Efficacy of Probiotic Supplements on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Inflammatory Biomarkers, Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Function in Patients with Alzheimer’s Dementia: A 12-Week Randomized, Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Probiotic Strains
2.3. Intervention and Measurements
2.3.1. Assessment of Biochemical Parameters
2.3.2. Assessment for Cognitive and Daily Living Function
2.3.3. Fecal DNA Extraction and NGS Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
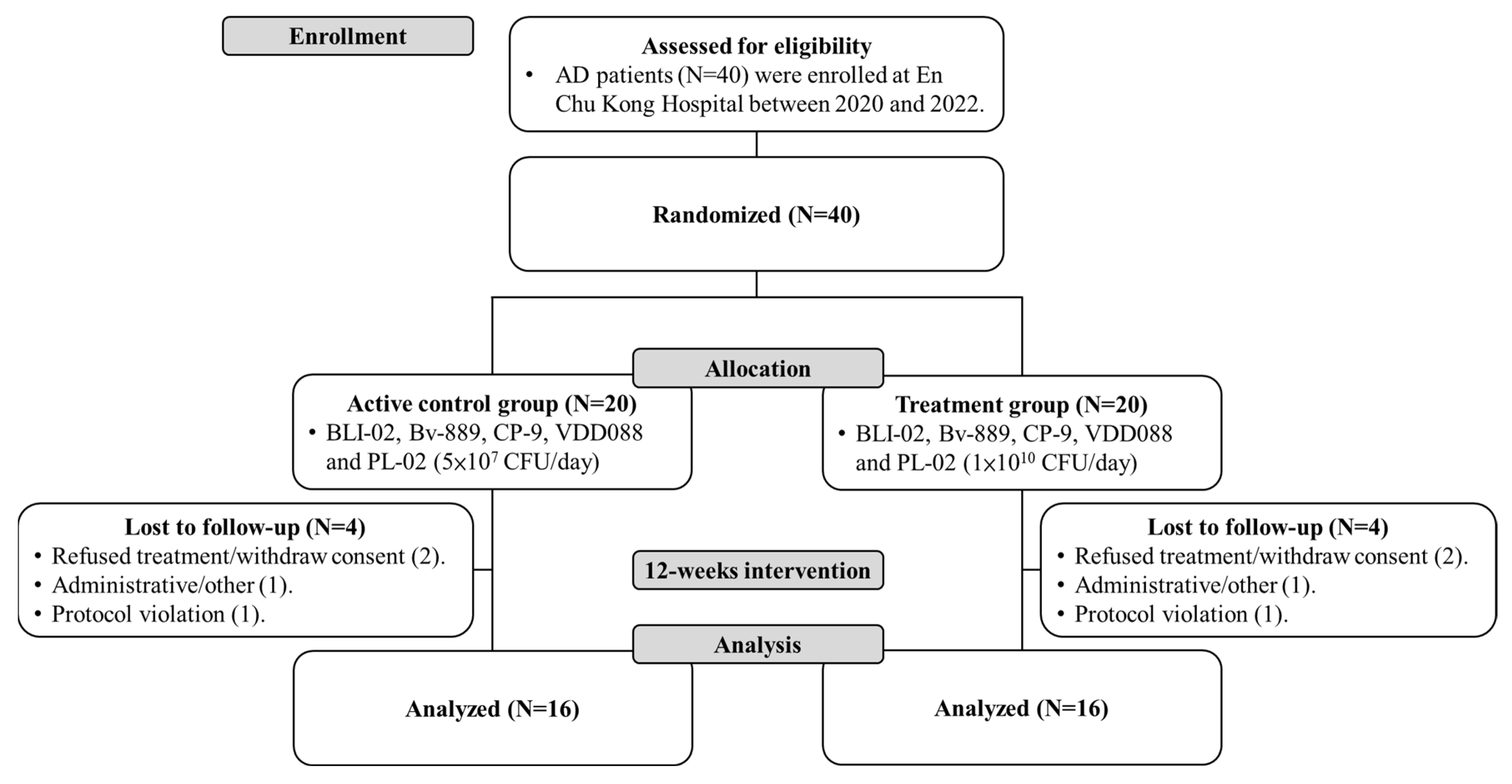
3.1. Participant Recruitment
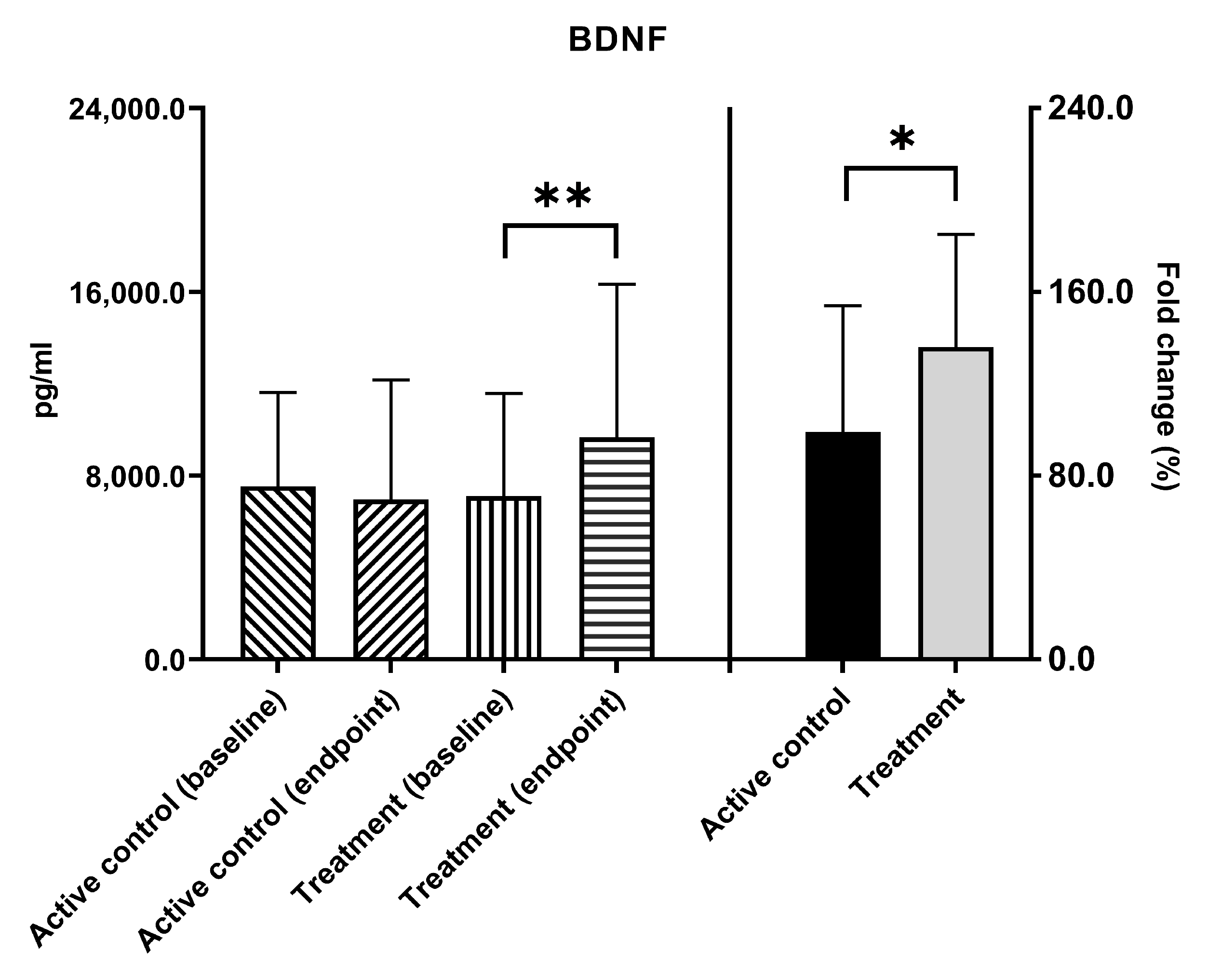
3.2. BDNF Levels
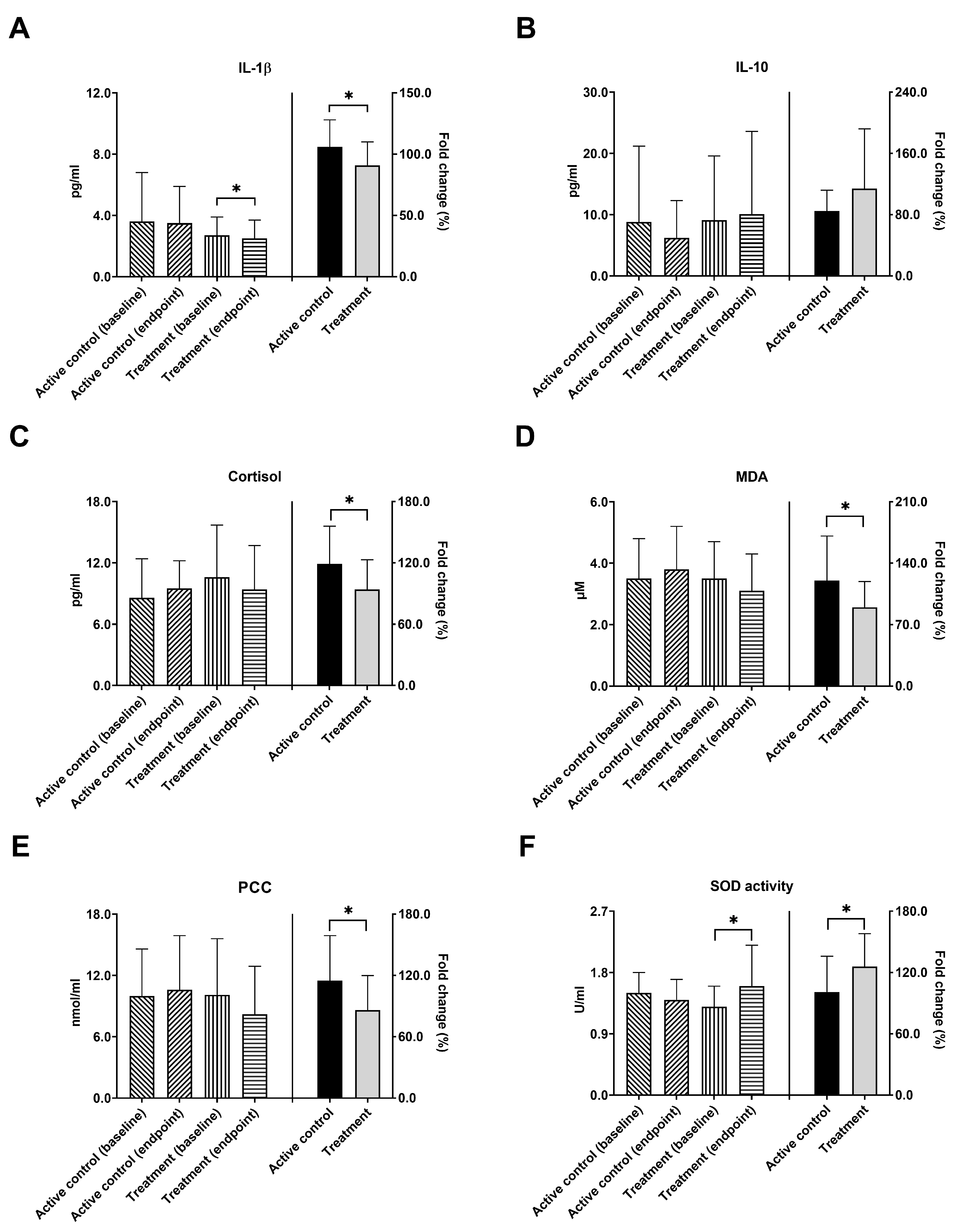
3.3. Inflammatory Biomarkers, Cortisol Levels, and Antioxidant Capacity
3.4. Cognitive Function
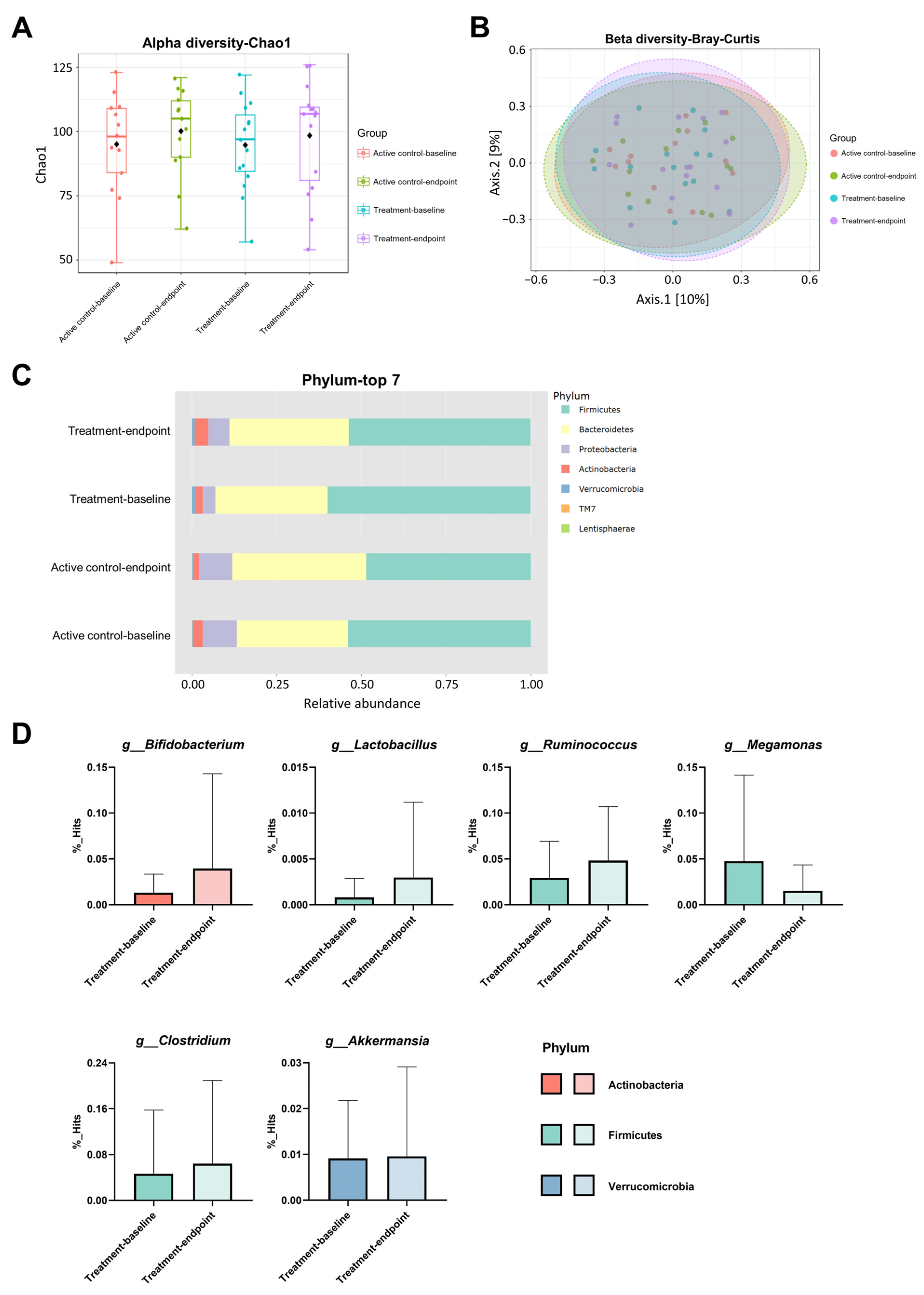
3.5. Changes in the Gut Microbiota Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on the Public Health Response to Dementia 2017–2025; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on the Public Health Response to Dementia; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; William, C.M.; Ferrer, I.; Uro-Coste, E.; Delisle, M.B.; Maurage, C.A.; Hock, C.; Nitsch, R.M.; Masliah, E.; Growdon, J.H.; et al. Beneficial effect of human anti-amyloid-beta active immunization on neurite morphology and tau pathology. Brain 2010, 133, 1312–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Siviero, P.; Minicuci, N.; Bellavista, E.; Mishto, M.; Olivieri, F.; Marchegiani, F.; Chiamenti, A.M.; Benussi, L.; Ghidoni, R.; et al. Effects of donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine in 938 Italian patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A prospective, observational study. CNS Drugs 2010, 24, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, C.G.; Stoffler, A.; Danysz, W. Memantine: A NMDA receptor antagonist that improves memory by restoration of homeostasis in the glutamatergic system—Too little activation is bad, too much is even worse. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 699–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hort, J.; Valis, M.; Angelucci, F. Administration of pre/probiotics with conventional drug treatment in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 448–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, E.M.M. Microbiota-Brain-Gut Axis and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Alam, M.T.; Dey, J.; Sasidharan, B.C.P.; Ray, U.; Srivastava, A.K.; Gandhi, S.; Tripathi, P.P. Healthy