The Inter-Organ Crosstalk Reveals an Inevitable Link between MAFLD and Extrahepatic Diseases
(This article belongs to the Section Nutrition and Metabolism)
Abstract
1. Introduction—What Is MAFLD?
1.1. The Relationship between Fatty Liver and Metabolic Abnormality
1.2. The Momentum for the Nomenclature of MAFLD and Its Definition
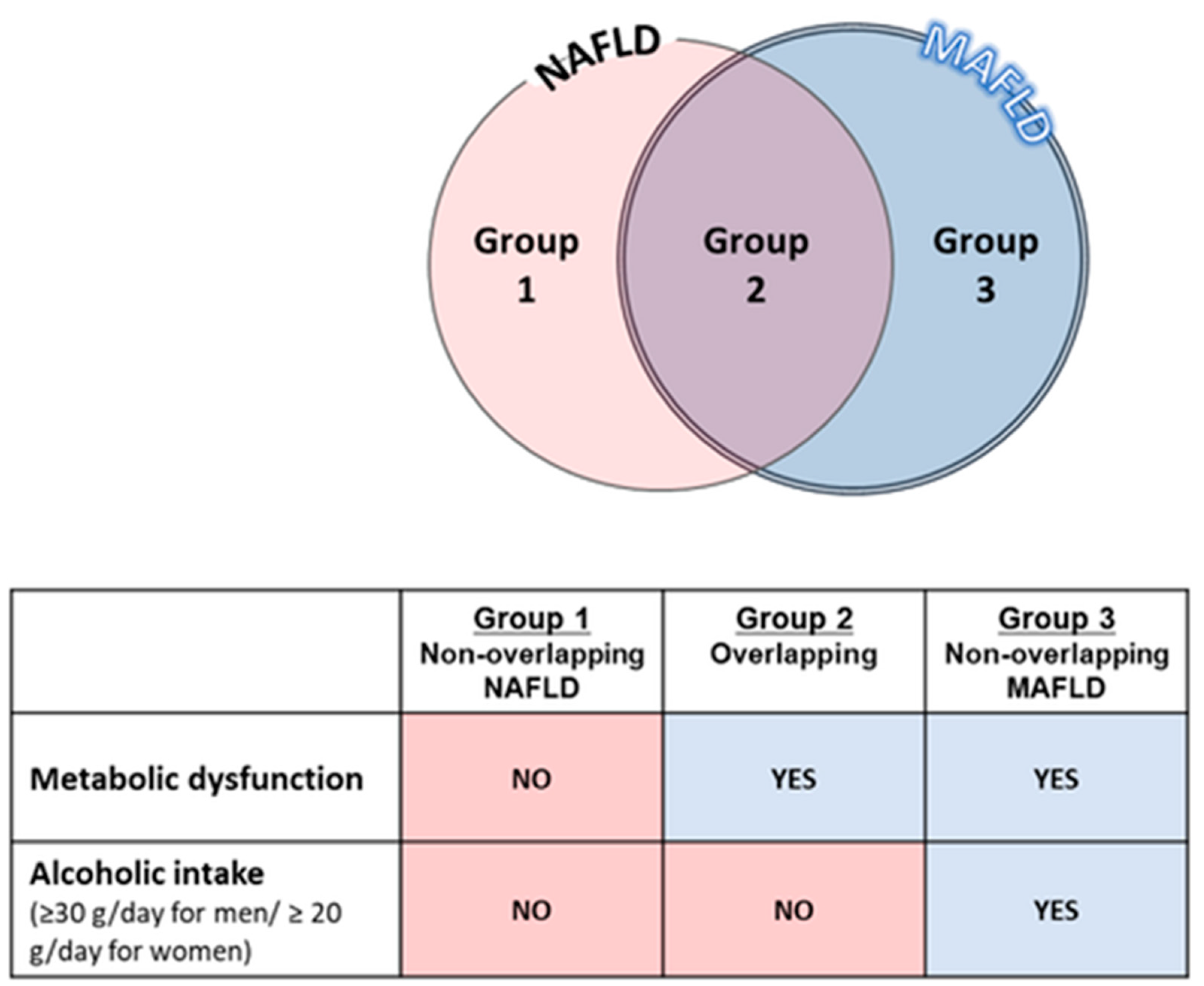
1.3. Differences between MAFLD and NAFLD
1.4. The Impact of MAFLD Subtypes on Clinical Outcomes and Treatment
2. The Relationship with Intrahepatic Lesions
2.1. The Relationship with Hepatic Fibrosis
2.2. The Relationship with Hepatic Carcinogenesis
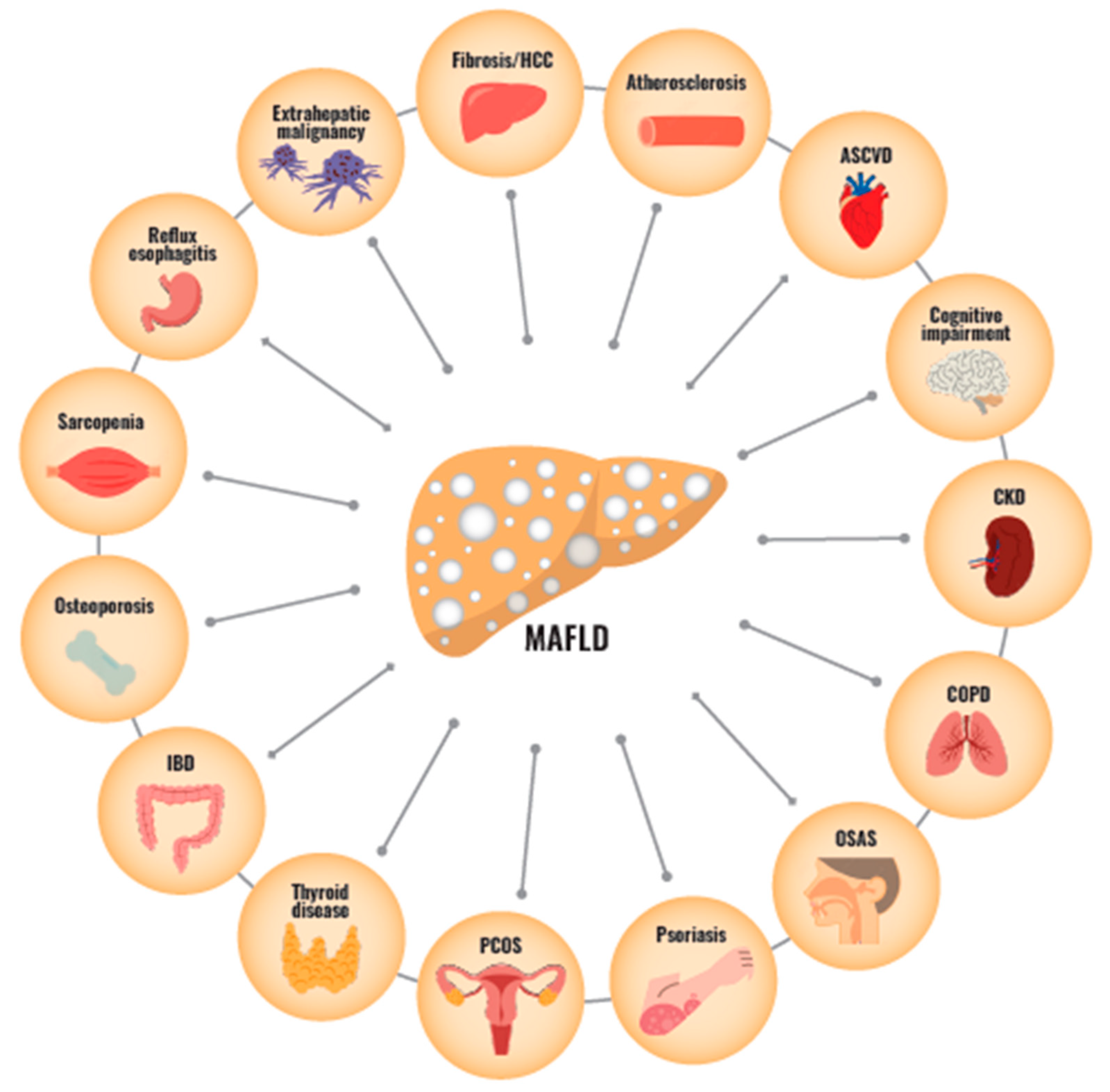
3. The Relationship between MAFLD and Multi-Organ Disease
3.1. The Relationship with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
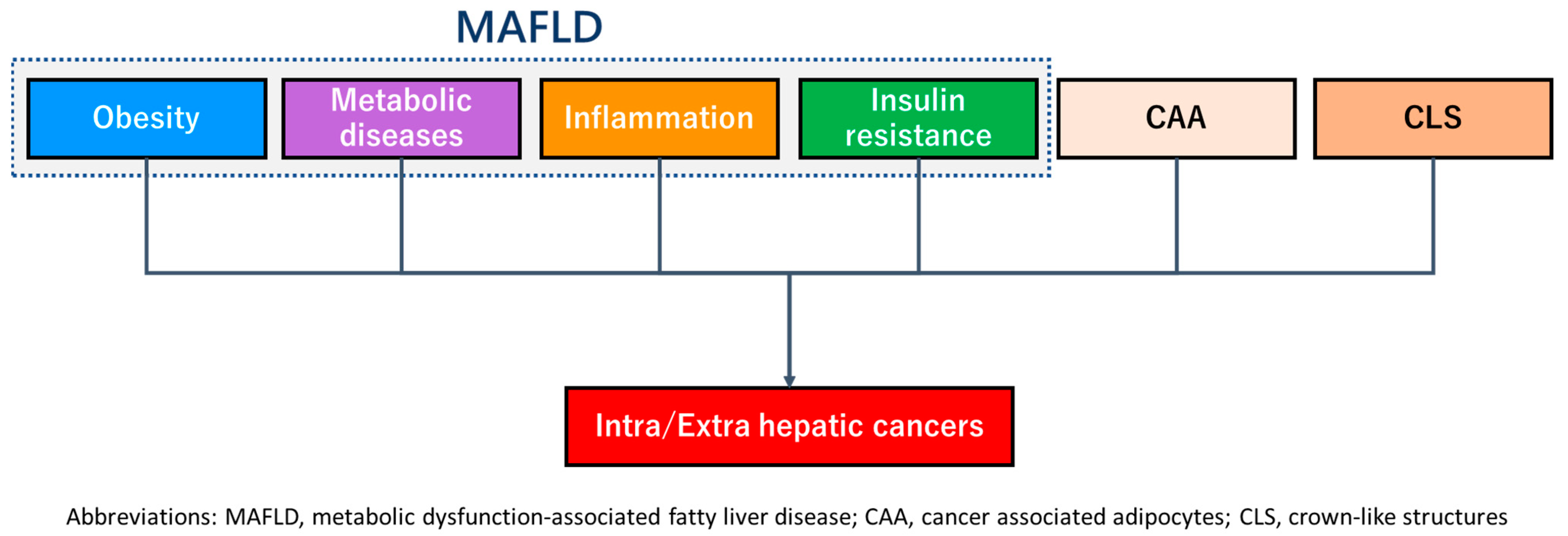
3.2. The Relationship with Extrahepatic Carcinoma
3.3. The Relationship with Chronic Kidney Disease
3.4. The Relationship with Sarcopenia
3.5. The Relationship with Thyroid Hormone
3.6. The Relationship with Other Extrahepatic Diseases
| Organ | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Brain |
| [71] |
| Esophagus |
| [72] |
| Gut |
| [73,74] |
| Lung |
| [75,76] |
| Skin |
| [77] |
| Bone |
| [80,81] |
3.7. Limitations Regarding the Present MAFLD Research
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watanabe, S.; Hashimoto, E.; Ikejima, K.; Uto, H.; Ono, M.; Sumida, Y.; Seike, M.; Takei, Y.; Takehara, T.; Tokushige, K.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Tatemichi, M.; Tsuruya, K.; Anzai, K.; Arase, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Suzuki, M.; Ieda, S.; Kagawa, T. Nineteen-year prognosis in Japanese patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Lean versus overweight patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.B.; Hu, E.D.; Xu, L.M.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.L.; Li, H.; Chen, D.Z.; Chen, Y.P. The relationship between obesity and the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 12, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niriella, M.A.; Kasturiratne, A.; Beddage, T.U.; Withanage, S.A.; Goonatilleke, D.C.; Abeysinghe, C.P.; De Mel, R.T.; Balapitiya, T.L.; De Silva, S.T.; Dassanayake, A.S.; et al. Metabolic syndrome, but not non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, increases 10-year mortality: A prospective, community-cohort study. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Ong, J.; Yilmaz, Y.; Duseja, A.; Eguchi, Y.; El Kassas, M.; Castellanos-Fernandez, M.; George, J.; Jacobson, I.M.; et al. Effects of Alcohol Consumption and Metabolic Syndrome on Mortality in Patients With Nonalcoholic and Alcohol-Related Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1625–1633.e1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; International Consensus, P. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sarin, S.K.; Wong, V.W.; Fan, J.G.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ahn, S.H.; Zheng, M.H.; Shiha, G.; Yilmaz, Y.; Gani, R.; et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 889–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Sanchez, N.; Bugianesi, E.; Gish, R.G.; Lammert, F.; Tilg, H.; Nguyen, M.H.; Sarin, S.K.; Fabrellas, N.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Fan, J.G.; et al. Global multi-stakeholder endorsement of the MAFLD definition. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Torimura, T. MAFLD: Renovation of clinical practice and disease awareness of fatty liver. Hepatol. Res. 2022, 52, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Torimura, T. MAFLD enhances clinical practice for liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.; Yamada, G.; Kimura, T.; Hagiwara, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kurakawa, K.I.; Nangaku, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Matsuyama, Y.; Kadowaki, T. Diagnostic ability using fatty liver and metabolic markers for metabolic-associated fatty liver disease stratified by metabolic/glycemic abnormalities. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Yang, W.; Gong, L.; Lyu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Fu, J.; Li, J.; Shi, J. Serum metabolomics-based heterogeneities and screening strategy for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 538, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessho, R.; Kashiwagi, K.; Ikura, A.; Yamataka, K.; Inaishi, J.; Takaishi, H.; Kanai, T. A significant risk of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease plus diabetes on subclinical atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Pang, J.; Tang, Y.; Ling, W. Are the different MAFLD subtypes based on the inclusion criteria correlated with all-cause mortality? J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Kessoku, T.; Kawanaka, M.; Nonaka, M.; Hyogo, H.; Fujii, H.; Nakajima, T.; Imajo, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kubotsu, Y.; et al. Ipragliflozin Improves the Hepatic Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes with NAFLD. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, S.; Lisco, G.; Fanelli, M.; Racaniello, D.; Colaianni, V.; Triggiani, D.; Donghia, R.; Crudele, L.; Rinaldi, R.; Sabba, C.; et al. Once-Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide Improves Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A 52-Week Prospective Real-Life Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.S.; Hong, J.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Ferrannini, E.; Nauck, M.A.; Lim, S. SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez-Vazquez, A.L.; Beltran-Gall, S.M.; Pal, S.C.; Mendez-Sanchez, N. Editorial: Treatment with Dual Incretin Receptor Agonists to Maintain Normal Glucose Levels May Also Maintain Normal Weight and Control Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD). Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e938365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrom, H.; Nasr, P.; Ekstedt, M.; Hammar, U.; Stal, P.; Hultcrantz, R.; Kechagias, S. Fibrosis stage but not NASH predicts mortality and time to development of severe liver disease in biopsy-proven NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Eslam, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K.; George, J.; Torimura, T. MAFLD identifies patients with significant hepatic fibrosis better than NAFLD. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kleef, L.A.; Ayada, I.; Alferink, L.J.M.; Pan, Q.; de Knegt, R.J. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease improves detection of high liver stiffness: The Rotterdam Study. Hepatology 2022, 75, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayada, I.; van Kleef, L.A.; Alferink, L.J.M.; Li, P.; de Knegt, R.J.; Pan, Q. Systematically comparing epidemiological and clinical features of MAFLD and NAFLD by meta-analysis: Focusing on the non-overlap groups. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, S.; Neyroud-Caspar, I.; Spahr, L.; Gkouvatsos, K.; Fournier, E.; Giostra, E.; Magini, G.; Frossard, J.L.; Bascaron, M.E.; Vernaz, N.; et al. NAFLD and MAFLD as emerging causes of HCC: A populational study. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, A.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Ortolani, A.; Cucco, M.; Dalla Riva, G.V.; Giannini, E.G.; Piscaglia, F.; Rapaccini, G.; Di Marco, M.; Caturelli, E.; et al. Epidemiological trends and trajectories of MAFLD-associated hepatocellular carcinoma 2002–2033: The ITA.LI.CA database. Gut 2023, 72, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimose, S.; Hiraoka, A.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Iwamoto, H.; Tada, F.; Rimini, M.; Tanaka, M.; Torimura, T.; et al. The beneficial impact of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease on lenvatinib treatment in patients with non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2023, 53, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, N.; Bai, C.; Fang, Y.; Srishord, M.; McCullough, A.; Gramlich, T.; Younossi, Z.M. Long-term follow-up of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; de Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, e1082–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, T.; Eslam, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Yamamura, S.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nakano, D.; Koseki, M.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K.; et al. MAFLD better predicts the progression of atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk than NAFLD: Generalized estimating equation approach. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Honda, Y.; Imajo, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Kessoku, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nogami, A.; Higurashi, T.; Kato, S.; et al. Risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with fatty liver disease as defined from the metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease point of view: A retrospective nationwide claims database study in Japan. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, H.C. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Incident Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2138–2147.e2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Konyn, P.; Sandhu, K.K.; Dennis, B.B.; Cheung, A.C.; Ahmed, A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is associated with increased all-cause mortality in the United States. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, J.; Ng, C.H.; Tang, A.S.P.; Chew, N.; Chan, M.; Khoo, C.M.; Wei, C.P.; Chin, Y.H.; Tay, P.; Lim, G.; et al. Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease Increases the Risk of Systemic Complications and Mortality. A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of 12 620 736 Individuals. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdz, K.; Nabrdalik, K.; Kwiendacz, H.; Hendel, M.; Olejarz, A.; Tomasik, A.; Bartman, W.; Nalepa, J.; Gumprecht, J.; Lip, G.Y.H. Risk factors for cardiovascular disease in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A machine learning approach. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhuang, X.; Li, X.; Gong, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Feng, S.; Wu, T.; Zhong, B. Novel metabolic classification for extrahepatic complication of metabolic associated fatty liver disease: A data-driven cluster analysis with international validation. Metabolism 2022, 136, 155294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and increased risk of incident extrahepatic cancers: A meta-analysis of observational cohort studies. Gut 2022, 71, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.A.; Lee, H.C.; Choe, J.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, M.J.; Chang, H.S.; Bae, I.Y.; Kim, H.K.; An, J.; Shim, J.H.; et al. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cancer incidence rate. J. Hepatol. 2017, 68, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.M.; Hicks, S.B.; Mara, K.C.; Larson, J.J.; Therneau, T.M. The risk of incident extrahepatic cancers is higher in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than obesity—A longitudinal cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Liao, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Associations Between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cancers in a Large Cohort in China. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 788–796.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.G.; Roelstraete, B.; Sharma, R.; Khalili, H.; Hagstrom, H.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Cancer Risk in Patients With Biopsy-Confirmed Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2410–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Douglas, I.J.; Smeeth, L. Association of BMI with overall and cause-specific mortality: A population-based cohort study of 3.6 million adults in the UK. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.G.; Roelstraete, B.; Khalili, H.; Hagstrom, H.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Mortality in biopsy-confirmed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Results from a nationwide cohort. Gut 2021, 70, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, K.; Tuomilehto, J.; Sund, R.; Keskimaki, I.; Hartikainen, S.; Pukkala, E. Cancer incidence among Finnish people with type 2 diabetes during 1989–2014. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 34, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Suo, C.; Shi, O.; Lin, C.; Zhao, R.; Yuan, H.; Jin, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X. The Health Impact of MAFLD, a Novel Disease Cluster of NAFLD, Is Amplified by the Integrated Effect of Fatty Liver Disease-Related Genetic Variants. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e855–e875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, C.; Suo, C.; Zhao, R.; Jin, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and the risk of 24 specific cancers. Metabolism 2022, 127, 154955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, S.; Nakano, D.; Kawaguchi, T.; Eslam, M.; Ouchi, A.; Nagata, T.; Kuroki, H.; Kawata, H.; Abe, H.; Nouno, R.; et al. Non-Obese MAFLD Is Associated with Colorectal Adenoma in Health Check Examinees: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, S.U.; Chang Kim, H. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Increases Colon Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e00435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.Y.; Bae, J.H.; Kwak, M.S.; Yang, J.I.; Chung, S.J.; Yim, J.