Add-On Bifidobacterium Bifidum Supplement in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A 12-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
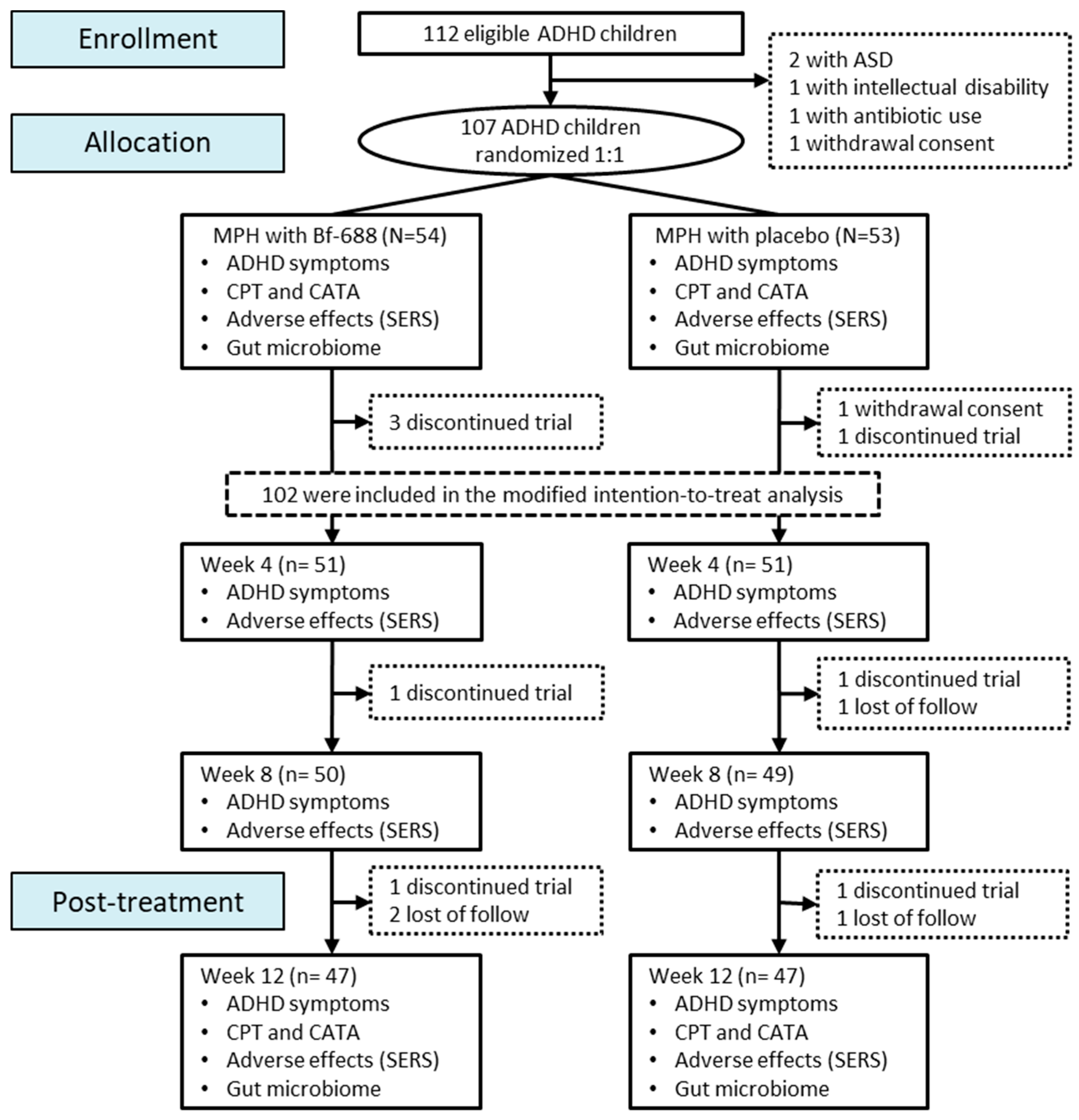
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Allocation
2.3. Study Procedures
2.4. Gut Microbiome Analysis
2.5. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
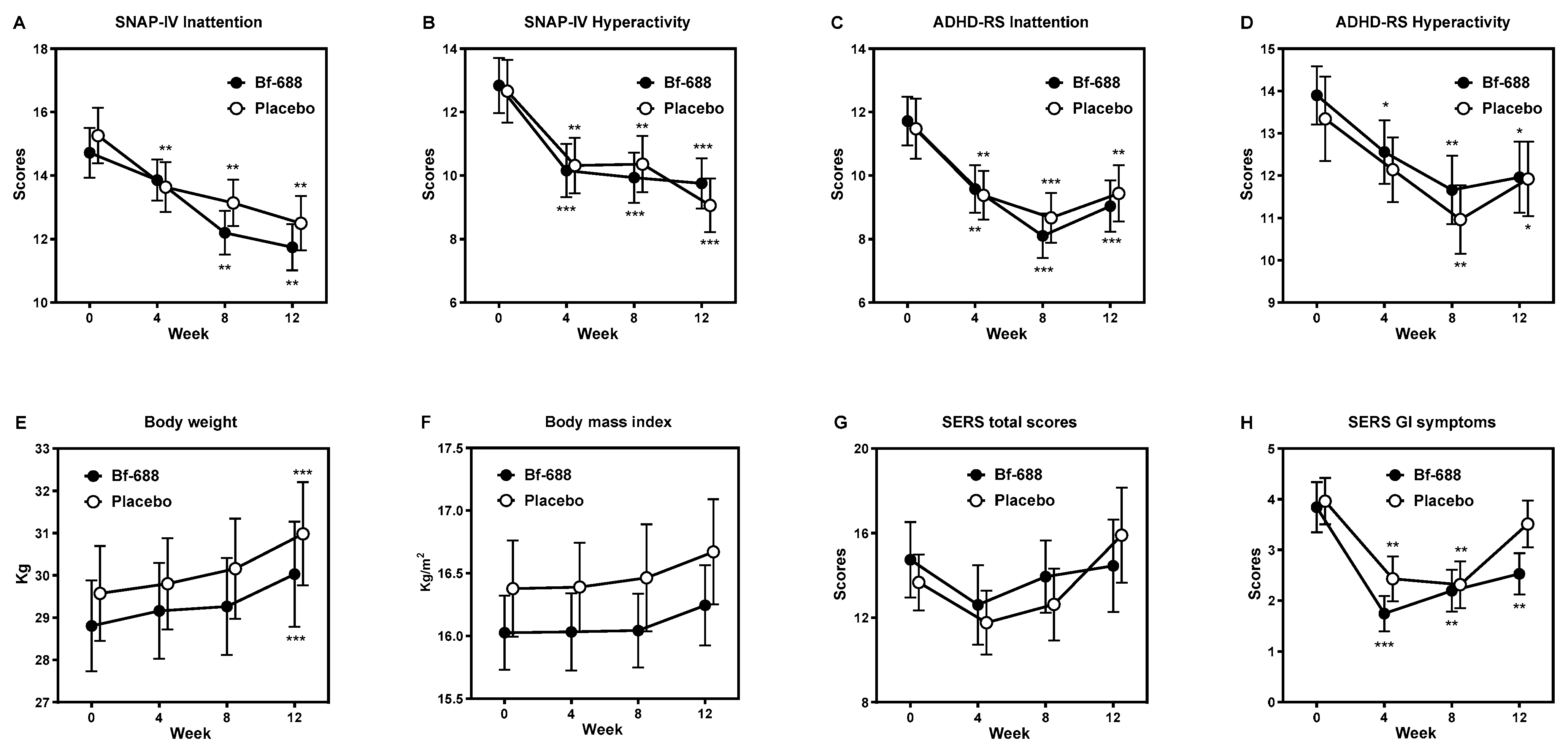
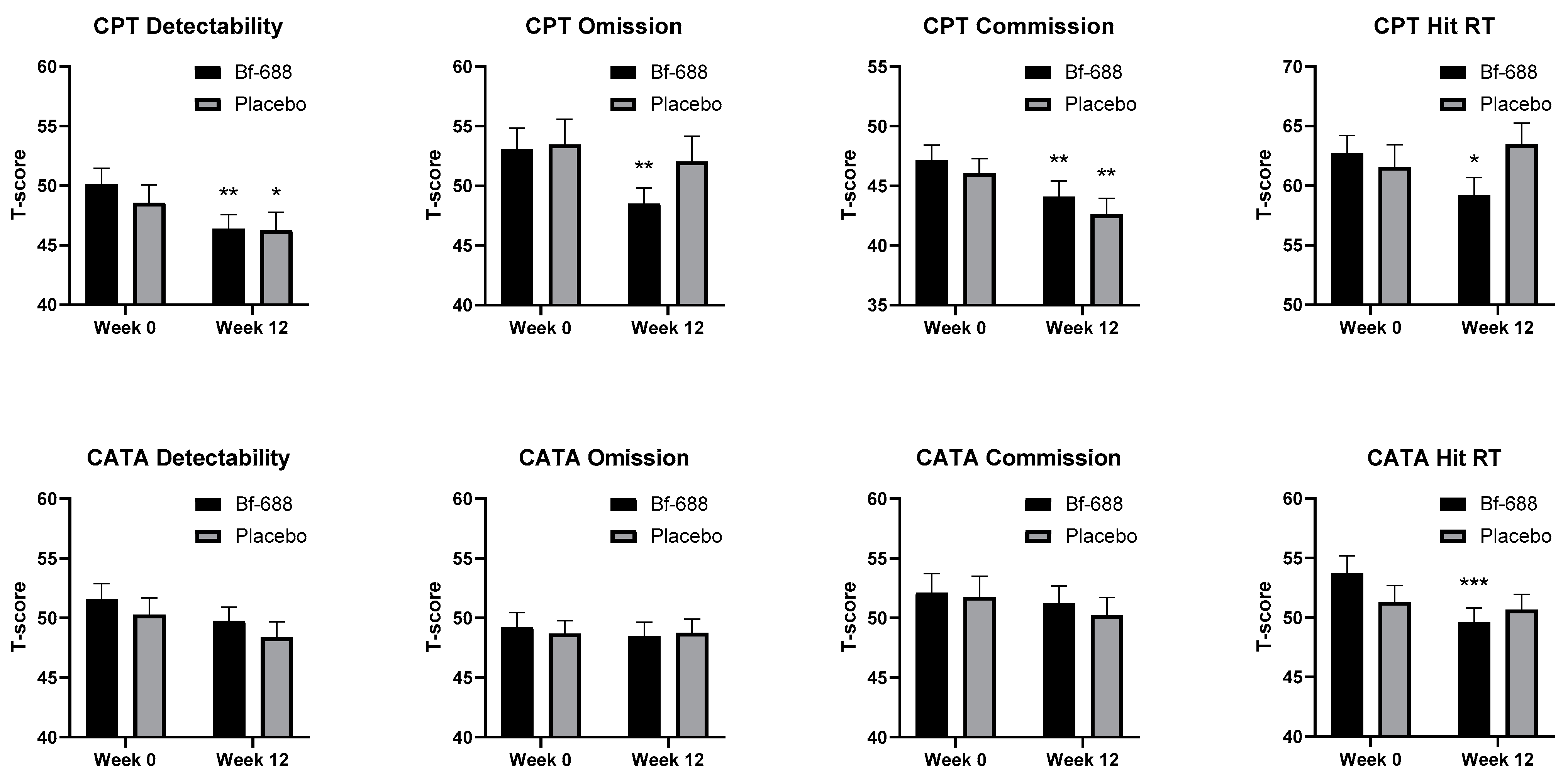
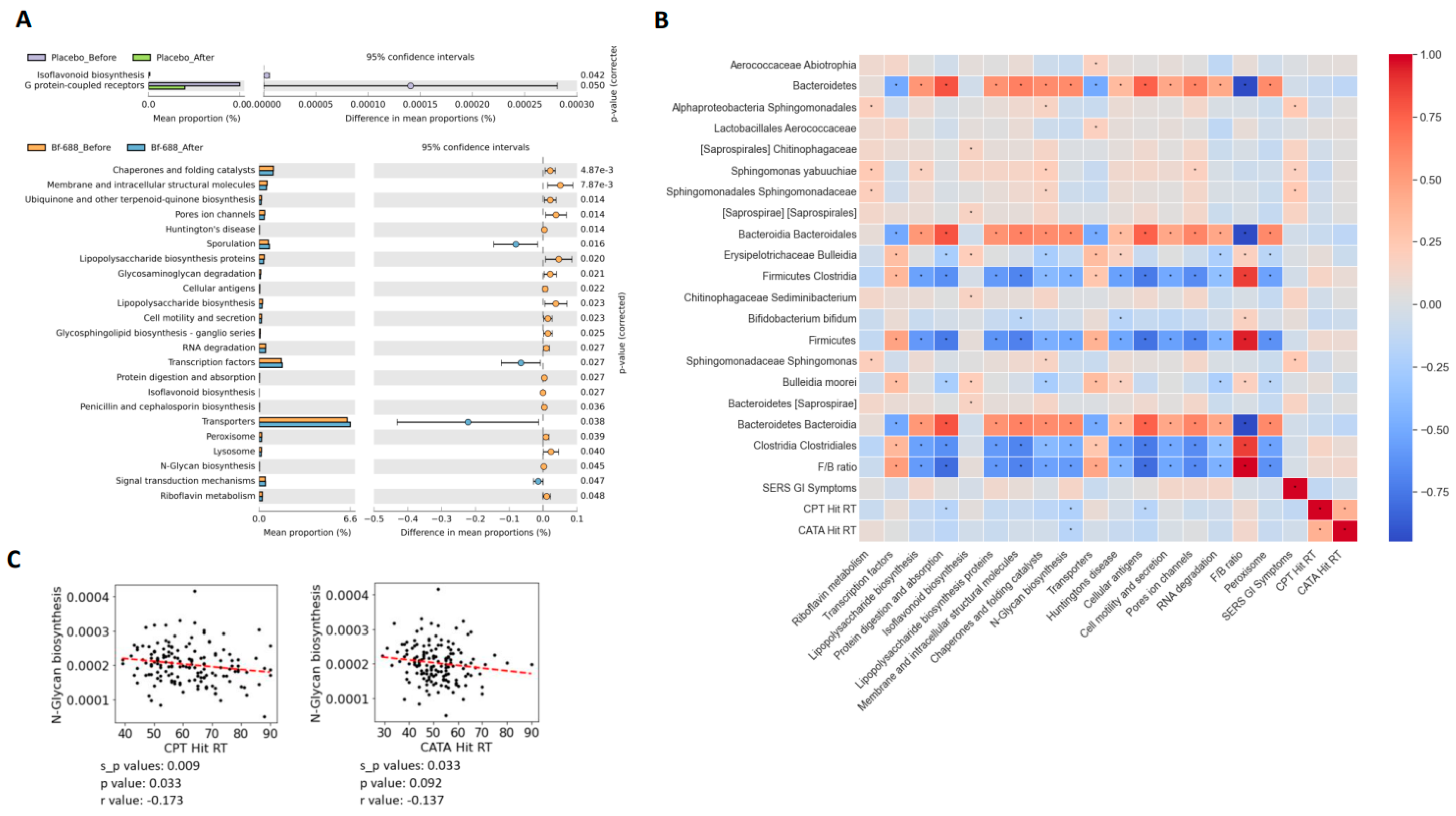
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Outcome Analysis
3.2. Gut Microbiome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortese, S.; Song, M.; Farhat, L.C.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, M.S.; Park, S.; Oh, J.W.; Lee, S.; Cheon, K.A.; et al. Incidence, prevalence, and global burden of ADHD from 1990 to 2019 across 204 countries: Data, with critical re-analysis, from the Global Burden of Disease study. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 4823–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayano, G.; Demelash, S.; Gizachew, Y.; Tsegay, L.; Alati, R. The global prevalence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 339, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L., VI; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. An updated overview on the relationship between human gut microbiome dysbiosis and psychiatric and psychological disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 128, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicknell, B.; Liebert, A.; Borody, T.; Herkes, G.; McLachlan, C.; Kiat, H. Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Diseases and the Gut-Brain Axis: The Potential of Therapeutic Targeting of the Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góralczyk-Bińkowska, A.; Szmajda-Krygier, D.; Kozłowska, E. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Chou, W.J.; Lee, M.J.; Chou, M.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Yeh, Y.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Huang, L.H.; Li, S.C. Gut microbiota and dietary patterns in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 29, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Li, S.C.; Li, S.W.; Kuo, H.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Huang, L.H.; Chin, C.Y.; Yang, C.Y. Gut microbiota and plasma cytokine levels in patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Li, S.C.; Yeh, Y.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Kuo, H.C.; Yang, C.Y. Gut mycobiome dysbiosis and its impact on intestinal permeability in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2023, 64, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Syed, Y.A.; Khan, M.R. