Mediterranean Diet Combined with Regular Aerobic Exercise and Hemp Protein Supplementation Modulates Plasma Circulating Amino Acids and Improves the Health Status of Overweight Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Participants, and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Dietary Intervention
2.3. Physical Activity Intervention
2.4. Clinical Measurement
2.5. Biochemical Measurements and Mineral and Amino Acid Content
2.6. Data Preprocessing and Exploratory and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric Data
3.2. Biochemical Parameters
3.3. Mineral Content
3.4. Plasma Circulating Amino Acids
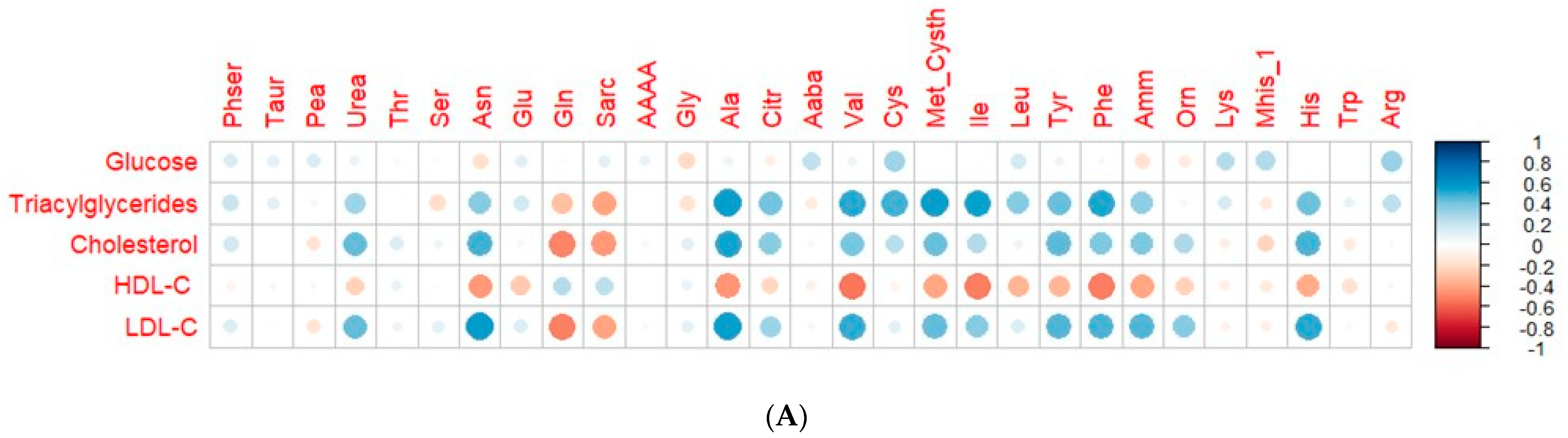
3.5. Correlation of Plasma Circulating Amino Acids and Biochemical and Mineral Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chan, R.S.M.; Woo, J. Prevention of Overweight and Obesity: How Effective Is the Current Public Health Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why Does Obesity Cause Diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; ISBN 9782930229980. [Google Scholar]
- Mata-Cases, M.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, B.; Mauricio, D.; Real, J.; Vlacho, B.; Franch-Nadal, J.; Oliva, J. The Association between Poor Glycemic Control and Health Care Costs in People with Diabetes: A Population-Based Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreo-Lopez, M.C.; Contreras-Bolivar, V.; Muñoz-Torres, M.; García-Fontana, B.; García-Fontana, C. Influence of the Mediterranean Diet on Healthy Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luc, K.; Schramm-Luc, A.; Guzik, T.J.; Mikolajczyk, T.P. Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers in Prediabetes and Diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, I.L.; Van Gaal, L.F. Overweight, Obesity, and Blood Pressure: The Effects of Modest Weight Reduction. Obes. Res. 2000, 8, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, R.; Watanabe, D.; Ito, K.; Ueda, K.; Nakayama, K.; Sanbongi, C.; Miyachi, M. Dose-Response Relationship between Protein Intake and Muscle Mass Increase: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 79, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudry, K.M.; Devries, M.C. Nutritional Strategies to Combat Type 2 Diabetes in Aging Adults: The Importance of Protein. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 465683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Lu, J.; Yoong, S.Q.; Tan, Y.Q.; Kusuyama, J.; Wu, X.V. Effect of Aerobic and Resistant Exercise Intervention on Inflammaging of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2022, 23, 823–830.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mhanna, S.B.; Rocha-Rodriguesc, S.; Mohamed, M.; Batrakoulis, A.; Aldhahi, M.I.; Afolabi, H.A.; Yagin, F.H.; Alhussain, M.H.; Gülü, M.; Abubakar, B.D.; et al. Effects of combined aerobic exercise and diet on cardiometabolic health in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Sport. Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 15, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mthembu, S.X.H.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Ziqubu, K.; Nyawo, T.A.; Obonye, N.; Nyambuya, T.M.; Nkambule, B.B.; Silvestri, S.; Tiano, L.; Muller, C.J.F.; et al. Impact of Physical Exercise and Caloric Restriction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Skeletal Muscle Insulin Resistance and Mitochondrial Dysfunction as Ideal Therapeutic Targets. Life Sci. 2022, 297, 120467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Pino, F.; Millan-Linares, M.C.; Montserrat-De la Paz, S. Hemp Protein. In Sustainable Food Science: A Comprehensive Approach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; ISBN 978-0-08-100596-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mollard, R.C.; Johnston, A.; Leon, A.S.; Wang, H.; Jones, P.J.; Mackay, D.S. Acute Effects of Hemp Protein Consumption on Glycemic and Satiety Control: Results of 2 Randomized Crossover Trials. