TM6SF2-rs58542926 Genetic Variant Modifies the Protective Effect of a “Prudent” Dietary Pattern on Serum Triglyceride Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. NAFLD Staging and Classification
2.3. Demographic, Clinical, and Anthropometric Data
2.4. Dietary Assessment and Dietary Patterns Extraction
2.5. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.P.; Younossi, Z.M. Epidemiology and Natural History of NAFLD and NASH. Clin. Liver Dis. 2007, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Day, C.P. The genetics of NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Genetic predisposition in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2017, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namjou, B.; Lingren, T.; Huang, Y.; Parameswaran, S.; Cobb, B.L.; Stanaway, I.B.; Connolly, J.J.; Mentch, F.D.; Benoit, B.; Niu, X.; et al. GWAS and enrichment analyses of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease identify new trait-associated genes and pathways across eMERGE Network. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Darlay, R.; Cockell, S.; Meroni, M.; Govaere, O.; Tiniakos, D.; Burt, A.D.; Bedossa, P.; Palmer, J.; Liu, Y.-L.; et al. Genome-wide association study of non-alcoholic fatty liver and steatohepatitis in a histologically characterised cohort. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlitina, J.; Smagris, E.; Stender, S.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Zhou, H.H.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Vogt, T.F.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Exome-wide association study identifies a TM6SF2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, S.M.; Reedy, J.; Millen, A.E.; Dixon, L.B.; Newby, P.K.; Tucker, K.L.; Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Guenther, P.M. Dietary Patterns: Challenges and Opportunities in Dietary Patterns Research: An Experimental Biology Workshop, April 1, 2006. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, S.H.; Mansoori, A.; Hosseinzadeh, M. Relationship between dietary patterns and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangouni, A.A.; Zadeh, S.H.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Hosseinzadeh, M. Effect of Mediterranean diet on liver enzymes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigh, L.; Kirk, C.; El Gendy, K.; Gallacher, J.; Errington, L.; Mathers, J.C.; Anstee, Q.M. The effectiveness and acceptability of Mediterranean diet and calorie restriction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1913–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-Q.; Shu, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhou, Y.; Xuan, Y.-J.; Wang, S.-F. Dietary Patterns Modulate the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chinese Adults. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4778–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H.; Du, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Dietary patterns are associated with prevalence of fatty liver disease in adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, L.S.; Sampaio, H.A.; Arruda, S.P.; Portela, C.L.; de Melo, M.L.P.; Carioca, A.A.; Soares, N.T. Healthy dietary pattern is inversely associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in elderly. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafati, I.P.; Borsa, D.; Dimitriou, M.; Revenas, K.; Kokkinos, A.; Dedoussis, G.V. Dietary patterns and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a Greek case–control study. Nutrition 2019, 61, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury-Sayegh, N.; Younes, H.; Heraoui, G.N.H.A.; Sayegh, R. Nutritional Profile and Dietary Patterns of Lebanese Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanseresht, N.; Jafarirad, S.; Alavinejad, S.P.; Mansoori, A. Association of the dietary patterns with the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among Iranian population: A case-control study. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafati, I.P.; Dimitriou, M.; Borsa, D.; Vlachogiannakos, J.; Revenas, K.; Kokkinos, A.; Ladas, S.D.; Dedoussis, G.V. Fish intake interacts with TM6SF2 gene variant to affect NAFLD risk: Results of a case–control study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Lee, J.; Chun, S.; Choi, J.-E.; Kim, M.N.; Chon, Y.E.; Ha, Y.; Hwang, S.-G.; Choi, S.-W.; Hong, K.-W. Interaction between the PNPLA3 Gene and Nutritional Factors on NAFLD Development: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Nutrients 2022, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallio, M.; Romeo, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Masarone, M.; Larussa, T.; Abenavoli, L.; Persico, M.; Loguercio, C.; Federico, A. Nutrigenomics and Nutrigenetics in Metabolic- (Dysfunction) Associated Fatty Liver Disease: Novel Insights and Future Perspectives. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, L.; Dall’Armi, V.; Cefalo, C.; Nedovic, B.; Arzani, D.; Amore, R.; Rapaccini, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ricciardi, W.; Grieco, A.; et al. A case–control study on the effect of metabolic gene polymorphisms, nutrition, and their interaction on the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.N.; Lê, K.-A.; Walker, R.W.; Vikman, S.; Spruijt-Metz, D.; Weigensberg, M.J.; Allayee, H.; I Goran, M. Increased hepatic fat in overweight Hispanic youth influenced by interaction between genetic variation in PNPLA3 and high dietary carbohydrate and sugar consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkovic, I.A.; Ericson, U.; Rukh, G.; Riddestråle, M.; Romeo, S.; Orho-Melander, M. The PNPLA3 Ile148Met interacts with overweight and dietary intakes on fasting triglyceride levels. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, S.; Li, J.Z.; Seo, Y.-K.; Osborne, T.F.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. A feed-forward loop amplifies nutritional regulation of PNPLA3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7892–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, N.; Savoye, M.; Kim, G.; Marotto, K.; Shaw, M.M.; Pierpont, B.; Caprio, S. Hepatic Fat Accumulation Is Modulated by the Interaction between the rs738409 Variant in the PNPLA3 Gene and the Dietary Omega6/Omega3 PUFA Intake. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadeh, S.; Younossi, Z.M.; Remer, E.M.; Gramlich, T.; Ong, J.P.; Hurley, M.; Mullen, K.D.; Cooper, J.N.; Sheridan, M.J. The utility of radiological imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma without use of the preparative ultra-centrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, G.; Bellentani, S.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Passalacqua, M.; Castiglione, A.; Tiribelli, C. The Fatty Liver Index: A simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavouras, S.; Maraki, M.; Kollia, M.; Gioxari, A.; Jansena, L.T.; Sidossis, L.S. Development, reliability and validity of a physical activity questionnaire for estimating energy expenditure in Greek adults. Sci. Sports 2016, 31, e47–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, G.R.; Black, A.E.; Jebb, S.A.; Cole, T.J.; Murgatroyd, P.R.; Coward, W.A.; Prentice, A.M. Critical evaluation of energy intake data using fundamental principles of energy physiology: Derivation of cut-off limits to identify under-recording. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 45, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Black, A.E. Critical evaluation of energy intake using the Goldberg cut-off for energy intake:basal metabolic rate. A practical guide to its calculation, use and limitations. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Butler, J.L.; Palmer, C.D.; Voight, B.F.; GIANT Consortium MIGen Consortium; NASH CRN; Hirschhorn, J.N. PNPLA3variants specifically confer increased risk for histologic nonalcoholic fatty liver disease but not metabolic disease. Hepatology 2010, 52, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligthart, S.; de Vries, P.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.; Chasman, D.I.; Dehghan, A. CHARGE Inflammation working group Pleiotropy among Common Genetic Loci Identified for Cardiometabolic Disorders and C-Reactive Protein. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mejías, R.; Genre, F.; Remuzgo-Martínez, S.; González-Juanatey, C.; Robustillo-Villarino, M.; Llorca, J.; Corrales, A.; Vicente, E.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Magro, C.; et al. Influence of elevated-CRP level-related polymorphisms in non-rheumatic Caucasians on the risk of subclinical atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wen, J.; Tao, X.; Lu, B.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Gong, W.; Ling, C.; et al. Genetic variation in the GCKR gene is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese people. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Pare, G.; Parker, A.; Zee, R.Y.; Danik, J.S.; Buring, J.E.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Cook, N.R.; Miletich, J.P.; Chasman, D.I. Loci Related to Metabolic-Syndrome Pathways Including LEPR,HNF1A, IL6R, and GCKR Associate with Plasma C-Reactive Protein: The Women’s Genome Health Study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Zhou, Y.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Leivonen, M.; Arola, J.; Orho-Melander, M.; Orešič, M.; Yki-Järvinen, H. The MBOAT7 variant rs641738 alters hepatic phosphatidylinositols and increases severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in humans. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1263–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, B.; Dongiovanni, P.; Romeo, S.; Meroni, M.; McCain, M.; Miele, L.; Petta, S.; Maier, S.; Rosso, C.; De Luca, L.; et al. MBOAT7 rs641738 variant and hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic individuals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viitasalo, A.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Paananen, J.; Atalay, M.; Lindi, V.; Lakka, T.A. Associations of TM6SF2 167K allele with liver enzymes and lipid profile in children: The PANIC Study. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, C.J.; Sookoian, S. The dual and opposite role of the TM6SF2-rs58542926 variant in protecting against cardiovascular disease and conferring risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1742–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdessian, H.; Taxiarchis, A.; Popov, S.; Silveira, A.; Franco-Cereceda, A.; Hamsten, A.; Eriksson, P.; van’t Hooft, F. TM6SF2 is a regulator of liver fat metabolism influencing triglyceride secretion and hepatic lipid droplet content. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8913–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Lang, S.; Goeser, T.; Demir, M.; Steffen, H.-M.; Kasper, P. Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2022, 24, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, J.; Shang, X.; Chawla, N.; Yang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, J. Physical activity and sedentary behavior can modulate the effect of the PNPLA3 variant on childhood NAFLD: A case-control study in a Chinese population. BMC Med. Genet. 2016, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Zhou, Y.; Haridas, P.N.; Dwivedi, O.P.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Ali, A.; Juuti, A.; Leivonen, M.; Tukiainen, T.; Ahonen, L.; et al. Impaired hepatic lipid synthesis from polyunsaturated fatty acids in TM6SF2 E167K variant carriers with NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, E.A.; Yang, R.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Sreenivasan, U.; McFarland, R.; Leitch, C.C.; Wilson, M.H.; Narina, S.; Gorden, A.; Ryan, K.A.; et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 impacts lipid processing in liver and small intestine. Hepatology 2016, 65, 1526–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Cipolla, U.; Cassader, M.; Pinach, S.; Saba, F.; De Michieli, F.; Paschetta, E.; Bongiovanni, D.; Framarin, L.; Leone, N.; et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 variant affects postprandial lipoprotein metabolism and glucose homeostasis in NAFLD. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorletti, E.; Bhatia, L.; McCormick, K.G.; Clough, G.F.; Nash, K.; Hodson, L.; Moyses, H.E.; Calder, P.C.; Byrne, C.D.; WELCOME Study. Effects of purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Results from the WELCOME* study. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sullivan, S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Green, M.; Roncal, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Sato, Y.; Kang, D.-H.; et al. Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Hoogerland, J.A.; Bloks, V.W.; Bos, T.; Bleeker, A.; Wolters, H.; Wolters, J.C.; Hijmans, B.S.; van Dijk, T.H.; Thomas, R.; et al. Hepatic Carbohydrate Response Element Binding Protein Activation Limits Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Development in a Mouse Model for Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1a. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1638–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Wolford, B.N.; Lu, H.; Liang, W.; Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Rom, O.; Mahajan, A.; Surakka, I.; Graham, S.E.; et al. Type 2 diabetes sex-specific effects associated with E167K coding variant in TM6SF. Iscience 2021, 24, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Controls (n = 217) | Cases (n = 134) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (% males) | 39.2 | 45.5 | 0.144 |
| Age (years) | 43.75 ± 11.23 | 50.36 ± 10.51 | <0.001 |
| Education years | 15.25 ± 3.60 | 14.02 ± 3.99 | 0.005 |
| PAL | 1.43 ± 0.22 | 1.38 ± 0.23 | 0.011 |
| Pack-years | 8.08 ± 13.71 | 15.19 ± 24.49 | 0.024 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.92 ± 3.27 | 31.11 ± 4.72 | <0.001 |
| WHR | 0.83 ± 0.09 | 0.92 ± 0.08 | <0.001 |
| Fat Mass (%) | 26.23 ± 8.64 | 33.76 ± 8.93 | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 21.44 ± 11.73 | 30.26 ± 14.51 | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 21.10 ± 6.77 | 23.75 ± 8.44 | 0.002 |
| γ-GT (U/L) | 19.98 ± 17.58 | 28.29 ± 21.72 | <0.001 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 195.44 ± 38.85 | 209.19 ± 33.66 | 0.001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 120.99 ± 33.05 | 132.77 ± 30.38 | 0.001 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 57.87 ± 14.42 | 50.98 ± 12.42 | <0.001 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 78.51 ± 37.31 | 127.43 ± 62.64 | <0.001 |
| FGlu (mg/dL) | 84.39 ± 8.27 | 93.33 ± 12.65 | <0.001 |
| FIns (µU/mL) | 9.09 (4.30) | 13.40 (7.81) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.23 ± 0.34 | 5.56 ± 0.44 | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.84 (1.84) | 3.06 (2.22) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 2.30 (4.30) | 2.34 (1.84) | <0.001 |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | 4.73 ± 1.17 | 5.65 ± 1.25 | <0.001 |
| NFS | −2.76 ± 0.93 | −1.99 ± 1.26 | <0.001 |
| FLI | 21.47 ± 20.23 | 64.78 ± 24.37 | <0.001 |
| PNPLA3-rs738409/G | TM6SF2-rs58542926/A | GCKR-rs780094/A | MBOAT7-rs641738/A | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P † | OR | 95% CI | P † | OR | 95% CI | P † | OR | 95% CI | P † | |
| NAFLD * | 1.575 | 1.104–2.245 | 0.012 | 1.482 | 0.710–3.092 | 0.294 | 1.108 | 0.775–1.584 | 0.574 | 1.147 | 0.829–1.588 | 0.407 |
| Beta | SE | P † | Beta | SE | P † | Beta | SE | P † | Beta | SE | P † | |
| WHR | −0.005 | 0.007 | 0.505 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.336 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.129 | −0.002 | 0.007 | 0.791 |
| Fat mass (%) | 0.084 | 0.680 | 0.902 | 0.715 | 1.44 | 0.620 | 0.833 | 0.668 | 0.213 | −0.734 | 0.624 | 0.241 |
| ALT (U/L) | 1.712 | 1.071 | 0.111 | −0.066 | 2.281 | 0.977 | 1.216 | 1.063 | 0.253 | 0.714 | 0.987 | 0.470 |
| AST (U/L) | 0.215 | 0.6186 | 0.728 | −0.250 | 1.313 | 0.850 | 1.377 | 0.614 | 0.026 | 0.041 | 0.569 | 0.943 |
| γ-GT (U/L) | −0.470 | 1.660 | 0.778 | 8.290 | 3.520 | 0.019 | 2.575 | 1.635 | 0.116 | −1.116 | 1.513 | 0.461 |
