Effectiveness of a Balanced Nine-Strain Synbiotic in Primary-Care Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients—A Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
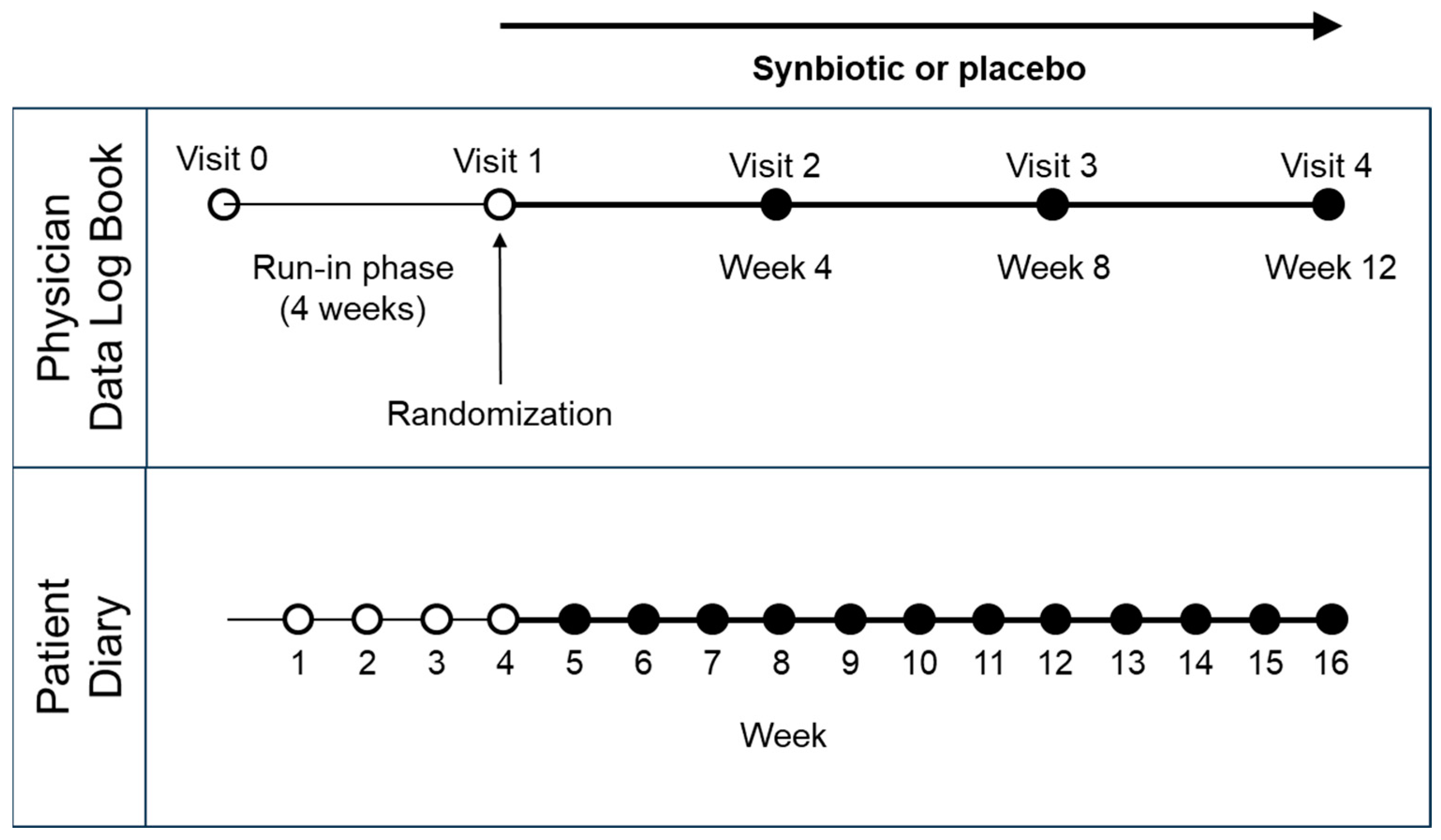
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Multi-Strain Synbiotic and Placebo Preparation
2.4. Examinations, Treatments, and Data Collection
2.5. Sample-Size Calculation
2.6. Randomization
2.7. IBS-Type Categorization
2.8. Primary Endpoints
2.9. Secondary Endpoints
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Flow, Study Progress, and Baseline Characteristics of Treatment Groups
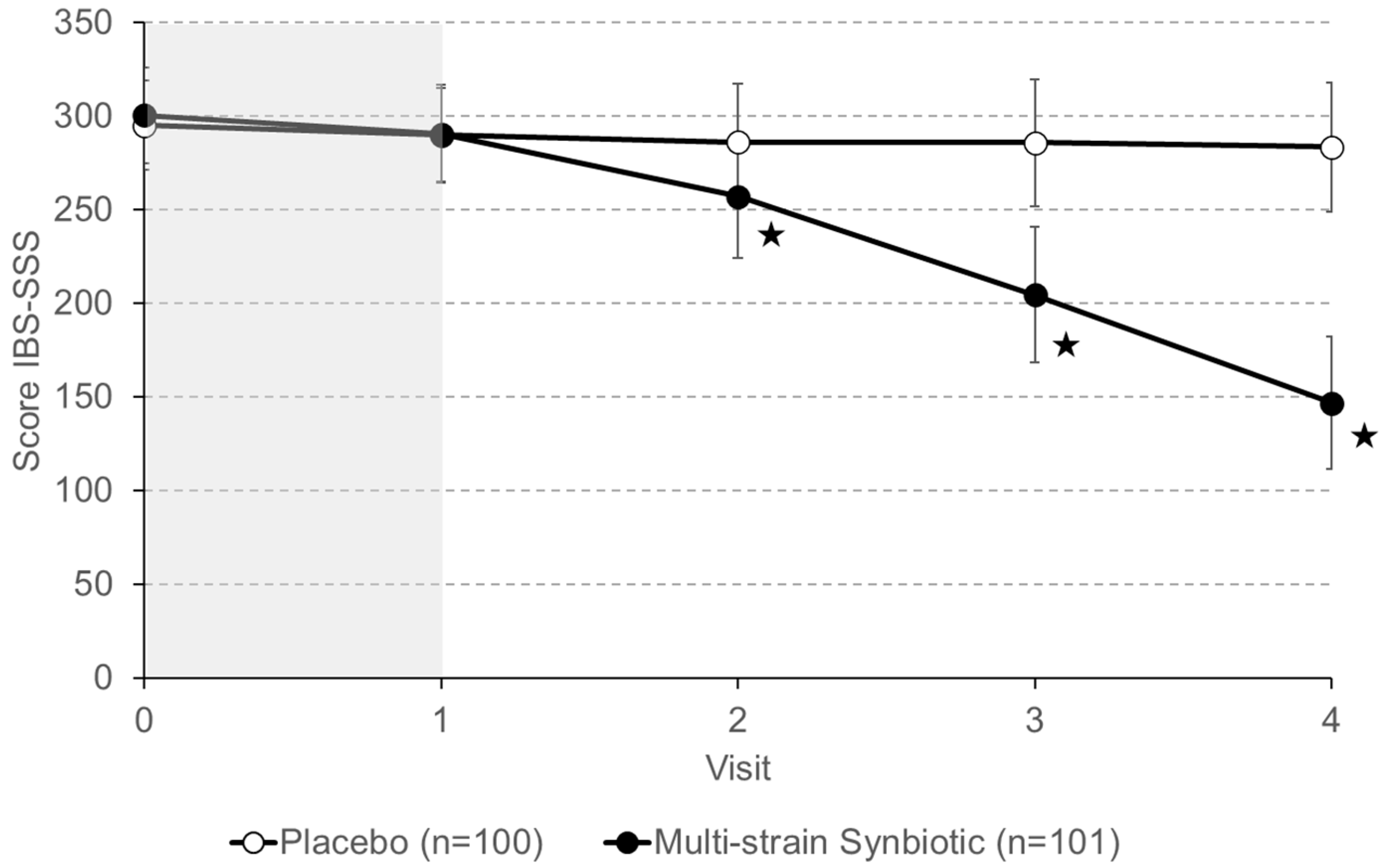
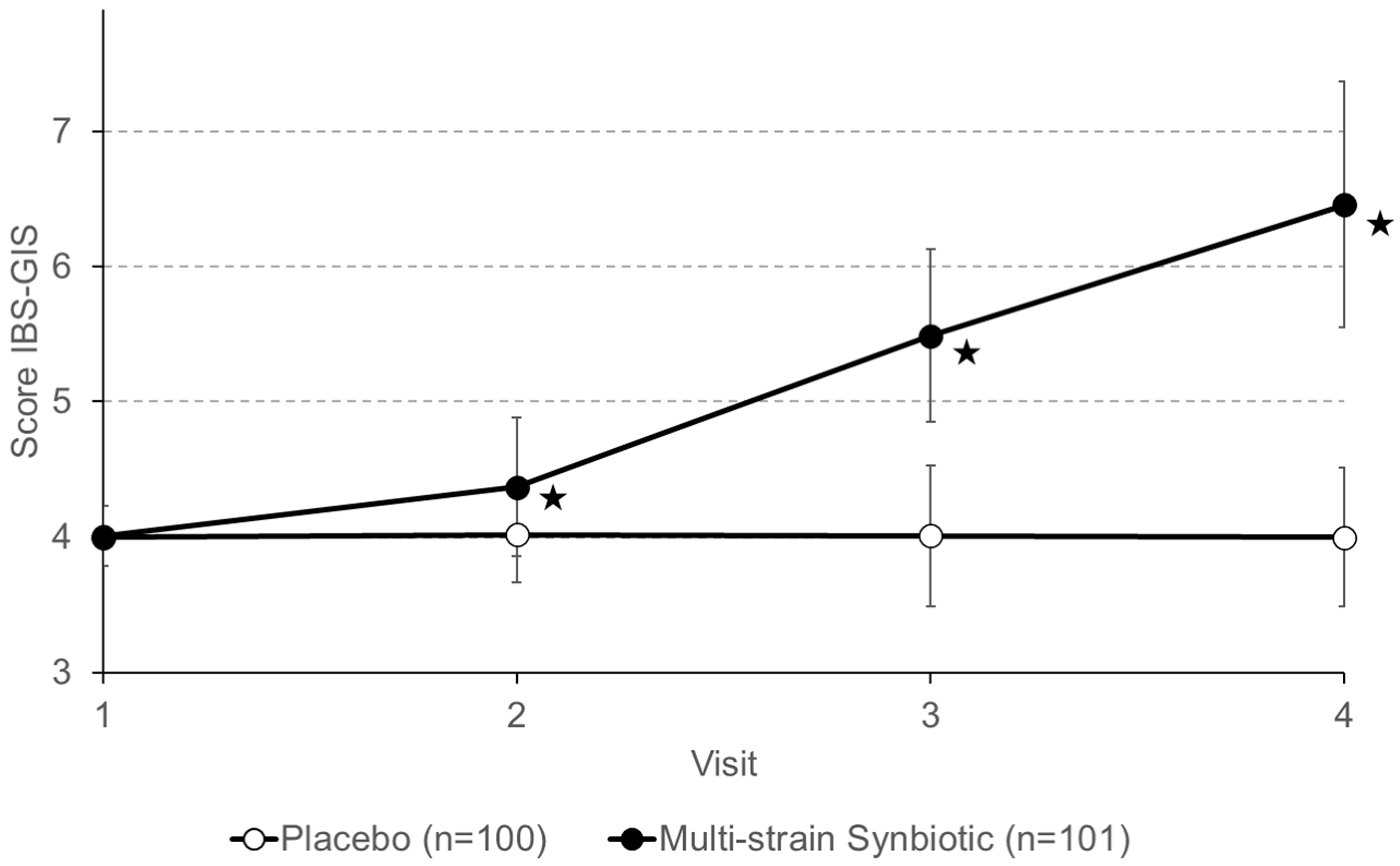
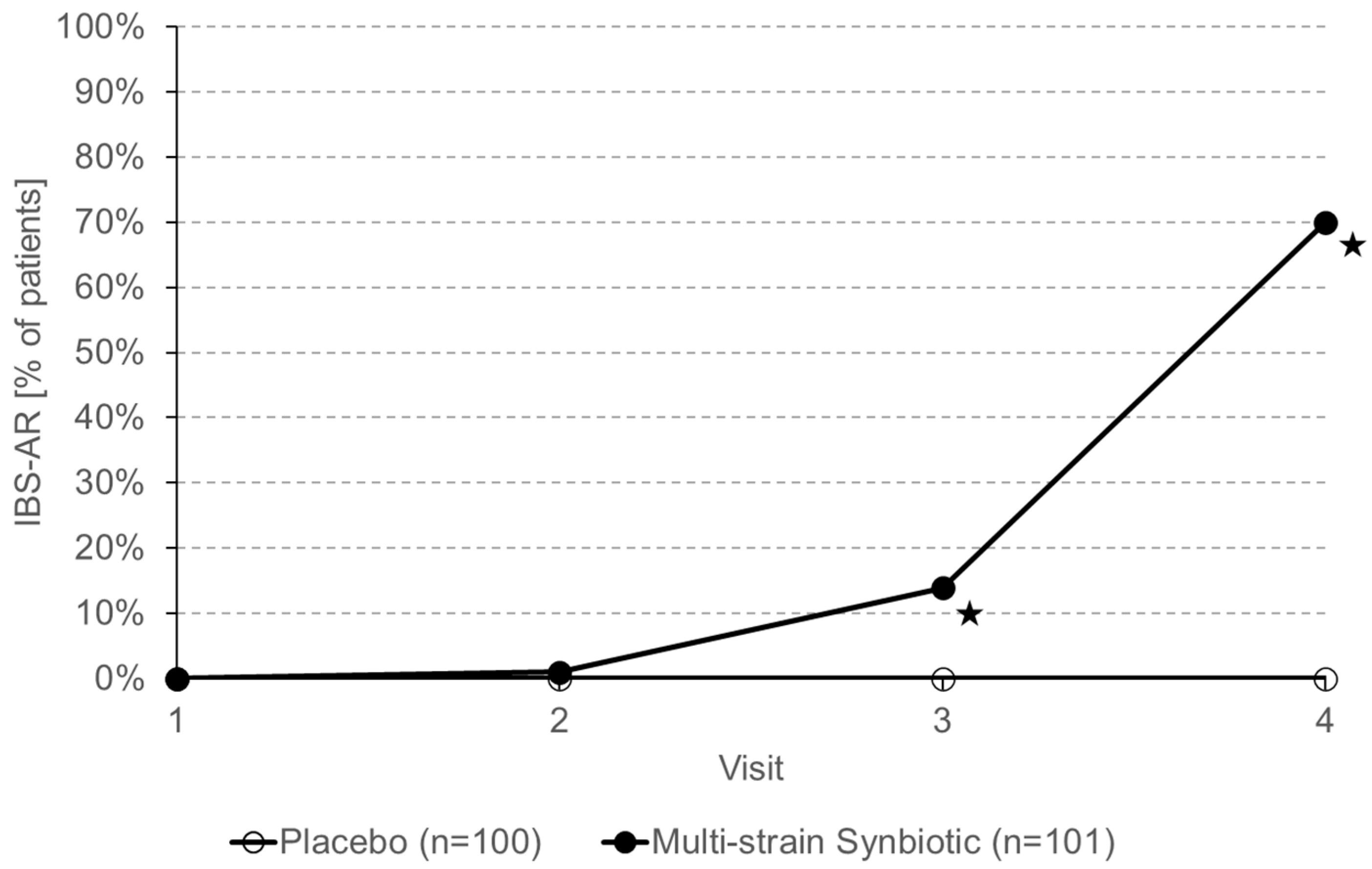
3.2. Study Primary Endpoints
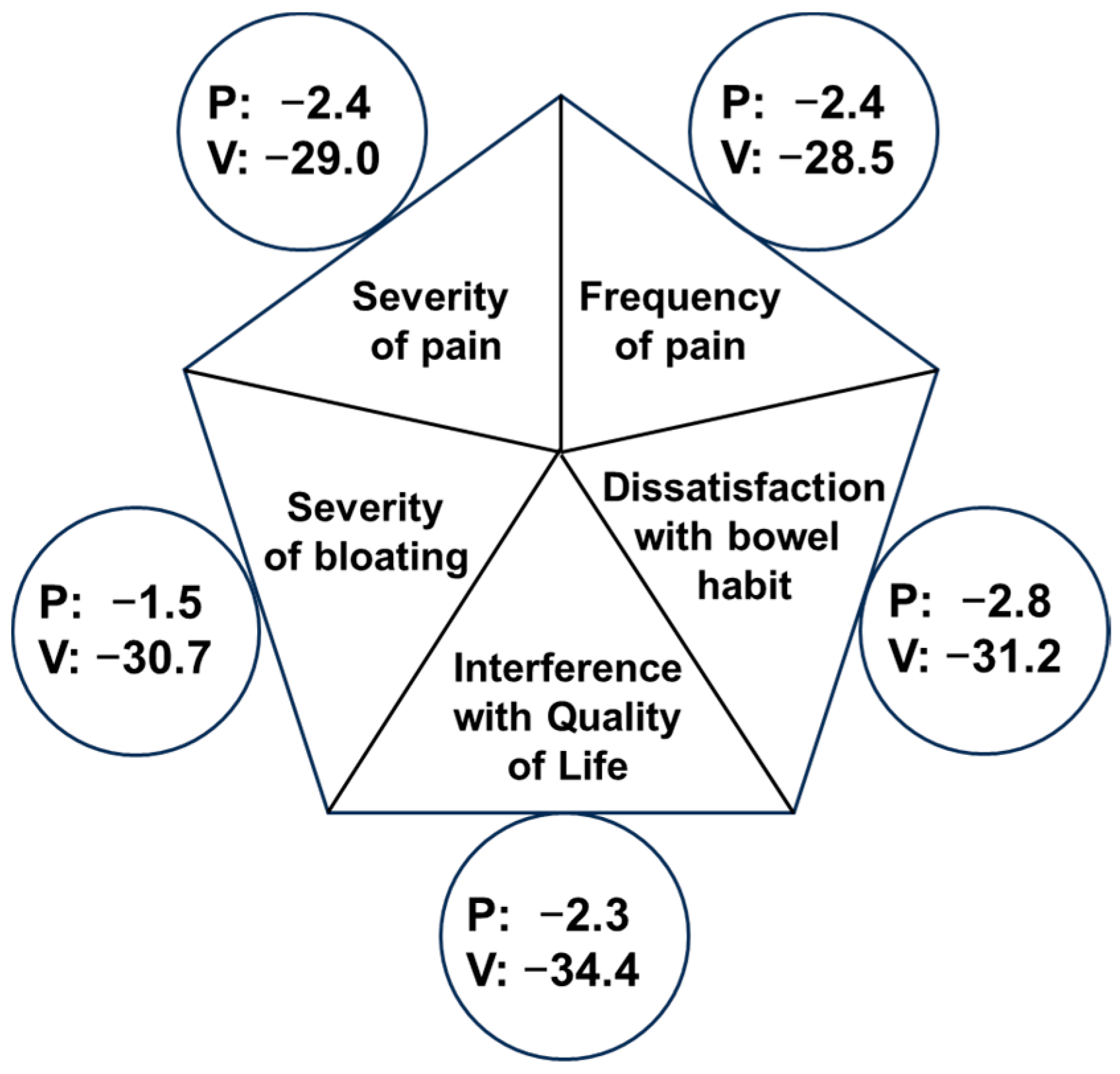
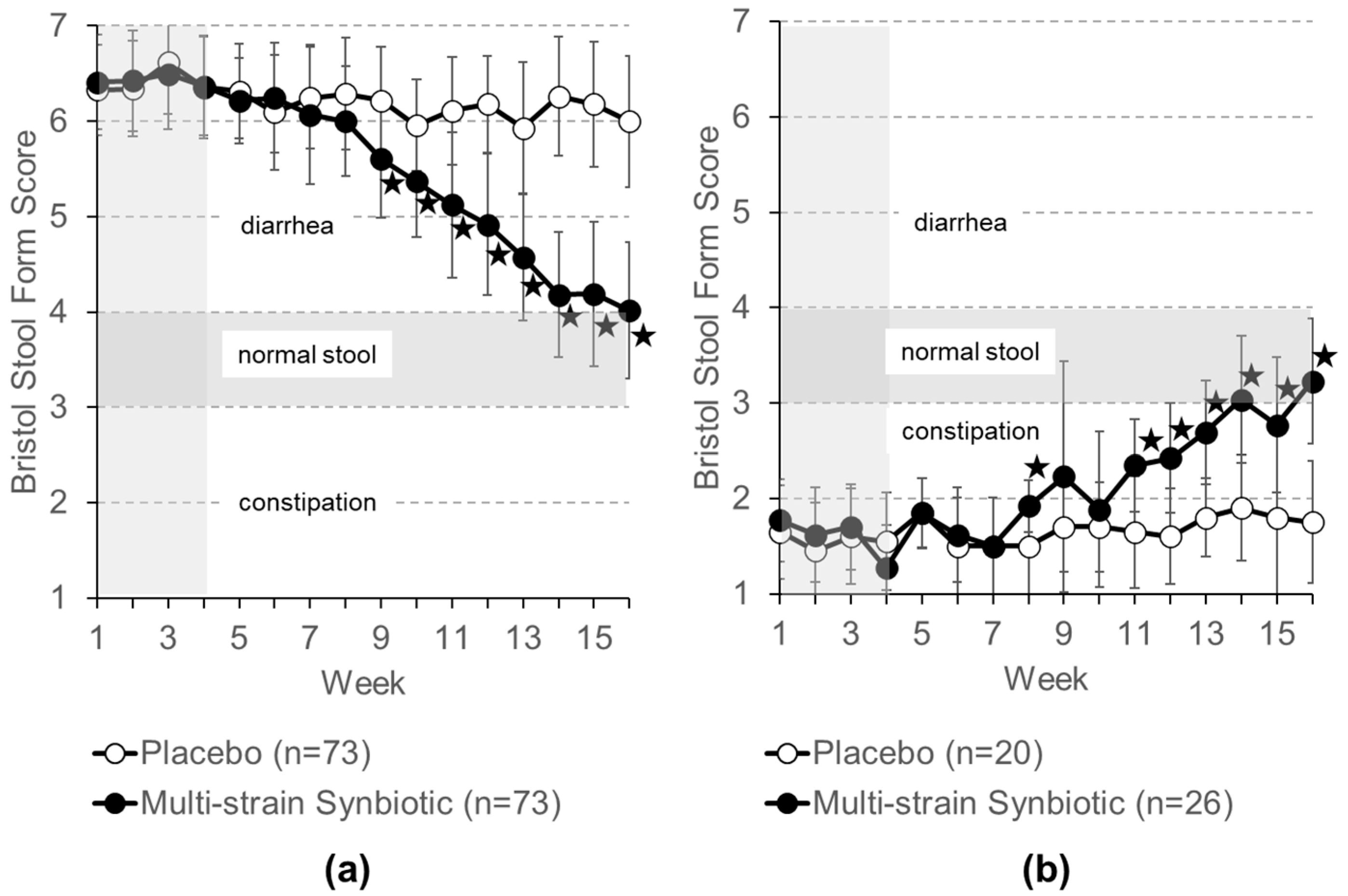
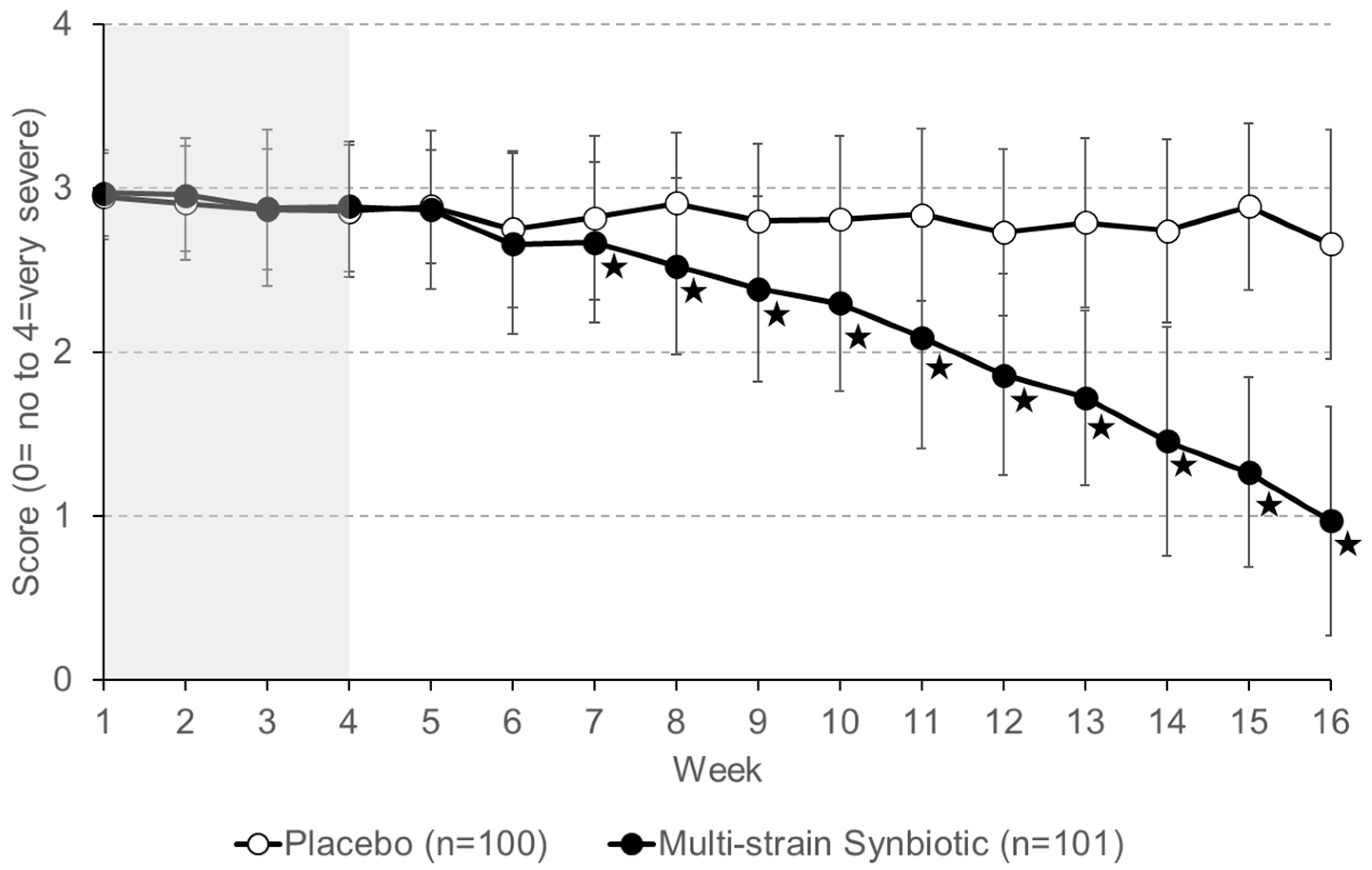
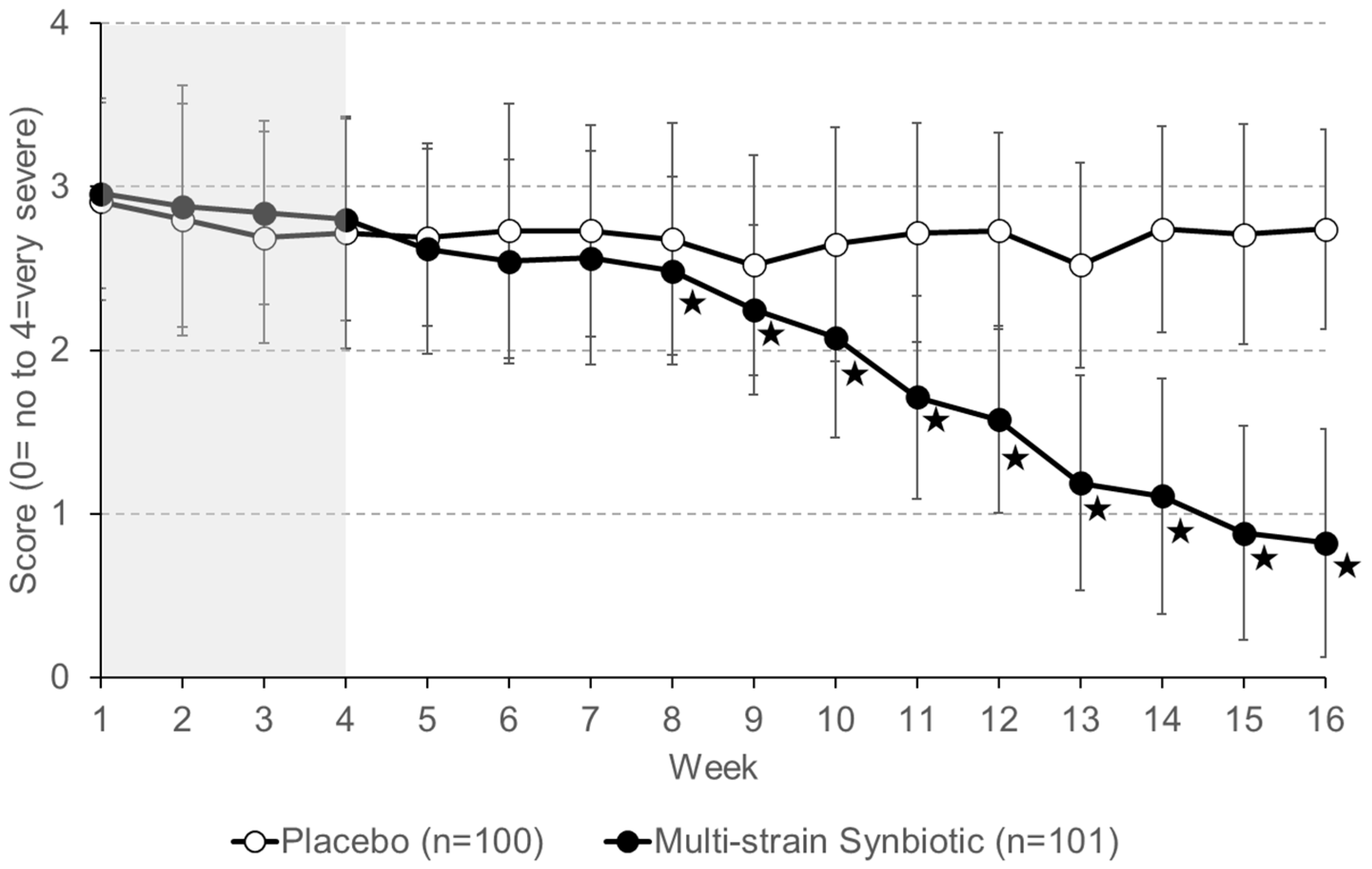
3.3. Study Secondary Endpoints
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths of the Study
4.2. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ford, A.C.; Sperber, A.D.; Corsetti, M.; Camilleri, M. Irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet 2020, 396, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C. Global burden of irritable bowel syndrome: Trends, predictions and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M. Diagnosis and Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 865–877, Erratum in JAMA 2021, 325, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Chang, L.; Schneck, S.; Blackman, C.; Norton, W.F.; Norton, N.J. A focus group assessment of patient perspectives on irritable bowel syndrome and illness severity. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornkvist, N.T.; Aziz, I.; Whitehead, W.E.; Sperber, A.D.; Palsson, O.S.; Hreinsson, J.P.; Simrén, M.; Törnblom, H. Health care utilization of individuals with Rome IV irritable bowel syndrome in the general population. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shah, E.D.; Salwen-Deremer, J.K.; Gibson, P.R.; Muir, J.G.; Eswaran, S.; Chey, W.D. Comparing Costs and Outcomes of Treatments for Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Diarrhea: Cost-Benefit Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 136–144.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, R.; Law, G.R.; Ford, A.C. Diagnosis of IBS: Symptoms, symptom-based criteria, biomarkers or ‘psychomarkers’? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, C.Y.; Morris, J.; Whorwell, P.J. The irritable bowel severity scoring system: A simple method of monitoring irritable bowel syndrome and its progress. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Chang, L.; Bellamy, N.; Gallo-Torres, H.E.; Lembo, A.; Mearin, F.; Norton, N.J.; Whorwell, P. Severity in irritable bowel syndrome: A Rome Foundation Working Team report. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1749–1759, quiz 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, M.R.; Raker, J.M.; Whelan, K. Validity and reliability of the Bristol Stool Form Scale in healthy adults and patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, R.M.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of and risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 712–721.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, P.; Parr, H.; Barberio, B.; Black, C.J.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome according to Rome III or IV criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 908–917, Erratum in Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020, 5, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, B.E.; Mearin, F.; Chang, L.; Chey, W.D.; Lembo, A.J.; Simren, J.; Spiller, R. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbara, G.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Quigley, E.M.; Santos, J.; Vanner, S.; Vergnolle, N.; Zoetendal, E.G. The Intestinal Microenvironment and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1305–1318.