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Brain Development and Its Association With Neurodevelopmental Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 880544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliu, O. The current state of research for psychobiotics use in the management of psychiatric disorders—A systematic literature review. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1074736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X. The microbiota-gut-brain axis and neurodevelopmental disorders. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundgaard-Nielsen, C.; Lauritsen, M.B.; Knudsen, J.K.; Rold, L.S.; Larsen, M.H.; Hindersson, P.; Villadsen, A.B.; Leutscher, P.D.C.; Hagstrom, S.; Nyegaard, M.; et al. Children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder share distinct microbiota compositions. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2211923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocean, A.M.; Vodnar, D.C. Exploring the gut-brain Axis: Potential therapeutic impact of Psychobiotics on mental health. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 134, 111073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurek, L.; Sevil, M.; Jay, A.; Schröder, C.; Baghdadli, A.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Geoffray, M.M. Is there a dysbiosis in individuals with a neurodevelopmental disorder compared to controls over the course of development? A systematic review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 30, 1671–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligezka, A.N.; Sonmez, A.I.; Corral-Frias, M.P.; Golebiowski, R.; Lynch, B.; Croarkin, P.E.; Romanowicz, M. A systematic review of microbiome changes and impact of probiotic supplementation in children and adolescents with neuropsychiatric disorders. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 108, 110187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checa-Ros, A.; Jeréz-Calero, A.; Molina-Carballo, A.; Campoy, C.; Muñoz-Hoyos, A. Current Evidence on the Role of the Gut Microbiome in ADHD Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Implications. Nutrients 2021, 13, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenik, A.; Kardaś, K.; Rahnama, A.; Sirojć, K.; Wolańczyk, T. Gut microbiota and probiotic therapy in ADHD: A review of current knowledge. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 110, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, S.; McGinn, K.; Højlund, M.; Apter, A.; Arango, C.; Baeza, I.; Banaschewski, T.; Buitelaar, J.; Castro-Fornieles, J.; Coghill, D.; et al. The future of child and adolescent clinical psychopharmacology: A systematic review of phase 2, 3, or 4 randomized controlled trials of pharmacologic agents without regulatory approval or for unapproved indications. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 149, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.W.; Lange, K.M.; Nakamura, Y.; Reissmann, A. Nutrition in the Management of ADHD: A Review of Recent Research. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Neshat, M.; Pourjafar, H.; Jafari, S.M.; Samakkhah, S.A.; Mirzakhani, E. The role of probiotics and prebiotics in modulating of the gut-brain axis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1173660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.H.; Tanpure, R.; Kim, J.I.; Jeon, B.H.; Park, H.K. Psychobiotics and fecal microbial transplantation for autism and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Microbiome modulation and therapeutic mechanisms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1238005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, C.; Arias-Sanchez, S.; Martin-Monzon, I. The gut microbiota-brain axis, psychobiotics and its influence on brain and behaviour: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 137, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pärtty, A.; Kalliomäki, M.; Wacklin, P.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. A possible link between early probiotic intervention and the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders later in childhood: A randomized trial. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumperscak, H.G.; Gricar, A.; Ülen, I.; Micetic-Turk, D. A Pilot Randomized Control Trial With the Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) in ADHD: Children and Adolescents Report Better Health-Related Quality of Life. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rianda, D.; Agustina, R.; Setiawan, E.A.; Manikam, N.R.M. Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function in children and adolescents: A systematic review of randomised trials. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhossiny, R.M.; Elshahawy, H.H.; Mohamed, H.M.; Abdelmageed, R.I. Assessment of probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus LB supplementation as adjunctive management of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: A randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skott, E.; Yang, L.L.; Stiernborg, M.; Söderström, Å.; Rȕegg, J.; Schalling, M.; Forsell, Y.; Giacobini, M.; Lavebratt, C. Effects of a synbiotic on symptoms, and daily functioning in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder—A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L.; Stiernborg, M.; Skott, E.; Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Landberg, R.; Arefin, S.; Kublickiene, K.; Millischer, V.; Nilsson, I.A.K.; et al. Effects of a Synbiotic on Plasma Immune Activity Markers and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Children and Adults with ADHD-A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, H.N.; Roy, S.; Shaikh, A.; Bandi, V. Emerging Role and Place of Probiotics in the Management of Pediatric Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Euroasian J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2022, 12, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonchooduang, N.; Louthrenoo, O.