Association between Lifestyle Modification and All-Cause, Cardiovascular, and Premature Mortality in Individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Definition of NAFLD
2.3. Definition of Lifestyle Factors
2.4. Follow-Up Time and Outcome
2.5. Assessment of Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Cohort
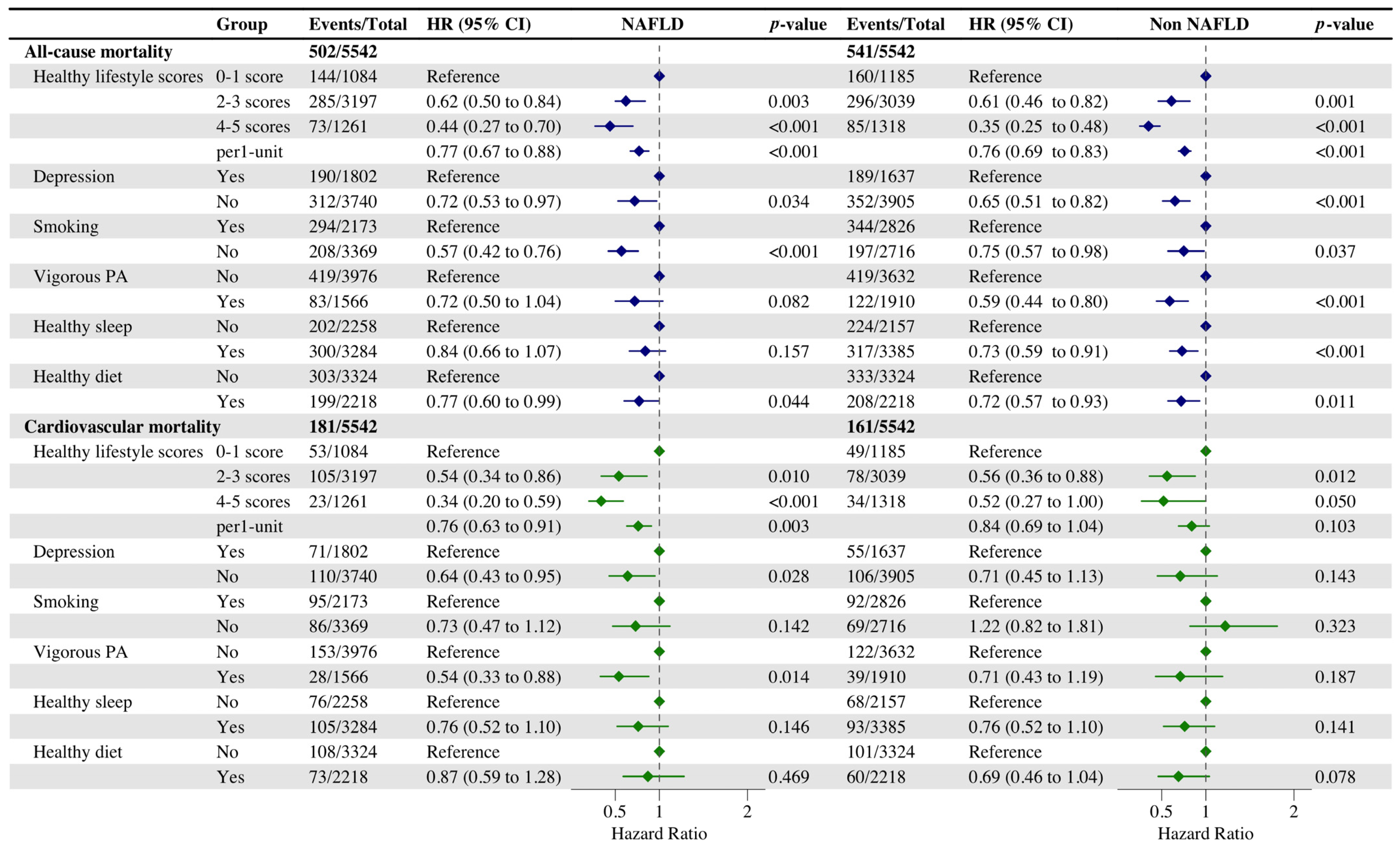
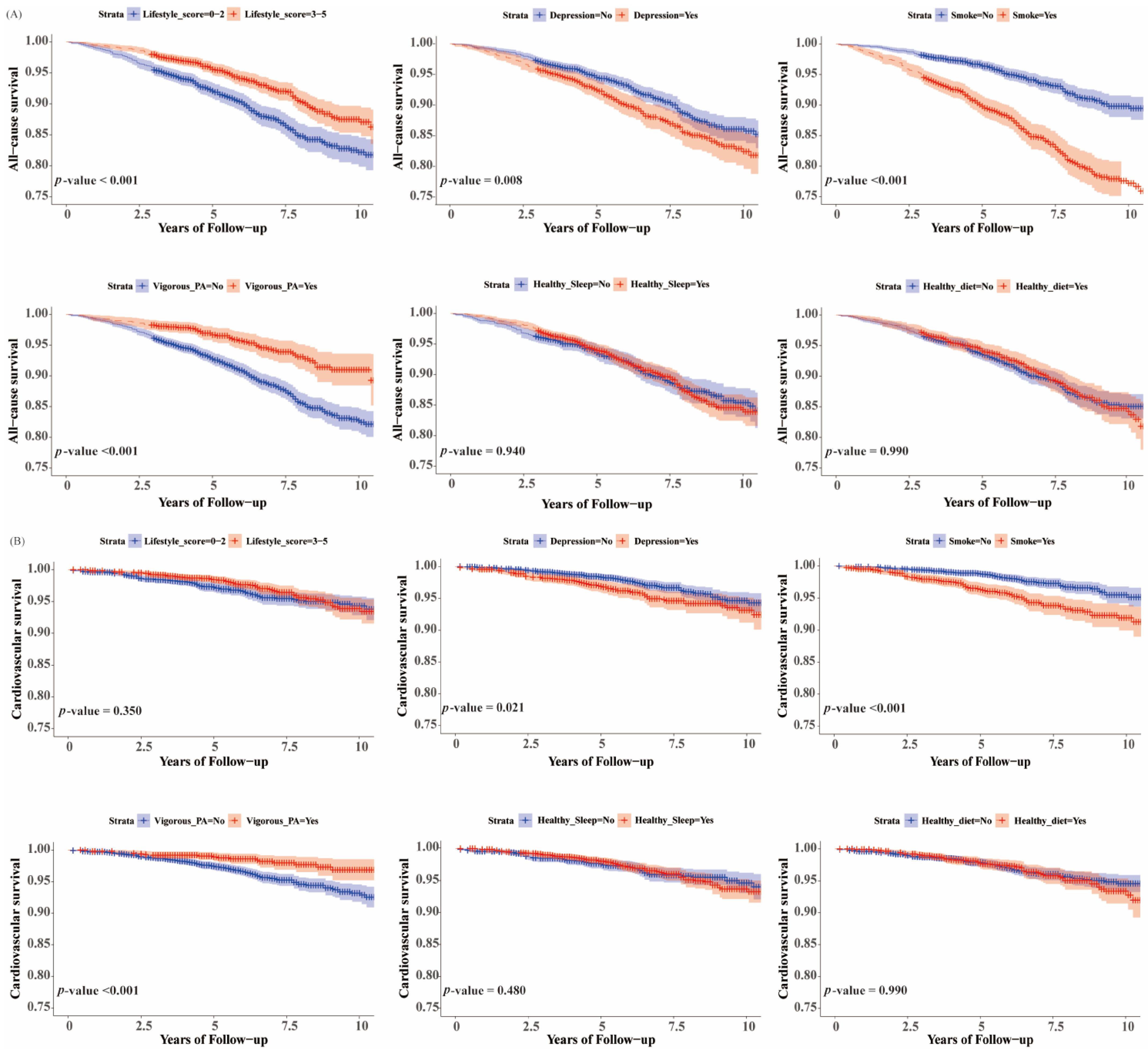
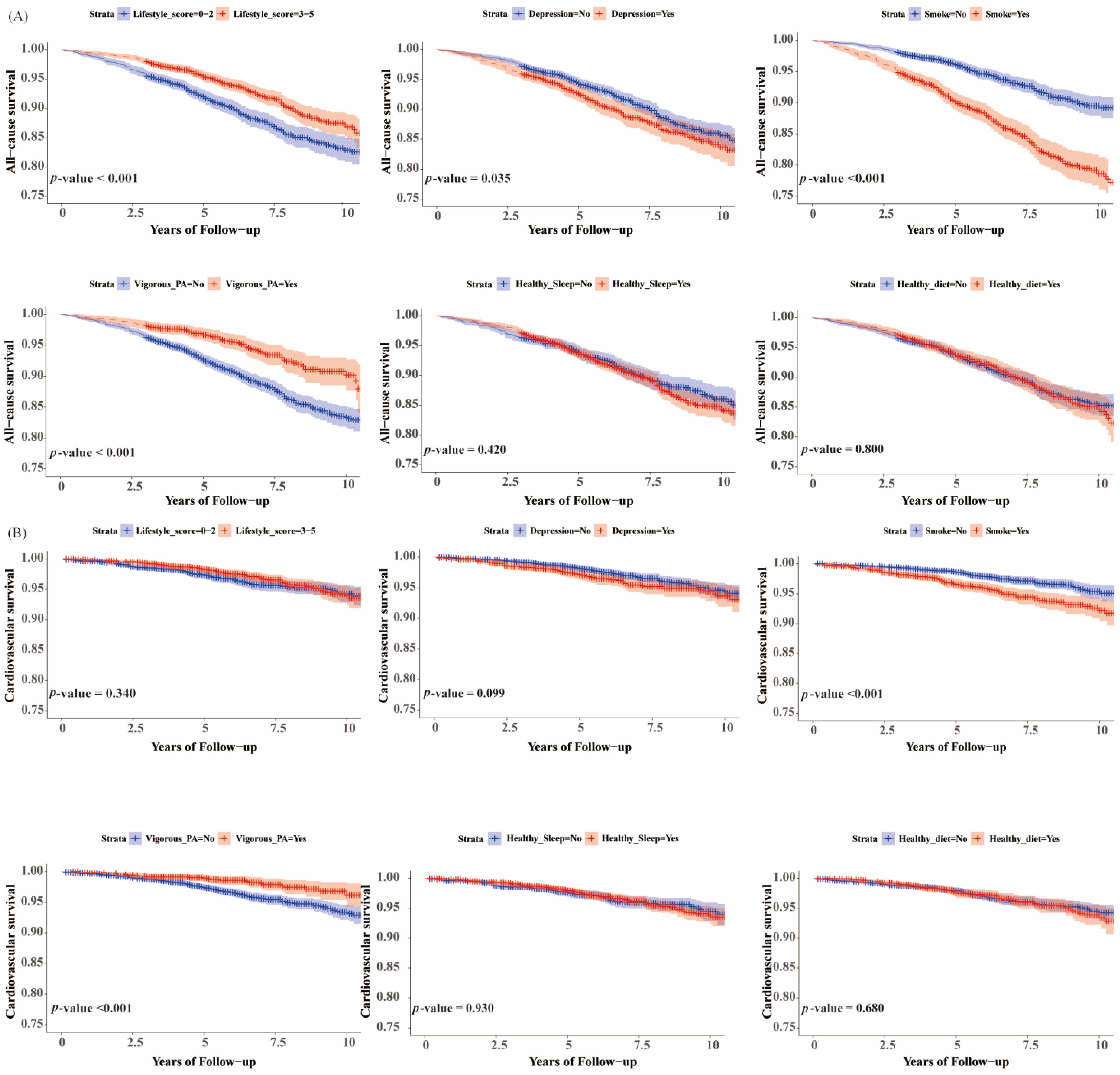
3.2. Associations of Healthy Lifestyle with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Individuals with/without NAFLD
3.3. Associations of Healthy Lifestyle with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Gender and Age Subgroups
3.4. Associations of Healthy Lifestyle with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Participants with NAFLD and Obesity by BMI and WC
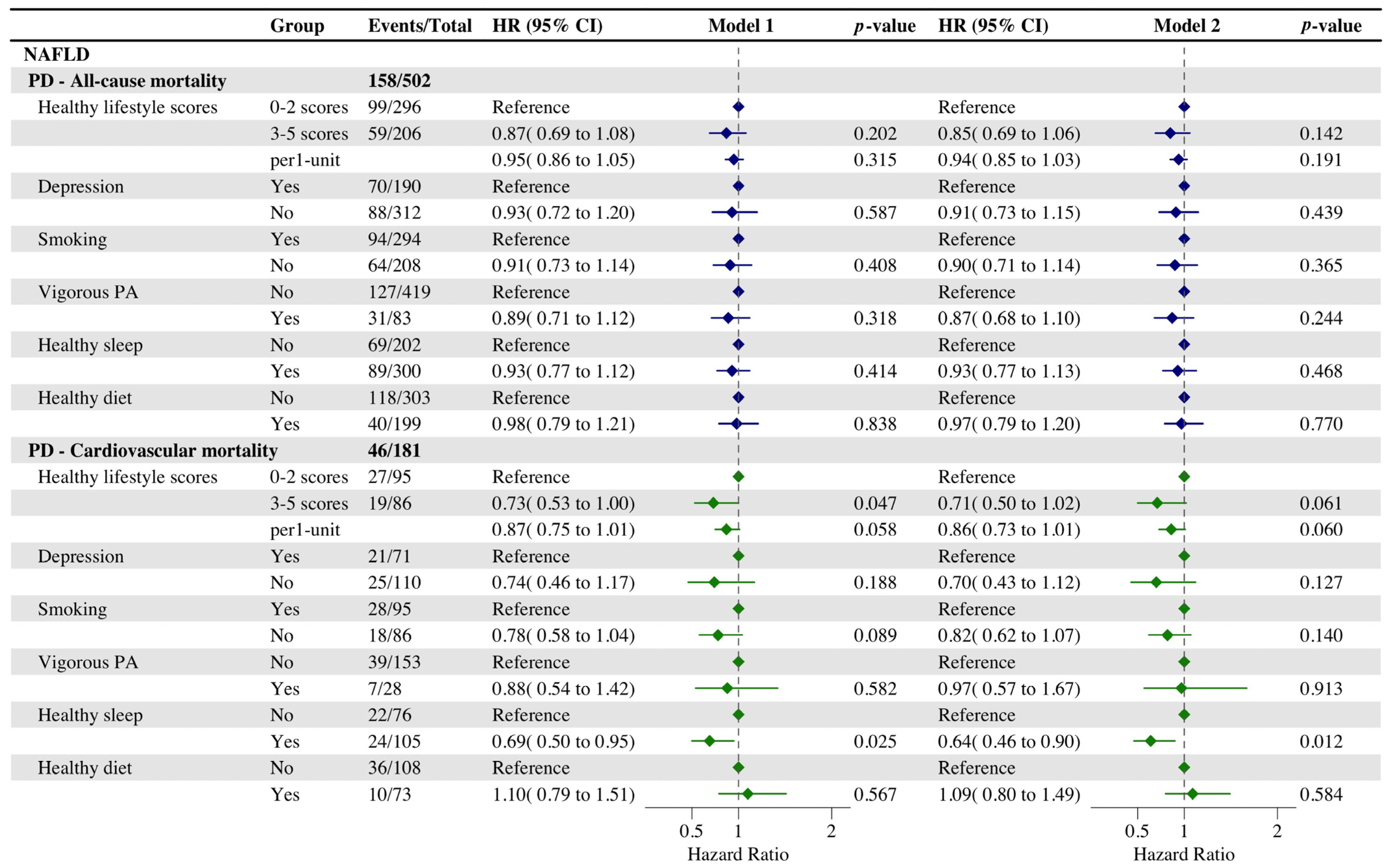
3.5. Correlations of Healthy Lifestyle with Premature Mortality in NAFLD Individual
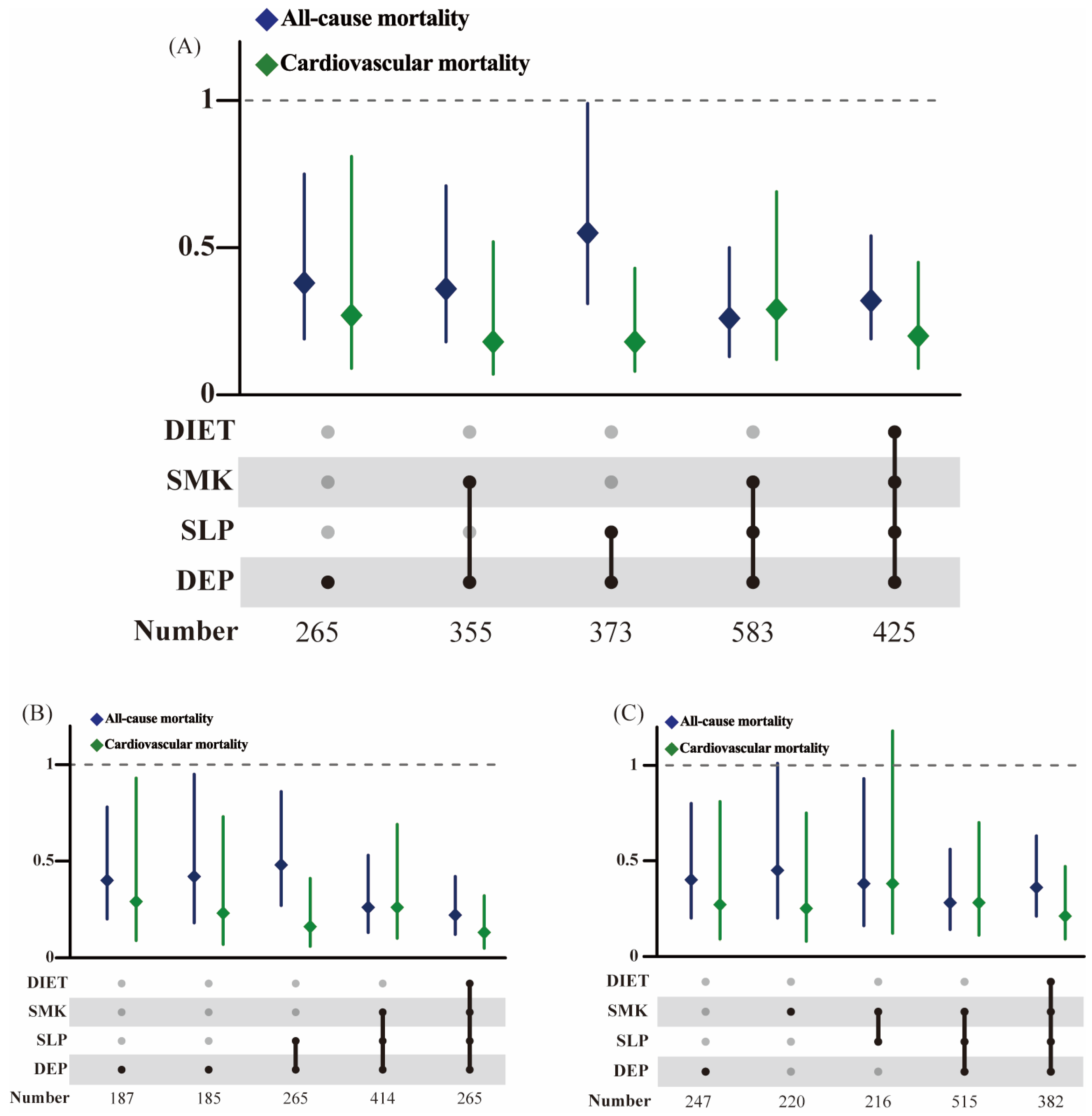
3.6. Associations of Randomized Combinations of Healthy Lifestyle with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
3.7. Sensitivity Analyses Using Subsample by USFLI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, J.G.; Kim, S.U.; Wong, V.W. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Azeem, H.A.; Khalek, E.S.A.; El-Akabawy, H.; Naeim, H.; Khalik, H.A.; Alfifi, A.A. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the incidence of cardiovascular and renal events. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2013, 25, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, R.S.; Shu, S.S.; Cheung, B.H.; Li, L.S.; Chim, A.M.; Chan, C.K.; Leung, J.K.; Chu, W.C.; et al. Beneficial effects of lifestyle intervention in non-obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, M.C.