Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Supplementation Blunts the Development of Offspring Hypertension in a Maternal Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate Exposure Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
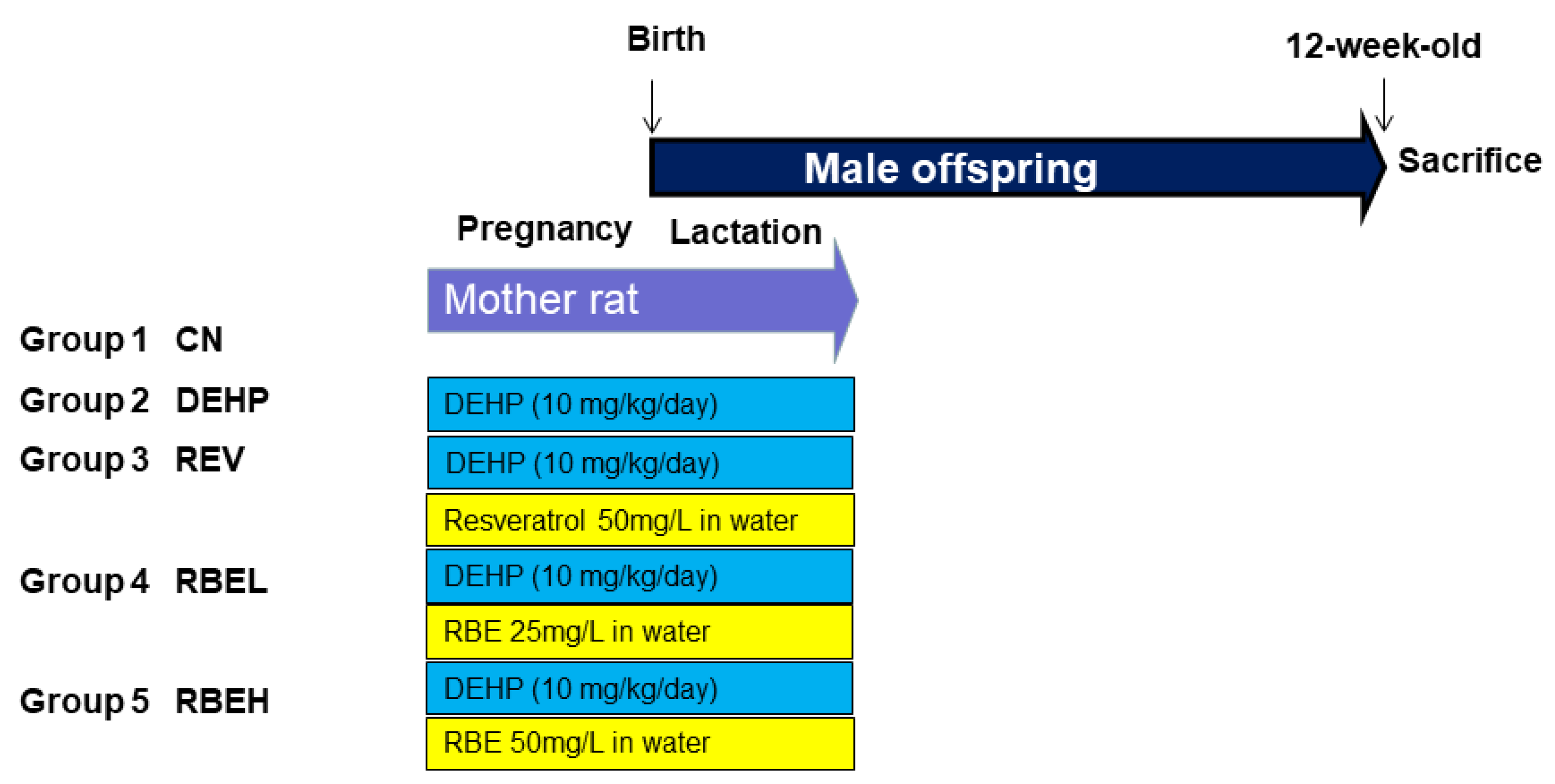
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Measurement of SCFAs by GC-MS
2.3. Measurement of NO Parameters by HPLC
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. Microbiota Sequencing
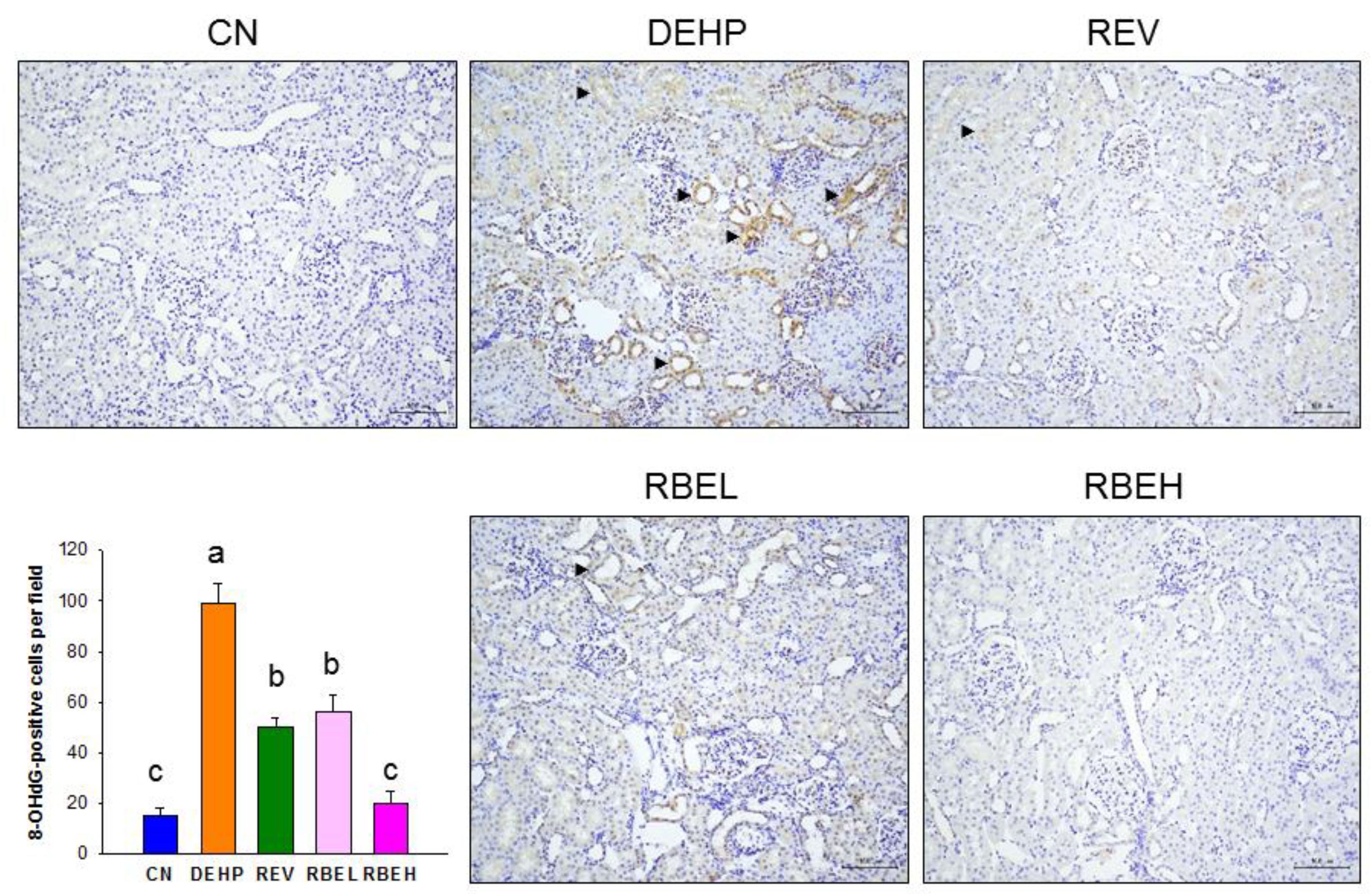
2.6. Immunohistochemical Detection of 8-OHdG
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
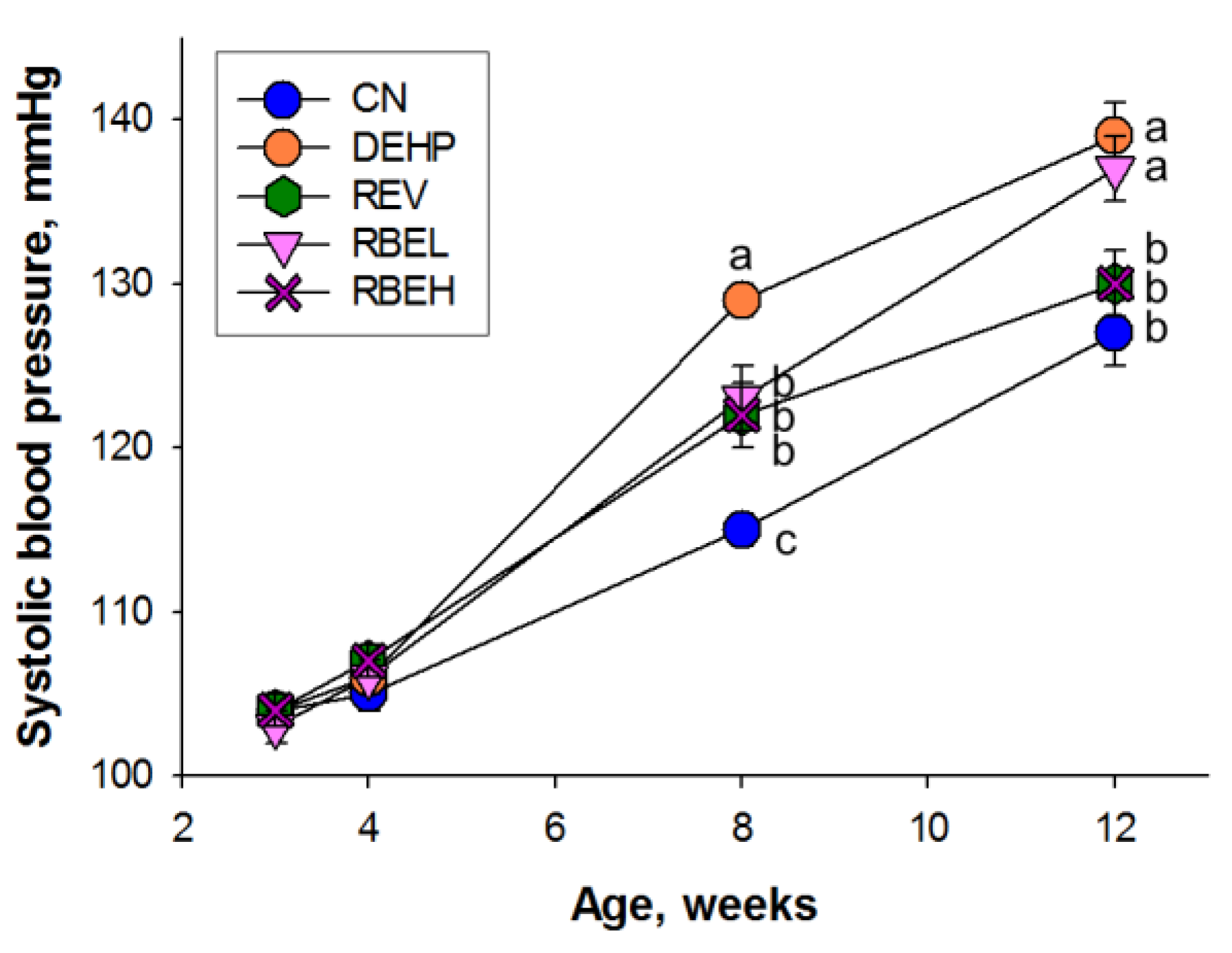
3.1. Body Weight and Blood Pressure
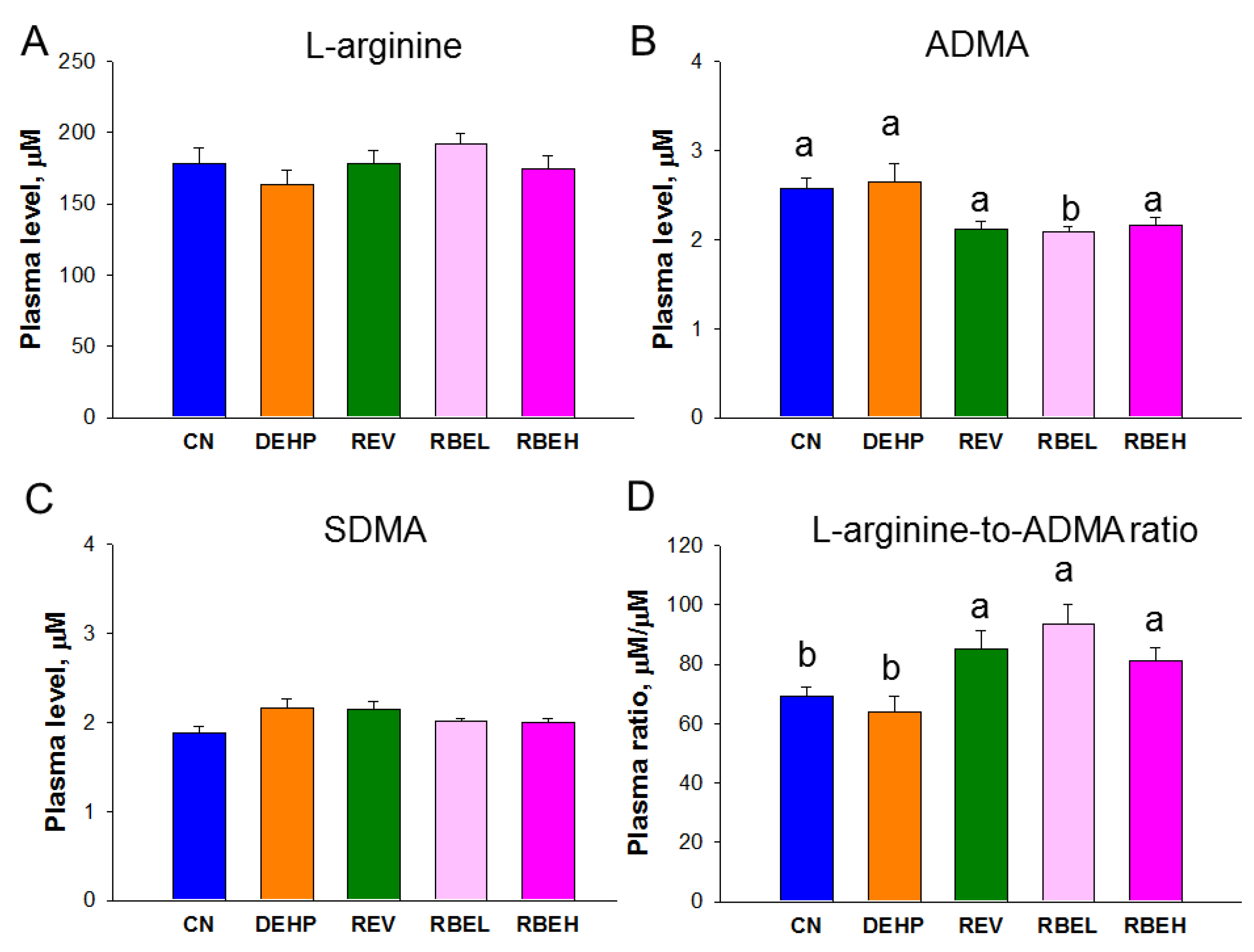
3.2. Oxidative Stress and NO Parameters
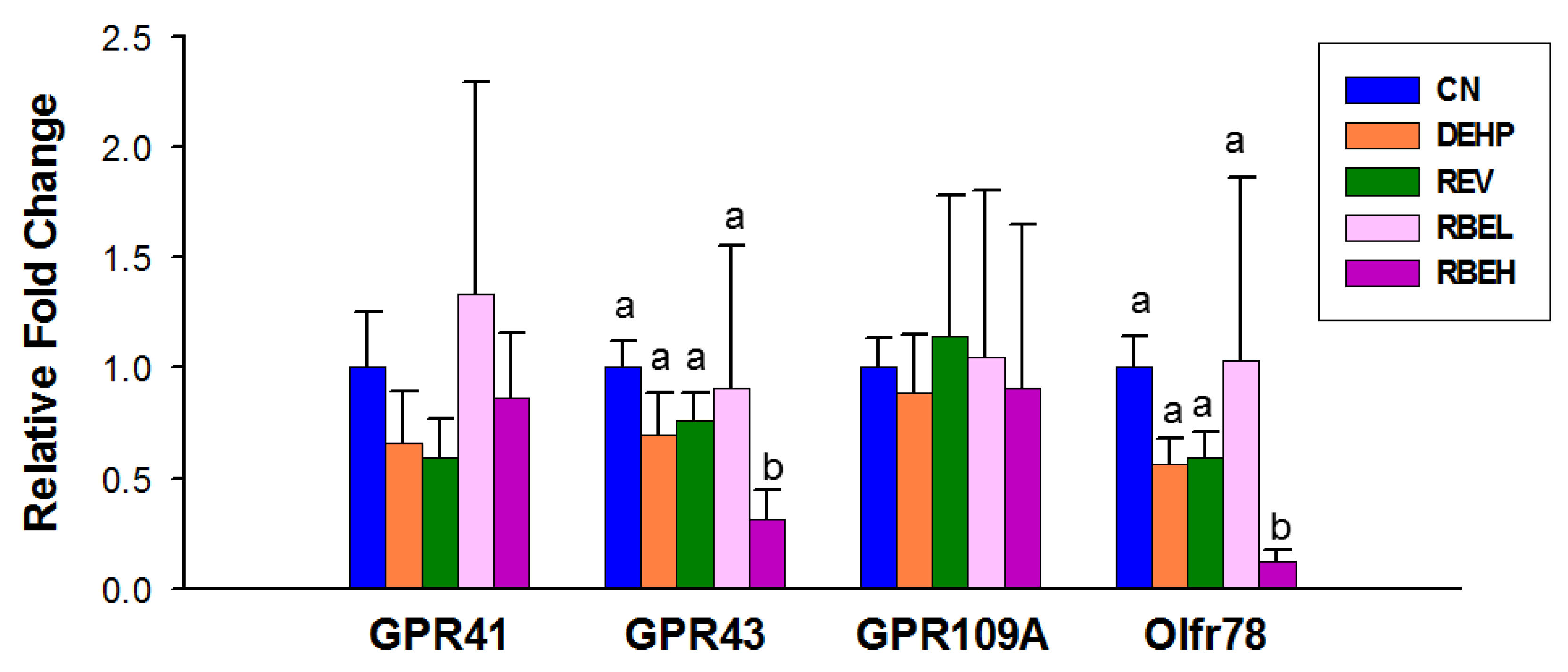
3.3. Plasma SCFA Concentrations and Renal SCFA Receptors
3.4. AHR Signaling
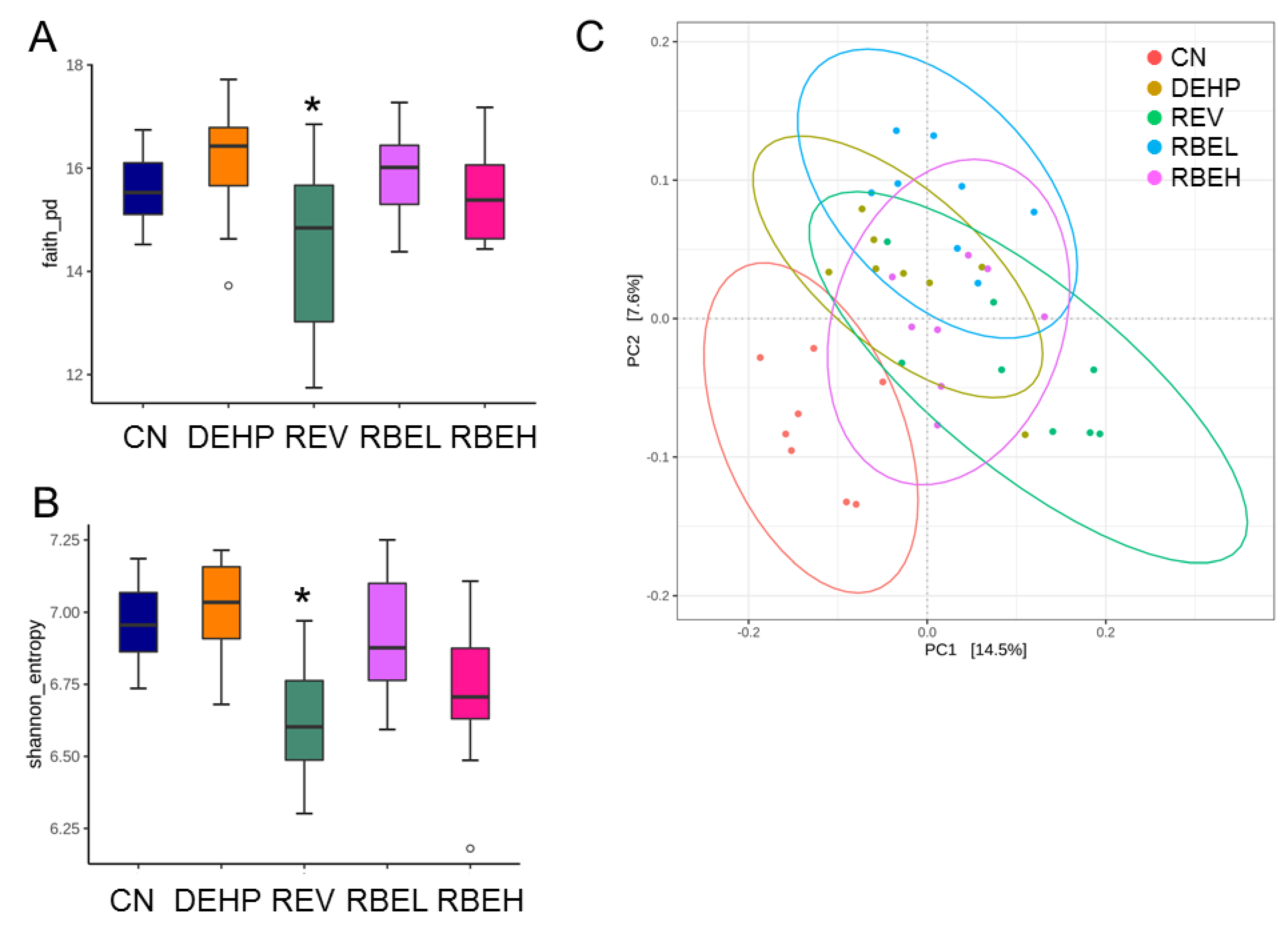
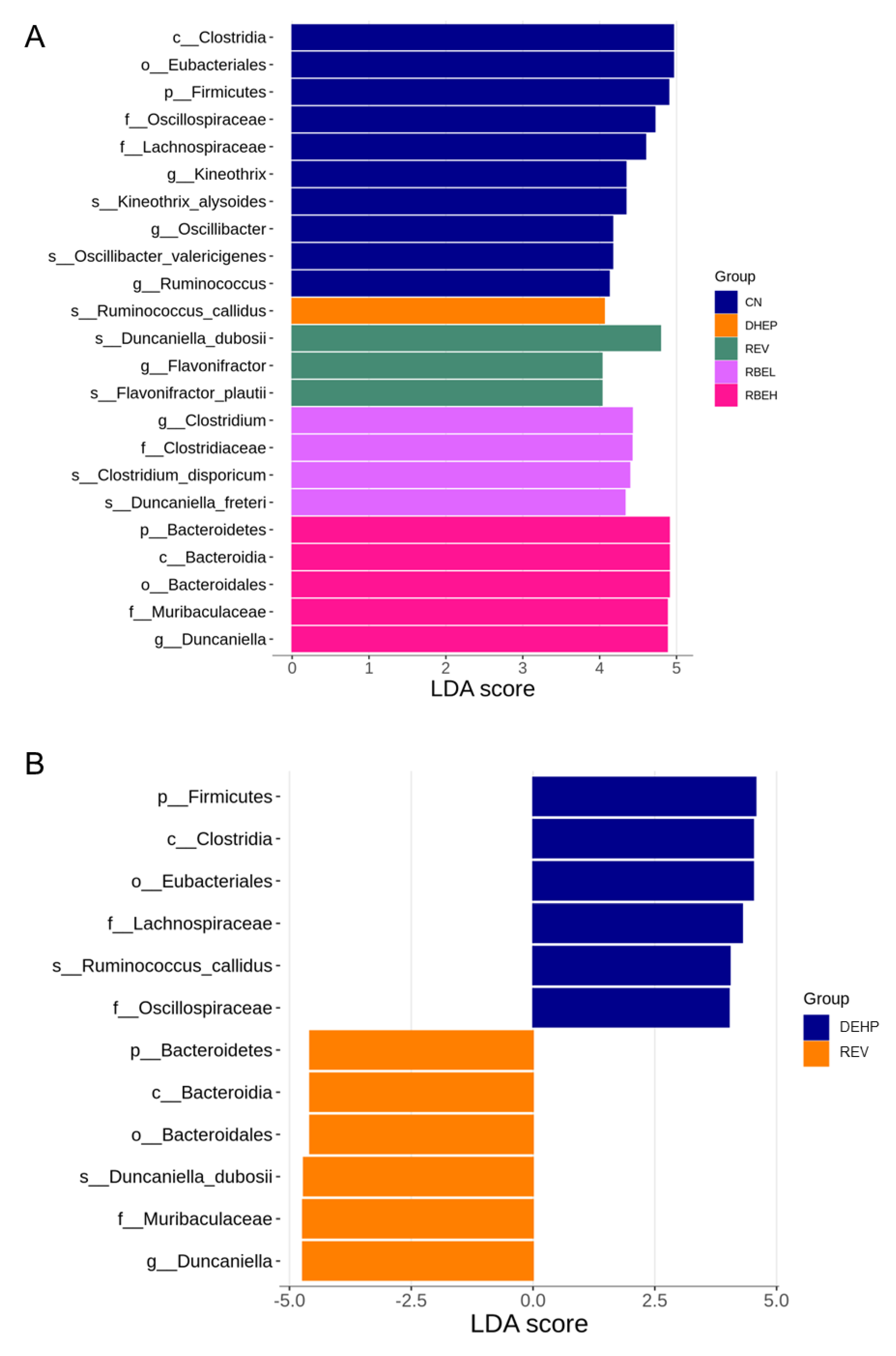
3.5. Differences in Microbiota Compositions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz-Gerevini, G.T.; Repossi, G.; Dain, A.; Tarres, M.C.; Das, U.N.; Eynard, A.R. Beneficial action of resveratrol: How and why? Nutrition 2016, 32, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Singh, R.; Verma, S.S.; Rai, V.; Kaschula, C.H.; Maiti, P.; Gupta, S.C. Health benefits of resveratrol: Evidence from clinical studies. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1851–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Daiber, A.; Förstermann, U.; Li, H. Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in the cardiovascular system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1633–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, S.M.; Dyck, J.R. Systemic and renal oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of hypertension: Modulation of long-term control of arterial blood pressure by resveratrol. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Tain, Y.L. Preventive Aspects of Early Resveratrol Supplementation in Cardiovascular and Kidney Disease of Developmental Origins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Chan, J.Y.H.; Lee, C.T.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal resveratrol therapy protected adult rat offspring against hypertension programmed by combined exposures to asymmetric dimethylarginine and trimethylamine-N-oxide. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 93, 108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hung, C.H.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang, C.I.; Tain, Y.L. Perinatal Resveratrol Therapy to Dioxin-Exposed Dams Prevents the Programming of Hypertension in Adult Rat Offspring. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Adverse Impact of Environmental Chemicals on Developmental Origins of Kidney Disease and Hypertension. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 745716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, M.; Gluckman, P. Developmental origins of noncommunicable disease: Population and public health implications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1754S–1758S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, A.; Zuccarini, M.; Cichelli, A.; Khan, H.; Reale, M. Critical Review on the Presence of Phthalates in Food and Evidence of Their Biological Impact. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, M.; Cairrao, E. Phthalates Implications in the Cardiovascular System. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2020, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Shao, H.; Ying, X.; Huang, W.; Hua, Y. The Endocrine Disruption of Prenatal Phthalate Exposure in Mother and Offspring. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Song, L.; Wei, J.; Chen, T.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Xia, W.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Maternal Exposure to Di- (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Alters Kidney Development Through the Renin Angiotensin System in Offspring. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 212, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, T. Bioavailability of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplin, A.; Carpéné, C.; Mercader, J. Resveratrol, Metabolic Syndrome, and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavis, L.D. Ester bonds in prodrugs. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Chang, S.K.C.; Liao, J.X.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, H.T.; Li, Y.L.; Hou, C.Y. Synthesis of Short-Chain-Fatty-Acid Resveratrol Esters and Their Antioxidant Properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Jheng, L.C.; Chang, S.K.