Low-Protein Formulas with Alpha-Lactalbumin-Enriched or Glycomacropeptide-Reduced Whey: Effects on Growth, Nutrient Intake and Protein Metabolism during Early Infancy: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
2.3. Sample Size and Statistical Power
2.4. Randomization and Blinding
2.5. Study Infant Formulas
2.6. Study Visits, Growth Parameters, Dietary and Symptom Records
2.7. Blood Sampling and Biochemical Analyses
2.8. Ethical Considerations
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Populations
3.2. Background and Baseline Characteristics
3.3. Nutrient Intake
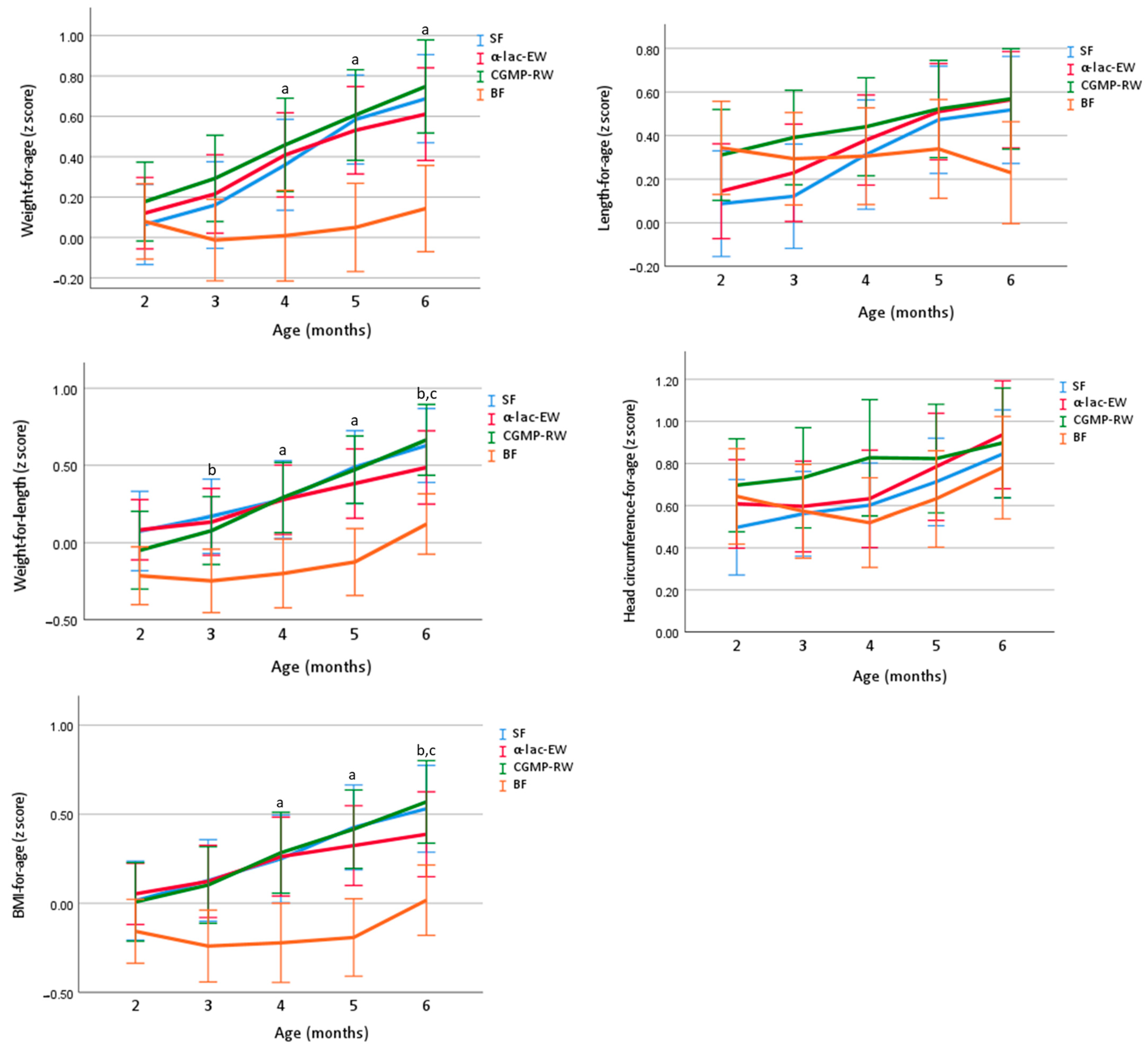
3.4. Growth
3.5. Energetic Efficiency
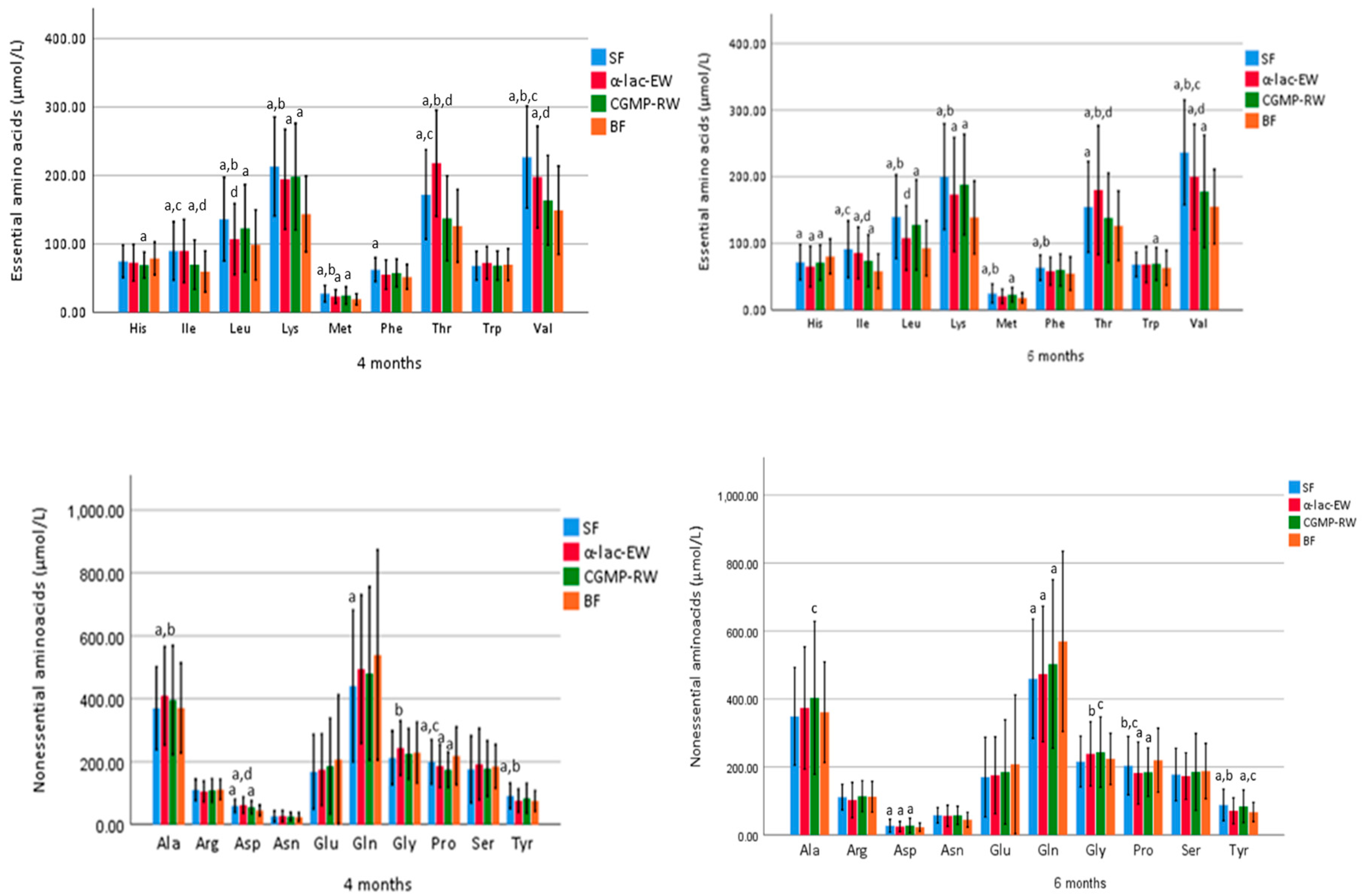
3.6. Biochemical Analyses
3.7. Gastrointestinal Symptoms
3.8. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk composition: Nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haschke, F.; Haiden, N.; Thakkar, S.K. Nutritive and Bioactive Proteins in Breastmilk. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta, B.L.; Loret de Mola, C.; Victora, C.G. Long-term consequences of breastfeeding on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, S.F.; Redsell, S.A.; Swift, J.A.; Yang, M.; Glazebrook, C.P. Systematic review and meta-analyses of risk factors for childhood overweight identifiable during infancy. Arch. Dis. Child. 2012, 97, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.; França, G.V.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngör, D.; Nadaud, P.; LaPergola, C.C.; Dreibelbis, C.; Wong, Y.P.; Terry, N.; Abrams, S.A.; Beker, L.; Jacobovits, T.; Järvinen, K.M.; et al. Infant milk-feeding practices and food allergies, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and asthma throughout the life span: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 772s–799s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/127 of 25 September 2015 Supplementing Regulation (EU) No 609/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards the Specific Compositional and Information Requirements for Infant Formula and Follow-on Formula and as Regards Requirements on Information Relating to Infant and Young Child Feeding. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02016R0127-20210715 (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Grote, V.; Verduci, E.; Scaglioni, S.; Vecchi, F.; Contarini, G.; Giovannini, M.; Koletzko, B.; Agostoni, C.; European Childhood Obesity Project. Breast milk composition and infant nutrient intakes during the first 12 months of life. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B. Infant formula and infant nutrition: Bioactive proteins of human milk and implications for composition of infant formulas. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 712s–717s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Brands, B.; Chourdakis, M.; Cramer, S.; Grote, V.; Hellmuth, C.; Kirchberg, F.; Prell, C.; Rzehak, P.; Uhl, O.; et al. The Power of Programming and the EarlyNutrition project: Opportunities for health promotion by nutrition during the first thousand days of life and beyond. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 64, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, V.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Escribano, J.; Ferré, N. Early Programming by Protein Intake: The Effect of Protein on Adiposity Development and the Growth and Functionality of Vital Organs. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2015, 8, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeson, P.M.; Axelsson, I.E.; Räihä, N.C. Growth and nutrient intake in three- to twelve-month-old infants fed human milk or formulas with varying protein concentrations. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1998, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, I.E.; Ivarsson, S.A.; Räihä, N.C. Protein intake in early infancy: Effects on plasma amino acid concentrations, insulin metabolism, and growth. Pediatr. Res. 1989, 26, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, I.E.; Jakobsson, I.; Räihä, N.C. Formula with reduced protein content: Effects on growth and protein metabolism during weaning. Pediatr. Res. 1988, 24, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsland Akeson, P.M.; Axelsson, I.E.; Räihä, N.C. Protein and amino acid metabolism in three- to twelve-month-old infants fed human milk or formulas with varying protein concentrations. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1998, 26, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Chen, C.L. Effects of formula protein level and ratio on infant growth, plasma amino acids and serum trace elements. I. Cow’s milk formula. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1990, 79, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räihä, N.C.; Fazzolari-Nesci, A.; Cajozzo, C.; Puccio, G.; Monestier, A.; Moro, G.; Minoli, I.; Haschke-Becher, E.; Bachmann, C.; Van’t Hof, M.; et al. Whey predominant, whey modified infant formula with protein/energy ratio of 1.8 g/100 kcal: Adequate and safe for term infants from birth to four months. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2002, 35, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Grillon, C.; Lachambre, E.; Robiliard, P.; Beck, L.; Maurin, J.L.; Kempf, C.; Bernet, J.P.; Marx, J.; Lebrun, F.; et al. Adequacy and safety of an infant formula with a protein/energy ratio of 1.8 g/100 kcal and enhanced protein efficiency for term infants during the first 4 months of life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B.; von Kries, R.; Closa, R.; Escribano, J.; Scaglioni, S.; Giovannini, M.; Beyer, J.; Demmelmair, H.; Gruszfeld, D.; Dobrzanska, A.; et al. Lower protein in infant formula is associated with lower weight up to age 2 y: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, E.E.; Fields, D.A.; Chernausek, S.D.; Steenhout, P.; Grathwohl, D.; Jeter, J.M.; Nelson, S.E.; Haschke, F. Adequacy of Infant Formula With Protein Content of 1.6 g/100 kcal for Infants Between 3 and 12 Months. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.D.; Yan, J.; Bylsma, L.C.; Northington, R.S.; Grathwohl, D.; Steenhout, P.; Erdmann, P.; Spivey-Krobath, E.; Haschke, F. Growth of infants consuming whey-predominant term infant formulas with a protein content of 1.8 g/100 kcal: A multicenter pooled analysis of individual participant data. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, D.K.; Lönnerdal, B.; Fernstrom, J.D. Applications for α-lactalbumin in human nutrition. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, S.M. Human Milk Proteins: Composition and Physiological Significance. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2019, 90, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Affolter, M.; Garcia-Rodenas, C.L.; Vinyes-Pares, G.; Jenni, R.; Roggero, I.; Avanti-Nigro, O.; de Castro, C.A.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; et al. Temporal Changes of Protein Composition in Breast Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers and Impact of Caesarean Section Delivery. Nutrients 2016, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleddermann, M.; Demmelmair, H.; Grote, V.; Nikolic, T.; Trisic, B.; Koletzko, B. Infant formula composition affects energetic efficiency for growth: The BeMIM study, a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, E.L.; Davis, A.M.; Euler, A.R. Growth and safety in term infants fed reduced-protein formula with added bovine alpha-lactalbumin. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropeza-Ceja, L.G.; Rosado, J.L.; Ronquillo, D.; Garcia, O.P.; Caamano, M.D.C.; Garcia-Ugalde, C.; Viveros-Contreras, R.; Duarte-Vázquez, M.