vitamin D status and risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of dose-response. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyles, D.W.; Liu, P.Y.; Josh, P.; Cui, X. Intracellular distribution of the vitamin D receptor in the brain: Comparison with classic target tissues and redistribution with development. Neuroscience 2014, 268, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Atifi, M.; Dreyfus, M.; Berger, F.; Wion, D. Expression of CYP2R1 and VDR in human brain pericytes. Neuroreport 2015, 26, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazdeh, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Hatami, M.; Eftekharian, M.M.; Ganji, M.; Sayad, A.; Arsang-Jang, S.; Taheri, M.; Omrani, M.D. Expression Analysis of Vitamin D Signaling Pathway Genes in Epileptic Patients. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Gooch, H.; Petty, A.; McGrath, J.J.; Eyles, D. Vitamin D and the brain: Genomic and non-genomic actions. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 453, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landel, V.; Stephan, D.; Cui, X.; Eyles, D.; Feron, F. Differential expression of vitamin D-associated enzymes and receptors in brain cell subtypes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 177, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żmijewski, M.A. Nongenomic Activities of Vitamin D. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Wang, Y.; Herman, T.R.; Boyan, B.D.; Schwartz, Z. Protein-disulfide isomerase-associated 3 (Pdia3) mediates the membrane response to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in osteoblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 37041–37050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyles, D.W. Vitamin D: Brain and Behavior. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; He, X.; Li, H.-D.; Deng, Y.; Yan, M.; Cai, H.-L.; Tang, M.-M.; Dang, R.-L.; Jiang, P. Simultaneous Quantification of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D 3 and 24,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D 3 in Rats Shows Strong Correlations between Serum and Brain Tissue Levels. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 296531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overeem, K.; Alexander, S.; Burne, T.H.J.; Ko, P.; Eyles, D.W. Developmental vitamin D deficiency in the rat impairs recognition memory, but has no effect on social approach or hedonia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, L.R.; Eyles, D.W.; McGrath, J.J.; Mackay-Sim, A.; Burne, T.H.J. Developmental vitamin D deficiency alters adult behaviour in 129/SvJ and C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 187, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, M.; Bradford, D.; Sullivan, R.K.P.; Kurniawan, N.D.; Moon, Y.; Han, S.-H.; Zalesky, A.; Burne, T.H.J. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with reduced hippocampal volume and disrupted structural connectivity in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, N.J.; Bradford, D.; Sullivan, R.K.P.; Conn, K.A.; Aljelaify, R.F.; McGrath, J.J.; Burne, T.H.J. Behavioural effects of adult Vitamin D deficiency in BALB/c mice are not associated with proliferation or survival of neurons in the adult hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Schuurman, T.; de Groot, L.C.P.M.G.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Lute, C.; Naninck, E.F.G.; Arndt, S.S.; van der Staay, F.J.; Bravenboer, N.; Korosi, A.; et al. No role for vitamin D or a moderate fat diet in aging induced cognitive decline and emotional reactivity in C57BL/6 mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 267, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeney, J.T.R.; Förster, S.; Sultana, R.; Brewer, L.D.; Latimer, C.S.; Cai, J.; Klein, J.B.; Porter, N.M.; Butterfield, D.A. Dietary vitamin D deficiency in rats from middle to old age leads to elevated tyrosine nitration and proteomics changes in levels of key proteins in brain: Implications for low vitamin D-dependent age-related cognitive decline. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, C.S.; Brewer, L.D.; Searcy, J.L.; Chen, K.C.; Popović, J.; Kraner, S.D.; Thibault, O.; Blalock, E.M.; Landfield, P.W.; Porter, N.M. Vitamin D prevents cognitive decline and enhances hippocampal synaptic function in aging rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4359–E4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Cai, C.; Duan, D.; Hu, X.; Hua, W.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Gao, Z. Postnatal Vitamin D Intake Modulates Hippocampal Learning and Memory in Adult Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavenuiter, A.W.D.; Arcidiacono, M.V.; Ferrantelli, E.; Keuning, E.D.; Vila Cuenca, M.; Ter Wee, P.M.; Beelen, R.H.J.; Vervloet, M.G.; Dusso, A.S. A Novel Rat Model of Vitamin D Deficiency: Safe and Rapid Induction of Vitamin D and Calcitriol Deficiency without Hyperparathyroidism. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 604275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gáll, Z.; Csukor, B.; Urkon, M.; Farczádi, L.; Kolcsár, M. Vitamin D Status Assessment: Lack of Correlation between Serum and Hair 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol Levels in Healthy Young Adults. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.C.; Fogaca, M.V.; Aguiar, D.C.