The Role of Diet in Children with Psoriasis: Emerging Evidence and Current Issues
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
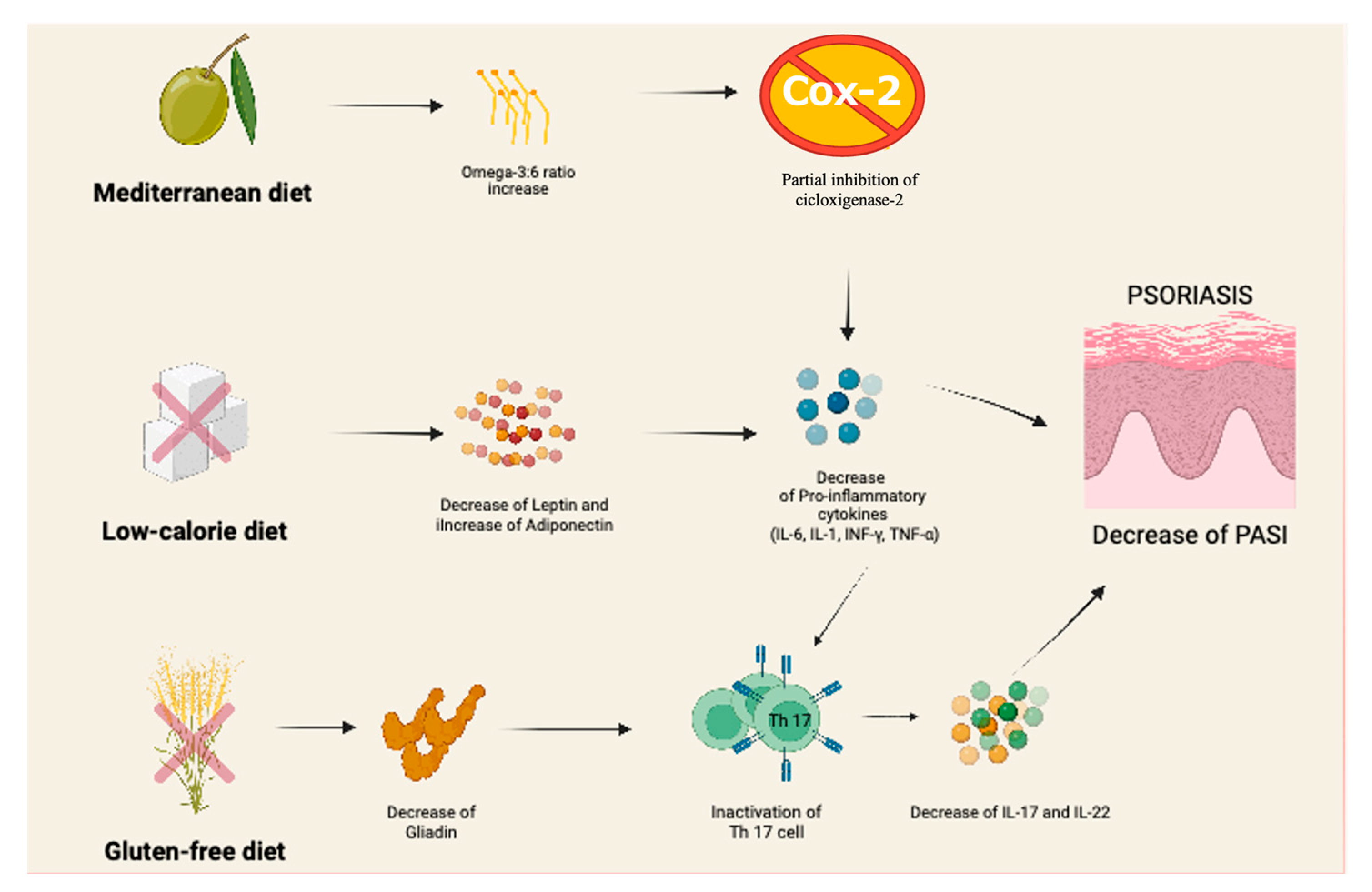
3.1. Mediterranean Diet
3.2. Gluten-Free Diet
3.3. Low-Calorie Diet
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, M.; Bartholomew, E.; Yeroushalmi, S.; Hakimi, M.; Bhutani, T.; Liao, W. Dietary Intervention and Supplements in the Management of Psoriasis: Current Perspectives. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2022, 12, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, O.; Lucarini, G.; Campanati, A.; Goteri, G.; Zizzi, A.; Marconi, B.; Ganzetti, G.; Minardi, D.; Di Primio, R.; Offidani, A. VEGF, survivin and NOS overexpression in psoriatic skin: Critical role of nitric oxide synthases. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 54, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lernia, V.; Bianchi, L.; Guerriero, C.; Stingeni, L.; Gisondi, P.; Filoni, A.; Guarneri, C.; Fortina, A.B.; Lasagni, C.; Simonetti, O.; et al. Adalimumab in severe plaque psoriasis of childhood: A multi-center, retrospective real-life study up to 52 weeks observation. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purzycka-Bohdan, D.; Nedoszytko, B.; Zabłotna, M.; Gleń, J.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A.; Nowicki, R.J. Chemokine Profile in Psoriasis Patients in Correlation with Disease Severity and Pruritus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahil, S.K.; Capon, F.; Barker, J.N. Update on psoriasis immunopathogenesis and targeted immunotherapy. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 38, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, S.W.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.A.; Park, G.Y.; Lee, W.W. Subclinical systemic and vascular inflammation detected by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with mild psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjuler, K.F.; Gormsen, L.C.; Vendelbo, M.H.; Egeberg, A.; Nielsen, J.; Iversen, L. Increased global arterial and subcutaneous adipose tissue inflammation in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korman, N. Management of psoriasis as a systemic disease: What is the evidence? Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 182, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Gotor, J.; Ferraz-Amaro, I.; Genre, F.; Mazón, I.G.; Corrales, A.; Portilla, V.; Llorca, J.; Agudo-Bilbao, M.; Aurrecoechea, E.; Expósito, R.; et al. Cardiovascular and disease-related features associated with extra-articular manifestations in axial spondyloarthritis. A multicenter study of 888 patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 57, 152096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marani, A.; Rizzetto, G.; Radi, G.; Molinelli, E.; Capodaglio, I.; Offidani, A.; Simonetti, O. Metabolic Comorbidities and Cardiovascular Disease in Pediatric Psoriasis: A Narrative Review. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Mercy, K.; Kwasny, M.; Choon, S.E.; Cordoro, K.; Girolomoni, G.; Menter, A.; Tom, W.L.; Mahoney, A.M.; Oostveen, A.M.; et al. Association of pediatric psoriasis severity with excess and central adiposity: An international cross-sectional study. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, L.; Tom, W.L.; Eshagh, K.; Benjamin, L.T.; Paller, A.S. Excess Adiposity Preceding Pediatric Psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.; Hogan, A.E.; Fallon, P.G.; Schwartz, C. Obesity-Mediated Immune Modulation: One Step Forward, (Th)2 Steps Back. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 932893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Jaramillo, P.; Gómez-Arbeláez, D.; López-López, J.; López-López, C.; Martínez-Ortega, J.; Gómez-Rodríguez, A.; Triana-Cubillos, S. The role of leptin/adiponectin ratio in metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2014, 18, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiroukidou, K.; Hatziagorou, E.