Gut, Healthy Brain: The Gut Microbiome in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemimah, S.; Chabib, C.M.M.; Hadjileontiadis, L.; AlShehhi, A. Gut microbiome dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.B.; Kobayashi, Y.; Xiao, J. Probiotics for preventing cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. In Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 85–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, T.K.S.; Ho, C.S.H.; Tam, W.W.S.; Kua, E.H.; Ho, R.C. Decreased Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease (AD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, F.; Abdollahi, S.; Shidfar, F.; Clark, C.C.T.; Soltani, S. Probiotics supplementation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Heidari-Soureshjani, R.; Mirhosseini, N.; Kouchaki, E.; Bahmani, F.; Aghadavod, E.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Asemi, Z. Probiotic and selenium co-supplementation, and the effects on clinical, metabolic and genetic status in Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.Y.; Lin, J.H.; Kuo, Y.W.; Chiang, P.R.; Ho, H.H. Probiotics and their Metabolites Reduce Oxidative Stress in Middle-Aged Mice. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanborn, V.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Updegraff, J.; Manderino, L.; Gunstad, J. Randomized Clinical Trial Examining the Impact of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Probiotic Supplementation on Cognitive Functioning in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 2765–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Katsumata, N.; Bernier, F.; Ohno, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Odamaki, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Ito, K.; Kaneko, T. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in Improving Cognitive Functions of Older Adults with Suspected Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 77, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, J.F.; Hillesheim, E.; Pereira, A.; Camargo, C.Q.; Rabito, E.I. Probiotics for dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Toshimitsu, T.; Okada, E.; Anzai, S.; Shiraishi, I.; Inamura, N.; Kobayashi, S.; Sashihara, T.; Hisatsune, T. Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum OLL2712 on Memory Function in Older Adults with Declining Memory: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-de-Lara-Sanchez, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.M. Probiotics treatment can improve cognition in patients with mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 89, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yang, D.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. Probiotic supplements are effective in people with cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, M.; Zou, Z. Efficacy of probiotics on cognition, and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in adults with Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment—A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Aging 2020, 12, 4010–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naomi, R.; Embong, H.; Othman, F.; Ghazi, H.F.; Maruthey, N.; Bahari, H. Probiotics for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morey, L.C.; Bender, D.S.; Skodol, A.E. Validating the proposed diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edition, severity indicator for personality disorder. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2013, 201, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group* under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.C. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): Current version and scoring rules. Neurology 1993, 43, 2412–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, W.G.; Mohs, R.C.; Davis, K.L. A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Psychiatry 1984, 141, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasko, D.; Bennett, D.; Sano, M.; Ernesto, C.; Thomas, R.; Grundman, M.; Ferris, S. An inventory to assess activities of daily living for clinical trials in Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1997, 11 (Suppl. 2), S33–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.S.; Shen, L.L.; Zhu, C.; Bu, X.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, C.H.; Yao, X.Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhou, H.D.; Walker, D.G.; et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects against tau-related neurodegeneration of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Van Hoecke, L.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. The Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 796867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouanes, S.; Popp, J. High Cortisol and the Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, E.; Polidori, M.C.; Cherubini, A.; Mecocci, P. Oxidative stress in brain aging, neurodegenerative and vascular diseases: An overview. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 827, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A.; Munoz, M.F.; Arguelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Makizako, H.; Doi, T.; Yoshida, D.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Anan, Y.; Uemura, K.; Lee, S.; Park, H.; Suzuki, T. A large, cross-sectional observational study of serum BDNF, cognitive function, and mild cognitive impairment in the elderly. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyhe, T.; Stransky, E.; Eschweiler, G.W.; Buchkremer, G.; Laske, C. Increase of BDNF serum concentration during donepezil treatment of patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 258, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.W.; Bressel, E.; Kim, D.Y. Effects of aquatic exercise on insulin-like growth factor-1, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and cognitive function in elderly women. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 132, 110842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Yun, S.W.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. DW2009 Elevates the Efficacy of Donepezil against Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Cha, L.; Sim, M.; Jung, S.; Chun, W.Y.; Baik, H.W.; Shin, D.M. Probiotic Supplementation Improves Cognitive Function and Mood with Changes in Gut Microbiota in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Trial. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Balazs, R.; Soiampornkul, R.; Thangnipon, W.; Cotman, C.W. Interleukin-1 beta impairs brain derived neurotrophic factor-induced signal transduction. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1380–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, E.L.; Ma, M.J. Alzheimer Disease: Clues from traditional and complementary medicine. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwilasz, A.J.; Grace, P.M.; Serbedzija, P.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. The therapeutic potential of interleukin-10 in neuroimmune diseases. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Andrade, V.; Navarrete, L.P.; Pastor, M.G.; Ramos-Escobar, N. Neuroinflammation as a Common Feature of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, G.A.; O’Connor, J.C. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and inflammation in depression: Pathogenic partners in crime? World J. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saresella, M.; La Rosa, F.; Piancone, F.; Zoppis, M.; Marventano, I.; Calabrese, E.; Rainone, V.; Nemni, R.; Mancuso, R.; Clerici, M. The NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes are activated in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.W.; Lui, C.C.; Chang, W.N.; Lu, C.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Chang, C.C. Elevated basal cortisol level predicts lower hippocampal volume and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 16, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniilidou, M.; Hagman, G.; Holleman, J.; Sindi, S.; Brinkmalm, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Solomon, A.; Sandebring-Matton, A.; Kivipelto, M. Stress and Alzheimer’s disease: Linking salivary cortisol to biomarkers of neurodegeneration and cognitive decline in a memory clinic cohort. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 17, e054907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laske, C.; Stransky, E.; Fritsche, A.; Eschweiler, G.W.; Leyhe, T. Inverse association of cortisol serum levels with T-tau, P-tau 181 and P-tau 231 peptide levels and T-tau/Abeta 1-42 ratios in CSF in patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 259, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, C.; Li, J.V.; Marchesi, J.R.; Plummer, S.; Garaiova, I.; Good, M.A. Long-term multi-species Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium dietary supplement enhances memory and changes regional brain metabolites in middle-aged rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 144, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markesbery, W.R. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padurariu, M.; Ciobica, A.; Lefter, R.; Lacramioara Serban, I.; Stefanescu, C.; Chirita, R. The oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatr. Danub. 2013, 25, 401–409. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, P.; Polidori, M.C.; Metastasio, A.; Mariani, E.; Mattioli, P.; Cherubini, A.; Catani, M.; Cecchetti, R.; Senin, U.; Mecocci, P. Plasma antioxidants are similarly depleted in mild cognitive impairment and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vina, J.; Lloret, A.; Orti, R.; Alonso, D. Molecular bases of the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease with antioxidants: Prevention of oxidative stress. Mol. Asp. Med. 2004, 25, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Delmas-Beauvieux, M.C.; Peuchant, E.; Richard-Harston, S.; Decamps, A.; Reignier, B.; Emeriau, J.P.; Rainfray, M. Antioxidant defences and oxidative stress markers in erythrocytes and plasma from normally nourished elderly Alzheimer patients. Age Ageing 2001, 30, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, A.; Fordjour, L.; Ahmad, A.; Cai, C.; Kumar, D.; Valencia, G.; Aranda, J.V.; Beharry, K.D. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on messenger RNA expression of caveolin-1, NOS, and genes regulating oxidative stress in the terminal ileum of formula-fed neonatal rats. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, D.; Kansal, V.K. Probiotic Dahi containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum alleviates age-inflicted oxidative stress and improves expression of biomarkers of ageing in mice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaoka, D.; Xiao, J.; Takeda, T.; Yanagisawa, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Matsubara, Y.; Sugiyama, H.; Endo, N.; Higa, M.; Kasanuki, K.; et al. Effect of Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in Improving Cognitive Function and Preventing Brain Atrophy in Older Patients with Suspected Mild Cognitive Impairment: Results of a 24-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 88, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609.e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Sisodia, S.S.; Vassar, R.J. The gut microbiome in Alzheimer’s disease: What we know and what remains to be explored. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Z.Q.; Shen, L.L.; Li, W.W.; Fu, X.; Zeng, F.; Gui, L.; Lu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhu, C.; Tan, Y.L.; et al. Gut Microbiota is Altered in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamujić-Čomić, H.; Ahmad, S.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Bonnechere, B.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.F.; Kraaij, R.; Ikram, M.A.; Amin, N.; van Duijn, C.M. Clostridium shows a higher abundance in less neurovascular and neurodegenerative changes: A microbiome-wide association study: Genetics/omics and systems biology. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, e044743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.B.; Zhang, Y.C.; Huang, H.H.; Lin, J. Prospects for clinical applications of butyrate-producing bacteria. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Deng, L.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F.; Liu, W.; Huang, D.; Peng, Y. Protective effects of Akkermansia muciniphila on cognitive deficits and amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Active Control Group | Treatment Group | a p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 75.8 ± 7.3 | 75.4 ± 8.0 | 0.872 | |||
