Metabolic Biomarkers of Red Beetroot Juice Intake at Rest and after Physical Exercise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Red Beetroot Juice Pretreatment for NMR Analysis
2.2. Analysis of Red Beetroot Juice Samples by NMR Spectroscopy
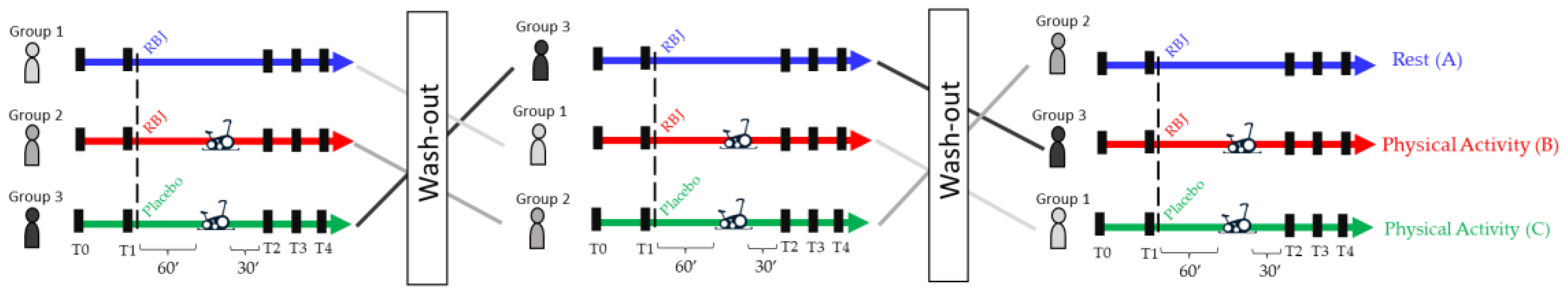
2.3. Characteristics of the Subjects and Experimental Setting
2.4. Subjects’ Physical Profile and Exercise Workload Assessment
2.5. Urine Sample Preparation
2.6. Analysis of Urine Samples by NMR Spectroscopy
2.7. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Red Beetroot Juice Composition
3.2. Experimental Setting
3.3. Urinary Metabolomics
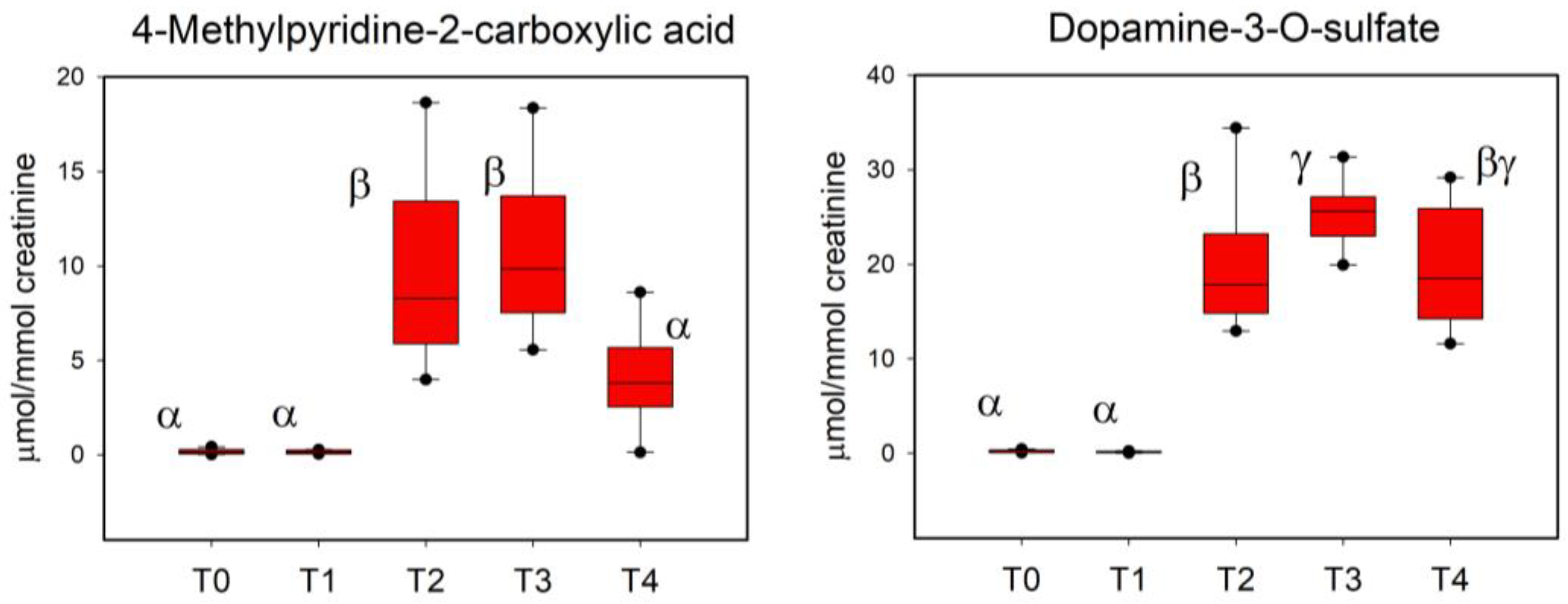
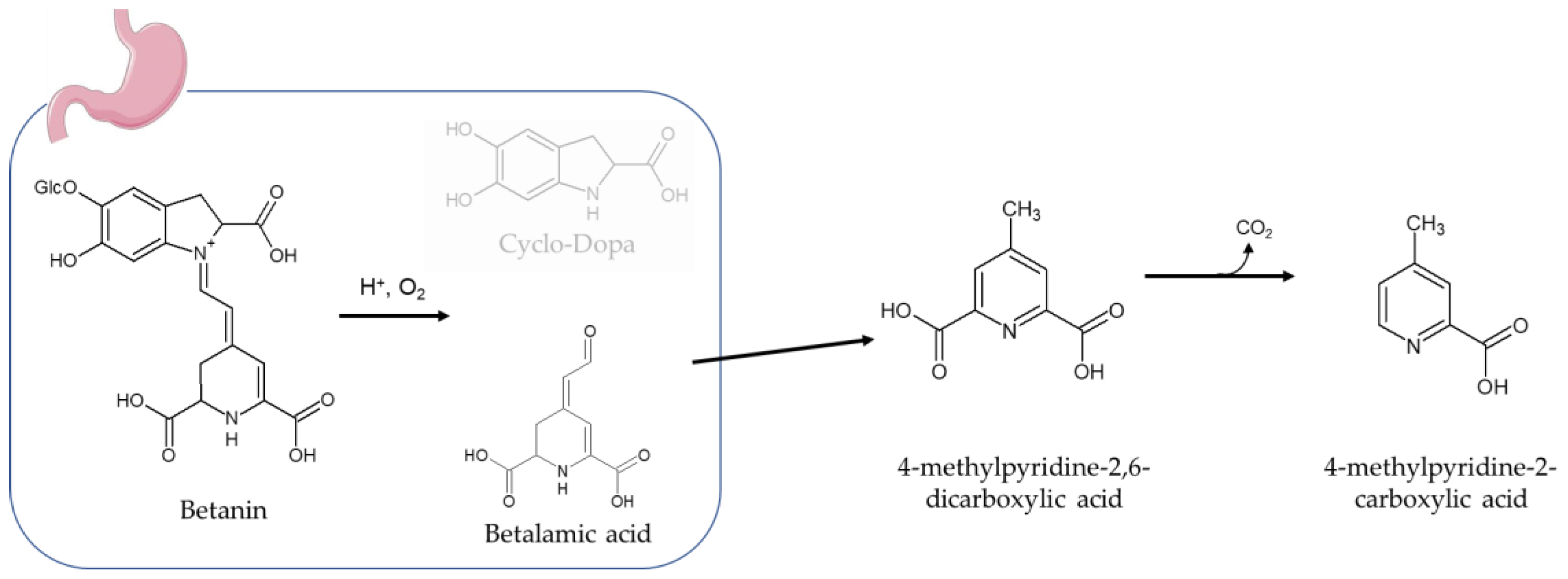
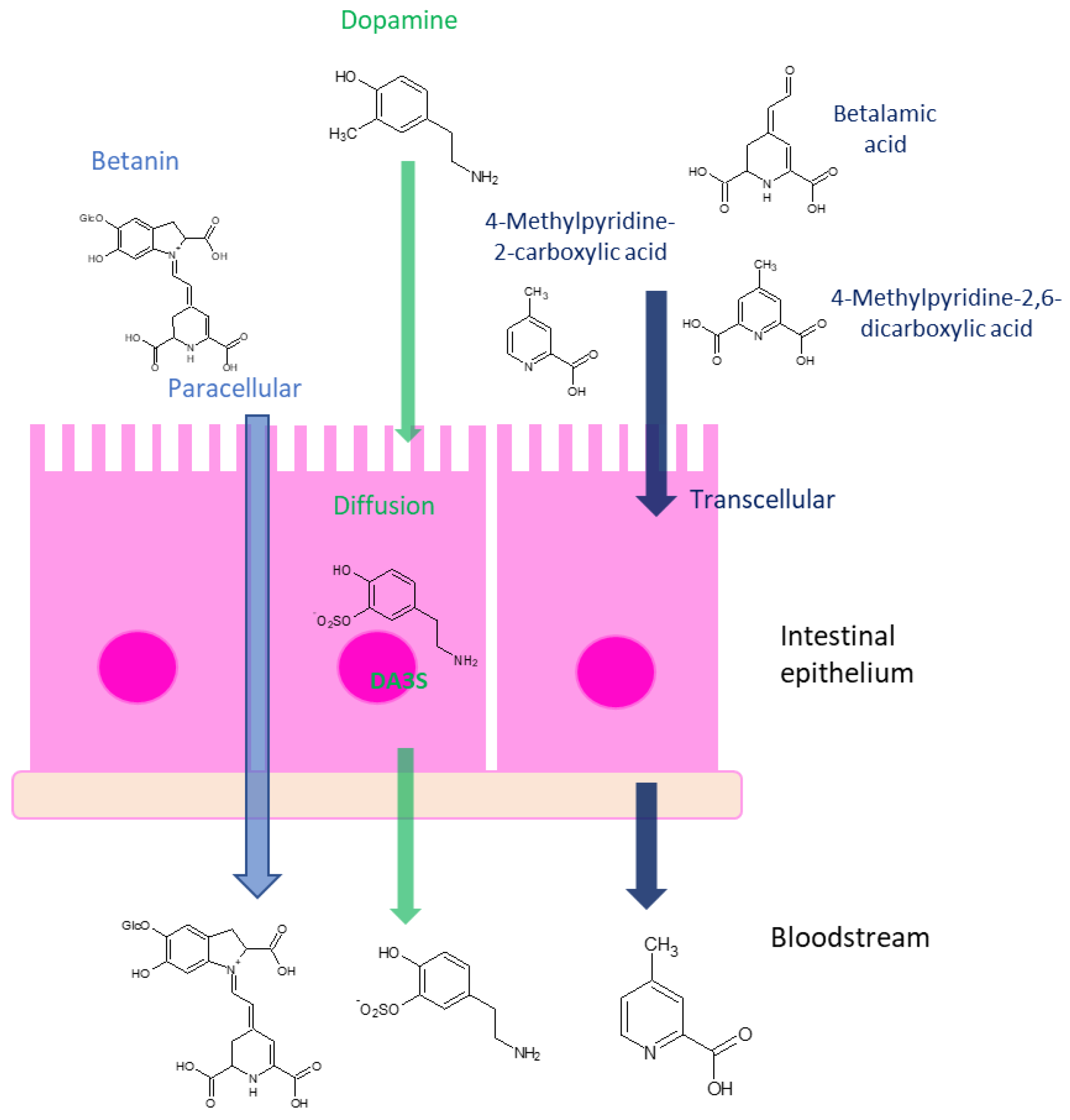
3.4. Urinary Biomarkers of RBJ Intake
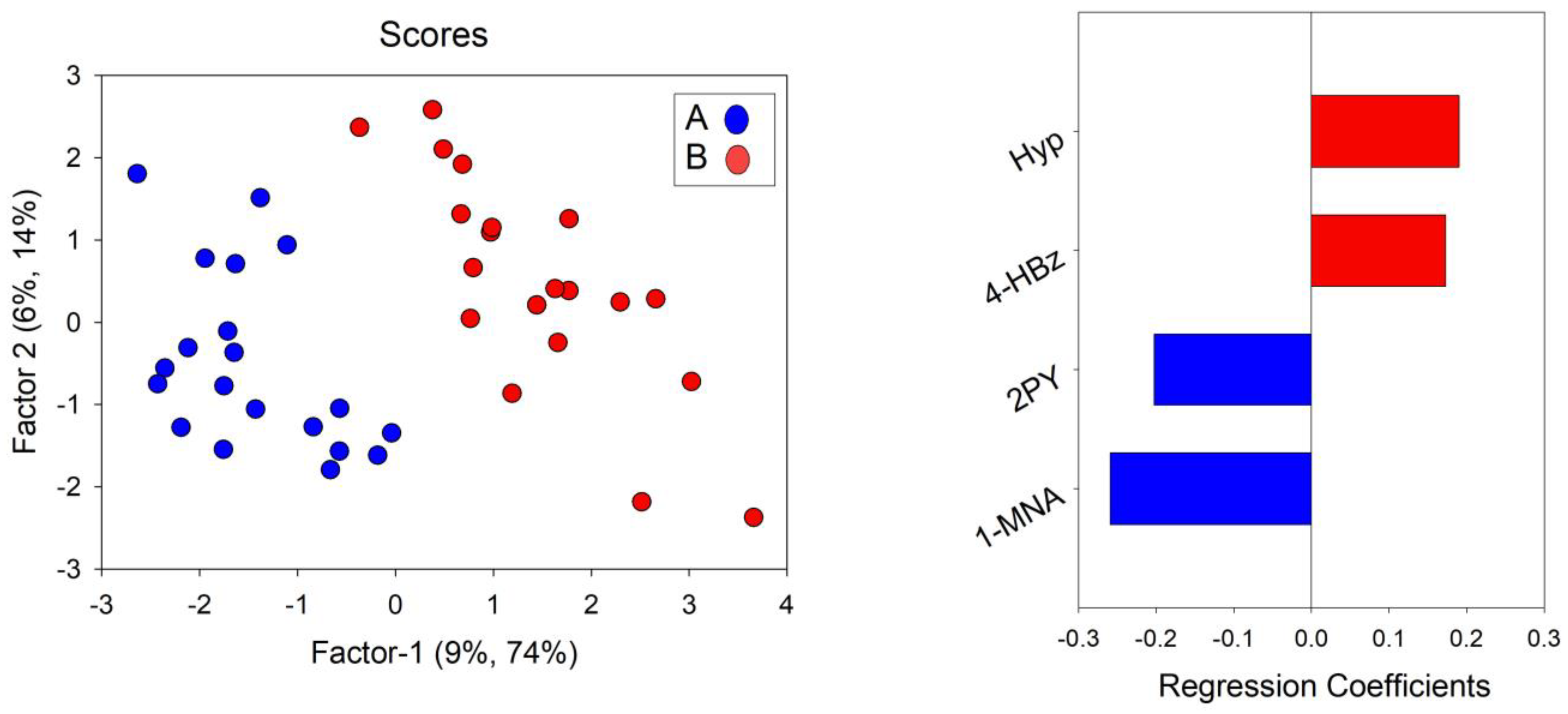
3.5. Metabolic Profile Related to Physical Activity
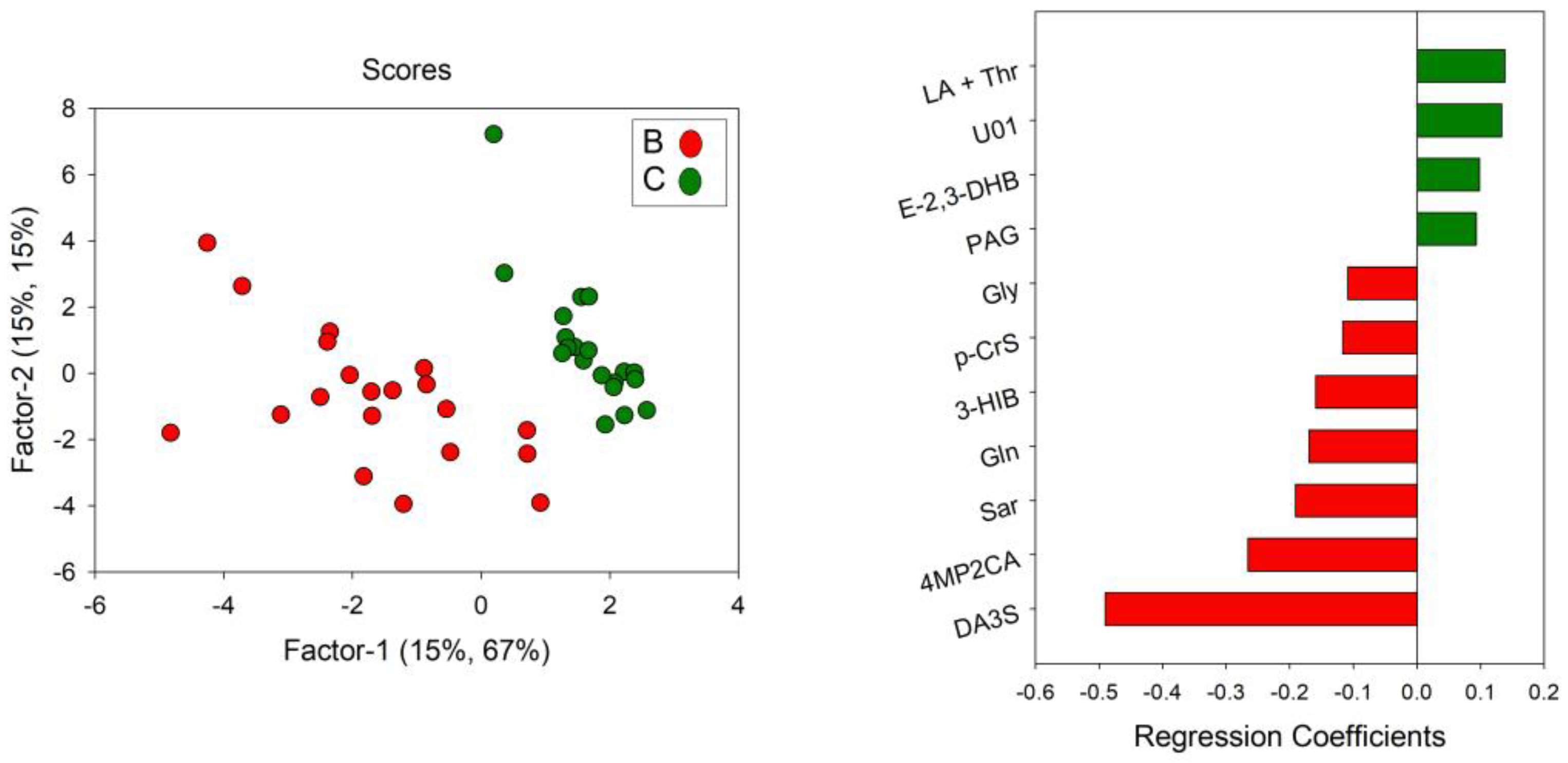
3.6. Metabolic Profile Related to Red Beetroot Juice Intake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chhikara, N.; Kushwaha, K.; Sharma, P.; Gat, Y.; Panghal, A. Bioactive Compounds of Beetroot and Utilization in Food Processing Industry: A Critical Review. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, V.G.; Weber, J.; Kneschke, E.-M.; Denev, P.N.; Bley, T.; Pavlov, A.I. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Content of Betalain Extracts from Intact Plants and Hairy Root Cultures of the Red Beetroot Beta Vulgaris Cv. Detroit Dark Red. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesoriere, L.; Allegra, M.; Butera, D.; Livrea, M.A. Absorption, Excretion, and Distribution of Dietary Antioxidant Betalains in LDLs: Potential Health Effects of Betalains in Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, J.; Xie, S.-Y.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E. Red Beetroot Betalains: Perspectives on Extraction, Processing, and Potential Health Benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11595–11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampaoli, O.; Sciubba, F.; Conta, G.; Capuani, G.; Tomassini, A.; Giorgi, G.; Brasili, E.; Aureli, W.; Miccheli, A. Red Beetroot’s NMR-Based Metabolomics: Phytochemical Profile Related to Development Time and Production Year. Foods 2021, 10, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Cuenca, E.; Maté-Muñoz, J.L.; García-Fernández, P.; Serra-Paya, N.; Estevan, M.C.L.; Herreros, P.V.; Garnacho-Castaño, M.V. Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Cardiorespiratory Endurance in Athletes. A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowska, L.; Mizera, O.; Mroz, A. An Untargeted Metabolomics Approach to Investigate the Metabolic Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation in Fencers—A Preliminary Study. Metabolites 2020, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, M.J.; Renouf, M.; Cruz-Hernandez, C.; Actis-Goretta, L.; Thakkar, S.K.; da Silva Pinto, M. Bioavailability of Bioactive Food Compounds: A Challenging Journey to Bioefficacy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, N.; Berweiler, V.; Wang, H.; Trajkovski, M. Intestinal Microbiota as a Route for Micronutrient Bioavailability. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2021, 20, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas-Galindo, D.E.; González Arnáiz, E.; Ferrero Vicente, P.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D. Effects of Physical Exercise in Sarcopenia. A Systematic Review. Endocrinol. Diabetes Y Nutr. 2021, 68, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, É.; Marinho, D.A.; Neiva, H.P.; Lourenço, O. Inflammatory Effects of High and Moderate Intensity Exercise—A Systematic Review. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiela, P.R.; Ghishan, F.K. Physiology of Intestinal Absorption and Secretion. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, M.; Gérard, P.; Mosca, A.; Leclerc, M. Interplay between Exercise and Gut Microbiome in the Context of Human Health and Performance. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 637010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dékány, M.; Nemeskéri, V.; Györe, I.; Harbula, I.; Malomsoki, J.; Pucsok, J. Antioxidant Status of Interval-Trained Athletes in Various Sports. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2006, 27, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassini, A.; Sciubba, F.; Di Cocco, M.E.; Capuani, G.; Delfini, M.; Aureli, W.; Miccheli, A. 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics Reveals a Pedoclimatic Metabolic Imprinting in Ready-to-Drink Carrot Juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5284–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucía, A.; Sánchez, O.; Carvajal, A.; Chicharro, J.L. Analysis of the Aerobic-Anaerobic Transition in Elite Cyclists during Incremental Exercise with the Use of Electromyography. Br. J. Sport. Med. 1999, 33, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; McNamara, A.E.; Brennan, L. Role of Metabolomics in Identification of Biomarkers Related to Food Intake. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.-B.S.; Kristensen, M.; Manach, C.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Poulsen, S.K.; Larsen, T.M.; Astrup, A.; Dragsted, L. Discovery and Validation of Urinary Exposure Markers for Different Plant Foods by Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.S.; Swoboda, K.J.; Miles, J.M.; Coppack, S.W.; Aneman, A.; Holmes, C.; Lamensdorf, I.; Eisenhofer, G. Sources and Physiological Significance of Plasma Dopamine Sulfate. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.A.; Baker, C.A.; Smith, R.T. Radioenzymatic Assay of Sulfate Conjugates of Catecholamines and DOPA in Plasma. Life Sci. 1980, 26, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renskers, K.J.; Feor, K.D.; Roth, J.A. Sulfation of Dopamine and Other Biogenic Amines by Human Brain Phenol Sulfotransferase. J. Neurochem. 1980, 34, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, E.D.; Kadlubar, S.S.; Falany, C.N. Expression and Localization of SULT1A1 and SULT1A3 in Normal Human Brain. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughtrie, M.W.H. Function and Organization of the Human Cytosolic Sulfotransferase (SULT) Family. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 259, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teubner, W.; Meinl, W.; Florian, S.; Kretzschmar, M.; Glatt, H. Identification and Localization of Soluble Sulfotransferases in the Human Gastrointestinal Tract. Biochem. J. 2007, 404, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Gillitt, N.D.; Sha, W.; Meaney, M.P.; John, C.; Pappan, K.L.; Kinchen, J.M. Metabolomics-Based Analysis of Banana and Pear Ingestion on Exercise Performance and Recovery. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 5367–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, K.; Sakakibara, H. High Content of Dopamine, a Strong Antioxidant, in Cavendish Banana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, T.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R.; Bitsch, I.; Quaas, D.; Straß, G.; Bitsch, R.; Netzel, M. Urinary Pharmacokinetics of Betalains Following Consumption of Red Beet Juice in Healthy Humans. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 52, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Bartosz, G. Biological Properties and Applications of Betalains. Molecules 2021, 26, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira Teixeira da Silva, D.; dos Santos Baião, D.; de Oliveira Silva, F.; Alves, G.; Perrone, D.; Mere Del Aguila, E.; M. Flosi Paschoalin, V. Betanin, a Natural Food Additive: Stability, Bioavailability, Antioxidant and Preservative Ability Assessments. Molecules 2019, 24, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbach, K.M.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. Betalain Stability and Degradation—Structural and Chromatic Aspects. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, R41–R50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabokina, S.M.; Kashyap, M.L.; Said, H.M. Mechanism and Regulation of Human Intestinal Niacin Uptake. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 289, C97–C103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Yu, Z.; You, G. Regulation of Organic Anion Transporters: Role in Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Drug Elimination. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 217, 107647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokladny, K.; Zuhl, M.N.; Moseley, P.L. Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function and Tight Junction Proteins with Heat and Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2016, 120, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shing, C.M.; Peake, J.M.; Lim, C.L.; Briskey, D.; Walsh, N.P.; Fortes, M.B.; Ahuja, K.D.K.; Vitetta, L. Effects of Probiotics Supplementation on Gastrointestinal Permeability, Inflammation and Exercise Performance in the Heat. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhl, M.; Dokladny, K.; Mermier, C.; Schneider, S.; Salgado, R.; Moseley, P. The Effects of Acute Oral Glutamine Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Gastrointestinal Permeability and Heat Shock Protein Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubert, C.; Kong, G.; Renoir, T.; Hannan, A.J. Exercise, Diet and Stress as Modulators of Gut Microbiota: Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Honda, A.; Ikegami, T.; Iwamoto, J.; Monma, T.; Hirayama, T.; Saito, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Matsuzaki, Y. Simultaneous Quantification of Salivary 3-Hydroxybutyrate, 3-Hydroxyisobutyrate, 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylbutyrate, and 2-Hydroxybutyrate as Possible Markers of Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Catabolic Pathways by LC–ESI–MS/MS. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechlivanis, A.; Kostidis, S.; Saraslanidis, P.; Petridou, A.; Tsalis, G.; Mougios, V.; Gika, H.G.; Mikros, E.; Theodoridis, G.A. 1H NMR-Based Metabonomic Investigation of the Effect of Two Different Exercise Sessions on the Metabolic Fingerprint of Human Urine. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6405–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechlivanis, A.; Papaioannou, K.G.; Tsalis, G.; Saraslanidis, P.; Mougios, V.; Theodoridis, G.A. Monitoring the Response of the Human Urinary Metabolome to Brief Maximal Exercise by a Combination of RP-UPLC-MS and 1H NMR Spectroscopy. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 4610–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, F.; Biolo, G. Effect of Physical Activity on Glutamine Metabolism. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, D.A.; Terjung, R.L. Amino Acid Metabolism During Exercise and Following Endurance Training. Sport Med. 1990, 9, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Niu, C.; Lu, J.; Li, N.; Li, J. Hydrolyzed Protein Supplementation Improves Protein Content and Peroxidation of Skeletal Muscle by Adjusting the Plasma Amino Acid Spectrums in Rats after Exhaustive Swimming Exercise: A Pilot Study. J. Int. Soc. Sport Nutr. 2014, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.B.; Pizza, F.X.; Paquet, A.; Davis, B.J.; Forrest, M.B.; Braun, W.A. Influence of Carbohydrate Status on Immune Responses before and after Endurance Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1998, 84, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, J.; Kusy, K. Pathways of Purine Metabolism: Effects of Exercise and Training in Competitive Athletes. Trends Sport Sci. 2015, 3, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbacher, P.; Eckl, P. Impact of Oxidative Stress on Exercising Skeletal Muscle. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 356–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre-Fernández, C.; Romero-Moraleda, B.; Cupeiro, R.; Peinado, A.B.; Butragueño, J.; Benito, P.J. The Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Exercise Economy, Rating of Perceived Exertion and Running Mechanics in Elite Distance Runners: A Double-Blinded, Randomized Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aura, A.-M.; O’Leary, K.A.; Williamson, G.; Ojala, M.; Bailey, M.; Puupponen-Pimiä, R.; Nuutila, A.M.; Oksman-Caldentey, K.-M.; Poutanen, K. Quercetin Derivatives Are Deconjugated and Converted to Hydroxyphenylacetic Acids but Not Methylated by Human Fecal Flora in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ho, L.; Faith, J.; Ono, K.; Janle, E.M.; Lachcik, P.J.; Cooper, B.R.; Jannasch, A.H.; D’Arcy, B.R.; Williams, B.A.; et al. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in the Generation of Polyphenol-Derived Phenolic Acid Mediated Attenuation of Alzheimer’s Disease β-Amyloid Oligomerization. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, J.A.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Boto-Ordoñez, M.; Llorach, R.; Farran-Codina, A.; Barupal, D.K.; Neveu, V.; Manach, C.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Scalbert, A. Systematic Analysis of the Polyphenol Metabolome Using the Phenol-Explorer Database. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic Acids: Natural Versatile Molecules with Promising Therapeutic Applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.E.; Sharif, T.; Martell, E.; Dai, C.; Kim, Y.; Lee, P.W.K.; Gujar, S.A. NAD+ Salvage Pathway in Cancer Metabolism and Therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 114, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanulović, M.; Chaykin, S. Aldehyde Oxidase: Catalysis of the Oxidation of N 1 -Methylnicotinamide and Pyridoxal. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1971, 145, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, K.; Matsubara, K.; Okada, K.; Fukushima, S.; Shimizu, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Uezono, T.; Satomi, M.; Hayase, N.; Ohta, S.; et al. N-Methylation Ability for Azaheterocyclic Amines Is Higher in Parkinson’s Disease: Nicotinamide Loading Test. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2000, 107, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Wei, X.; Kikukawa, Y.; Tzameli, I.; Prasad, D.; Lee, Y.; Asara, J.M.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Maratos-Flier, E.; et al. Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase Regulates Hepatic Nutrient Metabolism through Sirt1 Protein Stabilization. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radak, Z.; Suzuki, K.; Posa, A.; Petrovszky, Z.; Koltai, E.; Boldogh, I. The Systemic Role of SIRT1 in Exercise Mediated Adaptation. Redox Biol. 2020, 35, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Class | Metabolite | Amount (mg/100 mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Amino acids | Alanine | 90.7 ± 7.0 |
| Asparagine | 29.0 ± 2.3 | |
| GABA | 11.95 ± 0.88 | |
| Glutamate | 155.9 ± 6.8 | |
| Glutamine | 80.2 ± 8.4 | |
| Isoleucine | 15.9 ± 1.2 | |
| Leucine | 7.81 ± 0.59 | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.572 ± 0.051 | |
| Threonine | 10.78 ± 0.86 | |
| Tryptophan | 2.65 ± 0.19 | |
| Tyrosine | 6.09 ± 0.47 | |
| Valine | 15.4 ± 1.2 | |
| Organic acids | Betalamic acid | 0.763 ± 0.071 |
| Citrate | 169 ± 14 | |
| Formate | 1.421 ± 0.092 | |
| Fumarate | 0.694 ± 0.051 | |
