Effects of Dietary Supplementation of a Microalgae Extract Containing Fucoxanthin Combined with Guarana on Cognitive Function and Gaming Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
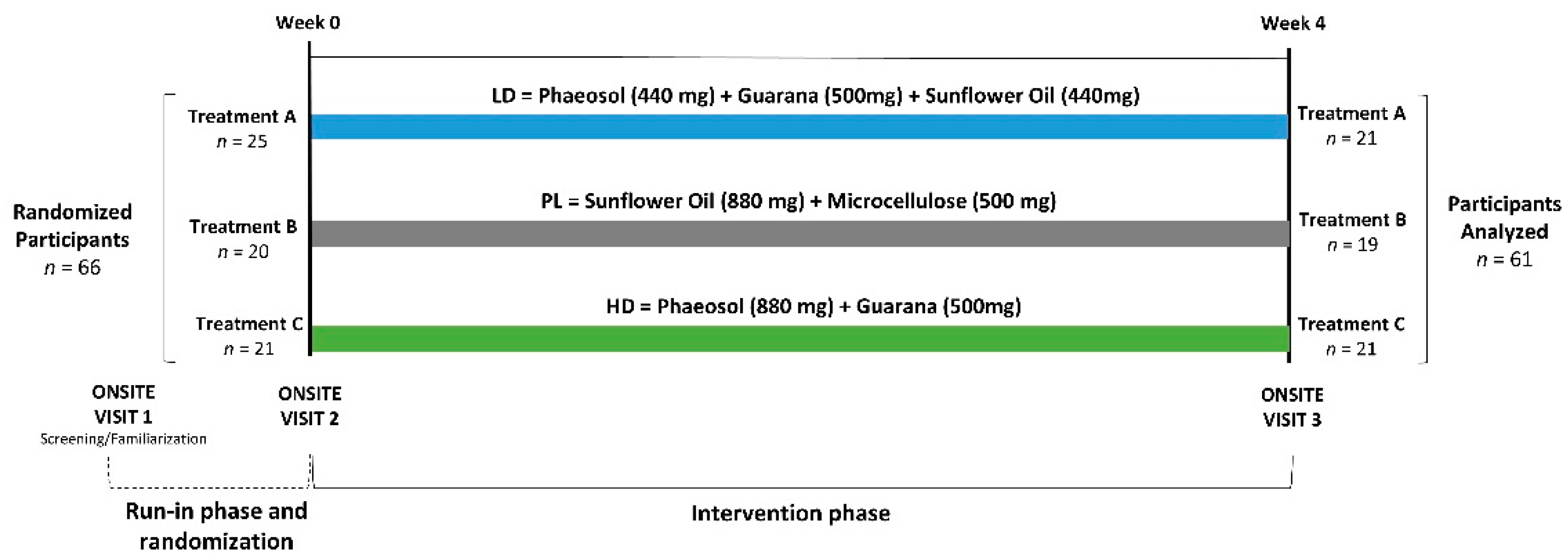
2.1. Design of Study
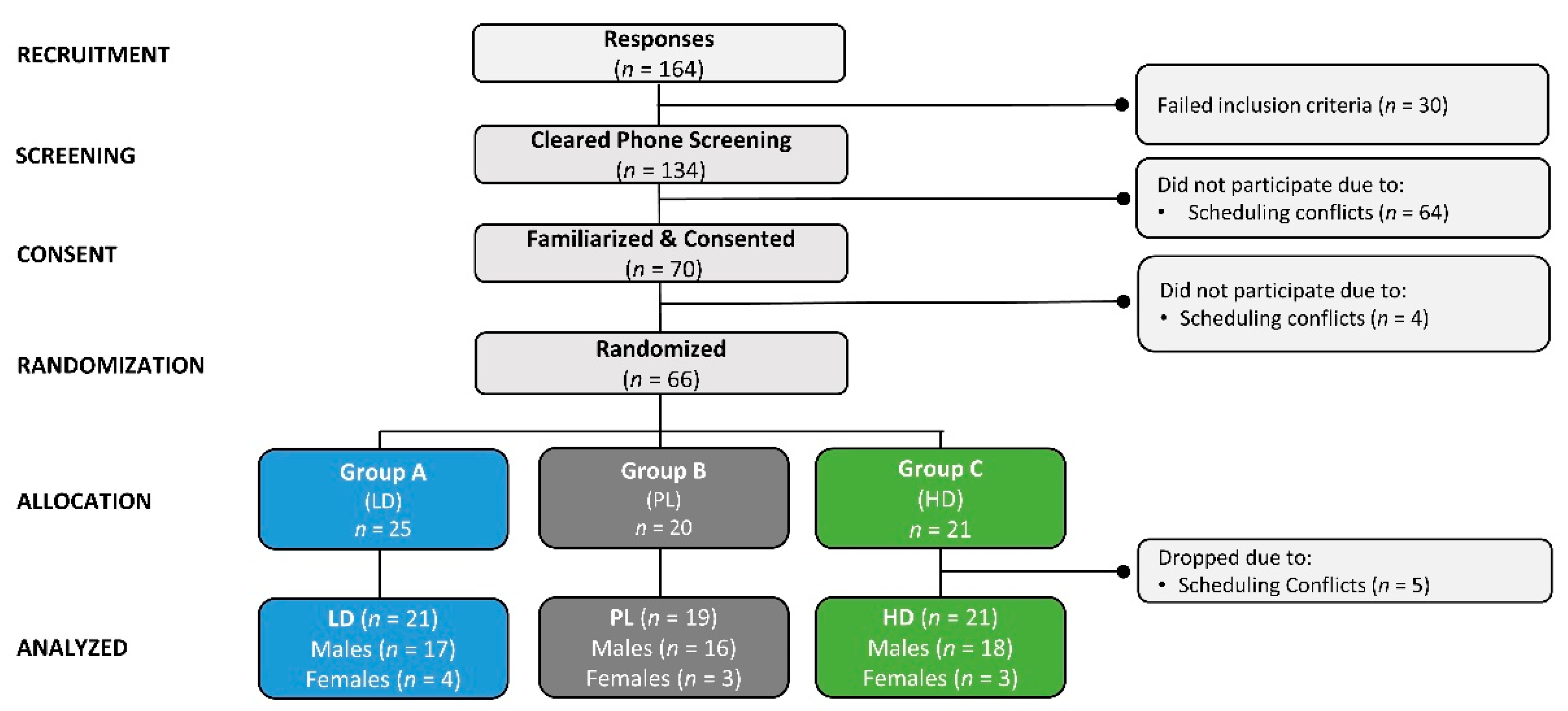
2.2. Study Participants
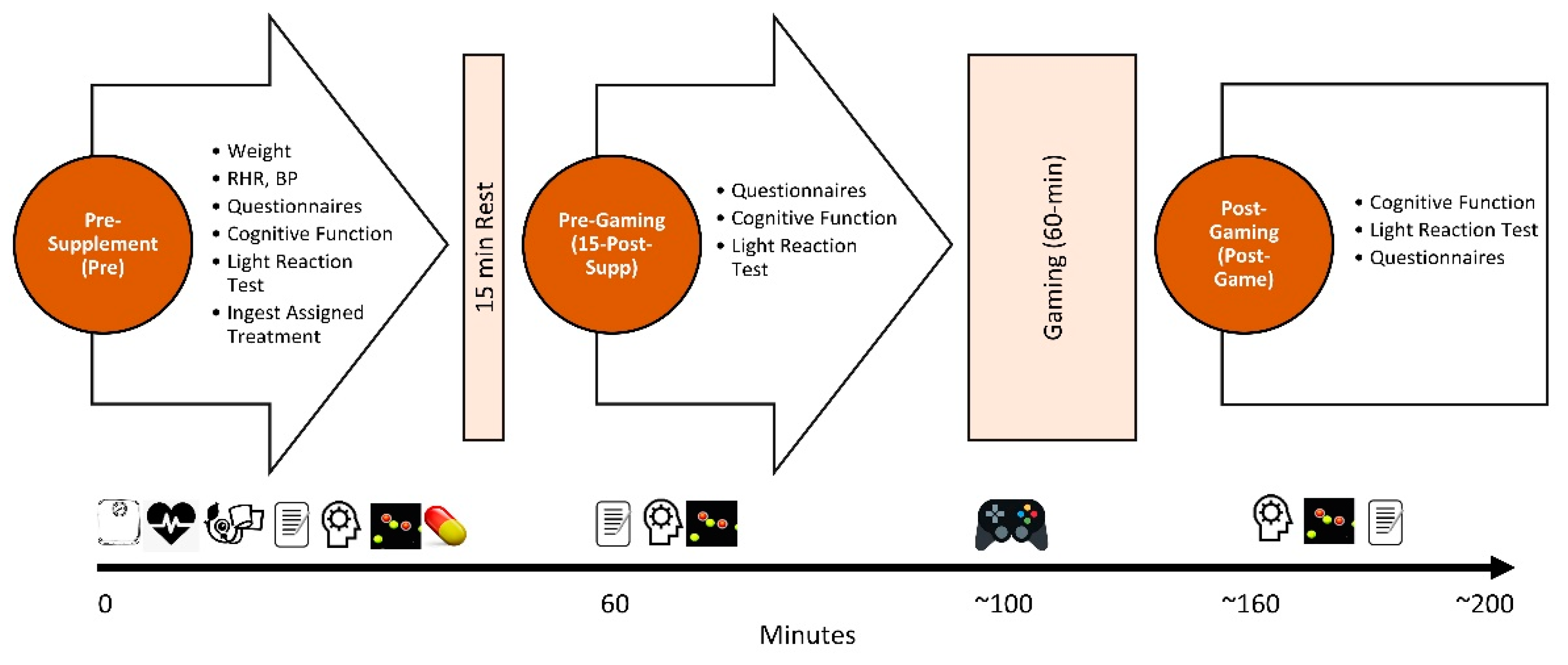
2.3. Testing Protocol
2.4. Supplementation Protocol
3. Procedures
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Diet Control
3.3. Cognitive Assessment
3.4. Light Tracking Reaction Test
3.5. Gaming Performance Assessment
3.6. Profile of Mood States
3.7. Ratings of Fatigue and Eye Irritability
3.8. Side Effects and Sleep Quality
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Data
4.2. PEBL Cognitive Function Assessment
4.2.1. Berg-Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
4.2.2. Go/No-Go Task Test
4.2.3. Sternberg Task Test
4.2.4. Psychomotor Vigilance Task Test
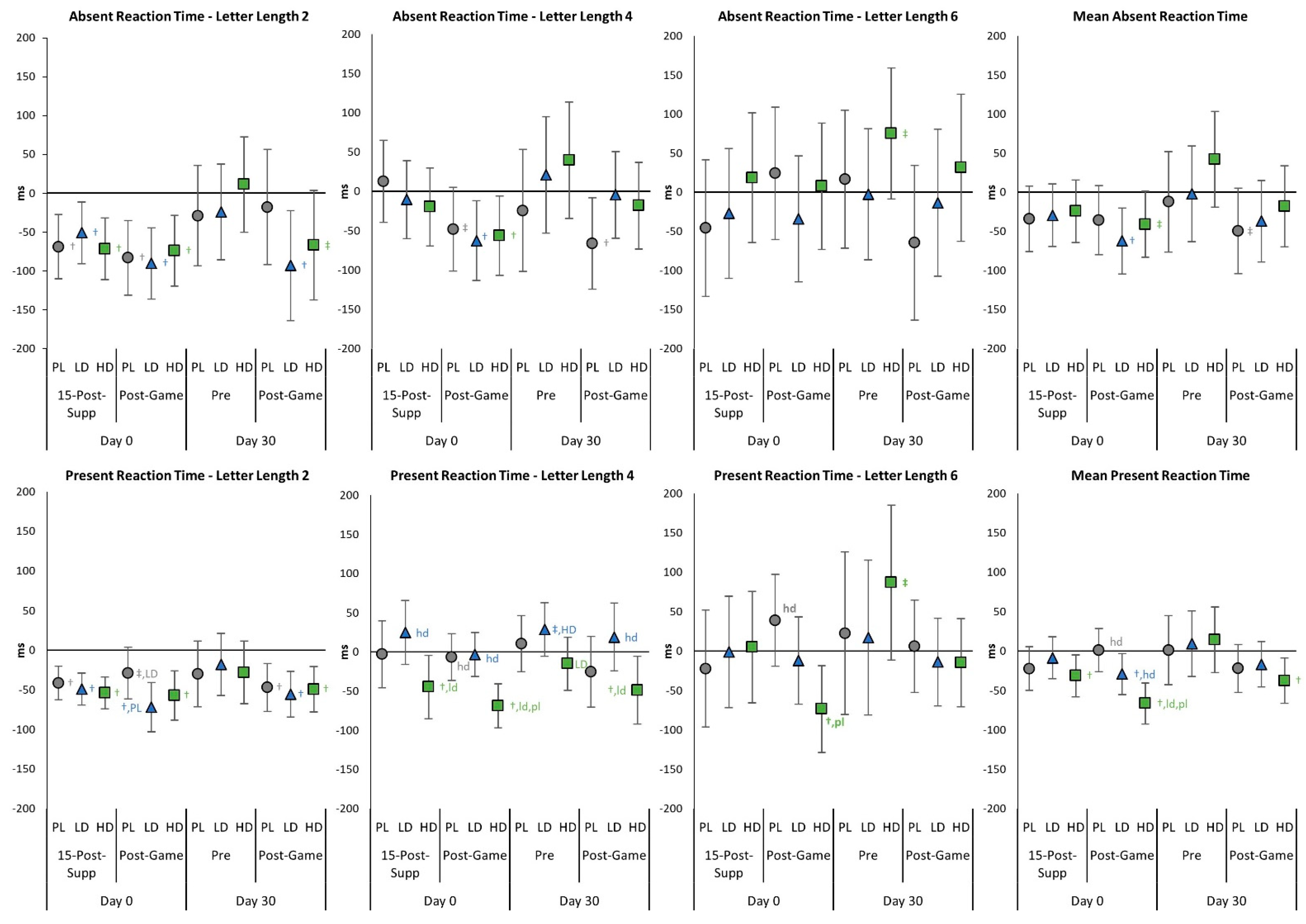
4.3. Light Reaction Test
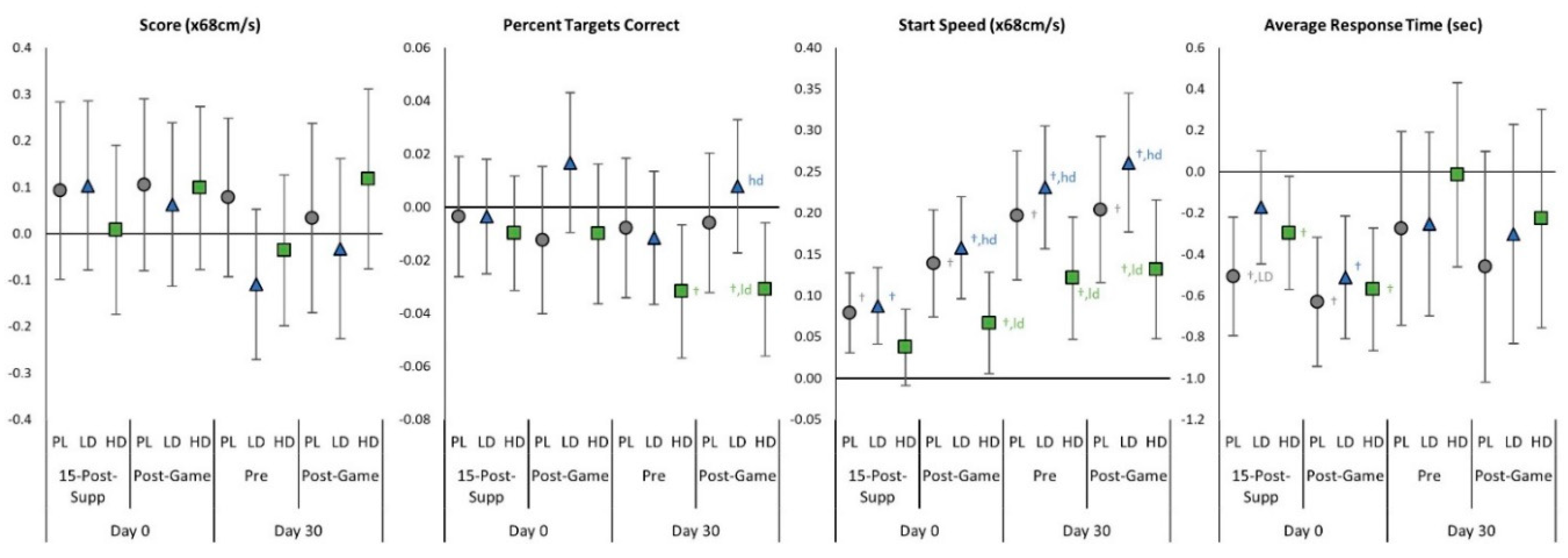
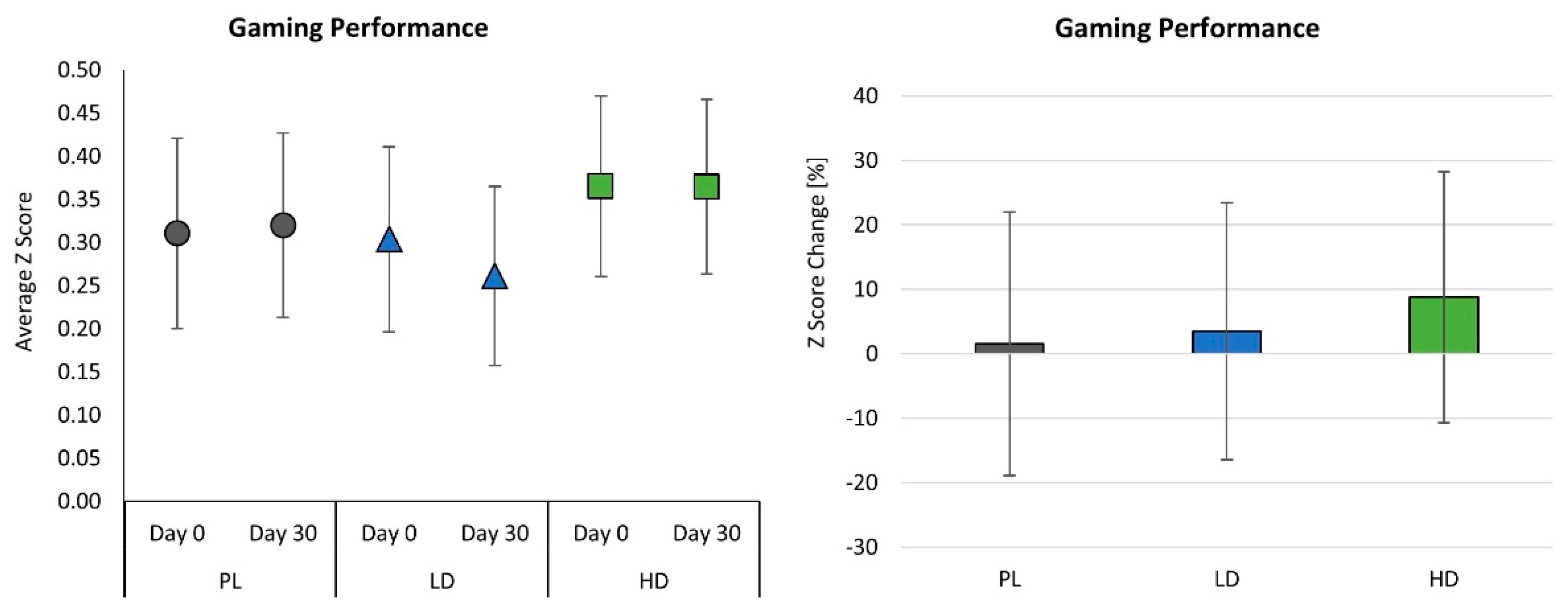
4.4. Gaming Performance
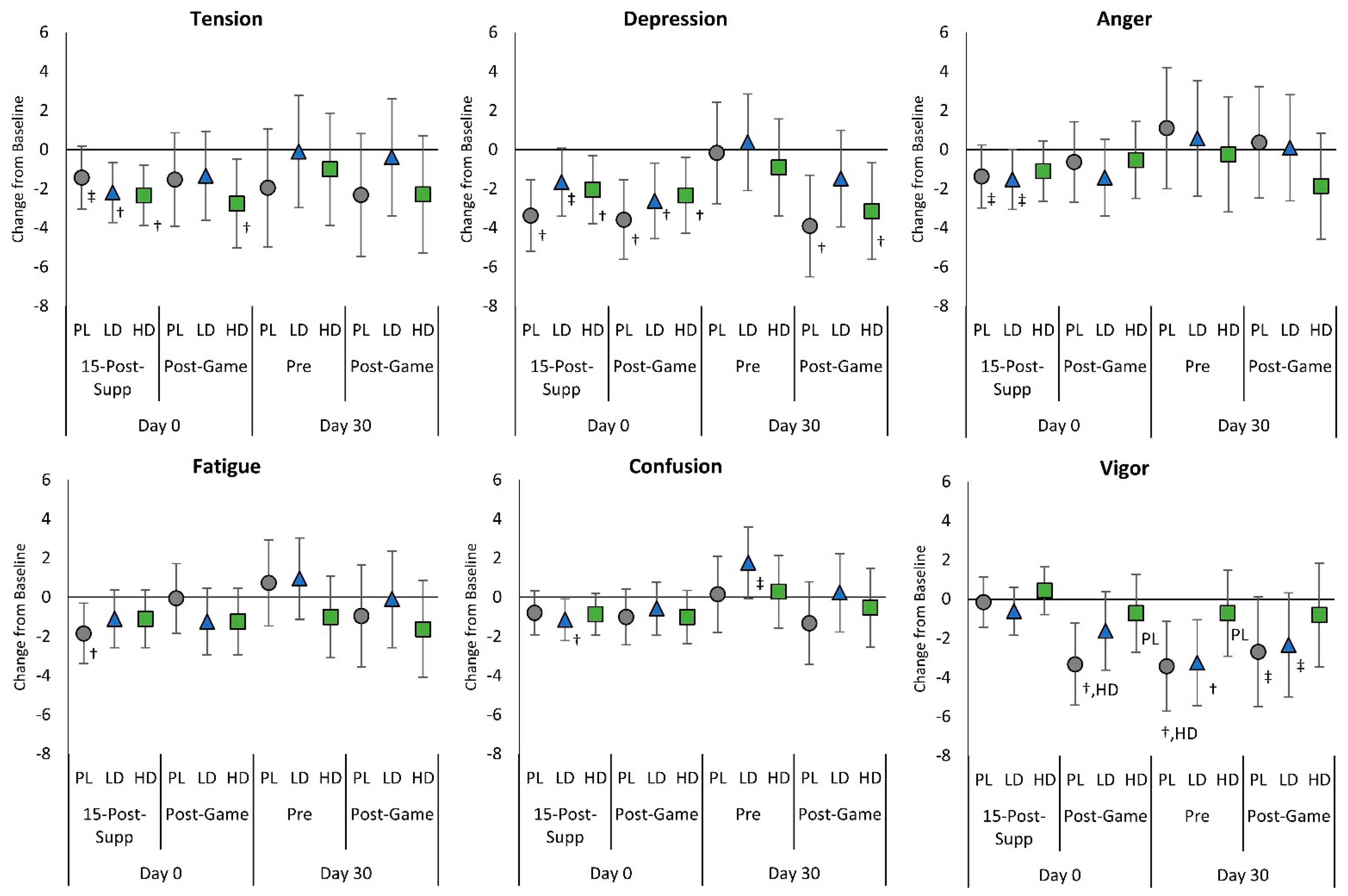
4.5. Mood State, Fatigue, and Eye Irritability Ratings
4.6. Safety and Sleep Assessments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez, D.E.; McAllister, M.J.; Waldman, H.S.; Ferrando, A.A.; Joyce, J.; Barringer, N.D.; Dawes, J.J.; Kieffer, A.J.; Harvey, T.; Kerksick, C.M.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Tactical athlete nutrition. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2022, 19, 267–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, M.S.; Landau, A.N.; Shimamura, A.P. Action video game experience reduces the cost of switching tasks. Atten. Percept. Psychophys 2012, 74, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, M.S.; Prinzmetal, W.; Shimamura, A.P.; Landau, A.N. Improved control of exogenous attention in action video game players. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzato, L.S.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; van den Wildenberg, W.P.; Hommel, B. DOOM’d to Switch: Superior Cognitive Flexibility in Players of First Person Shooter Games. Front. Psychol. 2010, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, B.D.; Maddox, W.T.; Love, B.C. Real-time strategy game training: Emergence of a cognitive flexibility trait. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.J.; Toth, A.J.; Moran, A.P.; Kowal, M.; Exton, C. eSports: A new window on neurocognitive expertise? Prog. Brain Res. 2018, 240, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, N.S.