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Thodis, T.; Ward, G.; Trost, N.; Hofferberth, S.; O’Dea, K.; Desmond, P.V.; Johnson, N.A.; Wilson, A.M. The Mediterranean diet improves hepatic steatosis and insulin sensitivity in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, C.; Day, C.P.; Trenell, M.I. Lifestyle interventions for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: A systematic review. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashida, R.; Kawaguchi, T.; Bekki, M.; Omoto, M.; Matsuse, H.; Nago, T.; Takano, Y.; Ueno, T.; Koga, H.; George, J.; et al. Aerobic vs. resistance exercise in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.; Kirk, E.P.; Mittendorfer, B.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S. Randomized trial of exercise effect on intrahepatic triglyceride content and lipid kinetics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezpeleta, M.; Gabel, K.; Cienfuegos, S.; Kalam, F.; Lin, S.; Pavlou, V.; Song, Z.; Haus, J.M.; Koppe, S.; Alexandria, S.J.; et al. Effect of alternate day fasting combined with aerobic exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 56–70.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Gao, J.; Ge, X.; Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Tian, T.; Xu, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, Q.; Ge, Z.; et al. Healthy Lifestyle Is Associated with Reduced Mortality in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.-M.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Whitbourne, S.; Houghton, S.; Hu, F.; Willett, W.; Gaziano, J.M.; Cho, K.; Wilson, P.W.F. PTFS07-07-23 Eight Modifiable Lifestyle Factors Associated With Increased Life Expectancy Among 719,147 U.S. Veterans. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2023, 7, 100200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiley, A.; King, D.; Bidulescu, A. The Association between Sleep Duration and Metabolic Syndrome: The NHANES 2013/2014. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krittanawong, C.; Maitra, N.S.; Qadeer, Y.K.; Wang, Z.; Fogg, S.; Storch, E.A.; Celano, C.M.; Huffman, J.C.; Jha, M.; Charney, D.S.; et al. Association of Depression and Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Med. 2023, 136, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Pan, X.F.; Chen, J.; Cao, A.; Zhang, Y.G.; Xia, L.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, G.; Pan, A. Combined lifestyle factors, incident cancer, and cancer mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Pan, X.F.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Geng, T.T.; Zhou, Y.F.; Liao, L.M.; Tu, Z.Z.; Chen, J.X.; Xia, P.F.; et al. Associations of combined healthy lifestyles with cancer morbidity and mortality among individuals with diabetes: Results from five cohort studies in the USA, the UK and China. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 2044–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Manikat, R.; Cholankeril, G.; Ahmed, A. Endogenous sex hormones and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in US adults. Liver Int. 2023, 44, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Ekstedt, M.; Hammar, U.; Stål, P.; Hultcrantz, R.; Kechagias, S. Risk for development of severe liver disease in lean patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A long-term follow-up study. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Du, Y.; Wu, Y.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Wallace, R.B.; Bao, W. Trends in obesity and adiposity measures by race or ethnicity among adults in the United States 2011-18: Population based study. BMJ 2021, 372, n365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Chen, C.; Pan, X.F.