Association of Eating Pattern, Chronotype, and Social Jetlag: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Data Accumulated in a Japanese Food-Logging Mobile Health Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Food-Logging mHealth App “Asken”
2.3. Participants, and Data Inclusion and Exclusion
2.4. Dietary Data
2.5. Questionnaires
2.6. Grouping of Chronotype and SJL
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics
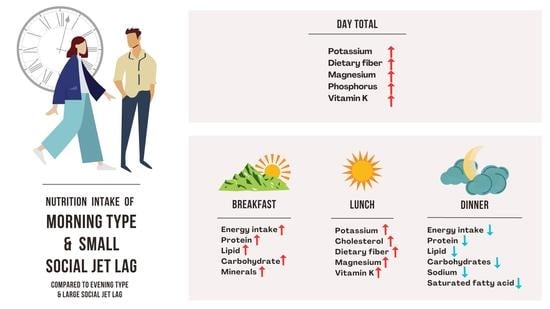
3.2. Chronotype/SJL Associated Eating Pattern
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roenneberg, T.; Merrow, M. The Circadian Clock and Human Health. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R432–R443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hida, A.; Kitamura, S.; Ohsawa, Y.; Enomoto, M.; Katayose, Y.; Motomura, Y.; Moriguchi, Y.; Nozaki, K.; Watanabe, M.; Aritake, S.; et al. In vitro circadian period is associated with circadian/sleep preference. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.E.; Lane, J.M.; Wood, A.R.; van Hees, V.T.; Tyrrell, J.; Beaumont, R.N.; Jeffries, A.R.; Dashti, H.S.; Hillsdon, M.; Ruth, K.S.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses of chronotype in 697,828 individuals provides insights into circadian rhythms. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roenneberg, T.; Allebrandt, K.V.; Merrow, M.; Vetter, C. Social jetlag and obesity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauducco, S.; Richardson, C.; Gradisar, M. Chronotype, circadian rhythms and mood. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2020, 34, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano-Hermoso, M.D.; Arbinaga, F.; Fernández-Ozcorta, E.J.; Gómez-Salgado, J.; Ruiz-Frutos, C. Influence of Sleeping Patterns in Health and Academic Performance Among University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facer-Childs, E.R.; Middleton, B.; Skene, D.J.; Bagshaw, A.P. Resetting the late timing of ‘night owls’ has a positive impact on mental health and performance. Sleep Med. 2019, 60, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, Y.; Shinto, T.; Inoue, K.; Roshanmehr, F.; Ito, A.; Michie, M.; Shibata, S. Changes in sleep phase and body weight of mobile health App users during COVID-19 mild lockdown in Japan. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 2277–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korman, M.; Tkachev, V.; Reis, C.; Komada, Y.; Kitamura, S.; Gubin, D.; Kumar, V.; Roenneberg, T. Outdoor daylight exposure and longer sleep promote wellbeing under COVID-19 mandated restrictions. J. Sleep Res. 2022, 31, e13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnebeck, E.C.; Vuori-Brodowski, M.T.; Biller, A.M.; Molenda, C.; Fischer, D.; Zerbini, G.; Roenneberg, T. Later school start times in a flexible system improve teenage sleep. Sleep 2020, 43, zsz307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoosawi, S.; Vingeliene, S.; Gachon, F.; Voortman, T.; Palla, L.; Johnston, J.D.; Van Dam, R.M.; Darimont, C.; Karagounis, L.G. Chronotype: Implications for Epidemiologic Studies on Chrono-Nutrition and Cardiometabolic Health. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazri, F.H.; Manaf, Z.A.; Shahar, S.; Mat Ludin, A.F. The Association between Chronotype and Dietary Pattern among Adults: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoi, Y.Y.; Rogers, M.; Bonham, M.P.; Dorrian, J.; Coates, A.M. A scoping review of chronotype and temporal patterns of eating of adults: Tools used, findings, and future directions. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2021, 35, 112–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Merwe, C.; Münch, M.; Kruger, R. Chronotype Differences in Body Composition, Dietary Intake and Eating Behavior Outcomes: A Scoping Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 2357–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato-Mito, N.; Shibata, S.; Sasaki, S.; Sato, K. Dietary intake is associated with human chronotype as assessed by both morningness-eveningness score and preferred midpoint of sleep in young Japanese women. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 62, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mito, N.; Fujimoto, E.; Sasaki, S.; The Three-Generation Study of Women on Diets and Health Study Group. Association of chronotype as assessed by the midpoint of sleep with the dietary intake and health-related quality of life for elderly Japanese women. J. Nutr. Sci. 2021, 10, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, T.; Togo, F. Objectively measured chronotype and social jetlag are associated with habitual dietary intake in undergraduate students. Nutr. Res. 2021, 90, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.C.; Silva, C.M.; Balieiro, L.C.T.; Gonçalves, B.F.; Fahmy, W.M.; Crispim, C.A. Association between social jetlag food consumption and meal times in patients with obesity-related chronic diseases. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asken. Available online: https://en.asken.inc/ (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Shimpo, M.; Fukkoshi, Y.; Akamatsu, R. Correlations between self-efficacy in resisting six temptations and dietary energy and macronutrient intake at each meal. Eat. Behav. 2014, 15, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, N.; Murakami, K. Evaluation of the Ability of Diet-Tracking Mobile Applications to Estimate Energy and Nutrient Intake in Japan. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S. Dietary Reference Intakes for Japanese (2015): An Outline and Its Academic and Practical Significance. Nippon. Eiyo Shokuryo Gakkaishi 2017, 70, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.; Hida, A.; Aritake, S.; Higuchi, S.; Enomoto, M.; Kato, M.; Vetter, C.; Roenneberg, T.; Mishima, K. Validity of the Japanese version of the Munich ChronoType Questionnaire. Chronobiol. Int. 2014, 31, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okajima, I.; Nakajima, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Inoue, Y. Development and validation of the Japanese version of the Athens Insomnia Scale. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 67, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, Y.; Makino, S.; Suiko, T.; Nagamori, Y.; Iwai, T.; Aono, M.; Shibata, S. Association between Irregular Meal Timing and the Mental Health of Japanese Workers. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, M.; Sasaki, H.; Shinto, T.; Tahara, Y.; Makino, S.; Kuwahara, M.; Tada, A.; Abe, N.; Michie, M.; Shibata, S. Association Between Na, K, and Lipid Intake in Each Meal and Blood Pressure. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 853118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinto, T.; Makino, S.; Tahara, Y.; Nitta, L.; Kuwahara, M.; Tada, A.; Abe, N.; Michie, M.; Shibata, S. Relationship Between Protein Intake in Each Traditional Meal and Physical Activity: Cross-sectional Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill 2022, 8, e35898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleig, D.; Randler, C. Association between chronotype and diet in adolescents based on food logs. Eat. Behav. 2009, 10, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maukonen, M.; Kanerva, N.; Partonen, T.; Kronholm, E.; Konttinen, H.; Wennman, H.; Männistö, S. The associations between chronotype, a healthy diet and obesity. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Veronese, N.; Solmi, M.; Caruso, M.G.; Giannelli, G.; Osella, A.R.; Evangelou, E.; Maggi, S.; Fontana, L.; Stubbs, B.; Tzoulaki, I. Dietary fiber and health outcomes: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.; Caballero, B.H.; Cousins, R.J.; Tucker, K.L.; Ziegler, T.R. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 11th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health ADIS (ESP): London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, A.R.; Anderson, C. Dietary Phosphorus Intake and the Kidney. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2017, 37, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salma; Ahmad, S.S.; Karim, S.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Alkreathy, H.M.; Alsieni, M.; Khan, M.A. Effect of Vitamin K on Bone Mineral Density and Fracture Risk in Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeron-Rugerio, M.F.; Cambras, T.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M. Social Jet Lag Associates Negatively with the Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Body Mass Index among Young Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, G.M.; Hale, L.; Chang, A.M. Social jetlag, eating behaviours and BMI among adolescents in the USA. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetiner, O.; Yildirim, G.; Kalyoncu, Z.B. Social Jetlag Is Associated with the Frequency of Consumption of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and a High BMI Percentile in Adolescents: Results of the Cross-Sectional Family Life, Activity, Sun, Health, and Eating (FLASHE) Study. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet 2021, 121, 1721–1731.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Shibata, S. Chronobiology and nutrition. Neuroscience 2013, 253, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, A.; Nagahama, H.; Tsuboi, T.; Hirao, M.; Tahara, Y.; Shibata, S. Combination of starvation interval and food volume determines the phase of liver circadian rhythm in Per2::Luc knock-in mice under two meals per day feeding. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G1045–G1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Fuse, Y.; Hirao, A.; Shibata, S. Refeeding after fasting elicits insulin-dependent regulation of Per2 and Rev-erbα with shifts in the liver clock. J. Biol. Rhythms. 