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Nelson, M.T.; Grgic, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Jenkins, N.D.M.; Arent, S.M.; Antonio, J.; Stout, J.R.; Trexler, E.T.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.J.; Rothschild, J.; Earnest, C.P.; Blaisdell, A. The Effects of Energy Drink Consumption on Cognitive and Physical Performance in Elite League of Legends Players. Sports 2019, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.; La Bounty, P.; Taylor, L.; Nelson, M.T.; Greenwood, M.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Lopez, H.L.; Hoffman, J.R.; Stout, J.R.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Energy drinks. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2013, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagim, A.R.; Harty, P.S.; Tinsley, G.M.; Kerksick, C.M.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Kreider, R.B.; Arent, S.M.; Jager, R.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Stout, J.R.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Energy drinks and energy shots. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2171314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Haskell, C.F.; Robertson, B.; Reay, J.; Brewster-Maund, C.; Luedemann, J.; Maggini, S.; Ruf, M.; Zangara, A.; Scholey, A.B. Improved cognitive performance and mental fatigue following a multi-vitamin and mineral supplement with added guarana (Paulliniacupana). Appetite 2008, 50, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Haskell, C.F.; Wesnes, K.A.; Scholey, A.B. Improved cognitive performance in human volunteers following administration of guarana (Paulliniacupana) extract: Comparison and interaction with Panax ginseng. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 79, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholey, A.; Bauer, I.; Neale, C.; Savage, K.; Camfield, D.; White, D.; Maggini, S.; Pipingas, A.; Stough, C.; Hughes, M. Acute effects of different multivitamin mineral preparations with and without Guarana on mood, cognitive performance and functional brain activation. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3589–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreider, R.B. Current perspectives of caffeinated energy drinks on exercise performance and safety assessment. Nutr. Diet. Suppl. 2018, 10, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros de Medeiros, V.P.; da Costa, W.K.A.; da Silva, R.T.; Pimentel, T.C.; Magnani, M. Microalgae as source of functional ingredients in new-generation foods: Challenges, technological effects, biological activity, and regulatory issues. