Effects of Nutritional Interventions in Older Adults with Malnutrition or at Risk of Malnutrition on Muscle Strength and Mortality: Results of Pooled Analyses of Individual Participant Data from Nine RCTs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection
2.2. Study Setting and Type of Intervention
2.3. Participant Data Extraction
2.4. Muscle Strength
2.5. Mortality
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Setting and Type of Intervention
3.2. Participants
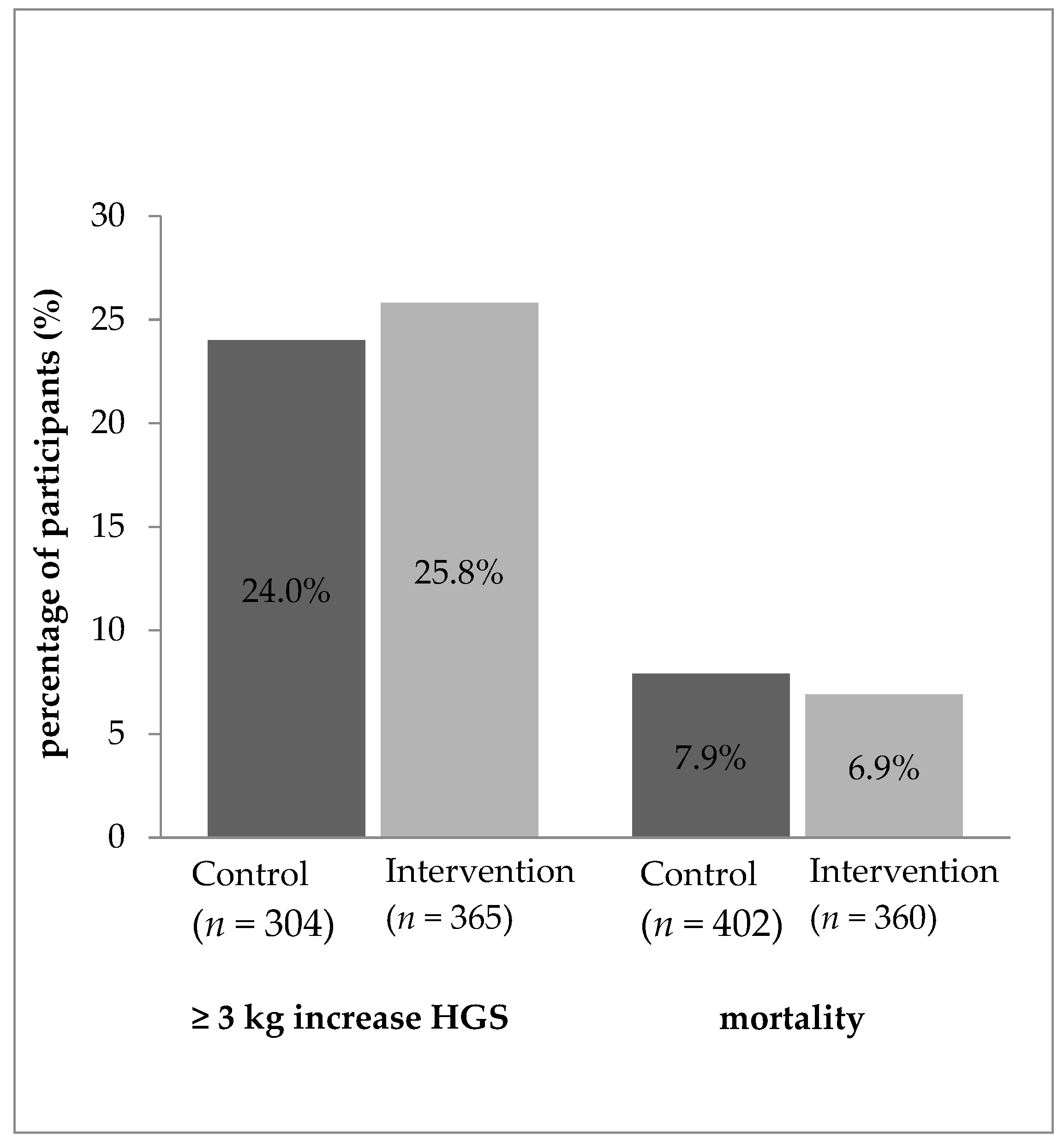
3.3. Treatment Effect on Handgrip Strength
3.4. Treatment Effect on Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norman, K.; Pichard, C.; Lochs, H.; Pirlich, M. Prognostic impact of disease-related malnutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, A.C.; Potter, J.; Avenell, A. Protein and energy supplementation in elderly people at risk from malnutrition. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 2, CD003288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereda, E.; Pedrolli, C.; Klersy, C.; Bonardi, C.; Quarleri, L.; Cappello, S.; Turri, A.; Rondanelli, M.; Caccialanza, R. Nutritional status in older persons according to healthcare setting: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence data using MNA®. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Pérez, A.; Abraha, I.; Cherubini, A.; Collinson, A.; Dardevet, D.; de Groot, L.C.; de van der Schueren, M.A.; Hebestreit, A.; Hickson, M.; Jaramillo-Hidalgo, J. Efficacy of non-pharmacological interventions to treat malnutrition in older persons: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The SENATOR project ONTOP series and MaNuEL knowledge hub project. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 49, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkent, J.W.; Naumann, E.; Vasse, E.; van der Heijden, E.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E. Prevalence and determinants of undernutrition in a sample of dutch community-dwelling older adults: Results from two online screening tools. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Brown, C.J.; Burgio, K.L.; Kilgore, M.L.; Ritchie, C.S.; Roth, D.L.; West, D.S.; Locher, J.L. Undernutrition at baseline and health services utilization and mortality over a 1-year period in older adults receiving Medicare home health services. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2011, 12, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiesswetter, E.; Pohlhausen, S.; Uhlig, K.; Diekmann, R.; Lesser, S.; Uter, W.; Heseker, H.; Stehle, P.; Sieber, C.C.; Volkert, D. Prognostic Differences of the Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form and Long Form in Relation to 1-Year Functional Decline and Mortality in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Receiving Home Care. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abizanda, P.; Sinclair, A.; Barcons, N.; Lizán, L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Costs of Malnutrition in Institutionalized and Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, K.; Nichols, C.; Bowden, S.; Milosavljevic, M.; Lambert, K.; Barone, L.; Mason, M.; Batterham, M. Poor nutritional status of older subacute patients predicts clinical outcomes and mortality at 18 months of follow-up. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders, I.; Volkert, D.; de Groot, L.C.; Beck, A.M.; Feldblum, I.; Jobse, I.; Neelemaat, F.; de van der Schueren, M.A.; Shahar, D.R.; Smeets, E.T. Effectiveness of nutritional interventions in older adults at risk of malnutrition across different health care settings: Pooled analyses of individual participant data from nine randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de van der Schueren, M.A.; Wijnhoven, H.A.; Kruizenga, H.M.; Visser, M. A critical appraisal of nutritional intervention studies in malnourished, community dwelling older persons. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munk, T.; Tolstrup, U.; Beck, A.M.; Holst, M.; Rasmussen, H.H.; Hovhannisyan, K.; Thomsen, T. Individualised dietary counselling for nutritionally at-risk older patients following discharge from acute hospital to home: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, C.; de van der Schueren, M.A.; Kruizenga, H.M.; Weekes, C.E. Dietary advice with or without oral nutritional supplements for disease-related malnutrition in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 12, CD002008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Council of the Netherlands. Undernutrition in the Elderly; Publication no. 2011/32E; Health Council of the Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, C.; Smith, R.; Gibbs, M.; Weekes, C.E.; Emery, P.W. Quality of the evidence supporting the role of oral nutritional supplements in the management of malnutrition: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.D.; Lambert, P.C.; Abo-Zaid, G. Meta-analysis of individual participant data: Rationale, conduct, and reporting. BMJ 2010, 340, c221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Volkert, D.; Corish, C.; Geisler, C.; Groot, L.C.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Lohrmann, C.; O’Connor, E.M.; Schindler, K.; Schueren, M.A. Tackling the increasing problem of malnutrition in older persons: The Malnutrition in the Elderly (MaNuEL) Knowledge Hub. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debray, T.P.A.; Moons, K.G.M.; Koffijberg, H.; Abo-Zaid, G.M.A.; Da Riley, R. Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis for a Binary Outcome: One-Stage or Two-Stage? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debray, T.P.; Moons, K.G.; van Valkenhoef, G.; Efthimiou, O.; Hummel, N.; Groenwold, R.H.; Reitsma, J.B. Get real in individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis: A review of the methodology. Res. Synth. Methods 2015, 6, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, R.W. Grip strength: An indispensable biomarker for older adults. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.; Lu, Y.; Yao, M.M.; Kosik, R.O. Correlation between hand grip strength and regional muscle mass in older Asian adults: An observational study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, M.; Mendonça, N.; Avgerinou, C.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Goisser, S.; Kiesswetter, E.; Siebentritt, H.M.; Volkert, D.; Torbahn, G. Towards developing a Core Outcome Set for malnutrition intervention studies in older adults: A scoping review to identify frequently used research outcomes. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2022, 13, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiber, N. Strong or weak handgrip? Normative reference values for the German population across the life course stratified by sex, age, and body height. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Pérez, A.; Lozano-Montoya, I.; Volkert, D.; Visser, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Relevant outcomes for nutrition interventions to treat and prevent malnutrition in older people: A collaborative senator-ontop and manuel delphi study. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaegi-Braun, N.; Tribolet, P.; Baumgartner, A.; Fehr, R.; Baechli, V.; Geiser, M.; Deiss, M.; Gomes, F.; Kutz, A.; Hoess, C. Value of handgrip strength to predict clinical outcomes and therapeutic response in malnourished medical inpatients: Secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berner, L.A.; Becker, G.; Wise, M.; Doi, J. Characterization of dietary protein among older adults in the United States: Amount, animal sources, and meal patterns. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.M.; Kjær, S.; Hansen, B.S.; Storm, R.L.; Thal-Jantzen, K.; Bitz, C. Follow-up home visits with registered dietitians have a positive effect on the functional and nutritional status of geriatric medical patients after discharge: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2013, 27, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.M.; Andersen, U.T.; Leedo, E.; Jensen, L.L.; Martins, K.; Rask, K.O.; Vedelspang, A.; Quvang, M.; Ronholt, F. Does adding a dietician to the liaison team after discharge of geriatric patients improve nutritional outcome: A randomised controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2015, 29, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, N.; Chin, A.; Paw, M.J.; de Groot, L.C.; Hiddink, G.J.; van Staveren, W.A. Dietary supplements and physical exercise affecting bone and body composition in frail elderly persons. Am. J. Public Health 2000, 90, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manders, M.; de Groot, C.P.G.M.; Blauw, Y.H.; Dhonukshe-Rutten, R.A.M.; van Hoeckel-Prüst, L.; Bindels, J.G.; Siebelink, E.; van Staveren, W.A. Effect of a nutrient-enriched drink on dietary intake and nutritional status in institutionalised elderly. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelemaat, F.; Bosmans, J.E.; Thijs, A.; Seidell, J.C.; van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren, M.A. Post-discharge nutritional support in malnourished elderly individuals improves functional limitations. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2011, 12, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilp, J.; Kruizenga, H.M.; Wijnhoven, H.A.; van Binsbergen, J.J.; Visser, M. Effects of a dietetic treatment in older, undernourished, community-dwelling individuals in primary care: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieland, M.; van de Rest, O.; Dirks, M.L.; van der Zwaluw, N.; Mensink, M.; van Loon, L.J.; de Groot, L.C. Protein supplementation improves physical performance in frail elderly people: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2012, 13, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stange, I.; Bartram, M.; Liao, Y.; Poeschl, K.; Kolpatzik, S.; Uter, W.; Sieber, C.C.; Stehle, P.; Volkert, D. Effects of a Low-Volume, Nutrient- and Energy-Dense Oral Nutritional Supplement on Nutritional and Functional Status: A Randomized, Controlled Trial in Nursing Home Residents. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 628.e1–628.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauretani, F.; Russo, C.R.; Bandinelli, S.; Bartali, B. Age-associated changes in skeletal muscles and their effect on mobility: An operational diagnosis of sarcopenia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 95, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldblum, I.; German, L.; Castel, H.; Harman-Boehm, I.; Shahar, D.R. Individualized Nutritional Intervention During and After Hospitalization: The Nutrition Intervention Study Clinical Trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition–a consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, M.; Momosaki, R.; Vakili, M.; Abo, M. Nutritional supplementation for activities of daily living and functional ability of older people in residential facilities: A systematic review. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieland, M.; Verdijk, L.B.; de Groot, L.C.; van Loon, L.J. Handgrip strength does not represent an appropriate measure to evaluate changes in muscle strength during an exercise intervention program in frail older people. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2015, 25, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Stobaus, N.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Schulzke, J.D.; Pirlich, M. Hand grip strength: Outcome predictor and marker of nutritional status. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlaan, S.; Maier, A.B.; Bauer, J.M.; Bautmans, I.; Brandt, K.; Donini, L.M.; Maggio, M.; McMurdo, M.E.; Mets, T.; Seal, C. Sufficient levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and protein intake required to increase muscle mass in sarcopenic older adults—The PROVIDE study. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 37, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locher, J.L.; Vickers, K.S.; Buys, D.R.; Ellis, A.; Lawrence, J.C.; Newton, L.E.; Roth, D.L.; Ritchie, C.S.; Bales, C.W. A randomized controlled trial of a theoretically-based behavioral nutrition intervention for community elders: Lessons learned from the behavioral nutrition intervention for community elders study. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkent, J. Malnutrition during the Journey of Ageing; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
| Baseline Characteristics | Handgrip Strength | Mortality | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 669) | Control (n = 304) | Intervention (n = 365) | All (n = 762) | Control (n= 402) | Intervention (n = 360) | |
| Age (y) mean (±SD) | 79.6 (±8.2) | 79.6 (8.4) | 79.5 (8.1) | 78.8 (8.5) | 78.4 (8.5) | 79.3 (8.6) |
| Sex n (% women) | 422 (63.1) | 188 (61.8) | 234 (64.1) | 491 (64.4) | 256 (64.4) | 232 (64.4) |
| HGS (kg) mean (±SD) | 20.5 (±8.6) | 20.9 (8.3) | 20.1 (8.8) | 19.6 (8.4) a | 19.8 (±8.0) | 19.5 (±8.7) |
| Normal HGS n (%) b | 231 (34.5) | 109 (35.9) | 122 (33.4) | 140 (29.9) | 66 (28.7) | 74 (31.1) |
| Low HGS n (%) | 438 (65.5) | 195 (64.1) | 243 (66.6) | 328 (70.1) | 164 (71.3) | 164 (68.9) |
| BMI (kg/m2) Mean (±SD) | 23.2(±4.1) | 23.0 (4.0) | 23.4 (4.3) | 23.2 (4.9) | 23.4 (5.1) | 22.9 (4.7) |
| BMI < 20 n (%) | 270 (40.4) | 127 (41.8) | 143 (39.2) | 345 (45.3) | 177(44.0) | 168 (46.7) |