| Gender (female/male) | 8/8 | 12/4 | 0.144 | |||
| AD assessment scales | Baseline | Endpoint | b p-value | Baseline | Endpoint | b p-value |
| ADAS-Cog | 21.3 ± 8.3 | 21.6 ± 7.7 | 0.711 | 25.9 ± 12.8 | 26.2 ± 10.8 | 0.768 |
| MMSE | 21.1 ± 3.8 | 21.4 ± 4.4 | 0.596 | 18.8 ± 4.5 | 18.9 ± 4.8 | 0.833 |
| ADL | 62.4 ± 12.3 | 62.7 ± 11.8 | 0.871 | 53.9 ± 12.7 | 51.0 ± 16.3 | 0.363 |
| CDR | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 0.497 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.751 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Lin, J.-H.; Ho, H.-H.; Chen, J.-F.; Hsia, K.-C.; Sun, Y. Efficacy of Probiotic Supplements on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Inflammatory Biomarkers, Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Function in Patients with Alzheimer’s Dementia: A 12-Week Randomized, Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010016
Hsu Y-C, Huang Y-Y, Tsai S-Y, Kuo Y-W, Lin J-H, Ho H-H, Chen J-F, Hsia K-C, Sun Y. Efficacy of Probiotic Supplements on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Inflammatory Biomarkers, Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Function in Patients with Alzheimer’s Dementia: A 12-Week Randomized, Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Yu-Chieh, Yen-Yu Huang, Shin-Yu Tsai, Yi-Wei Kuo, Jia-Hung Lin, Hsieh-Hsun Ho, Jui-Fen Chen, Ko-Chiang Hsia, and Yu Sun. 2024. "Efficacy of Probiotic Supplements on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Inflammatory Biomarkers, Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Function in Patients with Alzheimer’s Dementia: A 12-Week Randomized, Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study" Nutrients 16, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010016
APA StyleHsu, Y.-C., Huang, Y.-Y., Tsai, S.-Y., Kuo, Y.-W., Lin, J.-H., Ho, H.-H., Chen, J.-F., Hsia, K.-C., & Sun, Y. (2024). Efficacy of Probiotic Supplements on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Inflammatory Biomarkers, Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Function in Patients with Alzheimer’s Dementia: A 12-Week Randomized, Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study. Nutrients, 16(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010016