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Franco, O.H.; Liu, G.; Pan, A. Associations of healthy lifestyle and socioeconomic status with mortality and incident cardiovascular disease: Two prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2021, 373, n604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, J.; Xu, H.; Yu, C.; Wang, S. Higher HEI-2015 Score Is Associated with Reduced Risk of Depression: Result from NHANES 2005–2016. Nutrients 2021, 13, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunnan, L.; Shaomei, S.; Wannian, L. The association between sleep and depressive symptoms in US adults: Data from the NHANES (2007–2014). Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2022, 31, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldosari, M.; Helmi, M.; Kennedy, E.N.; Badamia, R.; Odani, S.; Agaku, I.; Vardavas, C. Depression, periodontitis, caries and missing teeth in the USA, NHANES 2009–2014. Fam. Med. Community Health 2020, 8, e000583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norheim, O.F.; Jha, P.; Admasu, K.; Godal, T.; Hum, R.J.; Kruk, M.E.; Gómez-Dantés, O.; Mathers, C.D.; Pan, H.; Sepúlveda, J.; et al. Avoiding 40% of the premature deaths in each country, 2010–2030: Review of national mortality trends to help quantify the UN sustainable development goal for health. Lancet 2015, 385, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y. Attributable risk function in the proportional hazards model for censored time-to-event. Biostatistics 2006, 7, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Yu, D.; Fan, J.; Yu, C.; Guo, Y.; Pei, P.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Du, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Healthy lifestyle and life expectancy at age 30 years in the Chinese population: An observational study. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e994–e1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, S.; Pang, Y. Associations between Healthy Lifestyle and All-Cause Mortality in Individuals with Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Doherty, M.G.; Cairns, K.; O’Neill, V.; Lamrock, F.; Jørgensen, T.; Brenner, H.; Schöttker, B.; Wilsgaard, T.; Siganos, G.; Kuulasmaa, K.; et al. Effect of major lifestyle risk factors, independent and jointly, on life expectancy with and without cardiovascular disease: Results from the Consortium on Health and Ageing Network of Cohorts in Europe and the United States (CHANCES). Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, R.; Yu, C.; Liu, N.; He, M.; Lv, J.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Association of Depression With All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Among Adults in China. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1921043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.H.; Duncan, M.J.; Cistulli, P.A.; Nassar, N.; Hamer, M.; Stamatakis, E. Sleep and physical activity in relation to all-cause, cardiovascular disease and cancer mortality risk. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Jin, X.; Shan, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Li, P.; Peng, X.; Peng, Z.; Yu, K.; Bao, W.; et al. Relationship of Sleep Duration With All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.C.; Loong, T.C.; Wei, J.L.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, A.W.; Choi, P.C.; Shu, S.S.; Chim, A.M.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W. Histological severity and clinical outcomes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonobese patients. Hepatology 2017, 65, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, D.; Yim, J.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Han, K.H.; Kim, S.M.; Hwang, K.R.; Ku, S.Y.; Suh, C.S.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome with hyperandrogenism as a risk factor for non-obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pan, A.; Wang, D.D.; Liu, X.; Dhana, K.; Franco, O.H.