2011, 26, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, P.; Hamnett, R.; Putker, M.; Hoyle, N.P.; Reed, M.; Karam, C.J.; Maywood, E.S.; Stangherlin, A.; Chesham, J.E.; Hayter, E.A.; et al. Insulin/IGF-1 Drives PERIOD Synthesis to Entrain Circadian Rhythms with Feeding Time. Cell 2019, 177, 896–909.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsamis, N.A.; Christou, G.A.; Kiortsis, D.N. A critical review of the effects of vitamin K on glucose and lipid homeostasis: Its potential role in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. Hormones 2021, 20, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa Melo, S.R.; Dos Santos, L.R.; da Cunha Soares, T.; Cardoso, B.E.P.; da Silva Dias, T.M.; Morais, J.B.S.; de Paiva Sousa, M.; de Sousa, T.G.V.; da Silva, N.C.; da Silva, L.D.; et al. Participation of Magnesium in the Secretion and Signaling Pathways of Insulin: An Updated Review. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Chijiki, H.; Nanba, T.; Ozaki, M.; Sasaki, H.; Takahashi, M.; Shibata, S. Ingestion of Helianthus tuberosus at Breakfast Rather Than at Dinner Is More Effective for Suppressing Glucose Levels and Improving the Intestinal Microbiota in Older Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, M.; Kim, H.K.; Ozaki, M.; Nanba, T.; Chijiki, H.; Fukazawa, M.; Okubo, J.; Mineshita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Shibata, S. Consumption of Biscuits with a Beverage of Mulberry or Barley Leaves in the Afternoon Prevents Dinner-Induced High, but Not Low, Increases in Blood Glucose among Young Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, A.; Fukuzawa, M.; Iwami, S.; Nishimura, Y.; Motohashi, H.; Tahara, Y.; Shibata, S. Night eating model shows time-specific depression-like behavior in the forced swimming test. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Kamagata, M.; Hirao, M.; Yasuda, S.; Iwami, S.; Sasaki, H.; Tsubosaka, M.; Hattori, Y.; Todoh, A.; Tamura, K.; et al. Glucagon and/or IGF-1 Production Regulates Resetting of the Liver Circadian Clock in Response to a Protein or Amino Acid-only Diet. EBioMedicine 2018, 28, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, S.; Kim, H.K.; Hirooka, R.; Tanaka, M.; Shimoda, T.; Chijiki, H.; Kojima, S.; Sasaki, K.; Takahashi, K.; Makino, S.; et al. Distribution of dietary protein intake in daily meals influences skeletal muscle hypertrophy via the muscle clock. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Akter, S.; Kochi, T.; Hu, H.; Eguchi, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kuwahara, K.; Kabe, I.; Mizoue, T. Association of social jetlag with metabolic syndrome among Japanese working population: The Furukawa Nutrition and Health Study. Sleep Med. 2018, 51, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cajochen, C.; Khatami, R. Social Jetlag and Chronotypes in the Chinese Population: Analysis of Data Recorded by Wearable Devices. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e13482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, N.; Ding, K.; Zeng, J.; Moore, J.B.; Li, R. Associations of Social Jetlag with Dietary Behavior, Physical Activity and Obesity among Chinese Adolescents. Nutrients 2022, 14, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.L. The emerging importance of tackling sleep-diet interactions in lifestyle interventions for weight management. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrabec, A.; Yuhas, M.; Deyo, A.; Kidwell, K. Social jet lag and eating styles in young adults. Chronobiol. Int. 2022, 39, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, A.; Bechtold, D.A.; Pot, G.K.; Johnston, J.D. Chrono-nutrition: From molecular and neuronal mechanisms to human epidemiology and timed feeding patterns. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerón-Rugerio, M.F.; Hernáez, Á.; Porras-Loaiza, A.P.; Cambras, T.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M. Eating Jet Lag: A Marker of the Variability in Meal Timing and Its Association with Body Mass Index. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarem, N.; Sears, D.D.; St-Onge, M.P.; Zuraikat, F.M.; Gallo, L.C.; Talavera, G.A.; Castaneda, S.F.; Lai, Y.; Aggarwal, B. Variability in Daily Eating Patterns and Eating Jetlag Are Associated With Worsened Cardiometabolic Risk Profiles in the American Heart Association Go Red for Women Strategically Focused Research Network. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e022024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Ozaki, M.; Kang, M.-I.; Sasaki, H.; Fukazawa, M.; Iwakami, T.; Lim, P.J.; Kim, H.-K.; Aoyama, S.; Shibata, S. Effects of Meal Timing on Postprandial Glucose Metabolism and Blood Metabolites in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Okuda, T.; Shinohara, H.; Yamasaki, R.S.; Hirano, N.; Kang, J.; Ogawa, M.; Nishi, N.N. Relationship between Seasonal Changes in Food Intake and Energy Metabolism, Physical Activity, and Body Composition in Young Japanese Women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Women | Men | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 3427 | N = 1199 | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age (years old) | 40.9 | 10.5 | 45.6 | 9.3 | |
