Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides Ameliorate Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis along the Nrf2 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
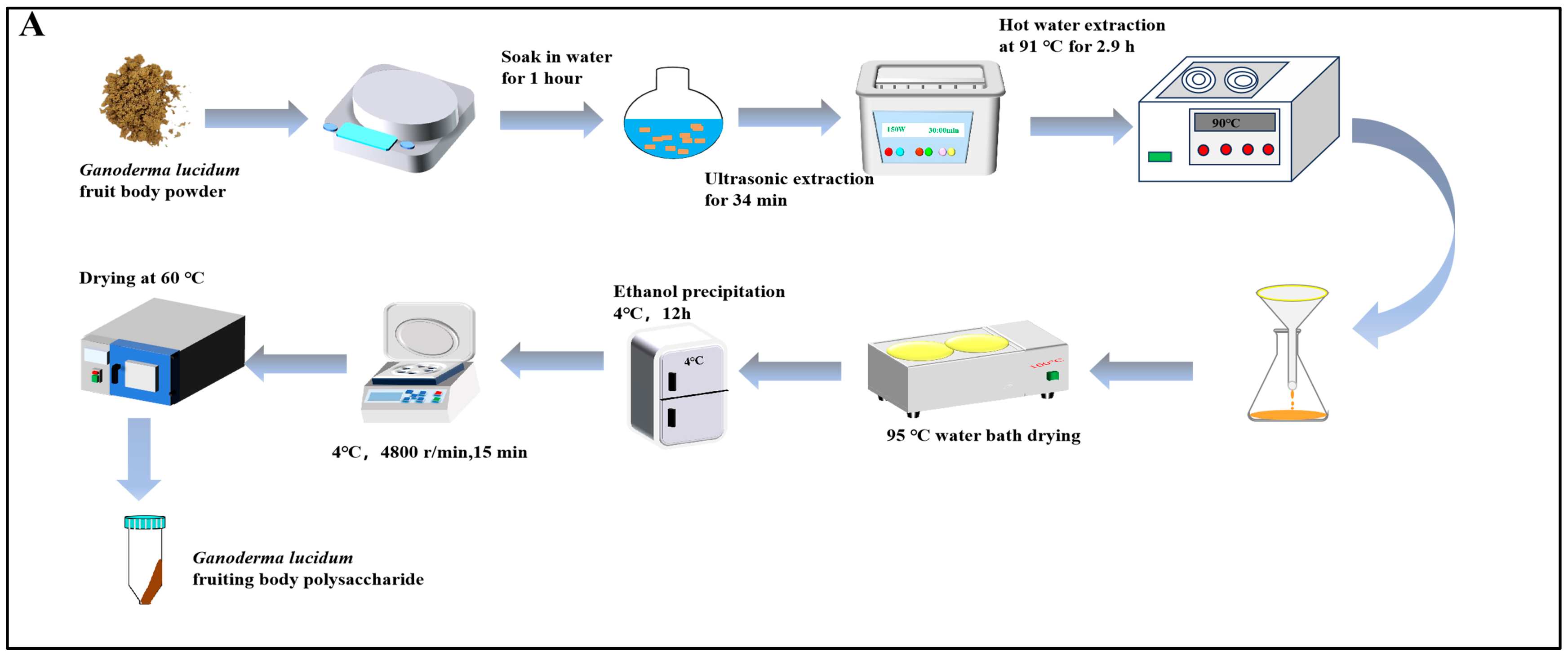
2.2. Preparation of GLPs
2.3. Determination of Polysaccharide Content
2.4. Absolute Molecular Weight Determination
2.5. Monosaccharide Composition Determination
2.6. Animal Experiments
2.6.1. Animals
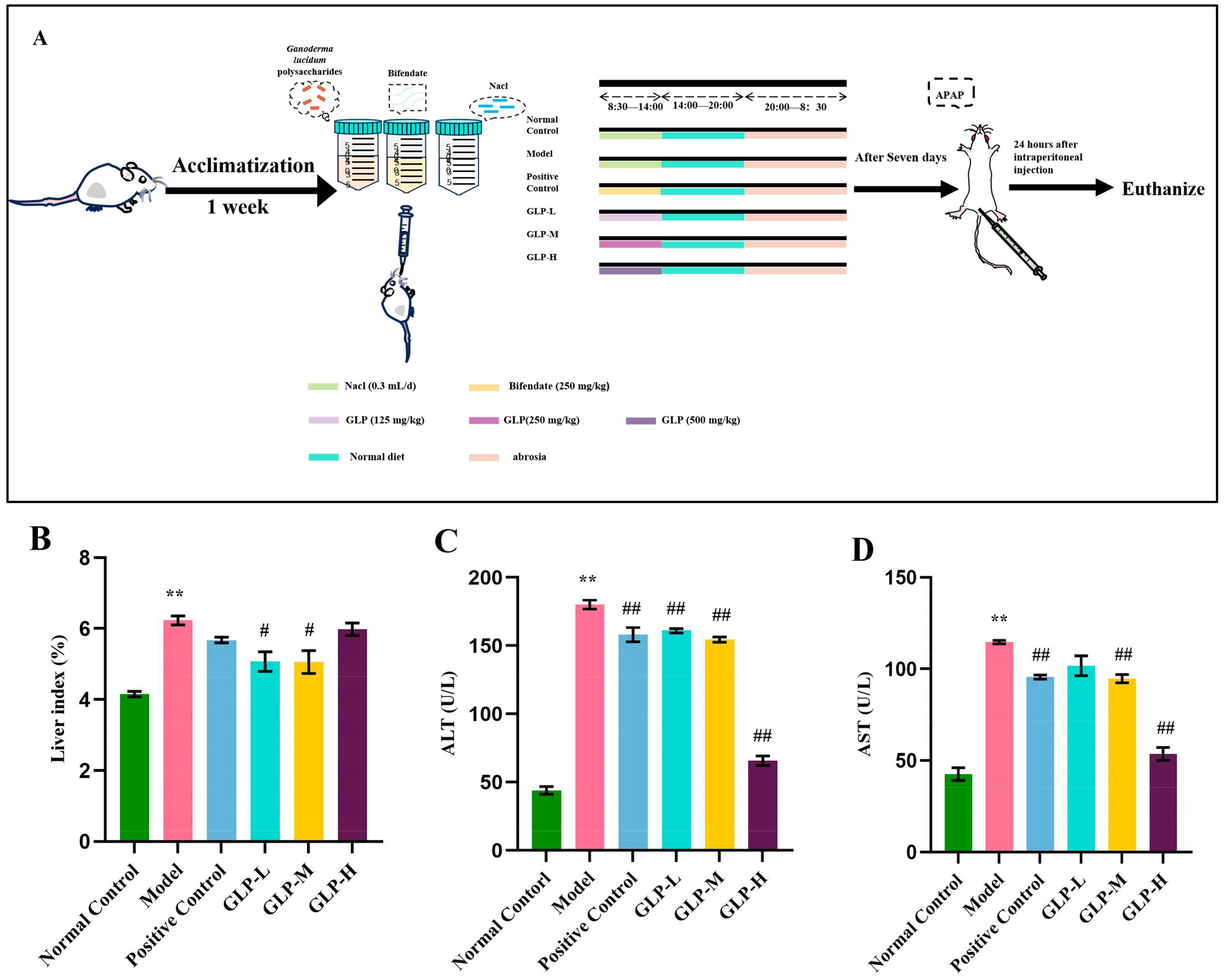
2.6.2. Experimental Design
2.6.3. Liver Histological Analysis
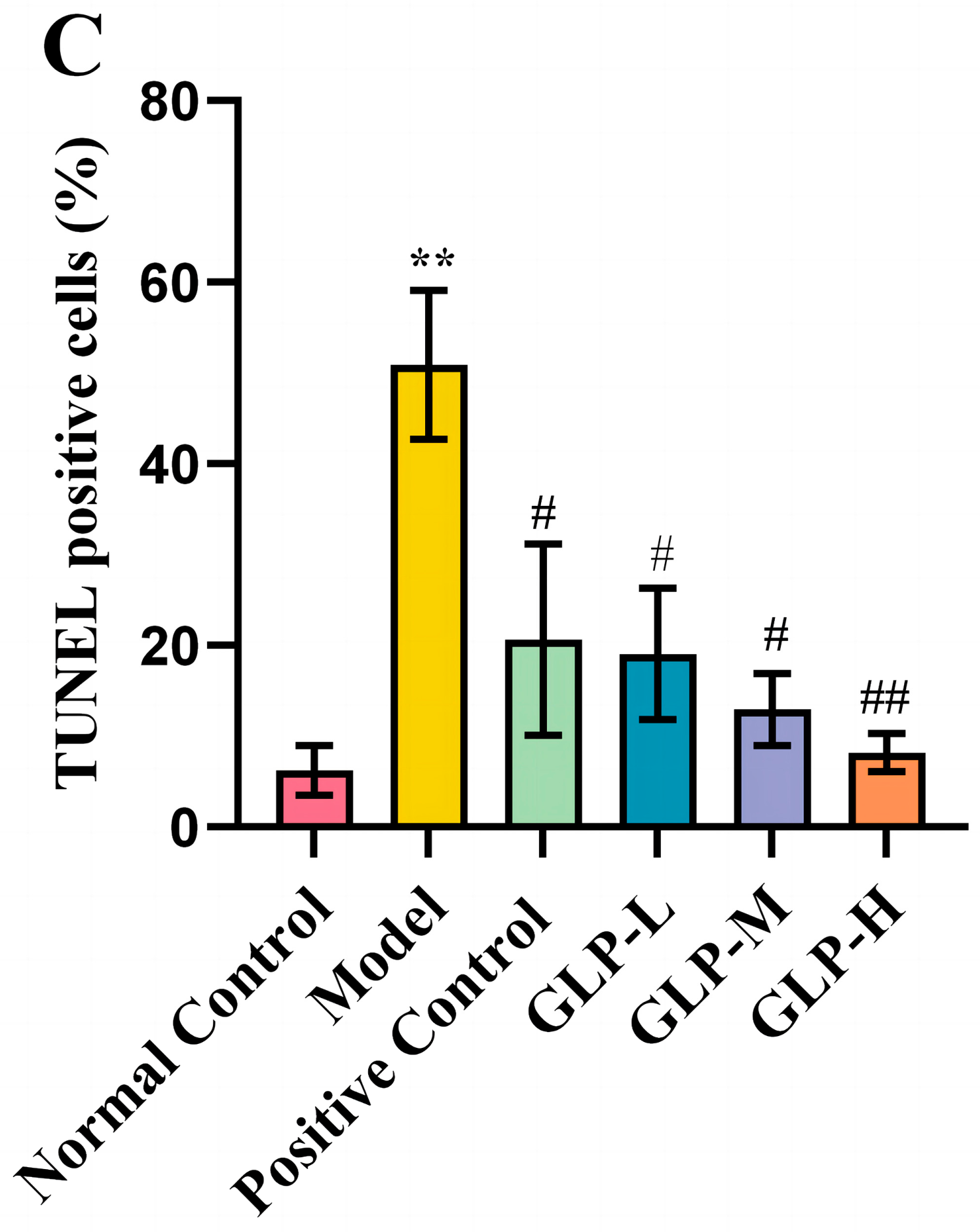
2.6.4. TUNEL Cell Apoptosis Detection
2.6.5. Serum and Liver Biochemical Assays
2.6.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.6.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.6.8. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties
3.2. Effects of GLPs on Liver Index and Serum Transaminase Levels
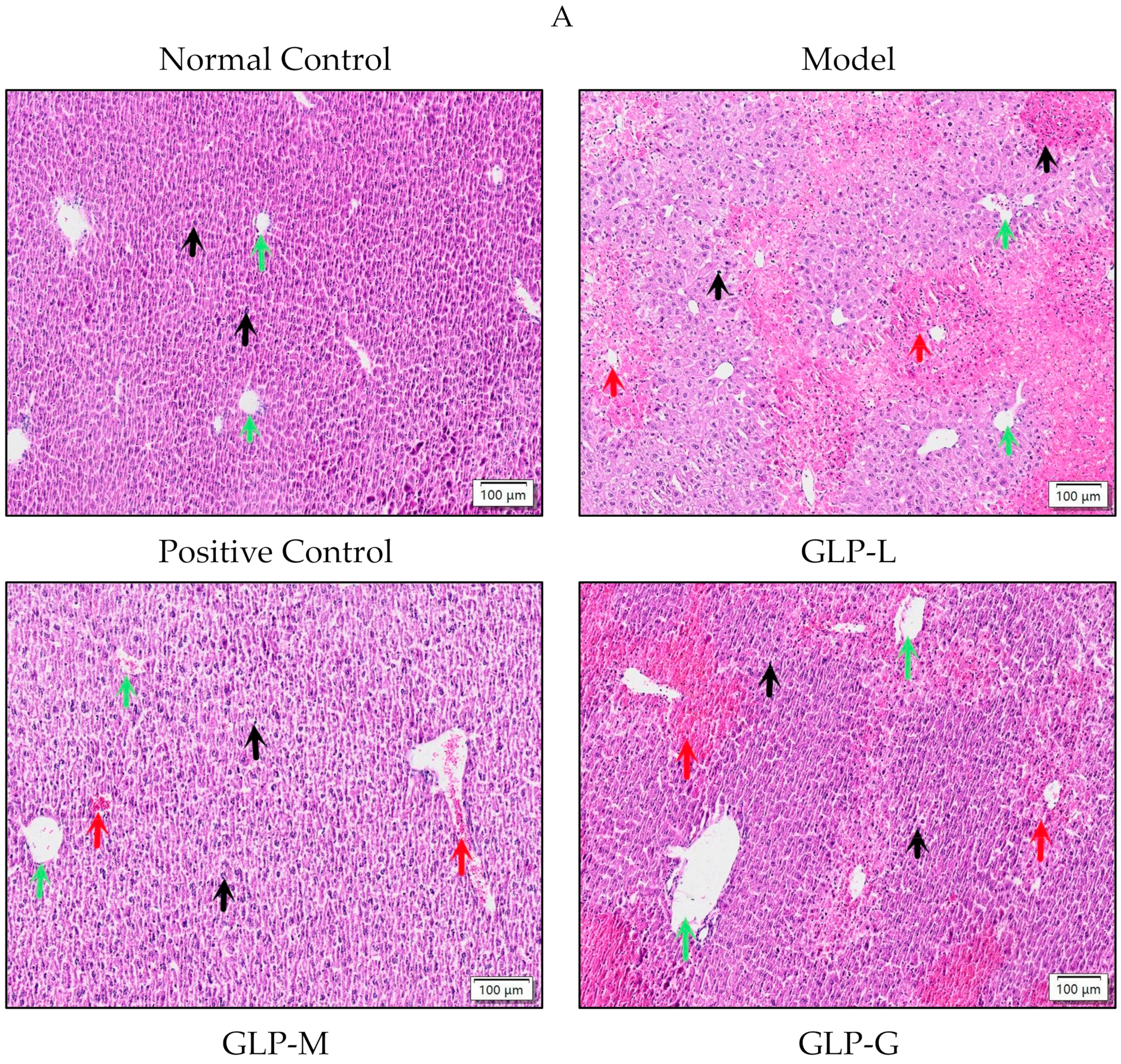
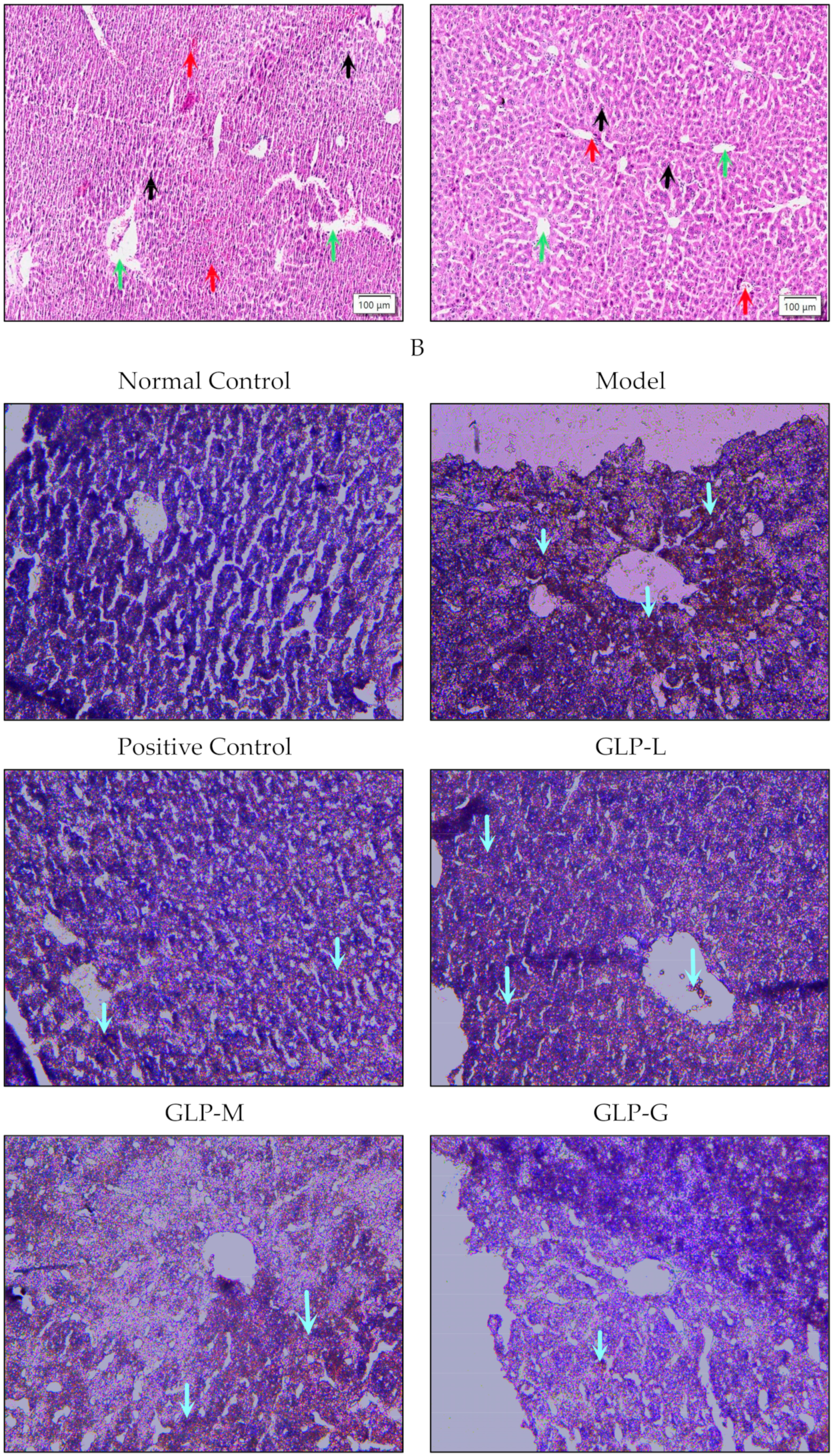
3.3. Effects of GLPs on Liver Histopathological Changes and Apoptosis
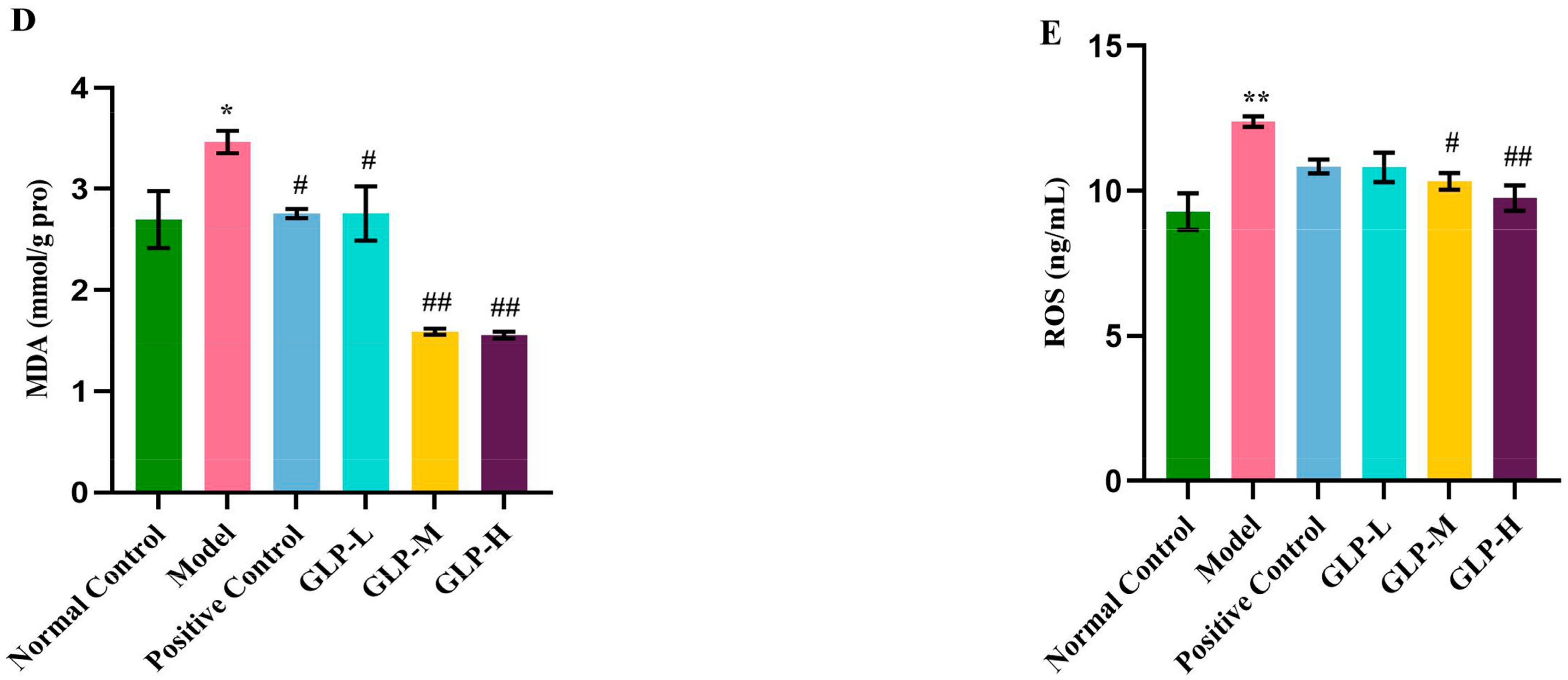
3.4. Effects of GLPs on Oxidative Stress Induced by APAP
3.5. Effect of GLPs on mRNA and Protein Expression Related to Nrf2 Pathway in Liver
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, G.B.; Miryam, M.; Luke, B.; David, F.V.; Rachel, A.R.; Elena, L.G.; Wei, Y.L.; Thomas, J.; Olivier, J.; Andrew, D.C.; et al. TGFβ inhibition restores a regenerative response in acute liver injury by suppressing paracrinesenescence. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan1230. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.Z.; Ma, H.L.; Jin, P.; Shen, X.; Zhen, X.H.; Yu, C.H.; Zhang, P.M.; Ji, F.; Wang, J.W. USP25 regulates KEAP1-NRF2 anti-oxidation axis and its inactivation protects acetaminophen-induced liver injury in male mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Tang, J.T.; Mao, Y.M. Incidence and risk factors of drug-induced liver injury. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2022, 42, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, X.J.; Wang, H.; Jaeschke, H.; Ding, W.X. Role and mechanisms of autophagy in acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2018, 38, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Lu, Z.; Jia, H.Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.S.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific Mas activation enhances lipophagy and fatty acid oxidation to protect against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björnsson, H.K.; Björnsson, E.S. Drug-induced liver injury: Pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, and practical management. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 97, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akakpo, J.Y.; Ramachandran, A.; Curry, S.C.; Rumack, B.H.; Jaeschke, H. Comparing N-acetylcysteine and 4-methylpyrazole as antidotes for acetaminophen overdose. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebeca, G.R.; Rubén, F. Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Damage in Hepatic Steatosis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 107, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanya, S.B.; Venkataraman, B.; Meeran, M.F.N.; Goyal, S.N.; Patil, C.R.; Ojha, S. Therapeutic Potential of Plants and Plant Derived Phytochemicals against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.C.; Lin, J.C.; Zhen, C.; Wang, F.; Sun, X.H.; Kong, X.N.; Gao, Y.Q. Amygdalin protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure by reducing inflammatory response and inhibiting hepatocyte death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 602, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossetta, G.; Marzioni, D. Targeting the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway in cervical and endometrial cancers. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 941, 175503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.H.; He, R.J.; Sun, P.L.; Zhang, F.M.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zhang, A.Q. Molecular mechanisms of bioactive polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi), a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruque, A.M. Ganoderma lucidum: Persuasive biologically active constituents and their health endorsement. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 507–519. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, D.J.; Yang, M.Y.; Li, Y.R.; Chen, W.J.; Hung, C.; Wang, C.J. Ganoderma lucidum repress injury of ethanol-induced steatohepatitis via anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation and reducing hepatic lipid in C57BL/6J mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chen, Q.Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Hua, C. Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Effects of Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury in Kunming Mice. Pharmacology 2019, 103, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Ni, W.; Teng, H.L.; Lin, Z.B. Hepatoprotective role of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide against BCG-induced immune liver injury in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Han, Z.M.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, N.; Yan, M.X. Protect Effects of Ganoderma lucidum Spore Polysaccharide on Liver Injury Caused by Acetaminophen. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2024, 45, 289–295, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.Y.; Wang, H.R.; Zhang, Y.N.; Gu, J.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Gong, X.H.; Hao, Z.H. Comprehensive Effect of Carbon Tetrachloride and Reversal of Gandankang Formula in Mice Liver: Involved in Oxidative Stress, Excessive Inflammation, and Intestinal Microflora. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.L.; Lu, Z.M.; Mao, X.; Chen, L.; Gong, J.S.; Ren, Y.; Geng, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, H.Y.; Xu, G.H.; et al. Structural characterization and anti-alcoholic liver injury activity of a polysaccharide from Coriolus versicolor mycelia. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Huang, Q.; Ling, C. Water-soluble yeast β-glucan fractions with different molecular weights: Extraction and separation by acidolysis assisted-size exclusion chromatography and their association with proliferative activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 123, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.; Fu, X. Physicochemical, functional, and biological properties of water-soluble polysaccharides from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gu, F.F.; Cai, C.; Hu, M.H.; Fan, L.D.; Hao, J.J.; Yu, G.L. Purification, structural characterization, and immunomodulatory activity of the polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Yu, M.; Hu, Y.; Ren, G.M.; Zang, T.T.; Xu, X.H.; Qu, J.J. Three kinds of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides attenuate DDC-induced chronic pancreatitis in mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 247, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.P.; Wu, Y.; Xu, M.G.; Kulyar, M.F.; Iqbale, M.; Wu, J.Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Jiang, B.T.; Hu, M.M.; et al. Protective effects of Emblica officinalis polysaccharide against lead induced liver injury in mice model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, M.R.; Jaeschke, H. Animal models of drug-induced liver injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1865, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.P.; Hua, S.Y.; Deng, J.W.; Du, Z.; Zhang, D.X.; Liu, Z.F.; Khan, N.U.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Z. Astaxanthin Activated the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway to Enhance Autophagy and Inhibit Ferroptosis, Ameliorating Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 42887–42903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, B.J.; Sang, R.; Wang, W.; Yan, K.X.; Yu, Y.F.; Lin, K.; Yu, M.H.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, X.M. Protection of taraxasterol against acetaminophen-induced liver injury elucidated through network pharmacology and in vitro and in vivo experiments. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.L.; Sun, J.Y.; Li, D.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Yu, X.W.; Hua, H.; Jing, X.; Chen, F.; Jia, Z.J.; Xu, J. Shikonin attenuates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Wang, Y.H.; Xie, S.W.; Lai, Y.Q.; Chan, M.; Zeng, T.; Kuang, S.S.; Deng, G.H.; Zhou, C.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; et al. Hepatic TGFβr1 Deficiency Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide/D-Galactosamine-Induced Acute Liver Failure Through Inhibiting GSK3β-Nrf2-Mediated Hepatocyte Apoptosis and Ferroptosis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 13, 1649–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatriz, L.P.; Lisa, R.; Paredes, S.D.; Schlumpf, M.; Lichtensteiger, W.; Vara, E.; Tresguerres, J.A.F. Low Dose of BPA Induces Liver Injury through Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis in Long-Evans Lactating Rats and Its Perinatal Effect on Female PND6 Offspring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.L.; Zheng, L.W.; Li, Z.; Jin, M.Y.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, J.Q.; Li, J.X.; Feng, H.H. Phellinus linteus polysaccharides mediates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via activating AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathways. Aging 2022, 14, 6993–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Qi, S.S.; Alberto, C.P.D.; Yan, J.K.; Zhang, X.Y. Hepatoprotective effect of Phellinus linteus mycelia polysaccharide (PL-N1) against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mouse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 154, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lu, J.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Guan, S. Sodium sulfite triggered hepatic apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis by inducing mitochondrial damage in mice and AML-12 cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 467, 133719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagappan, A.