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Vamvakis, A.; Kontouli, K.; Tzimos, C.; Tsanakas, J.; Spiliotis, B.E. Cardiorespiratory Fitness Predicted by Fibrinogen and Leptin Concentrations in Children with Obesity and Risk for Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study and a ROC Curve Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, A.; Grywalska, E.; Walankiewicz, M.; Lotti, T.; Roliński, J.; Myśliński, W.; Chabros, P.; Piekarska-Myślińska, D.; Reich, K. Psoriasis and metabolic syndrome in children: Current data. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, C.; Touvier, M.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Adjibade, M.; Hercberg, S.; Wolkenstein, P.; Chosidow, O.; Ezzedine, K.; Sbidian, E. Association Between Mediterranean Anti-inflammatory Dietary Profile and Severity of Psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, F.; Galderisi, A.; Moretti, C.; Ventura, L.; Fortina, A.B. Prevalence of psoriasis in a cohort of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e589–e591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidolin, L.; Borin, M.; Fontana, E.; Caroppo, F.; Piaserico, S.; Fortina, A. Central Obesity in Children with Psoriasis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2018, 98, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchetti, T.; Simonetti, O.; Ricotti, F.; Offidani, A.; Ferretti, G. Plasma oxidation status and antioxidant capacity in psoriatic children. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2019, 312, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, C.; Mazzantini, S.; Zuccotti, G.V. Nutrition in the First 1000 Days: The Origin of Childhood Obesity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Morizane, S.; Akagi, T.; Hiramatsu-Asano, S.; Tachibana, K.; Yahagi, A.; Iseki, M.; Kaneto, H.; Wada, J.; Ishihara, K.; et al. Obesity and Dyslipidemia Synergistically Exacerbate Psoriatic Skin Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimbri, P.; Korakas, E.; Kountouri, A.; Ikonomidis, I.; Tsougos, E.; Vlachos, D.; Papadavid, E.; Raptis, A.; Lambadiari, V. The Effect of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capacity of Diet on Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Phenotype: Nutrition as Therapeutic Tool? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monthé-Drèze, C.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Aris, I.M.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Sen, S.; Oken, E. Maternal diet in pregnancy is associated with differences in child body mass index trajectories from birth to adolescence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.R.; Siegel, M.; Bagel, J.; Cordoro, K.M.; Garg, A.; Gottlieb, A.; Green, L.J.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Koo, J.; Lebwohl, M.; et al. Dietary recommendations for adults with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis from the medical board of the national psoriasis foundation. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 934–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Purzycka-Bohdan, D.; Nedoszytko, B.; Reich, A.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A.; Bartosińska, J.; Batycka-Baran, A.; Czajkowski, R.; Dobrucki, I.; Dobrucki, L.; et al. Pathogenesis of psoriasis in the “omic” era. Part III. Metabolic disorders, metabolomics, nutrigenomics in psoriasis in psoriasis. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2020, 37, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopytalska, K.; Ciechanowicz, P.; Wiszniewski, K.; Szymańska, E.; Walecka, I. The Role of Epigenetic Factors in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.L.; Bentley, M.E. The critical period of infant feeding for the development of early disparities in obesity. Soc. Sci. Med. 2013, 97, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell-Birtill, P.; Hetherington, M.M. Determinants of Portion Size in Children and Adolescents: Insights from the UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey Rolling Programme (2008–2016). Nutrients 2019, 11, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihl, A.F.; Fonvig, C.E.; Stjernholm, T.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Holm, J.-C. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Childhood Obesity. Child. Obes. 2016, 12, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbicz, J.; Całyniuk, B.; Górski, M.; Buczkowska, M.; Piecuch, M.; Kulik, A.; Rozentryt, P. Nutritional Therapy in Persons Suffering from Psoriasis. Nutrients 2021, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingkapairoj, K.; Chularojanamontri, L.; Chaiyabutr, C.; Silpa-Archa, N.; Wongpraparut, C.; Bunyaratavej, S. Dietary habits and perceptions of psoriatic patients: Mediterranean versus Asian diets. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2021, 33, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, R.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Griffiths, C.E.; Ashcroft, D.M. Global Epidemiology of Psoriasis: A Systematic Review of Incidence and Prevalence. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Lagiou, P. Healthy Traditional Mediterranean Diet: An Expression of Culture, History, and Lifestyle. Nutr. Rev. 1997, 55, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Nappi, F.; Di Somma, C.; Savanelli, M.C.; Falco, A.; Balato, A.; Balato, N.; Savastano, S. Environmental Risk Factors in Psoriasis: The Point of View of the Nutritionist. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Balato, N.; Di Somma, C.; Macchia, P.E.; Napolitano, M.; Savanelli, M.C.; Esposito, K.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Nutrition and psoriasis: Is there any association between the severity of the disease and adherence to the Mediterranean diet? J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nani, A.; Murtaza, B.; Khan, A.S.; Khan, N.; Hichami, A. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Polyphenols Contained in Mediterranean Diet in Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms. Molecules 2021, 26, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massini, G.; Capra, N.; Buganza, R.; Nyffenegger, A.; de Sanctis, L.; Guardamagna, O. Mediterranean Dietary Treatment in Hyperlipidemic Children: Should It Be an Option? Nutrients 2022, 14, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Robles, M.A.; Ccami-Bernal, F.; Ortiz-Benique, Z.N.; Pinto-Ruiz, D.F.; Benites-Zapata, V.A.; Patiño, D.C. Adherence to Mediterranean diet associated with health-related quality of life in children and adolescents: A systematic review. BMC Nutr. 2022, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juton, C.; Berruezo, P.; Rajmil, L.; Lerin, C.; Fíto, M.; Homs, C.; Según, G.; Gómez, S.F.; Schröder, H. Prospective Association between Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Health-Related Quality of Life in Spanish Children. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Catassi, C. Celiac Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, P.; Mathur, M. Association between psoriasis and celiac disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 82, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Lindelöf, B.; Zingone, F.; Ciacci, C. Psoriasis in a Nationwide Cohort Study of Patients with Celiac Disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2010–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, B.K.; Millsop, J.W.; Debbaneh, M.; Koo, J.; Linos, E.; Liao, W. Diet and psoriasis, part II: Celiac disease and role of a gluten-free diet. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaëlsson, G.; Gerdén, B.; Hagforsen, E.; Nilsson, B.; Pihl-Lundin, I.; Kraaz, W.; Hjelmquist, G.; Lööf, L. Psoriasis patients with antibodies to gliadin can be improved by a gluten-free diet. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 142, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberry, C.; McKnight, L.; Sarav, M.; Pickett-Blakely, O. Going Gluten Free: The History and Nutritional Implications of Today’s Most Popular Diet. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, G.; Bacchetti, T.; Masciangelo, S.; Saturni, L. Celiac Disease, Inflammation and Oxidative Damage: A Nutrigenetic Approach. Nutrients 2012, 4, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Toma, A.; Volta, U.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; Sanders, D.S.; Cellier, C.; Mulder, C.J.; Lundin, K.E.A. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 583–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Kasprowicz-Furmańczyk, M.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Szepietowski, J. Effect of diet and weight loss on the severity of psoriasis. Postępy Hig. Med. Doświadczalnej 2022, 76, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infantino, M.; Manfredi, M.; Meacci, F.; Grossi, V.; Severino, M.; Benucci, M.; Bellio, E.; Bellio, V.; Nucci, A.; Zolfanelli, F.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of anti-gliadin antibodies in Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS) patients: A dual statistical approach. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 451, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, J. Role of intestinal microbiota and metabolites on gut homeostasis and human diseases. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, A.M.; Qureshi, A.A.; Thompson, J.M.; Li, T.; Cho, E. Gluten intake and risk of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and atopic dermatitis among United States women. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 82, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mutairi, N.; Nour, T. The effect of weight reduction on treatment outcomes in obese patients with psoriasis on biologic therapy: A randomized controlled prospective trial. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2014, 14, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, M.; Glaeske, G.; Radtke, M.; Christophers, E.; Reich, K.; Schäfer, I. Epidemiology and comorbidity of psoriasis in children. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 162, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, T.; Machado, S.; Mendonça, D.; Selores, M. Cardiovascular comorbidities in childhood psoriasis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2014, 24, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldminz, A.M.; Buzney, C.D.; Kim, N.; Au, S.-C.; Levine, D.E.; Wang, A.C.; Volf, E.M.; Yaniv, S.S.; Kerensky, T.A.; Bhandarkar, M.; et al. Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in Children with Psoriatic Disease. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2013, 30, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, O.; Ferretti, G.; Salvi, A.; Offidani, A.M.; Bossi, G. Plasma Lipid Changes in Psoriatic Children. Dermatology 1992, 185, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, G.; Simonetti, O.; Offidani, A.M.; Messini, L.; Cinti, B.; Marshiseppe, I.; Bossi, G.; Curatola, G. Changes of Plasma Lipids and Erythrocyte Membrane Fluidity in Psoriatic Children. Pediatr. Res. 1993, 33, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, O.; Bacchetti, T.; Ferretti, G.; Molinelli, E.; Rizzetto, G.; Bellachioma, L.; Offidani, A. Oxidative Stress and Alterations of Paraoxonases in Atopic Dermatitis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Kiluk, P.; Myśliwiec, H.; Flisiak, I. The role of lipids in psoriasis. Dermatol. Rev. 2017, 104, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millsop, J.W.; Bhatia, B.K.; Debbaneh, M.; Koo, J.; Liao, W. Diet and psoriasis, part III: Role of nutritional supplements. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, M.; Singh, P.K.; Maheshwari, K. Clinical evaluation of omega-3 fatty acids in psoriasis. Dermatol. Rev. 2017, 3, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicińska, P.; Pytel, E.; Kurowska, J.; Koter-Michalak, M. Supplementation with omega fatty acids in various diseases. Adv. Hyg. Exp. Med. 2015, 69, 838–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Macchia, P.E.; Tarantino, G.; Di Somma, C.; Pane, E.; Balato, N.; Napolitano, M.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Nutrition: A key environmental dietary factor in clinical severity and cardio-metabolic risk in psoriatic male patients evaluated by 7-day food-frequency questionnaire. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Fabbrocini, G.