The Role of Vitamin D in Obese Children with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Associated Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Groups and Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Participants
2.4. Patient Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Principles
3. Results
3.1. Initial Evaluation and Identification of NAFLD-Associated Parameters
3.2. Final Evaluation and Overall Treatment Effect
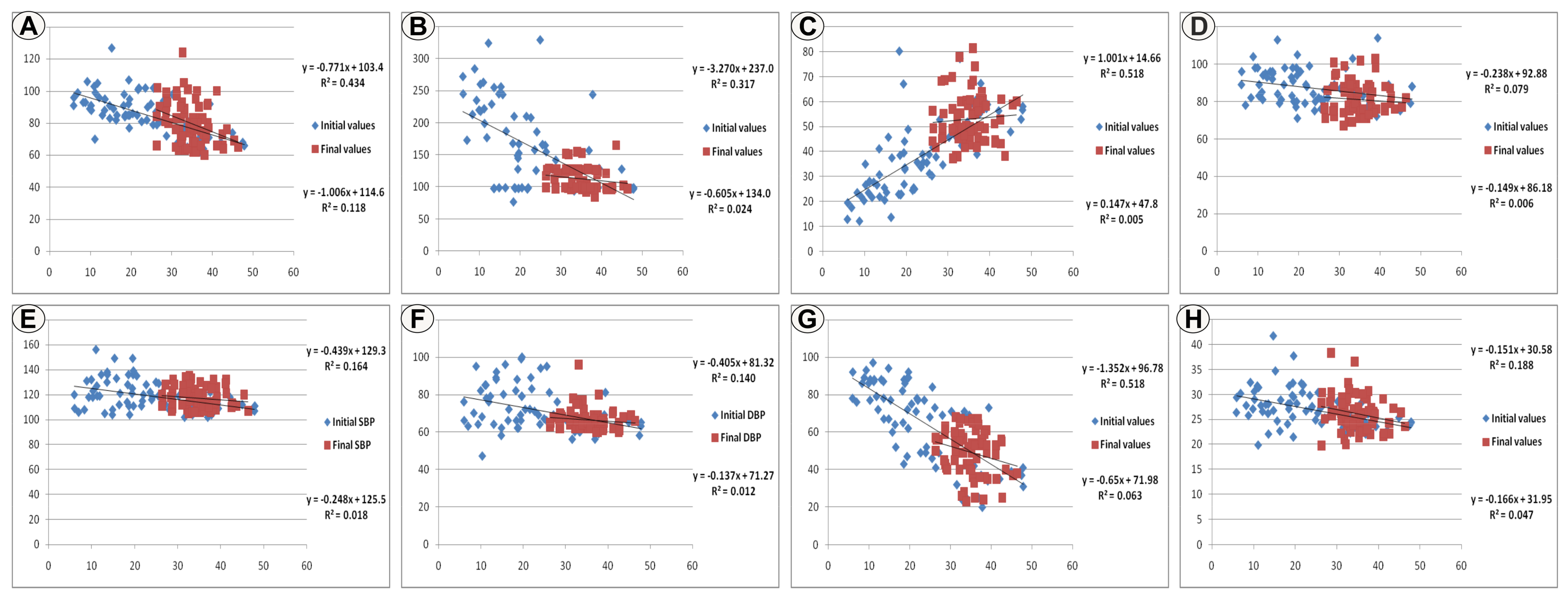
3.3. The Relation of Vitamin D with the Investigated Parameters
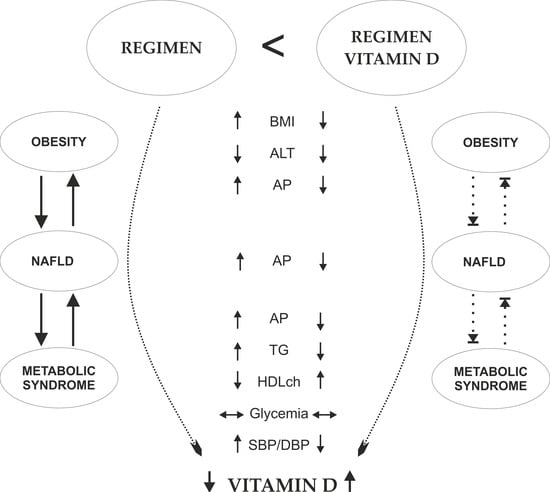
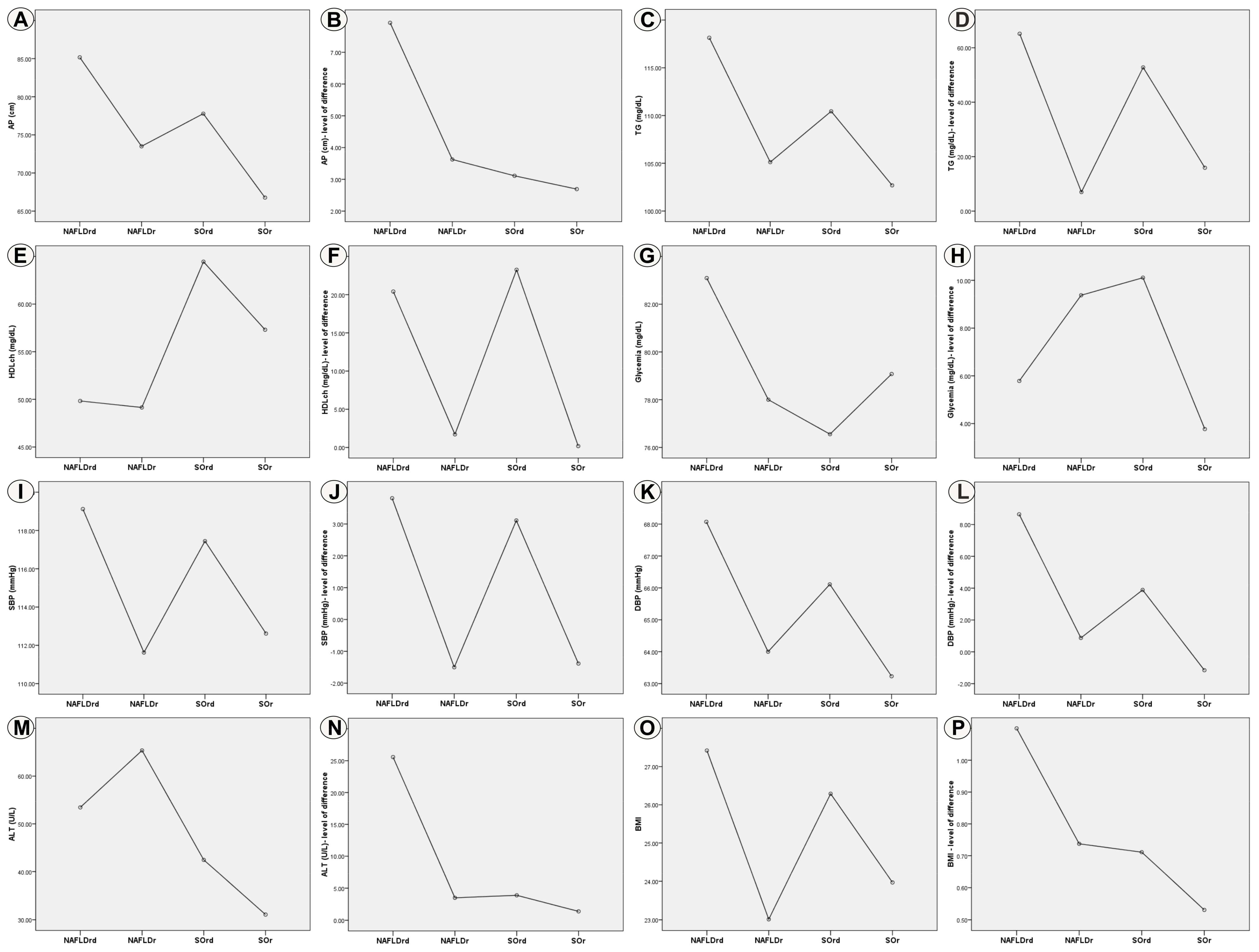
3.4. Evaluation of Effects Depending on the Type of Treatment
4. Discussion
Limits and Advantages of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| MAFLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease |
| SO | Simple obesity |
| MS | Metabolic syndrome |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| ALT | Alanine transaminase |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| HDLch | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| AP | Abdominal perimeter/circumference |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| NAFLDrd | Group of patients diagnosed with NAFLD treated with specific regimen and vitamin D supplementation |
| NAFLDr | Group of patients diagnosed with NAFLD treated with specific regimen |
| SOrd | Group of patients diagnosed with SO treated with specific regimen and vitamin D supplementation |
| SOr | Group of patients diagnosed with SO treated with specific regimen |
References
- Bush, H.; Golabi, P.; Younossi, Z.M. Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Children 2017, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Wu, S.; Zhou, N.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, X. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children with obesity. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.L.; Howe, L.D.; Jones, H.E.; Higgins, J.P.; Lawlor, D.A.; Fraser, A. The Prevalence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, M.G.; Mandato, C.; Poeta, M.; Vajro, P. Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Recent solutions, unresolved issues, and future research directions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8078–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.L.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.L.; Liang, L. Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescence: From “two hit theory” to “multiple hit model”. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2974–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sessa, A.; Marzuillo, P.; Guarino, S.; Cirillo, G.; Miraglia Del Giudice, E. When a secondary form of pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease should be suspected? Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchel, E.B.; Lavine, J.E. Review article: The management of paediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, C.; Carpino, G.; De Vito, R.; De Stefanis, C.; Alisi, A.; Cianfarani, S.; Overi, D.; Mosca, A.; Stronati, L.; Cucchiara, S.; et al. Docosahexanoic Acid Plus Vitamin D Treatment Improves Features of NAFLD in Children with Serum Vitamin D Deficiency: Results from a Single Centre Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoppo, J.I.C.; Pateda, V.; Prayogo, C.; Langi, F.; Nurkolis, F.; Tsopmo, A. Relationships of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children: A possible strategy to promote early screening of NAFLD. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1025396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.P.; Schwimmer, J.B. The Progression and Natural History of Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldner, D.; Lavine, J.E. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Unique Considerations and Challenges. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1967–1983.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.; Bremer, A.A.; Lustig, R.H. What is metabolic syndrome, and why are children getting it? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1281, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Fan, X.; Chen, Q. Efficacy of vitamin D supplement in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisinger, C.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N.; Fredriksen, P.M.; Goswami, N. The prevalence of pediatric metabolic syndrome-a critical look on the discrepancies between definitions and its clinical importance. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgio, V.; Prono, F.; Graziano, F.; Nobili, V. Pediatric non alcoholic fatty liver disease: Old and new concepts on development, progression, metabolic insight and potential treatment targets. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussler, S.; Penke, M.; Flemming, G.; Elhassan, Y.S.; Kratzsch, J.; Sergeyev, E.; Lipek, T.; Vogel, M.; Spielau, U.; Korner, A.; et al. Novel Insights in the Metabolic Syndrome in Childhood and Adolescence. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 88, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuillo, P.; Grandone, A.; Perrone, L.; Miraglia Del Giudice, E. Controversy in the diagnosis of pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6444–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkiewicz, K.; Horodnicka-Jozwa, A.; Jackowski, T.; Straczek, K.; Biczysko-Mokosa, A.; Walczak, M.; Petriczko, E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children with obesity- observations from one clinical centre in the Western Pomerania region. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 992264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, C.S.; Hosey-Cojocari, C.; Chan, S.S.; Csanaky, I.L.; Wagner, J.B.; Sweeney, B.R.; Friesen, A.; Fraser, J.D.; Shakhnovich, V. Efficacy of Weight Reduction on Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Opportunities to Improve Treatment Outcomes Through Pharmacotherapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 663351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, M.H.A.D.; Hewawasam, R.P.; Lekamwasam, S. Concordance between Body Composition