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, D.Y.; Jung, M.H. Cryptotanshinone from the Bunge Attenuates Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury by Activation of AMPK/SIRT1 and Nrf2 Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.H.; Klaassen, C.D. Nrf2 protects against furosemide-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 2014, 324, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuvel, D.J.; Nguyen, N.T.; Jaeschke, H.; Lemasters, J.J.; Wang, X.J.; Choo, Y.M.; Hamann, M.T.; Zhong, Z. Platanosides, a Potential Botanical Drug Combination, Decrease Liver Injury Caused by Acetaminophen Overdose in Mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Weng, Q.Q.; Gong, S.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, J.Q.; Huang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.J.; Guo, J.; Lan, T. Kaempferol prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury by suppressing hepatocyte ferroptosis Nrf2 pathway activation. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.M.; Wei, Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Huang, J.R.; Lan, T.; Dai, X.Y.; Xu, S.W.; Jin, Z.G.; Wu, X.Q. Urolithin A protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via sustained activation of Nrf2. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 2146–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.J.; Zhou, S.Z.; Wang, Y.; Di, S.T.; Wang, Y.L.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y. Leonurine alleviates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Antibody Name | Dilution Ratio | Item Number |
|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | 1:1000 | A21176 |
| HO-1 | 1:10,000 | A19062 |
| GCLC | 1:3000 | A1038 |
| NQO1 | 1:1000 | A1518 |
| β-actin | 1:50,000 | AC026 |
| IgG(H + L) | 1:5000 | A0208 |