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Chung, G.E. The Risk of Colorectal Adenoma in Nonalcoholic or Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Morley, T.S.; Kim, M.; Clegg, D.J.; Scherer, P.E. Obesity and cancer--mechanisms underlying tumour progression and recurrence. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Cha, Y.J.; Koo, J.S. Adipocyte biology in breast cancer: From silent bystander to active facilitator. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 69, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD as a driver of chronic kidney disease. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.Y.; Wang, R.F.; Bu, Z.Y.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Sun, D.Q.; Zheng, M.H. Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.Y.; Koh, H.B.; Park, K.H.; Joo, Y.S.; Kim, H.W.; Ahn, S.H.; Park, J.T.; Kim, S.U. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: A nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 48, 101344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Hamaguchi, M.; Okamura, T.; Nakanishi, N.; Obora, A.; Kojima, T.; Fukui, M. Metabolic associated fatty liver disease is a risk factor for chronic kidney disease. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Mori, K.; Takahashi, S.; Higashiura, Y.; Ohnishi, H.; Hanawa, N.; Furuhashi, M. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease predicts new onset of chronic kidney disease better than does fatty liver or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.Q.; Jin, Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Zheng, K.I.; Rios, R.S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Yuan, W.J.; Zheng, M.H. MAFLD and risk of CKD. Metabolism 2021, 115, 154433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Cho, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kwak, M.S.; Yang, J.I.; Chung, S.J.; Yim, J.Y.; Yoon, J.W.; Chung, G.E. The relationship between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and low muscle mass in an asymptomatic Korean population. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.S.; Chai, Y.H.; Gong, H.J.; Zhuldyz, Z.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Zhou, J.B.; Simo, R. The Association Between Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Sarcopenia: Accumulated Evidences From Observational Studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 782391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.S.; Kim, M.N.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, S.U. Risk stratification using sarcopenia status among subjects with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanji, R.A.; Narayanan, P.; Allen, A.M.; Malhi, H.; Watt, K.D. Sarcopenia in hiding: The risk and consequence of underestimating muscle dysfunction in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 2055–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henson, J.B.; Simon, T.G.; Kaplan, A.; Osganian, S.; Masia, R.; Corey, K.E. Advanced fibrosis is associated with incident cardiovascular disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshio, S.; Shimagaki, T.; Hashida, R.