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tana, C.; Umesaki, Y.; Imaoka, A.; Handa, T.; Kanazawa, M.; Fukudo, S. Altered profiles of intestinal microbiota and organic acids may be the origin of symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 512–519, e114–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerckhoffs, A.P.; Samsom, M.; van der Rest, M.E.; de Vogel, J.; Knol, J.; Ben-Amor, K.; Akkermans, L.M. Lower Bifidobacteria counts in both duodenal mucosa-associated and fecal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kassinen, A.; Krogius-Kurikka, L.; Mäkivuokko, H.; Rinttilä, T.; Paulin, L.; Corander, J.; Malinen, E.; Apajalahti, J.; Palva, A. The fecal microbiota of irritable bowel syndrome patients differs significantly from that of healthy subjects. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tap, J.; Derrien, M.; Törnblom, H.; Brazeilles, R.; Cools-Portier, S.; Doré, J.; Störsrud, S.; Le Nevé, B.; Öhman, L.; Simrén, M. Identification of an Intestinal Microbiota Signature Associated with Severity of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 111–123.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinen, E.; Krogius-Kurikka, L.; Lyra, A.; Nikkilä, J.; Jääskeläinen, A.; Rinttilä, T.; Vilpponen-Salmela, T.; von Wright, A.J.; Palva, A. Association of symptoms with gastrointestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4532–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ceccherini, C.; Daniotti, S.; Bearzi, C.; Re, I. Evaluating the Efficacy of Probiotics in IBS Treatment Using a Systematic Review of Clinical Trials and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van der Geest, A.M.; Schukking, I.; Brummer, R.J.M.; van de Burgwal, L.H.M.; Larsen, O.F.A. Comparing probiotic and drug interventions in irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Benef. Microbes 2022, 13, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didari, T.; Mozaffari, S.; Nikfar, S.; Abdollahi, M. Effectiveness of probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome: Updated systematic review with meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3072–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Harris, L.A.; Baffy, N. Modulation of the gut microbiota: A focus on treatments for irritable bowel syndrome. Postgrad. Med. 2017, 129, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, H.F.; Rasmussen, S.H.; Asiller, Ö.