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, L.T.; Liao, J.X.; Hou, C.Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Resveratrol Butyrate Esters That Have the Ability to Prevent Fat Accumulation in a Liver Cell Culture Model. Molecules 2020, 25, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang, C.I.; Tain, Y.L. Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Protects Adenine-Treated Rats against Hypertension and Kidney Disease by Regulating the Gut-Kidney Axis. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, G.; Bhaskaran, R.S.; Karundevi, B. Developmental exposure to DEHP alters hepatic glucose uptake and transcriptional regulation of GLUT2 in rat male offspring. Toxicology 2019, 413, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckelhoff, J.F. Gender differences in the regulation of blood pressure. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Chan, J.Y.H.; Wu, K.L.H.; Yu, H.R.; Lee, W.C.; Hou, C.Y.; Tain, Y.L. Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites in Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Exploring Differences between Fructose and Antibiotics Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrocco, I.; Altieri, F.; Peluso, I. Measurement and Clinical Significance of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Humans. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 6501046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.I.; Chiang, C.W.; Lin, H.C.; Zhao, J.F.; Li, C.T.; Shyue, S.K.; Lee, T.S. Maternal exposure to di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure deregulates blood pressure, adiposity, cholesterol metabolism and social interaction in mouse offspring. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Lu, P.C.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal resveratrol therapy protects male rat offspring against programmed hypertension induced by TCDD and dexamethasone exposures: Is it relevant to aryl hydrocarbon receptor? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal exposure to bisphenol A combined with high-fat diet-induced programmed hypertension in adult male rat offspring: Effects of resveratrol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Yang, H.W.; Tain, Y.L. Perinatal Resveratrol Therapy Prevents Hypertension Programmed by Maternal Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Male Offspring: Implications of the Gut Microbiome and Their Metabolites. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, M.; Sakaki, H.; Usami, M.; Iizuka, N.; Shuno, K.; Aoyama, M.; Usami, Y. Oral administration of tributyrin increases concentration of butyrate in the portal vein and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in rats. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluznick, J.L. Microbial Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Blood Pressure Regulation. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lin, J.; Talukder, M.; Zhu, S.Y.; Li, M.Z.; Wang, H.R.; Li, J.L. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor as a Target for Lycopene Preventing DEHP-Induced Spermatogenic Disorders. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4355–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casper, R.F.; Quesne, M.; Rogers, I.M.; Shirota, T.; Jolivet, A.; Milgrom, E.; Savouret, J.F. Resveratrol has antagonist activity on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor: Implications for prevention of dioxin toxicity. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franczak, A.; Nynca, A.; Valdez, K.E.; Mizinga, K.M.; Petroff, B.K. Effects of acute and chronic exposure to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on the transition to reproductive senescence in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 74, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, S.C.; Clare, S.; Beresford-Jones, B.S.; Harcourt, K.; Notley, G.; Stares, M.D.; Kumar, N.; Soderholm, A.T.; Adoum, A.; Wong, H.; et al. Identification of gut microbial species linked with disease variability in a widely used mouse model of colitis. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Yu, H.R.; Lin, I.C.; Tiao, M.M.; Huang, L.T.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Tain, Y.L. Sodium butyrate modulates blood pressure and gut microbiota in maternal tryptophan-free diet-induced hypertension rat offspring. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 108, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Gene Accession No. | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPR41 | NM_001108912 | 5 tcttcaccaccgtctatctcac 3 | 5 cacaagtcctgccaccctc 3 |
| GPR43 | NM_001005877 | 5 ctgcctgggatcgtctgtg 3 | 5 cataccctcggccttctgg 3 |