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, G.; Storz, M.A.; Calapai, G. The Role of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as a Functional Food in Vegetarian Nutrition. Foods 2023, 12, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Le Cao, K.-A. MixOmics: An R Package for ‘omics Feature Selection and Multiple Data Integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureda, A.; del Mar Bibiloni, M.; Julibert, A.; Bouzas, C.; Argelich, E.; Llompart, I.; Pons, A.; Tur, J.A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Inflammatory Markers. Nutrients 2018, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelman, L.; Egea Rodrigues, C.; Aleksandrova, K. Effects of Dietary Patterns on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Immune Responses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragala, M.S.; Clark, M.H.; Walsh, S.J.; Kleppinger, A.; Judge, J.O.; Kuchel, G.A.; Kenny, A.M. Gender Differences in Anthropometric Predictors of Physical Performance in Older Adults. Gend. Med. 2012, 9, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, N. Prediabetes Diagnosis and Treatment: A Review. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel-Albarreal, M.; Grao-Cruces, E.; Rivero-Pino, F.; Lopez-Enriquez, S.; Montserrat-De la Paz, S. Mediterranean Diet and Aerobic Exercise Modulate Immunome-Tabolism-Related Outcomes in Overweight Individuals. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1594. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, M.J. Protein: Metabolism and Effect on Blood Glucose Levels. Diabetes Educ. 1997, 23, 643–646, 648, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montserrat-De la Paz, S.; De Miguel-Albarreal, M.; Gonzalez-de la Rosa, T.; Millán-Linares, M.D.C.; Rivero-Pino, F. Protein-Based Nutritional Strategies to Manage the Development of Diabetes: Evidence and Challenges in Human Studies. Food Funct. 2023, 23, 9962–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grao-Cruces, E.; Varela, L.M.; Martin, M.E.; Bermudez, B.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S. High-Density Lipoproteins and Mediterranean Diet: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Leyva, D.; Pierce, G.N. The Cardiac and Haemostatic Effects of Dietary Hempseed. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhong, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J. Effects of Aerobic Exercise on TC, HDL-C, LDL-C and TG in Patients with Hyperlipidemia. Medicine 2021, 100, e25103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyh, C.; Kruger, K.; Peeling, P.; Castell, L. The Role of Minerals in the Optimal Functioning of the Immune System. Nutrients 2022, 14, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocchegiani, E.; Romeo, J.; Malavolta, M.; Costarelli, L.; Giacconi, R.; Diaz, L.E.; Marcos, A. Zinc: Dietary Intake and Impact of Supplementation on Immune Function in Elderly. Age 2013, 35, 839–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, H.K.; Hall, W.D.; Hurst, J.W. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations; Walker, H.K., Hall, W.D., Hurst, J.W., Eds.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; ISBN 0-409-90077-X. [Google Scholar]
- Mariño, M.M.; Grijota, F.J.; Bartolomé, I.; Siquier-Coll, J.; Román, V.T.; Muñoz, D. Influence of Physical Training on Erythrocyte Concentrations of Iron, Phosphorus and Magnesium. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2020, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musavian, A.S.; Soleimani, A.; Alavi, N.M.; Baseri, A.; Savari, F. Comparing the Effects of Active and Passive Intradialytic Pedaling Exercises on Dialysis Efficacy, Electrolytes, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, Blood Pressure and Health-Related Quality of Life. Nurs. Midwifery Stud. 2015, 4, e25922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsheim, E.; Bui, Q.