Evaluation of the Usefulness of an Automatable Immunoassay for Monitoring Celiac Disease by Quantification of Immunogenic Gluten Peptides in Urine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Urine Samples
2.3.1. Urine Collection
2.3.2. Spiked Urine Samples
2.3.3. Urinary GIP Preconcentration
2.3.4. Urinary GIP Stability
2.4. Assay Procedure: ELISA
2.5. LFIA
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
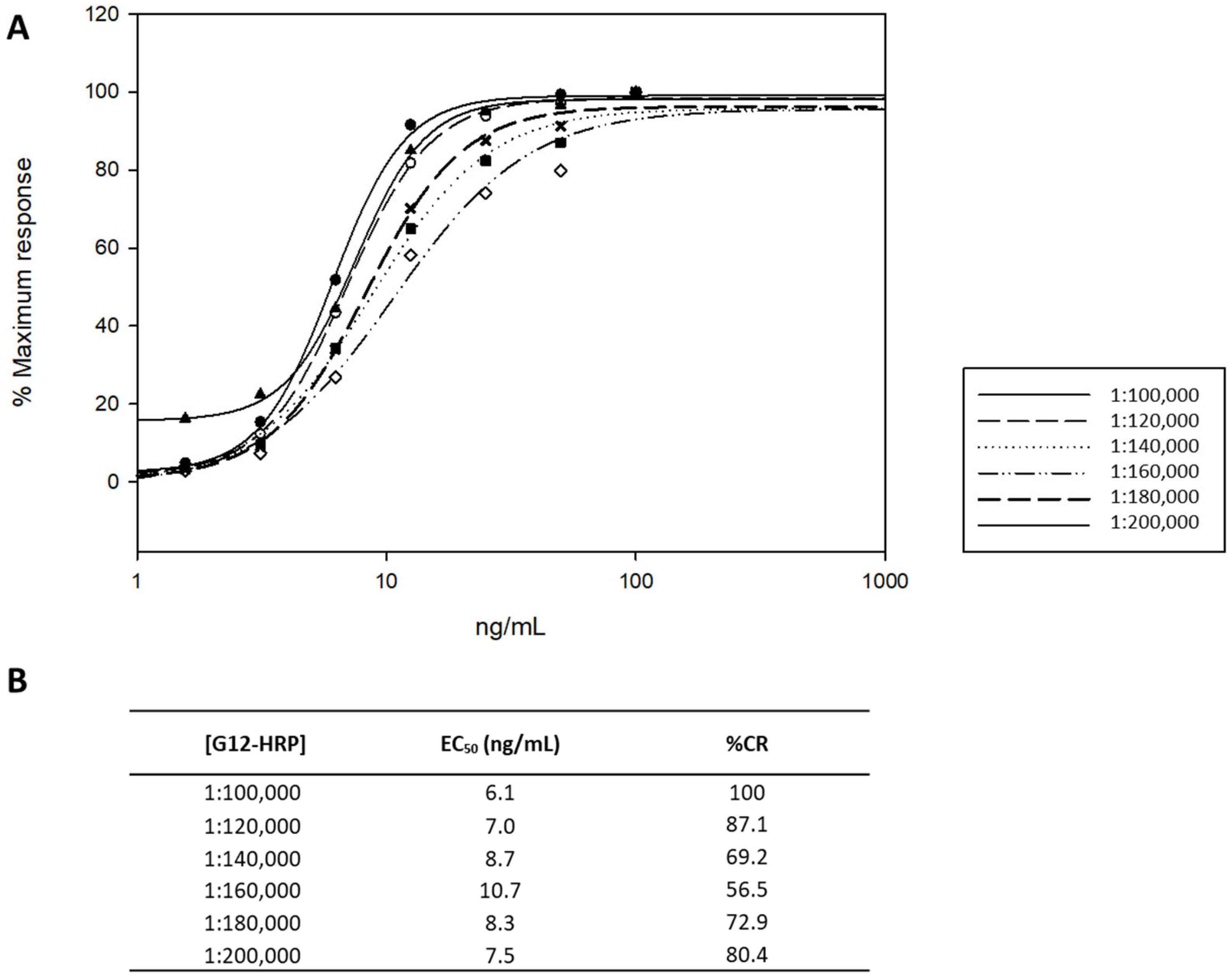
3.1. Optimization and Validation of the ELISA Working Conditions
3.1.1. Linearity and Working Range
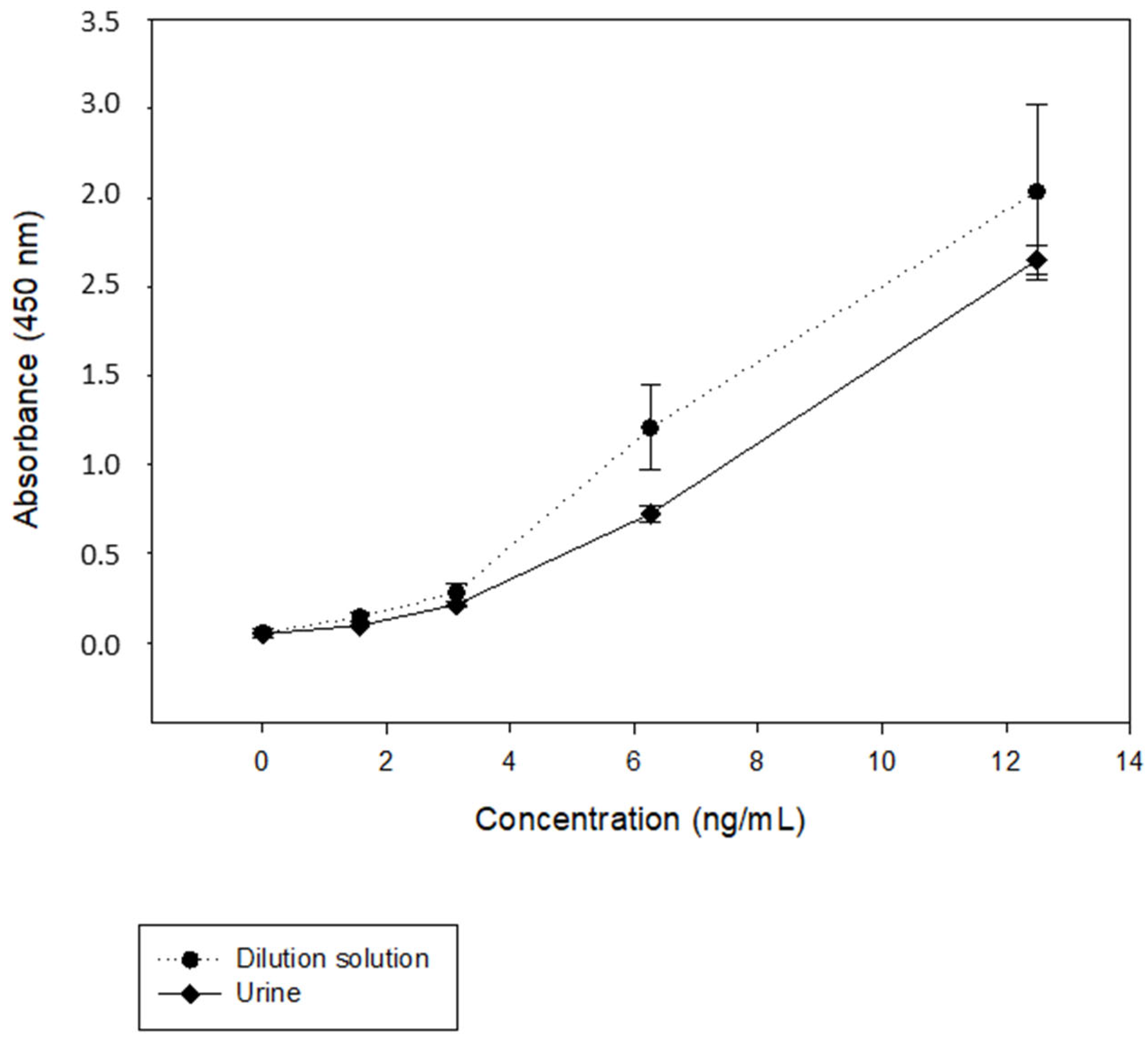
3.1.2. Matrix Study
3.1.3. Accuracy and Precision
3.2. Effect of the Urine Samples on the Assay Performance
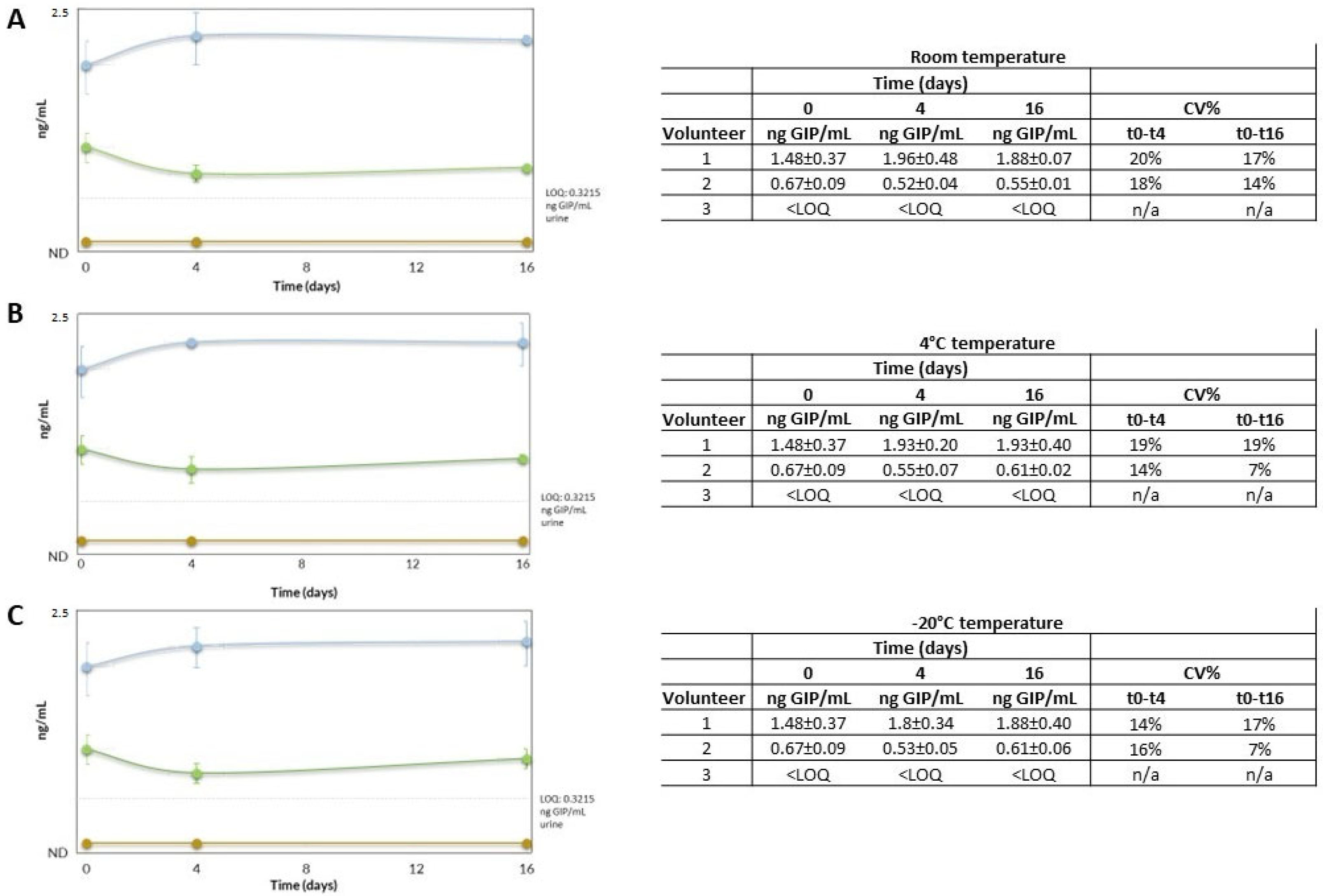
3.3. Stability of GIP
4. Clinical Study
4.1. Study Design and Population
4.2. Analysis of Urine GIP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Toma, A.; Volta, U.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; Sanders, D.S.; Cellier, C.; Mulder, C.J.; Lundin, K.E.A. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 583–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.; Kurppa, K.; Mearin, M.L.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; et al. European Society Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Guidelines for Diagnosing Coeliac Disease 2020. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungaro, L.; Manza, F.; Costanzini, A.; Barbalinardo, M.; Gentili, D.; Caputo, F.; Guarino, M.; Zoli, G.; Volta, U.; De Giorgio, R.; et al. Osteoporosis and celiac disease: Updates and hidden pitfalls. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Bai, J.C.; Biagi, F.; Card, T.R.; Ciacci, C.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Green, P.H.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Holdoway, A.; van Heel, D.A.; et al. BSG Coeliac Disease Guidelines Development Group; British Society of Gastroenterology. Diagnosis and management of adult coeliac disease: Guidelines from the British Society of Gastroenterology. Gut 2014, 63, 1210–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caio, G.