Nutrition-Related Knowledge, Diet Quality, Lifestyle, and Body Composition of 7–12-Years-Old Polish Students: Study Protocol of National Educational Project Junior-Edu-Żywienie (JEŻ)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
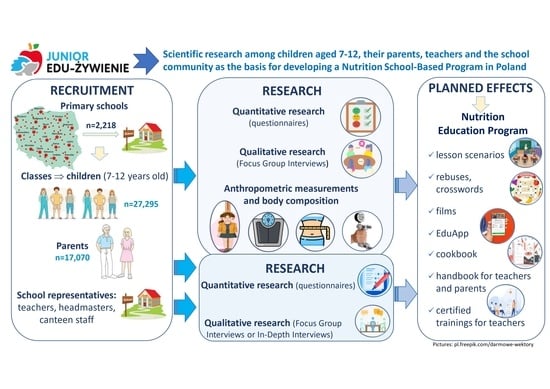
2.2. Study Design and Participants
2.3. Quantitative Research—Methods, Tools, and Data Collection
2.3.1. Pilot Study
2.3.2. Questionnaires Description
Questionnaires for Children Aged 7–9 Years
Questionnaire for Adolescents Aged 10–12 Years
Questionnaire for Parents
Questionnaire for Teachers
Questionnaire for Evaluation of School Food and Nutrition Environment
2.3.3. Data Collection
2.4. Qualitative Research
2.4.1. Focus Group Interviews (FGIs)
2.4.2. In-Depth Interviews (IDIs)
2.4.3. Qualitative Data Analysis
2.5. Anthropometric Measurements
2.6. Outcome Measures
2.6.1. Dietary Habits
- Never or almost never: 0 times/day.
- Less than once a week: 0.06 times/day.
- Once a week: 0.14 times/day.
- 2–4 times/week: 0.43 times/day.
- 5–6 times/week: 0.79 times/day.
- Every day: 1 time/day.
- Several times a day: 2 times/day.
- “pro-Healthy Diet Index” (pHDI).
- “non-Healthy Diet Index” (nHDI).
- “Diet-Quality Index” (DQI).
- −100–−26: high intensity of nonhealthy dietary characteristics.
- −25–26: low intensity of both nonhealthy and healthy dietary characteristics.
- 26–100: high intensity of healthy dietary characteristics.
2.6.2. Nutrition-Related Knowledge
2.6.3. Nutritional Status
| Parameter (Units) | Reference Values |
|---|---|
| Height (H) (cm) |
|
| Body weight (BW) (kg) |
|
| Waist circumference (WC) (cm) |
|
| Hip circumference (HC) (cm) |
|
| Body composition (BC) |
|
| Hand grip strength (HGS) (kg) |
|
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Nutrition Education Program
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montaño, Z.; Smith, J.D.; Dishion, T.J.; Shaw, D.S.; Wilson, M.N. Longitudinal relations between observed parenting behaviours and dietary quality of meals from ages 2 to 5. Appetite 2015, 87, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnane, J.M.; Jansen, E.; Mallan, K.M.; Daniels, L.A. Mealtime Structure and Responsive Feeding Practices Are Associated with Less Food Fussiness and More Food Enjoyment in Children. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 11–18.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Saat, N.Z.; Abd Talib, R.; Alarsan, S.F.; Saadeh, N.; Shahrour, G. Risk Factors of Overweight and Obesity Among School Children Aged 6 to 18 Years: A Scoping Review. Nutr. Dietary Suppl. 2023, 15, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, D.; Godos, J.; Bonaccio, M.; Vitaglione, P.; Grosso, G. Ultra-Processed Foods and Nutritional Dietary Profile: A Meta-Analysis of Nationally Representative Samples. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuenstel, J.W.; Wądołowska, L.; Słowińska, M.A.; Niedźwiedzka, E.; Kowalkowska, J.; Antoniak, L. Consumption Frequency of Fruit Juices and Sweetened Beverages: Differences Related to Age, Gender and the Prevalence of Overweight among Polish Adolescents. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 65, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszkowska-Ryciak, J.; Harton, A.; Lange, E.; Laskowski, W.; Gajewska, D. Nutritional Behaviours of Polish Adolescents: Results of the Wise Nutrition—Healthy Generation Project. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadolowska, L.; Hamulka, J.; Kowalkowska, J.; Ulewicz, N.; Gornicka, M.; Jeruszka-Bielak, M.; Kostecka, M.; Wawrzyniak, A. Skipping Breakfast and a Meal at School: Its Correlates in Adiposity Context. Report from the ABC of Healthy Eating Study of Polish Teenagers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sygit, K.; Kołłątaj, W.; Wojtyła, A.; Sygit, M.; Bojar, I.; Owoc, A. Engagement in risky behaviours by 15–19-year-olds from Polish urban and rural areas. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2011, 18, 404–409. [Google Scholar]