Ö.; Lied, G.A. Probiotics in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liang, D.; Longgui, N.; Guoqiang, X. Efficacy of different probiotic protocols in irritable bowel syndrome: A network meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Niu, H.L.; Xiao, J.Y. The efficacy and safety of probiotics in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: Evidence based on 35 randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 75, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, F.; Duan, L. Efficacy of Probiotics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 859967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xie, P.; Luo, M.; Deng, X.; Fan, J.; Xiong, L. Outcome-Specific Efficacy of Different Probiotic Strains and Mixtures in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gracie, D.J.; Ford, A.C. Symbiotics in irritable bowel syndrome—Better than probiotics alone? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.P.; Chin, V.K.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F.; Madhavan, P.; Yong, V.C. The Microbiome and Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Review on the Pathophysiology, Current Research and Future Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1136, Erratum in Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlebicz-Wójcik, A.; Śliżewska, K. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics in the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment: A Review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piątek, J.; Gibas-Dorna, M.; Olejnik, A.; Krauss, H.; Wierzbicki, K.; Żukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Głowacki, M. The viability and intestinal epithelial cell adhesion of probiotic strain combination—In vitro study. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piatek, J.; Sommermeyer, H.; Bernatek, M.; Ciechelska-Rybarczyk, A.; Oleskow, B.; Mikkelsen, L.S.; Barken, K.B. Persistent infection by Salmonella enterica servovar Typhimurium: Are synbiotics a therapeutic option?