Artificial Light-at-Night Exposure and Overweight and Obesity across GDP Levels among Chinese Children and Adolescents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
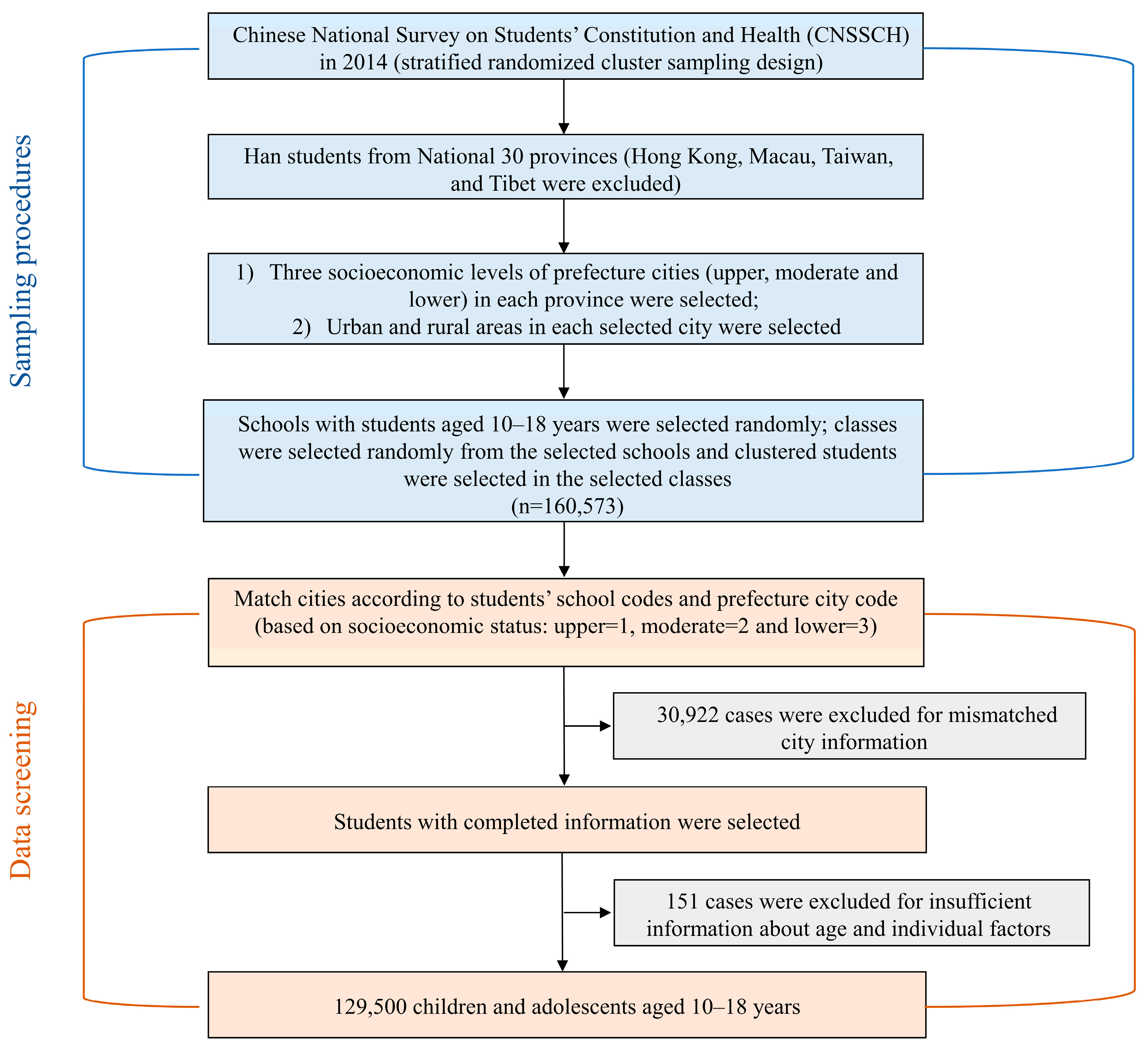
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Assessment of ALAN Exposure
2.3. Outcome Measurement
2.4. Questionnaire Survey and Procedures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
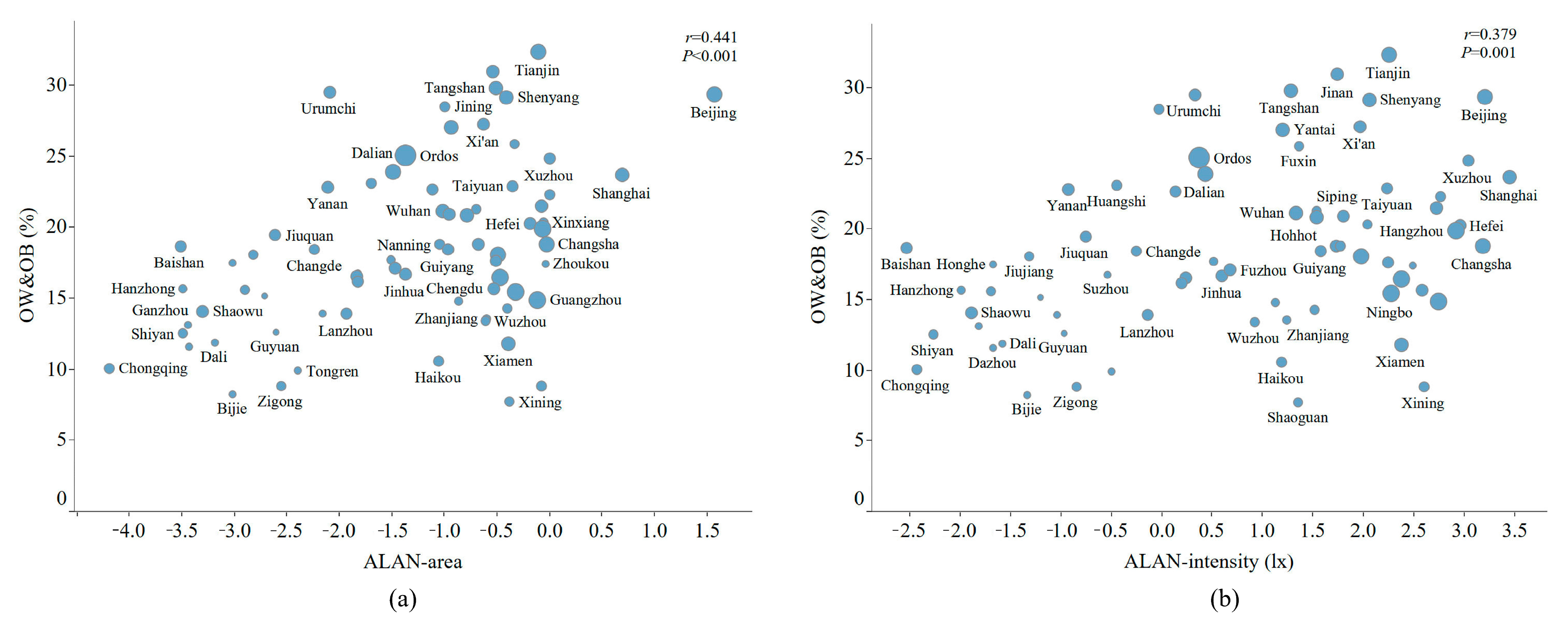
3.2. Distribution of ALAN Exposure and Overweight and Obesity
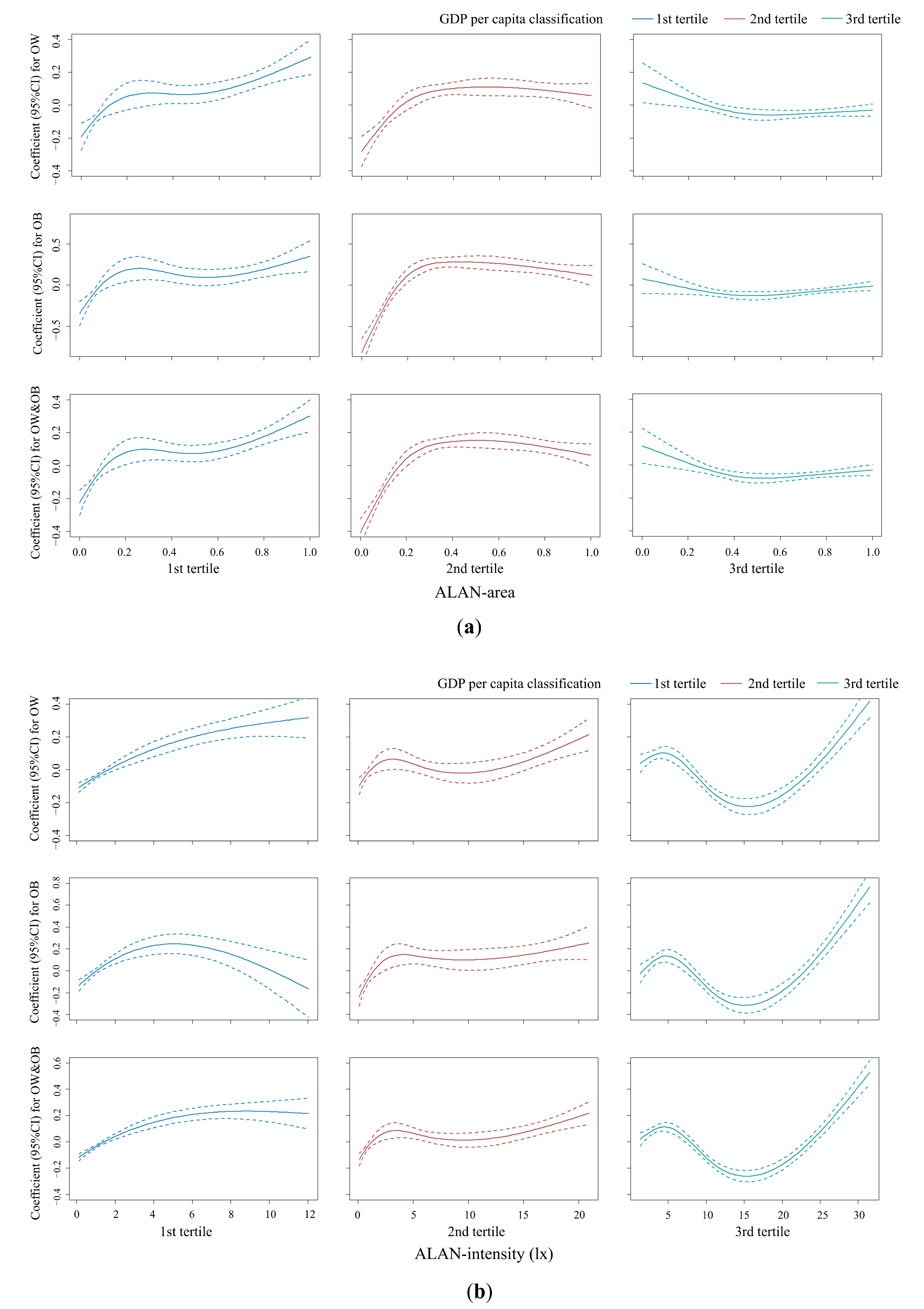
3.3. Associations between ALAN and Overweight and Obesity Stratified by GDPPC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mokdad, A.H.; Ford, E.S.; Bowman, B.A.; Dietz, W.H.; Vinicor, F.; Bales, V.S.; Marks, J.S. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003, 289, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaün, H.; Thariat, J.; Vignot, M.; Merrouche, Y.; Vignot, S. Obesity and cancer. Bull. Cancer 2017, 104, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.F.; Wang, L.; Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.Y.; Cheng, T.O. Epidemic increase in overweight and obesity in Chinese children from 1985 to 2005. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 132, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, L.; Pan, A.; Xue, H. Health policy and public health implications of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, I.; Rekleiti, M.; Saridi, M.; Beliotis, E.; Toska, A.; Souliotis, K.; Wozniak, G. Prevalence of obesity in children aged 6-12 years in Greece: Nutritional behaviour and physical activity. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.E.; Mainous, A.G., 3rd; Carnemolla, M.; Everett, C.J. Adherence to healthy lifestyle habits in US adults, 1988–2006. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioni, D.M.; Cacau, L.T.; De Carli, E.; Carvalho, A.M.; Rulli, M.C. Low Adherence to the EAT-Lancet Sustainable Reference Diet in the Brazilian Population: Findings from the National Dietary Survey 2017–2018. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinehr, T.; Wabitsch, M. Childhood obesity. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2011, 22, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominoni, D.M.; Nelson, R.J. Artificial light at night as an environmental pollutant: An integrative approach across taxa, biological functions, and scientific disciplines. J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2018, 329, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, D.; Frago, E.; Kehoe, R.; Patterson, C.; Gaston, K.J. A meta-analysis of biological impacts of artificial light at night. Nat. Ecol. Evol 2021, 5, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Duriscoe, D.; Kyba, C.C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Portnov, B.