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Donnarumma, M.; Marasca, C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Role of Nutrition and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in the Multidisciplinary Approach of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Evaluation of Nutritional Status and Its Association with Severity of Disease. Nutrients 2018, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Nakajima, K.; Tarutani, M.; Morishige, R.; Sano, S. Kinetics of circulating Th17 cytokines and adipokines in psoriasis patients. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.M. Cutaneous manifestations in celiac disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragballe, K.; Voorhees, J.J. Modulation of epidermal cell division and growth by oxygenation products of arachidonic acid. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1984, 74, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.L.J.; Keown-Stoneman, C.D.; Birken, C.S.; Jenkins, D.J.; Borkhoff, M.C.M. Vegetarian Diet, Growth, and Nutrition in Early Childhood: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Pediatrics 2022, 149, e2021052598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/dietary-reference-values (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Gangadevi, V.; Thatikonda, S.; Pooladanda, V.; Devabattula, G.; Godugu, C. Selenium nanoparticles produce a beneficial effect in psoriasis by reducing epidermal hyperproliferation and inflammation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanesco, S.; Hall, W.; Gibson, R.; Griffiths, C.; Maruthappu, T. Approaches to nutrition intervention in plaque psoriasis, a multi-system inflammatory disease—The Diet and Psoriasis Project (DIEPP). Nutr. Bull. 2022, 47, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Stahl, W. Vitamins E and C, beta-carotene, and other carotenoids as antioxidants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Keogh, J.; Clifton, P.M. Nuts and Cardio-Metabolic Disease: A Review of Meta-Analyses. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.; Peter, S.; Chopra, S. A fish a day, keeps the cardiologist away!-A review of the effect of omega-3 fatty acids in the cardiovascular system. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Savanelli, M.C.; Di Somma, C.; Napolitano, M.; Megna, M.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Vitamin D and its role in psoriasis: An overview of the dermatologist and nutritionist. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Bäckhed, F. The Impact of Dietary Fiber on Gut Microbiota in Host Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iebba, V.; Totino, V.; Gagliardi, A.; Santangelo, F.; Cacciotti, F.; Trancassini, M.; Mancini, C.; Cicerone, C.; Corazziari, E.; Pantanella, F.; et al. Eubiosis and dysbiosis: The two sides of the microbiota. New Microbiol. 2016, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Monir, R.L.; Schoch, J.J. Clinical Relevance of the Microbiome in Pediatric Skin Disease: A Review. Dermatol. Clin. 2022, 40, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balato, N.; Megna, M.; Palmisano, F.; Patruno, C.; Napolitano, M.; Scalvenzi, M.; Ayala, F. Psoriasis and Sport: A New Ally? J. Eur. Acad Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Simoni, E.; Rizzetto, G.; Molinelli, E.; Capodaglio, I.; Offidani, A.; Simonetti, O. The Role of Diet in Children with Psoriasis: Emerging Evidence and Current Issues. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071705
De Simoni E, Rizzetto G, Molinelli E, Capodaglio I, Offidani A, Simonetti O. The Role of Diet in Children with Psoriasis: Emerging Evidence and Current Issues. Nutrients. 2023; 15(7):1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071705
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Simoni, Edoardo, Giulio Rizzetto, Elisa Molinelli, Irene Capodaglio, Annamaria Offidani, and Oriana Simonetti. 2023. "The Role of Diet in Children with Psoriasis: Emerging Evidence and Current Issues" Nutrients 15, no. 7: 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071705
APA StyleDe Simoni, E., Rizzetto, G., Molinelli, E., Capodaglio, I., Offidani, A., & Simonetti, O. (2023). The Role of Diet in Children with Psoriasis: Emerging Evidence and Current Issues. Nutrients, 15(7), 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071705