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Campos, A.C.; Fogaca, M.V.; Aguiar, D.C.; Guimaraes, F.S. Animal models of anxiety disorders and stress. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2013, 35, S101–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, M.; Biala, G. The novel object recognition memory: Neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn. Process. 2012, 13, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gáll, Z.; Kelemen, K.; Tolokán, A.; Zolcseak, I.; Sável, I.; Bod, R.; Ferencz, E.; Vancea, S.; Urkon, M.; Kolcsár, M. Anticonvulsant Action and Long-Term Effects of Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment in the Rat Pentylenetetrazole-Kindling Model of Epilepsy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jîtcă, G.; Gáll, Z.; Jîtcă, C.-M.; Buț, M.-G.; Májai, E. Drug Repurposing of Metformin for the Treatment of Haloperidol-Related Behavior Disorders and Oxidative Stress: A Preliminary Study. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenk, G.L. Assessment of Spatial Memory Using the Radial Arm Maze and Morris Water Maze. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2004, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burne, T.H.J.; Johnston, A.N.B.; McGrath, J.J.; MacKay-Sim, A. Swimming behaviour and post-swimming activity in Vitamin D receptor knockout mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 69, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keisala, T.; Minasyan, A.; Järvelin, U.; Wang, J.; Hämäläinen, T.; Kalueff, A.V.; Tuohimaa, P. Aberrant nest building and prolactin secretion in vitamin D receptor mutant mice. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 104, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Keisala, T.; Minasyan, A.; Kuuslahti, M.; Miettinen, S.; Tuohimaa, P. Behavioural anomalies in mice evoked by “Tokyo” disruption of the Vitamin D receptor gene. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 54, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, J.H.; Voogt, M.; Turner, K.M.; Eyles, D.W.; McGrath, J.J.; Burne, T.H.J. The Impact of Adult Vitamin D Deficiency on Behaviour and Brain Function in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, N.J.; Kesby, J.P.; Eyles, D.W.; McGrath, J.J.; Mackay-Sim, A.; Burne, T.H.J. Adult vitamin D deficiency leads to behavioural and brain neurochemical alterations in C57BL/6J and BALB/c mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 241, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu-Wong, J.R.; Chen, Y.-W.; Nakane, M.; Wolf, M. Differential Effects of Vitamin D Receptor Agonists on Gene Expression in Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2011, 25, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarbali, S.; Khezri, S. Vitamin D3 attenuates oxidative stress and cognitive deficits in a model of toxic demyelination. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 19, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alrefaie, Z.; Moustafa, I. Vitamin D3 favorable outcome on recognition memory and prefrontal cortex expression of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase in experimental model of chronic high-fat feeding. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 130, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.L.; Ganaraja, B.; Murlimanju, B.V.; Joy, T.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Agrawal, A. Hippocampus and its involvement in Alzheimer’s disease: A review. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerasinghe-Mudiyanselage, P.D.E.; Ang, M.J.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.-S.; Moon, C. Structural Plasticity of the Hippocampus in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, R.; Morelli, M.E.; Caruso, P. Vitamin D in neurological diseases: A rationale for a pathogenic impact. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, M.J.; Alenezi, S.K.; Alhowail, A.H. Molecular insights into the pathogenic impact of vitamin D deficiency in neurological disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerbai, F.; Lana, D.; Nosi, D.; Petkova-Kirova, P.; Zecchi, S. The Neuron-Astrocyte-Microglia Triad in Normal Brain Ageing and in a Model of Neuroinflammation in the Rat Hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 45250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lana, D.; Melani, A.; Maria Pugliese, A.; Cipriani, S.; Nosi, D.; Pedata, F.; Grazia Giovannini, M.; Barreto, G.E.; Blalock, E. The neuron-astrocyte-microglia triad in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: Protective effect of dipyridamole. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lana, D.; Ugolini, F.; Giovannini, M.G. Space-dependent glia–neuron interplay in the hippocampus of transgenic models of β-amyloid deposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Wang, C.; Jin, F.; Yang, M.; Kong, L.; Han, W.; Jiang, P. Calcitriol confers neuroprotective effects in traumatic brain injury by activating Nrf2 signaling through an autophagy-mediated mechanism. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari-Zaer, A.; Hosseini, M.; Salmani, H.; Arab, Z.; Zareian, P. Vitamin D3 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment in rats by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2020, 253, 117703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Xu, P.; Li, G.; Qiao, Y.; Han, W.; Geng, C.; Liao, D.; Yang, M.; Chen, D.; Jiang, P. Vitamin D receptor activation regulates microglia polarization and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats and angiotensin II-exposed microglial cells: Role of renin-angiotensin system. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirarchi, A.; Albi, E.; Beccari, T.; Arcuri, C. Microglia and Brain Disorders: The Role of Vitamin D and Its Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.J. Vitamin D deficiency accelerates ageing and age-related diseases: A novel hypothesis. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 6825–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazi, H.A.; Rasouli, J.; Ciric, B.; Rostami, A.; Zhang, G.-X. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances neural stem cell proliferation and oligodendrocyte differentiation. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 98, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulla, Y.A.T.; Kurauchi, Y.; Hisatsune, A.; Seki, T.; Shudo, K.; Katsuki, H. Regulatory Mechanisms of Vitamin D3 on Production of Nitric Oxide and Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in Microglial BV-2 Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2848–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C.; Montero-Menei, C.N.; Bernard, R.; Couez, D. Vitamin D3 inhibits proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide production by the EOC13 microglial cell line. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 71, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, N.; Belardo, C.; Trotta, M.C.; Paino, S.; Boccella, S.; Gargano, F.; Pieretti, G.; Ricciardi, F.; Marabese, I.; Luongo, L.; et al. Vitamin D Deficiency Induces Chronic Pain and Microglial Phenotypic Changes in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvello, R.; Cianciulli, A.; Nicolardi, G.; De Nuccio, F.; Giannotti, L.; Salvatore, R.; Porro, C.; Trotta, T.; Panaro, M.A.; Lofrumento, D.D. Vitamin D Treatment Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease, Shifting M1 to M2 Microglia Responses. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017, 12, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Sierra, A.; Stevens, B.; Tremblay, M.E.; Aguzzi, A.; Ajami, B.; Amit, I.; Audinat, E.; Bechmann, I.; Bennett, M.; et al. Microglia states and nomenclature: A field at its crossroads. Neuron 2022, 110, 3458–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, S.; Taimuri, U.; Basnan, S.A.; Ai-Orabi, W.K.; Awadallah, A.; Almowald, F.; Hazazi, A. Low Vitamin D and Its Association with Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. J. Aging Res. 2020, 2020, 6097820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roof, R.; Stein, D. Gender differences in Morris water maze performance depend on task parameters. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 68, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.; Kelly, J.P. An investigation of whether there are sex differences in certain behavioural and neurochemical parameters in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 229, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Treatment Group | Mean | Standard Deviation | One-Way ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine aminotransferase ALT | VDD | 24.13 | 4.190 | F (2, 20) = 0.07007 |
| LVD | 22.14 | 9.616 | p = 0.9326 | |
| HVD | 23.88 | 15.83 | ||
| Aspartate aminotransferase AST | VDD | 100.0 | 21.40 | F (2, 20) = 1.025 |
| LVD | 126.0 | 44.94 | p = 0.3770 | |
| HVD | 109.9 | 36.96 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase | VDD | 122.9 | 38.52 | F (2, 20) = 0.3936 |
| LVD | 147.0 | 24.28 | p = 0.6797 | |
| HVD | 136.3 | 77.34 | ||
| Creatinine | VDD | 0.325 | 0.071 | F (2, 20) = 2.103 |
| LVD | 0.300 | 0.100 | p = 0.1482 | |
| HVD | 0.238 | 0.092 | ||
| Total cholesterol | VDD | 68.68 | 15.51 | F (2, 20) = 0.7690 |
| LVD | 58.36 | 11.07 | p = 0.4767 | |
| HVD | 63.60 | 19.84 | ||
| Blood glucose | VDD | 295.5 | 58.27 | F (2, 18) = 0.8933 |
| LVD | 253.6 | 53.81 | p = 0.4267 | |
| HVD | 269.7 | 73.24 | ||
| Potassium | VDD | 7.25 | 0.369 | F (2, 17) = 0.1295 |
| LVD | 7.39 | 0.501 | p = 0.8794 | |
| HVD | 7.31 | 0.649 | ||
| Sodium | VDD | 148.4 | 0.419 | F (2, 24) = 1.915 |
| LVD | 148.8 | 0.350 | p = 0.1692 | |
| HVD | 148.8 | 0.748 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gáll, Z.; Csüdör, Á.; Sável, I.-G.; Kelemen, K.; Kolcsár, M. Cholecalciferol Supplementation Impacts Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroglial Reorganization in Vitamin D-Deficient Rats. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142326
Gáll Z, Csüdör Á, Sável I-G, Kelemen K, Kolcsár M. Cholecalciferol Supplementation Impacts Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroglial Reorganization in Vitamin D-Deficient Rats. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142326
Chicago/Turabian StyleGáll, Zsolt, Ágnes Csüdör, István-Gábor Sável, Krisztina Kelemen, and Melinda Kolcsár. 2024. "Cholecalciferol Supplementation Impacts Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroglial Reorganization in Vitamin D-Deficient Rats" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142326
APA StyleGáll, Z., Csüdör, Á., Sável, I.-G., Kelemen, K., & Kolcsár, M. (2024). Cholecalciferol Supplementation Impacts Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroglial Reorganization in Vitamin D-Deficient Rats. Nutrients, 16(14), 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142326