-U.; Tissier, S.; Cree, M.G.; Ronsen, O.; Morio, B.; Ferrando, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Newcomer, B.R.; Wolfe, R. Amino Acid Supplementation Decreases Plasma and Liver Triglycerides in Elderly. Nutrition 2009, 25, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Sasai, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Sanbongi, C.; Ikegami, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Shioya, N.; Suzuki, S.; Nakata, Y. Randomized Trial of Amino Acid Mixture Combined with Physical Activity Promotion for Abdominal Fat Reduction in Overweight Adults. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsante, F.; Iacobelli, S.; Latorre, G.; Rigo, J.; De Felice, C.; Robillard, Y.; Gouyon, J.B. Initial Amino Acid Intake Influences Phosphorus and Calcium Homeostasis in Preterm Infants—It Is Time to Change the Composition of the Early Parenteral Nutrition. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlas, A.; Kurek, J.M.; Krejpcio, Z. The Potential of L-Arginine in Prevention and Treatment of Disturbed Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism-A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Bao, W.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, Y.Y.; Wang, D.; Rong, S.; Xiao, X.; Shan, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, P.; et al. Inflammatory Markers and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, H.; Youn, E.; Kim, J.; Son, S.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Shim, Y.-H. Effects of Phosphoethanolamine Supplementation on Mitochondrial Activity and Lipogenesis in a Caffeine Ingestion Caenorhabditis Elegans Model. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Witt, S.N. Ethanolamine and Phosphatidylethanolamine: Partners in Health and Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4829180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaranayaka, A.G.P.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Food-Derived Peptidic Antioxidants: A Review of Their Production, Assessment, and Potential Applications. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I. Regulation of Hepatic Mitochondrial Oxidation by Glucose-Alanine Cycling during Starvation in Humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4671–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Mori, T. Amino Acid Mixture Enriched With Arginine, Alanine, and Phenylalanine Stimulates Fat Metabolism During Exercise. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2016, 26, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosson, F.; Smith, E.; Melander, O.; Fernandez, C. Altered Asparagine and Glutamate Homeostasis Precede Coronary Artery Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3060–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Feng, X.; Yang, X.; Hou, R.; Fang, Z. Interactive Effects of Asparagine and Aspartate Homeostasis with Sex and Age for the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Risk. Biol. Sex Differ. 2020, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, T.; Cui, X.; Yan, L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, X.; Tang, Q.-Q.; Tang, H.; et al. Asparagine Reinforces MTORC 1 Signaling to Boost Thermogenesis and Glycolysis in Adipose Tissues. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e108069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samman, S.; Crossett, B.; Somers, M.; Bell, K.J.; Lai, N.T.; Sullivan, D.; Petocz, P. Metabolic Profiling of Plasma Amino Acids Shows That Histidine Increases Following the Consumption of Pork. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Shi, H.; Song, Z.; Ding, S.; Yang, X. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications Abnormal Histidine Metabolism Promotes Macrophage Lipid Accumulation under Ox-LDL Condition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 588, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, R.O.; Arias, E.; Diaz, A.; Burgos, E.S.; Guan, F.; Tiano, S.; Mao, K.; Green, C.L.; Qiu, Y.; Shah, H.; et al. Sarcosine Is Uniquely Modulated by Aging and Dietary Restriction in Rodents and Humans. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Rao, B. The Effects of Taurine Supplementation on Diabetes Mellitus in Humans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 4, 100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppe, L.; Nyam, E.; Vivot, K.; Fox, J.E.M.; Dai, X.; Nguyen, B.N.; Trudel, D.; Attané, C.; Moullé, V.S.; Macdonald, P.E.; et al. Urea Impairs β Cell Glycolysis and Insulin Secretion in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3598–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Huerta, O.D.; Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; Gil, A. Are We Close to Defining a Metabolomic Signature of Human Obesity? A Systematic Review of Metabolomics Studies. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwandhi, L.; Hausmann, S.; Braun, A.; Gruber, T.; Heinzmann, S.S.; Gálvez, E.J.C.; Buck, A.; Legutko, B.; Israel, A.; Feuchtinger, A.; et al. Chronic D-Serine Supplementation Impairs Insulin Secretion. Mol. Metab. 2018, 16, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Miao, R.; Wei, J.; Wu, H.; Tian, J. Advances in Multi-Omics Study of Biomarkers of Glycolipid Metabolism Disorder. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 5935–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Djazayery, A.; Farzadfar, F.; Qi, L.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Aslibekyan, S.; Chamari, M.; Hassani, H.; Koletzko, B.; Uhl, O. Plasma Metabolomic Profiling of Amino Acids and Polar Lipids in Iranian Obese Adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Peng, C.; Yan, C.; Yan, D. Metabolite Biomarkers of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Pre-Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.H. Emerging Perspectives on Essential Amino Acid Metabolism in Obesity and the Insulin-Resistant State. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Singhal, A.; Goyal, P. TG/HDL Ratio: A Marker for Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis in Prediabetics or Not? J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2021, 10, 3700–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsamikor, M.; Mackay, D.S.; Mollard, R.C.; Alashi, A.M.; Aluko, R.E. Hemp seed protein and its hydrolysate vs. casein protein consumption in adults with hypertension: A double-blind crossover study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | t0 (95% CI) | tf (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 91.19 (84.89–97.49) | 82.20 (76.42–87.97) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.88 (29.90–33.86) | 28.73 (26.78–30.68) | <0.001 |
| Abdominal circumference (cm) | 103.23 (99.27–107.20) | 91.87 (88.07–95.68) | <0.001 |
| Body Fat (%) | 39.08 (35.76–42.41) | 35.77 (32.31–39.22) | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 123.39 (118.44–128.34) | 117.56 (112.05–123.07) | 0.01718 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 81.17 (77.46–84.87) | 76.82 (73.07–80.57) | 0.006432 |
| Body Water (%) | 43.55 (41.32–45.77) | 45.34 (43.08–47.59) | <0.001 |
| Bone Mass (Kg) | 2.77 (2.55–3.00) | 2.65 (2.46–2.85) | 0.001574 |
| Basal Metabolism (kcal) | 1697.0 (1556.98–1837.62) | 1594.78 (1474.14–1715.42) | <0.001 |
| Muscle Mass (%) | 34.58 (29.37–39.78) | 32.61 (28.26–36.97) | <0.001 |
| Visceral Fat (%) | 10.76 (9.18–12.33) | 8.97 (7.44–10.51) | <0.001 |
| Beats per minute | 71.52 (66.93–76.11) | 73.08 (67.95–78.22) | 0.3346 |
| Metabolic Age (years) | 57.08 (53.14–61.02) | 53.73 (48.86–58.61) | 0.009444 |
| Variable | t0 (95% CI) | tf (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 84.82 (77.09–92.54) | 87.23 (83.82–90.63) | 0.5411 |
| TAG (mg/dL) | 130.23 (94.40–166.06) | 65.40 (54.24–76.57) | <0.001 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 207.26 (191.90–222.63) | 146.89 (131.53–157.01) | <0.001 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 47.48 (41.29–53.66) | 72.29 (59.79–84.79) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 133.73 (120.09–147.38) | 61.51 (49.00–74.01) | <0.001 |