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Furgoni, R. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, F.; Furgoni, R.; Gallaway, T.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Portnov, B.A.; Baugh, K.; Cinzano, P.; Elvidge, C.D. Light pollution in USA and Europe: The good, the bad and the ugly. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaston, K.J.; Visser, M.E.; Hölker, F. The biological impacts of artificial light at night: The research challenge. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubidat, A.E.; Haim, A. Artificial light-at-night—A novel lifestyle risk factor for metabolic disorder and cancer morbidity. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharm. 2017, 28, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Poggiogalle, E.; Barrea, L.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Garifalos, F.; Liccardi, A.; Pugliese, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Exposure to artificial light at night: A common link for obesity and cancer? Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 173, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayashi, K.; Saeki, K.; Iwamoto, J.; Okamoto, N.; Tomioka, K.; Nezu, S.; Ikada, Y.; Kurumatani, N. Exposure to light at night, nocturnal urinary melatonin excretion, and obesity/dyslipidemia in the elderly: A cross-sectional analysis of the HEIJO-KYO study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, Y.S.; Song, J.Y.; Joo, E.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.K.; Jung, K.Y. Outdoor artificial light at night, obesity, and sleep health: Cross-sectional analysis in the KoGES study. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; White, A.J.; Jackson, C.L.; Weinberg, C.R.; Sandler, D.P. Association of Exposure to Artificial Light at Night While Sleeping With Risk of Obesity in Women. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, R.M.; Blask, D.E.; Coogan, A.N.; Figueiro, M.G.; Gorman, M.R.; Hall, J.E.; Hansen, J.; Nelson, R.J.; Panda, S.; Smolensky, M.H.; et al. Health consequences of electric lighting practices in the modern world: A report on the National Toxicology Program’s workshop on shift work at night, artificial light at night, and circadian disruption. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haus, E.; Reinberg, A.; Mauvieux, B.; Le Floc’h, N.; Sackett-Lundeen, L.; Touitou, Y. Risk of obesity in male shift workers: A chronophysiological approach. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 1018–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, C.; Michel, U.; Randler, C. Outdoor light at night (LAN) is correlated with eveningness in adolescents. Chronobiol. Int. 2012, 29, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, S.; Shen, M.; Xiao, Y.; Su, J.; Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Shan, S.; Kang, X.; Wu, B.; et al. Association of exposure to artificial light at night with atopic diseases: A cross-sectional study in college students. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 241, 113932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jan, C.; Ma, Y.; Dong, B.; Zou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Song, Y.; Ma, J.; Sawyer, S.M.; et al. Economic development and the nutritional status of Chinese school-aged children and adolescents from 1995 to 2014: An analysis of five successive national surveys. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, T.; Uddin, S. How do economic and public finance statuses affect policy responses during a pandemic?—Learning from the COVID-19 first wave. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, L.; Wen, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Ma, J.; Lau, P.W.C. Individual-, Family-, and School-Level Ecological Correlates With Physical Fitness Among Chinese School-Aged Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Survey in 2014. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 684286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.; Straka, W.; Mills, S.; Elvidge, C.; Lee, T.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.; Weiss, S. Illuminating the Capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Day/Night Band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M. Nighttime Lights Compositing Using the VIIRS Day-Night Band: Preliminary Results. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Earth Observation Group (EOG). Available online: https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Levin, N.; Zhang, Q. A global analysis of factors controlling VIIRS nighttime light levels from densely populated areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Growth Reference Data for 5–19 Years. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/growth-reference-data-for-5to19-years (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2015. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Rybnikova, N.A.; Haim, A.; Portnov, B.A. Does artificial light-at-night exposure contribute to the worldwide obesity pandemic? Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Jones, R.R.