—A case report. Benef. Microbes 2018, 10, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatek, J.; Bernatek, M.; Ciechelska-Rybarczyk, A.; Oleskow, B.; Sommermeyer, H. Inhibition of Carbapenem-Resistant NDM-1 Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from a Hospital Outbreak Patient by a Synbiotic: A Non-antibiotic Treatment Option. Int. J. Med. Res. Health Sci. 2019, 8, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sommermeyer, H.; Pituch, H.M.; Wultanska, D.; Wojtyla-Buciora, P.; Piatek, J.; Bernatek, M. Inhibition of Quinolone- and Multi-Drug-Resistant Clostridioides Difficile Strains by Multi Strain Synbiotics—An Option for Diarrhea Management in Nursing Facilities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Prozorow-Król, B.; Cichoż-Lach, H.; Majsiak, E.; Bierła, J.B.; Kosikowski, W.; Szczerbiński, M.; Gantzel, J.; Cukrowska, B. The Effectiveness of Synbiotic Preparation Containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Probiotic Strains and Short Chain Fructooligosaccharides in Patients with Diarrhea Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome-A Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Skrzydło-Radomańska, B.; Prozorow-Król, B.; Cichoż-Lach, H.; Majsiak, E.; Bierła, J.B.; Kanarek, E.; Sowińska, A.; Cukrowska, B. The Effectiveness and Safety of Multi-Strain Probiotic Preparation in Patients with Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- IBS Questionnaire for HCP. Available online: https://www.worldgastroenterology.org/UserFiles/file/wdhd-2009-test-for-diagnosing-ibs.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- Gordon, S.; Ameen, V.; Bagby, B.; Shahan, B.; Jhingran, P.; Carter, E. Validation of irritable bowel syndrome Global Improvement Scale: An integrated symptom end point for assessing treatment efficacy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, M.C.; Lembo, A.J.; Conboy, L.A.; Kaptchuk, T.J.; Kelly, J.M.; Quilty, M.T.; Kerr, C.E.; Jacobson, E.E.; Hu, R.; Friedlander, E.; et al. Adequate relief in a treatment trial with IBS patients: A prospective assessment. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Min, Y.W.; Park, S.U.; Jang, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Rhee, P.L.; Ko, S.H.; Joo, N.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, C.H.; Chang, D.K. Effect of composite yogurt enriched with acacia fiber and Bifidobacterium lactis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 4563–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rogha, M.; Esfahani, M.Z.; Zargarzadeh, A.H. The efficacy of a synbiotic containing Bacillus Coagulans in treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed. Bench 2014, 7, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oh, J.H.; Jang, Y.S.; Kang, D.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, E.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Min, Y.W.; Chang, D.K. Efficacy of a Synbiotic Containing Lactobacillus paracasei DKGF1 and Opuntia humifusa in Elderly Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gut Liver 2023, 17, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shavakhi, A.; Minakari, M.; Farzamnia, S.; Peykar, M.S.; Taghipour, G.; Tayebi, A.; Hashemi, H.; Shavakhi, S. The effects of multi-strain probiotic compound on symptoms and quality-of-life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cappello, C.; Tremolaterra, F.; Pascariello, A.; Ciacci, C.; Iovino, P. A randomised clinical trial (RCT) of a symbiotic mixture in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Effects on symptoms, colonic transit and quality of life. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2013, 28, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Cho, D.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Han, K.S.; Yang, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.N. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Synbiotics in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Dose-Dependent Effects on Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Fatigue. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2019, 40, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaptchuk, T.J.; Friedlander, E.; Kelley, J.M.; Sanchez, M.N.; Kokkotou, E.; Singer, J.P.; Kowalczykowski, M.; Miller, F.G.; Kirsch, I.; Lembo, A.J. Placebos without deception: A randomized controlled trial in irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Asha, M.Z.; Khalil, S.F.H. Efficacy and Safety of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2020, 20, e13–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hahn, B.A.; Kirchdoerfer, L.J.; Fullerton, S.; Mayer, E. Evaluation of a new quality of life questionnaire for patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Patrick, D.L.; Whitehead, W.E.; Toner, B.B.; Diamant, N.E.; Hu, Y.; Jia, H.; Bangdiwala, S.I. Further validation of the IBS-QOL: A disease-specific quality-of-life questionnaire. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, D.; Vanner, S.J.; Depew, W.T.; DaCosta, L.R.; Simon, J.B.; Groll, A.; Roblin, N.; Paterson, W.G. The IBS-36: A new quality of life measure for irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Probiotic Strain | Colony-Forming Units (CFU) per Capsule 1 | % of Total CFU |
|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus helveticus SP 27 | 9.00 × 108 | 20 |
| Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Lr-32 | 4.50 × 108 | 10 |
| Lacticaseibacillus casei Lc-11 | 2.25 × 108 | 5 |
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Lp-115 | 2.25 × 108 | 5 |
| Lactococcus lactis Ll-23 | 9.00 × 108 | 20 |
| Bifidobacterium longum Bl-05 | 6.75 × 108 | 15 |
| Bifidobacterium breve Bb-03 | 4.50 × 108 | 10 |
| Bifidobacterium bifidum Bb-02 | 2.25 × 108 | 5 |
| Streptococcus thermophilus St-21 | 4.50 × 108 | 10 |
| Total CFU/capsule | 45 × 108 | 100 |
| Placebo (n = 100) | Multi-Strain Synbiotic (n = 101) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics assessed by physicians during visit 0 | |||
| Weight (kg) | 72.1 ± 12.3 | 70.1 ± 12.3 | 0.244 a |
| Height (cm) | 172.8 ± 9.5 | 171.2 ± 9.3 | 0.252 a |
| Body-Mass Index (kg/m2) | 24.0 ± 2.1 | 23.7 ± 2.1 | 0.820 a |
| Age | 40.8 ± 10.7 | 41.9 ± 9.5 | 0.424 a |
| Gender (female/male) | 55/45 | 64/37 | 0.228 b |
| WGO IBS questionnaire for HCP c | 25.0 ± 1.2 | 24.8 ± 1.6 | 0.455 a |
| IBS-SSS d | 295.1 ± 23.9 | 300.5 ± 25.7 | 0.131 a |