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Zoli, G.; De Giorgio, R.; Volta, U. Therapeutic options for coeliac disease: What else beyond gluten-free diet? Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caio, G.; Volta, U.; Sapone, A.; Leffler, D.A.; De Giorgio, R.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Celiac disease: A comprehensive current review. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H.; Reeves, S.; Jeanes, Y.M. Identifying and improving adherence to the gluten-free diet in people with coeliac disease. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Carnicer, Á.; Garzón-Benavides, M.; Fombuena, B.; Segura, V.; García-Fernández, F.; Sobrino-Rodríguez, S.; Gómez-Izquierdo, L.; Montes-Cano, M.A.; Rodríguez-Herrera, A.; Millán, R.; et al. Negative predictive value of the repeated absence of gluten immunogenic peptides in the urine of treated celiac patients in predicting mucosal healing: New proposals for follow-up in celiac disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto, L.; Mendia, I.; Sousa, C.; Bai, J.C.; Cebolla, A. Determination of gluten immunogenic peptides for the management of the treatment adherence of celiac disease: A systematic review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 6306–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanolo, J.P.; Tálamo, M.; Dodds, S.; de la Paz Temprano, M.; Costa, A.F.; Moreno, M.L.; Pinto-Sánchez, M.I.; Smecuol, E.; Vázquez, H.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Real-World gluten exposure in patients with celiac disease on gluten-free diets, determined from gliadin immunogenic peptides in urine and fecal samples. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 484–491.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, V.; Ruiz-Carnicer, Á.; Sousa, C.; Moreno, M.L. New insights into non-dietary treatment in celiac disease: Emerging therapeutic options. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, H.; Ruiz-Carnicer, Á.; Segura, V.; Comino, I.; Sousa, C. Challenges of monitoring the gluten-free diet adherence in the management and follow-up of patients with celiac disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, O.; Norström, F.; Carlsson, A.; Högberg, L.; van der Palz, M.; Stenhammar, L.; Webb, C.; Ivarsson, A.; Myléus, A. Five-year follow-up of new cases after a coeliac disease mass screening. Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.V. New Developments in celiac disease treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón-Benavides, M.; Ruiz-Carnicer, Á.; Segura, V.; Fombuena, B.; García-Fernandez, F.; Sobrino-Rodriguez, S.; Gómez-Izquierdo, L.; Montes-Cano, M.A.; Millan-Domínguez, R.; María del Carmen Rico, M.; et al. Regular monitoring of patients with coeliac disease by determinations of gluten immunogenic peptides in urine improved gluten-free diet adherence and the healing of duodenal mucosa: Proposal on a new algorithm for the follow-up of coeliac disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo, L.; Beteta-Gorriti, V.; Alvarez, N.; Gómez de Castro, C.; de Dios, A.; Palacios, L.; Santos-Juanes, J. Cutaneous and mucosal manifestations associated with celiac disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protocolo Para el Diagnóstico Precoz de la Enfermedad Celíaca. Available online: https://www3.gobiernodecanarias.org/sanidad/scs/contenidoGenerico.jsp?idDocument=ed8e95ff-578d-11e8-8844-65f683d38a9e&idCarpeta=0428f5bb-8968-11dd-b7e9-158e12a49309 (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Comino, I.; Real, A.; Vivas, S.; Síglez, M.Á.; Caminero, A.; Nistal, E.; Casqueiro, J.; Rodríguez-Herrera, A.; Cebolla, A.; Sousa, C. Monitoring of gluten-free diet compliance in celiac patients by assessment of gliadin 33-mer equivalent epitopes in feces. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, M.; Estevez, M.C.; del Moreno, M.; Cebolla, A.; Lechuga, L.M. Label-free SPR detection of gluten peptides in urine for non-invasive celiac disease follow-up. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.D.L.; Cebolla, Á.; Munõz-Suano, A.; Carrillo-Carrion, C.; Comino, I.; Pizarro, Á.; León, F.; Rodríguez-Herrera, A.; Sousa, C. Detection of gluten immunogenic peptides in the urine of patients with coeliac disease reveals transgressions in the gluten-free diet and incomplete mucosal healing. Gut 2017, 66, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, I.; Fernández-Bañares, F.; Esteve, M.; Ortigosa, L.; Castillejo, G.; Fambuena, B.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Sierra, C.; Rodríguez-Herrera, A.; Salazar, J.C.; et al. Fecal gluten peptides reveal limitations of serological tests and food questionnaires for monitoring gluten-free diet in celiac disease patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimidis, K.; Zafeiropoulou, K.; Mackinder, M.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Duncan, H.; Buchanan, E.; Cardigan, T.; Edwards, C.A.; McGrogan, P.; Russell, R.K. Comparison of clinical methods with the faecal gluten immunogenic peptide to assess gluten intake in coeliac disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peláez, E.C.; Estevez, M.C.; Domínguez, R.; Sousa, C.; Cebolla, A.; Lechuga, L.M. A compact SPR biosensor device for the rapid and efficient monitoring of gluten-free diet directly in human urine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 6407–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcelli, B.; Ferretti, F.; Biviano, I.; Santini, A.; Cinci, F.; Vascotto, M.; Grande, E.; Quagliarella, F.; Terzuoli, L.; Bizzaro, N.; et al. Testing for fecal gluten immunogenic peptides: A useful tool to evaluate compliance with gluten-free diet by celiacs. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2020, 33, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcelli, B.; Ferretti, F.; Cinci, F.; Biviano, I.; Santini, A.; Grande, E.; Quagliarella, F.; Terzuoli, L.; Bacarelli, M.R.; Bizzaro, N.; et al. Fecal gluten immunogenic peptides as indicators of dietary compliance in celiac patients. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2020, 66, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bañares, F.; Beltrán, B.; Salas, A.; Comino, I.; Ballester-Clau, R.; Ferrer, C.; Molina-Infante, J.; Rosinach, M.; Modolell, I.; Rodríguez-Moranta, F.; et al. Persistent villous atrophy in de novo adult patients with celiac disease and strict control of gluten-free diet adherence: A multicenter prospective study (CADER Study). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, J.; Kumar, C.; Zhang, Y.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. The human urinary proteome contains more than 1500 proteins, including a large proportion of membrane proteins. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, B.; Örnemark, U. (Eds.) Eurachem Guide: The Fitness for Purpose of Analytical Methods—A Laboratory Guide to Method Validation and Related Topics, 2nd ed.; Eurachem: Gembloux, Belgium, 2014; ISBN 978-91-87461-59-0. Available online: www.eurachem.org (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Comino, I.; Segura, V.; Ortigosa, L.; Espín, B.; Castillejo, G.; Garrote, J.A.; Sierra, C.; Millán, A.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Román, E.; et al. Prospective longitudinal study: Use of faecal gluten immunogenic peptides to monitor children diagnosed with coeliac disease during transition to a gluten-free diet. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Molberg, Ø.; Parrot, I.; Hausch, F.; Filiz, F.; Gray, G.M.; Sollid, L.M.; Khosla, C. Structural basis for gluten intolerance in celiac sprue. Science 2002, 297, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, M.; Hayward, S.; Ross, W.; Godefroy, S.B.; Ulberth, F.; Van Hengel, A.J.; Roberts, J.; Akiyama, H.; Popping, B.; Yeung, J.M.; et al. Validation procedures for quantitative food allergen ELISA methods: Community Guidance and Best Practices. J. AOAC Int. 2010, 93, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Spiked Sample (ng/mL) | N | ng/mL ± SD | % R | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | 20.0 | 9 | 20.3 ± 3.3 | 101 | 91% | 90% |
| 10.0 | 9 | 8.1 ± 0.5 | 81 | |||
| 5.0 | 9 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 91 | |||