| Height (cm) | 158.7 | 5.6 | 171.4 | 5.9 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.0 | 7.3 | 22.9 | 7.8 | |
| Weight (kg) | 58.1 | 11.0 | 74.1 | 13.7 | |
| Daily total energy intake (kcal) | 1652.9 | 283.1 | 2068.9 | 408.0 | |
| Breakfast energy intake (kcal) | 349.3 | 124.7 | 429.1 | 154.1 | |
| Lunch energy intake (kcal) | 518.6 | 119.8 | 647.2 | 145.5 | |
| Dinner energy intake (kcal) | 572.3 | 163.8 | 802.3 | 200.3 | |
| Snacks energy (kcal) | 222.8 | 98.1 | 263.3 | 135.4 | |
| Daily total | Protein (%) | 17.2 | 4.0 | 17.2 | 5.9 |
| Lipid (%) | 32.1 | 6.2 | 32.2 | 9.1 | |
| Carbohydrate (%) | 48.8 | 7.0 | 49.1 | 16.4 | |
| Breakfast | Protein (%) | 17.5 | 6.9 | 17.6 | 8.1 |
| Lipid (%) | 28.2 | 8.3 | 27.5 | 8.8 | |
| Carbohydrate (%) | 54.8 | 11.0 | 53.0 | 12.5 | |
| Lunch | Protein (%) | 16.9 | 4.3 | 16.1 | 4.7 |
| Lipid (%) | 30.8 | 6.1 | 30.2 | 6.1 | |
| Carbohydrate (%) | 50.8 | 7.7 | 50.4 | 7.9 | |
| Dinner | Protein (%) | 19.4 | 5.1 | 17.8 | 5.5 |
| Lipid (%) | 33.7 | 6.6 | 32.3 | 7.0 | |
| Carbohydrate (%) | 42.6 | 9.3 | 40.6 | 10.2 | |
| Morning | Intermediate | Evening | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MSFsc < 3) N = 950 | (3 ≤ MSFsc < 5) N = 1890 | (5 ≤ MSFsc) N = 587 | Kruskal–Wallis Test | Spearman’s | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | Correlation Coefficient | |
| Age (year) | 44.0 | 9.5 | 40.8 | 10.5 | 36.1 | 10.2 | <0.001 | −0.24 |
| Height (cm) | 158.5 | 5.5 | 158.8 | 5.6 | 158.7 | 5.6 | 0.658 | 0.01 |
| BMI | 20.7 | 7.2 | 21.0 | 7.2 | 21.6 | 7.6 | 0.002 | 0.06 |
| Weight (kg) | 57.2 | 11.0 | 58.1 | 10.8 | 59.6 | 11.8 | <0.001 | 0.07 |
| Daily intake (kcal) | 1645.3 | 276.3 | 1647.6 | 277.8 | 1682.0 | 308.5 | 0.101 | 0.02 |
| Breakfast intake (kcal) | 379.8 | 122.8 | 345.2 | 119.2 | 313.3 | 133.7 | <0.001 | −0.18 |
| Lunch intake (kcal) | 517.6 | 116.9 | 519.8 | 116.5 | 516.7 | 134.4 | 0.807 | 0.00 |
| Dinner intake (kcal) | 547.3 | 165.5 | 570.7 | 159.3 | 617.9 | 166.2 | <0.001 | 0.13 |
| Breakfast time (hh:mm) | 7:17 | 1:16 | 7:51 | 1:11 | 8:52 | 1:52 | <0.001 | 0.37 |
| Lunch time (hh:mm) | 12:17 | 1:09 | 12:29 | 1:13 | 13:03 | 1:35 | <0.001 | 0.20 |
| Dinner time (hh:mm) | 18:44 | 1:32 | 19:07 | 1:18 | 19:25 | 2:22 | <0.001 | 0.24 |
| SD of breakfast time (min) | 16.0 | 31.3 | 24.2 | 35.8 | 34.9 | 48.5 | <0.001 | 0.14 |
| SD of lunch time (min) | 12.7 | 27.7 | 18.5 | 31.2 | 30.2 | 41.4 | <0.001 | 0.16 |
| SD of dinner time (min) | 12.5 | 27.8 | 18.5 | 40.4 | 27.8 | 55.9 | <0.001 | 0.11 |
| Regularities in the rhythm of life (score) | 4.1 | 0.8 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 1.2 | <0.001 | −0.35 |
| MSFsc (h) | 2.3 | 0.6 | 3.9 | 0.6 | 5.7 | 0.5 | <0.001 | 0.90 |
| SJL (h) | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 0.24 |
| Frequency of breakfast (days/week) | 6.6 | 1.4 | 6.2 | 1.7 | 4.8 | 2.5 | <0.001 | −0.32 |
| Frequency of late-night snack (days/week) | 1.8 | 2.7 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 2.1 | 2.6 | <0.001 | 0.08 |
| METs (total physical activity) | 34.1 | 44.4 | 27.5 | 34.7 | 27.5 | 40.5 | 0.008 | −0.05 |
| AIS score | 4.1 | 3.3 | 4.4 | 3.3 | 5.0 | 3.6 | <0.001 | 0.09 |
| Physical strength (score) | 2.8 | 1.0 | 2.8 | 1.0 | 2.7 | 0.9 | 0.015 | −0.05 |
| Health (score) | 3.7 | 0.9 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 0.9 | <0.001 | −0.10 |
| Well-being (score) | 3.6 | 0.9 | 3.5 | 1.0 | 3.4 | 0.9 | <0.001 | −0.10 |
| Morning | Intermediate | Evening | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MSFsc < 3) | (3 ≤ MSFsc ≤ 5) | (5 < MSFsc) | ||||||
| N = 475 | N = 588 | N = 136 | Kruskal–Wallis Test | Speaman’s | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | Correlation Coefficient | |
| Age (year old) | 48.0 | 8.2 | 44.7 | 9.5 | 40.9 | 9.9 | <0.001 | −0.23 |
| Height (cm) | 171.2 | 5.9 | 171.6 | 5.9 | 171.7 | 6.0 | 0.455 | 0.04 |
| BMI | 22.5 | 7.5 | 23.0 | 7.8 | 24.1 | 8.2 | 0.054 | 0.07 |
| Weight (kg) | 72.8 | 12.7 | 74.4 | 13.3 | 77.3 | 17.6 | 0.027 | 0.08 |
| Daily intake (kcal) | 2061.1 | 415.3 | 2084.5 | 402.2 | 2028.9 | 406.6 | 0.383 | −0.01 |
| Breakfast intake (kcal) | 459.2 | 149.2 | 418.4 | 147.2 | 371.6 | 177.0 | <0.001 | −0.18 |
| Lunch intake (kcal) | 632.1 | 145.9 | 661.6 | 144.1 | 637.1 | 145.1 | 0.005 | 0.05 |
| Dinner intake (kcal) | 794.9 | 198.3 | 808.0 | 200.9 | 803.4 | 205.1 | 0.586 | 0.03 |
| Breakfast time (hh:mm) | 7:06 | 1:07 | 7:40 | 1:06 | 8:26 | 2:04 | <0.001 | 0.34 |
| Lunch time (hh:mm) | 12:16 | 0:56 | 12:26 | 0:55 | 12:51 | 1:17 | <0.001 | 0.18 |
| Dinner time (hh:mm) | 19:13 | 1:22 | 19:30 | 1:14 | 19:27 | 2:17 | <0.001 | 0.14 |
| SD of breakfast time (min) | 25.7 | 41.8 | 28.0 | 39.2 | 38.6 | 56.6 | 0.100 | 0.06 |