| GPR109A | NM_181476 | 5 cggtggtctactatttctcc 3 | 5 cccctggaatacttctgatt 3 |
| Olfr78 | NM_001000624 | 5 gaggaagctcacttttggtttgg 3 | 5 cagcttcaatgtccttgtcacag 3 |
| AHR | NM_001308254 | 5 gtcctcagcaggaacgaaag 3 | 5 ccagggaagtccaactgtgt 3 |
| AHRR | NM_001024285 | 5 cagcaacatggcttctttca 3 | 5 tgaagcactgcattccagac 3 |
| ARNT | NM_012780 | 5 gtctccctcccagatgatga 3 | 5 gctggtagccaacagtagcc 3 |
| CYP1A1 | NM_012540 | 5 gcactctggacaaacacctg 3 | 5 atatccaccttctcgcctgg 3 |
| R18S | X01117 | 5 gccgcggtaattccagctcca 3 | 5 cccgcccgctcccaagatc 3 |
| Groups | CN | DEHP | REV | RBEL | RBEH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (BW) (g) | 219 ± 10 b | 327 ± 16 a | 285 ± 15 a | 299 ± 6 a | 254 ± 7 b |
| Left kidney weight (g) | 1.21 ± 0.06 b | 1.7 ± 0.09 a | 1.46 ± 0.1 a | 1.4 ± 0.02 b | 1.19 ± 0.03 b |
| Left kidney weight/100 g BW | 0.55 ± 0.01 a | 0.52 ± 0.02 a | 0.51 ± 0.03 a | 0.47 ± 0.01 b | 0.47 ± 0.01 b |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 84 ± 1 | 88 ± 5 | 85 ± 1 | 90 ± 2 | 85 ± 1 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 99 ± 1 b | 105 ± 4 a | 100 ± 1 b | 108 ± 2 a | 100 ± 1 b |
| Groups | CN | DEHP | REV | RBEL | RBEH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid, ng/mL | 787 ± 124 | 770 ± 47 | 780 ± 72 | 1002 ± 52 | 819 ± 62 |
| Propionic acid, ng/mL | 7.0 ± 0.84 | 6.19 ± 0.41 | 6.43 ± 0.38 | 6.59 ± 0.57 | 6.58 ± 0.62 |
| Butyric acid, ng/mL | 3.12 ± 0.3 b | 2.47 ± 0.24 b | 2.26 ± 0.22 b | 6.38 ± 0.49 a | 7.1 ± 0.41 a |
| Valeric acid, ng/mL | 13.6 ± 0.32 | 0.97 ± 0.22 | 1.02 ± 0.21 | 1.23 ± 0.28 | 1.24 ± 0.23 |