| TC (mg/dL) § | 5.043 | 3.984 | 0.207 | −8.089 | 6.42 | 0.209 | −1.046 | 5.509 | 0.850 | 6.536 | 4.277 | 0.128 |
| HDL (mg/dL) § | 2.077 | 1.110 | 0.062 | −2.859 | 2.359 | 0.226 | 1.479 | 1.109 | 0.184 | 1.442 | 1.021 | 0.159 |
| LDL (mg/dL) § | 2.326 | 2.574 | 0.376 | −6.525 | 5.449 | 0.232 | 0.983 | 2.581 | 0.704 | 2.908 | −1.717 | 0.219 |
| TG (mg/dL) § | −5.504 | 4.036 | 0.174 | 0.334 | 8.581 | 0.969 | −0.442 | 4.047 | 0.913 | −3.126 | 3.712 | 0.400 |
| FGlu (mg/dL) ¶ | −0.617 | 0.794 | 0.438 | 1.483 | 1.651 | 0.369 | 0.407 | 0.779 | 0.602 | 0.541 | 0.715 | 0.450 |
| lnFIns (µU/mL) ¶ | −0.045 | 0.036 | 0.214 | −0.040 | 0.076 | 0.597 | −0.002 | 0.036 | 0.945 | 0.004 | 0.033 | 0.910 |
| HbA1C (%) ¶ | 0.068 | 0.038 | 0.072 | −0.076 | 0.090 | 0.400 | 0.039 | 0.037 | 0.296 | −0.010 | 0.033 | 0.764 |
| lnHOMA-IR ¶ | −0.037 | 0.040 | 0.360 | −0.029 | 0.084 | 0.727 | 0.010 | 0.039 | 0.794 | 0.016 | 0.036 | 0.665 |
| lnCRP (mg/L) | −0.024 | 0.034 | 0.484 | −0.022 | 0.073 | 0.322 | 0.098 | 0.033 | 0.003 | −0.005 | 0.030 | 0.873 |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | −0.227 | 0.103 | 0.029 | 0.179 | 0.228 | 0.433 | 0.075 | 0.102 | 0.464 | −0.147 | 0.093 | 0.116 |
| NFS ** | 0.016 | 0.091 | 0.859 | 0.244 | 0.193 | 0.207 | −0.038 | 0.090 | 0.673 | −0.049 | 0.083 | 0.552 |
| FLI *** | −3.969 | 1.871 | 0.035 | 0.950 | 3.998 | 0.812 | 5.011 | 1.840 | 0.007 | −2.848 | 1.689 | 0.093 |
| Model 1 * | Model 2 ** | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betainteraction | SEinteraction | Pinteraction† | Betainteraction | SEinteraction | Pinteraction† | |
| TM6SF2-rs58542926/A * “Prudent” Dietary Pattern | ||||||
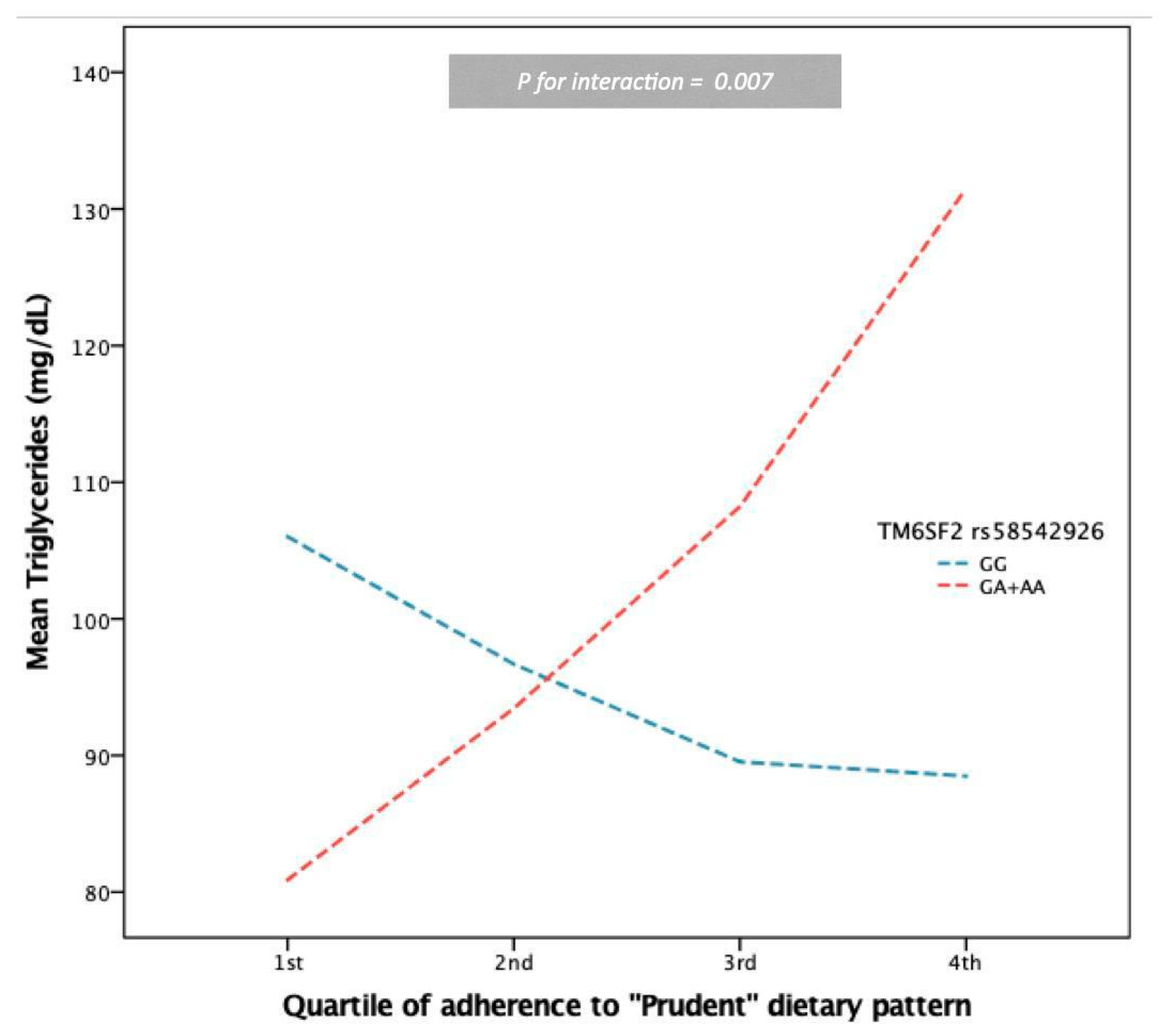
| TG (mg/dL) § | 20.170 | 7.435 | 0.007 | 20.530 | 7.262 | 0.005 |
| FLI | 9.351 | 3.545 | 0.009 | 9.568 | 3.503 | 0.007 |
| MBOAT7-rs641738/A * “Prudent” Dietary Pattern | ||||||
| TG (mg/dL) § | −10.060 | 3.400 | 0.003 | −9.993 | 3.375 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalafati, I.P.; Dimitriou, M.; Revenas, K.; Kokkinos, A.; Deloukas, P.; Dedoussis, G.V. TM6SF2-rs58542926 Genetic Variant Modifies the Protective Effect of a “Prudent” Dietary Pattern on Serum Triglyceride Levels. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051112
Kalafati IP, Dimitriou M, Revenas K, Kokkinos A, Deloukas P, Dedoussis GV. TM6SF2-rs58542926 Genetic Variant Modifies the Protective Effect of a “Prudent” Dietary Pattern on Serum Triglyceride Levels. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051112
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalafati, Ioanna Panagiota, Maria Dimitriou, Konstantinos Revenas, Alexander Kokkinos, Panos Deloukas, and George V. Dedoussis. 2023. "TM6SF2-rs58542926 Genetic Variant Modifies the Protective Effect of a “Prudent” Dietary Pattern on Serum Triglyceride Levels" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051112
APA StyleKalafati, I. P., Dimitriou, M., Revenas, K., Kokkinos, A., Deloukas, P., & Dedoussis, G. V. (2023). TM6SF2-rs58542926 Genetic Variant Modifies the Protective Effect of a “Prudent” Dietary Pattern on Serum Triglyceride Levels. Nutrients, 15(5), 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051112