- Sygit, K.M.; Sygit, M.; Wojtyła-Buciora, P.; Lubiniec, O.; Stelmach, W.; Krakowiak, J. Environmental variations of nutritional mistakes among Polish school-age adolescents from urban and rural areas. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2019, 26, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, K.; Jacquier, E.; Kineman, B.; Storm, H.; Carvalho, R. Nutrient intakes and sources of fiber among children with low and high dietary fiber intake: The 2016 feeding infants and toddlers study (FITS), a cross-sectional survey. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Legarre, N.; Miguel-Berges, M.L.; Flores-Barrantes, P.; Santaliestra-Pasías, A.M.; Moreno, L.A. Breakfast Characteristics and Its Association with Daily Micronutrients Intake in Children and Adolescents–A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Niu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Duo, B.; Effah, C.Y.; Guan, L. The effect of breakfast on childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 6, 1222536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfield, G.S.; Moore, C.; Henderson, K.; Buchholz, A.; Obeid, N.; Flament, M.F. Body dissatisfaction, dietary restraint, depression, and weight status in adolescents. J. Sch. Health 2010, 80, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, K.; Sahoo, B.; Choudhury, A.K.; Sofi, N.Y.; Kumar, R.; Bhadoria, A.S. Childhood obesity: Causes and consequences. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2015, 4, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juonala, M.; Viikari, J.S.; Raitakari, O.T. Main findings from the prospective Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013, 24, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, S.; Giussani, M.; Orlando, A.; Battaglino, M.G.; Nava, E.; Parati, G. Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases in Children and Adolescents. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2019, 26, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobstein, T.; Jackson-Leach, R. Planning for the worst: Estimates of obesity and comorbidities in school-age children in 2025. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO European Regional Obesity Report 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/publications/i/item/9789289057738 (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Reilly, J.J.; Kelly, J. Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: Systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, L.C.; Love, J.; Ratcliffe, B.; McNeill, G. Overweight and cardiovascular risk factors in 4- to 18-year-olds. Obes. Facts 2008, 1, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biener, A.; Cawley, J.; Meyerhoefer, C. The Impact of Obesity on Medical Care Costs and Labor Market Outcomes in the US. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Errico, M.; Pavlova, M.; Spandonaro, F. The economic burden of obesity in Italy: A cost-of-illness study. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2022, 23, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WOA World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2023. Available online: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=19 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Galmiche, M.; Déchelotte, P.; Lambert, G.; Tavolacci, M.P. Prevalence of eating disorders over the 2000-2018 period: A systematic literature review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.S.K.; Tan, L.E.S.; Davis, C.; Chew, C.S.E. Eating disorders in children and adolescents. Singapore Med. J. 2022, 63, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerle, F.; Huss, M.; Ernst, V.; Bürger, A. Thinking dimensional: Prevalence of DSM-5 early adolescent full syndrome, partial and subthreshold eating disorders in a cross-sectional survey in German schools. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, H.; Wan, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, D. An update on the prevalence of eating disorders in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.; O’Sullivan, E.; Kearney, J. Considerations for health and food choice in adolescents. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2022, 81, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore Heslin, A.; McNulty, B. Adolescent nutrition and health: Characteristics, risk factors and opportunities of an overlooked life stage. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2023, 82, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, S.G.; Sallis, J.F.; Pate, R.R.; Freedson, P.S.; Taylor, W.C.; Dowda, M. Evaluating a model of parental influence on youth physical activity. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2003, 25, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Conde, M.G.; Marin, L.; Maya, S.R.; Cuestas, P.J. Parental Attitudes to Childhood Overweight: The Multiple Paths through Healthy Eating, Screen Use, and Sleeping Time. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, L.; Wu, Y.; Wilson, R.F.; Weston, C.; Fawole, O.; Bleich, S.N.; Cheskin, L.J.; Showell, N.N.; Lau, B.D.; et al. What childhood obesity prevention programmes work? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metos, J.M.; Sarnoff, K.; Jordan, K.C. Teachers’ Perceived and Desired Roles in Nutrition Education. J. Sch. Health 2019, 89, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghazi, F.; Eslami, M.; Ehsani, A.; Ejtahed, H.S.; Qorbani, M. Eating habits of children and adolescents during the COVID-19 era: A systematic review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 18, 1004953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KomPAN®. Dietary Habits and Nutrition Beliefs Questionnaire and the Manual for Developing of Nutritional Data, 2nd ed.; Committee of Human Nutrition, Polish Academy of Sciences: Olsztyn, Poland, 2020; Available online: https://knozc.pan.pl/images/stories/MLonnie/KomPAN_manual_english_version_25-11-2020_last_korekta_2021.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Hamułka, J.; Wadolowska, L.; Hoffmann, M.; Kowalkowska, J.; Gutkowska, K. Effect of an Education Program on Nutrition Knowledge, Attitudes toward Nutrition, Diet Quality, Lifestyle, and Body Composition in Polish Teenagers. The ABC of Healthy Eating Project: Design, Protocol, and Methodology. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalkowska, J.; Wadolowska, L.; Hamulka, J.; Wojtas, N.; Czlapka-Matyasik, M.; Kozirok, W.; Bronkowska, M.; Sadowska, J.; Naliwajko, S.; Dziaduch, I.; et al. Reproducibility of a Short-Form, Multicomponent Dietary Questionnaire to Assess Food Frequency Consumption, Nutrition Knowledge, and Lifestyle (SF-FFQ4PolishChildren) in Polish Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzielska, A.; Mazur, J.; Małkowska-Szkutnik, A.; Kołoło, H. Adaptation of the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ-13) for school-aged adolescents in a population study. Probl. Hig. Epidemiol. 2009, 90, 362–369. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, H.S.; Greer, B. Participant observation and interviewing: A comparison. Hum. Organ. 1957, 16, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.W.; Shamdasani, D.M. Focus Groups: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed.; Sage Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, K.; Freeman, R. Critical health promotion and education: A new research challenge. Health Educ. Res. Theory Pract. 2004, 19, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Casadei, K.; Kiel, J. Anthropometric Measurement; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Świąder-Leśniak, A.; Kułaga, Z.; Grajda, A.; Gurzkowska, B.; Góźdź, M.; Wojtyło, M.; Różdżyńska-Świątkowska, A.; Litwin, M. References for waist and hip circumferences in Polish children and adolescents 3–18 year of age. Stand. Med. Pediatr. 2015, 12, 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Tanita Manual: Children & Body Fat. Available online: http://www.tanitapolska.pl/baza-wiedzy/analiza-wynikow-pomiarowych (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Ploegmakers, J.J.; Hepping, A.M.; Geertzen, J.H.; Bulstra, S.K.; Stevens, M. Grip strength is strongly associated with height, weight and gender in childhood: A cross sectional study of 2241 children and adolescents providing reference values. J. Physiother. 2013, 59, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.D.; Voss, C.; Taylor, M.J.; Stasinopoulos, D.M.; Delextrat, A.; Sandercock, G.R. Handgrip strength in English schoolchildren. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ou, J.; Hong, Q.; Ji, C.; Chi, X.; Tong, M. Hand anthropometry and its relation to grip/pinch strength in children aged 5 to 13 years. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520970768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piramida Zdrowego Zywienia i Aktywnosci Fizycznej. Available online: https://ncez.pzh.gov.pl/dzieci-i-mlodziez/piramida-zdrowego-zywienia-i-stylu-zycia-dzieci-i-mlodziezy-2/ (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Herforth, A.; Arimond, M.; Álvarez-Sánchez, C.; Coates, J.; Christianson, K.; Muehlhoff, E. A Global Review of Food-Based Dietary Guidelines. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 590–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kułaga, Z.; Świąder-Leśniak, A.; Kotowska, A.; Litwin, M. Population-based references for waist and hip circumferences, waist-to-hip and waist-to-height ratios for children and adolescents, and evaluation of their predictive ability. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 3217–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kułaga, Z.; Różdżyńska-Świątkowska, A.; Grajda, A.; Gurzkowska, B.; Wojtyło, M.; Góźdź, M.; Świąder-Leśniak, A.; Litwin, M. Percentile charts for growth and nutritional status assessment in Polish children and adolescents from birth to 18 year of age. Stand. Med. Pediatr. 2015, 12, 119–135. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, H.D.; Samani-Radia, D.; Jebb, S.A. Prentice AM. Skeletal muscle mass reference curves for children and adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 9, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, H.D.; Cole, T.J.; Fry, T.; Jebb, S.A.; Prentice, A.M. Body fat reference curves for children. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Nardone, P.; Starc, G.; Hejgaard, T.; Júlíusson, P.B.; Fismen, A.S.; Weghuber, D.; Musić Milanović, S.; García-Solano, M.; et al. Thinness, overweight, and obesity in 6- to 9-year-old children from 36 countries: The World Health Organization European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative-COSI 2015-2017. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.; Llewellyn, A.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Predicting adult obesity from childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, X.N.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.Q. Family-related risk factors of obesity among preschool children: Results from a series of national epidemiological surveys in China. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares, G.; De Ross, S.; Mueller, C.; Phillippe, K.; Pickard, A.; Nicklaus, S.; van Kleef, E.; Varela, P. Development of food literacy in children and adolescents: Implications for the design of strategies to promote healthier and more sustainable diets. Nutr. Rev. 2023, nuad072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jawaldeh, A.; Matbouli, D.; Diab, S.; Taktouk, M.; Hojeij, L.; Naalbandian, S.; Nasreddine, L. School-Based Nutrition Programs in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, T.; Agaronov, A.; Young, T.; Aftosmes-Tobio, A.; Davison, K.K. Family-based childhood obesity prevention interventions: A systematic review and quantitative content analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelino, M.; Tagi, V.M.; Chiarelli, F. Cardiovascular risk in children: A burden for future generations. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNICEF/WHO/World Bank Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates: 2021 Edition Interactive Dashboard; United Nations Children’s Fund: New York, NY, USA, 2021. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/resources/joint-child-malnutrition-estimates-interactive-dashboard-2021 (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Kobel, S.; Wartha, O.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Feather, K.E.; Steinacker, J.M. Intervention effects of a school-based health promotion programme on children’s nutrition behaviour. J. Public Health 2023, 31, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsaki, M.; Saltaouras, G.; Diamantopoulou, E.; Dardavessis, T.; Androutsos, O. Teachers’ awareness and perceptions of Health Education Nutrition Programmes in Greece: A qualitative study. Health Educ. J. 2022, 81, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, A.L.; Antikainen, A.; Mikkonen, S.; Kähkönen, K.; Talvia, S.; Varjonen, S.; Paavola, S.; Karhunen, L.; Tilles-Tirkkonen, T. The ’Tasty School’ model is feasible for food education in primary schools. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2023, 36, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudin, V.; Stranges, S.; Wilk, P.; Sarma, S. School nutrition policy and diet quality of children and youth: A quasi-experimental study from Canada. Can. J. Public Health 2023, 114, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egg, S.; Wakolbinger, M.; Reisser, A.; Schätzer, M.; Wild, B.; Rust, P. Relationship between nutrition knowledge, education and other determinants of food intake and lifestyle habits among adolescents from urban and rural secondary schools in Tyrol, Western Austria. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 3136–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follong, B.; Verdonschot, A.; Prieto-Rodriguez, E.; Miller, A.; Collins, C.; Bucher, T. Nutrition across the curriculum: A scoping review exploring the integration of nutrition education within primary schools. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2022, 35, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Macroregion: | Children/Adolescents | Parents/Caregivers | Teachers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aged 7–9 Years | Aged 10–12 Years | |||
| Central | 3980 (27.3) | 3113 (24.5) | 4105 (24.0) | 598 (22.9) |
| South-Eastern | 3194 (21.9) | 2767 (21.8) | 4166 (24.4) | 642 (24.5) |
| South-Western | 2017 (13.8) | 1548 (12.2) | 2167 (12.7) | 322 (12.3) |
| North-Eastern | 3481 (23.8) | 3243 (25.5) | 3738 (21.9) | 696 (26.6) |
| North-West | 1928 (13.2) | 2024 (16.0) | 2894 (17.0) | 358 (13.7) |
| Total | 14,600 | 12,695 | 17,070 | 2616 |
| Criteria | Children/Adolescents | Parents/Caregivers | Teachers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusion |
|
|
|
| Exclusion |
|
|
|
| Objectives | Methods and Tools | Population Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children/ Adolescents | Parents/ Caregivers | Teachers | ||
| Assessment of children’s dietary habits | Food frequency method using validated questionnaires: | |||
| x | x | ||
| x | ||||
| x | |||
| Assessment of children’s lifestyle including physical activity, screen, and sleep time | Questionnaire method: | |||
| x | x | ||
| Assessment of knowledge toward food and nutrition in children/adolescents, parents, and teachers | Questionnaire method: | |||
| x | x | x | |
| x | ||||
| x | |||
| x | |||
| Parameter (Units) | Procedure, Accuracy, and Equipment |
|---|---|
| Height (H) (cm) |
|
| Body weight (BW) (kg) |
|
| Waist circumference (WC) (cm) |
|
| Hip circumference (HC) (cm) |
|
| Body composition (BC) |
|
| Hand grip strength (HGS) (kg) |
|
| Macroregion: | Children/Adolescents | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aged 7–9 Years | Aged 10–12 Years | ||
| Central | 2694 (27.0) | 1993 (23.3) | 4687 (25.2) |
| South-Eastern | 1660 (16.7) | 1447 (16.9) | 3107 (16.8) |
| South-Western | 1002 (10.0) | 917 (10.8) | 1919 (10.4) |
| North-Eastern | 2866 (28.7) | 2609 (30.5) | 5475 (29.6) |
| North-West | 1751 (17.6) | 1582 (18.5) | 3333 (18.0) |
| Total | 9973 | 8548 | 18,521 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamulka, J.; Czarniecka-Skubina, E.; Gutkowska, K.; Drywień, M.E.; Jeruszka-Bielak, M. Nutrition-Related Knowledge, Diet Quality, Lifestyle, and Body Composition of 7–12-Years-Old Polish Students: Study Protocol of National Educational Project Junior-Edu-Żywienie (JEŻ). Nutrients 2024, 16, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010004
Hamulka J, Czarniecka-Skubina E, Gutkowska K, Drywień ME, Jeruszka-Bielak M. Nutrition-Related Knowledge, Diet Quality, Lifestyle, and Body Composition of 7–12-Years-Old Polish Students: Study Protocol of National Educational Project Junior-Edu-Żywienie (JEŻ). Nutrients. 2024; 16(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamulka, Jadwiga, Ewa Czarniecka-Skubina, Krystyna Gutkowska, Małgorzata Ewa Drywień, and Marta Jeruszka-Bielak. 2024. "Nutrition-Related Knowledge, Diet Quality, Lifestyle, and Body Composition of 7–12-Years-Old Polish Students: Study Protocol of National Educational Project Junior-Edu-Żywienie (JEŻ)" Nutrients 16, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010004
APA StyleHamulka, J., Czarniecka-Skubina, E., Gutkowska, K., Drywień, M. E., & Jeruszka-Bielak, M. (2024). Nutrition-Related Knowledge, Diet Quality, Lifestyle, and Body Composition of 7–12-Years-Old Polish Students: Study Protocol of National Educational Project Junior-Edu-Żywienie (JEŻ). Nutrients, 16(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010004