Indices Measured with Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Obese Children in Sri Lanka. Int. J. Pediatr 2021, 2021, 6638057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourigan, S.K.; Abrams, S.; Yates, K.; Pfeifer, K.; Torbenson, M.; Murray, K.; Roth, C.L.; Kowdley, K.; Scheimann, A.O.; Nash, C.R.N. Relation between vitamin D status and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.J.; Cho, E.J.; Chung, G.E.; Chang, Y.; Cho, Y.; Park, S.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Kim, B.Y.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is a Precursor of New-Onset Metabolic Syndrome in Metabolically Healthy Young Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Cavallo, M.G. Vitamin D and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, M.B.; Abrams, S.H.; Barlow, S.E.; Caprio, S.; Daniels, S.R.; Kohli, R.; Mouzaki, M.; Sathya, P.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Sundaram, S.S.; et al. NASPGHAN Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN). J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, J.M.; Hodge, A.; Farrell, G.C.; Kench, J.G.; Kriketos, A.; George, J. Beyond insulin resistance in NASH: TNF-alpha or adiponectin? Hepatology 2004, 40, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, M.; Rizk, R.; AlAnouti, F.; Papandreou, D.; Haidar, S.; Mahboub, N. The Health Effects of Vitamin D and Probiotic Co-Supplementation: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Wilding, J.P.; Bing, C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 protects against macrophage-induced activation of NFkappaB and MAPK signalling and chemokine release in human adipocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amrousy, D.; Abdelhai, D.; Shawky, D. Vitamin D and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranic, L.; Mikolasevic, I.; Milic, S. Vitamin D Deficiency: Consequence or Cause of Obesity? Medicina 2019, 55, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Blissett, D.; Blissett, R.; Henry, L.; Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Y.; Racila, A.; Hunt, S.; Beckerman, R. The economic and clinical burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States and Europe. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Tools and Toolkits. Growth Reference Data for 5–19 Years. BMI-for-Age (5–19 years). Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/growth-reference-data-for-5to19-years/indicators/bmi-for-age (accessed on 27 August 2021).
- Patton, H.M.; Yates, K.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Behling, C.A.; Huang, T.T.; Rosenthal, P.; Sanyal, A.J.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Lavine, J.E. Association between metabolic syndrome and liver histology among children with nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, M.C.; Shield, J. Pocket Guide to Pediatric Weight Management, 2nd ed.; Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Onis, M. World Health Organization Reference Curves. In The ECOG’s eBook on Child and Adolescent Obesity; Frelut, M.L., Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.L.