Á. Lower Protein Intake Supports Normal Growth of Full-Term Infants Fed Formula: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, H.; Nomayo, A.; Zelenka, R.; Foster, J.; Tvrdík, J.; Jochum, F. Adequacy and safety of α-lactalbumin-enriched low-protein infant formula: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrition 2020, 74, 110728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, O.; Lönnerdal, B.; Graverholt, G.; Hernell, O. Effects of alpha-lactalbumin-enriched formula containing different concentrations of glycomacropeptide on infant nutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabulsi, J.; Capeding, R.; Lebumfacil, J.; Ramanujam, K.; Feng, P.; McSweeney, S.; Harris, B.; DeRusso, P. Effect of an α-lactalbumin-enriched infant formula with lower protein on growth. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.M.; Harris, B.J.; Lien, E.L.; Pramuk, K.; Trabulsi, J. Alpha-lactalbumin-rich infant formula fed to healthy term infants in a multicenter study: Plasma essential amino acids and gastrointestinal tolerance. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova-Dávalos, L.E.; Jiménez, M.; Salinas, E. Glycomacropeptide Bioactivity and Health: A Review Highlighting Action Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways. Nutrients 2019, 11, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Swedish Food Agency. Good Food for Infants under One Year; The Swedish Food Agency: Uppsala, Sweden, 2012. Available online: https://www.livsmedelsverket.se/globalassets/publikationsdatabas/andra-sprak/bra-mat-for-spadbarn/good-food-for-infants-under-one-year-livsmedelsverket.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- WHO. Who Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height, and Body Mass Indeex-for-Age: Methods and Development. 2006. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/child-growth-standards/software (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- WHO. Who Child Growth Standards: Head Circumference-for-Age, Arm Circumference-for-Age, Triceps Skinfold-for-Age and Subscapular Skinfold-for-Age: Methodes and Development. 2007. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/child-growth-standards/software (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Domellöf, M.; Braegger, C.; Campoy, C.; Colomb, V.; Decsi, T.; Fewtrell, M.; Hojsak, I.; Mihatsch, W.; Molgaard, C.; Shamir, R.; et al. Iron requirements of infants and toddlers. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchi, F.D.; Shen, F.J.; Keck, R.G.; Harris, R.J. Amino acid analysis, using postcolumn ninhydrin detection, in a biotechnology laboratory. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 159, 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchberg, F.F.; Harder, U.; Weber, M.; Grote, V.; Demmelmair, H.; Peissner, W.; Rzehak, P.; Xhonneux, A.; Carlier, C.; Ferre, N.; et al. Dietary protein intake affects amino acid and acylcarnitine metabolism in infants aged 6 months. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, P.; Grote, V.; Gruszfeld, D.; Janas, R.; Demmelmair, H.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Subías, J.E.; Scaglioni, S.; Verduci, E.; Dain, E.; et al. Milk protein intake, the metabolic-endocrine response, and growth in infancy: Data from a randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1776s–1784s. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, N.; Mutungi, G.; Cubero, J. Diet and nutrients in the modulation of infant sleep: A review of the literature. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleddermann, M.; Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B. Energetic efficiency of infant formulae: A review. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 64, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Hernell, O. Effects of feeding ultrahigh-temperature (UHT)-treated infant formula with different protein concentrations or powdered formula, as compared with breast-feeding, on plasma amino acids, hematology, and trace element status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putet, G.; Labaune, J.M.; Mace, K.; Steenhout, P.; Grathwohl, D.; Raverot, V.; Morel, Y.; Picaud, J.C. Effect of dietary protein on plasma insulin-like growth factor-1, growth, and body composition in healthy term infants: A randomised, double-blind, controlled trial (Early Protein and Obesity in Childhood (EPOCH) study). Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timby, N.; Domellöf, E.; Hernell, O.; Lönnerdal, B.; Domellöf, M. Neurodevelopment, nutrition, and growth until 12 mo of age in infants fed a low-energy, low-protein formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Fissore, M.F.; Grassino, E.C.; Nanni, G.E.; Oggero, R.; Silvestro, L. Ghrelin, leptin and IGF-I levels in breast-fed and formula-fed infants in the first years of life. Acta Paediatr. 2005, 94, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouwenhoven, S.M.P.; Fleddermann, M.; Finken, M.J.J.; Twisk, J.W.R.; van der Beek, E.M.; Abrahamse-Berkeveld, M.; van de Heijning, B.J.M.; van Harskamp, D.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Koletzko, B.V. Early-Life Metabolic and Hormonal Markers in Blood and Growth until Age 2 Years: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial in Healthy Infants Fed a Modified Low-Protein Infant Formula. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellakooty, M.; Juul, A.; Boisen, K.A.; Damgaard, I.N.; Kai, C.M.; Schmidt, I.M.; Petersen, J.H.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Main, K.M. A prospective study of serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-3 in 942 healthy infants: Associations with birth weight, gender, growth velocity, and breastfeeding. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galante, L.; Pundir, S.; Lagström, H.; Rautava, S.; Reynolds, C.M.; Milan, A.M.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Vickers, M.H. Growth Factor Concentrations in Human Milk Are Associated With Infant Weight and BMI From Birth to 5 Years. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Rooki, H.; Vakili, R.; Hashemy, S.I.; Mirhafez, S.R.; Shakeri, M.T.; Kashanifar, R.; Pourbafarani, R.; Mirzaei, H.; et al. Comparative measurement of ghrelin, leptin, adiponectin, EGF and IGF-1 in breast milk of mothers with overweight/obese and normal-weight infants. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, I.Y.; Shilina, N.M.; Gmoshinskaya, M.V.; Ivanushkina, T.A. The study of breast milk IGF-1, leptin, ghrelin and adiponectin levels as possible reasons of high weight gain in breast-fed infants. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 65, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, A.L.; Larnkjær, A.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F. IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in healthy 9 month old infants from the SKOT cohort: Breastfeeding, diet, and later obesity. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2011, 21, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.; Kratzsch, J.; Kiess, W.; Dunger, D. Circulating IGF-I levels in childhood are related to both current body composition and early postnatal growth rate. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, F.; Costamagna, M.; Prino, A.; Oggero, R.; Silvestro, L. Leptin levels in breast-fed and formula-fed infants. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.A.; Fissore, M.F.; Palumeri, E.; Calabrese, R.; Oggero, R.; Silvestro, L.; Miniero, R. Looking for a relation between serum leptin concentration and body composition parameters in healthy term infants in the first 6 months of life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 46, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Goruk, S.; Becker, A.B.; Subbarao, P.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Lefebvre, D.; Sears, M.R.; Field, C.J.; Azad, M.B. Adiponectin, leptin and insulin in breast milk: Associations with maternal characteristics and infant body composition in the first year of life. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zepf, F.D.; Rao, P.; Moore, J.; Stewart, R.; Ladino, Y.M.; Hartmann, B.T. Human breast milk and adipokines—A potential role for the soluble leptin receptor (sOb-R) in the regulation of infant energy intake and development. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 86, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B. Excess iron intake as a factor in growth, infections, and development of infants and young children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1681s–1687s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björmsjö, M.; Hernell, O.; Lönnerdal, B.; Berglund, S.K. Reducing Iron Content in Infant Formula from 8 to 2 mg/L Does Not Increase the Risk of Iron Deficiency at 4 or 6 Months of Age: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.; Rivero, M.; Grillon, C.; Belaroussi, N.; Kalindjian, A.; Marin, V. Alpha-lactalbumin-enriched and probiotic-supplemented infant formula in infants with colic: Growth and gastrointestinal tolerance. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SF | α-lac-EW | CGMP-RW | Regulation 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal/100 mL) | 67.3 | 68.2 | 68.0 | 60 |
| Whey:casein ratio | 60:40 | 70:30 | 70:30 | |
| Protein (g/100 kcal) Protein (g/100 mL) | 2.20 1.48 | 1.75 1.19 | 1.76 1.20 | 1.8 |
| α-lactalbumin (%) 2 | 10 | 27 | 14 | |
| CGMP (%) 2 | 9 | 19 | - |
| SF n = 83 | α-lac-EW n = 81 | CGMP-RW n = 80 | p-Value 1 All FF ** | BF n = 83 | p-Value 2 All FF vs. BF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth weight (g) | 3471 ± 452 3 | 3527 ± 440 | 3605 ± 443 | 0.16 | 3540 ± 424 | 0.89 |
| Birth length (cm) | 50.2 ± 2.2 | 50.1 ± 1.9 | 50.5 ± 1.7 | 0.42 | 50.4 ± 1.9 | 0.51 |
| Birth head circumference (cm) | 34.6 ± 1.2 | 35.0 ± 1.3 | 35.0 ± 1.2 | 0.06 | 35.0 ± 1.5 | 0.23 |
| Gestational age (wk) | 39.5 ± 1.2 a | 39.7 ± 1.3 b | 40.1 ± 1.2 | 0.007 | 40.0 ± 1.1 | 0.11 |
| Age at inclusion (d) | 49.3 ± 5.0 | 49.4 ± 4.1 | 49.2 ± 5.8 | 0.97 | 50.5 ± 4.5 | 0.05 |
| Female [n (%)] | 40 (48) | 41 (51) | 40 (50) | 0.95 | 43 (52) | 0.73 |
| Ever breastfed before inclusion [n (%)] | 63 (76) | 66 (78) | 70 (88) | 0.17 | 83 (100) | n/a |
| Days of breast-feeding before inclusion (n) | 15.5 ± 14.6 | 18.0 ± 15.2 | 17.5 ± 13.9 | 0.50 | 50.4 ± 4.6 | n/a |
| Probiotics before inclusion [n (%)] 4 | 28 (34) | 24 (30) | 23 (29) | 0.94 | 13 (16) | 0.007 |
| Twins [n (%)] | 5 (6) | 7 (9) | 4 (5) | 0.63 | 0 (0) | 0.009 |
| Siblings [n (%)] | 54 (65) | 53 (65) | 47 (59) | 0.61 | 45 (54) | 0.15 |
| Maternal age (y) | 31.5 ± 4.8 | 31.1 ± 4.6 | 31.1 ± 4.6 | 0.83 | 32.6 ± 4.2 | 0.026 |
| Maternal origin [n (%)] | ||||||
| Nordic | 77 (93) | 70 (86) | 74 (93) | 0.29 | 75 (90) | 0.96 |
| European (non-Nordic) | 3 (4) | 3 (10) | 3 (4) | 1.0 | 5 (4) | 0.36 |
| Non-European | 3 (4) | 8 (10) | 3 (4) | 0.15 | 3 (4) | 0.58 |
| Maternal higher education [n (%)] 5 | 45(54) | 47 (58) | 57 (71) | 0.067 | 66 (80) | 0.002 |
| Maternal BMI at enrollment (kg/m2) | 27.9 ± 5.2 | 27.9 ± 5.6 | 26.1 ± 4.2 | 0.04 # | 25.2 ± 3.7 | <0.001 |
| Weight gain during pregnancy (kg) | 13.1 ± 6.2 | 13.4 ± 6.6 | 14.7 ± 6.0 | 0.20 | 14.1 ± 5.3 | 0.59 |
| Gestational diabetes [n (%)] | 4 (5) | 2 (3) | 4 (5) | 0.66 | 5 (6) | 0.54 |
| Gestational hypertension [n (%)] | 5 (6) | 8 (10) | 3 (4) | 0.28 | 5 (6) | 0.86 |
| Maternal smoking during pregnancy [n (%)] | 3 (4) | 4 (5) | 3 (4) | 0.61 | 0 (0) | 0.071 |
| Paternal origin [n (%)] 6 | ||||||
| Nordic | 65 (80) a | 68 (86) | 73 (94) | 0.047 | 65 (80) | 0.17 |
| European (non-Nordic) | 6 (7) | 3 (4) | 2 (3) | 0.30 | 10 (12) | 0.015 |
| Non-European | 10 (12) | 8 (10) | 3 (4) | 0.15 | 6 (7) | 0.69 |
| Paternal higher education [n (%)] 5 | 29 (36) | 31 (40) b | 46 (59) | 0.008 | 56 (69) | 0.052 |
| Paternal BMI (kg/m2) | 27.0 ± 4.2 | 27.3 ± 5.8 | 26.0 ± 4.0 | 0.24 | 25.9 ± 4.5 | 0.18 |
| Paternal smoking during pregnancy [n (%)] | 14 (17) | 11 (14) | 5 (7) | 0.12 | 9 (11) | 0.71 |
| SF | α-lac-EW | CGMP-RW | p-Value 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | n | |||||
| Number of meals per day | |||||||
| 3 mo | 74 | 7.0 ± 1.5 2 | 77 | 6.9 ± 1.6 | 74 | 6.7 ± 1.4 | 0.55 |
| 4 mo | 69 | 6.7 ± 1.6 | 74 | 6.8 ± 1.5 | 71 | 6.4 ± 1.5 | 0.31 |
| 5 mo | 69 | 6.2 ± 1.5 | 72 | 6.6 ± 1.5 | 69 | 6.0 ± 1.6 | 0.11 |
| 6 mo | 68 | 5.7 ± 1.6 | 68 | 6.2 ± 1.5 a | 67 | 5.4 ± 1.3 | 0.015 |
| Formula intake per day (mL/kg/d) | |||||||