| Target Gene | Primer | Sequence(5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | Forward | CGAGATATACGCAGGAGAGGTAAGA |
| Reverse | GCTCGACAATGTTCTCCAGCTT | |
| HO-1 | Forward | TGCAGGTGATGCTGACAGAGG |
| Reverse | GGGATGAGCTAGTGCTGATCTGG | |
| GCLC | Forward | CAGTCAAGGACCGGCACAAG |
| Reverse | CAAGAACATCGCCTCCATTCAG | |
| NQO1 | Forward | CAGCCAATCAGCGTTCGGTA |
| Reverse | CTTCATGGCGTAGTTGAATGATGTC | |
| β-actin | Forward | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG |
| Reverse | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Han, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, M. Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides Ameliorate Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis along the Nrf2 Pathway. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121859
Zhang N, Han Z, Zhang R, Liu L, Gao Y, Li J, Yan M. Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides Ameliorate Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis along the Nrf2 Pathway. Nutrients. 2024; 16(12):1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121859
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Nan, Zhongming Han, Rui Zhang, Linling Liu, Yanliang Gao, Jintao Li, and Meixia Yan. 2024. "Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides Ameliorate Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis along the Nrf2 Pathway" Nutrients 16, no. 12: 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121859
APA StyleZhang, N., Han, Z., Zhang, R., Liu, L., Gao, Y., Li, J., & Yan, M. (2024). Ganoderma lucidum Polysaccharides Ameliorate Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis along the Nrf2 Pathway. Nutrients, 16(12), 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121859