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; Nowicka, P.; Pietrobelli, A.; Weiss, R. Evaluation of the overweight/obese child--practical tips for the primary health care provider: Recommendations from the Childhood Obesity Task Force of the European Association for the Study of Obesity. Obes. Facts 2010, 3, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MSD Manuals. Professional Version. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, M.; Koryukova, K.; Bezzi, M.; Catalano, C. Imaging Features of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents. Children 2017, 4, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents: Summary report. Pediatrics 2011, 128 (Suppl. S5), S213–S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, G.; Kaufman, F.; Tajima, N.; Silink, M.; Arslanian, S.; Wong, G.; Bennett, P.; Shaw, J.; Caprio, S.; et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Lancet 2007, 369, 2059–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.; Kaufman, F.; Tajima, N.; Silink, M.; Arslanian, S.; Wong, G.; Bennett, P.; Shaw, J.; Caprio, S.; et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents—An IDF consensus report. Pediatr. Diabetes 2007, 8, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, Z.W.; Alemu, A.; Ayele, E.G.; Tenaw, Z.; Alebel, A.; Worku, T. Metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents in low and middle income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggese, G.; Vierucci, F.; Prodam, F.; Cardinale, F.; Cetin, I.; Chiappini, E.; De’ Angelis, G.L.; Massari, M.; Miraglia Del Giudice, E.; Miraglia Del Giudice, M.; et al. Vitamin D in pediatric age: Consensus of the Italian Pediatric Society and the Italian Society of Preventive and Social Pediatrics, jointly with the Italian Federation of Pediatricians. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, S.E.; Expert Committee. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: Summary report. Pediatrics 2007, 120 (Suppl. S4), S164–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ene, M.C.; Terțiu, O.; Vrâncianu, O.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Vitamin D status in adult and pediatric romanian population. Rom. Achiv. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 77, 198–212. [Google Scholar]
- Niculescu, D.A.; Capatina, C.A.M.; Dusceac, R.; Caragheorgheopol, A.; Ghemigian, A.; Poiana, C. Seasonal variation of serum vitamin D levels in Romania. Arch. Osteoporos. 2017, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Ballestri, S.; Fairweather, D.; Win, S.; Than, T.A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A. Sex Differences in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: State of the Art and Identification of Research Gaps. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.H.; Kim, J.W.; Shim, J.O.; Yang, H.R.; Chang, J.Y.; Moon, J.S.; Ko, J.S. Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Suspected Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in an Adolescent Population. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstedt, M.; Franzen, L.E.; Mathiesen, U.L.; Thorelius, L.; Holmqvist, M.; Bodemar, G.; Kechagias, S. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology 2006, 44, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Pardee, P.E.; Lavine, J.E.; Blumkin, A.K.; Cook, S. Cardiovascular risk factors and the metabolic syndrome in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Circulation 2008, 118, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Marchesini, G.; Angulo, P.; Loria, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A precursor of the metabolic syndrome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.S.; Zeitler, P.; Nadeau, K. The metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2009, 21, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorio, A.; Del Col, A.; Agosti, F.; Mazzilli, G.; Bellentani, S.; Tiribelli, C.; Bedogni, G. Predictors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cali, A.M.; Zern, T.L.; Taksali, S.E.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Dufour, S.; Otvos, J.D.; Caprio, S. Intrahepatic fat accumulation and alterations in lipoprotein composition in obese adolescents: A perfect proatherogenic state. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 3093–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harel, Z.; Flanagan, P.; Forcier, M.; Harel, D. Low vitamin D status among obese adolescents: Prevalence and response to treatment. J. Adolesc. Health 2011, 48, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliades, M.; Spyrou, E.; Agrawal, N.; Lazo, M.; Brancati, F.L.; Potter, J.J.; Koteish, A.A.; Clark, J.M.; Guallar, E.; Hernaez, R. Meta-analysis: Vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manco, M.; Ciampalini, P.; Nobili, V. Low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) in children with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2229; author reply 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitson, M.T.; Roberts, S.K. D-livering the message: The importance of vitamin D status in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Luo, F.; Liu, J.; Xiu, L.; Qin, J.; Wang, T.; Yu, N.; Wu, H.; Zou, T. The Level of Vitamin D in Children and Adolescents with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7643542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Cheng, Y.F.; Lai, C.Y.; Hsu, L.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Deng, J.Y.; Huang, Y.Z.; Honda, H.; Chen, K.D.; Wang, C.C.; et al. Impact of artificial sunlight therapy on the progress of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Ahmed, A.; Abdel Ghany, M.; Abdel Hakeem, G.L.; Kamal, A.; Khattab, R.; Abdalla, A.; Abou El Fotoh Lel, M.; El Mazary, A.A.; Sayed, M.A.; Abdel Fadil, A.M. Assessment of Vitamin D status in a group of Egyptian children with non alcoholic fatty liver disease (multicenter study). Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, M.; Maghsoudi, Z.; Ghiasvand, R.; Iraj, B.; Askari, G. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on C-reactive Protein in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 969–975. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, C.; Xiao, L.; Imayama, I.; Duggan, C.R.; Bain, C.; Foster-Schubert, K.E.; Kong, A.; Campbell, K.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Neuhouser, M.L.; et al. Effects of weight loss on serum vitamin D in postmenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakpal, M.; Satsangi, S.; Mehta, M.; Duseja, A.; Bhadada, S.; Das, A.; Dhiman, R.K.; Chawla, Y.K. Vitamin D supplementation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. JGH Open 2017, 1, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Hurst, P.R.; Stonehouse, W.; Coad, J. Vitamin D supplementation reduces insulin resistance in South Asian women living in New Zealand who are insulin resistant and vitamin D deficient—A randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achamrah, N.; Colange, G.; Delay, J.; Rimbert, A.; Folope, V.; Petit, A.; Grigioni, S.; Déchelotte, P.; Coëffier, M. Comparison of body composition assessment by DXA and BIA according to the body mass index: A retrospective study on 3655 measures. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirbasli, M.; Tanrikulu, A.M.; Berenson, G.S. Metabolic Syndrome: Bridging the Gap from Childhood to Adulthood. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2016, 34, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.C.; Yalamanchili, V.; Smith, L.M. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum 25(OH)D in thin and obese women. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 136, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter/No. Cases | SO (No. Cases) (%) | NAFLD (No. Cases) (%) | p Value (χ2 Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 6–9 | 9 (40.9) | 22 (44) | 0.807 |
| 10–14 | 13 (59.1) | 28 (56) | ||
| Gender | Male | 11 (50) | 32 (64) | 0.265 |
| Female | 11 (50) | 18 (36) | ||
| MS | High AP | 5 (22.7) | 47 (94) | <0.001 |
| High TG | 5 (22.7) | 30 (60%) | 0.064 | |
| Low HDLch | 7 (31.8) | 36 (72) | 0.001 | |
| High glycemia | 0 (0) | 5 (10) | 0.124 | |
| High SBP/DBP | 5 (22.7) | 27 (54) | 0.014 | |
| Present | 2 (9.1) | 33 (66) | <0.001 | |
| Absent | 20 (90.9) | 17 (34) | ||
| Vitamin D deficiency | Present | 9 (40.9) | 42 (84) | <0.001 |
| Absent | 13 (59.1) | 8 (16) | ||
| Parameter | Initial Measured Values | Final Measured Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO | NAFLD | SO | NAFLD | |
| AP (cm) | 74.1 ± 7.5 | 90.5 ± 11.5 | 71.2 ± 7.1 | 83.3 ± 13.7 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 136.8 ± 42.6 | 171.9 ± 69.2 | 105.8 ± 9.7 | 116 ± 19.4 |
| HDLch (mg/dL) | 50.6 ± 11.9 | 32.3 ± 13.2 | 60.2 ± 9.1 | 49.7 ± 7.7 |
| Glycemia (mg/dL) | 84.4 ± 8.5 | 88.6 ± 9.5 | 78 ± 6.9 | 82.2 ± 9.1 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 115 ± 8.1 | 120.8 ± 13 | 114.5 ± 6.7 | 117.9 ± 8.8 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 65.3 ± 6.7 | 74.8 ± 12.6 | 64.4 ± 2.5 | 67.4 ± 6.3 |
| BMI | 25.5 ± 2 | 27.7 ± 4.2 | 24.9 ± 1.9 | 26.7 ± 3.8 |