| IBS severity (moderate/severe) e | 57/43 | 53/48 | 0.615 b |
| IBS-SSS1 f | 59.1 ± 6.3 | 59.9 ± 6.2 | 0.413 a |
| IBS-SSS2 g | 58.3 ± 5.8 | 58.4 ± 6.0 | 0.889 a |
| IBS-SSS3 h | 58.7 ± 5.9 | 60.7 ± 6.1 | 0.021 a |
| IBS-SSS4 i | 59.3 ± 6.1 | 59.8 ± 7.8 | 0.580 a |
| IBS-SSS5 j | 59.8 ± 6.5 | 61.8 ± 6.1 | 0.025 a |
| Baseline characteristics assessed from patients’ reporting during run-in phase | |||
| IBS-Stool Type (D/C/M/U) k | 73/20/2/5 | 73/26/1/1 | 0.287 b |
| Bristol Stool Form Scale score IBS-D patients | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 0.306 a |
| Bristol Stool Form Scale score IBS-C patients | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.386 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sommermeyer, H.; Chmielowiec, K.; Bernatek, M.; Olszewski, P.; Kopczynski, J.; Piątek, J. Effectiveness of a Balanced Nine-Strain Synbiotic in Primary-Care Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients—A Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16101503
Sommermeyer H, Chmielowiec K, Bernatek M, Olszewski P, Kopczynski J, Piątek J. Effectiveness of a Balanced Nine-Strain Synbiotic in Primary-Care Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients—A Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2024; 16(10):1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16101503
Chicago/Turabian StyleSommermeyer, Henning, Krzysztof Chmielowiec, Malgorzata Bernatek, Pawel Olszewski, Jaroslaw Kopczynski, and Jacek Piątek. 2024. "Effectiveness of a Balanced Nine-Strain Synbiotic in Primary-Care Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients—A Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial" Nutrients 16, no. 10: 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16101503
APA StyleSommermeyer, H., Chmielowiec, K., Bernatek, M., Olszewski, P., Kopczynski, J., & Piątek, J. (2024). Effectiveness of a Balanced Nine-Strain Synbiotic in Primary-Care Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients—A Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 16(10), 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16101503