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Jia, P.; James, P.; Xiao, Q. A large prospective investigation of outdoor light at night and obesity in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, S.; Pellman, K. Living Without Electricity; Good Books: Brattleboro, VT, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Fonken, L.K.; Nelson, R.J. The effects of light at night on circadian clocks and metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 648–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, E.; Jones, M.E.; Schoemaker, M.J.; Ashworth, A.; Swerdlow, A.J. The relationship between obesity and exposure to light at night: Cross-sectional analyses of over 100,000 women in the Breakthrough Generations Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryakin, Y.; Lobstein, T.; James, W.P.; Suhrcke, M. The impact of economic, political and social globalization on overweight and obesity in the 56 low and middle income countries. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 133, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuboni, D.; Yan, L. Nighttime dim light exposure alters the responses of the circadian system. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonken, L.K.; Aubrecht, T.G.; Meléndez-Fernández, O.H.; Weil, Z.M.; Nelson, R.J. Dim light at night disrupts molecular circadian rhythms and increases body weight. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2013, 28, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froy, O. Metabolism and circadian rhythms—Implications for obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel-Mahan, K.L.; Patel, V.R.; Mohney, R.P.; Vignola, K.S.; Baldi, P.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Coordination of the transcriptome and metabolome by the circadian clock. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5541–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsbeek, A.; Fliers, E.; Romijn, J.A.; La Fleur, S.E.; Wortel, J.; Bakker, O.; Endert, E.; Buijs, R.M. The suprachiasmatic nucleus generates the diurnal changes in plasma leptin levels. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 2677–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter, M.; La Fleur, S.E.; van Heijningen, C.; van der Vliet, J.; Kalsbeek, A.; Buijs, R.M. The daily rhythm in plasma glucagon concentrations in the rat is modulated by the biological clock and by feeding behavior. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingley, D.; McClain, K.; Kaya, E.; Carpenter, J.; Buzsáki, G. A metabolic function of the hippocampal sharp wave-ripple. Nature 2021, 597, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.B.; Gong, Y.C.; Fang, Q.L.; Cui, X.X.; Dharmage, S.C.; Jalaludin, B.; Knibbs, L.D.; Bloom, M.S.; Guo, Y.; Lin, L.Z.; et al. Association Between Exposure to Outdoor Artificial Light at Night and Sleep Disorders Among Children in China. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2213247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, K.G.; Reid, K.J.; Horn, L.V.; Zee, P.C. Contribution of evening macronutrient intake to total caloric intake and body mass index. Appetite 2013, 60, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerman, B.; Liu, J. Does current scientific evidence support a link between light at night and breast cancer among female night-shift nurses? Review of evidence and implications for occupational and environmental health nurses. Workplace Health Saf. 2012, 60, 273–281, quiz 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Xu, T.; Yin, D. Understanding light pollution: Recent advances on its health threats and regulations. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jin, X.; Wu, S.; Jiang, F.; Yan, C.; Shen, X. The impact of media use on sleep patterns and sleep disorders among school-aged children in China. Sleep 2007, 30, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wan, Y.H.; Su, P.Y.; Tao, F.B.; Sun, Y. Exposure to bedroom light pollution and cardiometabolic risk: A cohort study from Chinese young adults. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roenneberg, T.; Allebrandt, K.V.; Merrow, M.; Vetter, C. Social jetlag and obesity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Total (N = 129,500) | GDP per Capita (USD) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Tertile | Second Tertile | Third Tertile | |||
| Age (year) | 14.5(4.5) | 14.5(4.5) | 14.4 (4.4) | 14.5 (4.4) | 0.125 |
| Sex | 0.957 | ||||
| Boys | 64,767 (50.0) | 21,226 (50.1) | 21,291 (50.0) | 22,250 (50.0) | |
| Girls | 64,733 (50.0) | 21,179 (49.9) | 21,267 (50.0) | 22,287 (50.0) | |
| Residence | <0.001 | ||||
| Urban | 63,844 (49.3) | 21,222 (50.0) | 21,256 (49.9) | 21,360 (48.0) | |
| Rural | 65,668 (50.7) | 21,183 (50.0) | 21,302 (50.1) | 23,177 (52.0) | |
| Height (cm) | 159.1 (15.4) | 157.5 (15.2) | 159.0 (15.4) | 161.0 (15.0) | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 49.8 (15.9) | 48.1 (15.1) | 49.5 (15.9) | 51.7 (16.3) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 19.3 (4.2) | 19.0 (4.0) | 19.3 (4.2) | 19.7 (4.4) | <0.001 |
| Overweight (%) | 16,249 (12.5) | 4922 (11.6) | 5750 (13.5) | 6980 (15.7) | <0.001 |
| Obesity (%) | 8160 (6.3) | 1420 (3.3) | 2097 (4.9) | 3012 (6.8) | <0.001 |
| ALAN area | 0.4 (0.6) | 0.1 (0.5) | 0.3 (0.5) | 0.6 (0.5) | <0.001 |
| ALAN intensity (lx) | 3.3 (8.9) | 0.4 (3.7) | 1.2 (8.9) | 7.8 (12.0) | <0.001 |