| ALT (U/L) | 38.1 ± 9.1 | 77.4± 10.4 | 35.7± 7.8 | 55.3 ± 7.2 |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) | 32.9 ± 9.7 | 18.9 ± 8.6 | 35.9 ± 5 | 34.2 ± 4.2 |
| Parameter/No. Cases | SO (No. Cases) (%) | NAFLD (No. Cases) (%) | p Value (χ2 Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | High AP | 1 (4.5) | 24 (48) | <0.001 |
| High TG | 0 (0) | 5 (10) | 0.124 | |
| Low HDLch | 0 (0) | 4 (8) | 0.172 | |
| High glycemia | 0 (0) | 3 (6) | 0.241 | |
| High SBP/DBP | 5 (22.7) | 15 (30) | 0.526 | |
| Present | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 0.504 | |
| Absent | 22 (100) | 49 (98) | ||
| Vitamin D deficiency | Present | 3 (13.6) | 8 (16) | 0.797 |
| Absent | 19 (38) | 42 (84) | ||
| Parameter | Initial Value | Final Value | p Value (Student’s t-Test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AP (mg/dL) | 85.5 ± 12.9 | 79.6 ± 13.2 | <0.001 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 161.1 ± 64.1 | 112.9 ± 17.6 | <0.001 |
| HDLch (mg/dL) | 37.8 ± 15.3 | 52.9 ± 9.4 | <0.001 |
| Glycemia (mg/dL) | 87.3 ± 9.3 | 80.9 ± 8.7 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 119 ± 11.9 | 116.9 ± 8.3 | 0.023 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 71.9 ± 11.9 | 66.5 ± 5.6 | <0.001 |
| BMI | 27 ± 3.8 | 26.1 ± 3.4 | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 65.4 ± 20.7 | 49.3 ± 11.7 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) | 23.2 ± 11 | 34.8 ± 4.5 | <0.001 |
| Parameters/p Values (χ2 Test) | Vitamin D—Initial Status (No. Cases) (%) | Vitamin D—Final Status (No. Cases) (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deficiency | Normal | Deficiency | Normal | ||
| Age | 6–9 | 16 (22.2) | 15 (20.8) | 4 (5.5) | 27 (37.5) |
| 10–14 | 35 (48.6) | 6 (8.3) | 7 (9.7) | 34 (47.2) | |
| p values | 0.002 | 0.626 | |||
| Gender | Male | 35 (48.6) | 8 (11.1) | 6 (8.3) | 37 (51.4) |
| Female | 16 (22.2) | 13 (18) | 5 (6.9) | 24 (33.3) | |
| p values | 0.016 | 0.704 | |||
| AP | High | 46 (63.9) | 6 (8.3) | 7 (9.7) | 18 (25) |
| Normal | 5 (6.9) | 15 (20.8) | 4 (5.5) | 43 (59.7) | |
| p values | <0.001 | 0.029 | |||
| TG | High | 36 (50) | 2 (2.8) | 0 (0) | 5 (6.9) |
| Normal | 15 (20.8) | 19 (26.4) | 11 (15.3) | 56 (77.8) | |
| p values | <0.001 | 0.325 | |||
| HDLch | Low | 42 (58.3) | 1 (1.4) | 0 (0) | 4 (5.5) |
| Normal | 9 (12.5) | 20 (27.8) | 11 (15.3) | 57 (79.1) | |
| p values | <0.001 | 0.382 | |||
| Glycemia | High | 3 (4.1) | 2 (2.8) | 1 (1.4) | 2 (2.8) |
| Normal | 48 (66.7) | 19 (26.4) | 10 (13.9) | 59 (81.9) | |
| p values | 0.581 | 0.375 | |||
| SBP/DBP | High | 29 (40.3) | 3 (4.1) | 3 (4.1) | 17 (23.6) |
| Normal | 22 (30.5) | 18 (25) | 8 (11.1) | 44 (61.1) | |
| p values | 0.001 | 0.968 | |||
| Pearson Test (p Value)/Group | NAFLDrd | NAFLDr | SOrd | SOr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D/AP | 0.001 (−) | 0.803 (+) | <0.001 (−) | 0.692 (−) |
| Vitamin D/TG | <0.001 (−) | 0.192 (+) | <0.001 (−) | 0.678 (−) |
| Vitamin D/HDLch | <0.001 (+) | 0.487 (+) | 0.026 (+) | 0.470 (−) |
| Vitamin D/Glycemia | 0.001 (−) | 0.222 (+) | 0.025 (−) | 0.812 (+) |