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsutsui, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Kawai, H.; Yoshikawa, S.; Yamazoe, T.; et al. Myostatin as a fibroblast-activating factor impacts on postoperative outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, R.A.; Arenhardt, F.; Ribeiro, R.T.; Wajner, S.M. Influence of Altered Thyroid Hormone Mechanisms in the Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction Associated with Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): A Systematic Review. Metabolites 2022, 12, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N. Thyromimetics as emerging therapeutic agents for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Rationale for the development of resmetirom (MGL-3196). Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Tian, S.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Liang, X.Y.; Adhikari, V.P.; Xiao, J.; Song, J.Y.; et al. Impact of thyroid function on the prevalence and mortality of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, S.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Suo, C.; Cao, L.; Zhang, T. Low thyroid function is associated with an increased risk of advanced fibrosis in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bashir, M.R.; Guy, C.D.; Zhou, R.; Moylan, C.A.; Frias, J.P.; Alkhouri, N.; Bansal, M.B.; Baum, S.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huang, S.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Wu, Y.; Lv, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, N.; Wang, L.; et al. Discovery of a novel, liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonist, CS271011, in the treatment of lipid metabolism disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1109615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; He, R.; Jiang, H.; Wu, J.; Xi, Z.; He, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Feng, M.; Wan, P.; et al. Association between Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Fatty Liver Disease and Cognitive Impairment. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, S.; Nakano, D.; Tsutsumi, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Eslam, M.; Yoshinaga, S.; Abe, H.; Nouno, R.; Joh, S.; Mitsuyama, K.; et al. Lean/normal-weight metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is a risk factor for reflux esophagitis. Hepatol. Res. 2022, 52, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Dan, L.; Tu, X.; Sun, Y.; Deng, M.; Chen, X.; Hesketh, T.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and liver function markers are associated with Crohn’s disease but not Ulcerative Colitis: A prospective cohort study. Hepatol. Int. 2022, 17, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Duque, J.C.; Calleja, J.L.; Iruzubieta, P.; Hernandez-Conde, M.; Rivas-Rivas, C.; Vera, M.I.; Garcia, M.J.; Pascual, M.; Castro, B.; Garcia-Blanco, A.; et al. Increased risk of MAFLD and Liver Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Independent of Classic Metabolic Risk Factors. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 406–414.e407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Yang, L.; Guo, L.S.; Shi, Q.Q.; Zhou, T.F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cai, H.; Xu, Z.W.; Yang, S.Y.; et al. Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Fatty Liver Disease is Associated with Greater Impairment of Lung Function than Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Kawaguchi, M.; Hashida, R.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K.; Kawaguchi, T. MAFLD associated with COPD via systemic inflammation independent of aging and smoking in men. Diabetol. Metab Syndr. 