| 3 mo | 74 | 152 ± 29 b,c | 77 | 140 ± 20 | 74 | 141 ± 16 | 0.003 |
| 4 mo | 69 | 144 ± 31 b,c | 74 | 131 ± 18 | 71 | 133 ± 18 | 0.001 |
| 5 mo | 69 | 131 ± 23 b,c | 72 | 122 ± 20 | 69 | 121 ± 19 | 0.013 |
| 6 mo | 68 | 117 ± 30 | 68 | 115 ± 29 | 67 | 109 ± 23 | 0.18 |
| Energy intake per day (kcal/kg/d) | |||||||
| 3 mo | 74 | 102 ± 20 b,c | 77 | 96 ± 13 | 74 | 96 ± 11 | 0.003 |
| 4 mo | 69 | 97 ± 21 b,c | 74 | 89 ± 12 | 71 | 90 ± 12 | 0.005 |
| 5 mo | 69 | 88 ± 15 | 72 | 84 ± 14 | 69 | 82 ± 13 | 0.043 ** |
| 6 mo | 68 | 79 ± 20 | 68 | 78 ± 20 | 67 | 74 ± 15 | 0.23 |
| Protein intake per day (g/kg/d) | |||||||
| 3 mo | 74 | 2.2 ± 0.4 b,c | 77 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 74 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| 4 mo | 69 | 2.1 ± 0.5 b,c | 74 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 71 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| 5 mo | 69 | 1.9 ± 0.3 b,c | 72 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 69 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | <0.001 |
| 6 mo | 68 | 1.7 ± 0.4 b,c | 68 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 67 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | <0.001 |
| SF | α-lac-EW | CGMP-RW | p-Value 1 (2) | BF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | n | n | ||||||
| Weight (g) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 83 | 5039 ± 58533 | 81 | 5092 ± 566 | 80 | 5162 ± 604 | 0.41 (0.47) | 83 | 5093 ± 610 |
| 3 mo | 75 | 6209 ± 699 | 77 | 6232 ± 712 | 74 | 6342 ± 715 | 0.47 (0.48) | 80 | 6022 ± 723 |
| 4 mo | 72 | 7067 ± 780 a | 75 | 7061 ± 834 a | 71 | 7120 ± 847 a | 0.89 (0.80) | 76 | 6685 ± 888 |
| 5 mo | 71 | 7781 ± 834 a | 73 | 7691 ± 923 a | 69 | 7762 ± 912 a | 0.82 (0.80) | 74 | 7263 ± 887 |
| 6 mo | 70 | 8323 ± 879 a | 73 | 8228 ± 1025 a | 69 | 8342 ± 1009 a | 0.76 (0.67) | 73 | 7771 ± 932 |
| Weight gain (g/d) | |||||||||
| 2–4 mo | 72 | 27 ± 6 a | 75 | 27 ± 6 a | 71 | 27 ± 6 a | 0.99 (0.98) | 76 | 23 ± 6 |
| 4–6 mo | 70 | 20 ± 5 a | 73 | 19 ± 6 | 69 | 20 ± 6 a | 0.17 (0.15) | 73 | 17 ± 5 |
| 2–6 mo | 70 | 24 ± 5 a | 73 | 23 ± 5 a | 69 | 24 ± 5 a | 0.59 (0.56) | 73 | 20 ± 5 |
| Length (cm) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 83 | 56.6 ± 2.2 | 81 | 56.7 ± 2.0 | 80 | 57.1 ± 1.8 | 0.13 (0.25) | 83 | 57.2 ± 2.0 |
| 3 mo | 75 | 60.7 ± 2.3 | 77 | 60.9 ± 2.1 | 74 | 61.4 ± 2.0 | 0.14 (0.15) | 80 | 60.9 ± 2.1 |
| 4 mo | 72 | 63.7 ± 2.6 | 75 | 63.7 ± 2.2 | 71 | 63.9 ± 2.0 | 0.56 (0.85) | 76 | 63.4 ± 2.3 |
| 5 mo | 71 | 66.1 ± 2.5 | 73 | 66.0 ± 2.4 | 69 | 66.1 ± 2.1 | 0.98 (0.94) | 74 | 65.7 ± 2.3 |
| 6 mo | 70 | 67.9 ± 2.5 | 73 | 67.9 ± 2.4 | 69 | 67.8 ± 2.3 | 0.99 (0.98) | 73 | 67.1 ± 2.6 |
| Length gain (cm/mo) | |||||||||
| 2–4 mo | 72 | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 75 | 2.9 ± 0.5 a | 71 | 2.9 ± 0.5 | 0.78 (0.56) | 76 | 2.7 ± 0.5 |
| 4–6 mo | 70 | 2.1 ± 0.6 a | 73 | 2.1 ± 0.5 a | 69 | 2.0 ± 0.4 a | 0.84 (0.80) | 73 | 1.8 ± 0.5 |
| 2–6 mo | 70 | 2.5 ± 0.4 a | 73 | 2.5 ± 0.3 a | 69 | 2.5 ± 0.3 a | 0.54 (0.35) | 73 | 2.3 ± 0.3 |
| HC (cm)4 | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 83 | 38.7 ± 1.3 | 81 | 38.7 ± 1.2 | 80 | 38.9 ± 1.2 | 0.53 (0.35) | 83 | 38.9 ± 1.3 |
| 3 mo | 75 | 40.6 ± 1.2 | 77 | 40.6 ± 1.3 | 74 | 40.8 ± 1.4 | 0.41 (0.49) | 80 | 40.5 ± 1.3 |
| 4 mo | 72 | 41.9 ± 1.2 | 75 | 41.8 ± 1.4 | 71 | 42.1 ± 1.5 | 0.27 (0.48) | 76 | 41.6 ± 1.3 |
| 5 mo | 71 | 42.9 ± 1.2 | 73 | 42.9 ± 1.5 | 69 | 43.0 ± 1.5 | 0.95 (0.90) | 74 | 42.8 ± 1.4 |
| 6 mo | 70 | 43.9 ± 1.2 | 73 | 43.9 ± 1.6 | 69 | 43.9 ± 1.6 | 0.84 (0.71) | 73 | 43.7 ± 1.5 |
| HC gain (cm/mo) | |||||||||
| 2–4 mo | 72 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 75 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 71 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 0.43 (0.57) | 76 | 1.2 ± 0.3 |
| 4–6 mo | 70 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 73 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 69 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 0.052 (0.032) a | 73 | 1.0 ± 0.3 |