| BMI > 22 n (%) | 399 (59.6) | 177(58.2) | 222 (60.8) | 417 (54.7) | 225 (56.0) | 192 (53.3) |
| Setting | ||||||
| Hospital n (%) | 291 (43.5) | 139 (45.7) | 152 (41.6) | 546 (71.7) | 298 (74.1) | 248 (68.9) |
| Community dwelling n (%) | 249 (37.2) | 125 (41.1) | 124 (34.0) | 129 (16.9) | 62 (15.4) | 67 (18.6) |
| Institutionalized n (%) | 129 (19.3) c | 40 (13.2) | 89 (24.4) | 87 (11.4) | 42 (10.4) | 45 (12.5) |
| Intervention type | ||||||
| Dietary counselling n (%) | - | - | 146 (40.0) | - | - | 228 (63.3) |
| ONS n (%) | - | - | 156 (42.7) | - | - | 45 (12.5) |
| Dietary counselling + ONS n (%) | - | - | 63 (17.3) | - | - | 87 (24.2) |
| Energy intake (kcal/day) mean (±SD) d | 1707 (558) | 1688 (525) | 1727 (589) | 1491 (574) c | 1449 (552) | 1539 (594) |
| Protein intake (g/kg/bw) mean (±SD) d,e | 1.00(0.38) | 1.00(0.38) | 1.00(0.38) | 0.91 (0.42) | 0.90 (0.41) | 0.94 (0.43) |
| protein < 0.8 g/kg/bw n (%) e | 158 (30.2) | 75 (28.8) | 83 (31.4) | 258 (41.1) | 142 (42.9) | 116 (39.2) |
| protein ≥ 0.8 g/kg/bw n (%) e | 366 (69.8) | 185 (71.2) | 181 (68.6) | 369 (48.4) | 189 (57.1) | 180 (60.8) |
| Handgrip Strength | Mortality | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Follow-Up Values | All (n = 669) | Control (n = 304) | Intervention (n = 365) | All (n = 762) | Control (n= 402) | Intervention (n = 360) |
| HGS (kg) mean (±SD) a | 20.6 (8.9) | 20.9 (8.6) | 20.3 (9.2) | 20.5 (8.6) a | 20.8 (8.2) | 20.2 (8.9) |
| Absolute change in HGS (kg) mean (±SD) | 0.1 (4.2) | −0.1 (4.4) | 0.2 (4.1) | 0.3 (4.6) | 0.2 (4.9) | 0.3 (4.3) |
| Energy intake (kcal/day) mean (±SD) b,c | 1840 (548) b | 1738 (511) | 1941 (565) | 1669 (614) b | 1554 (556.0) | 1803 (652) |
| Protein intake (g/day) mean (±SD) b,c | 70.5 (23.7) b | 66.4 (22.1) | 74.5 (24.6) | 65.7 (24.9) b | 61.6 (23.0) | 70.5 (26.2) |
| Absolute change in energy intake (kcal/day) mean (±SD) d | 123 (582) b | 46 (540) | 199 (613) | 168 (606) b | 105 (542) | 239 (664) |
| Absolute change in protein intake (g/day) mean (±SD) d | 5.0 (26.3) b | 1.3 (25) | 8.8 (26.7) | 6.2 (28.1) b | 3.5 (26.7) | 9.1 (29.6) |
| Absolute change in body weight (kg) mean (±SD) e | 0.5 (3.6) b | −0.1 (3.9) | 1.0 (3.2) | 0.6 (4.6) b,e | 0.1 (5.0) | 1.1 (3.9) |
| Weight gain ≥ 1 kg n (%) | 261 (39.0) b | 103 (33.9) | 158 (43.3) | 300 (42.0) b | 137 (36.1) | 163 (48.7) |
| Increase in energy intake ≥ 250 kcal n (%) | 186 (36.5) b | 72 (28.3) | 114 (44.7) | 229 (41.0) b | 100 (34.0) | 129 (48.7) |
| Increase in protein intake ≥ 4 g/day | 255 (50.1) b | 105 (41.3) | 150 (58.8) | 301 (54.1) b | 136 (46.4) | 165 (62.7) |
| Increase in HGS ≥ 2 kg n (%) a | 226 (33.8) | 99 (32.6) | 127 (34.8) | 154 (37.5) | 76 (38.2) | 78 (36.8) |
| Increase in HGS ≥ 4 kg n (%) a | 114 (17.0) | 49 (16.1) | 65 (17.8) | 80 (19.5) | 39 (19.6) | 41 (19.3) |
| OR * | CI 95% | |
|---|---|---|
| Increase HGS ≥ 3 kg | ||
| Crude | 1.146 | 0.822–1.598 |
| Adjusted for age and sex at baseline | 1.145 | 0.817–1.603 |
| Adjusted for age, sex, BMI and HGS at baseline | 1.110 | 0.766–1.588 |
| Mortality | ||
| Crude | 0.790 | 0.450–1.387 |
| Adjusted for age and sex at baseline | 0.767 | 0.421–1.397 |
| Adjusted for age, sex and BMI at baseline | 0.780 | 0.416–1.461 |
| N Subjects C/I | OR * | CI 95% | p Interaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase HGS ≥ 3 kg | ||||
| Age < 80 year | 147/159 | 0.942 | 0.633–1.400 | 0.100 |