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Possible links between gut-microbiota and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders in children and adolescents. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3391–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, E.; Ederveen, T.H.A.; Naaijen, J.; Zwiers, M.P.; Boekhorst, J.; Timmerman, H.M.; Smeekens, S.P.; Netea, M.G.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Franke, B.; et al. Gut microbiome in ADHD and its relation to neural reward anticipation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, A.; Tanaka, N.; Fukunaga, S.; Nakano-Doi, A.; Matsuyama, T.; Nakagomi, T.; Tsuji, M. Bifidobacterium breve during infancy attenuates mobility in low birthweight rats. Pediatr. Int. 2022, 64, e15209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, A.J.; Purcell, R.V.; Darling, K.A.; Eggleston, M.J.F.; Kennedy, M.A.; Rucklidge, J.J. Human gut microbiome changes during a 10 week Randomised Control Trial for micronutrient supplementation in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turroni, F.; Duranti, S.; Milani, C.; Lugli, G.A.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bifidobacterium bifidum: A Key Member of the Early Human Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makizaki, Y.; Uemoto, T.; Yokota, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohno, H. Improvement of loperamide-induced slow transit constipation by Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 is mediated by the correction of butyrate production and neurotransmitter profile due to improvement in dysbiosis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Kuo, H.C.; Chou, W.J.; Tsai, C.S.; Lee, S.Y. Effect of Bifidobacterium bifidum on Clinical Characteristics and Gut Microbiota in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groom, M.J.; Cortese, S. Current Pharmacological Treatments for ADHD. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 57, 19–50. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, L.; Carbone, S.; Gobbo, A.; Gamble, H.; Faraone, S.V. Pediatric attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): 2022 updates on pharmacological management. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 16, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmskov, M.; Storebø, O.J.; Moreira-Maia, C.R.; Ramstad, E.; Magnusson, F.L.; Krogh, H.B.; Groth, C.; Gillies, D.; Zwi, M.; Skoog, M.; et al. Gastrointestinal adverse events during methylphenidate treatment of children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review with meta-analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis of randomised clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storebø, O.J.; Storm, M.R.O.; Pereira Ribeiro, J.; Skoog, M.; Groth, C.; Callesen, H.E.; Schaug, J.P.; Darling Rasmussen, P.; Huus, C.L.; Zwi, M.; et al. Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 3, Cd009885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Storebø, O.J.; Pedersen, N.; Ramstad, E.; Kielsholm, M.L.; Nielsen, S.S.; Krogh, H.B.; Moreira-Maia, C.R.; Magnusson, F.L.; Holmskov, M.; Gerner, T.; et al. Methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents—Assessment of adverse events in non-randomised studies. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 5, Cd012069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andresen, V.; Gschossmann, J.; Layer, P. Heat-inactivated Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75 (SYN-HI-001) in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regier, D.A.; Kuhl, E.A.; Kupfer, D.J. The DSM-5: Classification and criteria changes. World Psychiatry 2013, 12, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, W.J.; Lin, K.C.; Shen, L.J.; Gau, S.S. Prevalence of DSM-5 mental disorders in a nationally representative sample of children in Taiwan: Methodology and main findings. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2019, 29, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, B. How to calculate sample size in randomized controlled trial? J. Thorac. Dis. 2009, 1, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gau, S.S.; Shang, C.Y.; Liu, S.K.; Lin, C.H.; Swanson, J.M.; Liu, Y.C.; Tu, C.L. Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham, version IV scale—Parent form. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 17, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussing, R.; Fernandez, M.; Harwood, M.; Wei, H.; Garvan, C.W.; Eyberg, S.M.; Swanson, J.M. Parent and teacher SNAP-IV ratings of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms: Psychometric properties and normative ratings from a school district sample. Assessment 2008, 15, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döpfner, M.; Steinhausen, H.C.; Coghill, D.; Dalsgaard, S.; Poole, L.; Ralston, S.J.; Rothenberger, A. Cross-cultural reliability and validity of ADHD assessed by the ADHD Rating Scale in a pan-European study. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2006, 15 (Suppl. S1), I46–I55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, R.A.; McMurray, M.B.; Edelbrock, C.S.; Robbins, K. Side effects of methylphenidate in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A systemic, placebo-controlled evaluation. Pediatrics 1990, 86, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonuga-Barke, E.J.; Coghill, D.; Wigal, T.; DeBacker, M.; Swanson, J. Adverse reactions to methylphenidate treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Structure and associations with clinical characteristics and symptom control. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2009, 19, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conners, C.; Mutli-Health Systems Staff. Conners’ Continuous Performance Test II (CPTII) for Windows Technical Guide and Software Manual; Multi-Health Systems Inc.: North Tonawanda, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rassovsky, Y.; Alfassi, T. Attention Improves During Physical Exercise in Individuals With ADHD. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Tsai, C.S.; Lee, M.J.; Chou, M.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Chou, W.J. Validity of Visual and Auditory Attention Tests for Detecting ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2021, 25, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.J.; Kuo, H.C.; Chou, W.J.; Tsai, C.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Wang, L.J. Cytokine Levels and Neuropsychological Function among Patients with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Atopic Diseases. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraha, I.; Montedori, A. Modified intention to treat reporting in randomised controlled trials: Systematic review. BMJ 2010, 340, c2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, A.P. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS, 2nd ed.; Sage Publication Ltd.: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nuga, O.A. An application of the two-factor mixed model design in educational research. I J. Math. Sci. Comput. 2019, 4, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Arrano, V.; Martin-Pelaez, S. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Weight Loss in Subjects with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon Homaei, S.; Barone, H.; Kleppe, R.; Betari, N.; Reif, A.; Haavik, J. ADHD symptoms in neurometabolic diseases: Underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 838–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Chou, M.C.; Lee, M.J.; Chou, W.J. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, free testosterone, and sex hormone-binding globulin on susceptibility to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 103, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull-Larsen, S.; Mohajeri, M.H. The Potential Influence of the Bacterial Microbiome on the Development and Progression of ADHD. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, K.W.; Vijay, I.K.; Marth, J.D. A recessive deletion in the GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase gene results in peri-implantation embryonic lethality. Glycobiology 1999, 9, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C.; Varki, A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marth, J.D.; Grewal, P.K. Mammalian glycosylation in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, K.; Marth, J.D. Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell 2006, 126, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skropeta, D. The effect of individual N-glycans on enzyme activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivac, N.; Knezević, A.; Gornik, O.; Pucić, M.; Igl, W.; Peeters, H.; Crepel, A.; Steyaert, J.; Novokmet, M.; Redzić, I.; et al. Human plasma glycome in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorders. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2011, 10, M110.004200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tao, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xie, M.; Ma, Q.; Yin, Y.; et al. The interactions between host genome and gut microbiome increase the risk of psychiatric disorders: Mendelian randomization and biological annotation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 113, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cickovski, T.; Mathee, K.; Aguirre, G.; Tatke, G.; Hermida, A.; Narasimhan, G.; Stollstorff, M. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and the gut microbiome: An ecological perspective. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0273890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiergeist, A.; Gessner, J.; Gessner, A. Current Limitations for the Assessment of the Role of the Gut Microbiome for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, E.; Ulgen, K.O. Understanding the ADHD-Gut Axis by Metabolic Network Analysis. Metabolites 2023, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Probiotic Group (n = 51) | Placebo Group (n = 51) | χ or t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | 0.703 a | 0.402 | ||
| Boys | 42 (82.4) | 45 (88.2) | ||
| Girls | 9 (17.6) | 6 (11.8) | ||
| Age, years | 9.1 ± 1.8 | 9.1 ± 1.8 | −0.117 | 0.97 |
| Height, cm | 133.0 ± 12.0 | 133.4 ± 10.1 | −0.151 | 0.88 |
| Body weight, kg | 28.8 ± 7.7 | 29.6 ± 8.0 | −0.494 | 0.622 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 16.0 ± 2.1 | 16.4 ± 2.7 | −0.722 | 0.472 |
| Birth weight, g | 3046.3 ± 483.0 | 3182.2 ± 519.3 | −1.369 | 0.174 |
| ADHD subtype, n (%) | 0.043 a | 0.835 | ||
| Inattentive | 17 (33.3) | 18 (35.3) | ||
| Hyperactive or combined | 34 (66.7) | 33 (64.7) | ||
| Comorbidity, n (%) | ||||