| 2–6 mo | 70 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 73 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 69 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.57 (0.20) | 73 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| SF | α-lac-EW | CGMP-RW | p-Value 1 (2) | BF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | n | n | ||||||
| Weight (g) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 83 | 5039 ± 585 3 | 81 | 5092 ± 566 | 80 | 5162 ± 604 | 0.41 (0.47) | 83 | 5093 ± 610 |
| 3 mo | 74 | 6202 ± 700 | 77 | 6232 ± 712 | 73 | 6336 ± 718 | 0.48 (0.45) | 80 | 6021 ± 723 |
| 4 mo | 68 | 7040 ± 734 | 75 | 7061 ± 834 | 71 | 7120 ± 847 a | 0.83 (0.72) | 73 | 6715 ± 888 |
| 5 mo | 67 | 7760 ± 781 a | 73 | 7690 ± 923 | 68 | 7756 ± 917 a | 0.87 (0.86) | 69 | 7308 ± 888 |
| 6 mo | 66 | 8306 ± 823 a | 72 | 8235 ±1031 | 68 | 8337 ± 1015 a | 0.82 (0.75) | 66 | 7829 ± 940 |
| Weight gain (g/d) | |||||||||
| 2–4 mo | 68 | 27 ± 6 a | 75 | 27 ± 6 a | 71 | 27 ± 6 a | 0.99 (0.98) | 73 | 23 ± 6 |
| 4–6 mo | 66 | 20 ± 5 a | 72 | 19 ± 6 | 68 | 20 ± 6 a | 0.18 (0.15) | 66 | 17 ± 5 |
| 2–6 mo | 66 | 24 ± 4 a | 72 | 24 ± 5 a | 68 | 24 ± 5 a | 0.72 (0.70) | 66 | 20 ± 5 |
| SF | α-lac-EW | CGMP-RW | p-Value 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | n | |||||
| Weight gain, g/100 kcal | |||||||
| 2–4 mo | 69 | 4.23 ± 1.06 2 | 74 | 4.47 ± 0.85 | 71 | 4.40 ± 0.78 | 0.28 |
| 4–6 mo | 66 | 3.14 ± 0.95 | 67 | 2.96 ± 0.84 | 67 | 3.24 ± 0.87 | 0.19 |
| 2–6 mo | 64 | 3.72 ± 0.82 | 67 | 3.76 ± 0.71 | 67 | 3.88 ± 0.57 | 0.39 |
| Weight gain, g/g protein | |||||||
| 2–4 mo | 69 | 1.92 ± 0.48 a,b | 74 | 2.56 ± 0.49 | 71 | 2.48 ± 0.44 | <0.0001 |
| 4–6 mo | 66 | 1.43 ± 0.43 a,b | 67 | 1.70 ± 0.49 | 67 | 1.83 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| 2–6 mo | 64 | 1.69 ± 0.38 a,b | 67 | 2.16 ± 0.41 | 67 | 2.19 ± 0.33 | <0.0001 |
| Length gain, mm/100 kcal | |||||||
| 2–4 mo | 69 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 74 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 71 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.094 |
| 4–6 mo | 66 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 67 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 67 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 0.93 |
| 2–6 mo | 64 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 67 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 67 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.41 |
| Length gain, mm/g protein | |||||||
| 2–4 mo | 69 | 0.068 ± 0.01 a,b | 74 | 0.092 ± 0.02 | 71 | 0.082 ± 0.02 | < 0.001 |
| 4–6 mo | 66 | 0.048 ± 0.017 a,b | 67 | 0.062 ± 0.02 | 67 | 0.061 ± 0.02 | <0.001 |
| 2–6 mo | 64 | 0.059 ± 0.01 a,b | 67 | 0.078 ± 0.01 | 67 | 0.075 ± 0.01 | <0.001 |
| SF | α-lac-EW | CGMP-RW | p-Value 1 (2) | BF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | n | n | ||||||
| BUN (mg/dL) 3 | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 50 | 13.8 ± 4.2 4,a | 50 | 14.2 ± 5.0 a | 50 | 13.5 ± 4.1 | 0.72 | 50 | 11.4 ± 4.1 |
| 4 mo | 50 | 15.1 ± 4.7 a,b,c | 50 | 11.0 ± 4.0 | 50 | 11.1 ± 3.8 | <0.0001 | 50 | 9.8 ± 4.5 |
| 6 mo | 50 | 14.5 ± 5.0 a,b,c | 50 | 11.6 ± 3.9 | 50 | 12.2 ± 4.7 | 0.004 | 50 | 10.3 ± 3.8 |
| IGF-1 (µg/L) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 80 | 87.2 ± 19.7 | 74 | 93.5 ± 18.2 a | 74 | 88.7 ± 16.8 | 0.094 (0.16) | 76 | 84.2 ± 20.0 |
| 4 mo | 67 | 71.8 ± 22.7 a | 72 | 71.4 ± 20.6 a | 67 | 69.1 ± 22.1 a | 0.74 (0.73) | 69 | 55.0 ± 18.7 |
| 6 mo | 67 | 60.2 ± 20.3 a | 69 | 62.9 ± 23.0 a | 65 | 61.1 ± 18.6 a | 0.74 (0.92) | 68 | 44.8 ± 15.2 |
| Insulin (mIU/L) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 80 | 11.8 ± 7.8 a | 74 | 9.9 ± 5.2 | 74 | 11.5 ± 6.9 a | 0.19 (0.42) | 75 | 8.4 ± 5.4 |
| 4 mo | 67 | 8.7 ± 5.2 a | 72 | 8.1 ± 4.6 a | 67 | 8.7 ± 6.0 a | 0.72 (0.68) | 68 | 4.9 ± 2.5 |
| 6 mo | 67 | 6.8 ± 4.4 a | 69 | 6.7 ± 5.2 a | 65 | 7.1 ± 4.7 a | 0.85 (0.83) | 68 | 4.0 ± 2.7 |