| Age ≥ 80 year | 157/206 | 1.348 | 0.930–1.954 | |
| Women | 188/234 | 0.694 | 0.694–1.618 | 0.925 |
| Men | 116/131 | 1.192 | 0.496–2.868 | |
| HGS normal a | 109/122 | 0.844 | 0.392–1.818 | 0.655 |
| HGS low | 195/243 | 1.266 | 0.871–1.840 | |
| BMI < 22 | 127/143 | 1.071 | 0.877–1.309 | 0.770 |
| BMI ≥ 22 | 177/222 | 1.145 | 0.669–1.962 | |
| Energy intake low b | 124/137 | 0.965 | 0.615–1.515 | 0.828 |
| Energy intake high | 136/127 | 1.834 | 1.002–3.356 | |
| Protein < 0.8 g/kg/bw c | 75/83 | 0.641 | 0.373–1.102 | 0.119 |
| Protein ≥ 0.8 g/kg/bw | 185/181 | 1.907 | 1.234–2.947 | |
| Mortality | ||||
| Age < 80 year | 222/172 | 1.068 | 0.532–2.144 | 0.727 |
| Age ≥ 80 year | 180/188 | 0.653 | 0.318–1.342 | |
| Women | 259/232 | 0.631 | 0.341–1.165 | 0.072 |
| Men | 143/128 | 1.125 | 0.602–2.104 | |
| HGS normal a | 66/74 | 1.741 | 0.383–7.920 | 0.474 |
| HGS low | 164/164 | 0.879 | 0.380–2.033 | |
| BMI < 22 | 177/168 | 0.592 | 0.360–0.973 | 0.941 |
| BMI ≥ 22 | 225/192 | 1.082 | 0.456–2.566 | |
| Energy intake low d | 171/143 | 1.090 | 0.447–2.662 | 0.004 |
| Energy intake high | 161/155 | 0.756 | 0.340–1.678 | |
| Protein < 0.8 g/kg/bw c | 142/116 | 1.725 | 0.641–4.639 | 0.052 |
| Protein ≥ 0.8 g/kg/bw | 189/180 | 0.536 | 0.211–1.362 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Zwienen-Pot, J.I.; Reinders, I.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M.; Beck, A.M.; Feldblum, I.; Jobse, I.; Neelemaat, F.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E.; Shahar, D.R.; Smeets, E.T.H.C.; et al. Effects of Nutritional Interventions in Older Adults with Malnutrition or at Risk of Malnutrition on Muscle Strength and Mortality: Results of Pooled Analyses of Individual Participant Data from Nine RCTs. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092025
van Zwienen-Pot JI, Reinders I, de Groot LCPGM, Beck AM, Feldblum I, Jobse I, Neelemaat F, de van der Schueren MAE, Shahar DR, Smeets ETHC, et al. Effects of Nutritional Interventions in Older Adults with Malnutrition or at Risk of Malnutrition on Muscle Strength and Mortality: Results of Pooled Analyses of Individual Participant Data from Nine RCTs. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092025
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Zwienen-Pot, Judith I., Ilse Reinders, Lisette C. P. G. M. de Groot, Anne Marie Beck, Ilana Feldblum, Inken Jobse, Floor Neelemaat, Marian A. E. de van der Schueren, Danit R. Shahar, Ellen T. H. C. Smeets, and et al. 2023. "Effects of Nutritional Interventions in Older Adults with Malnutrition or at Risk of Malnutrition on Muscle Strength and Mortality: Results of Pooled Analyses of Individual Participant Data from Nine RCTs" Nutrients 15, no. 9: 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092025
APA Stylevan Zwienen-Pot, J. I., Reinders, I., de Groot, L. C. P. G. M., Beck, A. M., Feldblum, I., Jobse, I., Neelemaat, F., de van der Schueren, M. A. E., Shahar, D. R., Smeets, E. T. H. C., Tieland, M., Wijnhoven, H. A. H., Volkert, D., & Visser, M. (2023). Effects of Nutritional Interventions in Older Adults with Malnutrition or at Risk of Malnutrition on Muscle Strength and Mortality: Results of Pooled Analyses of Individual Participant Data from Nine RCTs. Nutrients, 15(9), 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15092025