| Variable | t0 (95% CI) | tf (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 13.75 (12.81–14.68) | 11.79 (11.27–12.32) | <0.001 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 13.07 (11.45–14.69) | 5.65 (5.38–5.92) | <0.001 |
| Chloride (nMol/L) | 96.39 (92.02–99.86) | 104.67 (101.98–107.37) | <0.001 |
| Magnesium (mg/dL) | 1.97 (1.90–2.04) | 2.01 (1.97–2.06) | 0.3741 |
| Variable | t0 (95% CI) (μmol/L) | tf (95% CI) (μmol/L) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phser | 7.63 (7.08–8.18) | 6.91 (6.11–7.70) | 0.1324 |
| Taur | 14.88 (12.04–17.72) | 16.87 (13.58–20.15) | 0.3382 |
| Pea | 0.86 (0.62–1.11) | 1.46 (1.01–1.91) | 0.01695 |
| Urea | 1004.02 (926.99–1081.06) | 808.57 (716.13–901.01) | 0.001193 |
| Thr | 28.05 (25.54–30.55) | 23.94 (21.37–26.51) | 0.008221 |
| Ser | 24.62 (22.59–26.66) | 22.82 (20.48–25.17) | 0.1611 |
| Asn | 23.80 (21.56–26.05) | 12.01 (10.78–13.25) | <0.001 |
| Glu | 10.21 (8.09–12.32) | 8.21 (3.49–12.93) | 0.004339 |
| Gln | 102.75 (95.52–109.98) | 137.19 (118.20–156.17) | <0.001 |
| AAAA | 1.23 (0.82–1.63) | 1.07 (0.76–1.39) | 0.482 |
| Gly | 47.61 (41.86–53.37) | 43.70 (36.67–50.73) | 0.03543 |
| Ala | 85.12 (77.98–92.25) | 57.51 (52.40–62.63) | <0.001 |
| Aaba | 4.81 (4.24–5.38) | 4.83 (4.24–5.42) | 0.9566 |
| Val | 49.43 (45.17–53.69) | 36.54 (33.25–39.82) | <0.001 |
| Cys | 8.33 (7.51–9.15) | 7.96 (7.20–8.72) | 0.3419 |
| Met_Cysth | 5.45 (5.04–5.87) | 4.08 (3.74–4.42) | <0.001 |
| Ile | 14.51 (13.06–15.97) | 10.74 (9.68–11.79) | <0.001 |
| Leu | 28.86 (25.99–31.73) | 27.80 (25.75–29.84) | 0.3178 |
| Tyr | 16.97 (15.60–18.34) | 13.56 (12.69–14.43) | <0.001 |
| Phe | 12.93 (12.05–13.80) | 9.68 (9.10–10.26) | <0.001 |
| Amm | 39.53 (36.87–42.19) | 28.27 (25.04–31.49) | <0.001 |
| Orn | 21.57 (19.14–24.00) | 17.92 (16.13–19.70) | 0.00242 |
| Lys | 38.83 (36.56–41.10) | 39.34 (36.09–41.78) | 0.7381 |
| Mhis_1 | 3.18 (2.40–3.95) | 3.72 (2.68–4.75) | 0.56 |
| His | 17.04 (16.24–17.84) | 13.24 (12.52–13.96) | <0.001 |
| Trp | 6.32 (5.46–7.18) | 6.56 (5.51–7.61) | 0.72 |
| Arg | 8.73 (6.91–10.55) | 9.27 (8.11–10.43) | 0.4954 |
| Sarc | 15.35 (14.40–16.29) | 18.42 (16.87–19.97) | 0.002875 |
| Citr | 5.58 (5.09–6.06) | 4.46 (4.04–4.89) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miguel-Albarreal, A.D.; Rivero-Pino, F.; Marquez-Paradas, E.; Grao-Cruces, E.; Gonzalez-de la Rosa, T.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S. Mediterranean Diet Combined with Regular Aerobic Exercise and Hemp Protein Supplementation Modulates Plasma Circulating Amino Acids and Improves the Health Status of Overweight Individuals. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111594
Miguel-Albarreal AD, Rivero-Pino F, Marquez-Paradas E, Grao-Cruces E, Gonzalez-de la Rosa T, Montserrat-de la Paz S. Mediterranean Diet Combined with Regular Aerobic Exercise and Hemp Protein Supplementation Modulates Plasma Circulating Amino Acids and Improves the Health Status of Overweight Individuals. Nutrients. 2024; 16(11):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111594
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiguel-Albarreal, Antonio D., Fernando Rivero-Pino, Elvira Marquez-Paradas, Elena Grao-Cruces, Teresa Gonzalez-de la Rosa, and Sergio Montserrat-de la Paz. 2024. "Mediterranean Diet Combined with Regular Aerobic Exercise and Hemp Protein Supplementation Modulates Plasma Circulating Amino Acids and Improves the Health Status of Overweight Individuals" Nutrients 16, no. 11: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111594
APA StyleMiguel-Albarreal, A. D., Rivero-Pino, F., Marquez-Paradas, E., Grao-Cruces, E., Gonzalez-de la Rosa, T., & Montserrat-de la Paz, S. (2024). Mediterranean Diet Combined with Regular Aerobic Exercise and Hemp Protein Supplementation Modulates Plasma Circulating Amino Acids and Improves the Health Status of Overweight Individuals. Nutrients, 16(11), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111594