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Stampfer, M.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Impact of Healthy Lifestyle Factors on Life Expectancies in the US Population. Circulation 2018, 138, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan Rezayat, A.; Dadgar Moghadam, M.; Ghasemi Nour, M.; Shirazinia, M.; Ghodsi, H.; Rouhbakhsh Zahmatkesh, M.R.; Tavakolizadeh Noghabi, M.; Hoseini, B.; Akhavan Rezayat, K. Association between smoking and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. SAGE Open Med. 2018, 6, 2050312117745223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureddin, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wilkens, L.R.; Porcel, J.; Boushey, C.J.; Le Marchand, L.; Rosen, H.R.; Setiawan, V.W. Diet Associations With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in an Ethnically Diverse Population: The Multiethnic Cohort. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.H.; Ng, K.Y.; Chin, W.K. The impact of sleep amount and sleep quality on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2017, 31, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D. Sleep duration and depression among adults: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Depress. Anxiety 2015, 32, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.L.; Cathomas, F.; Russo, S.J. Central and Peripheral Inflammation Link Metabolic Syndrome and Major Depressive Disorder. Physiology 2019, 34, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labenz, C.; Huber, Y.; Michel, M.; Nagel, M.; Galle, P.R.; Kostev, K.; Schattenberg, J.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Increases the Risk of Anxiety and Depression. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Meyer, J.H.; Austin, M.C.; Albert, P.R.; Wang, J.; May, W.L.; Rajkowska, G.; Overholser, J.C.; Jurjus, G.; et al. The reduction of R1, a novel repressor protein for monoamine oxidase A, in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 2139–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, N.A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Binks, M.; Guy, C.D.; Omenetti, A.; Smith, A.D.; Diehl, A.M.; Suzuki, A. Associations of depression, anxiety and antidepressants with histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Non-NAFLD Population (N = 5542) | NAFLD Population (N = 5542) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic information | |||
| Age, years, mean (SE) | 53.5 (0.2) | 53.4 (0.2) | 0.904 |
| Gender, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 2915 (52.6) | 2572 (46.4) | |
| Female | 2627 (47.4) | 2970 (53.6) | |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Mexican American | 770 (13.9) | 902 (16.3) | |
| Other Hispanic | 540 (9.7) | 595 (10.7) | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 2578 (46.5) | 2343 (42.3) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 1019 (18.4) | 1227 (22.1) | |
| Other race, including multiracial | 635 (11.5) | 475 (8.6) | |
| Marital status, n (%) | 0.010 | ||
| Married/Living with partner | 3377 (60.9) | 3509 (63.3) | |
| Widowed/Divorced/Separated | 2165 (39.1) | 2033 (36.7) | |
| Educational level, n (%) | 0.085 | ||
| Less than high school | 1269 (22.9) | 1346 (24.3) | |
| High school or higher | 4273 (77.1) | 4196 (75.7) | |
| Poverty–income ratio, mean (SE) | 2.5 (0.02) | 2.5 (0.02) | 0.469 |
| Physical examination and laboratory analysis | |||
| Body mass index, kg/m², mean (SE) | 26.8 (0.1) | 33.0 (0.1) | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference, cm, mean (SE) | 95.0 (0.2) | 108.8 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| ALT, IU/L, mean (SE) | 23.5 (0.2) | 27.5 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| AST, IU/L, mean (SE) | 25.9 (0.2) | 25.3 (0.1) | 0.034 |
| Lifestyle and diseases | |||
