Vitamin D Supplementation and Its Impact on Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 80 Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Guidance
2.2. Intervention, Control and Outcome Measures
2.3. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.4. RCTs Selection
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. RCT Quality Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analyses
2.8. Subgroup Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Primary Outcomes
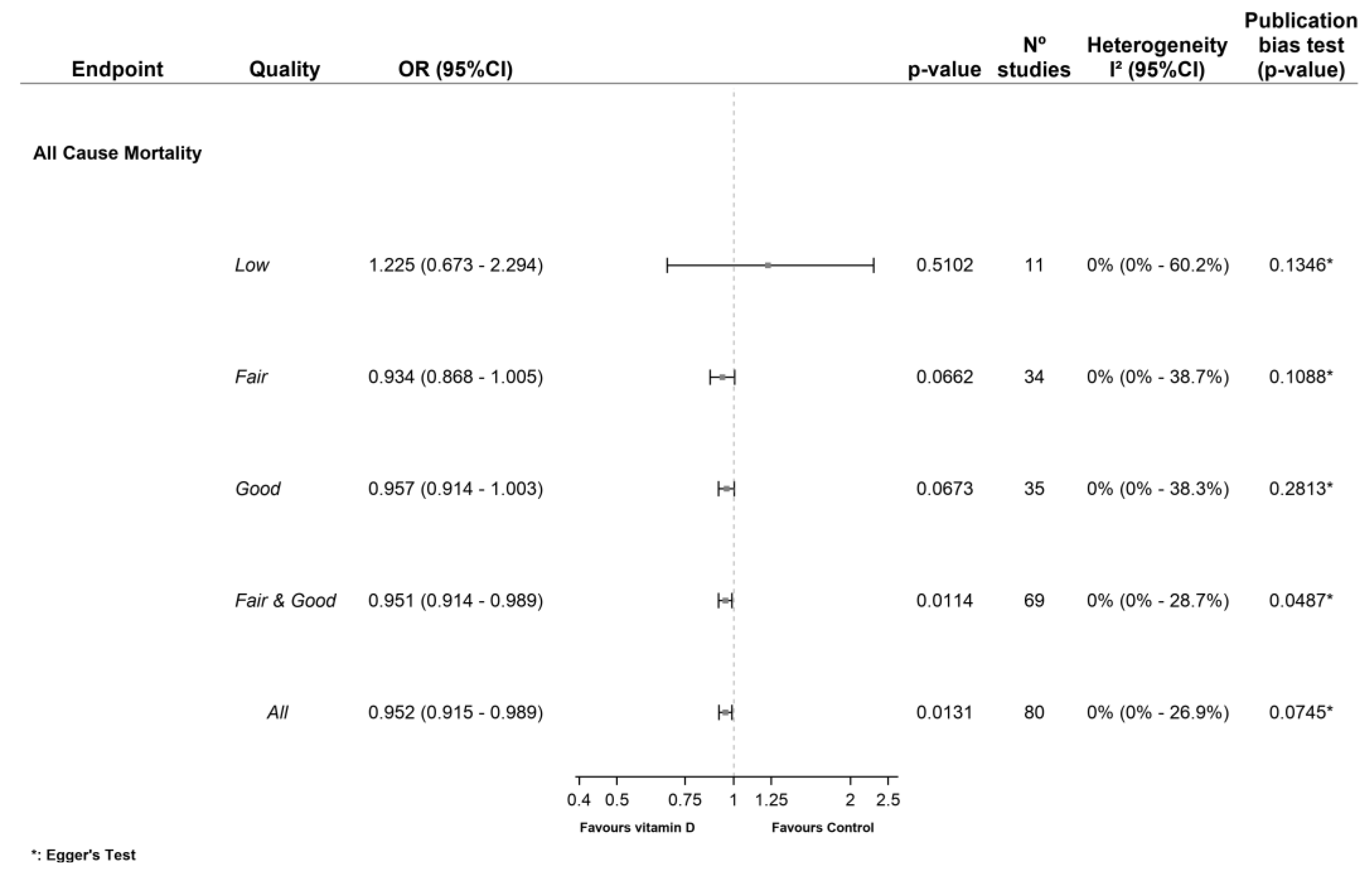
3.1.1. All-Cause Mortality (ACM)
3.1.2. Cardiovascular Mortality (CVM)
3.2. Secondary Outcomes
3.2.1. Non-Cardiovascular Mortality (Non-CVM)
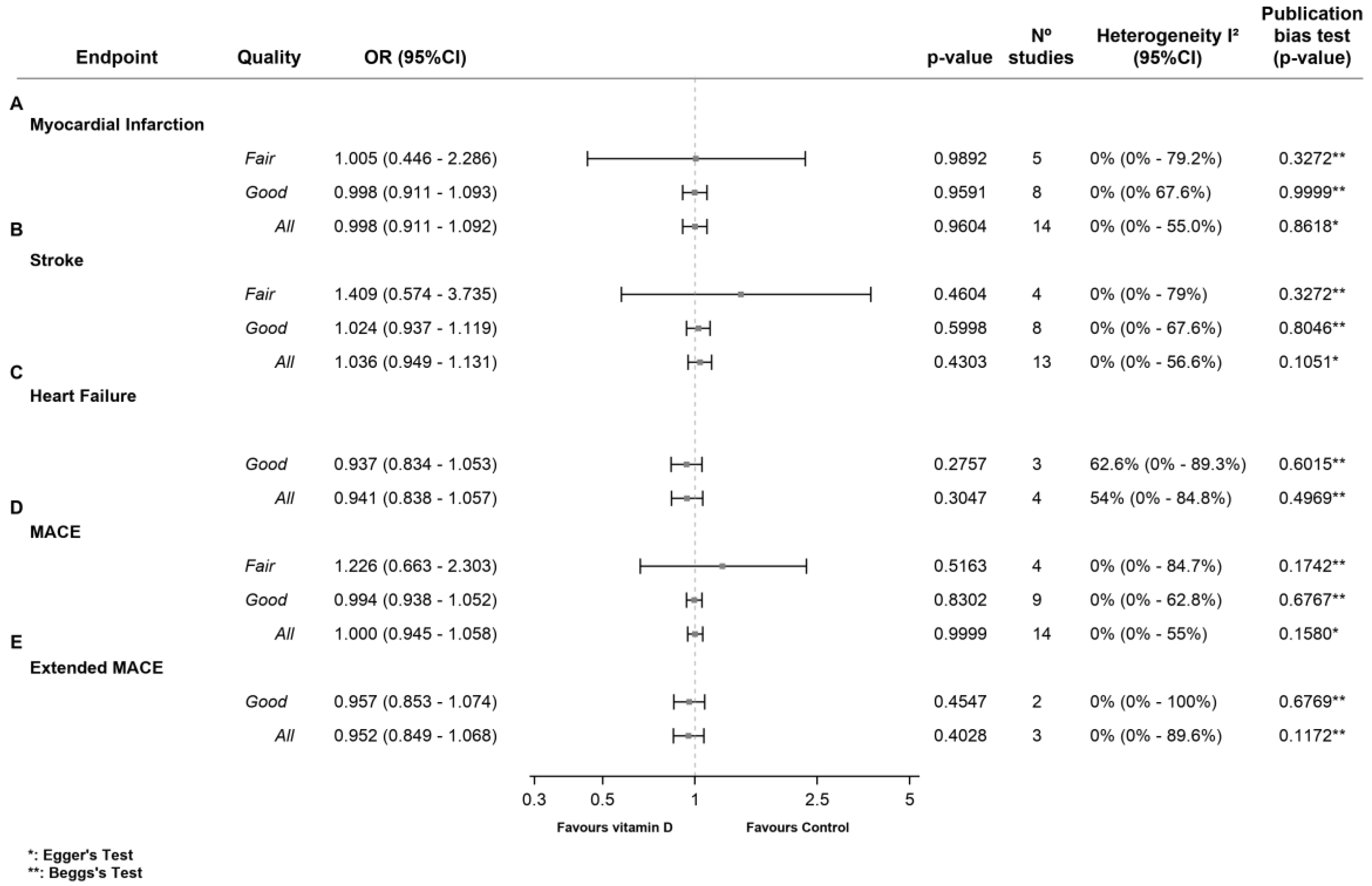
3.2.2. Myocardial Infarction (MI)
3.2.3. Stroke
3.2.4. Heart Failure (HF)
3.2.5. MACE
3.2.6. Extended MACE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Study Registration
Abbreviations
References
- Giustina, A.; Adler, R.A.; Binkley, N.; Bouillon, R.; Ebeling, P.R.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Marcocci, C.; Rizzoli, R.; Sempos, C.T.; Bilezikian, J.P. Controversies in Vitamin D: Summary Statement From an International Conference. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewison, M.; Burke, F.; Evans, K.N.; Lammas, D.A.; Sansom, D.M.; Liu, P.; Modlin, R.L.; Adams, J.S. Extra-renal 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-hydroxylase in human health and disease. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 103, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibaba, D.T. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum lipid profiles: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakas, M.; Thorand, B.; Zierer, A.; Huth, C.; Meisinger, C.; Roden, M.; Rottbauer, W.; Peters, A.; Koenig, W.; Herder, C. Low levels of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D are associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction, especially in women: Results from the MONICA/KORA Augsburg case-cohort study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittermann, A.; Iodice, S.; Pilz, S.; Grant, W.B.; Bagnardi, V.; Gandini, S. Vitamin D deficiency and mortality risk in the general population: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Li, B. Association between blood vitamin D and myocardial infarction: A meta-analysis including observational studies. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 471, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.B.; Abu Elnour, N.O.; Elamin, K.B.; Fatourechi, M.M.; Alkatib, A.A.; Almandoz, J.P.; Liu, H.; Lane, M.A.; Mullan, R.J.; Hazem, A.; et al. Vitamin D and cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.J.; Zhang, C.; Tang, L.; Xian, Y.Q.; Li, Y.S.; Wang, W.D.; Zhu, X.H.; Qiu, H.L.; He, J.; Zhou, Y.H. Effect of calcium or vitamin D supplementation on vascular outcomes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 169, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Kunutsor, S.; Vitezova, A.; Oliver-Williams, C.; Chowdhury, S.; Kiefte-de-Jong, J.C.; Khan, H.; Baena, C.P.; Prabhakaran, D.; Hoshen, M.B.; et al. Vitamin D and risk of cause specific death: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational cohort and randomised intervention studies. BMJ 2014, 348, g1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Gluud, L.L.; Nikolova, D.; Whitfield, K.; Wetterslev, J.; Simonetti, R.G.; Bjelakovic, M.; Gluud, C. Vitamin D supplementation for prevention of mortality in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 1, Cd007470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Liu, R.Y.; Xie, M. Exact meta-analysis approach for discrete data and its application to 2 × 2 tables with rare events. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2014, 109, 1450–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Furuya-Kanamori, L.; Zorzela, L.; Lin, L.; Vohra, S. A proposed framework to guide evidence synthesis practice for meta-analysis with zero-events studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 135, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lin, L.; Lian, Q.; Zou, H.; Chu, H. Real-world Performance of Meta-analysis Methods for Double-Zero-Event Studies with Dichotomous Outcomes Using the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Xie, M. Gmeta: Meta-Analysis via a Unified Framework of Confidence Distribution. R Package Version 2.3-1. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gmeta (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Sutton, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Terrin, N.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, J.; Carpenter, J.; Rücker, G.; Harbord, R.M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, P.; Graafmans, W.C.; Ooms, M.E.; Bezemer, P.D.; Bouter, L.M. Vitamin D supplementation and fracture incidence in elderly persons. A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 124, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.E.; Smedshaug, G.B.; Kvaavik, E.; Falch, J.A.; Tverdal, A.; Pedersen, J.I. Can vitamin D supplementation reduce the risk of fracture in the elderly? A randomized controlled trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, D.P.; Doll, R.; Khaw, K.T. Effect of four monthly oral vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) supplementation on fractures and mortality in men and women living in the community: Randomised double blind controlled trial. BMJ 2003, 326, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flicker, L.; MacInnis, R.J.; Stein, M.S.; Scherer, S.C.; Mead, K.E.; Nowson, C.A.; Thomas, J.; Lowndes, C.; Hopper, J.L.; Wark, J.D. Should older people in residential care receive vitamin D to prevent falls? Results of a randomized trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton-Smith, C.; McMurdo, M.E.; Paterson, C.R.; Mole, P.A.; Harvey, J.M.; Fenton, S.T.; Prynne, C.J.; Mishra, G.D.; Shearer, M.J. Two-year randomized controlled trial of vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and vitamin D3 plus calcium on the bone health of older women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, R.A.; Johansen, A.; Brophy, S.; Newcombe, R.G.; Phillips, C.J.; Lervy, B.; Evans, R.; Wareham, K.; Stone, M.D. Preventing fractures among older people living in institutional care: A pragmatic randomised double blind placebo controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation. Osteoporos. Int. 2007, 18, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, J.; Heiss, G.; Ren, H.; Allison, M.; Dolan, N.C.; Greenland, P.; Heckbert, S.R.; Johnson, K.C.; Manson, J.E.; Sidney, S.; et al. Calcium/vitamin D supplementation and cardiovascular events. Circulation 2007, 115, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, R.L.; Austin, N.; Devine, A.; Dick, I.M.; Bruce, D.; Zhu, K. Effects of ergocalciferol added to calcium on the risk of falls in elderly high-risk women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Devine, A.; Dick, I.M.; Wilson, S.G.; Prince, R.L. Effects of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on hip bone mineral density and calcium-related analytes in elderly ambulatory Australian women: A five-year randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, K.M.; Stuart, A.L.; Williamson, E.J.; Simpson, J.A.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Young, D.; Nicholson, G.C. Annual high-dose oral vitamin D and falls and fractures in older women: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 303, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehouck, A.; Mathieu, C.; Carremans, C.; Baeke, F.; Verhaegen, J.; Van Eldere, J.; Decallonne, B.; Bouillon, R.; Decramer, M.; Janssens, W. High doses of vitamin D to reduce exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 156, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdoch, D.R.; Slow, S.; Chambers, S.T.; Jennings, L.C.; Stewart, A.W.; Priest, P.C.; Florkowski, C.M.; Livesey, J.H.; Camargo, C.A.; Scragg, R. Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on upper respiratory tract infections in healthy adults: The VIDARIS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012, 308, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.B.; Duran, P.; Lee, M.L.; Friedman, T.C. High-dose vitamin D supplementation in people with prediabetes and hypovitaminosis D. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witham, M.D.; Price, R.J.; Struthers, A.D.; Donnan, P.T.; Messow, C.M.; Ford, I.; McMurdo, M.E. Cholecalciferol treatment to reduce blood pressure in older patients with isolated systolic hypertension: The VitDISH randomized controlled trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, J.A.; MacLennan, G.S.; Avenell, A.; Bolland, M.; Grey, A.; Witham, M. Cardiovascular disease and vitamin D supplementation: Trial analysis, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.A.; Barry, E.L.; Mott, L.A.; Rees, J.R.; Sandler, R.S.; Snover, D.C.; Bostick, R.M.; Ivanova, A.; Cole, B.F.; Ahnen, D.J.; et al. A Trial of Calcium and Vitamin D for the Prevention of Colorectal Adenomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.E.; Johnson, R.E.; Chambers, K.R.; Johnson, M.G.; Lemon, C.C.; Vo, T.N.; Marvdashti, S. Treatment of Vitamin D Insufficiency in Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusi-Rasi, K.; Patil, R.; Karinkanta, S.; Kannus, P.; Tokola, K.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Sievänen, H. Exercise and vitamin D in fall prevention among older women: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, A.R.; James, W.Y.; Hooper, R.L.; Barnes, N.C.; Jolliffe, D.A.; Greiller, C.L.; Islam, K.; McLaughlin, D.; Bhowmik, A.; Timms, P.M.; et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (ViDiCO): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Res. Med. 2015, 3, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, N.K.; Cro, S.; Sheard, S.; Doré, C.J.; Bara, A.; Tebbs, S.A.; Hunter, D.J.; James, S.; Cooper, C.; O’Neill, T.W.; et al. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on knee osteoarthritis, the VIDEO study: A randomised controlled trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, J.; Bérubé, S.; Diorio, C.; Mâsse, B.; Lemieux, J.; Duchesne, T.; Delvin, E.; Vieth, R.; Yaffe, M.J.; Chiquette, J. A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial of the Effect of Vitamin D(3) Supplementation on Breast Density in Premenopausal Women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2017, 26, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappe, J.; Watson, P.; Travers-Gustafson, D.; Recker, R.; Garland, C.; Gorham, E.; Baggerly, K.; McDonnell, S.L. Effect of Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation on Cancer Incidence in Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 317, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hin, H.; Tomson, J.; Newman, C.; Kurien, R.; Lay, M.; Cox, J.; Sayer, J.; Hill, M.; Emberson, J.; Armitage, J.; et al. Optimum dose of vitamin D for disease prevention in older people: BEST-D trial of vitamin D in primary care. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scragg, R.; Stewart, A.W.; Waayer, D.; Lawes, C.M.M.; Toop, L.; Sluyter, J.; Murphy, J.; Khaw, K.T.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Effect of Monthly High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation on Cardiovascular Disease in the Vitamin D Assessment Study: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Gallagher, J.C.; Kaufmann, M.; Jones, G. Effect of increasing doses of vitamin D on bone mineral density and serum N-terminal telopeptide in elderly women: A randomized controlled trial. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, M.K.; Fielding, R.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on lower-extremity power and function in older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Lee, I.M.; Christen, W.; Bassuk, S.S.; Mora, S.; Gibson, H.; Gordon, D.; Copeland, T.; D’Agostino, D.; et al. Vitamin D Supplements and Prevention of Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Koo, J.W.; Choi, K.D.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Oh, S.Y.; et al. Prevention of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with vitamin D supplementation: A randomized trial. Neurology 2020, 95, e1117–e1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukenda Zanko, V.; Domislovic, V.; Trkulja, V.; Krznaric-Zrnic, I.; Turk-Wensveen, T.; Krznaric, Z.; Filipec Kanizaj, T.; Radic-Kristo, D.; Bilic-Zulle, L.; Orlic, L.; et al. Vitamin D for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease detected by transient elastography: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, C.; Duan, K.; Jia, J.; Ma, F. Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Cognitive Function Through Reducing Oxidative Stress Regulated by Telomere Length in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A 12-Month Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 78, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Vellas, B.; Rizzoli, R.; Kressig, R.W.; da Silva, J.A.P.; Blauth, M.; Felson, D.T.; McCloskey, E.V.; Watzl, B.; Hofbauer, L.C.; et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation, Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation, or a Strength-Training Exercise Program on Clinical Outcomes in Older Adults: The DO-HEALTH Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1855–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rake, C.; Gilham, C.; Bukasa, L.; Ostler, R.; Newton, M.; Peto Wild, J.; Aigret, B.; Hill, M.; Gillie, O.; Nazareth, I.; et al. High-dose oral vitamin D supplementation and mortality in people aged 65–84 years: The VIDAL cluster feasibility RCT of open versus double-blind individual randomisation. Health Technol. Assess 2020, 24, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.; Suzuki, G.; Mizuno, S.; Inazu, T.; Kasagi, F.; Kawahara, C.; Okada, Y.; Tanaka, Y. Effect of active vitamin D treatment on development of type 2 diabetes: DPVD randomised controlled trial in Japanese population. BMJ 2022, 377, e066222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, R.E.; Baxter, C.; Romero, B.D.; McLeod, D.S.A.; English, D.R.; Armstrong, B.K.; Ebeling, P.R.; Hartel, G.; Kimlin, M.G.; O’Connell, R.; et al. The D-Health Trial: A randomised controlled trial of the effect of vitamin D on mortality. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, J.K.; Nurmi, T.; Aro, A.; Bertone-Johnson, E.R.; Hyppönen, E.; Kröger, H.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Manson, J.E.; Mursu, J.; Mäntyselkä, P.; et al. Vitamin D supplementation and prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer in the Finnish Vitamin D Trial: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, S.M.; Chesnut, C.H., 3rd. Calcitriol treatment is not effective in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1989, 110, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson-Hughes, B.; Dallal, G.E.; Krall, E.A.; Harris, S.; Sokoll, L.J.; Falconer, G. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on wintertime and overall bone loss in healthy postmenopausal women. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 115, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, M.C.; Arlot, M.E.; Duboeuf, F.; Brun, J.; Crouzet, B.; Arnaud, S.; Delmas, P.D.; Meunier, P.J. Vitamin D3 and calcium to prevent hip fractures in elderly women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.T.; Shiraki, M.; Hasumi, K.; Tanaka, N.; Katase, K.; Kato, T.; Hirai, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Ogata, E. 1-alpha-Hydroxyvitamin D3 treatment decreases bone turnover and modulates calcium-regulating hormones in early postmenopausal women. Bone 1997, 20, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson-Hughes, B.; Harris, S.S.; Krall, E.A.; Dallal, G.E. Effect of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on bone density in men and women 65 years of age or older. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeksgaard, L.; Andersen, K.P.; Hyldstrup, L. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation increases spinal BMD in healthy, postmenopausal women. Osteoporos. Int. 1998, 8, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, M.A.; Jacquet, A.F.; Bremgartner, M.; Cuttelod, S.; Thiébaud, D.; Burckhardt, P. Effect of supplementation with vitamin D3 and calcium on quantitative ultrasound of bone in elderly institutionalized women: A longitudinal study. Osteoporos. Int. 1999, 9, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komulainen, M.; Kröger, H.; Tuppurainen, M.T.; Heikkinen, A.M.; Alhava, E.; Honkanen, R.; Jurvelin, J.; Saarikoski, S. Prevention of femoral and lumbar bone loss with hormone replacement therapy and vitamin D3 in early postmenopausal women: A population-based 5-year randomized trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, J.C.; Fowler, S.E.; Detter, J.R.; Sherman, S.S. Combination treatment with estrogen and calcitriol in the prevention of age-related bone loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3618–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, M.C.; Pamphile, R.; Paris, E.; Kempf, C.; Schlichting, M.; Arnaud, S.; Garnero, P.; Meunier, P.J. Combined calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation in elderly women: Confirmation of reversal of secondary hyperparathyroidism and hip fracture risk: The Decalyos II study. Osteoporos. Int. 2002, 13, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.; Clifton-Bligh, P.B.; Nery, M.L.; Figtree, G.; Twigg, S.; Hibbert, E.; Robinson, B.G. Vitamin D supplementation and bone mineral density in early postmenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, E.R.; Mosekilde, L.; Foldspang, A. Vitamin D and calcium supplementation prevents osteoporotic fractures in elderly community dwelling residents: A pragmatic population-based 3-year intervention study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloia, J.F.; Talwar, S.A.; Pollack, S.; Yeh, J. A randomized controlled trial of vitamin D3 supplementation in African American women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1618–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, M.; Grados, F.; Kamel, S.; Mathieu, M.; Morel, A.; Maamer, M.; Sebert, J.L.; Fardellone, P. Clinical and laboratory safety of one year’s use of a combination calcium + vitamin D tablet in ambulatory elderly women with vitamin D insufficiency: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Ther. 2005, 27, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porthouse, J.; Cockayne, S.; King, C.; Saxon, L.; Steele, E.; Aspray, T.; Baverstock, M.; Birks, Y.; Dumville, J.; Francis, R.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of calcium and supplementation with cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) for prevention of fractures in primary care. BMJ 2005, 330, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.J.; Robertson, M.C.; La Grow, S.J.; Kerse, N.M.; Sanderson, G.F.; Jacobs, R.J.; Sharp, D.M.; Hale, L.A. Randomised controlled trial of prevention of falls in people aged > or =75 with severe visual impairment: The VIP trial. BMJ 2005, 331, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappe, J.M.; Travers-Gustafson, D.; Davies, K.M.; Recker, R.R.; Heaney, R.P. Vitamin D and calcium supplementation reduces cancer risk: Results of a randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.; Anderson, F.; Raphael, H.; Maslin, P.; Crozier, S.; Cooper, C. Effect of annual intramuscular vitamin D on fracture risk in elderly men and women--a population-based, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, M.; Begerow, B.; Minne, H.W.; Suppan, K.; Fahrleitner-Pammer, A.; Dobnig, H. Effects of a long-term vitamin D and calcium supplementation on falls and parameters of muscle function in community-dwelling older individuals. Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 20, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittermann, A.; Frisch, S.; Berthold, H.K.; Götting, C.; Kuhn, J.; Kleesiek, K.; Stehle, P.; Koertke, H.; Koerfer, R. Vitamin D supplementation enhances the beneficial effects of weight loss on cardiovascular disease risk markers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärkkäinen, M.; Tuppurainen, M.; Salovaara, K.; Sandini, L.; Rikkonen, T.; Sirola, J.; Honkanen, R.; Jurvelin, J.; Alhava, E.; Kröger, H. Effect of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on bone mineral density in women aged 65-71 years: A 3-year randomized population-based trial (OSTPRE-FPS). Osteoporos. Int. 2010, 21, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punthakee, Z.; Bosch, J.; Dagenais, G.; Diaz, R.; Holman, R.; Probstfield, J.; Ramachandran, A.; Riddle, M.; Rydén, L.E.; Zinman, B.; et al. Design, history and results of the Thiazolidinedione Intervention with vitamin D Evaluation (TIDE) randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.D.; Secombes, K.R.; Thies, F.; Aucott, L.; Black, A.J.; Mavroeidi, A.; Simpson, W.G.; Fraser, W.D.; Reid, D.M.; Macdonald, H.M. Vitamin D3 supplementation has no effect on conventional cardiovascular risk factors: A parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled RCT. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3557–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.; Xiao, L.; Imayama, I.; Duggan, C.; Wang, C.Y.; Korde, L.; McTiernan, A. Vitamin D3 supplementation during weight loss: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.C.; Jindal, P.S.; Smith, L.M. Vitamin D does not increase calcium absorption in young women: A randomized clinical trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barengolts, E.; Manickam, B.; Eisenberg, Y.; Akbar, A.; Kukreja, S.; Ciubotaru, I. Effect of high-dose vitamin D repletion on glycemic control in African-American males with prediabetes and hypovitaminosis d. Endocr. Pract. 2015, 21, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Jones, G.; Cicuttini, F.; Wluka, A.; Zhu, Z.; Han, W.; Antony, B.; Wang, X.; Winzenberg, T.; Blizzard, L.; et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Tibial Cartilage Volume and Knee Pain Among Patients With Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorde, R.; Sollid, S.T.; Svartberg, J.; Schirmer, H.; Joakimsen, R.M.; Njølstad, I.; Fuskevåg, O.M.; Figenschau, Y.; Hutchinson, M.Y. Vitamin D 20,000 IU per Week for Five Years Does Not Prevent Progression From Prediabetes to Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, K.K.; Byrom, R.; Gierula, J.; Paton, M.F.; Jamil, H.A.; Lowry, J.E.; Gillott, R.G.; Barnes, S.A.; Chumun, H.; Kearney, L.C.; et al. Effects of Vitamin D on Cardiac Function in Patients With Chronic HF: The VINDICATE Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zittermann, A.; Ernst, J.B.; Prokop, S.; Fuchs, U.; Dreier, J.; Kuhn, J.; Knabbe, C.; Birschmann, I.; Schulz, U.; Berthold, H.K.; et al. Effect of vitamin D on all-cause mortality in heart failure (EVITA): A 3-year randomized clinical trial with 4000 IU vitamin D daily. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittas, A.G.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Sheehan, P.; Ware, J.H.; Knowler, W.C.; Aroda, V.R.; Brodsky, I.; Ceglia, L.; Chadha, C.; Chatterjee, R.; et al. Vitamin D Supplementation and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloia, J.F.; Rubinova, R.; Fazzari, M.; Islam, S.; Mikhail, M.; Ragolia, L. Vitamin D and Falls in Older African American Women: The PODA Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.E.; Liu, H.; Storrick, E.; Zahrieh, D.; Le-Petross, H.C.; Jung, S.H.; Zekan, P.; Kemeny, M.M.; Charlamb, J.R.; Wang, L.X.; et al. The Influence of Vitamin D on Mammographic Density: Results from CALGB 70806 (Alliance) a Randomized Clinical Trial. Cancer Prev. Res. 2021, 14, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhi, X.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z. Effects of long-term vitamin D supplementation on metabolic profile in middle-aged and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 225, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkovaara, J.; Gothoni, G.; Halttula, R.; Heikinheimo, R.; Tokola, O. Calcium, vitamin D and anabolic steroid in treatment of aged bones: Double-blind placebo-controlled long-term clinical trial. Age Ageing 1983, 12, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, C.; Woitge, H.W.; Witte, K.; Lemmer, B.; Seibel, M.J. Supplementation with oral vitamin D3 and calcium during winter prevents seasonal bone loss: A randomized controlled open-label prospective trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, R.H.; Sahota, O.; Gaynor, K.; Masud, T.; Hosking, D.J. A randomised, controlled comparison of different calcium and vitamin D supplementation regimens in elderly women after hip fracture: The Nottingham Neck of Femur (NONOF) Study. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschonis, G.; Manios, Y. Skeletal site-dependent response of bone mineral density and quantitative ultrasound parameters following a 12-month dietary intervention using dairy products fortified with calcium and vitamin D: The Postmenopausal Health Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 96, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, R.M.; Nowson, C.A. Long-term effect of calcium-vitamin D(3) fortified milk on blood pressure and serum lipid concentrations in healthy older men. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves, J.W.; Cosman, F.; Grubert, E.; Ambrose, B.; Ralston, S.H.; Lindsay, R. Skeletal effects of vitamin D supplementation in postmenopausal black women. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2012, 91, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toss, G.; Magnusson, P. Is a daily supplementation with 40 microgram vitamin D3 sufficient? A randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Laway, B.A.; Bashir, M.I.; Wani, A.I.; Misgar, R.A.; Shah, Z.A. Effect of Vitamin D supplementation on glycemic parameters and progression of prediabetes to diabetes: A 1-year, open-label randomized study. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 19, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Hikim, I.; Duran, P.; Shen, R.; Lee, M.; Friedman, T.C.; Davidson, M.B. Effect of long term vitamin D supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation in Latino and African-American subjects with pre-diabetes and hypovitaminosis D. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.P.; Misra, A.; Pandey, R.M.; Upadhyay, A.D.; Gulati, S.; Singh, N. Vitamin D Supplementation in Overweight/obese Asian Indian Women with Prediabetes Reduces Glycemic Measures and Truncal Subcutaneous Fat: A 78 Weeks Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial (PREVENT-WIN Trial). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat, M.; Allahqoli, L.; Mirzaei, H.; Giovannucci, E.; Salehiniya, H.; Mansouri, G.; Alkatout, I. The effect of vitamin D on recurrence of uterine fibroids: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Complement Ther. Clin. Pract. 2022, 46, 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Marcocci, C.; Carmeliet, G.; Bikle, D.; White, J.H.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Lips, P.; Munns, C.F.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Giustina, A.; et al. Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1109–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warwick, T.; Schulz, M.H.; Gilsbach, R.; Brandes, R.P.; Seuter, S. Nuclear receptor activation shapes spatial genome organization essential for gene expression control: Lessons learned from the vitamin D receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 3745–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, S.; Brøndum-Jacobsen, P.; Bojesen, S.E.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Genetically low vitamin D concentrations and increased mortality: Mendelian randomisation analysis in three large cohorts. BMJ 2014, 349, g6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.L.; Gu, H.B.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xia, Q.Q.; Qi, J.; Chen, J.C. Vitamin D Supplementation in the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Cardiol. 2016, 39, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaksch, M.; Jorde, R.; Grimnes, G.; Joakimsen, R.; Schirmer, H.; Wilsgaard, T.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Njølstad, I.; Løchen, M.L.; März, W.; et al. Vitamin D and mortality: Individual participant data meta-analysis of standardized 25-hydroxyvitamin D in 26916 individuals from a Eur.opean consortium. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.K.; Kim, I.Y.; Hodge, A.M.; English, D.R.; Muller, D.C. Vitamin D Status and Mortality: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, R.; Mhaskar, K.; Tsiampalis, T.; Kassaw, N.A.; González MÁ, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Circulating 25-hydroxy-vitamin D and the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 3282–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, F.; Tang, J.; Jia, L.; Feng, Y.; Xu, P.; Faramand, A. Association between vitamin D supplementation and mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2019, 366, l4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration/EPIC-CVD/Vitamin D Studies Collaboration. Estimating dose-response relationships for vitamin D with coronary heart disease, stroke, and all-cause mortality: Observational and Mendelian randomisation analyses. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, V.; Ishak, A.; Peng Ang, S.; Babu Pokhrel, N.; Shama, N.; Lnu, K.; Susan Varghese, J.; Storozhenko, T.; Ee Chia, J.; Naz, S.; et al. Hypovitaminosis D and cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2022, 40, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X.C.; Liu, Z.R.; Xu, P.; Fang, F. Association of Vitamin D Supplementation with Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarawi, M.; Kheiri, B.; Zayed, Y.; Barbarawi, O.; Dhillon, H.; Swaid, B.; Yelangi, A.; Sundus, S.; Bachuwa, G.; Alkotob, M.L.; et al. Vitamin D Supplementation and Cardiovascular Disease Risks in More Than 83 000 Individuals in 21 Randomized Clinical Trials: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudy, M.; Krakowski, G.; Ghahramani, M.; Ruzieh, M.; Foy, A.J. Vitamin D supplementation, cardiac events and stroke: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2020, 28, 100537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, C. Vitamin D supplementation and risk of stroke: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 970111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yi, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Jamilian, P.; Gaman, M.A.; Prabahar, K.; Fan, J. The effect of vitamin D on the lipid profile as a risk factor for coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women: A meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 161, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahwati, L.C.; LeBlanc, E.; Weber, R.P.; Giger, K.; Clark, R.; Suvada, K.; Guisinger, A.; Viswanathan, M. Screening for Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2021, 325, 1443–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangione, C.M.; Barry, M.J.; Nicholson, W.K.; Cabana, M.; Chelmow, D.; Coker, T.R.; Davis, E.M.; Donahue, K.E.; Doubeni, C.A.; Jaén, C.R.; et al. Vitamin, Mineral, and Multivitamin Supplementation to Prevent Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2022, 327, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.A.; Evans, C.V.; Ivlev, I.; Rushkin, M.C.; Thomas, R.G.; Martin, A.; Lin, J.S. Vitamin and Mineral Supplements for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2022, 327, 2334–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-García, A.; Pallarés-Carratalá, V.; Turégano-Yedro, M.; Torres, F.; Sapena, V.; Martin-Gorgojo, A.; Martin-Moreno, J.M. Vitamin D Supplementation and Its Impact on Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 80 Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081810
Ruiz-García A, Pallarés-Carratalá V, Turégano-Yedro M, Torres F, Sapena V, Martin-Gorgojo A, Martin-Moreno JM. Vitamin D Supplementation and Its Impact on Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 80 Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients. 2023; 15(8):1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081810
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-García, Antonio, Vicente Pallarés-Carratalá, Miguel Turégano-Yedro, Ferran Torres, Víctor Sapena, Alejandro Martin-Gorgojo, and Jose M. Martin-Moreno. 2023. "Vitamin D Supplementation and Its Impact on Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 80 Randomized Clinical Trials" Nutrients 15, no. 8: 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081810
APA StyleRuiz-García, A., Pallarés-Carratalá, V., Turégano-Yedro, M., Torres, F., Sapena, V., Martin-Gorgojo, A., & Martin-Moreno, J. M. (2023). Vitamin D Supplementation and Its Impact on Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 80 Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients, 15(8), 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081810