| Malate | 84.6 ± 7.3 | |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoate | 0.393 ± 0.032 | |
| 4-Hydroxycumarate | 1.054 ± 0.054 | |
| Carbohydrates | Arabinose | 9.56 ± 0.78 |
| Fructose | 161 ± 11 | |
| Glucose | 393 ± 31 | |
| Sucrose | 5610 ± 454 | |
| Miscellaneous | Betaine | 245 ± 20 |
| Betanin | 12.6 ± 1.1 | |
| Choline | 1.91 ± 0.18 | |
| Dopamine | 7.26 ± 0.65 | |
| Myo-Inositol | 147 ± 12 | |
| Trigonelline | 1.13 ± 0.11 |
| Molecular Portion | Structure | δ 1H | Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Methylpyridine-2-carboxylic acid | |||
| CH-3 | 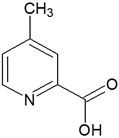 | 7.90 | d |
| CH-5 | 7.48 | dd | |
| CH-6 | 8.48 | d | |
| CH3 | 2.46 | s | |
| Dopamine-3-O-sulfate | |||
| CH2-α |  | 3.27 | t |
| CH2-β | 2.94 | t | |
| CH-2 | 6.92 | d | |
| CH-5 | 6.91 | d | |
| CH-6 | 6.75 | dd | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giampaoli, O.; Ieno, C.; Sciubba, F.; Spagnoli, M.; Miccheli, A.; Tomassini, A.; Aureli, W.; Fattorini, L. Metabolic Biomarkers of Red Beetroot Juice Intake at Rest and after Physical Exercise. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2026. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092026
Giampaoli O, Ieno C, Sciubba F, Spagnoli M, Miccheli A, Tomassini A, Aureli W, Fattorini L. Metabolic Biomarkers of Red Beetroot Juice Intake at Rest and after Physical Exercise. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2026. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092026
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiampaoli, Ottavia, Cristian Ieno, Fabio Sciubba, Mariangela Spagnoli, Alfredo Miccheli, Alberta Tomassini, Walter Aureli, and Luigi Fattorini. 2023. "Metabolic Biomarkers of Red Beetroot Juice Intake at Rest and after Physical Exercise" Nutrients 15, no. 9: 2026. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092026
APA StyleGiampaoli, O., Ieno, C., Sciubba, F., Spagnoli, M., Miccheli, A., Tomassini, A., Aureli, W., & Fattorini, L. (2023). Metabolic Biomarkers of Red Beetroot Juice Intake at Rest and after Physical Exercise. Nutrients, 15(9), 2026. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092026