| SD of lunch time (min) | 16.2 | 33.9 | 20.3 | 32.0 | 29.4 | 45.7 | 0.004 | 0.10 |
| SD of dinner time (min) | 23.3 | 46.6 | 28.9 | 56.6 | 46.2 | 107.1 | 0.116 | 0.06 |
| Regularities in the rhythm of life (score) | 4.1 | 0.8 | 3.9 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 1.2 | <0.001 | −0.22 |
| MSFsc (h) | 2.1 | 0.6 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 5.7 | 0.5 | <0.001 | 0.91 |
| SJL (h) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.9 | <0.001 | 0.32 |
| Frequency of breakfast (days/week) | 6.4 | 1.6 | 6.2 | 1.8 | 5.3 | 2.4 | <0.001 | −0.20 |
| Frequency of late night snack (days/week) | 2.0 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.9 | <0.001 | 0.11 |
| Mets (total physical activity) | 39.9 | 43.4 | 35.8 | 36.8 | 30.6 | 33.2 | 0.008 | −0.09 |
| AIS score | 3.9 | 3.3 | 4.1 | 3.2 | 4.5 | 3.3 | 0.047 | 0.07 |
| Physical strength (score) | 3.1 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 0.328 | −0.04 |
| Health (score) | 3.9 | 0.8 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 0.004 | −0.09 |
| Well-being (score) | 3.6 | 0.9 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 3.3 | 1.0 | 0.008 | −0.08 |
| Small SJL | Medium SJL | Large SJL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (SJL < 1) N = 2002 | (1 ≤ SJL < 2) N = 1138 | (2 ≤ SJL) N = 287 | Kruskal–Wallis Test | Spearman’s | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p Value | Correlation Coefficient | |
| Age (year) | 41.8 | 10.6 | 40.3 | 10.0 | 36.8 | 10.2 | <0.001 | −0.13 |
| Height (cm) | 158.6 | 5.6 | 158.7 | 5.7 | 158.9 | 5.4 | 0.724 | 0.01 |
| BMI | 21.0 | 7.2 | 21.1 | 7.2 | 21.1 | 7.7 | 0.084 | 0.04 |
| Weight (kg) | 57.8 | 11.3 | 58.3 | 10.7 | 59.3 | 10.8 | 0.019 | 0.05 |
| Daily intake (kcal) | 1641.9 | 285.5 | 1654.4 | 275.3 | 1723.2 | 287.6 | <0.001 | 0.05 |
| Breakfast intake (kcal) | 355.2 | 125.4 | 342.1 | 120.5 | 336.3 | 134.1 | 0.002 | −0.06 |
| Lunch intake (kcal) | 515.9 | 120.1 | 519.1 | 116.4 | 535.7 | 130.1 | 0.092 | 0.03 |
| Dinner intake (kcal) | 560.5 | 163.6 | 581.2 | 159.2 | 619.0 | 173.0 | <0.001 | 0.09 |
| Breakfast time (hh:mm) | 7.9 | 1.5 | 7.8 | 1.3 | 7.7 | 1.4 | 0.193 | −0.03 |
| Lunch time (hh:mm) | 12.5 | 1.4 | 12.5 | 1.2 | 12.6 | 0.9 | 0.69 | −0.01 |
| Dinner time (hh:mm) | 19.0 | 1.7 | 19.2 | 1.4 | 19.3 | 1.6 | <0.001 | 0.10 |
| SD of breakfast time (min) | 20.3 | 34.3 | 26.8 | 40.0 | 35.5 | 45.8 | <0.001 | 0.09 |
| SD of lunch time (min) | 18.2 | 30.8 | 19.4 | 35.7 | 22.5 | 33.7 | 0.159 | 0.02 |
| SD of dinner time (min) | 17.2 | 38.1 | 18.7 | 42.4 | 25.7 | 51.3 | 0.032 | 0.03 |
| Regularities in the rhythm of life (score) | 3.8 | 1.0 | 3.7 | 1.0 | 3.3 | 1.1 | <0.001 | −0.15 |
| MSFsc (h) | 3.5 | 1.3 | 3.9 | 1.1 | 4.6 | 0.9 | <0.001 | 0.28 |
| SJL (h) | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 2.3 | 0.4 | <0.001 | 0.88 |
| Frequency of breakfast (days/week) | 6.1 | 1.9 | 6.0 | 1.8 | 5.4 | 2.1 | <0.001 | −0.14 |
| Frequency of late-night snack (days/week) | 1.9 | 2.7 | 2.0 | 2.7 | 1.9 | 2.5 | 0.031 | 0.05 |
| METs (total physical activity) | 29.7 | 37.9 | 28.0 | 34.0 | 31.6 | 57.8 | 0.547 | −0.02 |
| AIS score | 4.3 | 3.3 | 4.5 | 3.4 | 5.2 | 3.6 | <0.001 | 0.07 |
| Physical strength (score) | 2.9 | 1.0 | 2.7 | 0.9 | 2.6 | 0.9 | <0.001 | −0.09 |
| Health (score) | 3.7 | 0.9 | 3.6 | 0.9 | 3.5 | 0.9 | <0.001 | −0.06 |
| Well-being (score) | 3.6 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 0.9 | <0.001 | −0.06 |
| Small SJL | Intermediate SJL | Large SJL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (SJL < 1) | (1 ≤ SJL < 2) | (2 ≤ SJL) | ||||||
| N = 780 | N = 348 | N = 71 | Kruskal–Wallis Test | Speaman’s | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p Value | Correlation Coefficient | |
| Age (year old) | 45.9 | 9.2 | 45.6 | 9.1 | 41.9 | 10.5 | 0.007 | −0.06 |
| Height (cm) | 171.4 | 5.8 | 171.5 | 6.2 | 171.4 | 5.5 | 1.000 | 0.00 |
| BMI | 22.8 | 7.5 | 22.8 | 8.4 | 25.1 | 6.1 | 0.016 | 0.06 |
| Weight (kg) | 73.5 | 13.4 | 74.8 | 14.0 | 77.2 | 14.9 | 0.062 | 0.06 |
| Daily intake (kcal) | 2077.5 | 394.4 | 2040.2 | 431.5 | 2114.3 | 433.0 | 0.541 | −0.01 |
| Breakfast intake (kcal) | 437.3 | 153.4 | 413.9 | 153.3 | 413.9 | 160.6 | 0.037 | −0.07 |
| Lunch intake (kcal) | 647.0 | 145.0 | 650.8 | 146.8 | 630.9 | 145.9 | 0.348 | −0.01 |
| Dinner intake (kcal) | 799.7 | 196.7 | 804.5 | 207.4 | 820.8 | 207.0 | 0.684 | 0.02 |
| Breakfast time (hh:mm) | 7:32 | 1:16 | 7:32 | 1:26 | 7:29 | 1:22 | 0.553 | 0.03 |
| Lunch time (hh:mm) | 12:24 | 0:54 | 12:25 | 1:02 | 12:34 | 1:27 | 0.243 | 0.05 |
| Dinner time (hh:mm) | 19:21 | 1:25 | 19:26 | 1:42 | 19:35 | 1:17 | 0.105 | 0.06 |
| SD of breakfast time (min) | 23.0 | 38.6 | 35.5 | 46.1 | 51.0 | 54.4 | <0.001 | 0.17 |
| SD of lunch time (min) | 17.6 | 34.0 | 22.9 | 35.1 | 27.8 | 38.8 | <0.001 | 0.11 |
| SD of dinner time (min) | 24.9 | 53.7 | 36.6 | 76.0 | 30.4 | 58.1 | 0.030 | 0.08 |