| 2.5 | 9 | <LOQ | ||||
| 1.25 | 9 | <LOQ | ||||
| 0 | 9 | <LOQ | ||||
| Day 2 | 20.0 | 9 | 17.8 ± 2.8 | 89 | 89% | |
| 10.0 | 9 | 8.2 ± 0.6 | 82 | |||
| 5.0 | 9 | 4.8 ± 0.3 | 96 | |||
| 2.5 | 9 | <LOQ | ||||
| 1.25 | 9 | <LOQ | ||||
| 0 | 9 | <LOQ |
| Characteristics | Patients, n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Female | 12 | 67 |
| Male | 6 | 33 |
| Age | ||
| Median age (42) | ||
| Duodenal histology | ||
| Marsh 0-I | 2 | 11 |
| Marsh II-III | 16 | 89 |
| Symptoms | ||
| Asymptomatic | 5 | 28 |
| Symptomatic | 13 | 72 |
| CD antibodies | ||
| CD antibodies positive | 17 | 94 |
| CD antibodies negative | 1 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segura, V.; Ruiz-Carnicer, Á.; Mendía, I.; Garzón-Benavides, M.; Pizarro, Á.E.; Comino, I.; Sousa, C. Evaluation of the Usefulness of an Automatable Immunoassay for Monitoring Celiac Disease by Quantification of Immunogenic Gluten Peptides in Urine. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071730
Segura V, Ruiz-Carnicer Á, Mendía I, Garzón-Benavides M, Pizarro ÁE, Comino I, Sousa C. Evaluation of the Usefulness of an Automatable Immunoassay for Monitoring Celiac Disease by Quantification of Immunogenic Gluten Peptides in Urine. Nutrients. 2023; 15(7):1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071730
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegura, Verónica, Ángela Ruiz-Carnicer, Irati Mendía, Marta Garzón-Benavides, Ángeles E. Pizarro, Isabel Comino, and Carolina Sousa. 2023. "Evaluation of the Usefulness of an Automatable Immunoassay for Monitoring Celiac Disease by Quantification of Immunogenic Gluten Peptides in Urine" Nutrients 15, no. 7: 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071730
APA StyleSegura, V., Ruiz-Carnicer, Á., Mendía, I., Garzón-Benavides, M., Pizarro, Á. E., Comino, I., & Sousa, C. (2023). Evaluation of the Usefulness of an Automatable Immunoassay for Monitoring Celiac Disease by Quantification of Immunogenic Gluten Peptides in Urine. Nutrients, 15(7), 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071730