| Oppositional defiant disorder | 4 (7.8) | 2 (3.9) | 0.708 a | 0.678 |
| Tic disorders | 0 (0) | 2 (3.9) | 2.040 a | 0.495 |
| Methylphenidate dose (mg/day) | 22.1 ± 11.7 | 23.4 ± 10.0 | −0.576 | 0.566 |
| MPH formulation, n (%) | 0.050 | 1.000 | ||
| Short-acting MPH | 14 (27.5) | 13 (25.5) | ||
| Long-acting MPH | 37 (72.5) | 38 (74.5) | ||
| Barkley’s Side Effects Rating Scale | ||||
| Total score | 14.8 ± 12.7 | 13.7 ± 9.4 | 0.487 | 0.628 |
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | 3.8 ± 3.5 | 4.0 ± 3.3 | −0.174 | 0.862 |
| SNAP-IV scores | ||||
| Inattention | 14.7 ± 5.6 | 15.3 ± 6.2 | −0.458 | 0.648 |
| Hyperactivity/impulsivity | 12.8 ± 6.1 | 12.7 ± 7.0 | 0.137 | 0.891 |
| ADHD-RS scores | ||||
| Inattention | 11.7 ± 5.4 | 11.5 ± 6.7 | 0.197 | 0.844 |
| Hyperactivity/impulsivity | 13.9 ± 4.9 | 13.3 ± 7.1 | 0.462 | 0.645 |
| CPT | ||||
| Detectability (d’) | 50.1 ± 9.7 | 48.6 ± 10.7 | 0.756 | 0.451 |
| Omissions | 53.0 ± 12.6 | 53.5 ± 12.2 | −0.135 | 0.893 |
| Commissions | 47.2 ± 8.9 | 46.1 ± 8.6 | 0.633 | 0.528 |
| Hit reaction time (RT) | 62.7 ± 10.5 | 61.6 ± 13.2 | 0.481 | 0.632 |
| CATA | ||||
| Detectability (d’) | 51.6 ± 9.4 | 50.3 ± 10.0 | 0.663 | 0.509 |
| Omissions | 49.2 ± 8.6 | 48.7 ± 7.6 | 0.328 | 0.743 |
| Commissions | 52.1 ± 11.6 | 51.8 ± 12.4 | 0.14 | 0.889 |
| Hit reaction time (RT) | 53.7 ± 10.6 | 51.3 ± 9.7 | 1.187 | 0.238 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.-J.; Tsai, C.-S.; Chou, W.-J.; Kuo, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Dai, H.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Li, C.-J.; Yeh, Y.-T. Add-On Bifidobacterium Bifidum Supplement in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A 12-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142260
Wang L-J, Tsai C-S, Chou W-J, Kuo H-C, Huang Y-H, Lee S-Y, Dai H-Y, Yang C-Y, Li C-J, Yeh Y-T. Add-On Bifidobacterium Bifidum Supplement in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A 12-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142260
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liang-Jen, Ching-Shu Tsai, Wen-Jiun Chou, Ho-Chang Kuo, Ying-Hsien Huang, Sheng-Yu Lee, Hong-Ying Dai, Chia-Yu Yang, Chia-Jung Li, and Yao-Tsung Yeh. 2024. "Add-On Bifidobacterium Bifidum Supplement in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A 12-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142260
APA StyleWang, L.-J., Tsai, C.-S., Chou, W.-J., Kuo, H.-C., Huang, Y.-H., Lee, S.-Y., Dai, H.-Y., Yang, C.-Y., Li, C.-J., & Yeh, Y.-T. (2024). Add-On Bifidobacterium Bifidum Supplement in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A 12-Week Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 16(14), 2260. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142260