2022, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, S.; Teraki, Y.; Katayama, E.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Nakano, D.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nagoshi, S.; Nakama, T.; Torimura, T. Effects of interleukin-17 inhibitors on hepatic fibrosis index in patients with psoriasis and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Directed acyclic graphs. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Cen, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Yu, C. Increased risk of low bone mineral density in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A cohort study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 182, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Lonardo, A.; Rossini, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and decreased bone mineral density: Is there a link? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Lin, R. Association of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Stiffness With Bone Mineral Density in American Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 891382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Geng, B. Metabolic associated fatty liver disease and bone mineral density: A cross-sectional study of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017–2018. Osteoporos. Int. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassio, A.; Idolazzi, L.; Rossini, M.; Gatti, D.; Adami, G.; Giollo, A.; Viapiana, O. The obesity paradox and osteoporosis. Eat. Weight Disord 2018, 23, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Organ | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Heart |
| [30,32] |
| [31] | |
| [33] |
| Organs | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Extrahepatic cancer |
| [45] |
| Cancer risk in MAFLD versus non-MAFLD | [46,48] | |
| Uterus | HR 2.36 | |
| Gallbladder | HR 2.20 | |
| Kidney | HR 1.77 | |
| Thyroid | HR 1.69 | |
| Esophagus | HR 1.48 | |
| Pancreas | HR 1.31 | |
| Bladder | HR 1.26 | |
| Breast | HR 1.26 | |
| Colorectal and anus | HR 1.32 | |
| Organ | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Kidney |
| [53,54,55,56,57] |
| Organ | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle |
| [59] |
| Organ | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Thyroid |
| [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Hashida, R.; Sano, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Amano, K.; Kawaguchi, T. The Inter-Organ Crosstalk Reveals an Inevitable Link between MAFLD and Extrahepatic Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051123
Tsutsumi T, Nakano D, Hashida R, Sano T, Kawaguchi M, Amano K, Kawaguchi T. The Inter-Organ Crosstalk Reveals an Inevitable Link between MAFLD and Extrahepatic Diseases. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051123
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsutsumi, Tsubasa, Dan Nakano, Ryuki Hashida, Tomoya Sano, Machiko Kawaguchi, Keisuke Amano, and Takumi Kawaguchi. 2023. "The Inter-Organ Crosstalk Reveals an Inevitable Link between MAFLD and Extrahepatic Diseases" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051123
APA StyleTsutsumi, T., Nakano, D., Hashida, R., Sano, T., Kawaguchi, M., Amano, K., & Kawaguchi, T. (2023). The Inter-Organ Crosstalk Reveals an Inevitable Link between MAFLD and Extrahepatic Diseases. Nutrients, 15(5), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051123