| Regularities in the rhythm of life (score) | 4.0 | 0.9 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 3.6 | 1.0 | <0.001 | −0.17 |
| MSFsc (h) | 3.1 | 1.2 | 3.7 | 1.2 | 4.5 | 1.1 | <0.001 | 0.32 |
| SJL (h) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 0.5 | <0.001 | 0.85 |
| Frequency of breakfast (days/week) | 6.3 | 1.8 | 6.1 | 1.9 | 5.8 | 2.2 | <0.001 | −0.11 |
| Frequency of late night snack (days/week) | 2.1 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 0.071 | 0.06 |
| Mets (total physical activity) | 37.7 | 38.8 | 33.1 | 36.4 | 45.9 | 53.2 | 0.004 | −0.06 |
| AIS score | 3.8 | 3.0 | 4.5 | 3.6 | 4.6 | 3.8 | 0.005 | 0.09 |
| Physical strength (score) | 3.1 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 0.011 | −0.09 |
| Health (score) | 3.9 | 0.8 | 3.6 | 0.9 | 3.8 | 0.8 | <0.001 | −0.15 |
| Well-being (score) | 3.6 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 0.9 | <0.001 | −0.10 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable: Chronotype | Independent Variable: SJL | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily Total Intake | R2 | B | Min | Max | p Value | R2 | B | Min | Max | p Value |
| Energy | 0.25 | 5.19 | −2.40 | 12.79 | 0.180 | 0.25 | 22.08 | 8.45 | 35.71 | 0.002 |
| Protein | 0.30 | −0.11 | −0.47 | 0.24 | 0.523 | 0.30 | −0.85 | −1.48 | −0.22 | 0.008 |
| Lipid | 0.54 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.021 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.047 |
| Carbohydrate | 0.59 | 0.21 | −0.57 | 1.00 | 0.592 | 0.59 | 0.65 | −0.76 | 2.06 | 0.365 |
| Sodium | 0.39 | −9.48 | −26.48 | 7.53 | 0.275 | 0.39 | 32.33 | 1.79 | 62.88 | 0.038 |
| Potassium | 0.14 | −40.24 | −53.90 | −26.59 | <0.001 | 0.13 | −44.13 | −68.72 | −19.54 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol | 0.09 | 0.42 | −1.21 | 2.05 | 0.613 | 0.09 | −1.88 | −4.81 | 1.04 | 0.207 |
| Fiber | 0.08 | −0.49 | −0.62 | −0.36 | <0.001 | 0.08 | −0.74 | −0.97 | −0.51 | <0.001 |
| Saturated fatty acid | 0.39 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.025 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.025 |
| Alcohol | 0.09 | −0.29 | −0.48 | −0.10 | 0.002 | 0.09 | 0.16 | −0.17 | 0.49 | 0.348 |
| Calcium | 0.05 | −0.76 | −6.43 | 4.91 | 0.793 | 0.05 | −14.15 | −24.33 | −3.96 | 0.006 |
| Magnesium | 0.10 | −3.63 | −5.82 | −1.44 | <0.001 | 0.10 | −7.41 | −11.34 | −3.48 | <0.001 |
| Phosphorus | 0.31 | −14.26 | −18.98 | −9.54 | <0.001 | 0.31 | −13.87 | −22.37 | −5.37 | <0.001 |
| Iron | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.11 | 0.17 | 0.663 | 0.01 | −0.06 | −0.31 | 0.19 | 0.630 |
| Zinc | 0.10 | 0.05 | −0.07 | 0.16 | 0.426 | 0.10 | −0.06 | −0.26 | 0.14 | 0.570 |
| Vitamin A | 0.02 | 9.40 | −5.29 | 24.09 | 0.210 | 0.02 | −6.28 | −32.68 | 20.13 | 0.641 |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 | 0.18 | −0.64 | 0.99 | 0.670 | 0.00 | 1.31 | −0.16 | 2.77 | 0.080 |
| Vitamin E | 0.00 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 1.07 | 0.047 | 0.00 | −0.05 | −1.01 | 0.91 | 0.915 |
| Vitamin K | 0.04 | −12.63 | −15.65 | −9.61 | <0.001 | 0.03 | −17.14 | −22.59 | −11.70 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.36 | 0.018 | 0.00 | −0.14 | −0.43 | 0.15 | 0.349 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.00 | 0.09 | −0.08 | 0.26 | 0.291 | 0.00 | −0.16 | −0.46 | 0.14 | 0.297 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.03 | 0.10 | −0.42 | 0.62 | 0.701 | 0.03 | −0.31 | −1.24 | 0.63 | 0.521 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.00 | 0.02 | −0.17 | 0.21 | 0.810 | 0.00 | −0.09 | −0.43 | 0.26 | 0.627 |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 | −0.07 | −0.99 | 0.85 | 0.880 | 0.00 | −1.05 | −2.71 | 0.60 | 0.213 |
| Folate | 0.02 | −3.41 | −8.11 | 1.29 | 0.155 | 0.02 | −8.99 | −17.43 | −0.55 | 0.037 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.02 | −0.06 | −0.21 | 0.09 | 0.427 | 0.02 | −0.34 | −0.61 | −0.07 | 0.014 |
| Vitamin C | 0.00 | 8.35 | 0.05 | 16.64 | 0.049 | 0.00 | 11.55 | −3.36 | 26.45 | 0.129 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable: Chronotype | Independent Variable: SJL | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brakfast Intake | R2 | B | Min | Max | p Value | R2 | B | Min | Max | p Value |
| Energy | 0.29 | −21.88 | −24.66 | −19.09 | <0.001 | 0.26 | −14.82 | −19.89 | −9.75 | <0.001 |
| Protein | 0.12 | −1.04 | −1.21 | −0.87 | <0.001 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Lipid | 0.19 | −0.71 | −0.83 | −0.59 | <0.001 | 0.17 | −0.51 | −0.73 | −0.30 | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrate | 0.23 | −2.99 | −3.41 | −2.56 | <0.001 | 0.20 | −1.71 | −2.48 | −0.94 | <0.001 |
| Sodium | 0.14 | −50.84 | −59.16 | −42.52 | <0.001 | 0.11 | −24.07 | −39.16 | −8.97 | 0.002 |
| Potassium | 0.08 | −44.69 | −51.56 | −37.81 | <0.001 | 0.05 | −39.94 | −52.36 | −27.52 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol | 0.06 | −6.71 | −7.83 | −5.59 | <0.001 | 0.03 | −4.87 | −6.90 | −2.83 | <0.001 |