| Vitamin D/SBP | 0.160 (−) | 0.455 (−) | 0.069 (−) | 0.822 (−) |
| Vitamin D/DBP | 0.007 (−) | 0.090 (+) | 0.075 (−) | 0.427 (+) |
| Vitamin D/ALT | <0.001 (−) | 0.535 (+) | 0.002 (−) | 0.024 (+) |
| Vitamin D/BMI | 0.180 (−) | 0.463 (−) | 0.020 (−) | 0.829 (−) |
| Parameter | Treatment Superiority (Final Measured Mean Values) | Treatment Effectiveness (Level of Difference Between Initial and Final Measured Values) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAFLD | SO | p Value (ANOVA Test) | NAFLD | SO | p Value (ANOVA Test) | |
| AP | regimen | <0.001 | mixed treatment | 0.007 | ||
| TG | regimen | 0.017 | mixed treatment | 0.007 | ||
| HDLch | mixed treatment | <0.001 | mixed treatment | <0.001 | ||
| Glycemia | regimen | mixed treatment | 0.095 | regimen | mixed treatment | 0.421 |
| SBP | mixed treatment | 0.020 | mixed treatment | 0.108 | ||
| DBP | regimen | mixed treatment | 0.022 | mixed treatment | 0.008 | |
| BMI | regimen | <0.001 | mixed treatment | 0.025 | ||
| ALT | mixed treatment | regimen | <0.001 | mixed treatment | <0.001 | |
| Vitamin D | mixed treatment | 0.078 | mixed treatment | <0.001 | ||
| Parameter | NAFLDrd | NAFLDr | SOrd | SOr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 7.9 ± 6.8 | 3.6 ± 3.4 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 2.6 ± 3.8 |
| TG | 65.1 ± 65.2 | 7 ± 21.5 | 52.7 ± 25.5 | 15.9 ± 40.3 |
| HDLch | 20.4 ± 8.6 | 1.7 ± 2.3 | 23.2 ± 10.2 | 0.1 ± 4.4 |
| Glycemia | 5.7 ± 10.7 | 9.3 ± 11.4 | 10.1 ± 11.1 | 3.7 ± 6.3 |
| SBP | 3.8 ± 9.3 | −1.5 ± 1.7 | 3.1 ± 5.8 | −1.3 ± 5.1 |
| DBP | 8.6 ± 11.6 | 0.8 ± 5.6 | 3.8 ± 6.8 | −1.1 ± 3.6 |
| BMI | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 0.7 ± 0.6 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.5 ± 0.3 |
| ALT | 25.5 ± 10.7 | 3.5 ± 1.6 | 3.8 ± 2.1 | 1.3 ± 2.7 |
| Vitamin D | 18.3 ± 6.4 | −0.1 ± 1.5 | 10.3 ± 2.7 | −1.9 ± 3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stepan, M.D.; Vintilescu, Ș.B.; Streață, I.; Podeanu, M.A.; Florescu, D.N. The Role of Vitamin D in Obese Children with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Associated Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092113
Stepan MD, Vintilescu ȘB, Streață I, Podeanu MA, Florescu DN. The Role of Vitamin D in Obese Children with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Associated Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092113
Chicago/Turabian StyleStepan, Mioara Desdemona, Ștefănița Bianca Vintilescu, Ioana Streață, Mihaela Andreea Podeanu, and Dan Nicolae Florescu. 2023. "The Role of Vitamin D in Obese Children with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Associated Metabolic Syndrome" Nutrients 15, no. 9: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092113
APA StyleStepan, M. D., Vintilescu, Ș. B., Streață, I., Podeanu, M. A., & Florescu, D. N. (2023). The Role of Vitamin D in Obese Children with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Associated Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients, 15(9), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092113