| C-peptide (nmol/L) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 80 | 0.69 ± 0.23 a | 74 | 0.66 ± 0.20 a | 74 | 0.72 ± 0.22 a | 0.26 (0.13) | 74 | 0.53 ± 0.20 |
| 4 mo | 67 | 0.63 ± 0.22 a | 72 | 0.61 ± 0.22 a | 67 | 0.63 ± 0.24 a | 0.90 (0.84) | 68 | 0.43 ± 0.16 |
| 6 mo | 67 | 0.53 ± 0.19 a | 69 | 0.54 ± 0.25 a | 65 | 0.55 ± 0.22 a | 0.95 (0.97) | 68 | 0.37 ± 0.17 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 68 | 6.9 ± 3.6 | 63 | 6.4 ± 2.9 | 70 | 6.6 ± 3.9 | 0.74 (0.54) | 62 | 7.3 ± 5.2 |
| 4 mo | 62 | 5.3 ± 2.8 | 60 | 6.1 ± 3.7 | 62 | 6.3 ± 3.4 | 0.22 (0.079) | 59 | 6.5 ± 4.3 |
| 6 mo | 61 | 4.9 ± 2.6 | 64 | 5.3 ± 3.7 | 60 | 5.2 ± 2.7 | 0.71 (0.57) | 58 | 4.7 ± 2.6 |
| Soluble leptin receptor (ng/mL) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 73 | 28.1 ± 4.8 a | 64 | 27.7 ± 6.0 a | 71 | 28.3 ± 5.6 a | 0.83 (0.74) | 67 | 32.0 ± 7.1 |
| 4 mo | 64 | 42.5 ± 9.1 | 63 | 39.4 ± 7.9 | 62 | 39.8 ± 9.5 | 0.081 (0.26) | 62 | 42.2 ± 9.6 |
| 6 mo | 62 | 46.5 ± 9.1 | 66 | 42.9 ± 11.0 | 61 | 43.4 ± 9.3 | 0.081 (0.16) | 60 | 45.2 ± 9.4 |
| Free leptin index 5 | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 68 | 0.25 ± 0.14 | 63 | 0.24 ± 0.12 | 70 | 0.25 ± 0.18 | 0.86 (0.49) | 62 | 0.26 ± 0.2 |
| 4 mo | 62 | 0.13 ± 0.09 c | 60 | 0.16 ± 0.11 | 62 | 0.18 ± 0.1 | 0.054 (0.015) | 59 | 0.17 ± 0.15 |
| 6 mo | 61 | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 64 | 0.14 ± 0.12 | 60 | 0.13 ± 0.07 | 0.38 (0.27) | 58 | 0.12 ± 0.11 |
| Hb (g/L) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 68 | 111.5 ± 13.0 a | 59 | 115.2 ± 15.2 | 67 | 113.5 ± 13.2 | 0.33 | 66 | 119.4 ± 12.0 |
| 4 mo | 58 | 115.5 ± 8.3 | 61 | 115.8 ± 8.2 | 54 | 115.8 ± 8.4 | 0.97 | 61 | 116.5 ± 9.1 |
| 6 mo | 56 | 116.4 ± 7.0 | 65 | 117.4 ± 8.3 | 59 | 115.3 ± 7.5 | 0.34 | 60 | 115.8 ± 7.6 |
| Ferritin (µg/L) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 78 | 309.5 ±126.8 a | 71 | 310.2 ± 144.9 a | 74 | 353.2 ± 157.3 | 0.11 | 71 | 396.8 ± 154.7 |
| 4 mo | 66 | 106.8 ± 61.4 a | 68 | 122.0 ± 65.5 a | 65 | 145.6 ± 93.9 c | 0.013 | 66 | 172.5 ± 80.8 |
| 6 mo | 65 | 74.6 ± 41.2 | 69 | 90.4 ± 60.6 | 65 | 91.1 ± 48.2 | 0.11 | 65 | 75.4 ± 45.3 |
| Iron (µmol/L) | |||||||||
| 2 mo | 78 | 17.1 ± 4.7 | 71 | 17.8 ± 4.3 | 74 | 17.4 ± 4.2 | 0.65 | 71 | 16.1 ± 3.9 |
| 4 mo | 66 | 10.0 ± 2.9 | 68 | 11.0 ± 3.7 a | 65 | 10.2 ± 3.1 | 0.12 | 66 | 9.2 ± 2.2 |
| 6 mo | 65 | 9.1 ± 3.5 | 69 | 9.5 ± 3.3 | 65 | 9.7 ± 2.9 a | 0.53 | 65 | 8.2 ± 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tinghäll Nilsson, U.; Hernell, O.; Lönnerdal, B.; Hartvigsen, M.L.; Jacobsen, L.N.; Kvistgaard, A.S.; Karlsland Åkeson, P. Low-Protein Formulas with Alpha-Lactalbumin-Enriched or Glycomacropeptide-Reduced Whey: Effects on Growth, Nutrient Intake and Protein Metabolism during Early Infancy: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041010
Tinghäll Nilsson U, Hernell O, Lönnerdal B, Hartvigsen ML, Jacobsen LN, Kvistgaard AS, Karlsland Åkeson P. Low-Protein Formulas with Alpha-Lactalbumin-Enriched or Glycomacropeptide-Reduced Whey: Effects on Growth, Nutrient Intake and Protein Metabolism during Early Infancy: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041010
Chicago/Turabian StyleTinghäll Nilsson, Ulrika, Olle Hernell, Bo Lönnerdal, Merete Lindberg Hartvigsen, Lotte Neergaard Jacobsen, Anne Staudt Kvistgaard, and Pia Karlsland Åkeson. 2023. "Low-Protein Formulas with Alpha-Lactalbumin-Enriched or Glycomacropeptide-Reduced Whey: Effects on Growth, Nutrient Intake and Protein Metabolism during Early Infancy: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Controlled Trial" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041010
APA StyleTinghäll Nilsson, U., Hernell, O., Lönnerdal, B., Hartvigsen, M. L., Jacobsen, L. N., Kvistgaard, A. S., & Karlsland Åkeson, P. (2023). Low-Protein Formulas with Alpha-Lactalbumin-Enriched or Glycomacropeptide-Reduced Whey: Effects on Growth, Nutrient Intake and Protein Metabolism during Early Infancy: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 15(4), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041010