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4929–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Fan, C.; Wu, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Health Benefits, Food Applications, and Sustainability of Microalgae-Derived N-3 PUFA. Foods 2022, 11, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subermaniam, K.; Teoh, S.L.; Yow, Y.Y.; Tang, Y.Q.; Lim, L.W.; Wong, K.H. Marine algae as emerging therapeutic alternatives for depression: A review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Chen, W.; Tian, F.; Yuan, C.; Wang, H.; Yue, H. Neuroprotective role of fucoxanthin against cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarmeas, N.; Anastasiou, C.A.; Yannakoulia, M. Nutrition and prevention of cognitive impairment. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Fucoxanthin provides neuroprotection in models of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE and Nrf2-autophagy pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, W.; Liu, T. Combined production of fucoxanthin and EPA from two diatom strains Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Cylindrotheca fusiformis cultures. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójtowicz, S.; Strosznajder, A.K.; Jeżyna, M.; Strosznajder, J.B. The Novel Role of PPAR Alpha in the Brain: Promising Target in Therapy of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minghetti, L.; Salvi, R.; Lavinia Salvatori, M.; Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; De Nuccio, C.; Visentin, S.; Bultel-Ponce, V.; Oger, C.; Guy, A.; Galano, J.M.; et al. Nonenzymatic oxygenated metabolites of alpha-linolenic acid B1- and L1-phytoprostanes protect immature neurons from oxidant injury and promote differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitors through PPAR-gamma activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ye, M.; Guo, H. An Updated Review of Randomized Clinical Trials Testing the Improvement of Cognitive Function of Ginkgo biloba Extract in Healthy People and Alzheimer’s Patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartar, J.L.; Kalman, D.; Hewlings, S. A Prospective Study Evaluating the Effects of a Nutritional Supplement Intervention on Cognition, Mood States, and Mental Performance in Video Gamers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowinski, R.; Gonzalez, D.; Xing, D.; Yoo, C.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Humphries, M.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J.; et al. Effects of Inositol-Enhanced Bonded Arginine Silicate Ingestion on Cognitive and Executive Function in Gamers. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, D.; Harvey, P.D.; Perez Ojalvo, S.; Komorowski, J. Randomized Prospective Double-Blind Studies to Evaluate the Cognitive Effects of Inositol-Stabilized Arginine Silicate in Healthy Physically Active Adults. Nutrients 2016, 8, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, R.J.; Martin, K.R.; Pence, J.C. Impact of AmaTea® Max on physiological measures and gaming performance in active gamers: A placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized study. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2022, 8, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, B. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription 9th Ed. 2014. J. Can. Chiropr. Assoc. 2014, 58, 328. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, V.; Voci, S.M.; Mendes-Netto, R.S.; da Silva, D.G. The relative validity of a food record using the smartphone application MyFitnessPal. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 75, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.W.; Morgan, N.; Ward, D.; Tangney, C.; Alshurafa, N.; Van Horn, L.; Spring, B. Comparative Validity of Mostly Unprocessed and Minimally Processed Food Items Differs Among Popular Commercial Nutrition Apps Compared with a Research Food Database. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 122, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, B.J.; Mueller, S.T.; Geerken, A.R.; Dixon, K.L.; Kroliczak, G.; Olsen, R.H.; Miller, J.K. Reliability and validity of neurobehavioral function on the Psychology Experimental Building Language test battery in young adults. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, C.; Xing, D.; Gonzalez, D.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J.; Faries, M.; Kephart, W.; et al. Acute Paraxanthine Ingestion Improves Cognition and Short-Term Memory and Helps Sustain Attention in a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.T.; Piper, B.J. The Psychology Experiment Building Language (PEBL) and PEBL Test Battery. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 222, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.T. The Psychology Experiment Building Language; Lulu Publishers: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2021; 270p. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, E.A. A simple objective technique for measuring flexibility in thinking. J. Gen. Psychol. 1948, 39, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, F.; Logan, G.D. Automatic and controlled response inhibition: Associative learning in the go/no-go and stop-signal paradigms. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2008, 137, 649–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdjian, S.; Baker, L.A.; Lozano, D.I.; Raine, A. Assessing inattention and impulsivity in children during the Go/NoGo task. Br. J. Dev. Psychol. 2009, 27, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, S. High-Speed Scanning in Human Memory. Science 1966, 153, 652–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leark, R.A.; Greenberg, L.K.; Kindschi, C.L.; Dupuy, T.R.; Hughes, S.J. Test of Variables of Attention: Professional Manual; The TOVA Company: Langley, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, L.K.; Kindschi, C.L.; Dupuy, T.R.; Holder, C. Test of Variables of Attention: Clinical Manual; The TOVA Company: Langley, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Peshawa, J.; Ali, M.; Faraj, R.H. Data Normalization and Standardization: A Technical Report; Koya University: Koya, Iraq, 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shacham, S. A shortened version of the Profile of Mood States. J. Pers. Assess. 1983, 47, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.M.; Snyder, M.; Krichbaum, K. Translation and equivalence: The Profile of Mood States Short Form in English and Chinese. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2002, 39, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, W.K.; Liang, Y.X.; Nell, V.; Kang, S.K.; Cole, D.; Bazylewicz-Walczak, B.; Rohlman, D.S.; Sizemore, O.J. Lessons learned--15 years of the WHO-NCTB: A review. Neurotoxicology 2000, 21, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grubic, T.J.; Sowinski, R.J.; Nevares, B.E.; Jenkins, V.M.; Williamson, S.L.; Reyes, A.G.; Rasmussen, C.; Greenwood, M.; Murano, P.S.; Earnest, C.P.; et al. Comparison of ingesting a food bar containing whey protein and isomalto-oligosaccharides to carbohydrate on performance and recovery from an acute bout of resistance-exercise and sprint conditioning: An open label, randomized, counterbalanced, crossover pilot study. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2019, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.P.; Earnest, C.P.; Koozehchian, M.; Galvan, E.; Dalton, R.; Walker, D.; Rasmussen, C.; Murano, P.S.; Greenwood, M.; Kreider, R.B. Effects of acute ingestion of a pre-workout dietary supplement with and without p-synephrine on resting energy expenditure, cognitive function and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.B.; Earnest, C.P.; Dalton, R.L.; Sowinski, R.J.; Grubic, T.J.; Favot, C.J.; Coletta, A.M.; Rasmussen, C.; Greenwood, M.; Kreider, R.B. Short-Term Effects of a Ready-to-Drink Pre-Workout Beverage on Exercise Performance and Recovery. Nutrients 2017, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, R.L.; Sowinski, R.J.; Grubic, T.J.; Collins, P.B.; Coletta, A.M.; Reyes, A.G.; Sanchez, B.; Koozehchian, M.; Jung, Y.P.; Rasmussen, C.; et al. Hematological and Hemodynamic Responses to Acute and Short-Term Creatine Nitrate Supplementation. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, E.; Walker, D.K.; Simbo, S.Y.; Dalton, R.; Levers, K.; O’Connor, A.; Goodenough, C.; Barringer, N.D.; Greenwood, M.; Rasmussen, C.; et al. Acute and chronic safety and efficacy of dose dependent creatine nitrate supplementation and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2016, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P. Beyond statistical significance: Clinical interpretation of rehabilitation research literature. Int. J. Sport. Phys. Ther. 2014, 9, 726–736. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Social Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cereda, G.; Scolari, M. Effect of an energy stimulator on the performance of a group of young people: Evaluation by a video-game test. Acta Vitam. Enzym. 1984, 6, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Doma, K.M.; Lewis, E.D.; Barracato, J.M.; Brink, L.R.; Gratson, A.A.; Pandey, N.; Crowley, D.C.; Evans, M. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Study Investigating the Efficacy of a Whole Coffee Cherry Extract and Phosphatidylserine Formulation on Cognitive Performance of Healthy Adults with Self-Perceived Memory Problems. Neurol. Ther. 2023. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, D.; Roman, P.; Canadas, F.; Sanchez-Labraca, N. The Effect of Multiprobiotics on Memory and Attention in Fibromyalgia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kackley, M.L.; Brownlow, M.L.; Buga, A.; Crabtree, C.D.; Sapper, T.N.; O’Connor, A.; Volek, J.S. The effects of a 6-week controlled, hypocaloric ketogenic diet, with and without exogenous ketone salts, on cognitive performance and mood states in overweight and obese adults. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 971144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.; Yoo, C.; Gonzalez, D.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J.; Faries, M.; Kephart, W.; et al. Dose-Response of Paraxanthine on Cognitive Function: A Double Blind, Placebo Controlled, Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.; Yoo, C.; Gonzalez, D.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J.; Faries, M.; Kephart, W.; et al. Effects of Acute Ashwagandha Ingestion on Cognitive Function. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.P.; Earnest, C.P.; Koozehchian, M.; Cho, M.; Barringer, N.; Walker, D.; Rasmussen, C.; Greenwood, M.; Murano, P.S.; Kreider, R.B. Effects of ingesting a pre-workout dietary supplement with and without synephrine for 8 weeks on training adaptations in resistance-trained males. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Wightman, E.L. Mental Performance and Sport: Caffeine and Co-consumed Bioactive Ingredients. Sport. Med. 2022, 52, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meule, A. Reporting and Interpreting Task Performance in Go/No-Go Affective Shifting Tasks. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labonte, K.; Nielsen, D.E. Measuring food-related inhibition with go/no-go tasks: Critical considerations for experimental design. Appetite 2023, 185, 106497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen, D.G.; Taylor, D.V.; Ojala, K.; Kaur, J.; Willeumier, K. Effects of brain-directed nutrients on cerebral blood flow and neuropsychological testing: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Adv. Mind Body Med. 2013, 27, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, E.; Gualano, B.; Rawson, E.S. Beyond muscle: The effects of creatine supplementation on brain creatine, cognitive processing, and traumatic brain injury. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.P.; Droste, J.N.; Giessing, J.; Kreider, R.B. Role of Creatine Supplementation in Conditions Involving Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, R.L.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Youdim, K.A.; Joseph, J.A. Fruit polyphenolics and brain aging: Nutritional interventions targeting age-related neuronal and behavioral deficits. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 959, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinot, N.; Jouin, M.; Lhomme-Duchadeuil, A.; Guesnet, P.; Alessandri, J.M.; Aujard, F.; Pifferi, F. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil lower anxiety, improve cognitive functions and reduce spontaneous locomotor activity in a non-human primate. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M.J.; Butt, C.M.; Mohajeri, M.H. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Cognition throughout the Lifespan. Nutrients 2016, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, F.C.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Joseph, J.A. Nutritional intervention in brain aging: Reducing the effects of inflammation and oxidative stress. Subcell Biochem. 2007, 42, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hannan, M.A.; Dash, R.; Haque, M.N.; Mohibbullah, M.