| Sleep duration (h) | 7.5 (2.0) | 7.5 (2.0) | 7.5 (2.0) | 7.5 (2.0) | <0.001 |
| Screen time (h) | 1.3 (1.3) | 1.3 (1.5) | 1.3 (1.3) | 1.3 (1.5) | <0.001 |
| Physical activity (min) | 45.0 (15.0) | 45.0 (15.0) | 45.0 (15.0) | 45.0 (45.0) | <0.001 |
| Daily breakfast (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| never | 2187 (1.7) | 873 (2.1) | 588 (1.4) | 726 (1.6) | |
| 1–2 days/week | 8004 (6.2) | 3293 (7.8) | 2335 (5.5) | 2375 (5.3) | |
| 3–5 days/week | 22,868 (17.7) | 8691 (20.5) | 7420 (17.4) | 6755 (15.2) | |
| everyday | 96,453 (74.5) | 29,548 (69.7) | 32,215 (75.7) | 34,681 (77.9) | |
| Daily milk (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| never | 8192 (6.3) | 3263 (7.7) | 2582 (6.1) | 2347 (5.3) | |
| 1–2 days/week | 77,813 (60.1) | 29,392 (69.3) | 24,959 (58.6) | 23,454 (52.7) | |
| 3–5 days/week | 36,399 (28.1) | 8315 (19.6) | 12,796 (30.1) | 15,284 (34.3) | |
| everyday | 7108 (5.5) | 1435 (3.4) | 2221 (5.2) | 3452 (7.8) | |
| Daily eggs (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| never | 13,541 (10.5) | 5108 (12.0) | 4830 (11.3) | 3602 (8.1) | |
| 1–2 days/week | 66,184 (51.1) | 24,108 (56.9) | 21,373 (50.2) | 20,698 (46.5) | |
| 3–5 days/week | 33,927 (26.2) | 9738 (23.0) | 11,080 (26.0) | 13,105 (29.4) | |
| everyday | 15,860 (12.2) | 3451 (8.1) | 5275 (12.4) | 7132 (16.0) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dang, J.; Shi, D.; Li, X.; Ma, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, P.; Yan, X.; Zhang, J.; Lau, P.W.C.; Dong, Y.; et al. Artificial Light-at-Night Exposure and Overweight and Obesity across GDP Levels among Chinese Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2023, 15, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040939
Dang J, Shi D, Li X, Ma N, Liu Y, Zhong P, Yan X, Zhang J, Lau PWC, Dong Y, et al. Artificial Light-at-Night Exposure and Overweight and Obesity across GDP Levels among Chinese Children and Adolescents. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040939
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Jiajia, Di Shi, Xi Li, Ning Ma, Yunfei Liu, Panliang Zhong, Xiaojin Yan, Jingshu Zhang, Patrick W. C. Lau, Yanhui Dong, and et al. 2023. "Artificial Light-at-Night Exposure and Overweight and Obesity across GDP Levels among Chinese Children and Adolescents" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040939
APA StyleDang, J., Shi, D., Li, X., Ma, N., Liu, Y., Zhong, P., Yan, X., Zhang, J., Lau, P. W. C., Dong, Y., Song, Y., & Ma, J. (2023). Artificial Light-at-Night Exposure and Overweight and Obesity across GDP Levels among Chinese Children and Adolescents. Nutrients, 15(4), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040939