| Fiber | 0.04 | −0.41 | −0.48 | −0.34 | <0.001 | 0.02 | −0.42 | −0.55 | −0.30 | <0.001 |
| Saturated fatty acid | 0.15 | −0.18 | −0.22 | −0.14 | <0.001 | 0.14 | −0.13 | −0.20 | −0.06 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol | 0.05 | −0.02 | −0.02 | −0.01 | <0.001 | 0.04 | −0.01 | −0.03 | 0.00 | 0.058 |
| Calcium | 0.03 | −8.87 | −11.96 | −5.79 | <0.001 | 0.03 | −6.70 | −12.24 | −1.16 | 00.018 |
| Magnesium | 0.05 | −4.74 | −5.85 | −3.63 | <0.001 | 0.04 | −4.53 | −6.53 | −2.53 | <0.001 |
| Phosphorus | 0.13 | −19.15 | −21.56 | −16.75 | <0.001 | 0.09 | −14.67 | −19.07 | −10.26 | <0.001 |
| Iron | 0.00 | −0.12 | −0.23 | −0.02 | 0.023 | 0.00 | −0.03 | −0.22 | 0.16 | 0.752 |
| Zinc | 0.04 | −0.10 | −0.16 | −0.05 | <0.001 | 0.03 | −0.06 | −0.15 | 0.04 | 0.225 |
| Vitamin A | 0.02 | −6.93 | −13.17 | −0.70 | 0.029 | 0.02 | 0.03 | −11.15 | 11.21 | 0.996 |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 | −0.42 | −0.72 | −0.11 | 0.008 | 0.00 | −0.24 | −0.80 | 0.31 | 0.388 |
| Vitamin E | 0.00 | −0.24 | −0.57 | 0.09 | 0.149 | 0.00 | 0.16 | −0.43 | 0.74 | 0.594 |
| Vitamin K | 0.04 | −9.77 | −11.46 | −8.09 | <0.001 | 0.02 | −9.57 | −12.63 | −6.52 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.00 | −0.04 | −0.13 | 0.06 | 0.422 | 0.00 | −0.08 | −0.25 | 0.09 | 0.348 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.00 | −0.07 | −0.18 | 0.03 | 0.160 | 0.00 | −0.09 | −0.28 | 0.09 | 0.318 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.01 | −0.40 | −0.71 | −0.10 | 0.010 | 0.01 | −0.24 | −0.78 | 0.31 | 0.397 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.00 | −0.08 | −0.18 | 0.03 | 0.151 | 0.00 | −0.14 | −0.33 | 0.05 | 0.137 |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 | −0.07 | −0.45 | 0.31 | 0.722 | 0.00 | −0.14 | −0.83 | 0.54 | 0.681 |
| Folate | 0.01 | −5.75 | −8.60 | −2.90 | <0.001 | 0.01 | −4.72 | −9.83 | 0.39 | 0.070 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.01 | −0.18 | −0.27 | −0.08 | <0.001 | 0.01 | −0.22 | −0.39 | −0.05 | 0.013 |
| Vitamin C | 0.00 | 2.82 | −1.80 | 7.43 | 0.232 | 0.00 | 2.10 | −6.18 | 10.37 | 0.620 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable: Chronotype | Independent Variable: SJL | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lunch Intake | R2 | B | Min | Max | p Value | R2 | B | Min | Max | p Value |
| Energy | 0.46 | −2.67 | −5.12 | −0.22 | 0.033 | 0.46 | −0.91 | −5.31 | 3.50 | 0.686 |
| Protein | 0.18 | −0.21 | −0.36 | −0.07 | 0.004 | 0.18 | −0.27 | −0.53 | −0.01 | 0.040 |
| Lipid | 0.26 | 0.06 | −0.07 | 0.19 | 0.355 | 0.26 | 0.03 | −0.20 | 0.26 | 0.808 |
| Carbohydrate | 0.38 | −0.48 | −0.85 | −0.11 | 0.010 | 0.38 | −0.09 | −0.75 | 0.57 | 0.791 |
| Sodium | 0.23 | −6.71 | −15.63 | 2.21 | 0.140 | 0.23 | 10.58 | −5.44 | 26.60 | 0.196 |
| Potassium | 0.05 | −15.47 | −20.92 | −10.02 | <0.001 | 0.04 | −17.32 | −27.10 | −7.53 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol | 0.03 | −2.02 | −2.99 | −1.06 | <0.001 | 0.03 | −4.26 | −5.99 | −2.53 | <0.001 |
| Fiber | 0.03 | −0.15 | −0.20 | −0.10 | <0.001 | 0.03 | −0.23 | −0.32 | −0.14 | <0.001 |
| Saturated fatty acid | 0.18 | 0.02 | −0.02 | 0.06 | 0.280 | 0.18 | −0.01 | −0.07 | 0.06 | 0.895 |
| Alcohol | 0.04 | −0.03 | −0.05 | −0.01 | 0.004 | 0.03 | 0.00 | −0.04 | 0.04 | 0.883 |
| Calcium | 0.02 | −0.35 | −1.96 | 1.27 | 0.673 | 0.02 | −4.08 | −6.97 | −1.18 | 0.006 |
| Magnesium | 0.05 | −1.48 | −2.14 | −0.81 | <0.001 | 0.05 | −2.19 | −3.38 | −1.00 | <0.001 |
| Phosphorus | 0.13 | −5.64 | −7.70 | −3.57 | <0.001 | 0.12 | −5.60 | −9.32 | −1.89 | 0.003 |
| Iron | 0.03 | −0.03 | −0.05 | 0.00 | 0.057 | 0.03 | −0.06 | −0.10 | −0.01 | 0.015 |
| Zinc | 0.05 | −0.03 | −0.06 | 0.01 | 0.136 | 0.05 | 0.02 | −0.04 | 0.08 | 0.576 |
| Vitamin A | 0.01 | −8.26 | −12.76 | −3.76 | <0.001 | 0.00 | −6.00 | −14.10 | 2.09 | 0.146 |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 | 0.22 | −0.16 | 0.60 | 0.257 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.15 | 1.50 | 0.017 |
| Vitamin E | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.06 | 0.11 | 0.551 | 0.01 | −0.07 | −0.22 | 0.08 | 0.375 |
| Vitamin K | 0.01 | −2.87 | −4.02 | −1.72 | <0.001 | 0.01 | −5.45 | −7.52 | −3.39 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.00 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.177 | 0.00 | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.711 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.00 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.206 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.06 | 0.06 | 0.993 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.09 | −0.11 | −0.18 | −0.03 | 0.005 | 0.08 | −0.09 | −0.22 | 0.04 | 0.191 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.00 | 0.01 | −0.02 | 0.04 | 0.499 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.05 | 0.05 | 0.991 |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 | −0.10 | −0.25 | 0.05 | 0.205 | 0.00 | −0.16 | −0.43 | 0.11 | 0.247 |