| No depression, n (%) | 3905 (74.5) | 3740 (67.5) | <0.001 |
| No smoking, n (%) | 2716 (49.0) | 3369 (60.8) | <0.001 |
| Vigorous PA, n (%) | 1910 (34.5) | 1566 (28.3) | <0.001 |
| Healthy sleep, n (%) | 3385 (61.1) | 3284 (59.3) | 0.050 |
| HEI–2015 score, mean (SE) | 52.5 (0.2) | 50.8 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol assumption, gram, mean (SE) | 34.6 (0.5) | 9.0 (0.1) | <0.001 |
| CVD, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| No | 4950 (89.3) | 4803 (86.7) | |
| Yes | 592 (10.7) | 739 (13.3) | |
| Cancer, n (%) | 0.436 | ||
| No | 46,902 (88.5) | 4928 (88.9) | |
| Yes | 640 (11.6) | 614 (11.1) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Wan, T.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Association between Lifestyle Modification and All-Cause, Cardiovascular, and Premature Mortality in Individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132063
Huang Y, Xu J, Yang Y, Wan T, Wang H, Li X. Association between Lifestyle Modification and All-Cause, Cardiovascular, and Premature Mortality in Individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients. 2024; 16(13):2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132063
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yanqiu, Jinfan Xu, Yang Yang, Tingya Wan, Hui Wang, and Xiaoguang Li. 2024. "Association between Lifestyle Modification and All-Cause, Cardiovascular, and Premature Mortality in Individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease" Nutrients 16, no. 13: 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132063
APA StyleHuang, Y., Xu, J., Yang, Y., Wan, T., Wang, H., & Li, X. (2024). Association between Lifestyle Modification and All-Cause, Cardiovascular, and Premature Mortality in Individuals with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients, 16(13), 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132063