| Hexanoic acid, ng/mL | 6.14 ± 0.35 b | 7.82 ± 0.35 a | 6.35 ± 0.37 a | 6.84 ± 0.54 a | 6.16 ± 0.35 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tain, Y.-L.; Hou, C.-Y.; Chang-Chien, G.-P.; Lin, S.; Hsu, C.-N. Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Supplementation Blunts the Development of Offspring Hypertension in a Maternal Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate Exposure Rat Model. Nutrients 2023, 15, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030697
Tain Y-L, Hou C-Y, Chang-Chien G-P, Lin S, Hsu C-N. Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Supplementation Blunts the Development of Offspring Hypertension in a Maternal Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate Exposure Rat Model. Nutrients. 2023; 15(3):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030697
Chicago/Turabian StyleTain, You-Lin, Chih-Yao Hou, Guo-Ping Chang-Chien, Sufan Lin, and Chien-Ning Hsu. 2023. "Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Supplementation Blunts the Development of Offspring Hypertension in a Maternal Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate Exposure Rat Model" Nutrients 15, no. 3: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030697
APA StyleTain, Y.-L., Hou, C.-Y., Chang-Chien, G.-P., Lin, S., & Hsu, C.-N. (2023). Resveratrol Butyrate Ester Supplementation Blunts the Development of Offspring Hypertension in a Maternal Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate Exposure Rat Model. Nutrients, 15(3), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030697