| Folate | 0.01 | −2.78 | −4.14 | −1.41 | <0.001 | 0.01 | −3.83 | −6.27 | −1.38 | 0.002 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.03 | −0.02 | −0.05 | 0.00 | 0.085 | 0.03 | −0.05 | −0.10 | 0.00 | 0.048 |
| Vitamin C | 0.00 | 0.33 | −1.18 | 1.84 | 0.671 | 0.00 | −1.39 | −4.11 | 1.32 | 0.314 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable: Chronotype | Independent Variable: SJL | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dinner Intake | R2 | B | Min | Max | p Value | R2 | B | Min | Max | p Value |
| Energy | 0.55 | 15.76 | 12.55 | 18.98 | <0.001 | 0.55 | 16.54 | 10.72 | 22.36 | <0.001 |
| Protein | 0.29 | 0.70 | 0.52 | 0.87 | <0.001 | 0.28 | 0.64 | 0.33 | 0.96 | <0.001 |
| Lipid | 0.33 | 0.63 | 0.47 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.43 | 1.00 | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrate | 0.37 | 2.67 | 2.21 | 3.12 | <0.001 | 0.35 | 2.12 | 1.28 | 2.95 | <0.001 |
| Sodium | 0.23 | 41.60 | 31.22 | 51.99 | <0.001 | 0.22 | 43.06 | 24.33 | 61.78 | <0.001 |
| Potassium | 0.12 | 9.24 | 2.46 | 16.01 | 0.008 | 0.12 | −0.64 | −12.79 | 11.52 | 0.918 |
| Cholesterol | 0.11 | 1.90 | 0.90 | 2.90 | <0.001 | 0.11 | 2.20 | 0.41 | 3.99 | 0.016 |
| Fiber | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.039 | 0.09 | −0.06 | −0.16 | 0.04 | 0.209 |
| Saturated fatty acid | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.22 | <0.001 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.30 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol | 0.09 | −0.34 | −0.51 | −0.17 | <0.001 | 0.09 | 0.16 | −0.14 | 0.47 | 0.294 |
| Calcium | 0.03 | 0.25 | −1.94 | 2.45 | 0.821 | 0.03 | −1.53 | −5.47 | 2.41 | 0.447 |
| Magnesium | 0.09 | 0.61 | −0.35 | 1.57 | 0.210 | 0.09 | −0.35 | −2.07 | 1.38 | 0.694 |
| Phosphorus | 0.22 | 6.63 | 4.06 | 9.20 | <0.001 | 0.22 | 6.42 | 1.80 | 11.04 | 0.006 |
| Iron | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.009 | 0.02 | 0.09 | −0.01 | 0.19 | 0.092 |
| Zinc | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.009 | 0.05 | −0.03 | −0.15 | 0.09 | 0.572 |
| Vitamin A | 0.01 | 15.06 | 3.99 | 26.14 | 0.008 | 0.00 | 1.88 | −18.04 | 21.79 | 0.854 |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 | 0.08 | −0.14 | 0.31 | 0.468 | 0.00 | 0.16 | −0.25 | 0.57 | 0.444 |
| Vitamin E | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 0.014 | 0.00 | −0.10 | −0.47 | 0.27 | 0.607 |
| Vitamin K | 0.02 | −0.35 | −2.05 | 1.35 | 0.688 | 0.02 | −1.90 | −4.95 | 1.16 | 0.223 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.010 | 0.00 | −0.04 | −0.15 | 0.07 | 0.462 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.00 | 0.04 | −0.03 | 0.11 | 0.217 | 0.00 | −0.08 | −0.21 | 0.04 | 0.205 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 0.14 | 0.71 | 0.004 | 0.01 | 0.18 | −0.34 | 0.70 | 0.487 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.00 | 0.03 | −0.03 | 0.09 | 0.353 | 0.00 | −0.03 | −0.15 | 0.08 | 0.556 |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 | 0.17 | −0.54 | 0.88 | 0.644 | 0.00 | −0.40 | −1.67 | 0.88 | 0.543 |
| Folate | 0.02 | 1.69 | −0.16 | 3.54 | 0.073 | 0.02 | 0.21 | −3.11 | 3.53 | 0.900 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.01 | 0.05 | −0.01 | 0.10 | 0.093 | 0.01 | −0.02 | −0.12 | 0.08 | 0.741 |
| Vitamin C | 0.00 | 1.49 | −1.97 | 4.94 | 0.399 | 0.00 | 5.24 | −0.96 | 11.44 | 0.098 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nitta, L.; Tahara, Y.; Shinto, T.; Makino, S.; Kuwahara, M.; Tada, A.; Abe, N.; Michie, M.; Shibata, S. Association of Eating Pattern, Chronotype, and Social Jetlag: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Data Accumulated in a Japanese Food-Logging Mobile Health Application. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092165
Nitta L, Tahara Y, Shinto T, Makino S, Kuwahara M, Tada A, Abe N, Michie M, Shibata S. Association of Eating Pattern, Chronotype, and Social Jetlag: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Data Accumulated in a Japanese Food-Logging Mobile Health Application. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092165
Chicago/Turabian StyleNitta, Lyie, Yu Tahara, Takae Shinto, Saneyuki Makino, Mai Kuwahara, Ayako Tada, Nanako Abe, Mikiko Michie, and Shigenobu Shibata. 2023. "Association of Eating Pattern, Chronotype, and Social Jetlag: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Data Accumulated in a Japanese Food-Logging Mobile Health Application" Nutrients 15, no. 9: 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092165
APA StyleNitta, L., Tahara, Y., Shinto, T., Makino, S., Kuwahara, M., Tada, A., Abe, N., Michie, M., & Shibata, S. (2023). Association of Eating Pattern, Chronotype, and Social Jetlag: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Data Accumulated in a Japanese Food-Logging Mobile Health Application. Nutrients, 15(9), 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092165