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Alam, M.; Moon, I.S. Neuroprotective Potentials of Marine Algae and Their Bioactive Metabolites: Pharmacological Insights and Therapeutic Advances. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepmeier, A.T.; Etnier, J.L. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a potential mechanism of the effects of acute exercise on cognitive performance. J. Sport Health Sci. 2015, 4, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghazwi, M.; Smid, S.; Musgrave, I.; Zhang, W. In vitro studies of the neuroprotective activities of astaxanthin and fucoxanthin against amyloid beta (Aβ(1-42)) toxicity and aggregation. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 124, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, T.M.; Caldwell, J.A.; Lieberman, H.R. A review of caffeine’s effects on cognitive, physical and occupational performance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leonard, M.; Maury, J.; Dickerson, B.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Kendra, J.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Yoo, C.; Xing, D.; Ko, J.; et al. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of a Microalgae Extract Containing Fucoxanthin Combined with Guarana on Cognitive Function and Gaming Performance. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081918
Leonard M, Maury J, Dickerson B, Gonzalez DE, Kendra J, Jenkins V, Nottingham K, Yoo C, Xing D, Ko J, et al. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of a Microalgae Extract Containing Fucoxanthin Combined with Guarana on Cognitive Function and Gaming Performance. Nutrients. 2023; 15(8):1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081918
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeonard, Megan, Jonathan Maury, Broderick Dickerson, Drew E. Gonzalez, Jacob Kendra, Victoria Jenkins, Kay Nottingham, Choongsung Yoo, Dante Xing, Joungbo Ko, and et al. 2023. "Effects of Dietary Supplementation of a Microalgae Extract Containing Fucoxanthin Combined with Guarana on Cognitive Function and Gaming Performance" Nutrients 15, no. 8: 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081918
APA StyleLeonard, M., Maury, J., Dickerson, B., Gonzalez, D. E., Kendra, J., Jenkins, V., Nottingham, K., Yoo, C., Xing, D., Ko, J., Pradelles, R., Faries, M., Kephart, W., Sowinski, R., Rasmussen, C. J., & Kreider, R. B. (2023). Effects of Dietary Supplementation of a Microalgae Extract Containing Fucoxanthin Combined with Guarana on Cognitive Function and Gaming Performance. Nutrients, 15(8), 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081918







